RM_Intro_Fall2012.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

WIUU BBA RM COURSE: Risk Management INSTRUCTOR: Andriy Zaporozhetz, MBA, CPA E-MAIL: andriyzatz@gmail. com CLASS HOURS: Fridays, 15: 20 - 17: 55 COURSE DESCRIPTION: Pls see the Syllabus WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 1

CLASS RULES Ø No phone calls please Ø 15: 20 – 17: 55 Ø Q&A welcome Ø Group work and class discussions Ø WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz Sharing your work experience 2

Class 1 Introduction Definitions of Risk and RM: Modern history. Types of Risks. “Risk Universe”. IRM Standard of 2002. Study materials: IRM Standard 2002 Slides WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 3

DEFINITIONS (1) “Risk can be defined as the combination of the probability of event and its consequences. ” (ISO/IEC Guide 73: 2002) Harrington, Niehaus (2004): One situation is riskier than another if it has greater: a) expected loss, b) variability around the expected loss. E. g. : The possible fire loss at a spare parts w/house is estimated at $800, 000 (= impact), and the probability (= likelihood) within 1 year is 5%. What is the risk exposure in USD terms? Solution: $800, 000 * 5% = $40, 000 (within 1 year). WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 4
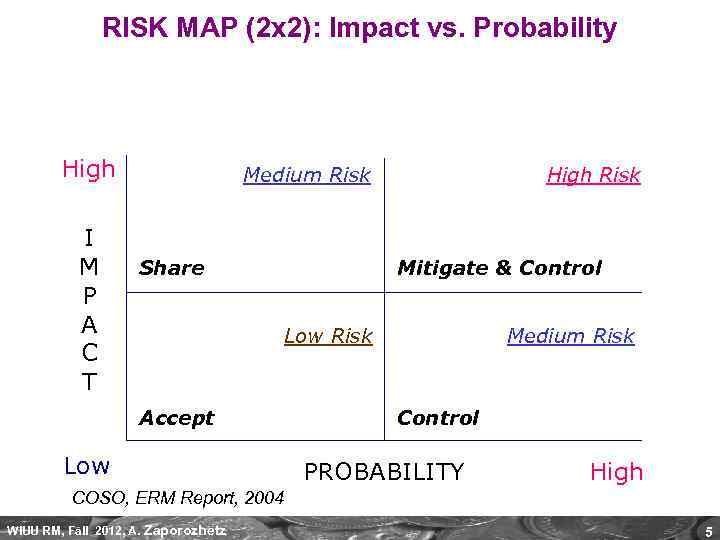
RISK MAP (2 x 2): Impact vs. Probability High I M P A C T Medium Risk Share High Risk Mitigate & Control Low Risk Accept Low Medium Risk Control PROBABILITY High COSO, ERM Report, 2004 WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 5

DEFINITIONS (2) “The distribution of possible outcomes in a Business Unit’s performance over a given time horizon due to changes in key underlying variables. The greater the dispersion of possible outcomes, the higher the Business Unit’s level of exposure. . . The organization’s sensitivity to risk is a function of: (1) the significance of its exposures to changes and events, (2) the likelihood of those different changes and events occurring and (3) its ability to manage the business implications of those different possible future changes and events, if they occur. ” (CAT University) WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 6

