0cdcada9bc6463962ef95ec4c616865d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Work, Energy, and Power AP Physics 1
Work, Energy, and Power AP Physics 1
 Work tells us how much a force or combination of forces changes the energy of a system. Work is the bridge between force (a vector) and energy (a scalar). F: force (N) d : displacement (m) : angle between force and displacement
Work tells us how much a force or combination of forces changes the energy of a system. Work is the bridge between force (a vector) and energy (a scalar). F: force (N) d : displacement (m) : angle between force and displacement
 Units of Work SI System: Joule (N m) 1 Joule of work is done when 1 N acts on a body moving it a distance of 1 meter British System: foot-pound (not used in Physics 1) cgs System: erg (dyne-cm) (not used in Physics 1) Atomic Level: electron-Volt (e. V)
Units of Work SI System: Joule (N m) 1 Joule of work is done when 1 N acts on a body moving it a distance of 1 meter British System: foot-pound (not used in Physics 1) cgs System: erg (dyne-cm) (not used in Physics 1) Atomic Level: electron-Volt (e. V)
 Force and direction of motion both matter in defining work! There is no work done by a force if it causes no displacement. Forces can do positive, negative, or zero work. When a box is pushed on a flat floor, for example… The normal force and gravity do no work, since they are perpendicular to the direction of motion. The person pushing the box does positive work, since she is pushing in the direction of motion. Friction does negative work, since it points opposite the direction of motion.
Force and direction of motion both matter in defining work! There is no work done by a force if it causes no displacement. Forces can do positive, negative, or zero work. When a box is pushed on a flat floor, for example… The normal force and gravity do no work, since they are perpendicular to the direction of motion. The person pushing the box does positive work, since she is pushing in the direction of motion. Friction does negative work, since it points opposite the direction of motion.
 Question If a man holds a 50 kg box at arms length for 2 hours as he stands still, how much work does he do on the box? ZERO
Question If a man holds a 50 kg box at arms length for 2 hours as he stands still, how much work does he do on the box? ZERO
 Question If a man holds a 50 kg box at arms length for 2 hours as he walks 1 km forward, how much work does he do on the box? ZERO
Question If a man holds a 50 kg box at arms length for 2 hours as he walks 1 km forward, how much work does he do on the box? ZERO
 Question If a man lifts a 50 kg box 2. 0 meters at a constant speed, how much work does he do on the box? 1000 J
Question If a man lifts a 50 kg box 2. 0 meters at a constant speed, how much work does he do on the box? 1000 J
 Sample problem Jane uses a vine wrapped around a pulley to lift a 70 -kg Tarzan at a constant speed to a tree house 9. 0 meters above the ground. a)How much work does Jane do when she lifts Tarzan? 6300 J b) How much work does gravity do when Jane lifts Tarzan? -6300 J
Sample problem Jane uses a vine wrapped around a pulley to lift a 70 -kg Tarzan at a constant speed to a tree house 9. 0 meters above the ground. a)How much work does Jane do when she lifts Tarzan? 6300 J b) How much work does gravity do when Jane lifts Tarzan? -6300 J
 Sample problem A droplet of water of mass 50 mg falls at constant speed under the influence of gravity and air resistance. After the drop has fallen 1. 0 km, what is the work done by a) gravity? 0. 500 J b) air resistance? -0. 500 J c) What is the net work? 0 J When an object moves at a constant speed the net work done on the object is zero.
Sample problem A droplet of water of mass 50 mg falls at constant speed under the influence of gravity and air resistance. After the drop has fallen 1. 0 km, what is the work done by a) gravity? 0. 500 J b) air resistance? -0. 500 J c) What is the net work? 0 J When an object moves at a constant speed the net work done on the object is zero.
 Sample problem A father pulls his child in a little red wagon with constant speed. If the father pulls with a force of 16 N for 10. 0 m, and the handle of the wagon is inclined at an angle of 60 o above the horizontal, how much work does the father do on the wagon? 80 J
Sample problem A father pulls his child in a little red wagon with constant speed. If the father pulls with a force of 16 N for 10. 0 m, and the handle of the wagon is inclined at an angle of 60 o above the horizontal, how much work does the father do on the wagon? 80 J
 Sample problem Joe pushes a 10 -kg box and slides it across the floor at constant velocity of 3. 0 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and floor is 0. 50. a) How much work does Joe do if he pushes the box for 15 meters? 750 J b) How much work does friction do as Joe pushes the box? - 750 J
Sample problem Joe pushes a 10 -kg box and slides it across the floor at constant velocity of 3. 0 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and floor is 0. 50. a) How much work does Joe do if he pushes the box for 15 meters? 750 J b) How much work does friction do as Joe pushes the box? - 750 J
 Kinetic Energy due to motion K = ½ m v 2 K: Kinetic Energy in J m: mass in kg v: speed in m/s Unit: Joules Kinetic is independent of the direction of motion.
Kinetic Energy due to motion K = ½ m v 2 K: Kinetic Energy in J m: mass in kg v: speed in m/s Unit: Joules Kinetic is independent of the direction of motion.
 Sample problem A 10. 0 g bullet has a speed of 1. 2 km/s. a) What is the kinetic energy of the bullet? 7200 J b) What is the bullet’s kinetic energy if the speed is halved? 1800 J c) What is the bullet’s kinetic energy if the speed is doubled? 28800 J
Sample problem A 10. 0 g bullet has a speed of 1. 2 km/s. a) What is the kinetic energy of the bullet? 7200 J b) What is the bullet’s kinetic energy if the speed is halved? 1800 J c) What is the bullet’s kinetic energy if the speed is doubled? 28800 J
 Work and Energy Work changes mechanical energy! If an applied force does positive work on a system, it tries to increase mechanical energy. If an applied force does negative work, it tries to decrease mechanical energy. The two forms of mechanical energy are called potential and kinetic energy.
