Lecture 4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Word meaning and its structure Semasiology - the branch of linguistics concerned with the meaning of words and word equivalents. (Greek) semasia - signification (значение, смысл) and logos - learning.
Word meaning and its structure Semasiology - the branch of linguistics concerned with the meaning of words and word equivalents. (Greek) semasia - signification (значение, смысл) and logos - learning.
 The main objects of semasiological study: types of lexical meaning polysemy and semantic structure of words semantic development of words the main tendencies of the change of word -meanings semantic grouping in the vocabulary system (synonyms, antonyms) semantic fields
The main objects of semasiological study: types of lexical meaning polysemy and semantic structure of words semantic development of words the main tendencies of the change of word -meanings semantic grouping in the vocabulary system (synonyms, antonyms) semantic fields
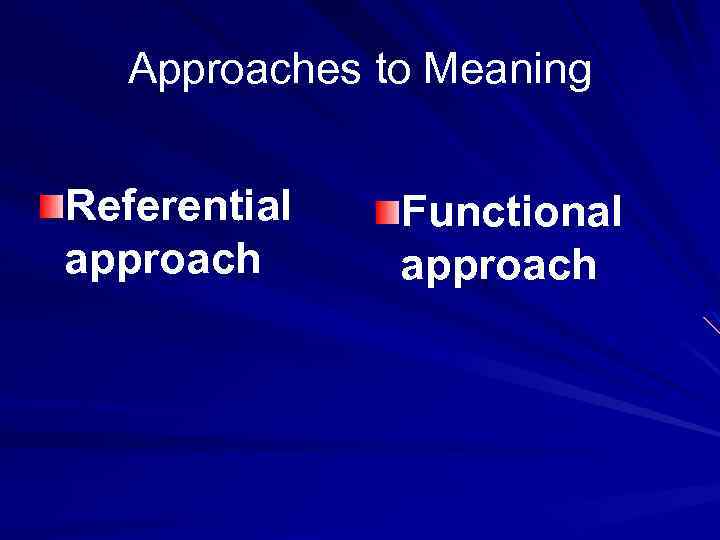 Approaches to Meaning Referential Functional approach
Approaches to Meaning Referential Functional approach
 Referential approach to meaning The meaning is in some form or other connected with the referent (object of reality denoted by the word). The meaning is formulated by establishing the interdependence between words and objects of reality they denote. The meaning is often understood as an object or phenomenon in the outside world that is referred to by a word.
Referential approach to meaning The meaning is in some form or other connected with the referent (object of reality denoted by the word). The meaning is formulated by establishing the interdependence between words and objects of reality they denote. The meaning is often understood as an object or phenomenon in the outside world that is referred to by a word.
 Functional approach to meaning Words are studied in context; a word is defined by its functioning within phrase or a sentence. The meaning of linguistic unit is studied only through its relation to other linguistic units. The meaning is viewed as the function of a word in speech.
Functional approach to meaning Words are studied in context; a word is defined by its functioning within phrase or a sentence. The meaning of linguistic unit is studied only through its relation to other linguistic units. The meaning is viewed as the function of a word in speech.
 Concept a category of human cognition (понятие, идея; общее представление; концепция). the thought of the object that singles out the most typical, the most essential features of the object.
Concept a category of human cognition (понятие, идея; общее представление; концепция). the thought of the object that singles out the most typical, the most essential features of the object.
