24e095e5243f42b0be8046aa4b118278.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60

Wireless Technology Evolution to 3 G By Okechukwu Ugweje, Ph. D. Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja, Nigeria Presented at MTN-Nigerian Academy of Engineering Colloquium on Wireless Communications Thursday August 13, 2009 © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 1
Wireless Technology Evolution to 3 G Outline ¦ Wireless Standards/Generations ? ¦ First Generation Technologies ¦ Second Generation Technologies ¦ Transition Technologies (2. 5 G Systems) ¦ Third Generation Technologies ¦ Evolution Paths to 3 G l TDMA l CDMA l GSM: 3 steps of GSM to 3 G ¦ Beyond 3 G (i. e. 4 G) ¦ Conclusion © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 2

Wireless Standards & Generations ? ¦Standards are well established protocols for wireless or mobile communication systems l Interacting systems require standardization ¦Companies want their systems adopted as standard ¦Worldwide standards determined by ITU-T ¦Standards in the US is determined by TIA/CTIA l IEEE standards often adopted ¦These standards are sometimes referred to as “generations” Until lately standards process fraught with inefficiencies and conflicts of interest © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 3

Wireless Technology Evolution to 3 G 1 st Generation (1 G) Technologies © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 4

1 G Technologies ¦Developed in the late 70’s early 80’s, deployed in 80’s ¦Used only for Voice Communications to mobile users over large area (no data) ¦Is Analog: based on circuit-switched technology ¦Major 1 G Systems: l USA: Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) l UK: Total Access Communications Systems (TACS) l Scandinavia: Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT) l West Germany: C 450 l Japan: Nippon Telephone & Telegraph (NTT) ¦Although systems have similar characteristics, they are incompatible and uses different frequencies © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 5

Characteristics of 1 G Systems ¦Use mobile cellular concept to provide service to a geographic area l Frequency reuse concept implemented l Handoff/Handover necessary ¦Systems uses FDMA/FDD ¦Common Air Interface (CAI) standards l Analog voice communications using FM l Digital control channels for signaling - FSK ¦Adjustable mobile power levels – Power control necessary ¦Macro Cells: 1 -40 km radius © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 6
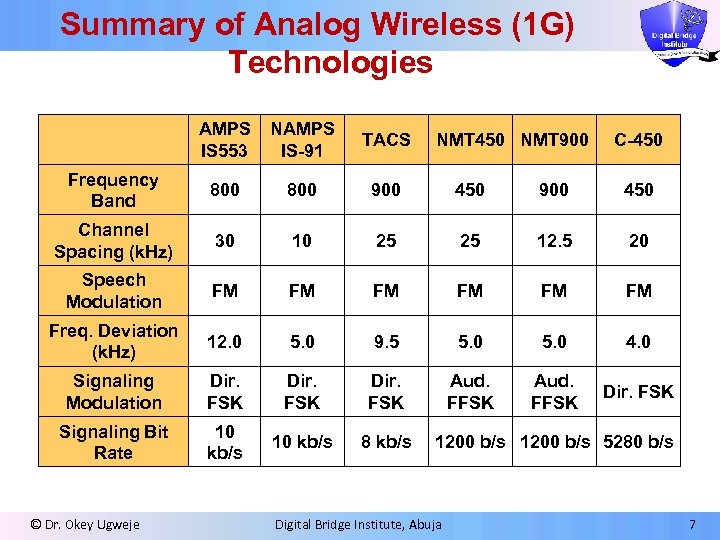
Summary of Analog Wireless (1 G) Technologies AMPS IS 553 NAMPS IS-91 TACS Frequency Band 800 900 450 Channel Spacing (k. Hz) 30 10 25 25 12. 5 20 Speech Modulation FM FM FM Freq. Deviation (k. Hz) 12. 0 5. 0 9. 5 5. 0 4. 0 Signaling Modulation Dir. FSK Aud. FFSK Dir. FSK Signaling Bit Rate 10 kb/s 8 kb/s © Dr. Okey Ugweje NMT 450 NMT 900 C-450 1200 b/s 5280 b/s Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 7
Wireless Technology Evolution to 3 G 2 nd Generation (2 G) Technologies © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 8
2 nd Generation (2 G) Technologies - 1 ¦Motivation for 2 G Digital Cellular l Increase system capacity l Additional services/features (SMS, caller ID, etc. . ) l Reduce cost l Improve security l Interoperability among components/systems ¦Appeared about 10 years after 1 G systems ¦Mid 1990 s - PCS Auctions ¦Offers “Digital Voice” over circuit switched networks ¦Provides better voice quality, higher capacity, lower power requirements and global roaming capabilities © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 9

Major 2 G Technologies - 2 ¦Pacific Digital Cellular (PDC) ¦Global System for Mobile (GSM) ¦CDMA systems - IS-95, cellular CDMA, cdma. One ¦North American TDMA (NA-TDMA) l Basically a digital OVERLAY on top of AMPS with increase capacity & more features l. Several Variants w IS-54 Rev A and Rev B w IS-136 Rev A and Rev B w Standards have many names: TDMA, NA -TDMA, Digital AMPS (DAMPS), US Digital Cellular (USDC), IS-54 © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 10
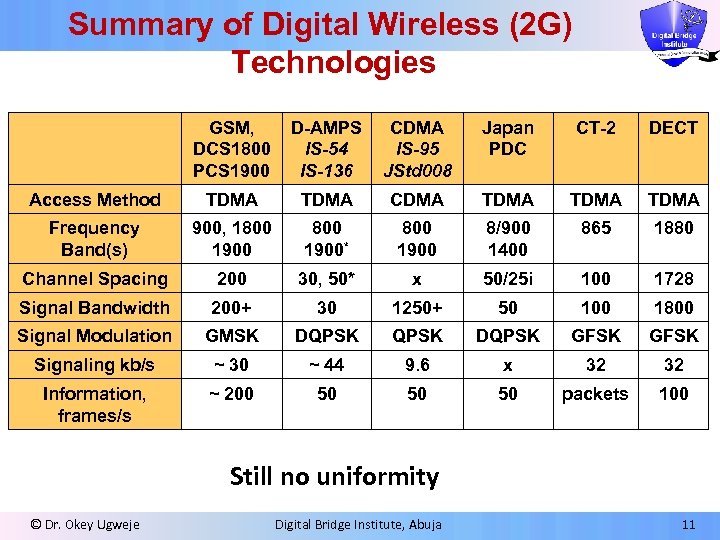
Summary of Digital Wireless (2 G) Technologies GSM, DCS 1800 PCS 1900 D-AMPS IS-54 IS-136 CDMA IS-95 JStd 008 Japan PDC CT-2 DECT Access Method TDMA CDMA TDMA Frequency Band(s) 900, 1800 1900* 800 1900 8/900 1400 865 1880 Channel Spacing 200 30, 50* x 50/25 i 100 1728 Signal Bandwidth 200+ 30 1250+ 50 100 1800 Signal Modulation GMSK DQPSK GFSK Signaling kb/s ~ 30 ~ 44 9. 6 x 32 32 Information, frames/s ~ 200 50 50 50 packets 100 Still no uniformity © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 11
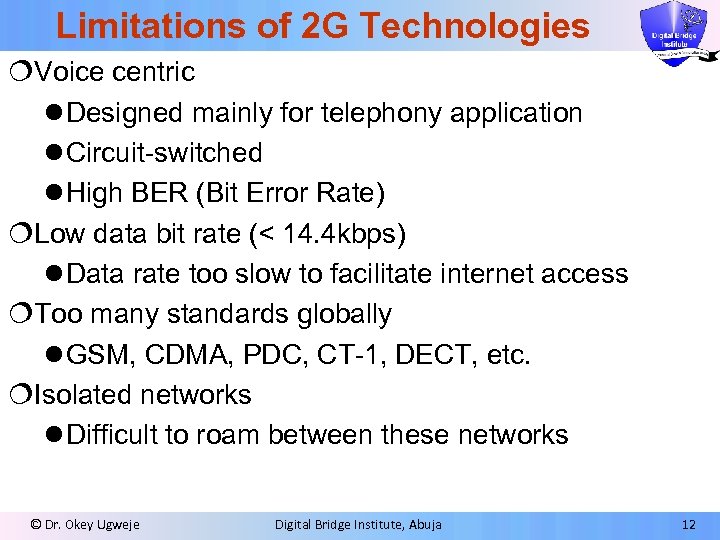
Limitations of 2 G Technologies ¦Voice centric l Designed mainly for telephony application l Circuit-switched l High BER (Bit Error Rate) ¦Low data bit rate (< 14. 4 kbps) l Data rate too slow to facilitate internet access ¦Too many standards globally l GSM, CDMA, PDC, CT-1, DECT, etc. ¦Isolated networks l Difficult to roam between these networks © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 12

