ab2c504f1dee2918286dc5e354c16fd1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Chapter 15
Wireless Personal Area Networks Chapter 15
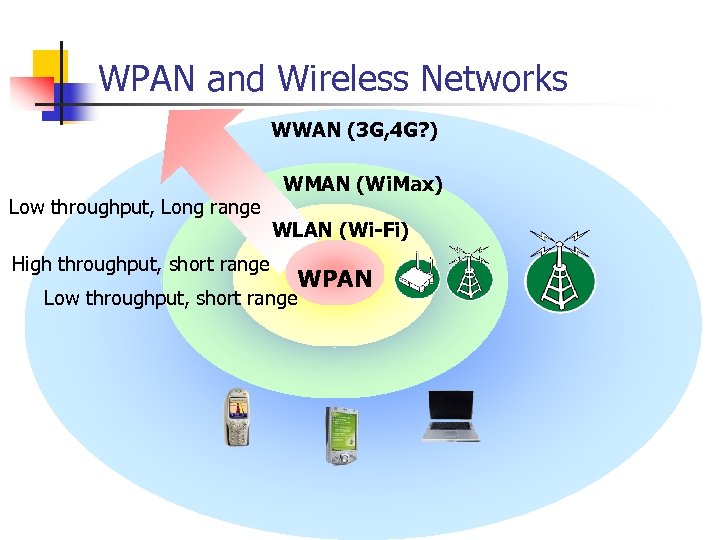 WPAN and Wireless Networks WWAN (3 G, 4 G? ) Low throughput, Long range High throughput, short range WMAN (Wi. Max) WLAN (Wi-Fi) WPAN Low throughput, short range
WPAN and Wireless Networks WWAN (3 G, 4 G? ) Low throughput, Long range High throughput, short range WMAN (Wi. Max) WLAN (Wi-Fi) WPAN Low throughput, short range
 Wireless Personal Area Networks A WPAN (wireless personal area network) is a personal area network - a network for interconnecting devices centered around an individual person's workspace - in which the connections are wireless. WPAN uses some technology that permits communications in a very short range (10 – 100 m). Topics discussed in this section: Used Technologies IEEE 802. 15 Standards
Wireless Personal Area Networks A WPAN (wireless personal area network) is a personal area network - a network for interconnecting devices centered around an individual person's workspace - in which the connections are wireless. WPAN uses some technology that permits communications in a very short range (10 – 100 m). Topics discussed in this section: Used Technologies IEEE 802. 15 Standards
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Unlicensed Spectrum for Wireless Networks ISM – Industrial, Scientific and Medical band) • The only ISM band guaranteed to be available in every country is the one at 2. 4 GHz (2. 4– 2. 483 GHz). • Free for anyone to use for almost any purpose. • Employed by most wireless technologies, many cordless phones and Bluetooth.
Wireless Personal Area Networks Unlicensed Spectrum for Wireless Networks ISM – Industrial, Scientific and Medical band) • The only ISM band guaranteed to be available in every country is the one at 2. 4 GHz (2. 4– 2. 483 GHz). • Free for anyone to use for almost any purpose. • Employed by most wireless technologies, many cordless phones and Bluetooth.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks WPAN Technologies 1. Bluetooth 2. Ir. DA (Infrared) 3. Zigbee 4. UWB (Ultra Wideband ) 5. RFID 6. NFC
Wireless Personal Area Networks WPAN Technologies 1. Bluetooth 2. Ir. DA (Infrared) 3. Zigbee 4. UWB (Ultra Wideband ) 5. RFID 6. NFC
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth History 1998 – Its primary purpose is to be a wire replacement technology in order to transfer voice and data. 1999 – Bluetooth 1. 0 specification is introduced. 2003 – Bluetooth 1. 2 Core Specification 2004 – Bluetooth 2. 0 Core Specification + EDR (Enhanced Data Rate). 2009 – Bluetooth 3. 0 Core Specification + HS (High Speed).
Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth History 1998 – Its primary purpose is to be a wire replacement technology in order to transfer voice and data. 1999 – Bluetooth 1. 0 specification is introduced. 2003 – Bluetooth 1. 2 Core Specification 2004 – Bluetooth 2. 0 Core Specification + EDR (Enhanced Data Rate). 2009 – Bluetooth 3. 0 Core Specification + HS (High Speed).
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Technology BT is a short-range wireless radio technology that allows electronic devices to connect to one another. BT ranges: 10 m, or 100 m. Its popularity increases as consumers always look for BT to be included in all products they buy.
Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Technology BT is a short-range wireless radio technology that allows electronic devices to connect to one another. BT ranges: 10 m, or 100 m. Its popularity increases as consumers always look for BT to be included in all products they buy.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Specifications 1. Bluetooth devices in a piconet share a common communication channel, its capacity 1 Mbps (3 Mbps or more in newer versions). 2. The frequency range is 2. 4 GHz to 2. 483 GHz. 3. A piconet has a master and up to seven slaves.
Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Specifications 1. Bluetooth devices in a piconet share a common communication channel, its capacity 1 Mbps (3 Mbps or more in newer versions). 2. The frequency range is 2. 4 GHz to 2. 483 GHz. 3. A piconet has a master and up to seven slaves.
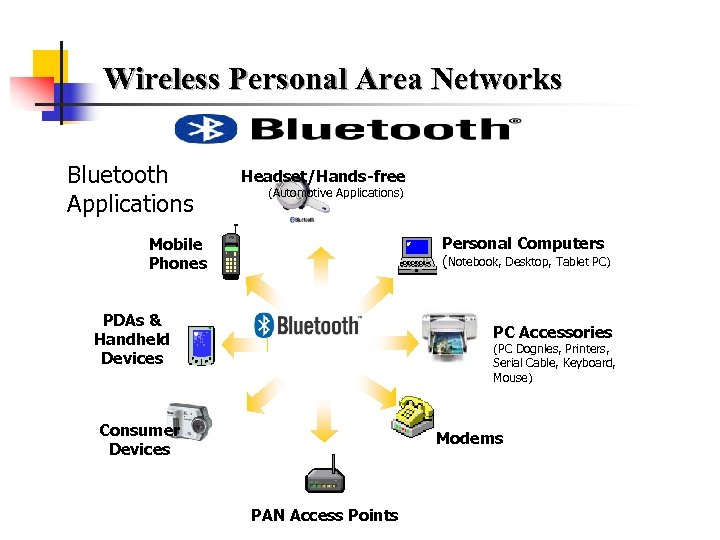 Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Applications Headset/Hands-free (Automotive Applications) Personal Computers Mobile Phones (Notebook, Desktop, Tablet PC) PDAs & Handheld Devices PC Accessories (PC Dognles, Printers, Serial Cable, Keyboard, Mouse) Consumer Devices Modems PAN Access Points
Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Applications Headset/Hands-free (Automotive Applications) Personal Computers Mobile Phones (Notebook, Desktop, Tablet PC) PDAs & Handheld Devices PC Accessories (PC Dognles, Printers, Serial Cable, Keyboard, Mouse) Consumer Devices Modems PAN Access Points
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Applications n Keyboard, file transfer, handsfree (and headset), etc…
Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Applications n Keyboard, file transfer, handsfree (and headset), etc…
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Applications Activity Temperature Blood analysis EMG Coagulation Oxygen saturation Blood pressure Glucose Peak flow Heartbeats ECG Body weight
Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Applications Activity Temperature Blood analysis EMG Coagulation Oxygen saturation Blood pressure Glucose Peak flow Heartbeats ECG Body weight
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Advantages 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Bluetooth devices are wireless. BT is inexpensive. Bluetooth is Automatic. Standardized Protocol = Interoperability Low Interferences. Low energy Consumption. Share voice and data.
Wireless Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Advantages 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Bluetooth devices are wireless. BT is inexpensive. Bluetooth is Automatic. Standardized Protocol = Interoperability Low Interferences. Low energy Consumption. Share voice and data.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Infrared communication is achieved using transmitters/Receivers (transceivers) that modulate noncoherent infrared light. Transceivers must be within the line of sight of each other either directly or via reflection. Infrared does not penetrate walls (+ advantages security, and no interference problems). No license required thus no frequency allocation issue.
Wireless Personal Area Networks Infrared communication is achieved using transmitters/Receivers (transceivers) that modulate noncoherent infrared light. Transceivers must be within the line of sight of each other either directly or via reflection. Infrared does not penetrate walls (+ advantages security, and no interference problems). No license required thus no frequency allocation issue.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Infrared Transmission Techniques Three transmission techniques: 1 – Directed Beam Infrared (point-to-point link). 2 – Ominidirectional (single base station that is within line of sight of all other stations (typically, this station is mounted on the ceiling). The base station acts as a multiport repeater. 3 – Diffused (all of the IR transmitters are focused and aimed at a point on a diffusely reflecting ceiling. IR radiation striking the ceiling is reradiated ominidirectional and picked up by all of the receivers in the area.
Wireless Personal Area Networks Infrared Transmission Techniques Three transmission techniques: 1 – Directed Beam Infrared (point-to-point link). 2 – Ominidirectional (single base station that is within line of sight of all other stations (typically, this station is mounted on the ceiling). The base station acts as a multiport repeater. 3 – Diffused (all of the IR transmitters are focused and aimed at a point on a diffusely reflecting ceiling. IR radiation striking the ceiling is reradiated ominidirectional and picked up by all of the receivers in the area.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Infrared Waves Infrared waves: with frequencies from 300 GHz to 400 THz (wavelengths from 1 mm to 770 nm). We cannot use infrared outside a building because the sun’s rays contain infrared waves that can interfere with the communication.