DEFINITIONS (3) “The chance that an investment's actual return will be different from expected. This includes the possibility of losing some/all of the original investment. Usually measured by the standard deviation of the historical returns. ” (Investopedia. com) NB: This implies that there could be both downside risks, and upside risks. Also, risk is NOT uncertainty (when probabilities of outcomes cannot be estimated for various reasons). WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 7
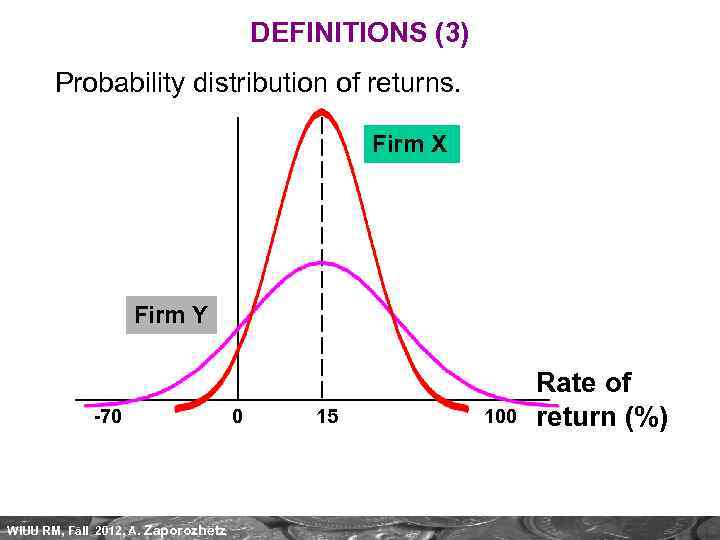
DEFINITIONS (3) Probability distribution of returns. Firm X Firm Y -70 WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 0 15 100 Rate of return (%)
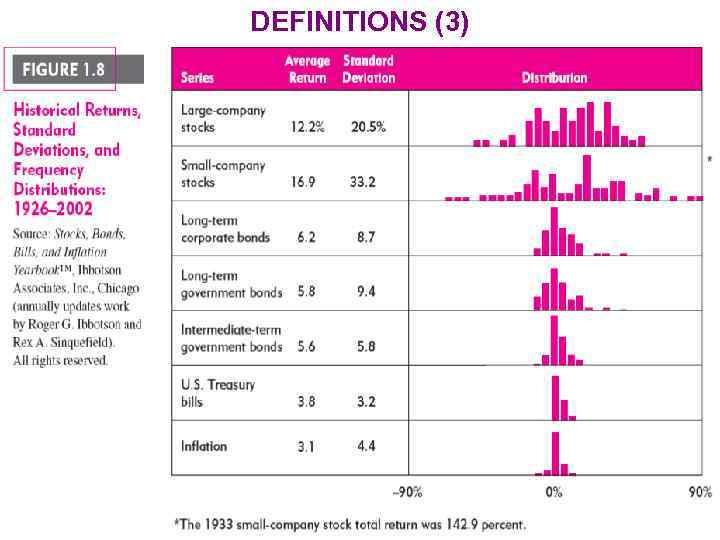
DEFINITIONS (3) 2. Risk and return relationship WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 9

DEFINITIONS (4) “The chance that an outcome will be different than expected; can be measured as the degree of variability in either an individual’s or an organization’s anticipated investment outcomes. ” (SMA 2 A “Management Accounting Glossary”) Also, not only financial investments are taken into consideration. WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 10

DEFINITION (5) Modern approach states that both threats and opportunities are associated with risk. A Word of Wisdom: ü“Who never risks, never wins. ” (English proverb) ü“Who never risks, does not drink champagne. ” (Russian proverb) ü“The policy of being too cautious is the greatest risk of all. ” (Jawaharlal Nehru, Indian politician) In financial markets, “hedging” are activities to manage (avoid) risks, but “speculating” are activities to take on risks. WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 11

DEFINITIONS: “PURE RISK” WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 12

RISK MANAGEMENT WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 13

BUSINESS RISK & BR MANAGEMENT WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 14

RISK MGT AS A SCIENCE WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 15

RISK MGT: Modern History 1953: International Organization of Supreme Audit Institutions (IOSAI) 1986: Institute of Risk Management, London (IRM) 1996: Global Association of Risk Professionals (GARP) 2002: ISO/IEC Guide 73: 2002 Risk Vocabulary (2009 upd) IRM RM Standard 2002. Sarbanes – Oxley Act, USA. 2004: COSO ERM Report 2006: SMA “Enterprise Risk Management: Frameworks, Elements, and Integration”, by IMA 2007: SMA “Enterprise Risk Management: Tools and Techniques for Effective Implementation”, by IMA 2009: ISO 31000 Principles and Guidelines on Implementation ISO 31010 Risk Management - Risk Assessment Techniques WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 16

RISK & RISK MGT: Ukrainian gurus Dr. Kaminsky A. B. , KNU, Na. UKMA Dr. Yastrmsky O. I. , Rector of the ICU Kyiv. WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 17