Wireless Technology Evolution to 3 G Transition Technologies (2. 5 G) © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 13
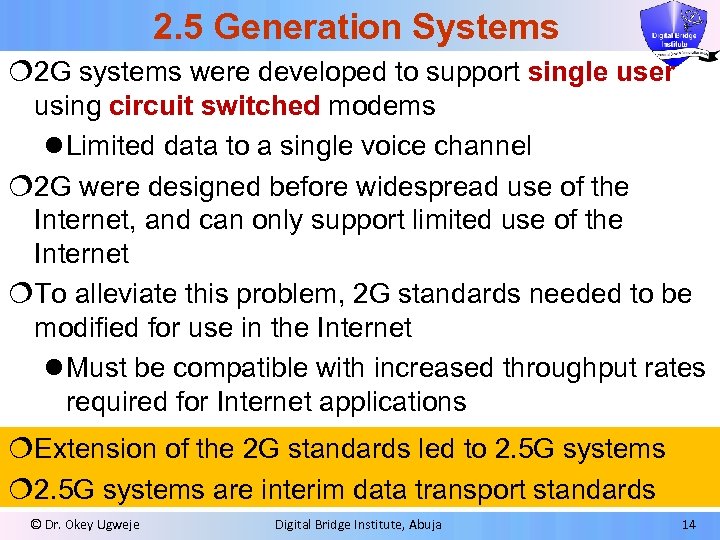
2. 5 Generation Systems ¦ 2 G systems were developed to support single user using circuit switched modems l Limited data to a single voice channel ¦ 2 G were designed before widespread use of the Internet, and can only support limited use of the Internet ¦To alleviate this problem, 2 G standards needed to be modified for use in the Internet l Must be compatible with increased throughput rates required for Internet applications ¦Extension of the 2 G standards led to 2. 5 G systems ¦ 2. 5 G systems are interim data transport standards © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 14

2. 5 Generation Technologies - 1 ¦ 2. 5 G standards can be overlaid upon existing 2 G technologies ¦Evolved based on many complex tradeoffs including: l User demand, l Regulatory conditions, l Cost, l Backward compatibility, and l Assessment of dominant 3 G standards ¦ 2. 5 G systems allow existing 2 G equipment to be modified and supplemented with new add-ons and software upgrades to support higher data rate transmissions for the Internet © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 15
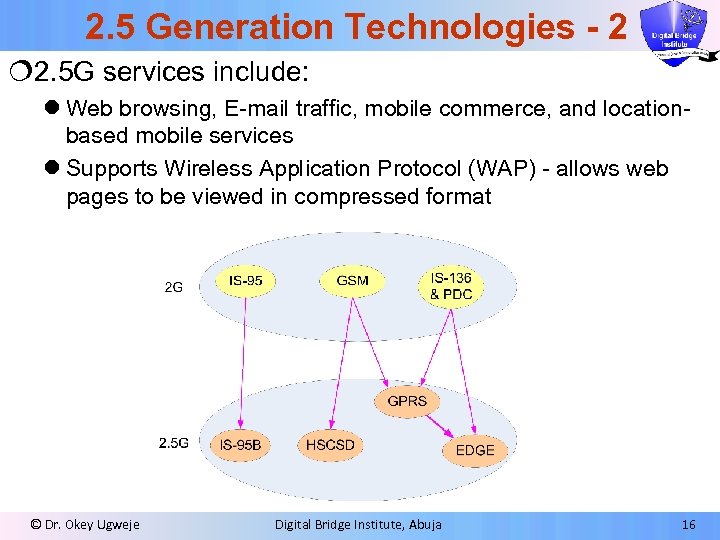
2. 5 Generation Technologies - 2 ¦ 2. 5 G services include: l Web browsing, E-mail traffic, mobile commerce, and locationbased mobile services l Supports Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) - allows web pages to be viewed in compressed format © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 16
Wireless Technology Evolution to 3 G 3 rd Generation (3 G) Technologies © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 17

What is 3 G Wireless Systems ? - 1 ¦ Initiated around 2000 and standard based on wideband CDMA ¦ FCC Definition: l “ 3 G systems will provide access, by means of one or more radio links, to a wide range of telecommunication services supported by the fixed telecommunication networks and to other services that are specific to mobile users. A range of mobile terminal types will be encompassed, linking to terrestrial and/or satellite-based networks, and the terminals may be designed for mobile or fixed use” ¦ Another Definition: l “ability to receive live music, conduct interactive web sessions, and have simultaneous voice and data access with multiple parties at the same time using a single mobile handset, whether driving, walking, or standing still in an office setting” © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 18

What is 3 G Wireless Systems ? - 2 ¦ 3 G is a collection of standards and technologies defined by international organizations, to improve the PERFORMANCE, QUALITY and EFFICIENCY of wireless systems ¦ 3 G is based on the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) family of standards under the IMT-2000 ¦An organization called 3 rd Generation Partnership Project (3 GPP) worked on defining a mobile system that fulfills the IMT-2000 standards ¦ This system (3 G plane of capabilities) is called the Universal Mobile Telecommunications Services (UMTS) © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 19
3 rd Generation Vision ¦Common spectrum worldwide ¦ 1920 -1980 MHz and 2110 -2170 MHz ¦Wide range of new services ¦Data centric (eg. Internet) and multimedia oriented ¦Data bit rates up to 2 Mbps ¦Seamless global roaming ¦Improved security and performance ¦Support a variety of terminal (from PDA to desktop) ¦Intensive use of Intelligent Network (IN) technology © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 20
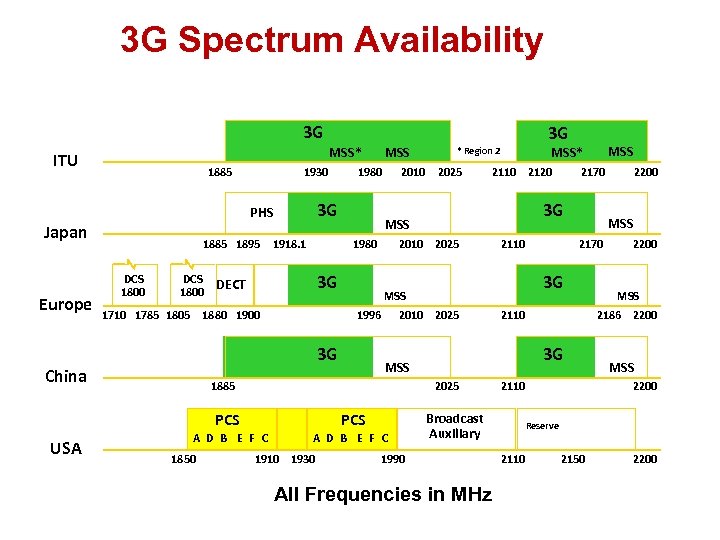
3 G Spectrum Availability 3 G MSS* ITU 1885 1930 Europe 1885 1895 DCS 1800 1980 3 G PHS Japan 1918. 1 1996 Unl. A D B E F C PCS 2010 2025 A D B E F C 2170 2110 Broadcast Auxiliary 1990 All Frequencies in MHz 2200 MSS 2186 2200 3 G MSS PCS 1910 1930 2110 2200 MSS 3 G 2025 PCS 2170 3 G MSS 1885 1850 2110 2120 2010 2025 3 G 1710 1785 1805 1880 1900 2025 MSS* * Region 2 MSS 3 G USA 2010 1980 DCS DECT 1800 China MSS 3 G MSS 2200 Reserve 2110 2150 2200

