e42a8a753eec8ec1caabd29ab53a4628.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89

Witschi Electronic Basic course Watches – Measuring technology and troubleshooting www. witschi. com Start >>

Welcome to. . .

Contents Introduction Mechanical Watches Quartz Watches Water-resistance Helpful and practical Exit

Introduction About us Back Witschi Electronic AG develops, manufactures and sells Pioneering test and measurement technology for: • Watch production • Watch service • Testing devices for automotive industry, medical industry and instrument manufacturing Home

Introduction Aim of this course Back Home This basic course is intended to optimize our customers’ and the users’ knowledge of the Witschi devices and their operating skills in this field. . . End. .

Contents Introduction Mechanical Watches Quartz Watches Water-resistance Helpful and practical Exit

Mechanical Watches Home
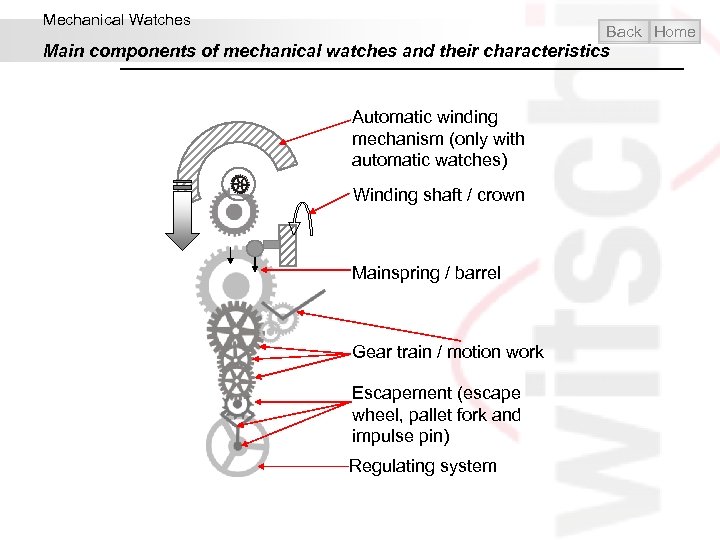
Mechanical Watches Back Home Main components of mechanical watches and their characteristics Automatic winding mechanism (only with automatic watches) Winding shaft / crown Mainspring / barrel Gear train / motion work Escapement (escape wheel, pallet fork and impulse pin) Regulating system
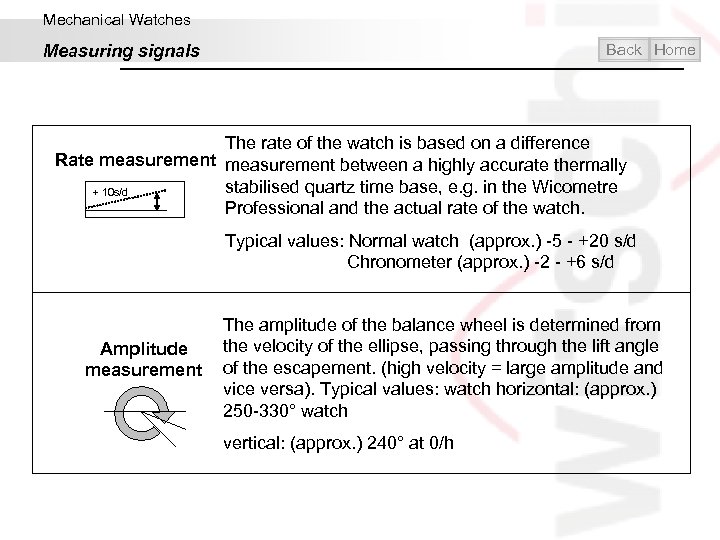
Mechanical Watches Back Home Measuring signals The rate of the watch is based on a difference Rate measurement between a highly accurate thermally stabilised quartz time base, e. g. in the Wicometre + 10 s/d Professional and the actual rate of the watch. Typical values: Normal watch (approx. ) -5 - +20 s/d Chronometer (approx. ) -2 - +6 s/d The amplitude of the balance wheel is determined from the velocity of the ellipse, passing through the lift angle Amplitude measurement of the escapement. (high velocity = large amplitude and vice versa). Typical values: watch horizontal: (approx. ) 250 -330° watch vertical: (approx. ) 240° at 0/h
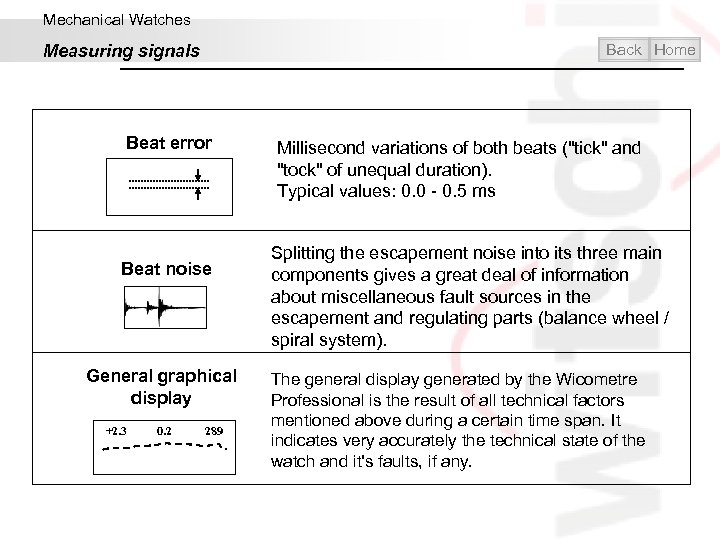
Mechanical Watches Back Home Measuring signals Beat error Beat noise General graphical display +2. 3 0. 2 289 Millisecond variations of both beats ("tick" and "tock" of unequal duration). Typical values: 0. 0 - 0. 5 ms Splitting the escapement noise into its three main components gives a great deal of information about miscellaneous fault sources in the escapement and regulating parts (balance wheel / spiral system). The general display generated by the Wicometre Professional is the result of all technical factors mentioned above during a certain time span. It indicates very accurately the technical state of the watch and it's faults, if any.
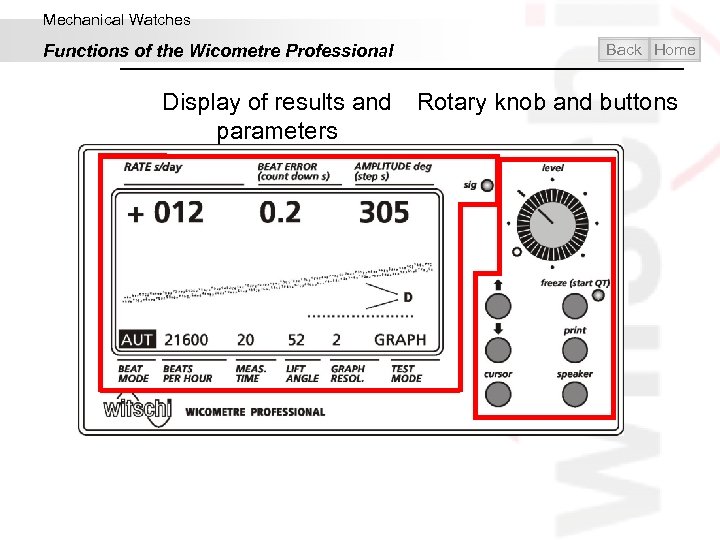
Mechanical Watches Functions of the Wicometre Professional Back Home Display of results and Rotary knob and buttons parameters
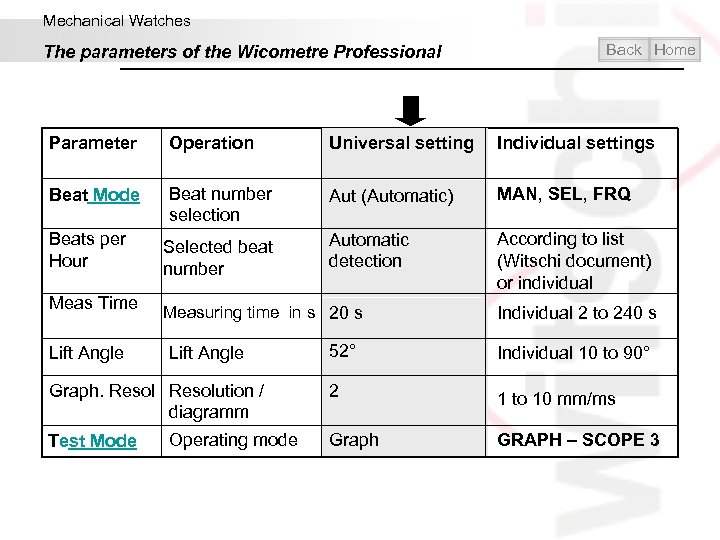
Mechanical Watches The parameters of the Wicometre Professional Back Home Parameter Operation Universal setting Individual settings Beat Mode Beat number selection Aut (Automatic) MAN, SEL, FRQ Beats per Hour Selected beat number Automatic detection According to list (Witschi document) or individual Meas Time Lift Angle Measuring time in s 20 s Lift Angle Graph. Resolution / diagramm Test Mode Operating mode Individual 2 to 240 s 52° Individual 10 to 90° 2 1 to 10 mm/ms Graph GRAPH – SCOPE 3
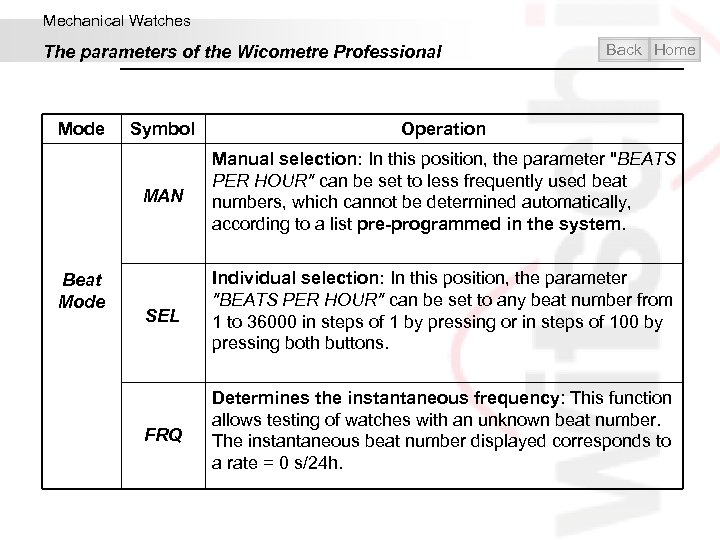
