4705a7f6b473f2c07df4ada7041859f4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Wireless Security by: Frank Pfleger

Overview Introduction to Wireless Networks Secure the Network ◦ Wireless Security Mechanisms Unsecure the Network ◦ Security Mechanism Weaknesses ◦ Tools and Techniques Wardriving / Procedures
Introduction Private Wi-Fi ◦ Easy installation security problems ◦ Location freedom Office Wi-Fi ◦ Location freedom ◦ Laptop popularity Public Hotspot ◦ Non-private ( mostly with fee ) ◦ Public places Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Secure the Network Non Encryption ◦ Static IP addresses E R U Deactivate DHCP Assign IP address on every host ◦ MAC address filter S N C E Restrict access to unique hardware address Add MAC address for every host ◦ Hide SSID I Deactivate the SSID broadcasting Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Secure the Network Encryption ◦ WEP – Wired Equivalent Privacy Based on RC 4 (pseudo-random generator) XOR between data and random (bitstream) RC 4 uses WEP key + Initialization vector INSECURE ◦ WPA – Wi-Fi Protected Access Based on the WEP architecture ( RC 4 ) TKIP – Temporal Key Integrity Protocol RC 4 uses WPA key (PSK or EAP) + Initialization vector + Per packet key mixing + Re Keying + Message Integrity Check SECURE Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Secure the Network Encryption ◦ WPA 2 – Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 Implements IEEE 802. 11 a, b, g and basic/mandatory functions of IEEE 802. 11 i New architecture based on AES – Advanced Encryption Standard Symmetric crypto system Complies with the requirements of FIPS 140 -2 Choose strong password / passphrase (63 characters) SECURE Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Secure the Network RADIUS ◦ Remote Authentification Dial-In Server ◦ Client – Server system ◦ AAA protocol Authentification ( who ) Authorization ( what ) Accounting ( track consumption ) VPN – Virtual Private Network ◦ Tunnel ◦ Authentification ◦ Secure Encryption ( Public Key / RSA ) Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Unsecure the Network Weaknesses ◦ Serveral techniques to compromise Sniffing a IP address ◦ Deactivated DHCP ◦ IP address transmitted in every packet Spoofing a MAC address ◦ MAC address filter ◦ MAC address transmitted in every frame Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Unsecure the Network Hacking WEP ◦ ◦ Introduced in 1999 Serious weaknesses identified in 2001 IV – Initialization Vector used for decryption ICV – Integrity Check Value CRC 32 checksum CRC 32 is strict linear ◦ Calculation of the Key Attack based on security flaw in CRC 32 500 000 – 1 000 IV‘s for 128 bit encryption Techniques: Packet Reinjection / Deauthenticate Client TU Darmstadt ( PTW ) 50 000 IV‘s for 128 bit (50%) Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion

Unsecure the Network WPA / WPA 2 ◦ Currently no weakness or security flaw ◦ Weak Passwords Choose a strong password At least 12 characters Mixed letters, numbers and symbols ◦ Dictionary Attack ◦ Brute-Force Attack Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Unsecure the Network Tools and Techniques ◦ MAC address spoofing Linux macchanger –s wlan 0 Windows supported by some Wi-Fi cards SMAC or other tools ◦ ARP spoofing Spoof the wrong MAC – IP combination Windows Win. Arp. Spoofer Linux arpspoof –t 10. 0. 0. 1 ( all packets to your host) Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Unsecure the Network Tools and Techniques ◦ Man-in-the-Middle ( MITM ) Use ARP spoofing to get packets Analyze packets Forward packets to victim Linux: fragroute/fragrouter sslsniff ( https MITM ) ◦ DNS Spoofing Spoof the wrong Hostname – IP combination Linux: dnsspoof Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Unsecure the Network Tools and Techniques ◦ Sniffing data Used for MITM or passive listening Capture and analyze data Linux / Windows: Wireshark ( Ethereal ) ◦ Aircrack Toolkit Cracking a WEP encryption Airodump Logging / Scanning IV‘s Aireplay Re-inject packets Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
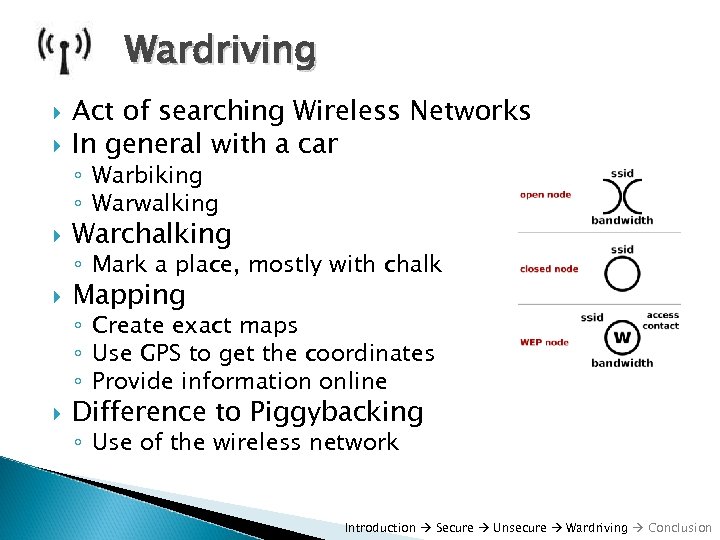
Wardriving Act of searching Wireless Networks In general with a car ◦ Warbiking ◦ Warwalking Warchalking ◦ Mark a place, mostly with chalk Mapping ◦ Create exact maps ◦ Use GPS to get the coordinates ◦ Provide information online Difference to Piggybacking ◦ Use of the wireless network Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion

Wardriving Equipment ◦ Good equipment for effective Wardriving ◦ Notebook with Tools ◦ Wireless Network Card Regular Card Special Card with an external antenna interface ◦ Antenna Directional Onmidirectional Parabolic (not for Wardriving) ◦ GPS receiver Logging / Mapping Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion

Wardriving Tools ◦ Operating System Windows ( just for Mapping and Logging ) Linux (Special Distributions) All tools and drivers preinstalled Run from CD Eg. Backtrack ( Auditor ) ◦ Scanning and Mapping Windows Netstumbler Linux Kismet Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Procedures Wardriving ◦ Scan for wireless networks ( Netstumbler / Kismet ) ◦ Save the GPS position Piggybacking ◦ Connect to the wireless network ◦ Use the network Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion

Hacking WEP Using Backtrack ( Auditor ) Hidden SSID ◦ aircrack to deauthenticate ( force reconnect ) ◦ Scan with airodump for the SSID Scan and log IV‘s ◦ airodump to log ◦ Filters, Stores and analyzes packets for IV‘s Reinject packets ◦ aireplay reinjects found IV‘s ◦ Increases the retransmitted IV‘s Crack the Key ◦ aircrack to calculate the WEP key ◦ Enough IV‘s needed Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion

Compromise the Network MAC filter ◦ Scan packets with Wireshark ( Ethereal ) ◦ Spoof a MAC address with macchanger DHCP deactivated ◦ Scan packets with Wireshark ( Ethereal ) ◦ Set your IP address Man-in-the-Middle ◦ ◦ Spoof your MAC with the gateways IP Spoof your MAC with the victims IP Reroute packets Using arpspoof and fragroute Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
Compromise the Network Spoof DNS Entry ◦ Spoof your IP address for different hostnames ◦ Eg. hostname of the victims bank Intercept SSL connections ◦ ◦ SSL MITM attack Fake SSL certificate Sniff data transmitted via SSL Using sslsniff Sniff Data ◦ Log and analyze all transmitted data ◦ Using Wireshark ( Ethereal ) Get access to Computers ◦ Using various Windows / Linux tools Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion

Conclusion Secure your wireless network properly! Don‘t rely on ◦ ◦ Hidden SSID MAC filter Deactivated DHCP WEP Use a proper encryption ◦ WPA / WPA 2 ( choose a strong password ) ◦ VPN ( secure with multi user ) Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion

Wireless Security Thanks for your attention. Any Question? Frank Pfleger mail@frankpfleger. com Introduction Secure Unsecure Wardriving Conclusion
4705a7f6b473f2c07df4ada7041859f4.ppt