3 G System Capabilities - 1 ¦ Improved performance over 2 G, 2. 5 G including: l Improved capacity l Improved coverage, enabling migration from a 2 G deployment ¦ Capability to support circuit & packet data at high bit rates: l 144 kbps or higher in high mobility (vehicular) traffic l 384 kbps for pedestrian traffic l 2 Mbps or higher for indoor traffic ¦ Interoperability and roaming ¦ Common billing/user profiles: l Sharing of usage/rate information between service providers l Standardized call detail recording l Standardized user profiles © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 22

3 G System Capabilities - 2 ¦ Capability to determine geographic position of mobiles and report it to both the network and the mobile terminal ¦ A high degree of operator flexibility, including: l Support of asynchronous inter-base-station operation; l Efficient support of different deployment scenarios, including hierarchical cell structure and hot-spot scenarios; l Support of evolutionary technologies such as adaptive antenna arrays and multi-user detection ¦ Support of multimedia services/capabilities: l Fixed and variable rate bit traffic l Bandwidth on demand l Asymmetric data rates in the forward and reverse links l Multimedia mail store and forward l Broadband access up to 2 Megabits/second © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 23

Why 3 G? ¦Higher bandwidth enables a range of new applications! ¦For the consumer l Video streaming, TV broadcast l Video calls, video clips – news, music, sports l Enhanced gaming, chat, location services… ¦For business l High speed networking / VPN access l Sales force automation l Video conferencing l Real-time financial information © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 24

How fast Exactly is 3 G? ¦ The data speed of 3 G is determined based on a combination of various factors including: l Chip rate l Channel structure l Power control l Number of users in a cell l Distance of user from cell l User is moving or stationary l Synchronization ¦ There is no clear definition of the speeds users can expect from 3 G equipment or providers ¦ Thus customer using the 3 G service may not be able to point to a standard and say that the speed it specifies are not being met © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 25
Issues on 3 G Technologies ¦Several issues continue to hamper its growth. l. Huge capital required to build infrastructure for 3 G services l. High spectrum licensing fees for the 3 G services l. Health impact of electromagnetic waves l. Prices are very high for 3 G mobile services l. Will 2 G users switch to 3 G services l. Takes time to catch up as the service is new © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 26

Potential 3 G Applications ¦Interactive news delivery (voice, video, graphics, email) ¦ Voice/High quality audio ¦Still photography ¦Video ¦Data transmission services ¦Internet gaming ¦Interactive audio ¦File transfer from the Internet © Dr. Okey Ugweje m. Voice/CD quality music m. Multimedia email (graphics, voice and video) m. Video Conferencing m. Web Browser § On-line services § Time schedule § Global positioning services § Geographical information systems Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 27
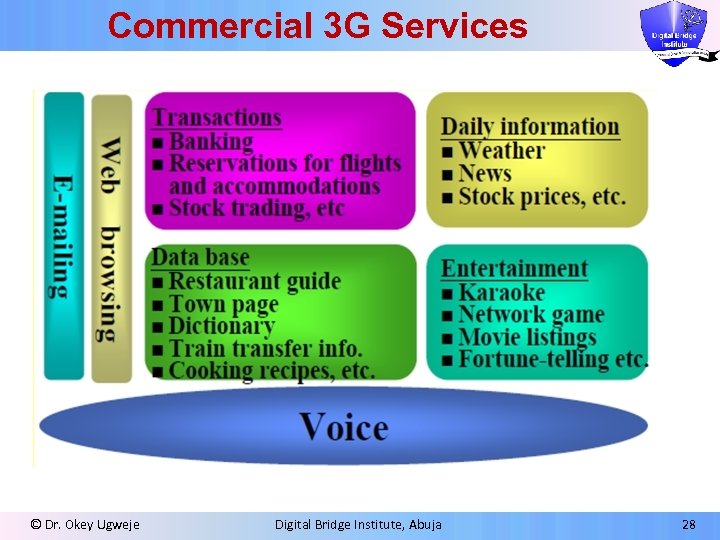
Commercial 3 G Services © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 28

Wireless Technology Evolution to 3 G Technologies © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 29
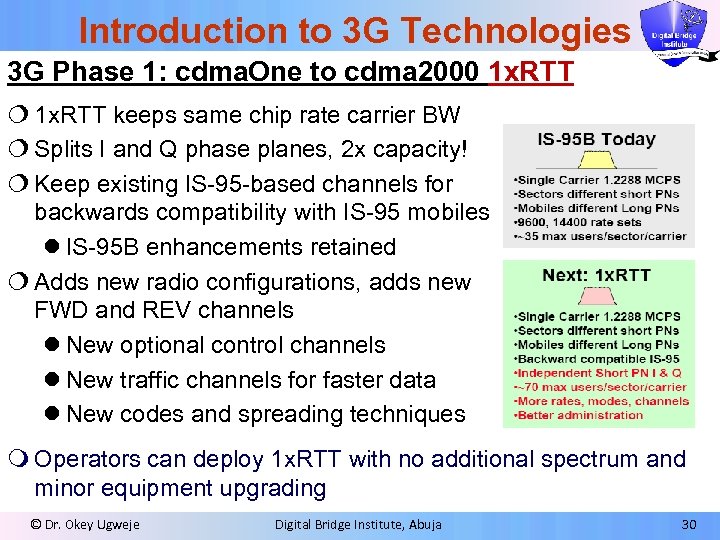
Introduction to 3 G Technologies 3 G Phase 1: cdma. One to cdma 2000 1 x. RTT ¦ 1 x. RTT keeps same chip rate carrier BW ¦ Splits I and Q phase planes, 2 x capacity! ¦ Keep existing IS-95 -based channels for backwards compatibility with IS-95 mobiles l IS-95 B enhancements retained ¦ Adds new radio configurations, adds new FWD and REV channels l New optional control channels l New traffic channels for faster data l New codes and spreading techniques m Operators can deploy 1 x. RTT with no additional spectrum and minor equipment upgrading © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 30
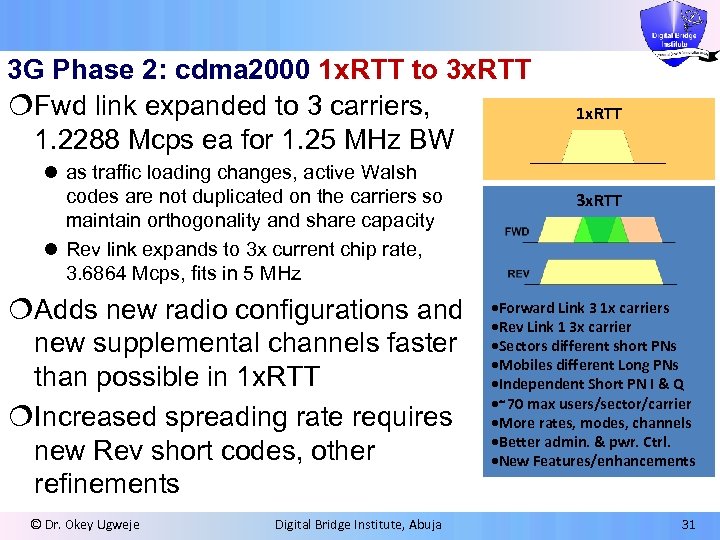
3 G Phase 2: cdma 2000 1 x. RTT to 3 x. RTT ¦Fwd link expanded to 3 carriers, 1. 2288 Mcps ea for 1. 25 MHz BW l as traffic loading changes, active Walsh codes are not duplicated on the carriers so maintain orthogonality and share capacity l Rev link expands to 3 x current chip rate, 3. 6864 Mcps, fits in 5 MHz ¦Adds new radio configurations and new supplemental channels faster than possible in 1 x. RTT ¦Increased spreading rate requires new Rev short codes, other refinements © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 1 x. RTT 3 x. RTT • Forward Link 3 1 x carriers • Rev Link 1 3 x carrier • Sectors different short PNs • Mobiles different Long PNs • Independent Short PN I & Q • ∼ 70 max users/sector/carrier • More rates, modes, channels • Better admin. & pwr. Ctrl. • New Features/enhancements 31