Mechanical Watches The parameters of the Wicometre Professional Mode Back Home Operation MAN Beat Mode Symbol Manual selection: In this position, the parameter "BEATS PER HOUR" can be set to less frequently used beat numbers, which cannot be determined automatically, according to a list pre-programmed in the system. SEL Individual selection: In this position, the parameter "BEATS PER HOUR" can be set to any beat number from 1 to 36000 in steps of 1 by pressing or in steps of 100 by pressing both buttons. FRQ Determines the instantaneous frequency: This function allows testing of watches with an unknown beat number. The instantaneous beat number displayed corresponds to a rate = 0 s/24 h.
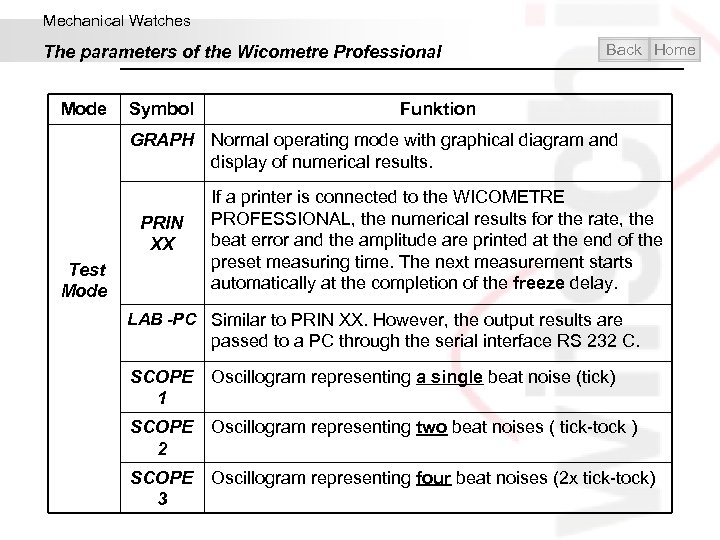
Mechanical Watches The parameters of the Wicometre Professional Mode Symbol Back Home Funktion GRAPH Normal operating mode with graphical diagram and display of numerical results. PRIN XX Test Mode If a printer is connected to the WICOMETRE PROFESSIONAL, the numerical results for the rate, the beat error and the amplitude are printed at the end of the preset measuring time. The next measurement starts automatically at the completion of the freeze delay. LAB -PC Similar to PRIN XX. However, the output results are passed to a PC through the serial interface RS 232 C. SCOPE Oscillogram representing a single beat noise (tick) 1 SCOPE Oscillogram representing two beat noises ( tick-tock ) 2 SCOPE Oscillogram representing four beat noises (2 x tick-tock) 3
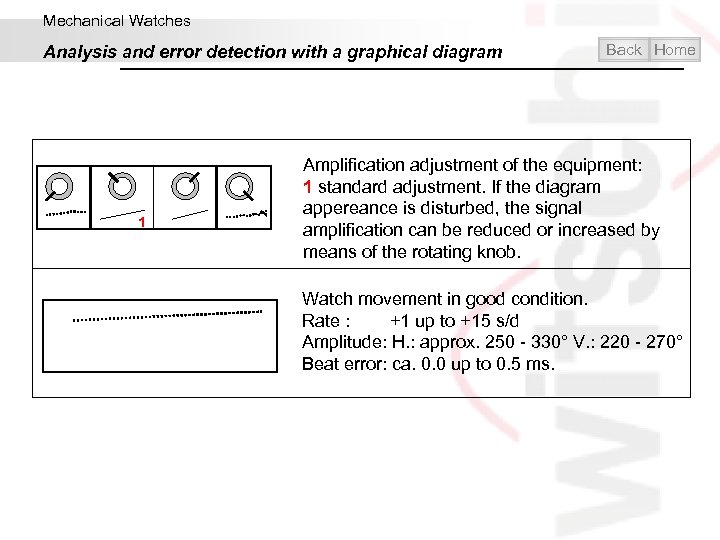
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection with a graphical diagram 1 Back Home Amplification adjustment of the equipment: 1 standard adjustment. If the diagram appereance is disturbed, the signal amplification can be reduced or increased by means of the rotating knob. Watch movement in good condition. Rate : +1 up to +15 s/d Amplitude: H. : approx. 250 - 330° V. : 220 - 270° Beat error: ca. 0. 0 up to 0. 5 ms.
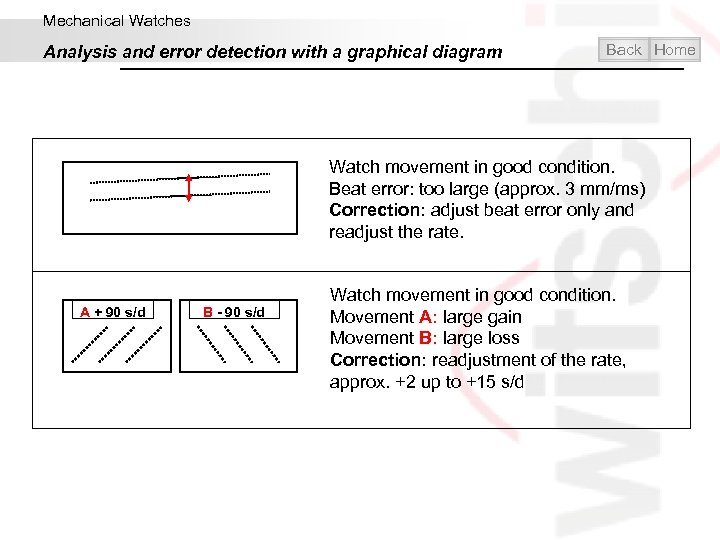
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection with a graphical diagram Back Home Watch movement in good condition. Beat error: too large (approx. 3 mm/ms) Correction: adjust beat error only and readjust the rate. A + 90 s/d B - 90 s/d Watch movement in good condition. Movement A: large gain Movement B: large loss Correction: readjustment of the rate, approx. +2 up to +15 s/d
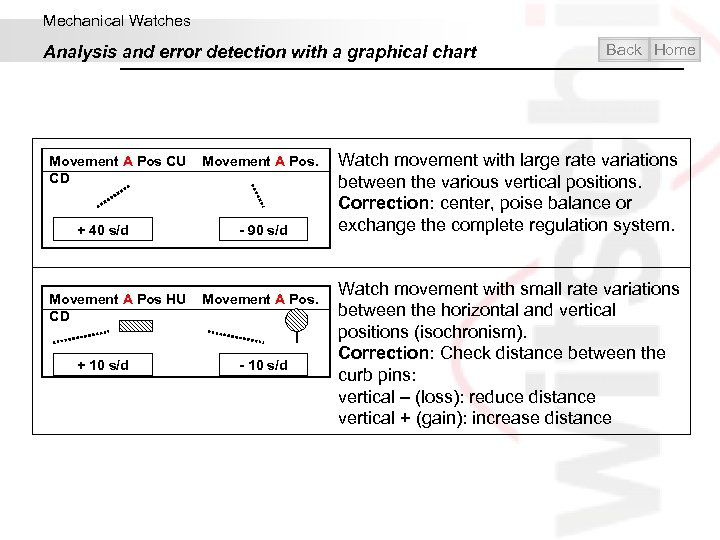
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection with a graphical chart Movement A Pos CU Movement A Pos. CD + 40 s/d - 90 s/d Movement A Pos HU Movement A Pos. CD + 10 s/d - 10 s/d Back Home Watch movement with large rate variations between the various vertical positions. Correction: center, poise balance or exchange the complete regulation system. Watch movement with small rate variations between the horizontal and vertical positions (isochronism). Correction: Check distance between the curb pins: vertical – (loss): reduce distance vertical + (gain): increase distance
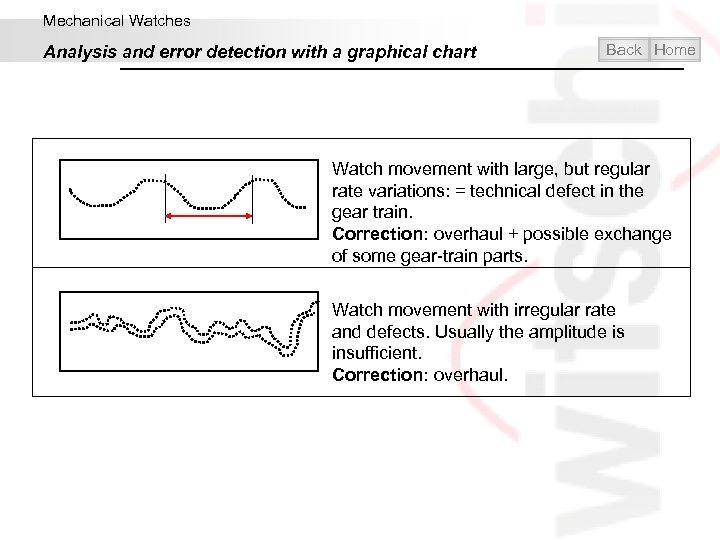
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection with a graphical chart Back Home Watch movement with large, but regular rate variations: = technical defect in the gear train. Correction: overhaul + possible exchange of some gear-train parts. Watch movement with irregular rate and defects. Usually the amplitude is insufficient. Correction: overhaul.
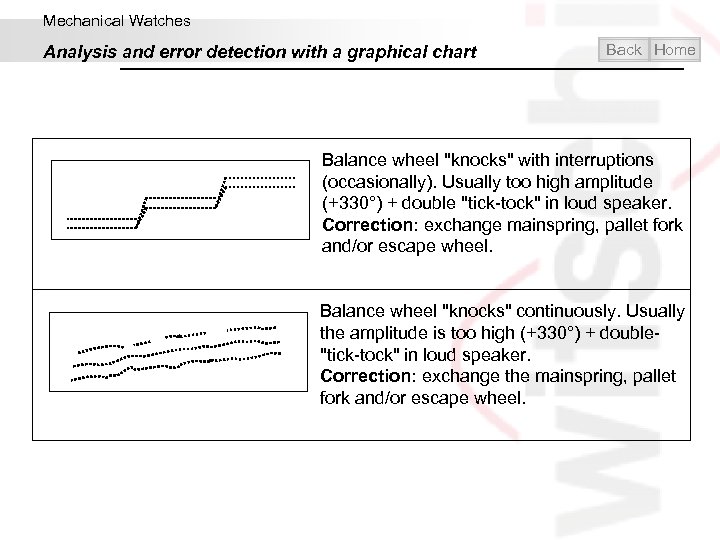
