lect.1. 2012.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Words, words What do you know about words?

The structure of English words • The notion of ‘word’ is central in the study of lexicology. • What do you know about the structure of English words?

Morphological structure lungentlemanly lgarbology (gar+bol+uh+jee the study of a society or culture by examining what it discards)
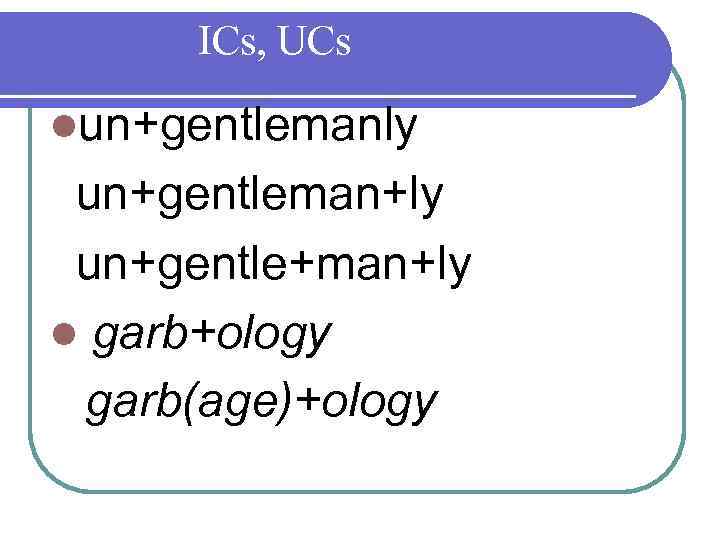
ICs, UCs lun+gentlemanly un+gentleman+ly un+gentle+man+ly l garb+ology garb(age)+ology
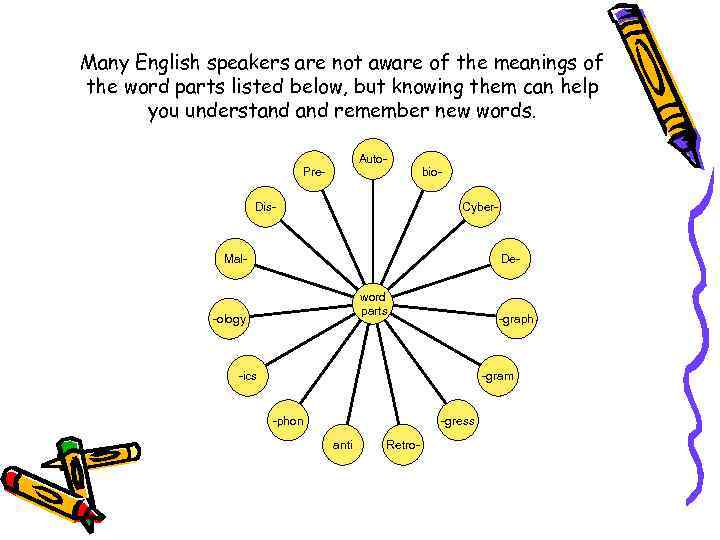
Many English speakers are not aware of the meanings of the word parts listed below, but knowing them can help you understand remember new words. Auto- Pre. Dis- bio. Cyber- De- Malword parts -ology -graph -gram -ics -gress -phon anti Retro-

What is lexicology? • 1. 1. What is the scope of lexicology? • Objectives of the lecture: • the academic and practical goals of the subject of Lexicology; • scientific conception of major factors and trends in the development of words; • to be word conscious, be able to guess the meaning of words from the meaning of morphemes • 1. 2 Lexicology as a level of language analysis (related fields: phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, etymology, and lexicography)

English Lexicology • Lexicology may be defined as the study of lexis, understood as the stock of words in a given language, i. e. its vocabulary or lexicon (from Gr. lexis, ‘word’, lexikos, ‘of/for words’). Lexicology is a science about the vocabulary of a foreign language under study; • Word is central in the study of lexicology, it is the basic unit of a given language.
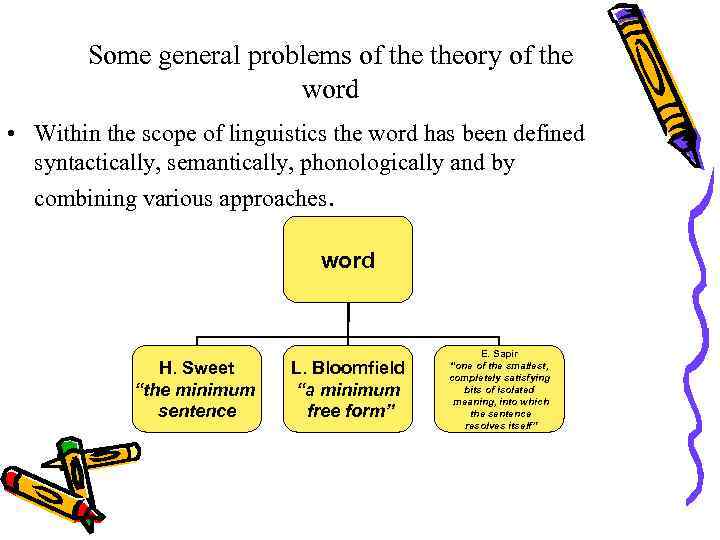
Some general problems of theory of the word • Within the scope of linguistics the word has been defined syntactically, semantically, phonologically and by combining various approaches. word H. Sweet “the minimum sentence L. Bloomfield “a minimum free form” E. Sapir “one of the smallest, completely satisfying bits of isolated meaning, into which the sentence resolves itself”