Work and Energy Work changes mechanical energy! If an applied force does positive work on a system, it tries to increase mechanical energy. If an applied force does negative work, it tries to decrease mechanical energy. The two forms of mechanical energy are called potential and kinetic energy.
 The Work-Energy Theorem to all forces equals The net work due the change in the kinetic energy of a system. Wnet = K Wnet: work due to all forces acting on an object K: change in kinetic energy (Kf – Ki)
The Work-Energy Theorem to all forces equals The net work due the change in the kinetic energy of a system. Wnet = K Wnet: work due to all forces acting on an object K: change in kinetic energy (Kf – Ki)
 WORK-KINETIC ENERGY A spider monkey (mass 40 kg) is frolicking through the jungle at a speed of 3. 0 m/s. All of a sudden, a jaguar appears and tries to eat the monkey. The monkey begins to run frantically—now he has a speed of 14. 0 m/s. How much work does the monkey do to increase its speed? 3740 J
WORK-KINETIC ENERGY A spider monkey (mass 40 kg) is frolicking through the jungle at a speed of 3. 0 m/s. All of a sudden, a jaguar appears and tries to eat the monkey. The monkey begins to run frantically—now he has a speed of 14. 0 m/s. How much work does the monkey do to increase its speed? 3740 J
 WORK-KINETIC ENERGY A 1000 kg car traveling at 30 m/s suddenly its brakes and comes to a stop. If the wheels locked and friction applied a force of 5000 N, how far does the car travel? 90 m
WORK-KINETIC ENERGY A 1000 kg car traveling at 30 m/s suddenly its brakes and comes to a stop. If the wheels locked and friction applied a force of 5000 N, how far does the car travel? 90 m
 Power is the rate of which work is done. P = W/ t W: work in Joules t: elapsed time in seconds When we run upstairs, t is small so P is big. When we walk upstairs, t is large so P is small.
Power is the rate of which work is done. P = W/ t W: work in Joules t: elapsed time in seconds When we run upstairs, t is small so P is big. When we walk upstairs, t is large so P is small.
 Unit of Power SI unit for Power is the Watt. 1 Watt = 1 Joule/s Named after the Scottish engineer James Watt (17761819) who perfected the steam engine. British system horsepower 1 hp = 746 W
Unit of Power SI unit for Power is the Watt. 1 Watt = 1 Joule/s Named after the Scottish engineer James Watt (17761819) who perfected the steam engine. British system horsepower 1 hp = 746 W
 How We Buy Energy… The kilowatt-hour is a commonly used unit by the electrical power company. Power companies charge you by the kilowatt-hour (k. Wh), but this not power, it is really energy consumed. 1 k. W = 1000 W 1 h = 3600 s 1 k. Wh = 1000 J/s • 3600 s = 3. 6 x 106 J
How We Buy Energy… The kilowatt-hour is a commonly used unit by the electrical power company. Power companies charge you by the kilowatt-hour (k. Wh), but this not power, it is really energy consumed. 1 k. W = 1000 W 1 h = 3600 s 1 k. Wh = 1000 J/s • 3600 s = 3. 6 x 106 J
 Sample problem A man runs up the 1600 steps of the Empire State Building in 20 minutes. If the height gain of each step was 0. 20 m, and the man’s mass was 80. 0 kg, what was his average power output during the climb? Give your answer in both watts and horsepower. 0. 933 Watts 0. 00125 hp
Sample problem A man runs up the 1600 steps of the Empire State Building in 20 minutes. If the height gain of each step was 0. 20 m, and the man’s mass was 80. 0 kg, what was his average power output during the climb? Give your answer in both watts and horsepower. 0. 933 Watts 0. 00125 hp
