WORD FORMATION1. morphemes.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 WORD FORMATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Word structure. Segmentation of Words into Morphemes. Principles of Morphemic Analysis. Types of Word Segmentability. Classification of Morphemes. Word-Formation. Definition. Types of word-formation. Productivity of Word-Formation.
WORD FORMATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Word structure. Segmentation of Words into Morphemes. Principles of Morphemic Analysis. Types of Word Segmentability. Classification of Morphemes. Word-Formation. Definition. Types of word-formation. Productivity of Word-Formation.
 Word structure Segmentation of Words into Morphemes Ø many words have a composite nature and are made up of smaller units, each possessing sound-form and meaning
Word structure Segmentation of Words into Morphemes Ø many words have a composite nature and are made up of smaller units, each possessing sound-form and meaning
 Ø Morphemes are the smallest further indivisible two-facet language units
Ø Morphemes are the smallest further indivisible two-facet language units
 Ø Like a word a morpheme is a two-facet language unit, an association of a certain meaning with a certain sound-pattern Ø Unlike a word a morpheme is not an autonomous unit and can occur in speech only as a constituent part of the word
Ø Like a word a morpheme is a two-facet language unit, an association of a certain meaning with a certain sound-pattern Ø Unlike a word a morpheme is not an autonomous unit and can occur in speech only as a constituent part of the word
 Remember: Ø morphemes may have different phonemic shapes e. g: please, pleasing, pleasure, pleasant [pli: z] in please, pleasing, [pleз] in pleasure and [plez] in pleasant.
Remember: Ø morphemes may have different phonemic shapes e. g: please, pleasing, pleasure, pleasant [pli: z] in please, pleasing, [pleз] in pleasure and [plez] in pleasant.
 In such cases we say that they ear allomorphs of that morpheme or morpheme variants. Thus [pli: z, plez] and [рlез] are allomorphs of оnе and the same morpheme
In such cases we say that they ear allomorphs of that morpheme or morpheme variants. Thus [pli: z, plez] and [рlез] are allomorphs of оnе and the same morpheme
 Principles of Morphemic Analysis. Types of Word Segmentability Structurally English words fall into two classes: 1. segmentable words: allow segmentation into morphemes, e. g. agreement, information, fearless; 2. non-segmentable words: do not allow such segmentation, e. g. house, girl, woman
Principles of Morphemic Analysis. Types of Word Segmentability Structurally English words fall into two classes: 1. segmentable words: allow segmentation into morphemes, e. g. agreement, information, fearless; 2. non-segmentable words: do not allow such segmentation, e. g. house, girl, woman
 WHAT IS MORPHEMIC ANALYSIS? The morphemic analysis aims at splitting a segmentable word into its constituent morphemes — the basic units at this level of word-structure analysis — and at determining their number and types
WHAT IS MORPHEMIC ANALYSIS? The morphemic analysis aims at splitting a segmentable word into its constituent morphemes — the basic units at this level of word-structure analysis — and at determining their number and types
 Types of segmentability of words Three types of morphemic segmentability of words are distinguished: complete, conditional and defective
Types of segmentability of words Three types of morphemic segmentability of words are distinguished: complete, conditional and defective
 Ø COMPLETE: the morphemic structure of words is transparent enough, individual morphemes clearly stand out easily to be isolated: Ø driver, agreement
Ø COMPLETE: the morphemic structure of words is transparent enough, individual morphemes clearly stand out easily to be isolated: Ø driver, agreement
 Ø CONDITIONAL: segmentation into the constituent morphemes is doubtful for semantic reasons: like retain, contain, detain or receive, deceive, Ø the sound-clusters [ri-], [di-], [кэn-] seem to be singled out quite easily BUT they have nothing in common with the phonetically identical morphemes re-, de- as found in words like rewrite
Ø CONDITIONAL: segmentation into the constituent morphemes is doubtful for semantic reasons: like retain, contain, detain or receive, deceive, Ø the sound-clusters [ri-], [di-], [кэn-] seem to be singled out quite easily BUT they have nothing in common with the phonetically identical morphemes re-, de- as found in words like rewrite
 Ø DEFECTIVE: the property of words whose component morphemes seldom or never recur in other words: ringlet, leaflet BUT hamlet.
Ø DEFECTIVE: the property of words whose component morphemes seldom or never recur in other words: ringlet, leaflet BUT hamlet.