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection with a graphical chart Back Home Balance wheel "knocks" with interruptions (occasionally). Usually too high amplitude (+330°) + double "tick-tock" in loud speaker. Correction: exchange mainspring, pallet fork and/or escape wheel. Balance wheel "knocks" continuously. Usually the amplitude is too high (+330°) + double- "tick-tock" in loud speaker. Correction: exchange the mainspring, pallet fork and/or escape wheel.
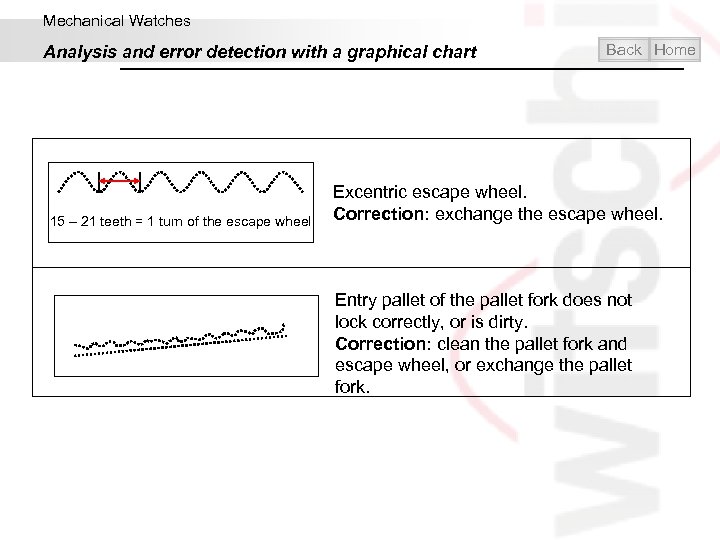
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection with a graphical chart 15 – 21 teeth = 1 turn of the escape wheel Back Home Excentric escape wheel. Correction: exchange the escape wheel. Entry pallet of the pallet fork does not lock correctly, or is dirty. Correction: clean the pallet fork and escape wheel, or exchange the pallet fork.
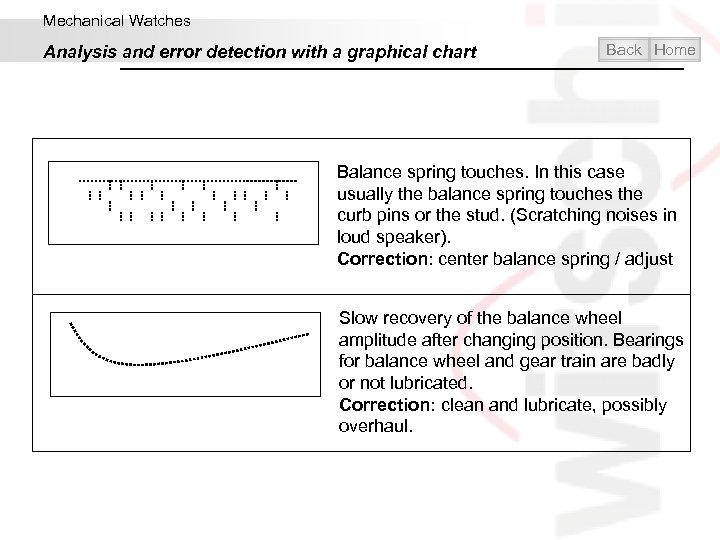
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection with a graphical chart Back Home Balance spring touches. In this case usually the balance spring touches the curb pins or the stud. (Scratching noises in loud speaker). Correction: center balance spring / adjust Slow recovery of the balance wheel amplitude after changing position. Bearings for balance wheel and gear train are badly or not lubricated. Correction: clean and lubricate, possibly overhaul.
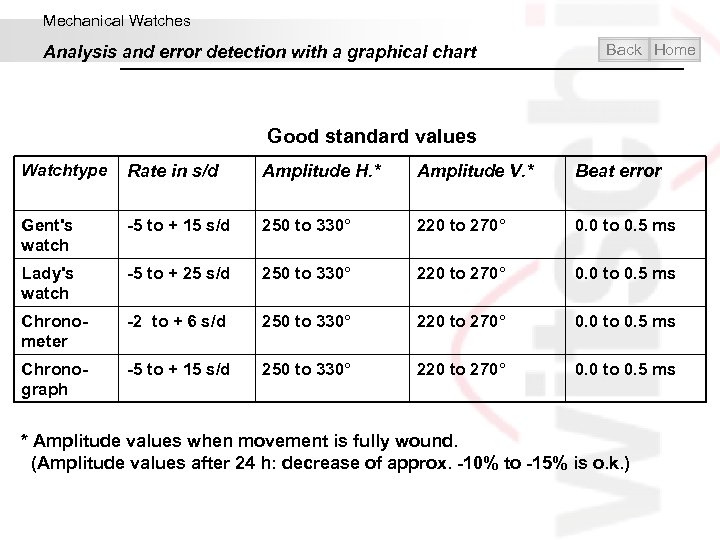
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection with a graphical chart Back Home Good standard values Watchtype Rate in s/d Amplitude H. * Amplitude V. * Beat error Gent's watch -5 to + 15 s/d 250 to 330° 220 to 270° 0. 0 to 0. 5 ms Lady's watch -5 to + 25 s/d 250 to 330° 220 to 270° 0. 0 to 0. 5 ms Chronometer -2 to + 6 s/d 250 to 330° 220 to 270° 0. 0 to 0. 5 ms Chronograph -5 to + 15 s/d 250 to 330° 220 to 270° 0. 0 to 0. 5 ms * Amplitude values when movement is fully wound. (Amplitude values after 24 h: decrease of approx. -10% to -15% is o. k. )
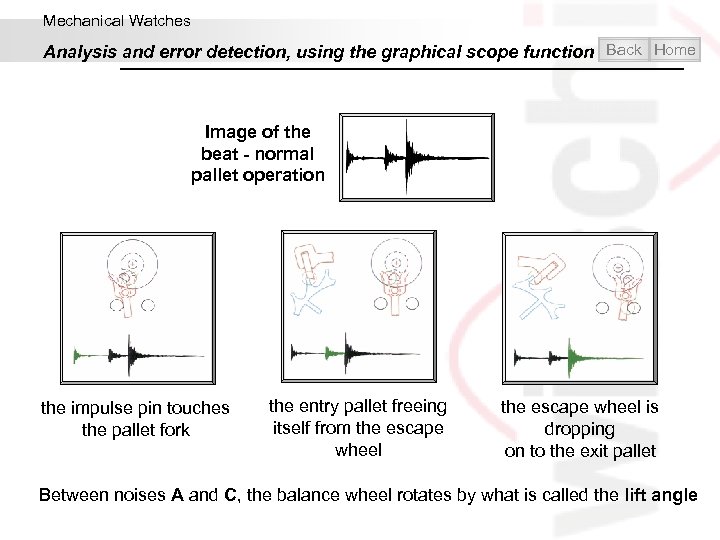
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection, using the graphical scope function Back Home Image of the beat - normal pallet operation the impulse pin touches the pallet fork the entry pallet freeing itself from the escape wheel is dropping on to the exit pallet Between noises A and C, the balance wheel rotates by what is called the lift angle
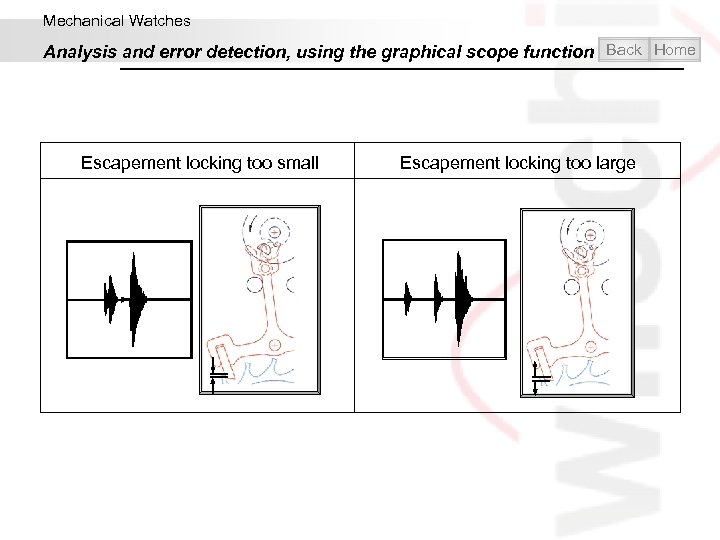
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection, using the graphical scope function Back Home Escapement locking too small Escapement locking too large
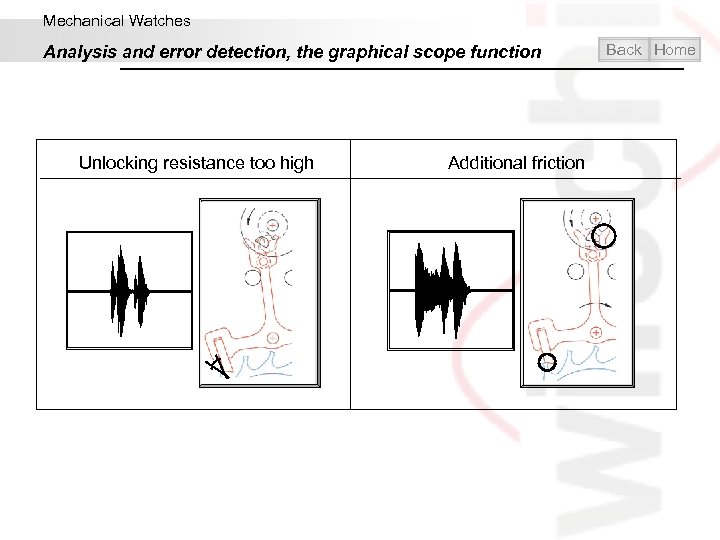
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection, the graphical scope function Unlocking resistance too high Additional friction Back Home
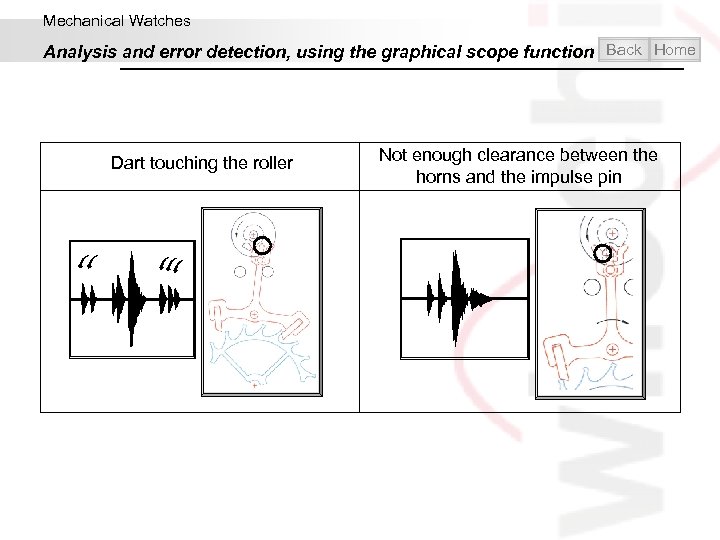
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection, using the graphical scope function Back Home Dart touching the roller Not enough clearance between the horns and the impulse pin
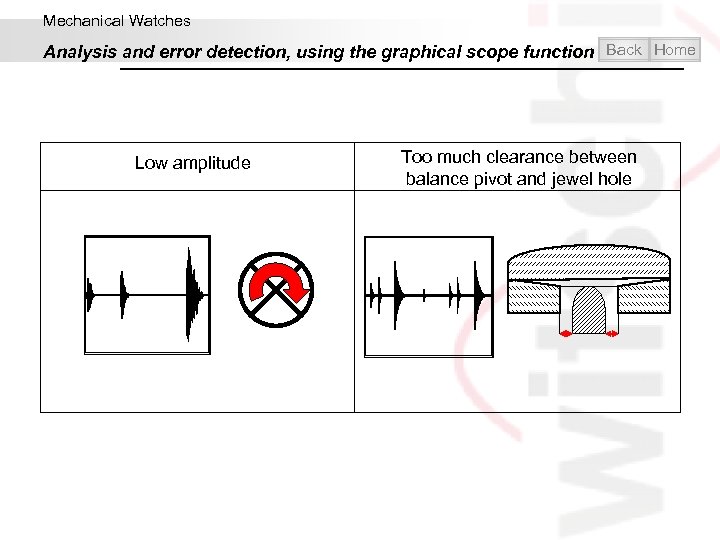
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection, using the graphical scope function Back Home Low amplitude Too much clearance between balance pivot and jewel hole
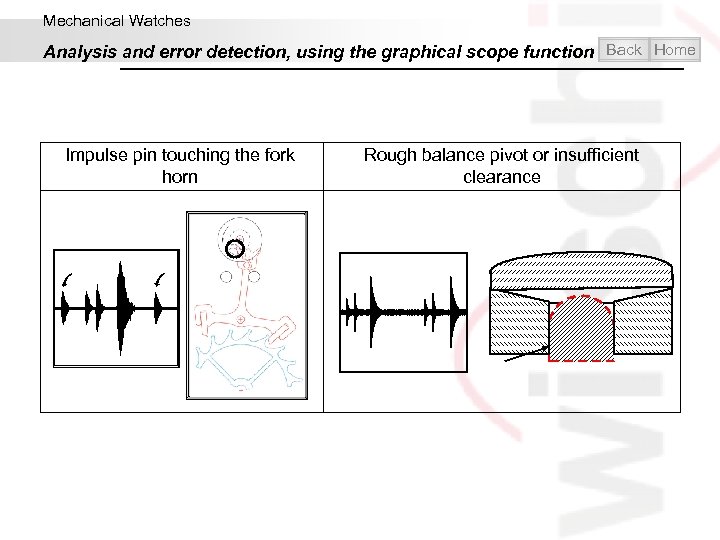
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection, using the graphical scope function Back Home Impulse pin touching the fork horn Rough balance pivot or insufficient clearance
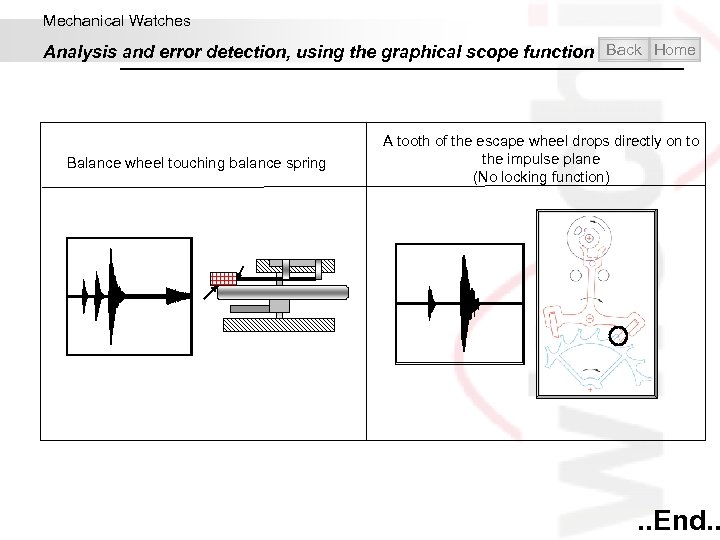
Mechanical Watches Analysis and error detection, using the graphical scope function Back Home Balance wheel touching balance spring A tooth of the escape wheel drops directly on to the impulse plane (No locking function) . . End. .

