 With two or more alternatives, costs that differ among or between alternatives Costs that change in response to an alternative course of action Differential costs differ between actions. Alternative A Alternative B
With two or more alternatives, costs that differ among or between alternatives Costs that change in response to an alternative course of action Differential costs differ between actions. Alternative A Alternative B
 Costs incurred in the past that cannot be changed by present or future decisions A sunk cost is NOT relevant for making decisions.
Costs incurred in the past that cannot be changed by present or future decisions A sunk cost is NOT relevant for making decisions.
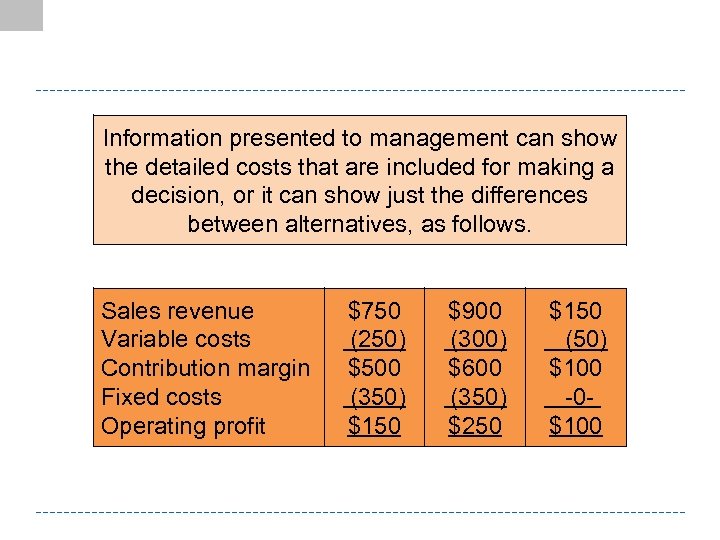 Information presented to management can show the detailed costs that are included for making a decision, or it can show just the differences between alternatives, as follows. Sales revenue Variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs Operating profit $750 (250) $500 (350) $150 $900 (300) $600 (350) $250 $150 (50) $100 -0$100
Information presented to management can show the detailed costs that are included for making a decision, or it can show just the differences between alternatives, as follows. Sales revenue Variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs Operating profit $750 (250) $500 (350) $150 $900 (300) $600 (350) $250 $150 (50) $100 -0$100
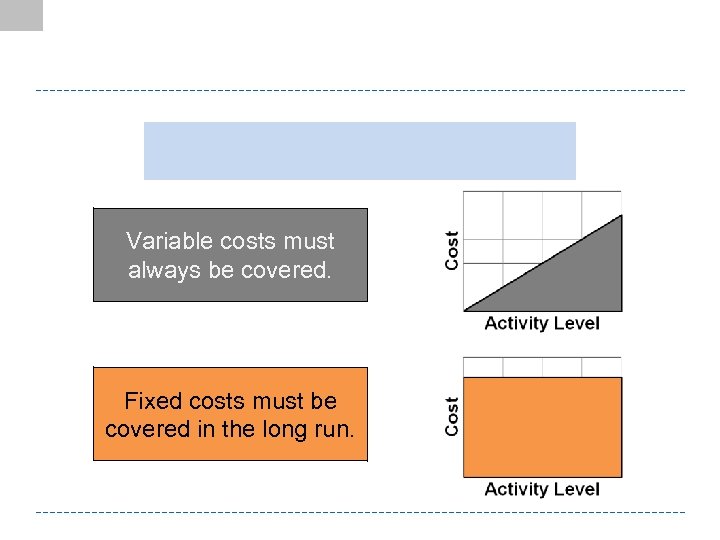 Variable costs must always be covered. Fixed costs must be covered in the long run.
Variable costs must always be covered. Fixed costs must be covered in the long run.
 Pricing a one-time special order. Pricing a new product.
Pricing a one-time special order. Pricing a new product.