 the concept of "a building for human habitation" English Ukrainian house дім "fixed residence of family or household" − home домівкa
the concept of "a building for human habitation" English Ukrainian house дім "fixed residence of family or household" − home домівкa
 The difference between meaning and concept: Concepts are always emotionally neutral Meaning of many words not only conveys some reflection of objective reality but also the speaker's attitude to what he is speaking about, his state of mind. The concept of size: big / large / tremendous
The difference between meaning and concept: Concepts are always emotionally neutral Meaning of many words not only conveys some reflection of objective reality but also the speaker's attitude to what he is speaking about, his state of mind. The concept of size: big / large / tremendous
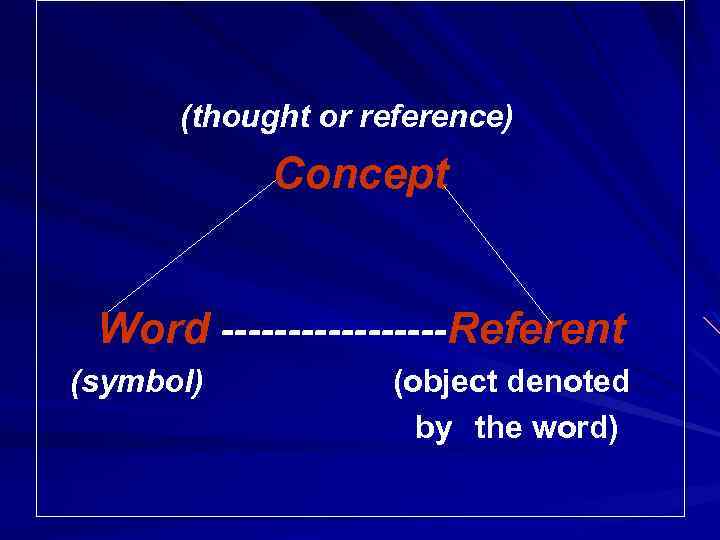 (thought or reference) Concept Word ---------Referent (symbol) (object denoted by the word)
(thought or reference) Concept Word ---------Referent (symbol) (object denoted by the word)
 The branch of linguistics which specializes in the study of meaning is called semantics. Meaning is a certain reflection in our mind of objects, phenomena or relations that makes part of the linguistic sign − its so-called inner facet (аспект, грань, сторона), whereas the sound-form functions as its outer facet.
The branch of linguistics which specializes in the study of meaning is called semantics. Meaning is a certain reflection in our mind of objects, phenomena or relations that makes part of the linguistic sign − its so-called inner facet (аспект, грань, сторона), whereas the sound-form functions as its outer facet.
 grammatical and lexical meanings Grammatical Lexical meaning − the expression in realization of speech the concept or relationships emotion by between words. means of a definite language system.
grammatical and lexical meanings Grammatical Lexical meaning − the expression in realization of speech the concept or relationships emotion by between words. means of a definite language system.
 three types of lexical meaning of words: 1. Nominative meaning determined by reality. The direct nominative meaning stands in one-to-one relationship with a word. cat, table, sun 2. Phraseologically bound meaning of words depending on the peculiarities of their usage in a given language, e. g. to take care, to have a smoke, to catch a cold.
three types of lexical meaning of words: 1. Nominative meaning determined by reality. The direct nominative meaning stands in one-to-one relationship with a word. cat, table, sun 2. Phraseologically bound meaning of words depending on the peculiarities of their usage in a given language, e. g. to take care, to have a smoke, to catch a cold.
 3. Syntactically conditioned meanings of words are those which change with the change of the environment. Compare the following verbs: «to look» - to look for-- to look after
3. Syntactically conditioned meanings of words are those which change with the change of the environment. Compare the following verbs: «to look» - to look for-- to look after
 The structure of lexical meaning of a word denotative meaning connotative meaning
The structure of lexical meaning of a word denotative meaning connotative meaning
 Denotative meaning a linguistic expression for a concept or a name for an individual object. makes communication possible. is bound up with its referent. may have one constant referent – a moon may have several referents - a hand
Denotative meaning a linguistic expression for a concept or a name for an individual object. makes communication possible. is bound up with its referent. may have one constant referent – a moon may have several referents - a hand
 Connotative meaning additional non-literal meaning of a word. contains various shades of meaning called connotations reflect subjective, emotional attitude of people toward object or phenomenon. is unstable. In most cases it reveals itself only through contexts.