3 G Phase 2 Alternatives: 1 x. EV ¦ 1 x alternatives offers data rates just as fast as 3 x! l 1 x. EV -1 x EVolution is the term used to describe technology l Qualcomm’s proprietary High Data Rates (HDR) technology dedicates a 1 x carrier for fast data only use - no voice l This is called 1 x. EV DO (Data Only) ¦ Motorola and Nokia teamed up to develop and promote an alternative 1 x technology under the trade name 1 Xtreme l Uses more complex modulation techniques l Offers up to 4. 9 Mb/s data rates l Backwards compatible with voice and data on same carrier l This is called 1 x. EV DV (Data and Voice) ¦ Both 1 x. EV DO and 1 x. EV DV use fragile modulation schemes l Maximum claimed rates available only under ideal conditions (near unloaded base stations) ¦ Despite drawbacks, 1 x. EV is still more attractive to operators than 3 x. RTT l 3 x. RTT requires three physical carriers and substantially more BTS equipment than 1 x. EV! © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 32
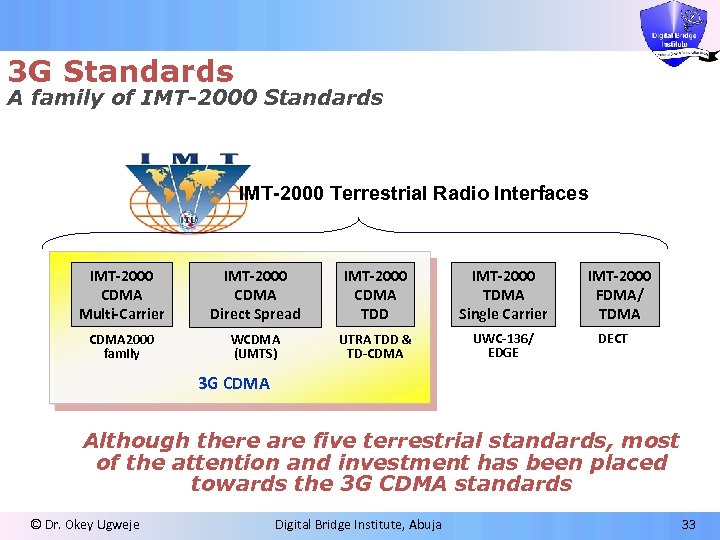
3 G Standards A family of IMT-2000 Standards IMT-2000 Terrestrial Radio Interfaces IMT-2000 CDMA Multi-Carrier IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread IMT-2000 CDMA TDD IMT-2000 TDMA Single Carrier CDMA 2000 family WCDMA (UMTS) UTRA TDD & TD-CDMA UWC-136/ EDGE IMT-2000 FDMA/ TDMA DECT 3 G CDMA Although there are five terrestrial standards, most of the attention and investment has been placed towards the 3 G CDMA standards © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 33
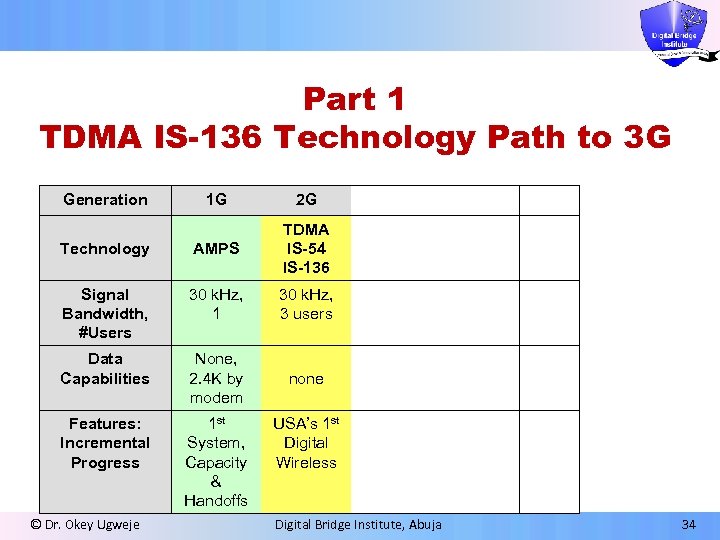
Part 1 TDMA IS-136 Technology Path to 3 G Generation 1 G 2 G Technology AMPS TDMA IS-54 IS-136 Signal Bandwidth, #Users 30 k. Hz, 1 30 k. Hz, 3 users Data Capabilities None, 2. 4 K by modem none Features: Incremental Progress 1 st System, Capacity & Handoffs © Dr. Okey Ugweje USA’s 1 st Digital Wireless Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 34
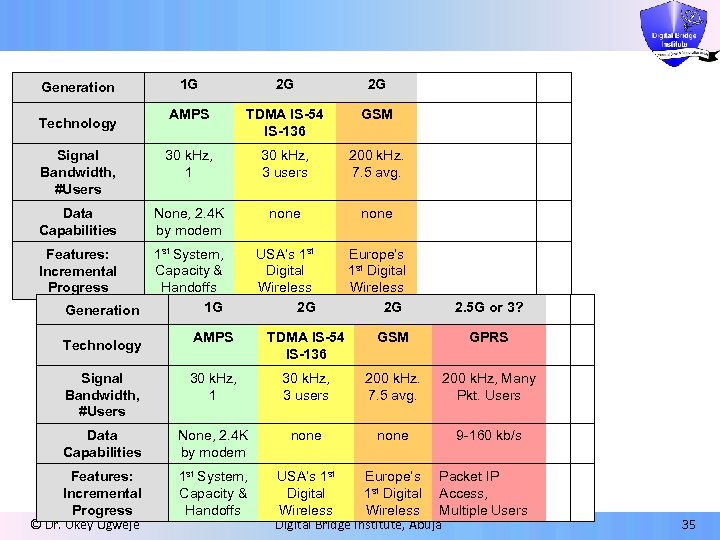
1 G 2 G 2 G AMPS TDMA IS-54 IS-136 GSM Signal Bandwidth, #Users 30 k. Hz, 1 30 k. Hz, 3 users 200 k. Hz. 7. 5 avg. Data Capabilities None, 2. 4 K by modem none Features: Incremental Progress 1 st System, Capacity & Handoffs 1 G USA’s 1 st Digital Wireless 2 G Europe’s 1 st Digital Wireless 2 G Generation Technology Generation 2. 5 G or 3? AMPS TDMA IS-54 IS-136 GSM GPRS Signal Bandwidth, #Users 30 k. Hz, 1 30 k. Hz, 3 users 200 k. Hz. 7. 5 avg. 200 k. Hz, Many Pkt. Users Data Capabilities None, 2. 4 K by modem none 9 -160 kb/s Features: Incremental Progress © Dr. Okey Ugweje 1 st System, Capacity & Handoffs Technology USA’s 1 st Europe’s Packet IP Digital 1 st Digital Access, Wireless Multiple Users Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 35