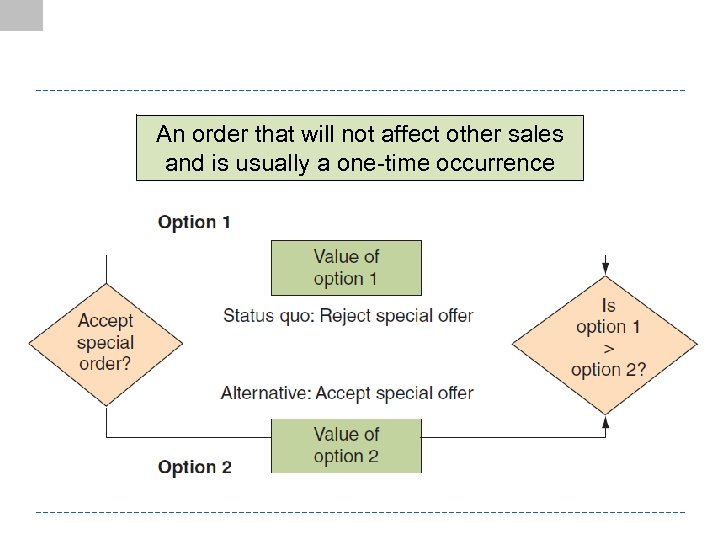 An order that will not affect other sales and is usually a one-time occurrence
An order that will not affect other sales and is usually a one-time occurrence
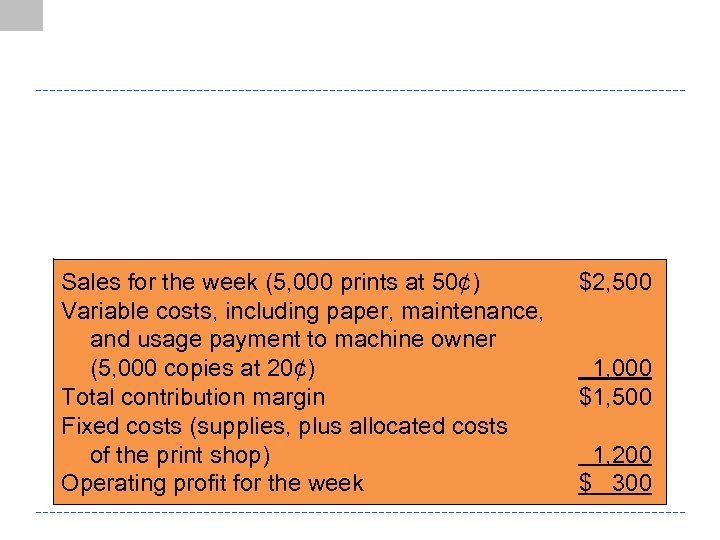 Sales for the week (5, 000 prints at 50¢) Variable costs, including paper, maintenance, and usage payment to machine owner (5, 000 copies at 20¢) Total contribution margin Fixed costs (supplies, plus allocated costs of the print shop) Operating profit for the week $2, 500 1, 000 $1, 500 1, 200 $ 300
Sales for the week (5, 000 prints at 50¢) Variable costs, including paper, maintenance, and usage payment to machine owner (5, 000 copies at 20¢) Total contribution margin Fixed costs (supplies, plus allocated costs of the print shop) Operating profit for the week $2, 500 1, 000 $1, 500 1, 200 $ 300
 Analysis of Special Order: U-Develop
Analysis of Special Order: U-Develop
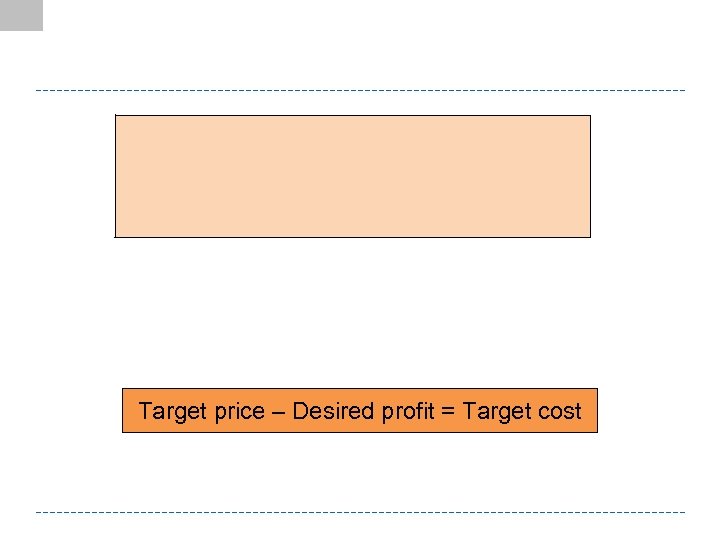 Target price – Desired profit = Target cost
Target price – Desired profit = Target cost
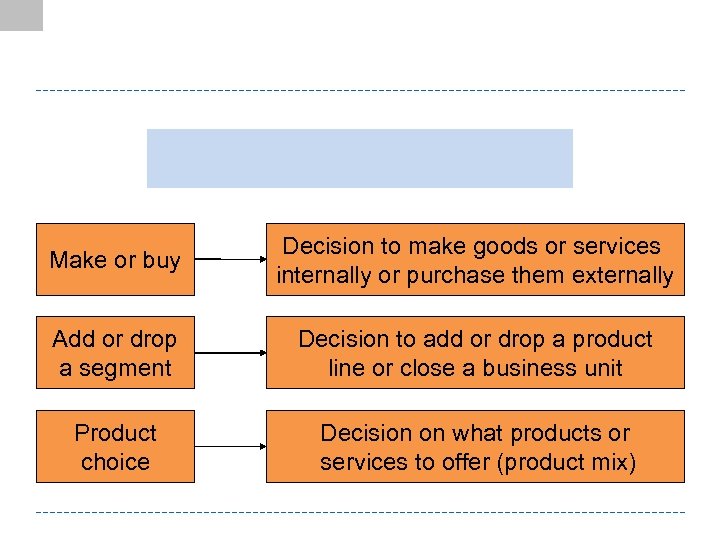 Make or buy Decision to make goods or services internally or purchase them externally Add or drop a segment Decision to add or drop a product line or close a business unit Product choice Decision on what products or services to offer (product mix)