Connotative meaning additional non-literal meaning of a word. contains various shades of meaning called connotations reflect subjective, emotional attitude of people toward object or phenomenon. is unstable. In most cases it reveals itself only through contexts.
 four main types of connotations: stylistic connotation is what the word conveys about the speaker's attitude to the social circumstances and the appropriate functional style (slay vs kill) emotional connotation conveys the speaker's emotions (mummy vs mother)
four main types of connotations: stylistic connotation is what the word conveys about the speaker's attitude to the social circumstances and the appropriate functional style (slay vs kill) emotional connotation conveys the speaker's emotions (mummy vs mother)
 evaluative connotation may show his approval or disapproval of the object spoken of (clique vs group) expressive/intensifying connotation is conveyed by degree of intensity (adore vs love)
evaluative connotation may show his approval or disapproval of the object spoken of (clique vs group) expressive/intensifying connotation is conveyed by degree of intensity (adore vs love)
 terrific the denotative component of the lexical meaning of the word is "frightening“. the expressive or intensifying connotation is "very, very good" or "very great": terrific beauty, terrific pleasure
terrific the denotative component of the lexical meaning of the word is "frightening“. the expressive or intensifying connotation is "very, very good" or "very great": terrific beauty, terrific pleasure
 It is the connotative meaning in a word which helps create irony, sarcasm, metaphor and other figures of speech.
It is the connotative meaning in a word which helps create irony, sarcasm, metaphor and other figures of speech.
 POLYSEMY the ability of words to have more than one meaning. A word having several meanings is called polysemantic and most English words are like this.
POLYSEMY the ability of words to have more than one meaning. A word having several meanings is called polysemantic and most English words are like this.
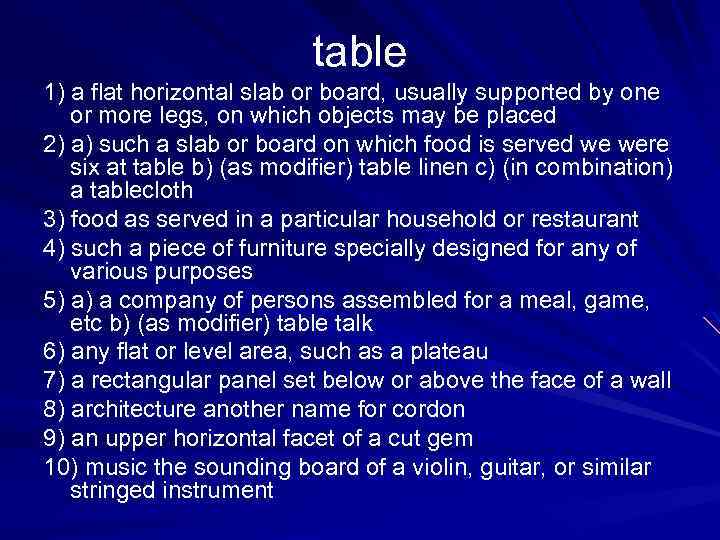 table 1) a flat horizontal slab or board, usually supported by one or more legs, on which objects may be placed 2) a) such a slab or board on which food is served we were six at table b) (as modifier) table linen c) (in combination) a tablecloth 3) food as served in a particular household or restaurant 4) such a piece of furniture specially designed for any of various purposes 5) a) a company of persons assembled for a meal, game, etc b) (as modifier) table talk 6) any flat or level area, such as a plateau 7) a rectangular panel set below or above the face of a wall 8) architecture another name for cordon 9) an upper horizontal facet of a cut gem 10) music the sounding board of a violin, guitar, or similar stringed instrument
table 1) a flat horizontal slab or board, usually supported by one or more legs, on which objects may be placed 2) a) such a slab or board on which food is served we were six at table b) (as modifier) table linen c) (in combination) a tablecloth 3) food as served in a particular household or restaurant 4) such a piece of furniture specially designed for any of various purposes 5) a) a company of persons assembled for a meal, game, etc b) (as modifier) table talk 6) any flat or level area, such as a plateau 7) a rectangular panel set below or above the face of a wall 8) architecture another name for cordon 9) an upper horizontal facet of a cut gem 10) music the sounding board of a violin, guitar, or similar stringed instrument
 Change of lexical meaning in words linguistic extra-linguistic - the influence of - cultural linguistic - social environment - psychological - analogy - the context
Change of lexical meaning in words linguistic extra-linguistic - the influence of - cultural linguistic - social environment - psychological - analogy - the context
 ways of change of word- meaning: 1. extension of meaning (generalization); 2. narrowing of meaning (specialization); 3. transference of meaning (metaphor and metonymy); 4. elevation of meaning (amelioration); 5. degradation of meaning
ways of change of word- meaning: 1. extension of meaning (generalization); 2. narrowing of meaning (specialization); 3. transference of meaning (metaphor and metonymy); 4. elevation of meaning (amelioration); 5. degradation of meaning
 1. Extension /expanding of meaning (or generalization). In the process of extension a word- meaning may acquire a higher degree of abstraction or more generalized character. “manuscript” originally meant only something handwritten. Now it refers to any copy either written by hand or printed.