TYPES OF RISKS: “RISK UNIVERSE” (the term coined by E&Y, 1999) Source: IRM WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 18
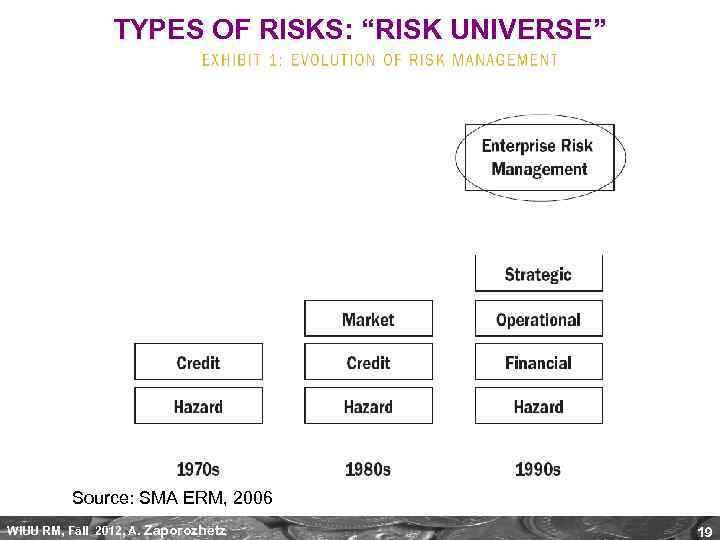
TYPES OF RISKS: “RISK UNIVERSE” Source: SMA ERM, 2006 WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 19
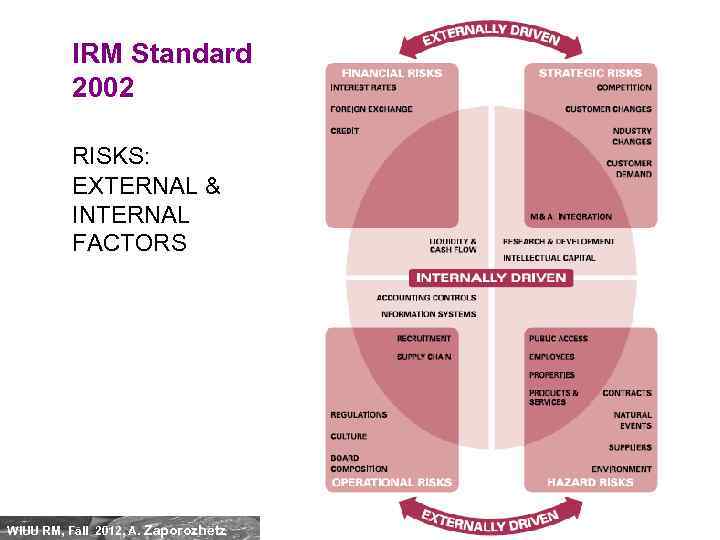
IRM Standard 2002 RISKS: EXTERNAL & INTERNAL FACTORS WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 20