What does lexicology deal with? • Simple words within all their aspects; complex and compound words, the meaningful units of language. • Morphology (the study of the forms of words and their components). • Semantics (the study of word meanings). • Phonetics, grammar, history of the • language, stylistics.

Problems • Word-structure and word-formation in Modern English, the semantic structure of English words, relations between various lexical layers of the English vocabulary, the source and growth of the Enlg. vocabulary, the changes it has undergone in its history and so on.

Denotative and connotative meaning • “Specialists are not in agreement in their treatment of the distinction between denotation and connotation, or denotative vs connotative meaning. • For the supporters of the binary distinction between denotation and connotation, denotative meaning refers to the relationship between a linguistic sign and its denotatum or referent. However connotations constitute additional properties of lexemes, e. g. poetic, slang, baby language, biblical” and so on. (Howard Jackson & Etienne Ze Amvela)

Morphemes – the smallest meaningful element of a language – hope, life, small, old (1 morpheme words) – helpful, lifeless(2 morpheme words) – non-productive, ungrateful (3 morpheme words) – unsuccessfully (4 morpheme words)
The role and function of morphemes • Constructing words. Roots, affixes. • Function: derivational, functional, productive, non-productive affixes. Various types of words with components of lexical and lexico-grammatical meaning

Functional affixes • convey grammatical meaning • different forms of one and the same word: small (er, est), mother (‘s, s, ‘s) • The system of grammatical forms characteristic of a word is called a paradigm.

Word forming activity of affixes • Productive affixes: re-, pre-, non-, un-, ness, -er, -ism, -ist and so on. (reconsider, pre-historic) • Non-productive affixes are separate morphemes possessing semantic characteristics: fasten, heighten; beatiful (ful adj. forming) • Dead aff. deed, seed; sail, walk, talk, friend • Native aff. –d, -dom, -ed, -en, -hood, -ful • Borrowed aff. –able Lat. ), -ade (Fr. )
Types of morphemes • The root morpheme is the lexical nucleus of the word, it has a general meaning common to a set of words: teach, teacher, teaching. • Stem – the basic unit at derivational level of analysis; the part of a word that remains unchanged throughout its paradigm: list-en, hand-some, on-ly, darling (dear-ing; there is no semantic link between them). The stem expresses the lexical and the part of speech meaning.

structure • Free morphemes: coincide with a stem or a word-form (scholarship) • Bound morphemes: a constituent part of a word (suffixes, prefixes) • Semi-free morphemes: can function in a morphemic sequence both as an affix and a free morpheme (well-known, half-eaten, step-mother).

What did you learn from the lecture? Word structure n Morphemes; classification of morphemes n Root, stem n Structure of morphemes n Task: Read about Immediate, Ultimate constituents of words. n

1. Г. Н. Бабич Lexicology: A Current Guide Учебное пособие М. 2010 2. Э. М. Дубенец Modern English Lexicology Theory and Practice M. 2002 3. Arnold J. V. Лексикология современного английского языка. M. 1973 4. Ginsburg P. S. , Khidekel S. S. , Knyazeva G. Y. , Sankin A. A. A Course in Modern English Lexicology M. 1966. 5. Crystal D. The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the English Language G. B. Cambridge University Press, 1996.

references • Antrushina G. B. , Afanasieva, O. V. Morozova N. N. English Lexicology M. 1999. • Arnold J. V. The English Word M. 1973. • Ginsburg P. S. , Khidekel S. S. , Knyazeva G. Y. , Sankin A. A. A Course in Modern English Lexicology M. 1966. • Khidekel S. S. , Knyazeva G. Y. , Sankin A. A. Readings in Modern English Lexicology. L. 1975. • Кунин А. В. Английская фразеология (теоретической курс) М. , 1970. • Электронный учебник лексикологии английского языка. • Составители: Булатова С. М. , Сыздыкова Г. Н.
lect.1. 2012.ppt