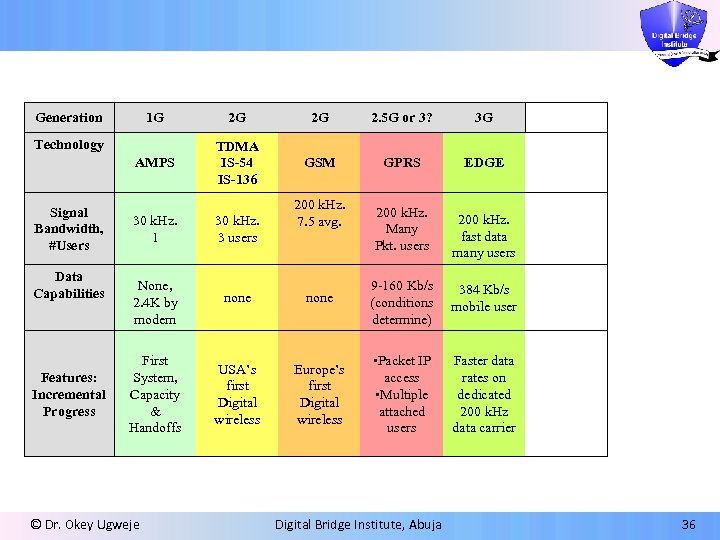
Generation 1 G 2 G 2 G 2. 5 G or 3? 3 G AMPS TDMA IS-54 IS-136 GSM GPRS EDGE Technology Signal Bandwidth, #Users Data Capabilities Features: Incremental Progress 200 k. Hz. 7. 5 avg. 200 k. Hz. Many Pkt. users 200 k. Hz. fast data many users 30 k. Hz. 1 30 k. Hz. 3 users None, 2. 4 K by modem none 9 -160 Kb/s (conditions determine) 384 Kb/s mobile user First System, Capacity & Handoffs USA’s first Digital wireless Europe’s first Digital wireless • Packet IP access • Multiple attached users Faster data rates on dedicated 200 k. Hz data carrier © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 36
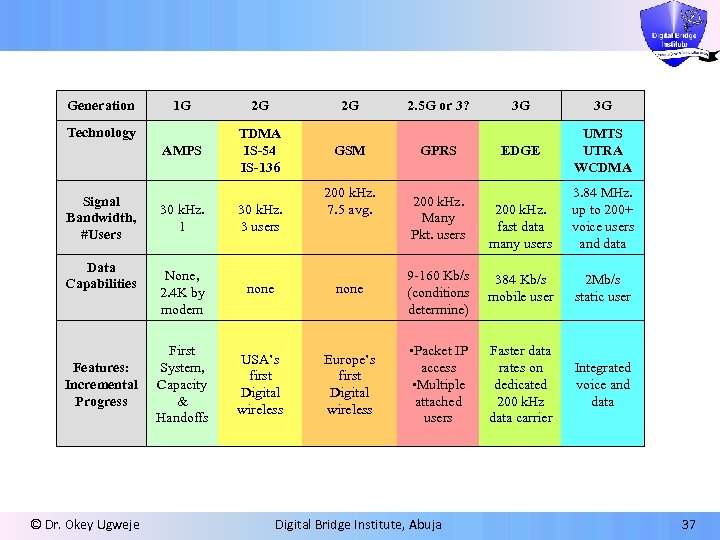
Generation 1 G 2 G AMPS TDMA IS-54 IS-136 Technology Signal Bandwidth, #Users Data Capabilities Features: Incremental Progress © Dr. Okey Ugweje 2 G GSM 200 k. Hz. 7. 5 avg. 30 k. Hz. 1 30 k. Hz. 3 users None, 2. 4 K by modem none First System, Capacity & Handoffs USA’s first Digital wireless Europe’s first Digital wireless 2. 5 G or 3? GPRS 3 G 3 G EDGE UMTS UTRA WCDMA 200 k. Hz. fast data many users 3. 84 MHz. up to 200+ voice users and data 9 -160 Kb/s (conditions determine) 384 Kb/s mobile user 2 Mb/s static user • Packet IP access • Multiple attached users Faster data rates on dedicated 200 k. Hz data carrier Integrated voice and data 200 k. Hz. Many Pkt. users Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 37
IS-95 CDMA Technology Path to 3 G ¦ 2 G CDMA - IS-95 A and J-Std 008 l Signal Structure: w 1. 2288 Mcps spreading, signal ∼ 1. 25 MHz wide l Traffic Channel Capabilities: w Data Rate: 9. 6 kb/s or 14. 4 kb/s traffic channels ¦IS-95 B: CDMA 2 G Enhancements l IS-95 B is still considered 2 G, but offers some needed enhancements to IS-95 A l Improved Access Methods l Improved Handoff Methods l Faster Data Services © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 38
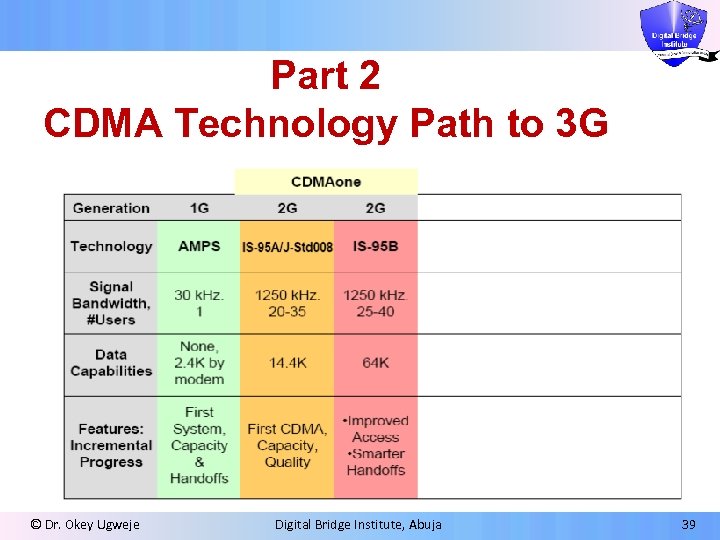
Part 2 CDMA Technology Path to 3 G © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 39
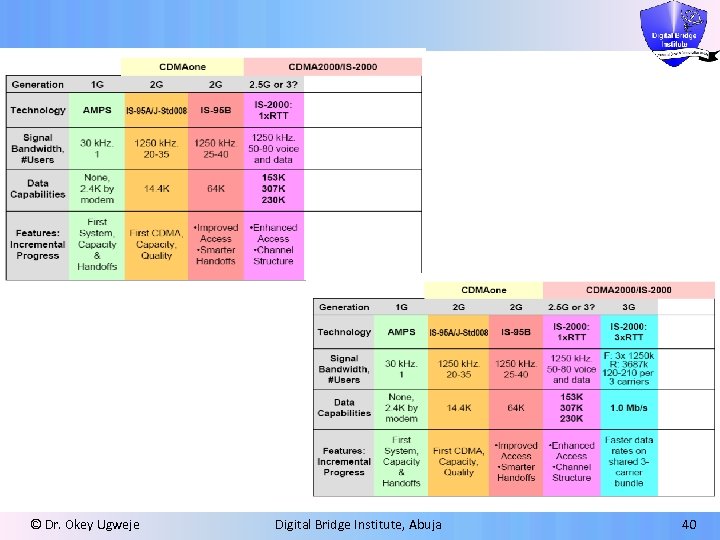
© Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 40
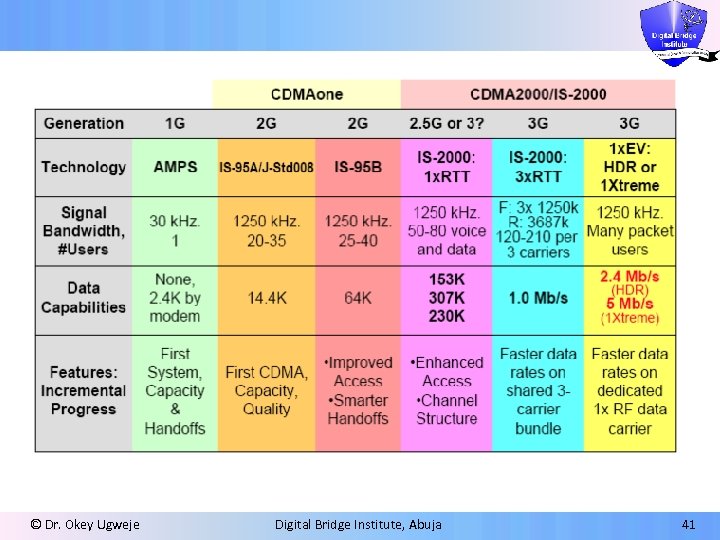
© Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 41