Contents Introduction Mechanical Watches Quartz Watches Water-resistance Helpful and practical Exit

Quartz Watches Home
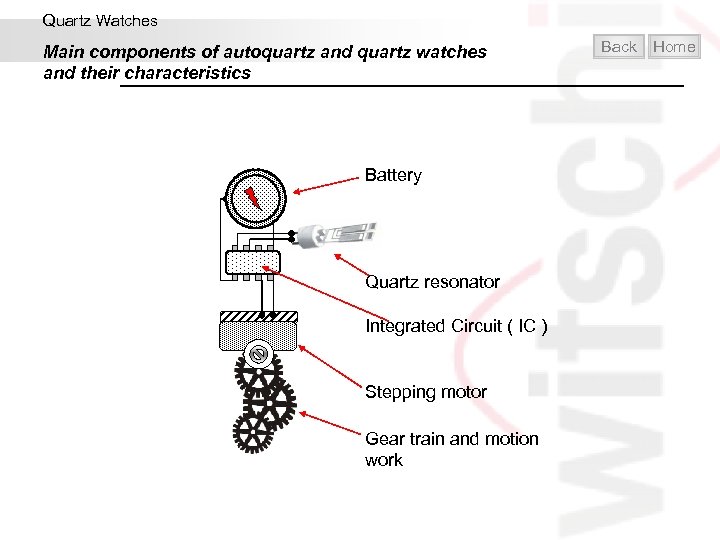
Quartz Watches Main components of autoquartz and quartz watches and their characteristics Battery Quartz resonator Integrated Circuit ( IC ) Stepping motor Gear train and motion work Back Home
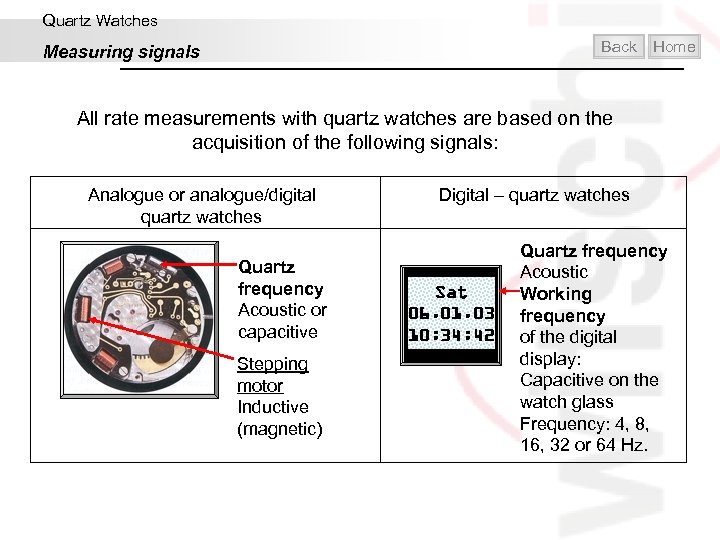
Quartz Watches Back Measuring signals Home All rate measurements with quartz watches are based on the acquisition of the following signals: Analogue or analogue/digital quartz watches Quartz frequency Acoustic or capacitive Stepping motor Inductive (magnetic) Digital – quartz watches Sat 06. 01. 03 10: 34: 42 Quartz frequency Acoustic Working frequency of the digital display: Capacitive on the watch glass Frequency: 4, 8, 16, 32 or 64 Hz.
Quartz Watches Measuring signals Back Home Quartz oscillator The measurement of the quartz frequency (nominal: 32'768 Hz) occurs over the acoustic or the capacitive (by opened watches) sensor. For the rate adjustment 2 different methods are usually used: Quartz Trim. IC / Oscillator Quartz IC /mit EEPROM A: Adjusted quartz oscillator frequency. Adjustment with a trimmer (out dated) or fixed capacitor "fix cap". The true rate can either be obtained via acoustical / capacitive measurements of the quartz frequency or magnetically via the motor pulses. B: The quartz oscillator frequency is not adjustable. The programmable IC is digitally adjusted (inhibition). A programmable number of oscillator pulses is inhibited once per minute (for some IC's every 20 s, 30 s or every 2, 4 and 8 minutes) during frequency division, i. e. they are not transferred to the next divider stage. By using this method the quartz oscillator runs fast, approx. +3 -5 s/d. The true rate can only be measured via the motor pulse with a measuring time of => 60 s
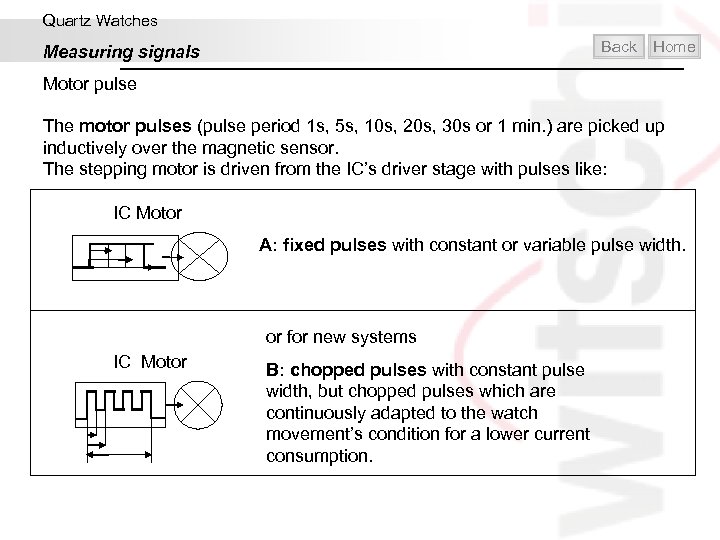
Quartz Watches Back Measuring signals Home Motor pulse The motor pulses (pulse period 1 s, 5 s, 10 s, 20 s, 30 s or 1 min. ) are picked up inductively over the magnetic sensor. The stepping motor is driven from the IC’s driver stage with pulses like: IC Motor A: fixed pulses with constant or variable pulse width. or for new systems IC Motor B: chopped pulses with constant pulse width, but chopped pulses which are continuously adapted to the watch movement’s condition for a lower current consumption.
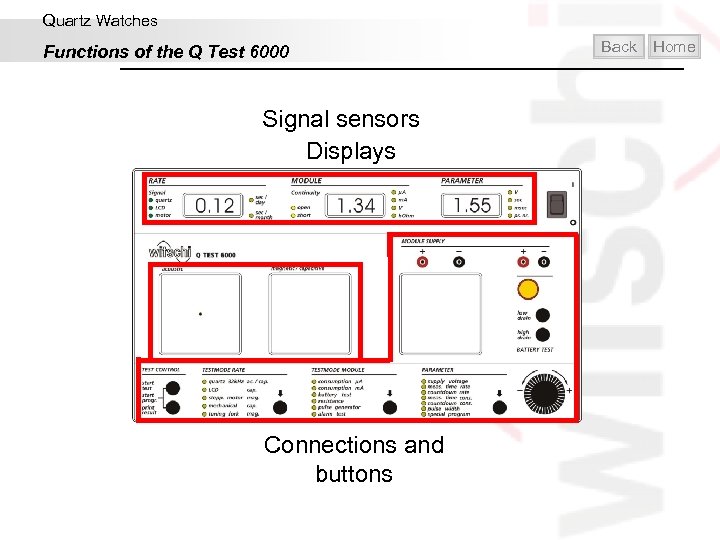
Quartz Watches Functions of the Q Test 6000 Signal sensors Displays Connections and buttons Back Home
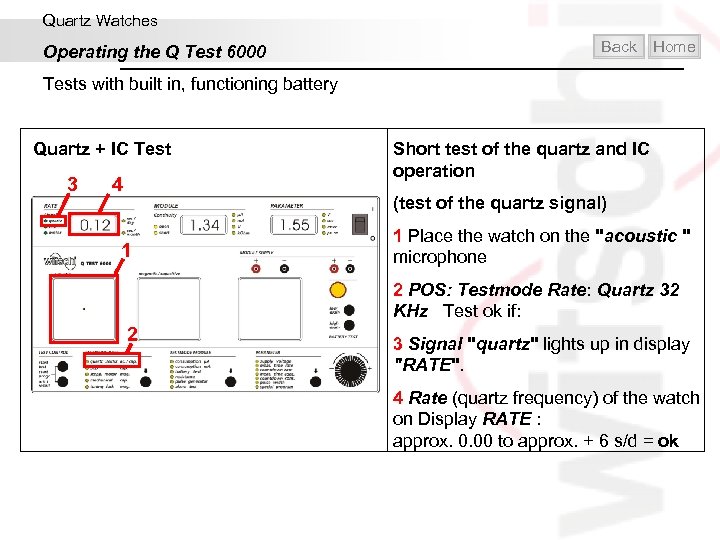
Quartz Watches Operating the Q Test 6000 Back Home Tests with built in, functioning battery Quartz + IC Test 3 4 Short test of the quartz and IC operation (test of the quartz signal) 1 1 Place the watch on the "acoustic " microphone 2 POS: Testmode Rate: Quartz 32 KHz Test ok if: 2 3 Signal "quartz" lights up in display "RATE". 4 Rate (quartz frequency) of the watch on Display RATE : approx. 0. 00 to approx. + 6 s/d = ok
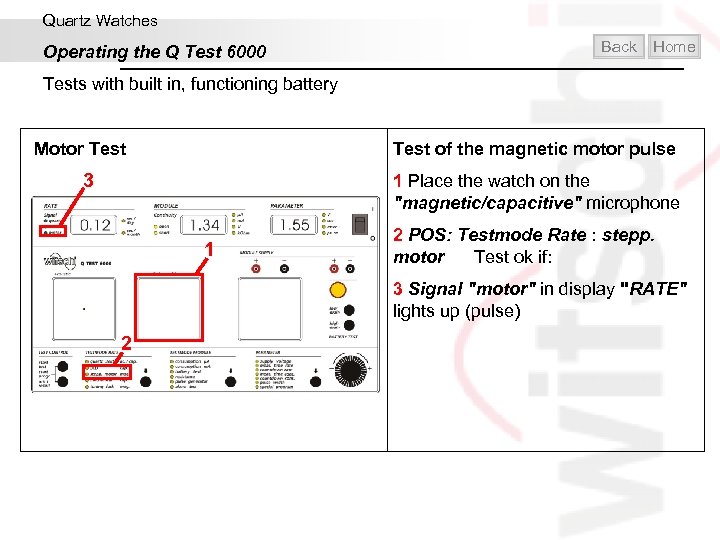
Quartz Watches Operating the Q Test 6000 Back Home Tests with built in, functioning battery Test of the magnetic motor pulse Motor Test 3 1 Place the watch on the "magnetic/capacitive" microphone 1 2 POS: Testmode Rate : stepp. motor Test ok if: 3 Signal "motor" in display "RATE" lights up (pulse) 2
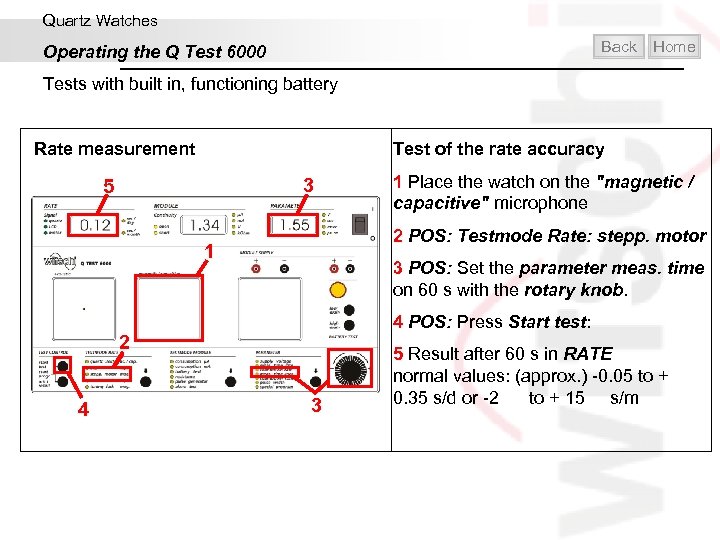
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Tests with built in, functioning battery Rate measurement Test of the rate accuracy 3 5 2 POS: Testmode Rate: stepp. motor 1 3 POS: Set the parameter meas. time on 60 s with the rotary knob. 4 POS: Press Start test: 2 4 1 Place the watch on the "magnetic / capacitive" microphone 3 5 Result after 60 s in RATE normal values: (approx. ) -0. 05 to + 0. 35 s/d or -2 to + 15 s/m
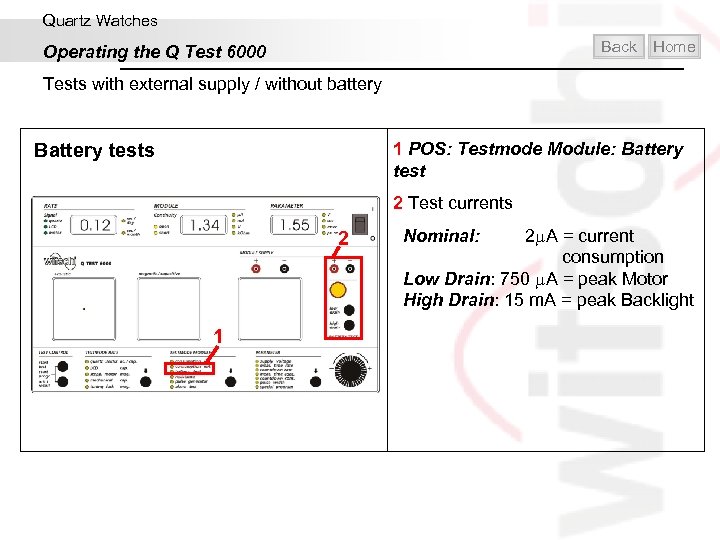
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Tests with external supply / without battery 1 POS: Testmode Module: Battery tests 2 Test currents 2 1 Nominal: 2 A = current consumption Low Drain: 750 A = peak Motor High Drain: 15 m. A = peak Backlight
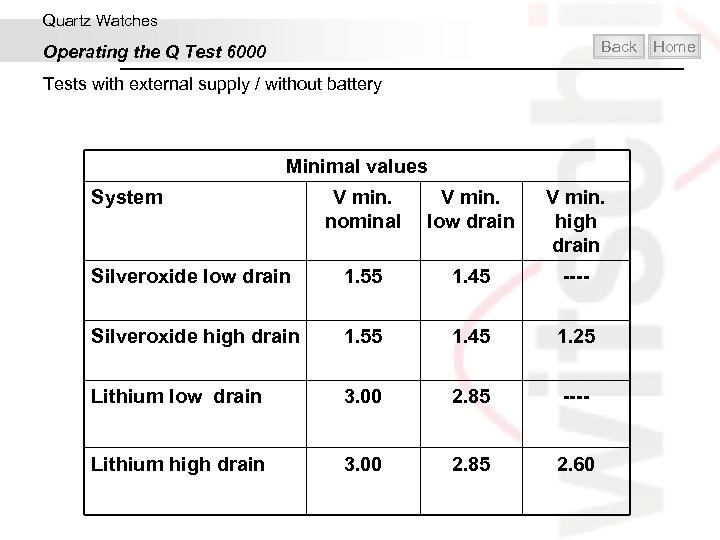