1. Extension /expanding of meaning (or generalization). In the process of extension a word- meaning may acquire a higher degree of abstraction or more generalized character. “manuscript” originally meant only something handwritten. Now it refers to any copy either written by hand or printed.
 2. Narrowing of meaning/contraction, (specialization). In the process of narrowing, a word- meaning acquires a specialized sense in which it is applicable only to some of the objects or phenomena it previously denoted. a corpse - a human or animal body, living or dead. Now this word has been specialized to mean «a dead body» , usually that of a human being.
2. Narrowing of meaning/contraction, (specialization). In the process of narrowing, a word- meaning acquires a specialized sense in which it is applicable only to some of the objects or phenomena it previously denoted. a corpse - a human or animal body, living or dead. Now this word has been specialized to mean «a dead body» , usually that of a human being.
 3. Elevation of meaning (amelioration ) In the process of elevation a word acquires the meaning of a greater importance than its original meaning. marshal - originally meant a horse servant, now its meaning is «an officer of the highest rank»
3. Elevation of meaning (amelioration ) In the process of elevation a word acquires the meaning of a greater importance than its original meaning. marshal - originally meant a horse servant, now its meaning is «an officer of the highest rank»
 4. Degradation of Meaning (degeneration, pejoration). In the process of pejoration the word acquires unfavourable connotations or falls into disrepute. «vulgar» - originally meant «common, ordinary» ; «gossip» - originally meant «a god parent» ; «silly» - originally meant «happy» .
4. Degradation of Meaning (degeneration, pejoration). In the process of pejoration the word acquires unfavourable connotations or falls into disrepute. «vulgar» - originally meant «common, ordinary» ; «gossip» - originally meant «a god parent» ; «silly» - originally meant «happy» .
 5. Transference of meaning takes place when the figures of speech are used. Figures of speech are expressive means and stylistic devices such as metaphor and metonymy.
5. Transference of meaning takes place when the figures of speech are used. Figures of speech are expressive means and stylistic devices such as metaphor and metonymy.
 Metaphor the transference of the literal meaning in a word based on the association of similarity between the objects or phenomena. a woman can be called «a peach» if she is young and beautiful, or «a lemon» if she is ugly and boring.
Metaphor the transference of the literal meaning in a word based on the association of similarity between the objects or phenomena. a woman can be called «a peach» if she is young and beautiful, or «a lemon» if she is ugly and boring.
 Metonymy the transference of the literal meaning of a word based on the association of contiguity between objects or phenomena. «cash» is an adaptation of the French word "caisse" which means "box" and in which money was contained. Now the meaning of this word is "money". «crown» in the meaning of "monarchy"
Metonymy the transference of the literal meaning of a word based on the association of contiguity between objects or phenomena. «cash» is an adaptation of the French word "caisse" which means "box" and in which money was contained. Now the meaning of this word is "money". «crown» in the meaning of "monarchy"