 Sample problem Calculate the power output of a 0. 10 g fly as it walks straight up a window pane at 2. 0 cm/s. 2 E -5 Watts
Sample problem Calculate the power output of a 0. 10 g fly as it walks straight up a window pane at 2. 0 cm/s. 2 E -5 Watts
 Force vs. Position Graphs
Force vs. Position Graphs
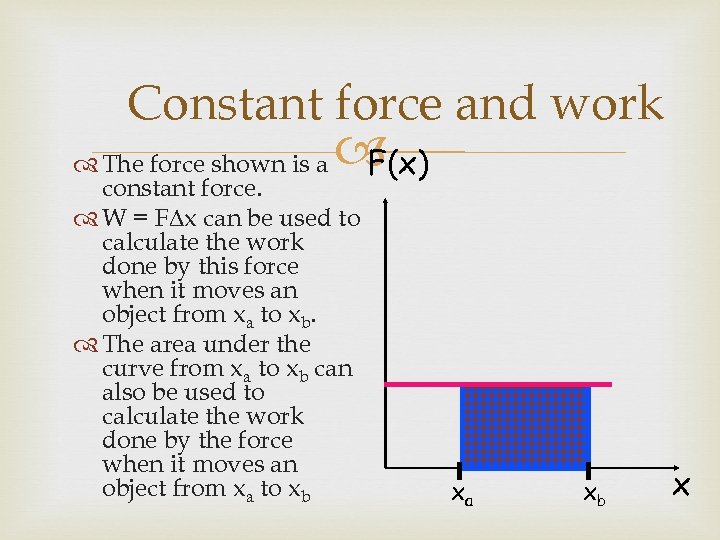 Constant force and work The force shown is a F(x) constant force. W = F x can be used to calculate the work done by this force when it moves an object from xa to xb. The area under the curve from xa to xb can also be used to calculate the work done by the force when it moves an object from xa to xb xa xb x
Constant force and work The force shown is a F(x) constant force. W = F x can be used to calculate the work done by this force when it moves an object from xa to xb. The area under the curve from xa to xb can also be used to calculate the work done by the force when it moves an object from xa to xb xa xb x
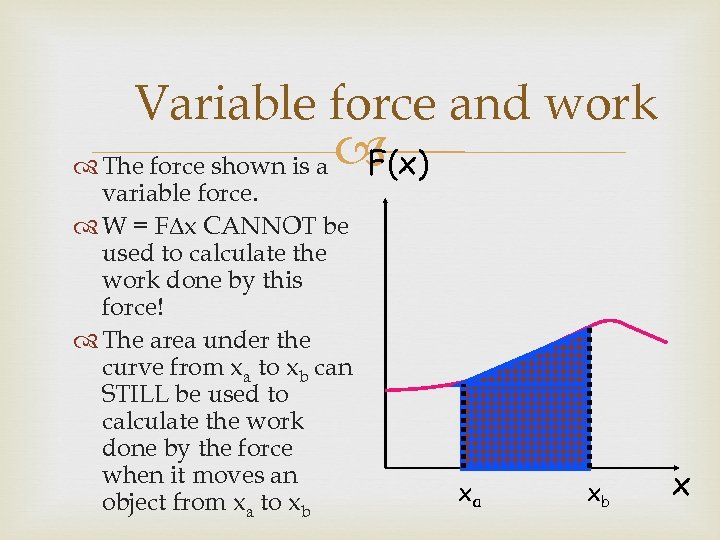 Variable force and work F(x) The force shown is a variable force. W = F x CANNOT be used to calculate the work done by this force! The area under the curve from xa to xb can STILL be used to calculate the work done by the force when it moves an object from xa to xb xa xb x
Variable force and work F(x) The force shown is a variable force. W = F x CANNOT be used to calculate the work done by this force! The area under the curve from xa to xb can STILL be used to calculate the work done by the force when it moves an object from xa to xb xa xb x
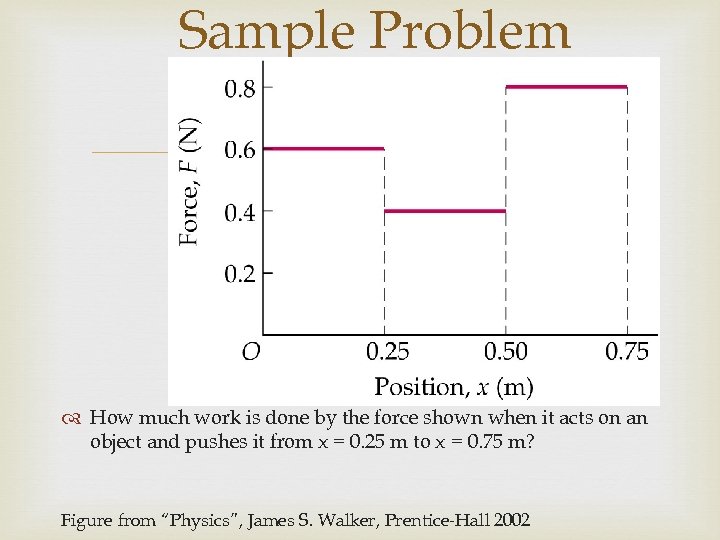 Sample Problem How much work is done by the force shown when it acts on an object and pushes it from x = 0. 25 m to x = 0. 75 m? Figure from “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002
Sample Problem How much work is done by the force shown when it acts on an object and pushes it from x = 0. 25 m to x = 0. 75 m? Figure from “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002
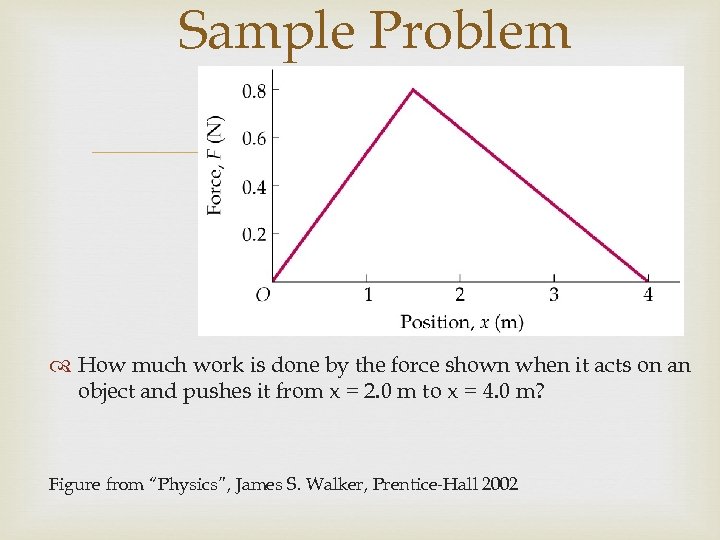 Sample Problem How much work is done by the force shown when it acts on an object and pushes it from x = 2. 0 m to x = 4. 0 m? Figure from “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002
Sample Problem How much work is done by the force shown when it acts on an object and pushes it from x = 2. 0 m to x = 4. 0 m? Figure from “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002
 Springs When a spring is stretched or compressed from its equilibrium position, it does negative work, since the spring pulls opposite the direction of motion. Ws = - ½ k x 2 Ws: work done by spring (J) k: force constant of spring (N/m) x: displacement from equilibrium (m) The force doing the stretching does positive work equal to the magnitude of the work done by the spring. Wapp = ½ k x 2
Springs When a spring is stretched or compressed from its equilibrium position, it does negative work, since the spring pulls opposite the direction of motion. Ws = - ½ k x 2 Ws: work done by spring (J) k: force constant of spring (N/m) x: displacement from equilibrium (m) The force doing the stretching does positive work equal to the magnitude of the work done by the spring. Wapp = ½ k x 2
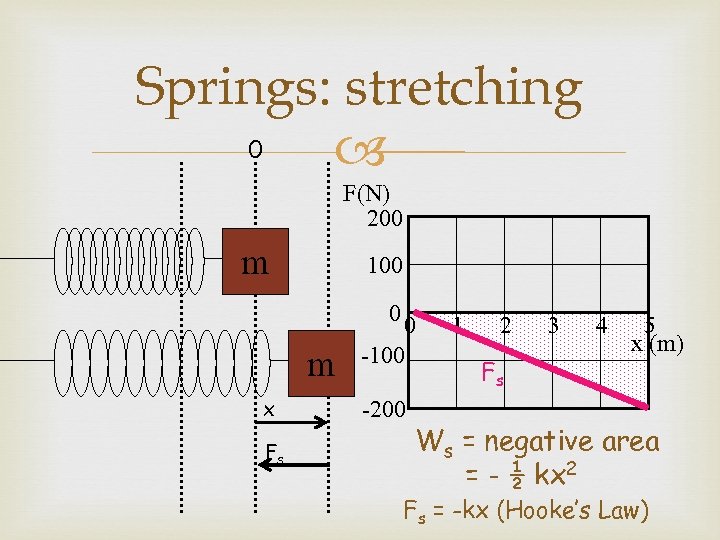 Springs: stretching 0 F(N) 200 m 100 0 m x Fs 0 -100 -200 1 2 Fs 3 4 5 x (m) Ws = negative area = - ½ kx 2 Fs = -kx (Hooke’s Law)
Springs: stretching 0 F(N) 200 m 100 0 m x Fs 0 -100 -200 1 2 Fs 3 4 5 x (m) Ws = negative area = - ½ kx 2 Fs = -kx (Hooke’s Law)