SMA ERM 2007 WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 21
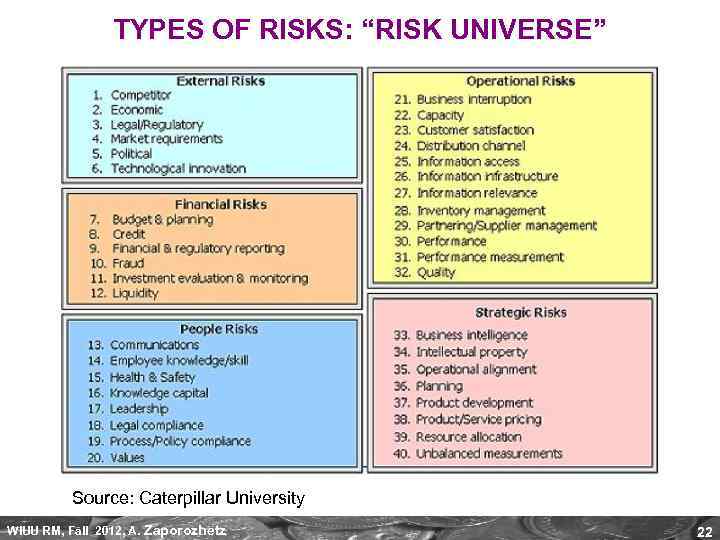
TYPES OF RISKS: “RISK UNIVERSE” Source: Caterpillar University WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 22
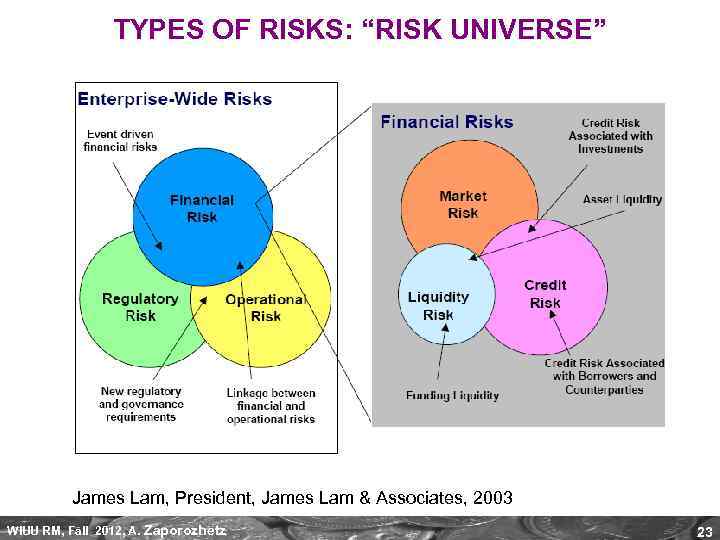
TYPES OF RISKS: “RISK UNIVERSE” James Lam, President, James Lam & Associates, 2003 WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 23
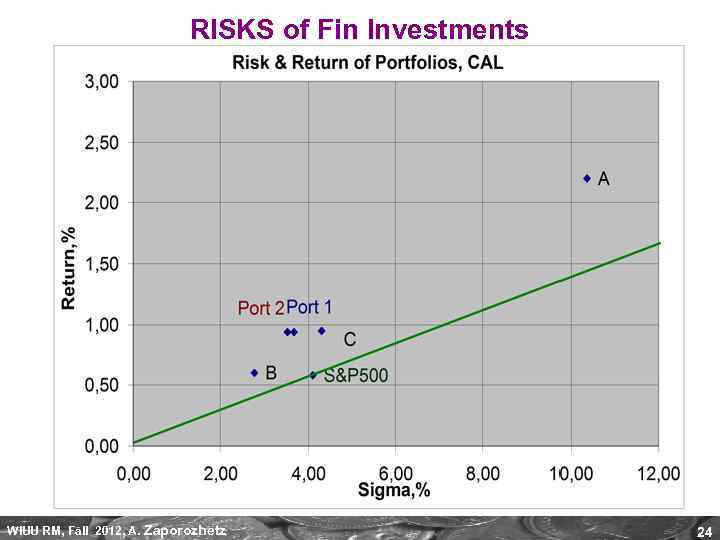
RISKS of Fin Investments WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 24

NEW: SYSTEMIC RISK This new financial model was brimming with systemic risk, a potential breakdown of the financial system when problems in one market spill over and disrupt others. Many of these market innovations had unwittingly created new feedback loops for systemic risk to feed on itself. When firms are fully leveraged (i. e. , have borrowed to their maximum capacity), losses on their portfolios can force them to sell some of their assets to bring their leverage back into line. But waves of selling from institutions that simultaneously need to “de-leverage” can drive down asset prices and exacerbate portfolio losses—forcing additional sales and further price declines in a downward spiral. (Zvi Bodie, “Investments”, 2011, p. 21) WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 25

NEW: SYSTEMIC RISK Systemic risk is generally used in reference to an event that can trigger a collapse in a certain industry or economy, whereas systematic risk refers to overall market risk. Systemic risk does not have an exact definition, many have used systemic risk to describe narrow problems, such as problems in the payments system, while others have used it to describe an economic crisis that was triggered by failures in the financial system. Generally, systemic risk can be described as a risk caused by an event at the firm level that is severe enough to cause instability in the financial system. (Investopedia. com) WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 26
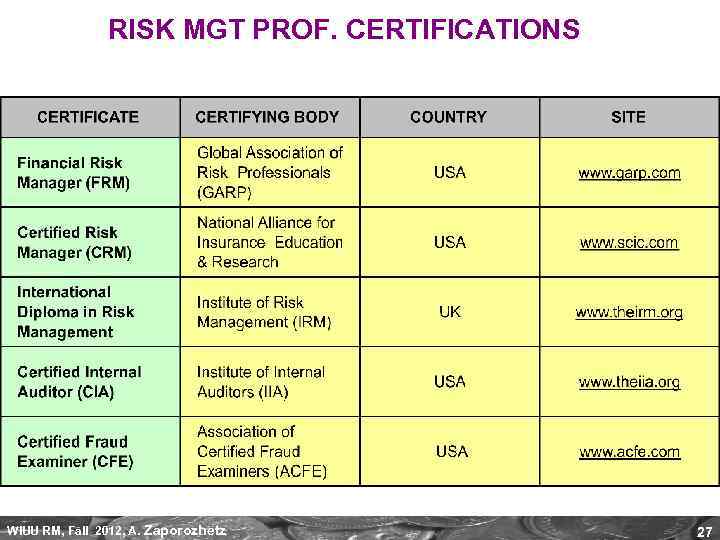
RISK MGT PROF. CERTIFICATIONS WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 27