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Tests with external supply / without battery Minimal values System V min. nominal V min. low drain V min. high drain Silveroxide low drain 1. 55 1. 45 ---- Silveroxide high drain 1. 55 1. 45 1. 25 Lithium low drain 3. 00 2. 85 ---- Lithium high drain 3. 00 2. 85 2. 60 Home
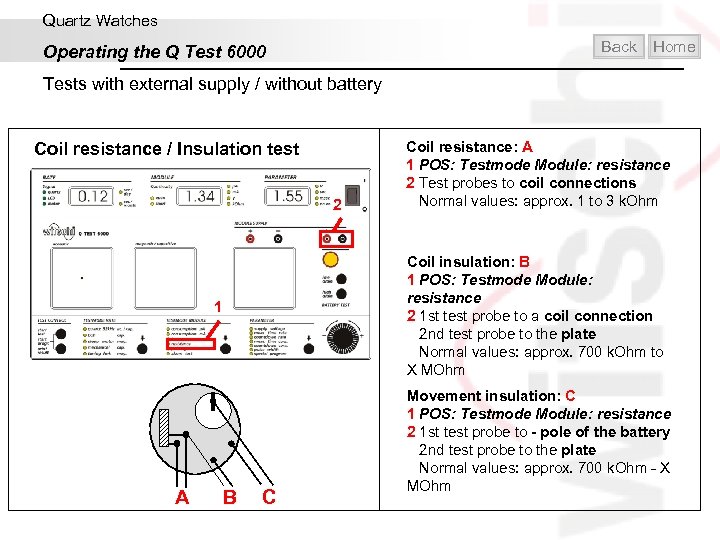
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Tests with external supply / without battery Coil resistance / Insulation test 2 Coil insulation: B 1 POS: Testmode Module: resistance 2 1 st test probe to a coil connection 2 nd test probe to the plate Normal values: approx. 700 k. Ohm to X MOhm 1 A Coil resistance: A 1 POS: Testmode Module: resistance 2 Test probes to coil connections Normal values: approx. 1 to 3 k. Ohm B C Movement insulation: C 1 POS: Testmode Module: resistance 2 1 st test probe to - pole of the battery 2 nd test probe to the plate Normal values: approx. 700 k. Ohm - X MOhm
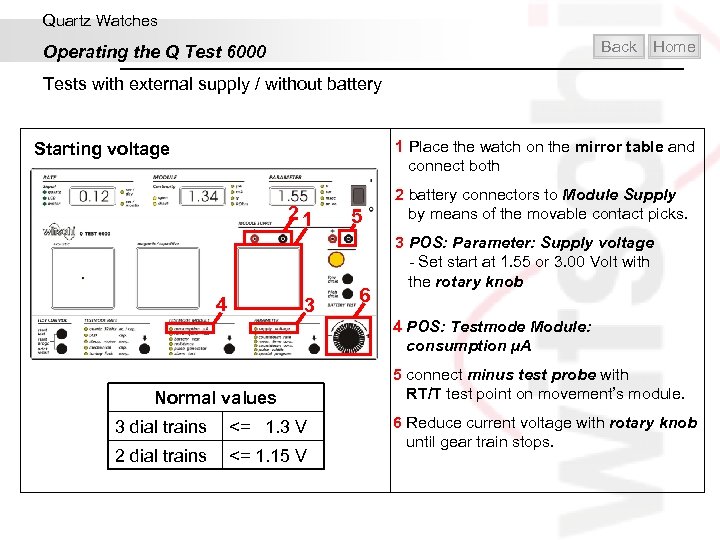
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Tests with external supply / without battery 1 Place the watch on the mirror table and connect both Starting voltage 21 4 3 5 6 2 battery connectors to Module Supply by means of the movable contact picks. 3 POS: Parameter: Supply voltage - Set start at 1. 55 or 3. 00 Volt with the rotary knob 4 POS: Testmode Module: consumption µA Normal values 3 dial trains <= 1. 3 V 2 dial trains <= 1. 15 V 5 connect minus test probe with RT/T test point on movement’s module. 6 Reduce current voltage with rotary knob until gear train stops.
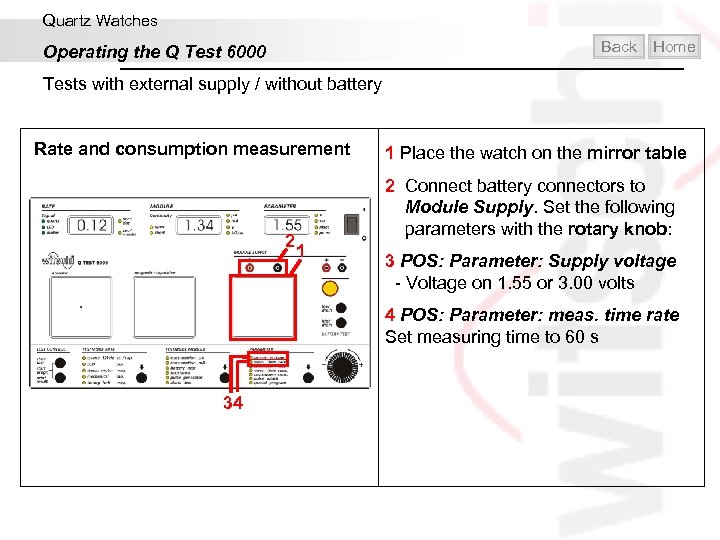
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Tests with external supply / without battery Rate and consumption measurement 2 1 Place the watch on the mirror table 2 Connect battery connectors to Module Supply. Set the following parameters with the rotary knob: 1 3 POS: Parameter: Supply voltage - Voltage on 1. 55 or 3. 00 volts 4 POS: Parameter: meas. time rate Set measuring time to 60 s 34
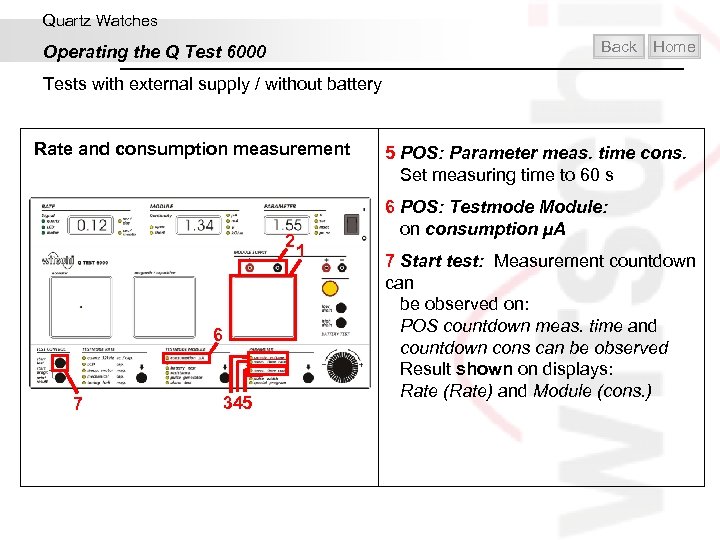
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Tests with external supply / without battery Rate and consumption measurement 2 6 7 345 5 POS: Parameter meas. time cons. Set measuring time to 60 s 6 POS: Testmode Module: on consumption µA 1 7 Start test: Measurement countdown can be observed on: POS countdown meas. time and countdown cons can be observed Result shown on displays: Rate (Rate) and Module (cons. )
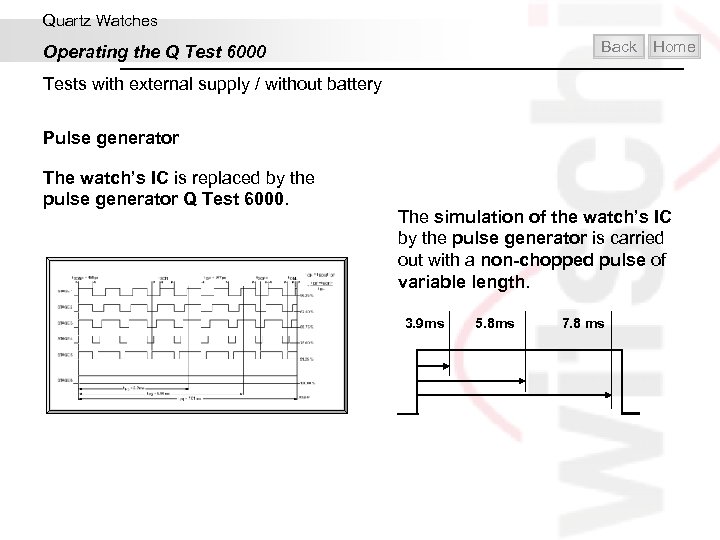
Quartz Watches Operating the Q Test 6000 Back Home Tests with external supply / without battery Pulse generator The watch’s IC is replaced by the pulse generator Q Test 6000. The simulation of the watch’s IC by the pulse generator is carried out with a non-chopped pulse of variable length. 3. 9 ms 5. 8 ms 7. 8 ms
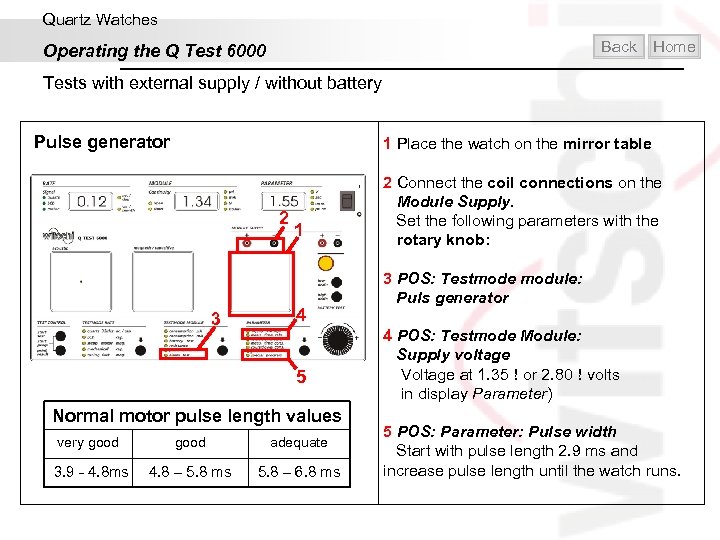
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Tests with external supply / without battery Pulse generator 1 Place the watch on the mirror table 2 3 1 4 5 Normal motor pulse length values very good adequate 3. 9 - 4. 8 ms 4. 8 – 5. 8 ms 5. 8 – 6. 8 ms 2 Connect the coil connections on the Module Supply. Set the following parameters with the rotary knob: 3 POS: Testmode module: Puls generator 4 POS: Testmode Module: Supply voltage Voltage at 1. 35 or 2. 80 volts in display Parameter) 5 POS: Parameter: Pulse width Start with pulse length 2. 9 ms and increase pulse length until the watch runs.
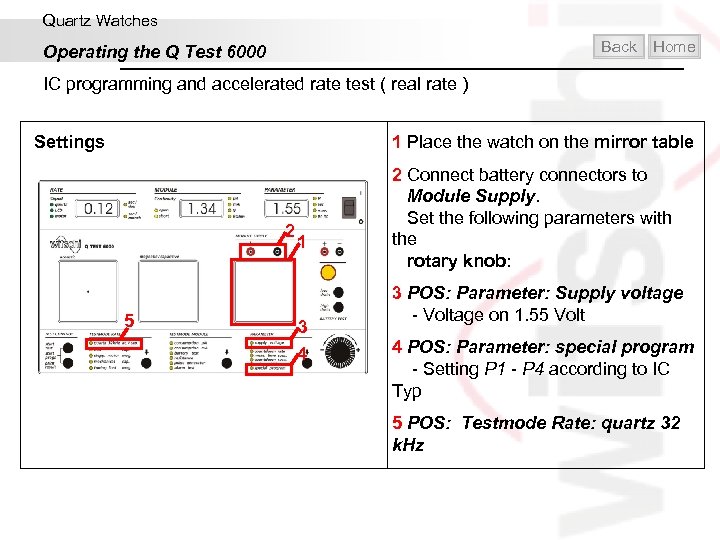
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home IC programming and accelerated rate test ( real rate ) 1 Place the watch on the mirror table Settings 2 5 1 3 4 2 Connect battery connectors to Module Supply. Set the following parameters with the rotary knob: 3 POS: Parameter: Supply voltage - Voltage on 1. 55 Volt 4 POS: Parameter: special program - Setting P 1 - P 4 according to IC Typ 5 POS: Testmode Rate: quartz 32 k. Hz
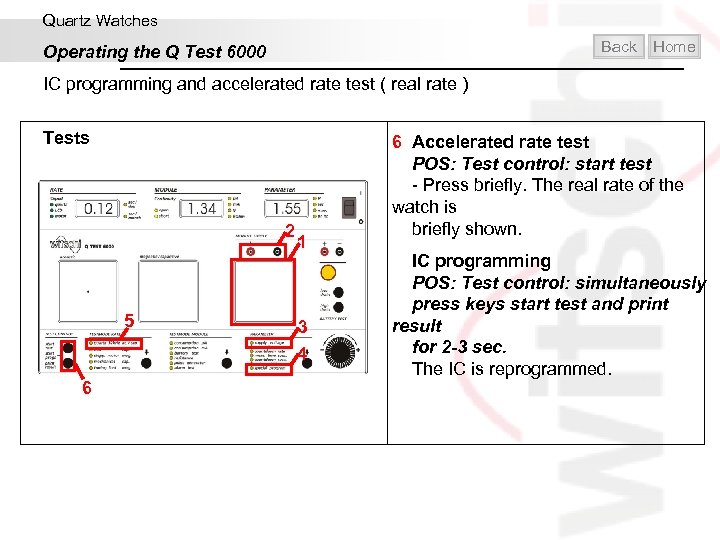
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home IC programming and accelerated rate test ( real rate ) Tests 2 5 6 1 3 4 6 Accelerated rate test POS: Test control: start test - Press briefly. The real rate of the watch is briefly shown. IC programming POS: Test control: simultaneously press keys start test and print result for 2 -3 sec. The IC is reprogrammed.