 Sample problem A spring with force constant 250 N/m is initially at its equilibrium length. a) How much work must you do to stretch the spring 0. 050 m? 0. 3125 J b) How much work must you do to compress it 0. 050 m? 0. 3125 J
Sample problem A spring with force constant 250 N/m is initially at its equilibrium length. a) How much work must you do to stretch the spring 0. 050 m? 0. 3125 J b) How much work must you do to compress it 0. 050 m? 0. 3125 J
 Sample problem It takes 1000 J of work to compress a certain spring 0. 10 m. a) What is the force constant of the spring? 2 E 5 N/m b) To compress the spring an additional 0. 10 m, does it take 1000 J, more than 1000 J, or less than 1000 J? Verify your answer with a calculation. 3000 J
Sample problem It takes 1000 J of work to compress a certain spring 0. 10 m. a) What is the force constant of the spring? 2 E 5 N/m b) To compress the spring an additional 0. 10 m, does it take 1000 J, more than 1000 J, or less than 1000 J? Verify your answer with a calculation. 3000 J
 Potential energy Energy of position or configuration “Stored” energy For gravity: Ug = mgh m: mass g: acceleration due to gravity h: height above the “zero” point For springs: Us = ½ k x 2 k: spring force constant x: displacement from equilibrium position
Potential energy Energy of position or configuration “Stored” energy For gravity: Ug = mgh m: mass g: acceleration due to gravity h: height above the “zero” point For springs: Us = ½ k x 2 k: spring force constant x: displacement from equilibrium position
 Sample problem A diver drops to the water from a height of 20. 0 m, his gravitational potential energy decreases by 12, 500 J. How much does the diver weigh? 625 N
Sample problem A diver drops to the water from a height of 20. 0 m, his gravitational potential energy decreases by 12, 500 J. How much does the diver weigh? 625 N
 Sample problem If 30. 0 J of work are required to stretch a spring from a 2. 00 cm elongation to a 4. 00 cm elongation, how much work is needed to stretch it from a 4. 00 cm elongation to a 6. 00 cm elongation? 50 J
Sample problem If 30. 0 J of work are required to stretch a spring from a 2. 00 cm elongation to a 4. 00 cm elongation, how much work is needed to stretch it from a 4. 00 cm elongation to a 6. 00 cm elongation? 50 J
 Force types Forces acting on a system can be divided into two types according to how they affect potential energy. Conservative forces can be related to potential energy changes. Non-conservative forces cannot be related to potential energy changes. So, how exactly do we distinguish between these two types of forces?
Force types Forces acting on a system can be divided into two types according to how they affect potential energy. Conservative forces can be related to potential energy changes. Non-conservative forces cannot be related to potential energy changes. So, how exactly do we distinguish between these two types of forces?
 Conservative forces Work is path independent. the starting and ending Work can be calculated from points only. The actual path is ignored in calculations. Work along a closed path is zero. If the starting and ending points are the same, no work is done by the force. Work changes potential energy. Examples: Gravity Spring force Conservation of mechanical energy holds!
Conservative forces Work is path independent. the starting and ending Work can be calculated from points only. The actual path is ignored in calculations. Work along a closed path is zero. If the starting and ending points are the same, no work is done by the force. Work changes potential energy. Examples: Gravity Spring force Conservation of mechanical energy holds!