Part 3 CDMA Technology Path to 3 G ¦GSM technology transition to 3 G is in 3 phases l Phase 1: adds a packet-switched radio network as an overlay on the existing physical structure l Phase 2: replaces base stations and controllers with the new UTRA sub-network l Phase 3: introduces UMTS handsets and their corresponding Subscriber Identity Modules (SIM) ¦Core functionality of the existing network is maintained throughout the three phases of migration © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 42
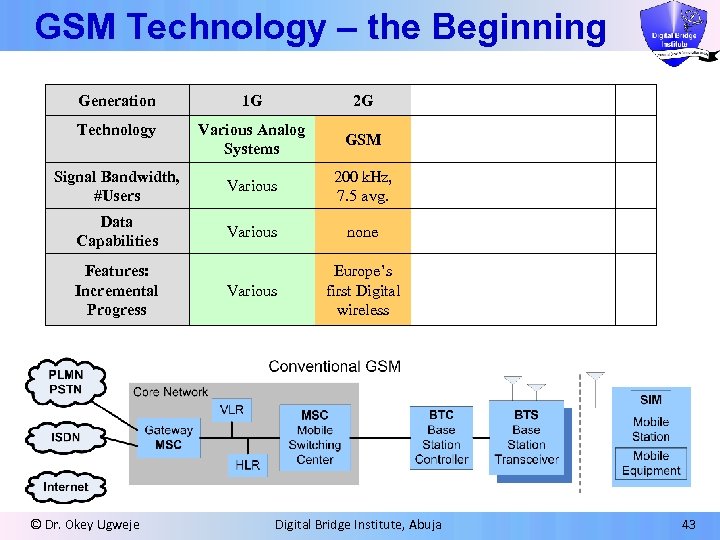
GSM Technology – the Beginning Generation 1 G 2 G Technology Various Analog Systems GSM Signal Bandwidth, #Users Various 200 k. Hz, 7. 5 avg. Data Capabilities Various none Various Europe’s first Digital wireless Features: Incremental Progress © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 43
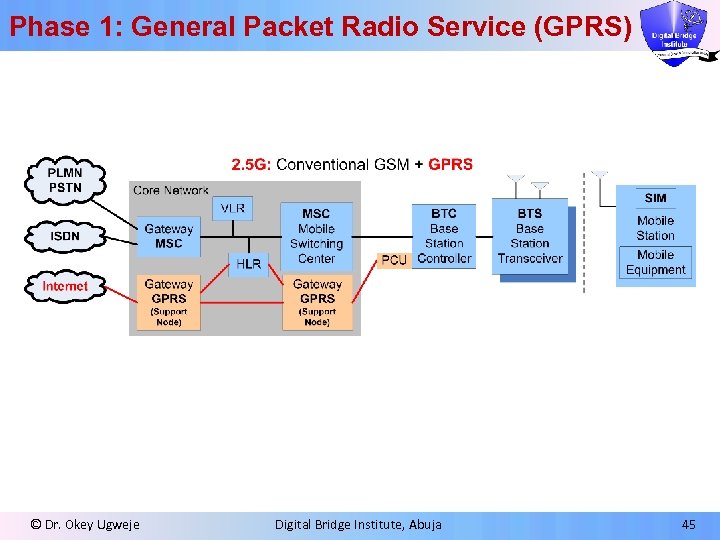
Phase 1: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) ¦GPRS uses aggregated timeslots of existing GSM base stations to transmit packet data l IP routers and Gateway GPRS support nodes added to forward IP packets to users l GPRS supports multiple data rates: 9. 06, 13. 4, 15. 6, and 21. 4 kb/s per GSM timeslot and total rates of 40 -60 kb/s ¦Each BSC has a parallel Packet Controller Unit (PCU), which manages all packet streams ¦GPRS provides IP capability in the near term, well in advance of the higher bandwidths possible on fullyimplemented UMTS systems © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 44
Phase 1: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 45
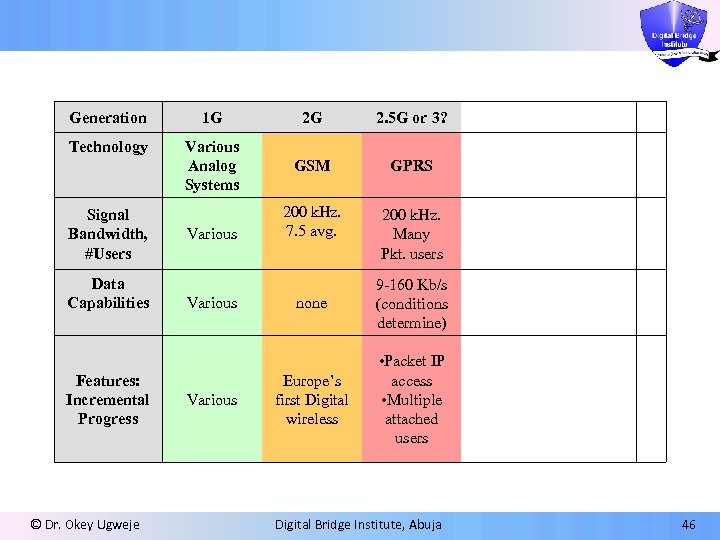
Generation 1 G 2 G 2. 5 G or 3? Technology Various Analog Systems GSM GPRS 200 k. Hz. 7. 5 avg. 200 k. Hz. Many Pkt. users Signal Bandwidth, #Users Data Capabilities Features: Incremental Progress © Dr. Okey Ugweje Various none 9 -160 Kb/s (conditions determine) Europe’s first Digital wireless • Packet IP access • Multiple attached users Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 46
EDGE: Shortcut to Fast Data or Unneeded Detour on the Road to UMTS? ¦ Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) is a speedenhancing modulation upgrade for data transmission & has variants for both GSM-GPRS & TDMA IS-136 systems l EDGE uses Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) and 8 -phase Phase Shift Keying (8 -PSK) to allow 144 kb/s bit rates for mobile users and up to 384 kb/s for pedestrian users ¦ EDGE interest has fluctuated and many GSM and TDMA operators have chosen not to pursue it, believing it is more efficient to move directly to UMTS l This has led to several manufacturers abandoning their EDGE development activities © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 47