Quartz Watches Operating the Q Test 6000 IC programming and accelerated rate test ( real rate ) IC Typen Special Programm / programmed IC types P 1 Philips Series PCA 1400 P 2 Philips Series 1460 / 1480 / 1600 P 3 MEM H 1138/ H 1140/ H 1238/ H 1338/ H 1538 P 4 MEM H 1221/ H 5222 SPL Note Rate: Must appear in display RATE after accelerated test and after programming. If not: select another programming program (P 1 -P 4). Back Home

Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Systematic troubleshooting Tests and settings Battery test POS: Testmode module: battery test Caution: Always check the movement for corrosion and the insulation of the battery case! Test sequence Situation: watch stopped Remove and test the battery Battery not ok Battery ok Home
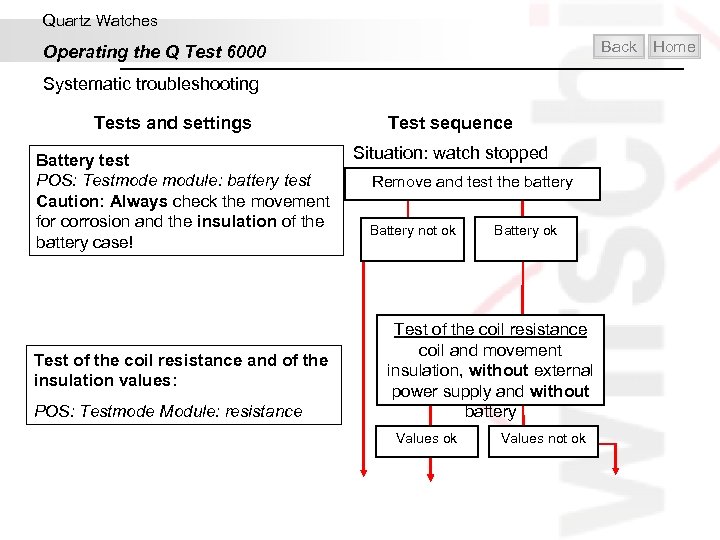
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Systematic troubleshooting Tests and settings Battery test POS: Testmode module: battery test Caution: Always check the movement for corrosion and the insulation of the battery case! Test of the coil resistance and of the insulation values: POS: Testmode Module: resistance Test sequence Situation: watch stopped Remove and test the battery Battery not ok Battery ok Test of the coil resistance coil and movement insulation, without external power supply and without battery Values ok Values not ok Home
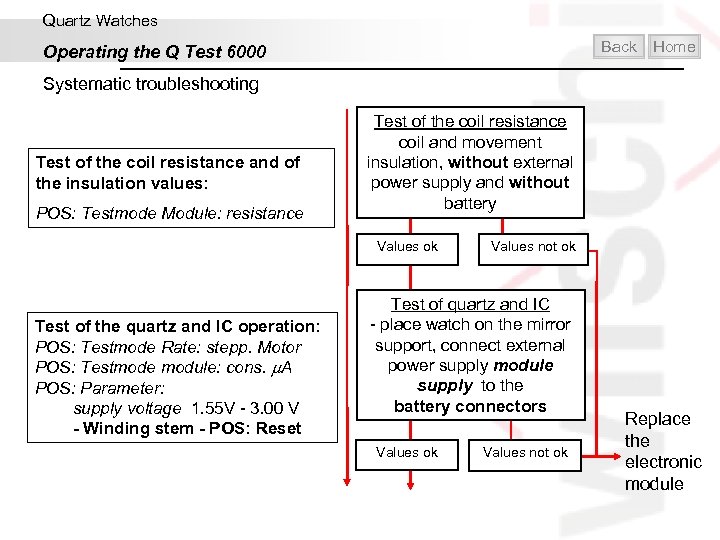
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Systematic troubleshooting Test of the coil resistance and of the insulation values: POS: Testmode Module: resistance Test of the coil resistance coil and movement insulation, without external power supply and without battery Values ok Test of the quartz and IC operation: POS: Testmode Rate: stepp. Motor POS: Testmode module: cons. A POS: Parameter: supply voltage 1. 55 V - 3. 00 V - Winding stem - POS: Reset Values not ok Test of quartz and IC - place watch on the mirror support, connect external power supply module supply to the battery connectors Values ok Values not ok Replace the electronic module
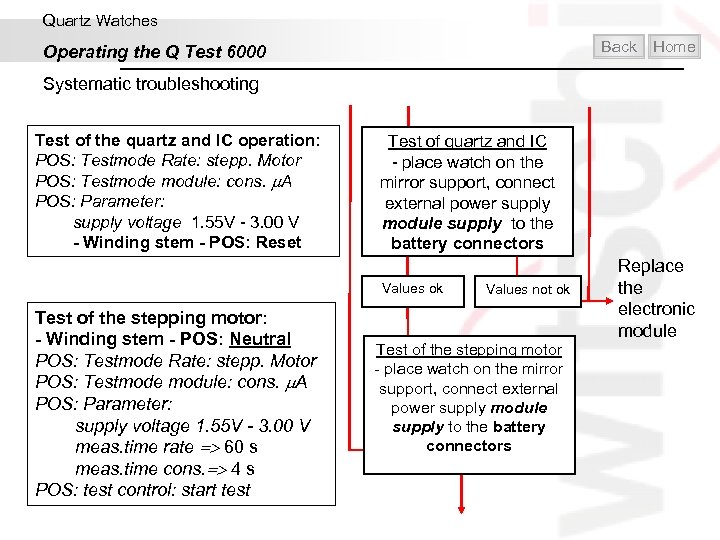
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Systematic troubleshooting Test of the quartz and IC operation: POS: Testmode Rate: stepp. Motor POS: Testmode module: cons. A POS: Parameter: supply voltage 1. 55 V - 3. 00 V - Winding stem - POS: Reset Test of quartz and IC - place watch on the mirror support, connect external power supply module supply to the battery connectors Values ok Test of the stepping motor: - Winding stem - POS: Neutral POS: Testmode Rate: stepp. Motor POS: Testmode module: cons. A POS: Parameter: supply voltage 1. 55 V - 3. 00 V meas. time rate 60 s meas. time cons. 4 s POS: test control: start test Values not ok Test of the stepping motor - place watch on the mirror support, connect external power supply module supply to the battery connectors Replace the electronic module
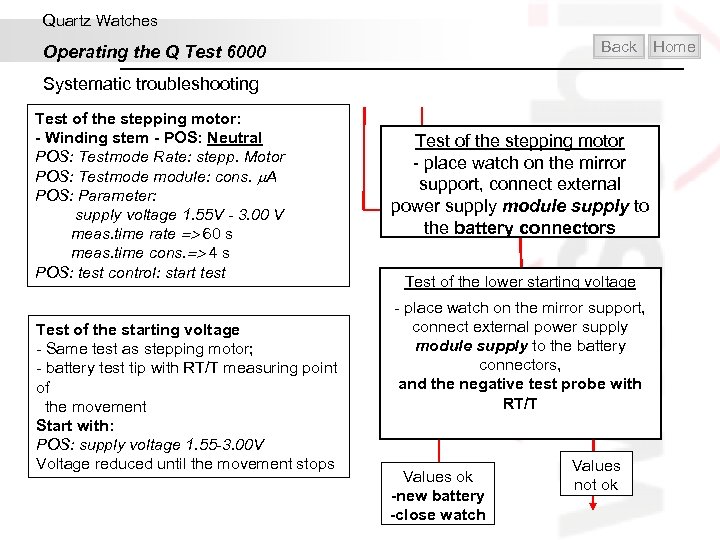
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Systematic troubleshooting Test of the stepping motor: - Winding stem - POS: Neutral POS: Testmode Rate: stepp. Motor POS: Testmode module: cons. A POS: Parameter: supply voltage 1. 55 V - 3. 00 V meas. time rate 60 s meas. time cons. 4 s POS: test control: start test Test of the starting voltage - Same test as stepping motor; - battery test tip with RT/T measuring point of the movement Start with: POS: supply voltage 1. 55 -3. 00 V Voltage reduced until the movement stops Test of the stepping motor - place watch on the mirror support, connect external power supply module supply to the battery connectors Test of the lower starting voltage - place watch on the mirror support, connect external power supply module supply to the battery connectors, and the negative test probe with RT/T Values ok -new battery -close watch Values not ok
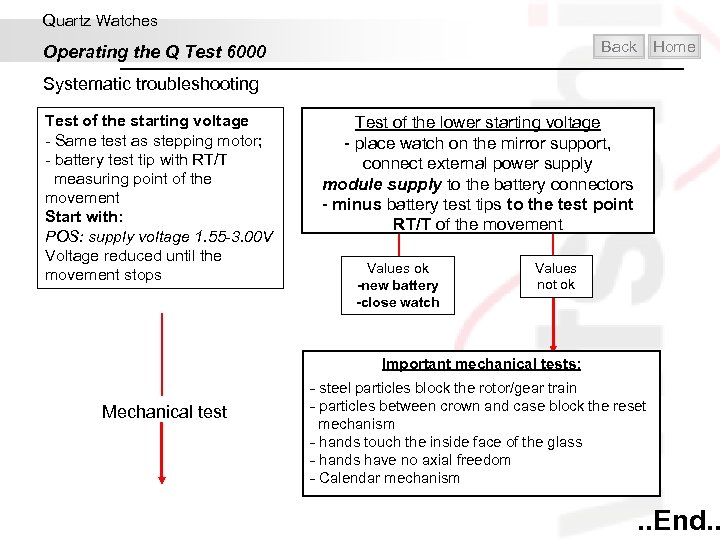
Quartz Watches Back Operating the Q Test 6000 Home Systematic troubleshooting Test of the starting voltage - Same test as stepping motor; - battery test tip with RT/T measuring point of the movement Start with: POS: supply voltage 1. 55 -3. 00 V Voltage reduced until the movement stops Test of the lower starting voltage - place watch on the mirror support, connect external power supply module supply to the battery connectors - minus battery test tips to the test point RT/T of the movement Values ok -new battery -close watch Values not ok Important mechanical tests: Mechanical test - steel particles block the rotor/gear train - particles between crown and case block the reset mechanism - hands touch the inside face of the glass - hands have no axial freedom - Calendar mechanism . . End. .

Contents Introduction Mechanical Watches Quartz Watches Water-resistance Helpful and practical Exit

Water-Resistance Home
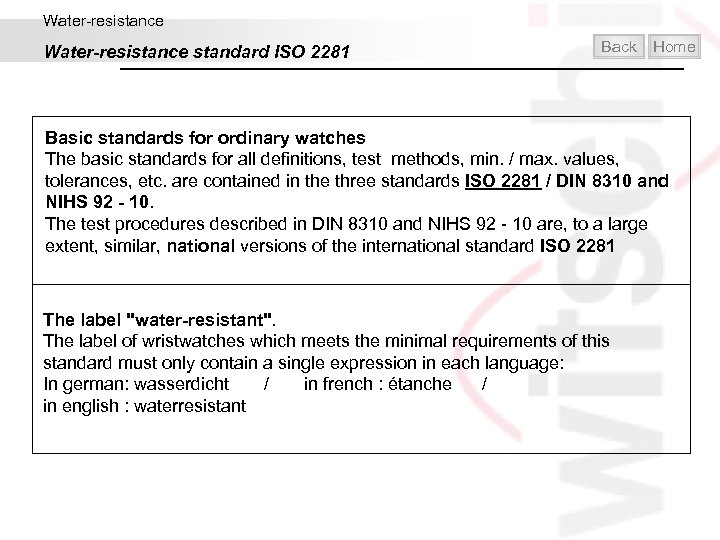
Water-resistance standard ISO 2281 Back Home Basic standards for ordinary watches The basic standards for all definitions, test methods, min. / max. values, tolerances, etc. are contained in the three standards ISO 2281 / DIN 8310 and NIHS 92 - 10. The test procedures described in DIN 8310 and NIHS 92 - 10 are, to a large extent, similar, national versions of the international standard ISO 2281 The label "water-resistant". The label of wristwatches which meets the minimal requirements of this standard must only contain a single expression in each language: In german: wasserdicht / in french : étanche / in english : waterresistant

Water-resistance standard ISO 2281 Back Home Practical aspects of the label "water-resistant". Watches which are designated as water-resistant must be resistant to sweat, water drops, rain, etc. and to immersion into water: - at a depth of 10 cm (excess pressure of 0. 01 bar) for 1 hour and … - at a depth of 20 meter (excess pressure of 2. 0 bar) for 1 min. Minimal requirements ( standard converted to air pressure measurements ) A watch fulfils these requirements if: - the air penetration into the watch - under an excess air pressure of 2 bar - for a 1 minute test - does not exceed 50 g ( microgram )
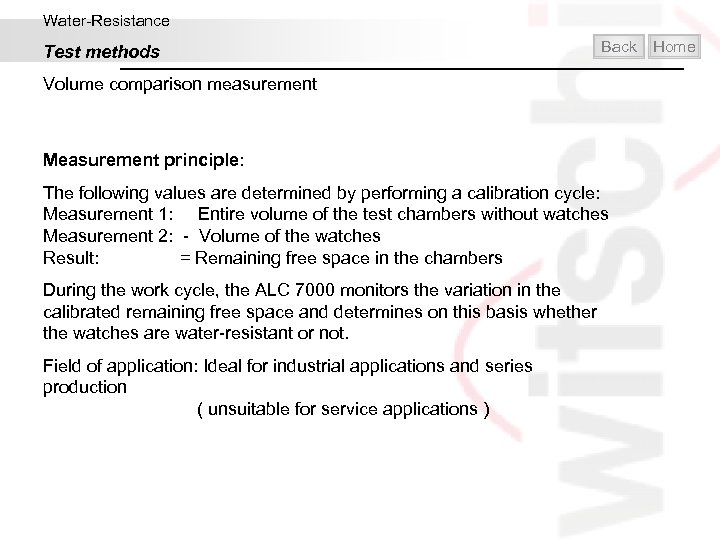
Water-Resistance Test methods Back Volume comparison measurement Measurement principle: The following values are determined by performing a calibration cycle: Measurement 1: Entire volume of the test chambers without watches Measurement 2: - Volume of the watches Result: = Remaining free space in the chambers During the work cycle, the ALC 7000 monitors the variation in the calibrated remaining free space and determines on this basis whether the watches are water-resistant or not. Field of application: Ideal for industrial applications and series production ( unsuitable for service applications ) Home

Water-Resistance Test methods Back Deformation measurement Measurement principle: A given pressure or vacuum is created in a measuring chamber. The external geometry of the watch undergoes a deformation due to the elasticity of the case materials. The sensory part of the system then tracks the reversal of the deformation of the watchcase’s parts during the whole measurement process and, based on it, determines if the watch does or does not correspond to the given tolerances for water-resistance. Field of applications: Industry: small and medium series Services: Repair shop and und retail business Home