Make or buy Decision to make goods or services internally or purchase them externally Add or drop a segment Decision to add or drop a product line or close a business unit Product choice Decision on what products or services to offer (product mix)
 U-Develop’s current costs of developing prints:
U-Develop’s current costs of developing prints:
 U-Develop received an offer from an outside developer to process any number of prints for 25¢ each. The accounting department prepared cost analyses at volume levels of 50, 000 and 100, 000 prints per year.
U-Develop received an offer from an outside developer to process any number of prints for 25¢ each. The accounting department prepared cost analyses at volume levels of 50, 000 and 100, 000 prints per year.
 U-Develop’s expected volume is 100, 000 prints. Assume that the facilities used to process prints could be used to offer a new service that would provide a $2, 000 incremental contribution.
U-Develop’s expected volume is 100, 000 prints. Assume that the facilities used to process prints could be used to offer a new service that would provide a $2, 000 incremental contribution.
 U-Develop Fourth Quarter Product Line Income Statement
U-Develop Fourth Quarter Product Line Income Statement
 U-Develop Differential Analysis
U-Develop Differential Analysis
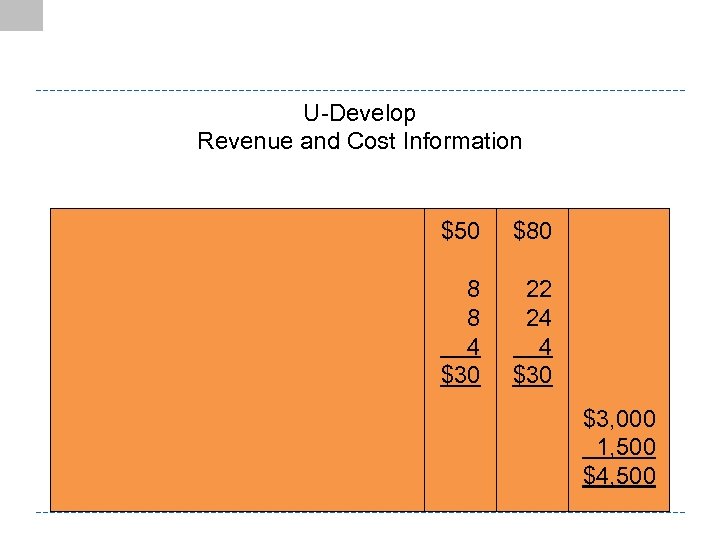 U-Develop Revenue and Cost Information $50 $80 8 8 4 $30 22 24 4 $30 $3, 000 1, 500 $4, 500
U-Develop Revenue and Cost Information $50 $80 8 8 4 $30 22 24 4 $30 $3, 000 1, 500 $4, 500
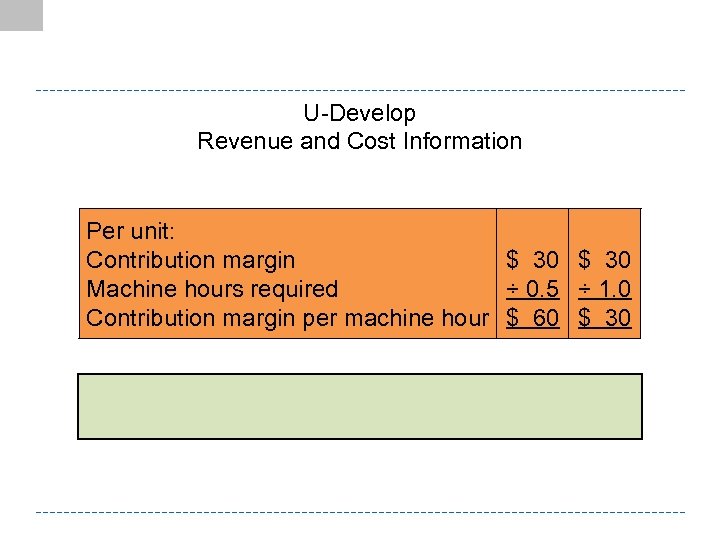 U-Develop Revenue and Cost Information Per unit: Contribution margin $ 30 Machine hours required ÷ 0. 5 ÷ 1. 0 Contribution margin per machine hour $ 60 $ 30
U-Develop Revenue and Cost Information Per unit: Contribution margin $ 30 Machine hours required ÷ 0. 5 ÷ 1. 0 Contribution margin per machine hour $ 60 $ 30
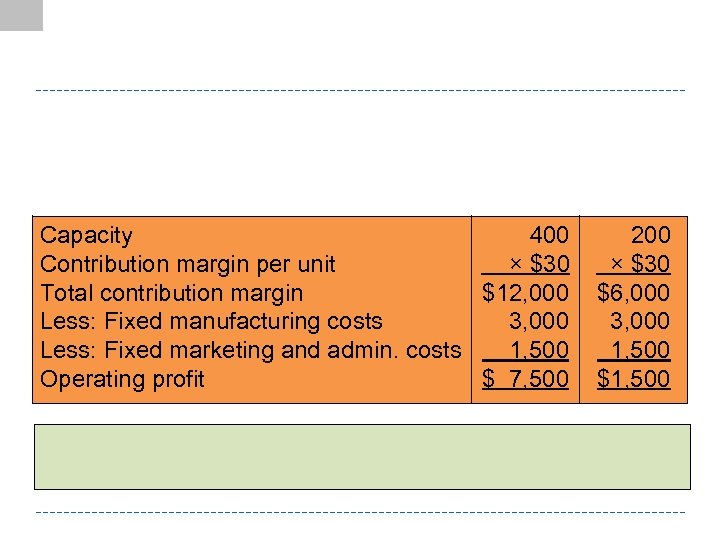 Capacity 400 Contribution margin per unit × $30 Total contribution margin $12, 000 Less: Fixed manufacturing costs 3, 000 Less: Fixed marketing and admin. costs 1, 500 Operating profit $ 7, 500 200 × $30 $6, 000 3, 000 1, 500 $1, 500
Capacity 400 Contribution margin per unit × $30 Total contribution margin $12, 000 Less: Fixed manufacturing costs 3, 000 Less: Fixed marketing and admin. costs 1, 500 Operating profit $ 7, 500 200 × $30 $6, 000 3, 000 1, 500 $1, 500