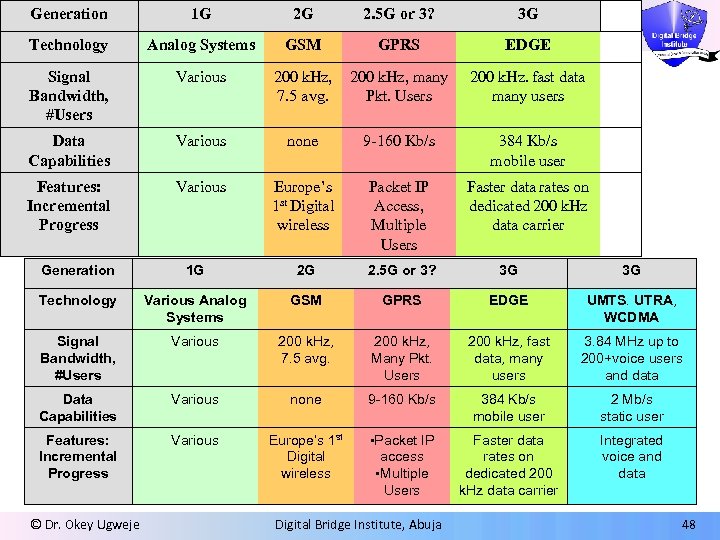
Generation 1 G 2 G 2. 5 G or 3? 3 G Technology Analog Systems GSM GPRS EDGE Signal Bandwidth, #Users Various 200 k. Hz, 7. 5 avg. 200 k. Hz, many Pkt. Users 200 k. Hz. fast data many users Data Capabilities Various none 9 -160 Kb/s 384 Kb/s mobile user Features: Incremental Progress Various Europe’s 1 st Digital wireless Packet IP Access, Multiple Users Faster data rates on dedicated 200 k. Hz data carrier Generation 1 G 2 G 2. 5 G or 3? 3 G 3 G Technology Various Analog Systems GSM GPRS EDGE UMTS. UTRA, WCDMA Signal Bandwidth, #Users Various 200 k. Hz, 7. 5 avg. 200 k. Hz, Many Pkt. Users 200 k. Hz, fast data, many users 3. 84 MHz up to 200+voice users and data Data Capabilities Various none 9 -160 Kb/s 384 Kb/s mobile user 2 Mb/s static user Features: Incremental Progress Various Europe’s 1 st Digital wireless • Packet IP access • Multiple Users Faster data rates on dedicated 200 k. Hz data carrier Integrated voice and data © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 48
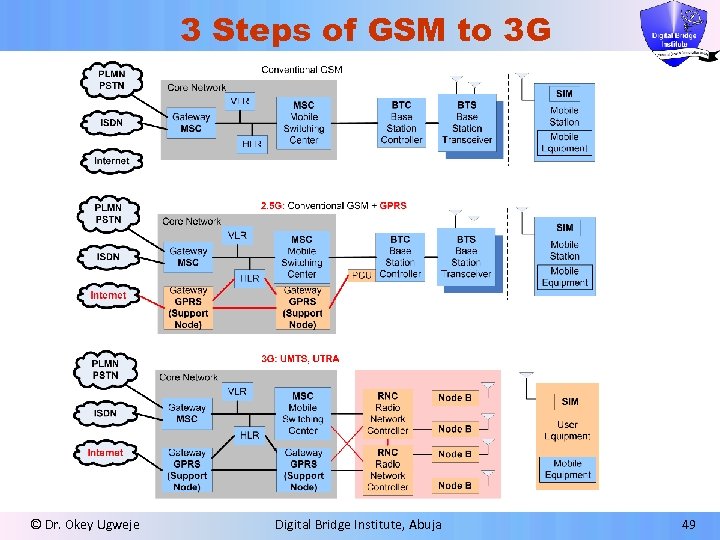
3 Steps of GSM to 3 G © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 49
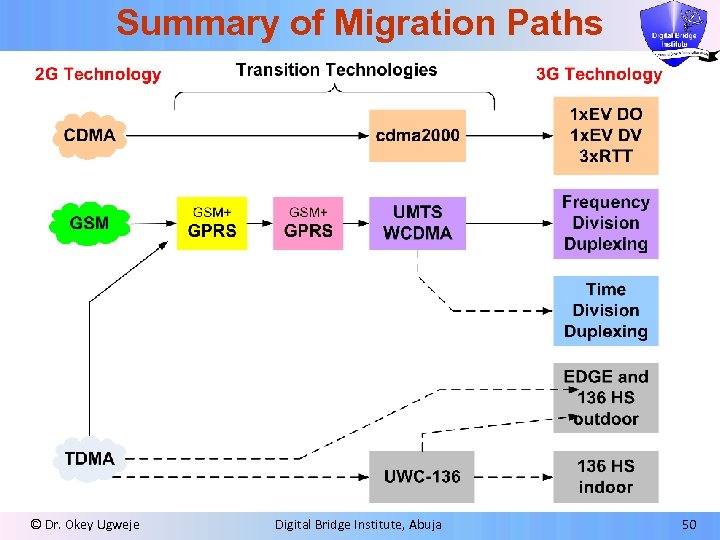
Summary of Migration Paths © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 50
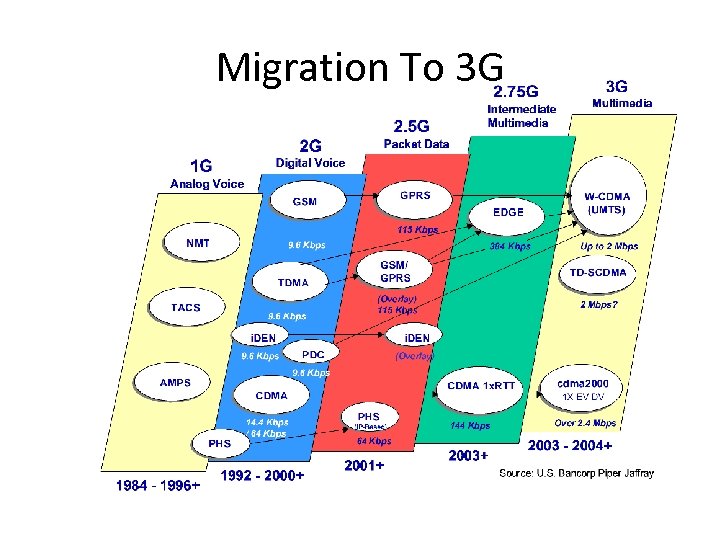
Migration To 3 G
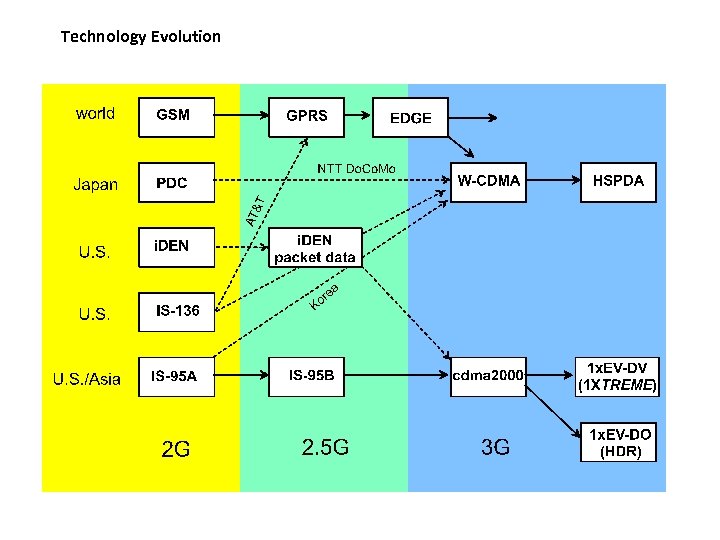
Technology Evolution
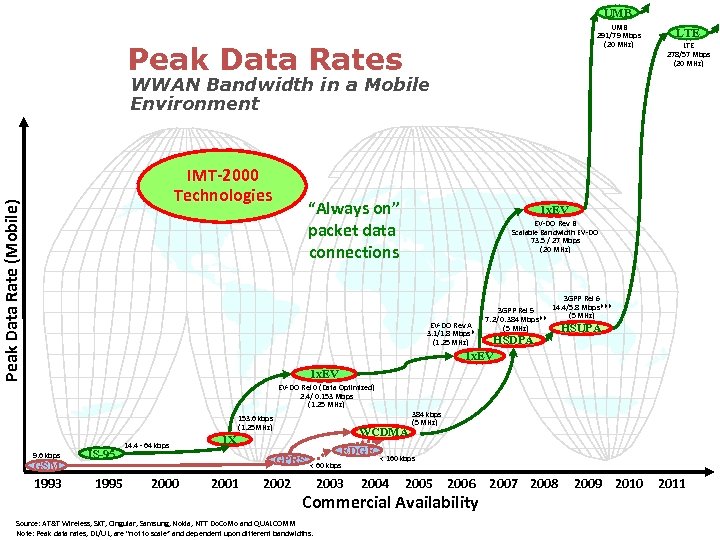
UMB 291/79 Mbps (20 MHz) Peak Data Rates LTE 278/57 Mbps (20 MHz) WWAN Bandwidth in a Mobile Environment Peak Data Rate (Mobile) IMT-2000 Technologies “Always on” packet data connections 1 x. EV EV-DO Rev B Scalable Bandwidth EV-DO 73. 5 / 27 Mbps (20 MHz) EV-DO Rev A 3. 1/1. 8 Mbps* (1. 25 MHz) 3 GPP Rel 6 14. 4/5. 8 Mbps*** 3 GPP Rel 5 (5 MHz) 7. 2/ 0. 384 Mbps** (5 MHz) HSUPA HSDPA 1 x. EV EV-DO Rel 0 (Data Optimized) 2. 4/ 0. 153 Mbps (1. 25 MHz) 153. 6 kbps (1. 25 MHz) 9. 6 kbps GSM 1993 IS-95 1995 14. 4 - 64 kbps WCDMA 1 X GPRS 2000 2001 2002 EDGE < 60 kbps 2003 384 kbps (5 MHz) < 160 kbps 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Commercial Availability Source: AT&T Wireless, SKT, Cingular, Samsung, Nokia, NTT Do. Co. Mo and QUALCOMM Note: Peak data rates, DL/UL, are “not to scale” and dependent upon different bandwidths. 2009 2010 2011 * Based on QUALCOMM’s chipset (MSM 6800) ** Based on QUALCOMM’s 2 nd HSDPA chipset (MSM 6280)
Wireless Technology Evolution to 3 G Forth Generation (4 G) Wireless (beyond 3 G) © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 54