Water-Resistance Test methods Back Condensation test Measurement principle: The watch, first tested under pressure underwater, is then brought to a temperature of 40 to 45 degree on a heating plate for approx. 30 min. One then pours a drop of warm water ( 18 - 25 degree ) onto the watch-glass. Water condenses on the inside face of the glass if the watch is not water-resistant. Field of applications: Manufacturing and laboratory Home
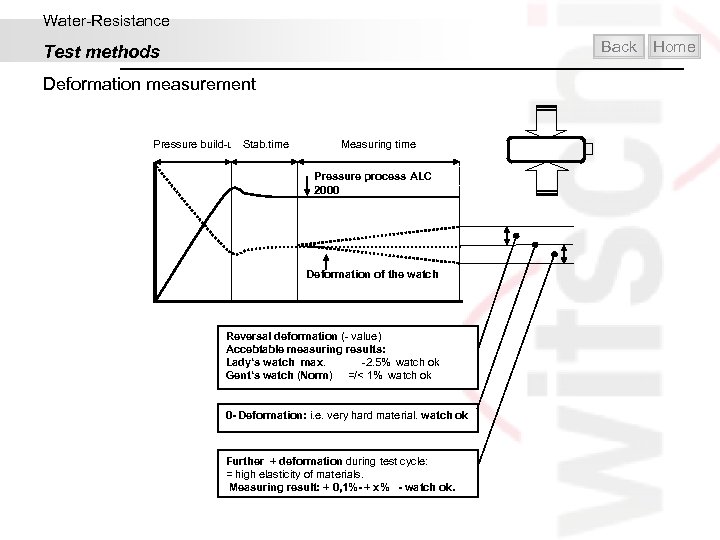
Water-Resistance Back Test methods Deformation measurement Pressure build-up Stab. time Measuring time Pressure process ALC 2000 Deformation of the watch Reversal deformation (- value) Accebtable measuring results: Lady‘s watch max. -2. 5% watch ok Gent‘s watch (Norm) =/< 1% watch ok 0 - Deformation: i. e. very hard material. watch ok Further + deformation during test cycle: = high elasticity of materials. Measuring result: + 0, 1%- + x% - watch ok. Home
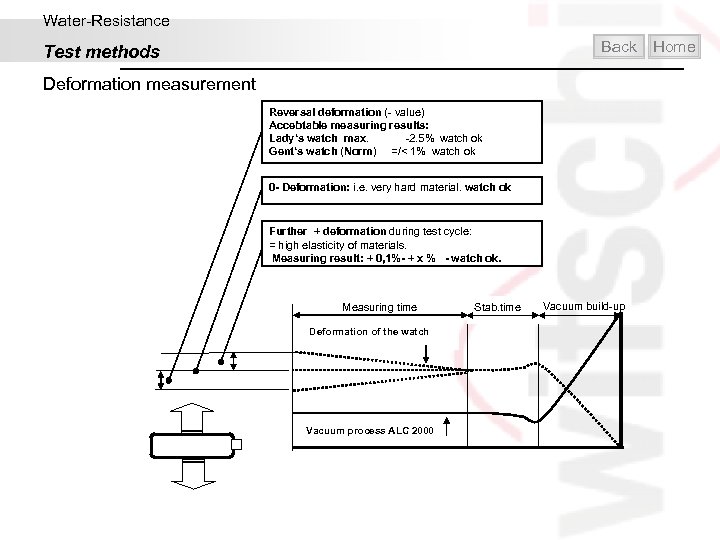
Water-Resistance Back Test methods Deformation measurement Reversal deformation (- value) Accebtable measuring results: Lady‘s watch max. -2. 5% watch ok Gent‘s watch (Norm) =/< 1% watch ok 0 - Deformation: i. e. very hard material. watch ok Further + deformation during test cycle: = high elasticity of materials. Measuring result: + 0, 1%- + x % - watch ok. Measuring time Deformation of the watch Vacuum process ALC 2000 Stab. time Vacuum build-up Home
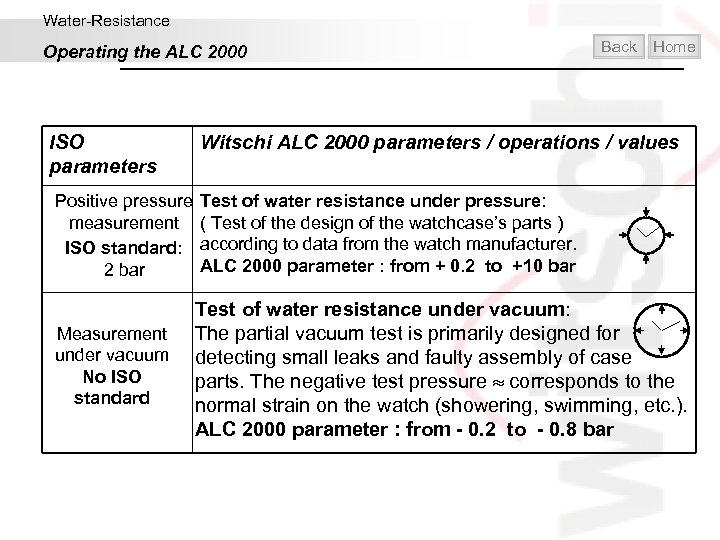
Water-Resistance Operating the ALC 2000 ISO parameters Back Home Witschi ALC 2000 parameters / operations / values Positive pressure Test of water resistance under pressure: measurement ( Test of the design of the watchcase’s parts ) ISO standard: according to data from the watch manufacturer. ALC 2000 parameter : from + 0. 2 to +10 bar 2 bar Measurement under vacuum No ISO standard Test of water resistance under vacuum: The partial vacuum test is primarily designed for detecting small leaks and faulty assembly of case parts. The negative test pressure corresponds to the normal strain on the watch (showering, swimming, etc. ). ALC 2000 parameter : from - 0. 2 to - 0. 8 bar
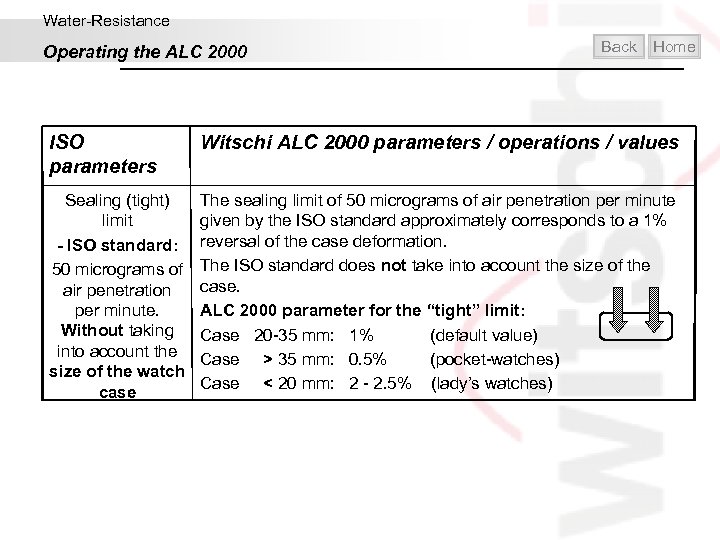
Water-Resistance Operating the ALC 2000 Back Home ISO parameters Witschi ALC 2000 parameters / operations / values Sealing (tight) limit - ISO standard: 50 micrograms of air penetration per minute. Without taking into account the size of the watch case The sealing limit of 50 micrograms of air penetration per minute given by the ISO standard approximately corresponds to a 1% reversal of the case deformation. The ISO standard does not take into account the size of the case. ALC 2000 parameter for the “tight” limit: Case 20 -35 mm: 1% (default value) Case > 35 mm: 0. 5% (pocket-watches) Case < 20 mm: 2 - 2. 5% (lady’s watches)
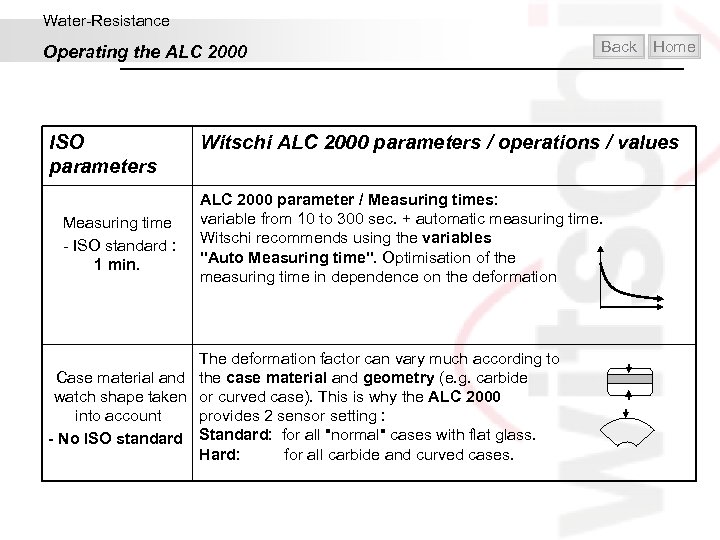
Water-Resistance Operating the ALC 2000 ISO parameters Measuring time - ISO standard : 1 min. Back Home Witschi ALC 2000 parameters / operations / values ALC 2000 parameter / Measuring times: variable from 10 to 300 sec. + automatic measuring time. Witschi recommends using the variables "Auto Measuring time". Optimisation of the measuring time in dependence on the deformation The deformation factor can vary much according to Case material and the case material and geometry (e. g. carbide watch shape taken or curved case). This is why the ALC 2000 into account provides 2 sensor setting : - No ISO standard Standard: for all "normal" cases with flat glass. Hard: for all carbide and curved cases.

Water-Resistance Operating the ALC 2000 Back Witschi’s ALC 2000 has been designed to be a highly accurate, professional test system. The adjustable parameters have been given a great flexibility, allowing checking practically all makes of watches with the utmost reliability. The parameterization offered by Witschi’s ALC 2000 is significantly more specific and tailored to the type of watch than the minimal requirements from the ISO 2281 standard. Home

Water-Resistance Back Operating the ALC 2000 becomes yellow when the watch is correctly placed on the sensor Home Test 1 good (green), Test 2 good (green), bad (red) or undetermined (yellow) entering the desired values + and - back to the main menu or to the standard measurement program PO parameter selection
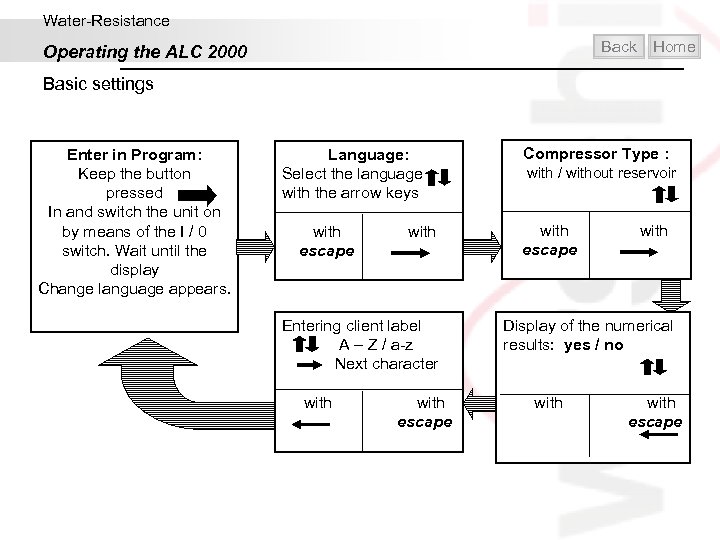
Water-Resistance Back Operating the ALC 2000 Home Basic settings Enter in Program: Keep the button pressed In and switch the unit on by means of the I / 0 switch. Wait until the display Change language appears. Language: Select the language with the arrow keys with escape Compressor Type : with / without reservoir with escape Entering client label A – Z / a-z Next character Display of the numerical results: yes / no with escape
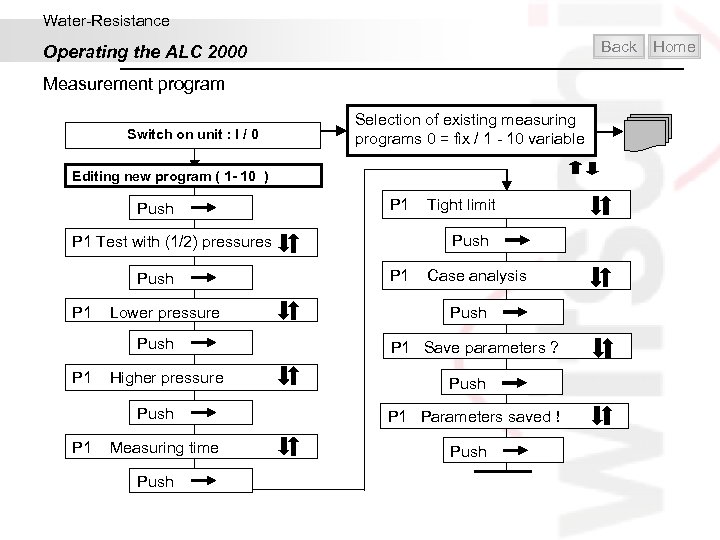
Water-Resistance Back Operating the ALC 2000 Measurement program Switch on unit : I / 0 Selection of existing measuring programs 0 = fix / 1 - 10 variable Editing new program ( 1 - 10 ) Push P 1 Test with (1/2) pressures Push P 1 Lower pressure Push P 1 Higher pressure Push P 1 Measuring time Push P 1 Tight limit Push P 1 Case analysis Push P 1 Save parameters ? Push P 1 Parameters saved Push Home

Water-Resistance Main reasons for a faulty water-resistance Back Home Advantages of the test with excess pressure and partial vacuum There can be 3 main reasons for a faulty water-resistance: • Faulty water-resistance due to bad manufacturing (out of truth in the round or in the flat) of the case and of other components. • Faulty water resistance due to parts of the case and gaskets being deformed in the course of an excess pressure test. This faulty water-resistance only appears in excess pressure tests. • Faulty water-resistance due to inaccurate assembly and a to weak press-fit of components. (seat of the glass and back gasket). Such cases of faulty water- resistance can only be detected with low test pressure, especially with partial vacuum. The stress on the parts is very different according to whether the test is performed under positive pressure or partial vacuum.
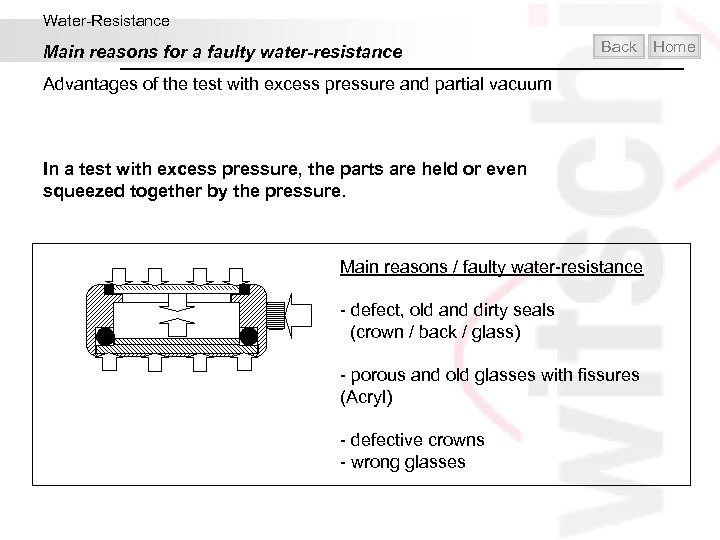
Water-Resistance Main reasons for a faulty water-resistance Back Advantages of the test with excess pressure and partial vacuum In a test with excess pressure, the parts are held or even squeezed together by the pressure. Main reasons / faulty water-resistance - defect, old and dirty seals (crown / back / glass) - porous and old glasses with fissures (Acryl) - defective crowns - wrong glasses Home
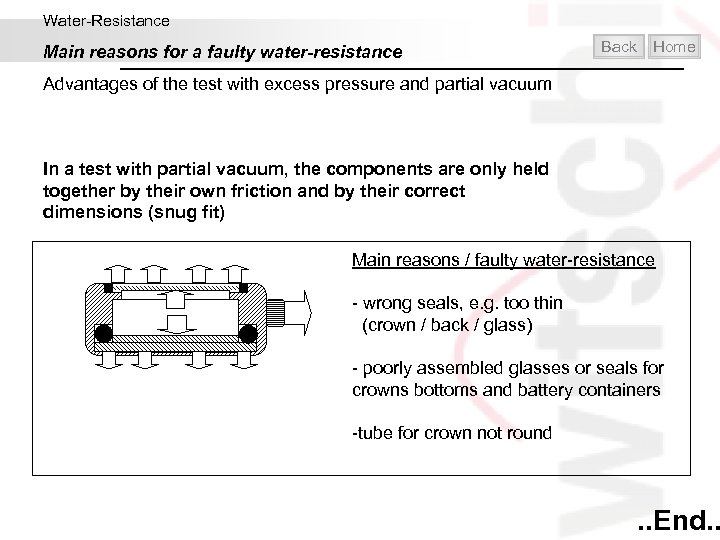
Water-Resistance Main reasons for a faulty water-resistance Back Home Advantages of the test with excess pressure and partial vacuum In a test with partial vacuum, the components are only held together by their own friction and by their correct dimensions (snug fit) Main reasons / faulty water-resistance - wrong seals, e. g. too thin (crown / back / glass) - poorly assembled glasses or seals for crowns bottoms and battery containers -tube for crown not round . . End. .