 Classification of Morphemes may be classified: from the structural point of view Ø from the semantic point of view Ø
Classification of Morphemes may be classified: from the structural point of view Ø from the semantic point of view Ø
 Ø Structurally morphemes fall into three types: free morphemes, bound morphemes, semi-free (semi- bound) morphemes.
Ø Structurally morphemes fall into three types: free morphemes, bound morphemes, semi-free (semi- bound) morphemes.
 Ø A free morpheme coincides with the stem or a word-form: friend in friendship is a free morpheme because it coincides with one of the forms of the noun friend.
Ø A free morpheme coincides with the stem or a word-form: friend in friendship is a free morpheme because it coincides with one of the forms of the noun friend.
 Ø A bound morpheme occurs only as a constituent part of a word. Affixes are bound morphemes, they always make part of a word, e. g. the suffixes -ness, -ship, ise (-ize), etc. , the prefixes un, dis
Ø A bound morpheme occurs only as a constituent part of a word. Affixes are bound morphemes, they always make part of a word, e. g. the suffixes -ness, -ship, ise (-ize), etc. , the prefixes un, dis
 Ø Root-morphemes can be bound too. Unique roots and pseudo-roots are-bound morphemes: theor- in theory, theoretical, etc. , barbar- in barbarism, barbarian
Ø Root-morphemes can be bound too. Unique roots and pseudo-roots are-bound morphemes: theor- in theory, theoretical, etc. , barbar- in barbarism, barbarian
 Semi-bound morphemes can function in a morphemic sequence both as an affix and as a free morpheme. Well and half occur as free morphemes that coincide with the stem on the other hand they occur as bound morphemes in words like well-known, half-eaten, halfdone
Semi-bound morphemes can function in a morphemic sequence both as an affix and as a free morpheme. Well and half occur as free morphemes that coincide with the stem on the other hand they occur as bound morphemes in words like well-known, half-eaten, halfdone
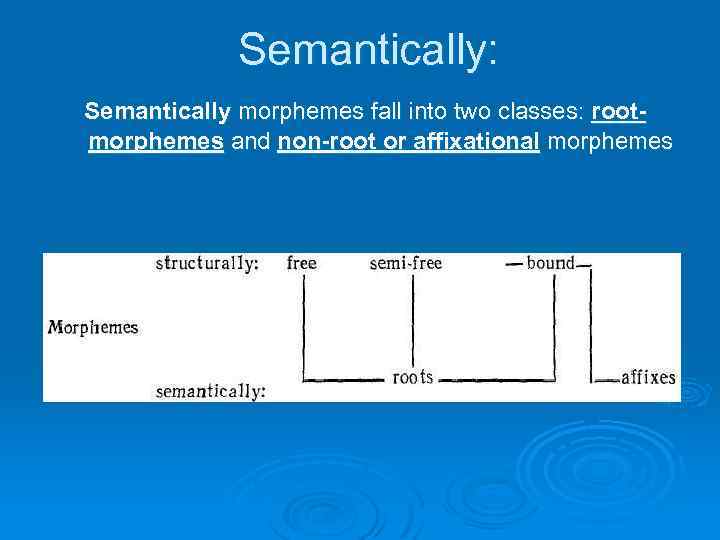 Semantically: Semantically morphemes fall into two classes: rootmorphemes and non-root or affixational morphemes
Semantically: Semantically morphemes fall into two classes: rootmorphemes and non-root or affixational morphemes
 Derivationally all words form two structural classes: simplexes, i. e. simple, non-derived words and complexes, or derivatives. Derivatives fall into: suffixal derivatives, prefixal derivatives, conversions and compounds
Derivationally all words form two structural classes: simplexes, i. e. simple, non-derived words and complexes, or derivatives. Derivatives fall into: suffixal derivatives, prefixal derivatives, conversions and compounds
 WAYS OF FORMING WORDS Word-Formation is the system of derivative types of words and the process of creating new words from the material available in the language after certain structural and semantic formulas and patterns.
WAYS OF FORMING WORDS Word-Formation is the system of derivative types of words and the process of creating new words from the material available in the language after certain structural and semantic formulas and patterns.
 Ø Word-formation is that branch of Lexicology which studies the derivative structure of existing words and the patterns on which a language builds new words
Ø Word-formation is that branch of Lexicology which studies the derivative structure of existing words and the patterns on which a language builds new words
 Types of word-formation in Modern English: word- derivation and wordcomposition.
Types of word-formation in Modern English: word- derivation and wordcomposition.