SUMMARY 1. Risk is the probability of event and its consequences. 2. Business risk is the risk of NOT earning the desired EBIT due to a number of “bad” events. 3. Risk is NOT the same as uncertainty. 4. Common approach to classify risks: Operational, Strategic, Financial, and Hazard risks. 5. Risks in financial markets: specific; found in any financial asset; sigma, beta, etc. WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 28

Political Risks: Mechel Story “В четверг (23 июля) премьерминистр Владимир Путин встретился в Нижнем Новгороде с представителями крупнейших российских металлургических и угольных компаний и высказался о ситуации на российском рынке стали. Премьер-министр неожиданно сделал ряд жестких заявлений в отношении Мечела (ОАО «ЧМЗ» ). По сути, он обвинил компанию в нерыночном поведении и предположил, что прокуратуре следует обратить внимание на торговую деятельность компании. Этих заявлений оказалось достаточно, чтобы обрушить котировки Мечела – с четверга они упали на 37, 6%, заставив инвесторов гадать о будущем компании – ведущего производителя коксующегося угля в России. ” «Тройка-Диалог» , 25 июля 2008 г. WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. (www. troika. ru) Zaporozhetz 29
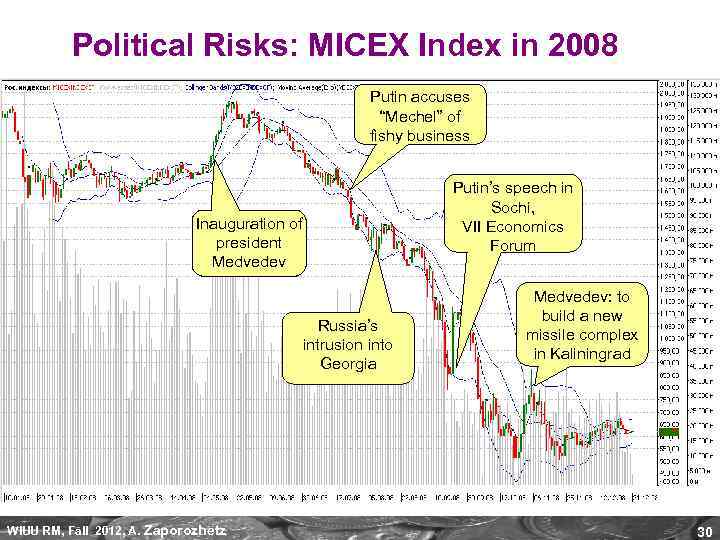
Political Risks: MICEX Index in 2008 Putin accuses “Mechel” of fishy business Inauguration of president Medvedev Russia’s intrusion into Georgia WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz Putin’s speech in Sochi, VII Economics Forum Medvedev: to build a new missile complex in Kaliningrad 30
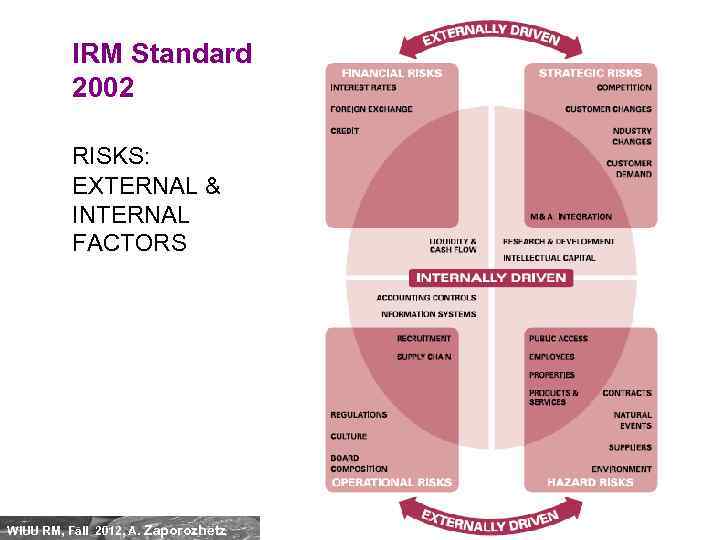
IRM Standard 2002 RISKS: EXTERNAL & INTERNAL FACTORS WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 31
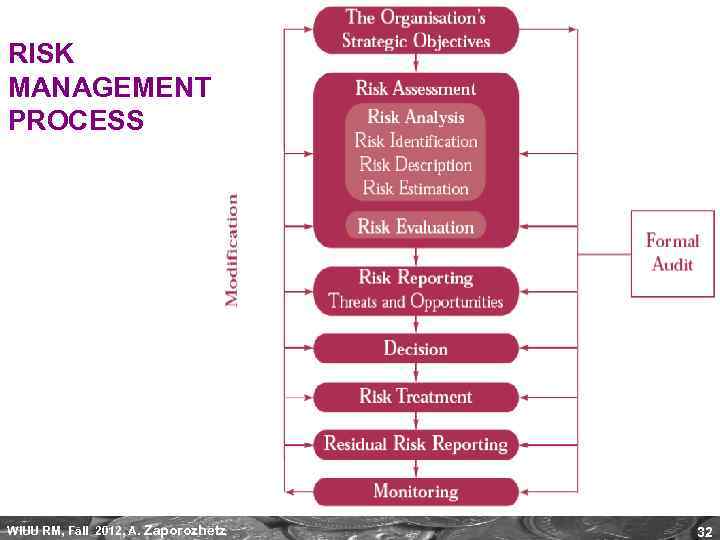
RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 32
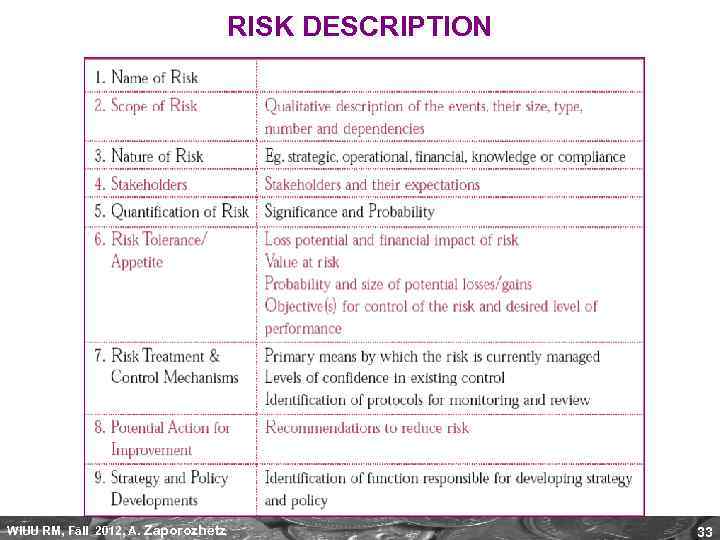
RISK DESCRIPTION WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 33
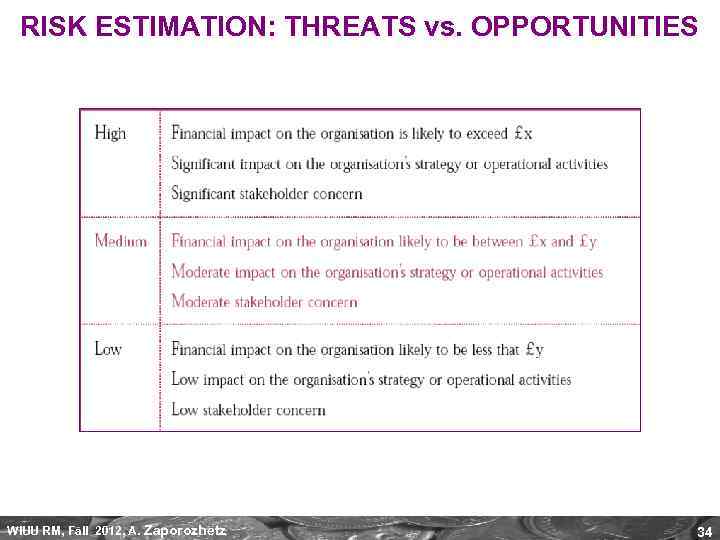
RISK ESTIMATION: THREATS vs. OPPORTUNITIES WIUU RM, Fall 2012, A. Zaporozhetz 34
RM_Intro_Fall2012.ppt