Contents Introduction Mechanical Watches Quartz Watches Water-resistance Helpful and practical Exit

Witschi measuring tips Home
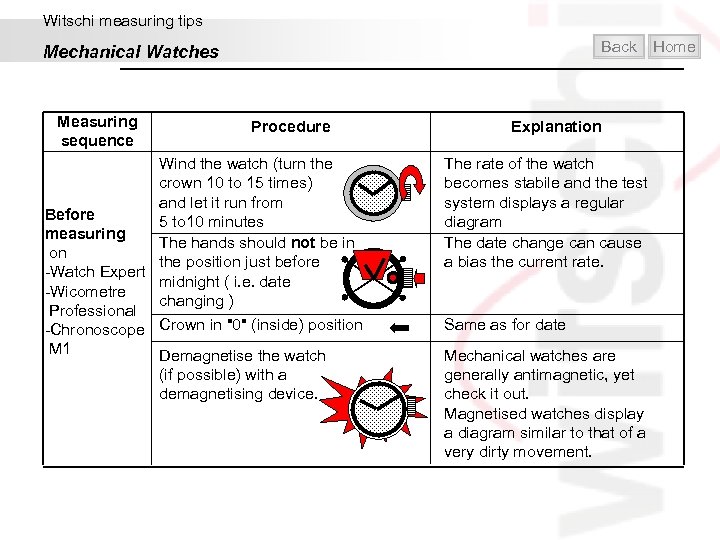
Witschi measuring tips Back Mechanical Watches Measuring sequence Procedure Wind the watch (turn the crown 10 to 15 times) and let it run from Before 5 to 10 minutes measuring The hands should not be in on the position just before -Watch Expert midnight ( i. e. date -Wicometre changing ) Professional -Chronoscope Crown in "0" (inside) position M 1 Demagnetise the watch (if possible) with a demagnetising device. Explanation The rate of the watch becomes stabile and the test system displays a regular diagram The date change can cause a bias the current rate. Same as for date Mechanical watches are generally antimagnetic, yet check it out. Magnetised watches display a diagram similar to that of a very dirty movement. Home
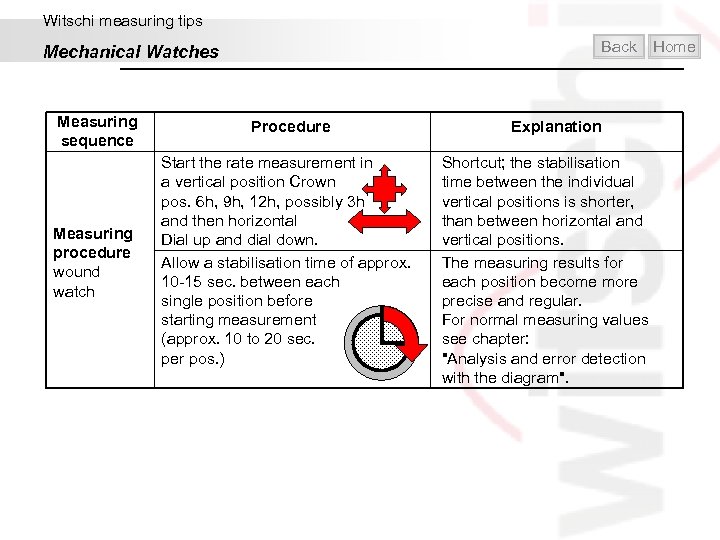
Witschi measuring tips Back Mechanical Watches Measuring sequence Procedure Measuring procedure wound watch Start the rate measurement in a vertical position Crown pos. 6 h, 9 h, 12 h, possibly 3 h and then horizontal Dial up and dial down. Allow a stabilisation time of approx. 10 -15 sec. between each single position before starting measurement (approx. 10 to 20 sec. per pos. ) Home Explanation Shortcut; the stabilisation time between the individual vertical positions is shorter, than between horizontal and vertical positions. The measuring results for each position become more precise and regular. For normal measuring values see chapter: "Analysis and error detection with the diagram".
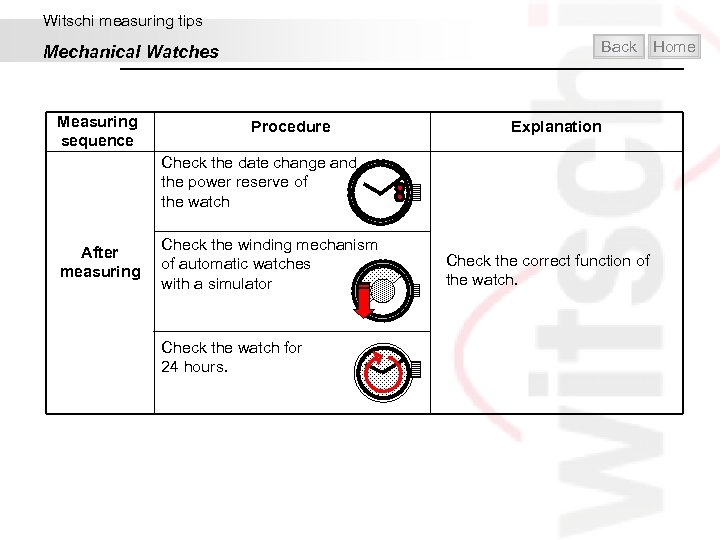
Witschi measuring tips Back Mechanical Watches Measuring sequence Procedure Home Explanation Check the date change and the power reserve of the watch After measuring Check the winding mechanism of automatic watches with a simulator Check the watch for 24 hours. Check the correct function of the watch.
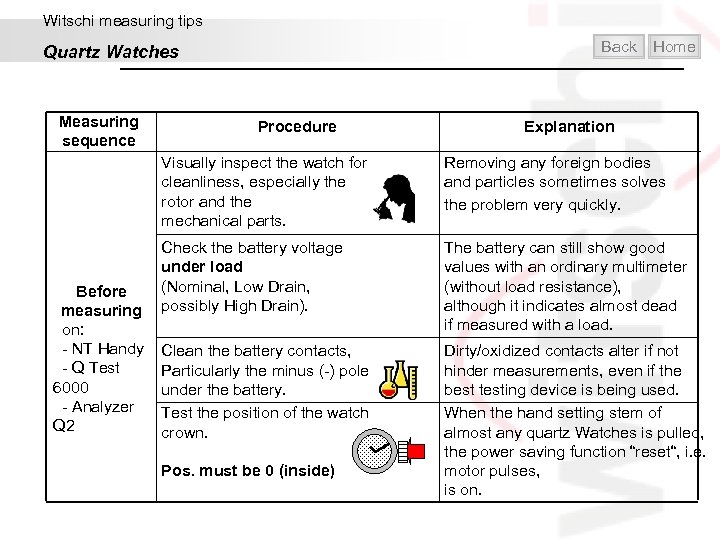
Witschi measuring tips Back Quartz Watches Measuring sequence Procedure Home Explanation Visually inspect the watch for cleanliness, especially the rotor and the mechanical parts. Before measuring on: - NT Handy - Q Test 6000 - Analyzer Q 2 Removing any foreign bodies and particles sometimes solves the problem very quickly. Check the battery voltage under load (Nominal, Low Drain, possibly High Drain). The battery can still show good values with an ordinary multimeter (without load resistance), although it indicates almost dead if measured with a load. Clean the battery contacts, Particularly the minus (-) pole under the battery. Test the position of the watch crown. Pos. must be 0 (inside) Dirty/oxidized contacts alter if not hinder measurements, even if the best testing device is being used. When the hand setting stem of almost any quartz Watches is pulled, the power saving function “reset“, i. e. motor pulses, is on.
Suggestions for measuring Back Quartz Watches Measuring sequence Procedure Explanation Start the rate measurement after checking both the battery with the acoustic microphone and the function of the quartz/IC. Measuring procedure The battery, as well as the Quartz/IC unit, drive the stepping motor. Getting no signal means that the quartz or IC is faulty! A) Analogue quartz watches Place the watch on the magnetic sensor (inductive) and check that motor pulses are present. No pulse means a faulty coil. If pulses are ok but the hands do not move, check the motor, the gear train and the motion work. B) Digital quartz watches -Place the digital watch with the display downwards on the capacitive sensor (pos. LCD). Then check the rate. No signal and nothing on the display: replace the module Home
Suggestions for measuring Back Quartz Watches Measuring sequence Procedure Check the date change in the watch. Test for more than 24 hours 24 After measuring Check the hands function in “dial down“ pos. Test for more than 1 hour. Explanation Test of the mechanical date function. 25 Test the function of the hands. (they could touch the glass). Home
Suggestions for measuring Back Water-Resistance Measuring sequence Procedure Home Explanation Test the material of the watch case and glass for visible damage and dirt on the case and glass. Before measuring Watches with a faulty (cracked) glass should not be tested. The watch to be measured must be clean. Crown position: 0 (internal position) or screwed in. Pay particular care and attention to position screwed -in crowns. Do not keep the watch in your hand too long. When being tested, the watch must have the same ambient temperature as the device. Fluctuation of the temperature during the measurement may falsify the measuring results.
Suggestions for measuring Back Water-Resistance Measuring sequence Before measuring Procedure Home Explanation Remove any synthetic dust-proof adhesive from case back and/or from the glass Foils alter the results due to the air trapped inside Notice the information concerning water-resistance (test pressure) from the manufacturer. When testing, follow the suggestions of the manufacturer. 2 bar-3 bar-5 bar-10 bar 20 -xbar.
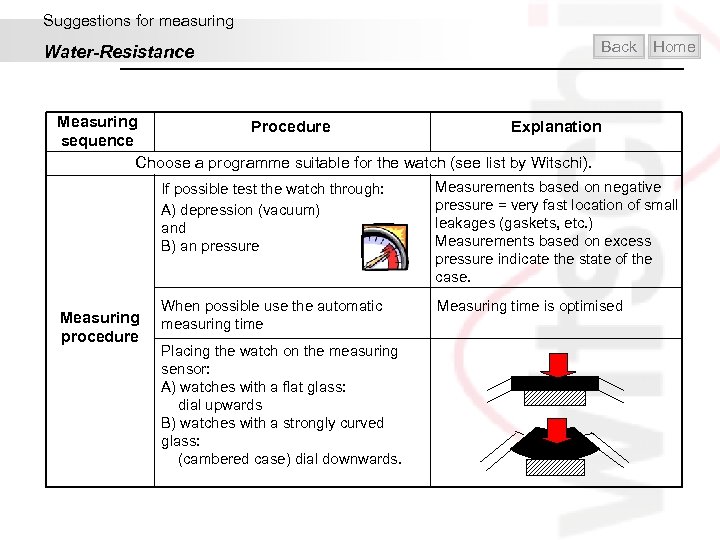
Suggestions for measuring Water-Resistance Back Home Measuring Procedure Explanation sequence Choose a programme suitable for the watch (see list by Witschi). If possible test the watch through: A) depression (vacuum) and B) an pressure Measuring procedure Measurements based on negative pressure = very fast location of small leakages (gaskets, etc. ) Measurements based on excess pressure indicate the state of the case. When possible use the automatic measuring time Measuring time is optimised Placing the watch on the measuring sensor: A) watches with a flat glass: dial upwards B) watches with a strongly curved glass: (cambered case) dial downwards.
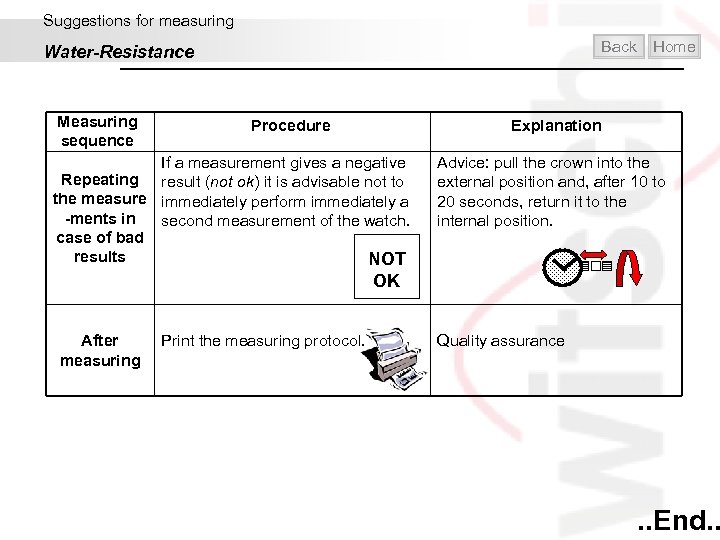
Suggestions for measuring Back Water-Resistance Measuring sequence Procedure If a measurement gives a negative Repeating result (not ok) it is advisable not to the measure immediately perform immediately a -ments in second measurement of the watch. case of bad results NOT OK After measuring Print the measuring protocol. Home Explanation Advice: pull the crown into the external position and, after 10 to 20 seconds, return it to the internal position. Quality assurance . . End. .

Contents Introduction Mechanical Watches Quartz Watches Water-resistance Helpful and practical Exit

Home
e42a8a753eec8ec1caabd29ab53a4628.ppt