 Conservative forces and Potential energy Wc = - U If a conservative force does positive work on a system, potential energy is lost. If a conservative force does negative work, potential energy is gained. For gravity Wg = - Ug = -(mghf – mghi) For springs Ws = - Us = -(½ k xf 2 – ½ k xi 2)
Conservative forces and Potential energy Wc = - U If a conservative force does positive work on a system, potential energy is lost. If a conservative force does negative work, potential energy is gained. For gravity Wg = - Ug = -(mghf – mghi) For springs Ws = - Us = -(½ k xf 2 – ½ k xi 2)
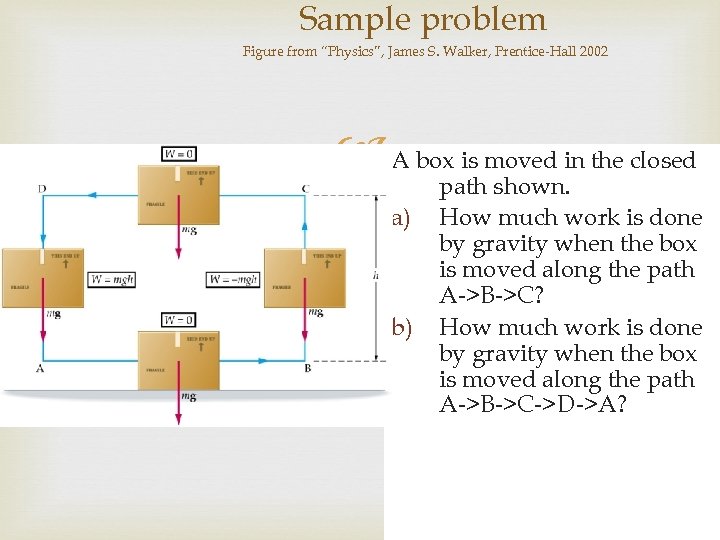 Sample problem Figure from “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A box is moved in the closed a) b) path shown. How much work is done by gravity when the box is moved along the path A->B->C? How much work is done by gravity when the box is moved along the path A->B->C->D->A?
Sample problem Figure from “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A box is moved in the closed a) b) path shown. How much work is done by gravity when the box is moved along the path A->B->C? How much work is done by gravity when the box is moved along the path A->B->C->D->A?
 Non-conservative forces Work is path dependent. Knowing the starting and ending points is not sufficient to calculate the work. Work along a closed path is NOT zero. Work changes mechanical energy. Examples: Friction Drag (air resistance) Conservation of mechanical energy does not hold!
Non-conservative forces Work is path dependent. Knowing the starting and ending points is not sufficient to calculate the work. Work along a closed path is NOT zero. Work changes mechanical energy. Examples: Friction Drag (air resistance) Conservation of mechanical energy does not hold!
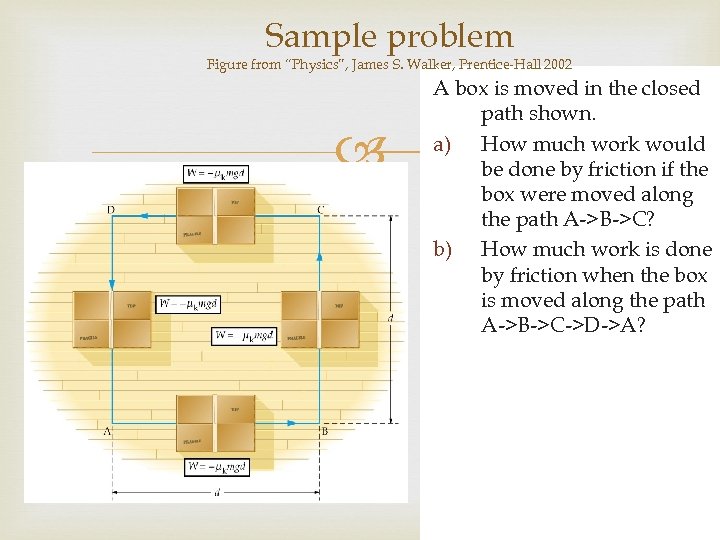 Sample problem Figure from “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A box is moved in the closed path shown. a) How much work would be done by friction if the box were moved along the path A->B->C? b) How much work is done by friction when the box is moved along the path A->B->C->D->A?
Sample problem Figure from “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A box is moved in the closed path shown. a) How much work would be done by friction if the box were moved along the path A->B->C? b) How much work is done by friction when the box is moved along the path A->B->C->D->A?
 Law of Conservation of Energy In any isolated system, the total energy remains constant. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but can only be transformed from one type of energy to another.
Law of Conservation of Energy In any isolated system, the total energy remains constant. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but can only be transformed from one type of energy to another.
 Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy E = K + U = Constant K: Kinetic Energy (1/2 mv 2) U: Potential Energy (gravity or spring) E = U + K = 0 K: Change in kinetic energy U: Change in gravitational or spring potential energy
Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy E = K + U = Constant K: Kinetic Energy (1/2 mv 2) U: Potential Energy (gravity or spring) E = U + K = 0 K: Change in kinetic energy U: Change in gravitational or spring potential energy
 Energy conservation
Energy conservation
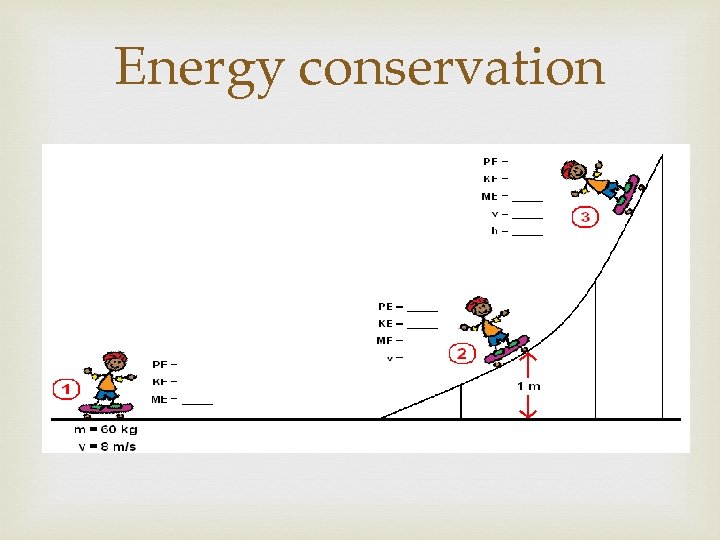
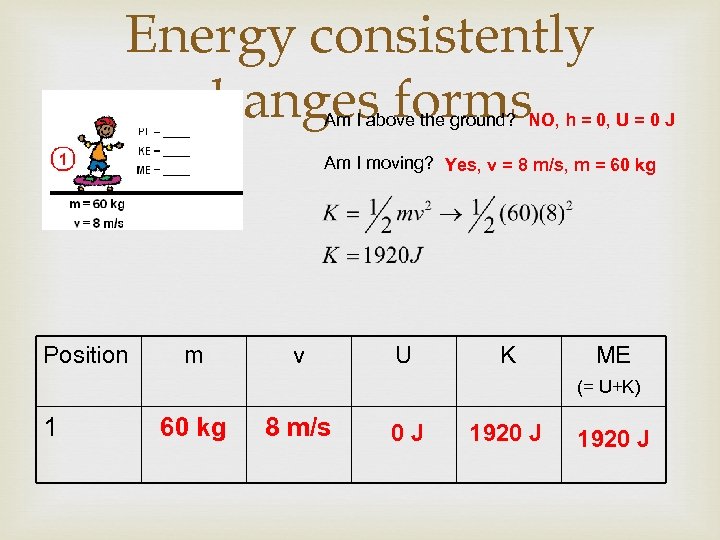 Energy consistently changes forms Am I above the ground? NO, h = 0, U = 0 J Am I moving? Yes, v = 8 m/s, m = 60 kg Position m v U K ME (= U+K) 1 60 kg 8 m/s 0 J 1920 J
Energy consistently changes forms Am I above the ground? NO, h = 0, U = 0 J Am I moving? Yes, v = 8 m/s, m = 60 kg Position m v U K ME (= U+K) 1 60 kg 8 m/s 0 J 1920 J
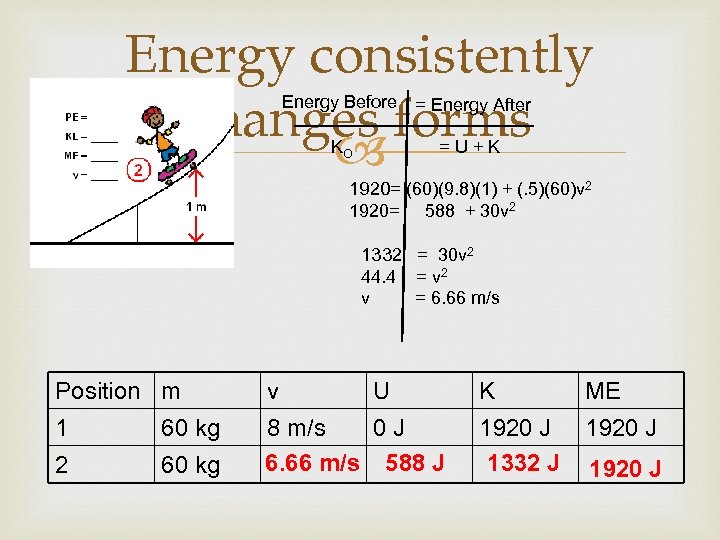 Energy consistently changes forms Energy Before = Energy After KO =U+K 1920= (60)(9. 8)(1) + (. 5)(60)v 2 1920= 588 + 30 v 2 1332 = 30 v 2 44. 4 = v 2 v = 6. 66 m/s Position m v U 1 60 kg 2 60 kg 8 m/s 0 J 6. 66 m/s 588 J K ME 1920 J 1332 J 1920 J
Energy consistently changes forms Energy Before = Energy After KO =U+K 1920= (60)(9. 8)(1) + (. 5)(60)v 2 1920= 588 + 30 v 2 1332 = 30 v 2 44. 4 = v 2 v = 6. 66 m/s Position m v U 1 60 kg 2 60 kg 8 m/s 0 J 6. 66 m/s 588 J K ME 1920 J 1332 J 1920 J
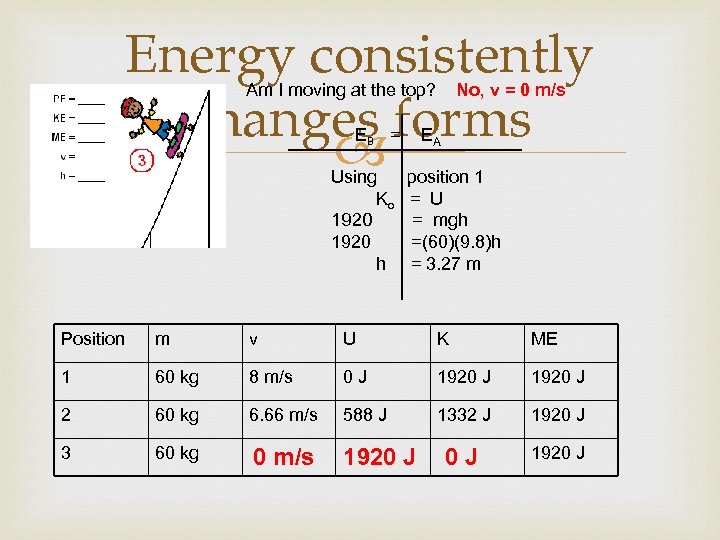 Energy consistently changes forms Am I moving at the top? EB = Using Ko 1920 h No, v = 0 m/s EA position 1 = U = mgh =(60)(9. 8)h = 3. 27 m Position m v U K ME 1 60 kg 8 m/s 0 J 1920 J 2 60 kg 6. 66 m/s 588 J 1332 J 1920 J 3 60 kg 0 m/s 1920 J 0 J 1920 J