Forth Generation (4 G) Wireless (beyond 3 G) ¦ 4 G vision is centered on globally integrated communication network interconnecting in a transparent way l A multitude of heterogeneous networks and systems ¦Entirely IP base ¦ 4 G slogan - “Any Service at Any Time” ¦A flexible re-configurable network that enables simultaneous optimization of bandwidth, and Qo. S m Future Wireless Networks l Ubiquitous Communication Among People and Devices © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 55
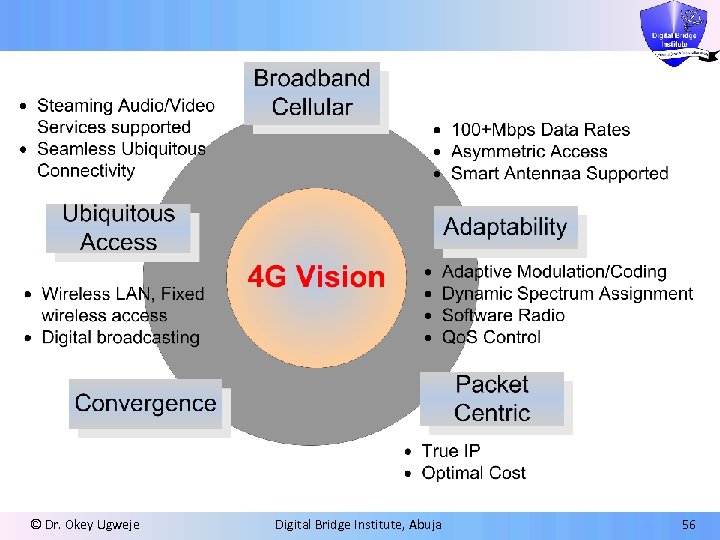
© Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 56
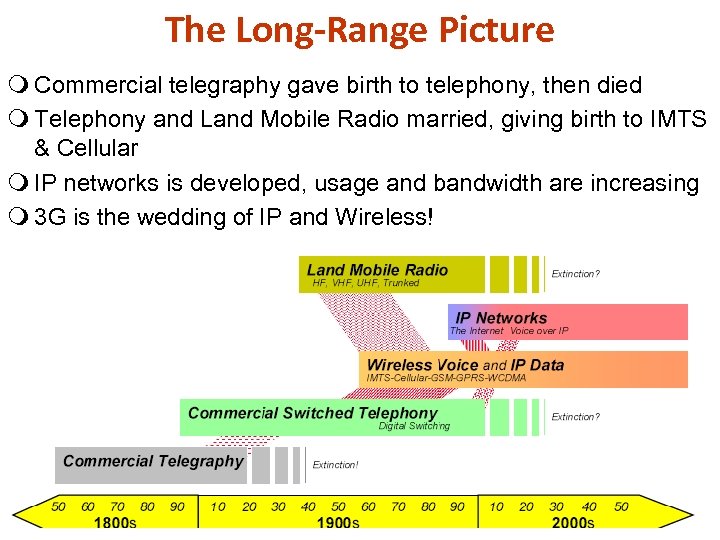
The Long-Range Picture m Commercial telegraphy gave birth to telephony, then died m Telephony and Land Mobile Radio married, giving birth to IMTS & Cellular m IP networks is developed, usage and bandwidth are increasing m 3 G is the wedding of IP and Wireless!
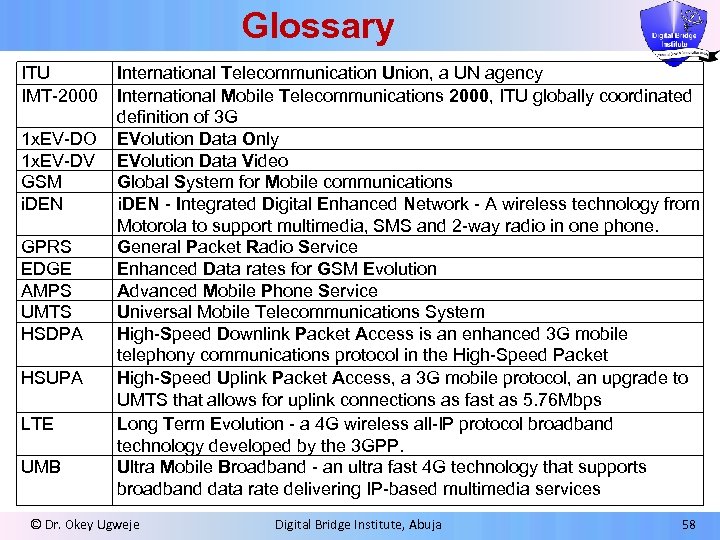
Glossary ITU IMT-2000 1 x. EV-DO 1 x. EV-DV GSM i. DEN GPRS EDGE AMPS UMTS HSDPA HSUPA LTE UMB International Telecommunication Union, a UN agency International Mobile Telecommunications 2000, ITU globally coordinated definition of 3 G EVolution Data Only EVolution Data Video Global System for Mobile communications i. DEN - Integrated Digital Enhanced Network - A wireless technology from Motorola to support multimedia, SMS and 2 -way radio in one phone. General Packet Radio Service Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution Advanced Mobile Phone Service Universal Mobile Telecommunications System High-Speed Downlink Packet Access is an enhanced 3 G mobile telephony communications protocol in the High-Speed Packet High-Speed Uplink Packet Access, a 3 G mobile protocol, an upgrade to UMTS that allows for uplink connections as fast as 5. 76 Mbps Long Term Evolution - a 4 G wireless all-IP protocol broadband technology developed by the 3 GPP. Ultra Mobile Broadband - an ultra fast 4 G technology that supports broadband data rate delivering IP-based multimedia services © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 58

Conclusion ¦ 3 G is a new technology but has vast unexploited market and revenue base ¦ 3 G - Anywhere Anytime Connectivity? ¦Still many Challenges to 3 G implementation ¦Coming 4 G and beyond…. . ¦Its not the end, Way ahead… m Future Wireless Networks l Ubiquitous Communication Among People and Devices © Dr. Okey Ugweje Digital Bridge Institute, Abuja 59

Dr. Okey Ugweje okeyusa@gmail. com '09 -290 -4968 '0806 -974 -3551
24e095e5243f42b0be8046aa4b118278.ppt