Energy consistently changes forms Am I moving at the top? EB = Using Ko 1920 h No, v = 0 m/s EA position 1 = U = mgh =(60)(9. 8)h = 3. 27 m Position m v U K ME 1 60 kg 8 m/s 0 J 1920 J 2 60 kg 6. 66 m/s 588 J 1332 J 1920 J 3 60 kg 0 m/s 1920 J 0 J 1920 J
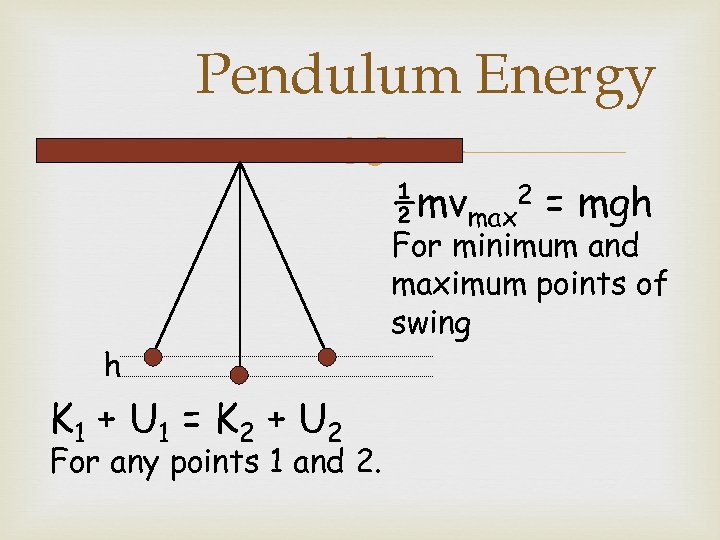 Pendulum Energy h K 1 + U 1 = K 2 + U 2 For any points 1 and 2. ½mvmax 2 = mgh For minimum and maximum points of swing
Pendulum Energy h K 1 + U 1 = K 2 + U 2 For any points 1 and 2. ½mvmax 2 = mgh For minimum and maximum points of swing
 Pendulums and Energy Conservation Energy goes back and forth between K and U. At highest point, all energy is U. As it drops, U goes to K. At the bottom , energy is all K.
Pendulums and Energy Conservation Energy goes back and forth between K and U. At highest point, all energy is U. As it drops, U goes to K. At the bottom , energy is all K.
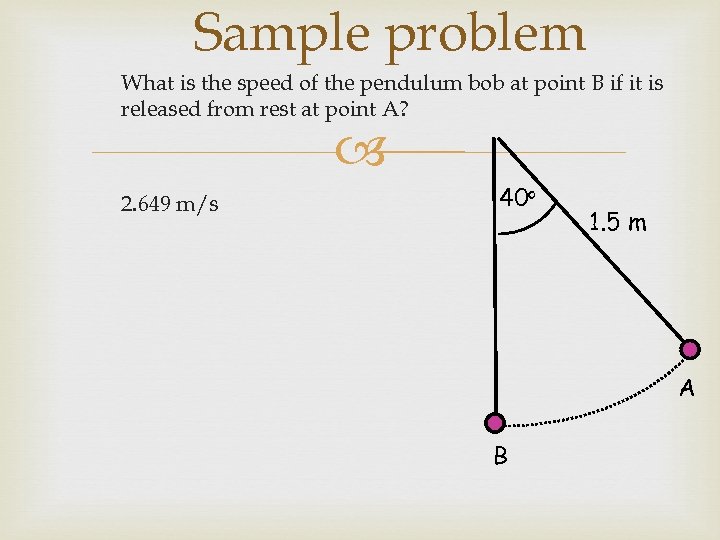 Sample problem What is the speed of the pendulum bob at point B if it is released from rest at point A? 2. 649 m/s 40 o 1. 5 m A B
Sample problem What is the speed of the pendulum bob at point B if it is released from rest at point A? 2. 649 m/s 40 o 1. 5 m A B
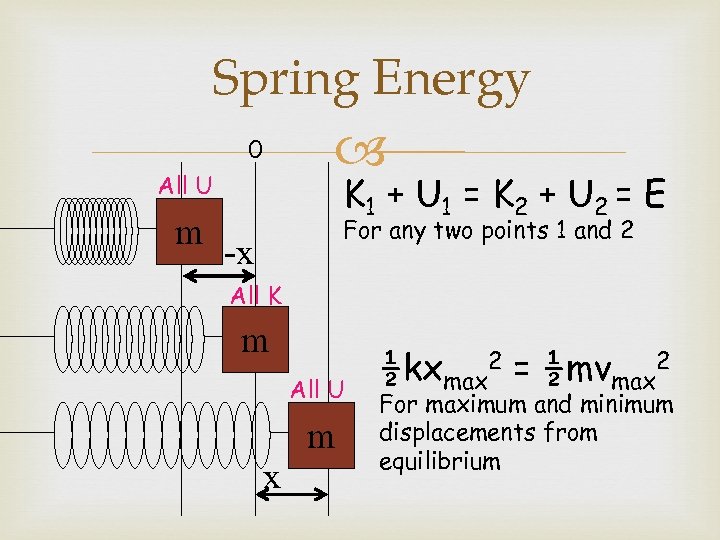 Spring Energy 0 K 1 + U 1 = K 2 + U 2 = E All U m For any two points 1 and 2 -x All K m All U m x ½kxmax 2 = ½mvmax 2 For maximum and minimum displacements from equilibrium
Spring Energy 0 K 1 + U 1 = K 2 + U 2 = E All U m For any two points 1 and 2 -x All K m All U m x ½kxmax 2 = ½mvmax 2 For maximum and minimum displacements from equilibrium
 Springs and Energy Conservation Transforms energy back and forth between K and U. When fully stretched or extended, all energy is U. When passing through equilibrium, all its energy is K. At other points in its cycle, the energy is a mixture of U and K.
Springs and Energy Conservation Transforms energy back and forth between K and U. When fully stretched or extended, all energy is U. When passing through equilibrium, all its energy is K. At other points in its cycle, the energy is a mixture of U and K.
 Sample problem Problem copyright “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A 0. 21 kg apple falls from a tree to the ground, 4. 0 m below. Ignoring air resistance, determine the apple’s gravitational potential energy, U, kinetic energy, K, and total mechanical energy, E, when its height above the ground is each of the following: 4. 0 m, 2. 0 m, and 0. 0 m. Take ground level to be the point of zero potential energy.
Sample problem Problem copyright “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A 0. 21 kg apple falls from a tree to the ground, 4. 0 m below. Ignoring air resistance, determine the apple’s gravitational potential energy, U, kinetic energy, K, and total mechanical energy, E, when its height above the ground is each of the following: 4. 0 m, 2. 0 m, and 0. 0 m. Take ground level to be the point of zero potential energy.
 Sample problem Problem copyright “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A 1. 60 kg block slides with a speed of 0. 950 m/s on a frictionless, horizontal surface until it encounters a spring with a force constant of 902 N/m. The block comes to rest after compressing the spring 4. 00 cm. Find the spring potential energy, U, the kinetic energy of the block, K, and the total mechanical energy of the system, E, for the following compressions: 0 cm, 2. 00 cm, 4. 00 cm.
Sample problem Problem copyright “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A 1. 60 kg block slides with a speed of 0. 950 m/s on a frictionless, horizontal surface until it encounters a spring with a force constant of 902 N/m. The block comes to rest after compressing the spring 4. 00 cm. Find the spring potential energy, U, the kinetic energy of the block, K, and the total mechanical energy of the system, E, for the following compressions: 0 cm, 2. 00 cm, 4. 00 cm.
 Law of Conservation of Energy E = U + K + Eint= Constant Eint is thermal energy. U + K + Eint = 0 Mechanical energy may be converted to and from heat.
Law of Conservation of Energy E = U + K + Eint= Constant Eint is thermal energy. U + K + Eint = 0 Mechanical energy may be converted to and from heat.
 Work done by nonconservative forces Wnet = Wc + Wnc Net work is done by conservative and non-conservative forces Wc = - U Potential energy is related to conservative forces only! Wnet = K Kinetic energy is related to net force (work-energy theorem) K = - U + Wnc From substitution Wnc = U + K = E Nonconservative forces change mechanical energy. If nonconservative work is negative, as it often is, the mechanical energy of the system will drop.
Work done by nonconservative forces Wnet = Wc + Wnc Net work is done by conservative and non-conservative forces Wc = - U Potential energy is related to conservative forces only! Wnet = K Kinetic energy is related to net force (work-energy theorem) K = - U + Wnc From substitution Wnc = U + K = E Nonconservative forces change mechanical energy. If nonconservative work is negative, as it often is, the mechanical energy of the system will drop.
 WORK-KINETIC ENERGY A 30 kg child goes down a 15 m slide that’s angled at 30 degrees above the horizontal. If the slide is frictionless, what would be the speed of the child at the bottom of the slide? 12. 247 m/s If the child’s speed is 10 m/s at the bottom, calculate the work done by friction. 750 J Calculate the coefficient of friction. 0. 333
WORK-KINETIC ENERGY A 30 kg child goes down a 15 m slide that’s angled at 30 degrees above the horizontal. If the slide is frictionless, what would be the speed of the child at the bottom of the slide? 12. 247 m/s If the child’s speed is 10 m/s at the bottom, calculate the work done by friction. 750 J Calculate the coefficient of friction. 0. 333
 Sample problem Problem copyright “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 Catching a wave, a 72 -kg surfer starts with a speed of 1. 3 m/s, drops through a height of 1. 75 m, and ends with a speed of 5. 2 m/s. How much non-conservative work was done on the surfer? 347. 4 J
Sample problem Problem copyright “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 Catching a wave, a 72 -kg surfer starts with a speed of 1. 3 m/s, drops through a height of 1. 75 m, and ends with a speed of 5. 2 m/s. How much non-conservative work was done on the surfer? 347. 4 J
 Sample problem Problem copyright “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A 1. 75 -kg rock is released from rest at the surface of a pond 1. 00 m deep. As the rock falls, a constant upward force of 4. 10 N is exerted on it by water resistance. Calculate the nonconservative work, Wnc, done by the water resistance on the rock, the gravitational potential energy of the system, U, the kinetic energy of the rock, K, and the total mechanical energy of the system, E, for the following depths below the water’s surface: d = 0. 00 m, d = 0. 500 m, d = 1. 00 m. Let potential energy be zero at the bottom of the pond.
Sample problem Problem copyright “Physics”, James S. Walker, Prentice-Hall 2002 A 1. 75 -kg rock is released from rest at the surface of a pond 1. 00 m deep. As the rock falls, a constant upward force of 4. 10 N is exerted on it by water resistance. Calculate the nonconservative work, Wnc, done by the water resistance on the rock, the gravitational potential energy of the system, U, the kinetic energy of the rock, K, and the total mechanical energy of the system, E, for the following depths below the water’s surface: d = 0. 00 m, d = 0. 500 m, d = 1. 00 m. Let potential energy be zero at the bottom of the pond.