Wireless Personal Area Networks Infrared Waves Infrared waves: with frequencies from 300 GHz to 400 THz (wavelengths from 1 mm to 770 nm). We cannot use infrared outside a building because the sun’s rays contain infrared waves that can interfere with the communication.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Infrared Applications - The Infrared band, almost 400 THz. It can be used to transmit digital data with a very high data rate. - The Infrared Data Association (Ir. DA) sponsors the use of infrared waves by setting standard for using these signals for communication between devices such as keyboards, mice, PCs, and printers. - Ir. DA port may be present in a device - The standard originally defines a data rate of 75 Kbps for a distance up to 8 m. The recent standard defines a data rate of 4 Mbps. - Ir. DA transmit through line of sight.
Wireless Personal Area Networks Infrared Applications - The Infrared band, almost 400 THz. It can be used to transmit digital data with a very high data rate. - The Infrared Data Association (Ir. DA) sponsors the use of infrared waves by setting standard for using these signals for communication between devices such as keyboards, mice, PCs, and printers. - Ir. DA port may be present in a device - The standard originally defines a data rate of 75 Kbps for a distance up to 8 m. The recent standard defines a data rate of 4 Mbps. - Ir. DA transmit through line of sight.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Zig. Bee Technology Zig. Bee is a standard for embedded application software that has been approved in late 2004 under 802. 15. 4 wireless networking standards. Zig. Bee IEEE 802. 15. 4 is an established set of specifications for wireless personal area networking (WPAN). Zig. Bee addresses remote monitoring and controlling applications. Reference: http: //www. tutorial-reports. com/wireless/zigbee/tutorial. php
Wireless Personal Area Networks Zig. Bee Technology Zig. Bee is a standard for embedded application software that has been approved in late 2004 under 802. 15. 4 wireless networking standards. Zig. Bee IEEE 802. 15. 4 is an established set of specifications for wireless personal area networking (WPAN). Zig. Bee addresses remote monitoring and controlling applications. Reference: http: //www. tutorial-reports. com/wireless/zigbee/tutorial. php
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Zig. Bee Features 1 – Low power consumption (ranging from months up to years on standard batteries ). 2 - Maximum data rate 250 Kbps @ 2. 4 GHz, 40 Kbps @ 915 MHz, and 20 Kbps @ 868 MHz. 3 – Needed for only two major modes (Tx/Rx or Sleep). 4 – High density of nodes per network. 5 – Low cost. 6 – Simplementation. 7 – high reliability and Adequate security. 8 – Acceptable Latency (10 ms for PC, 100 ms for
Wireless Personal Area Networks Zig. Bee Features 1 – Low power consumption (ranging from months up to years on standard batteries ). 2 - Maximum data rate 250 Kbps @ 2. 4 GHz, 40 Kbps @ 915 MHz, and 20 Kbps @ 868 MHz. 3 – Needed for only two major modes (Tx/Rx or Sleep). 4 – High density of nodes per network. 5 – Low cost. 6 – Simplementation. 7 – high reliability and Adequate security. 8 – Acceptable Latency (10 ms for PC, 100 ms for
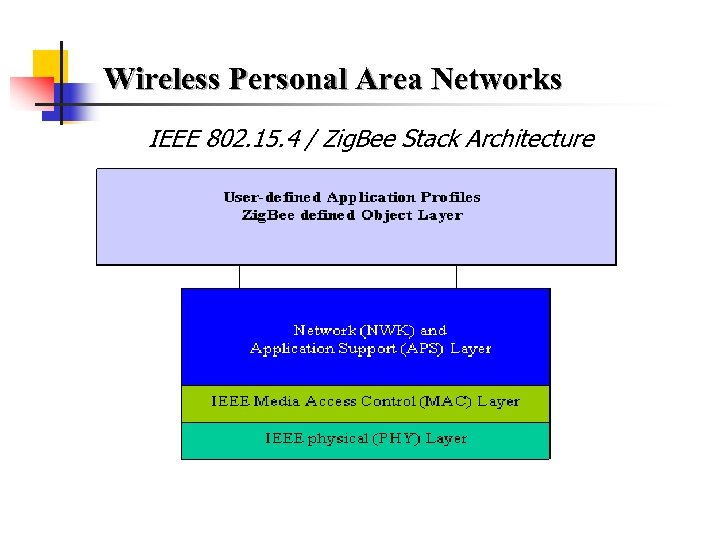 Wireless Personal Area Networks IEEE 802. 15. 4 / Zig. Bee Stack Architecture
Wireless Personal Area Networks IEEE 802. 15. 4 / Zig. Bee Stack Architecture
 Wireless Personal Area Networks 1 - Network and Application Support layer - APS sub-layer responsible for maintaining tables that enable matching between two devices and communication among them, discovery, identify other devices that operate in the operating space of any device. - Zig. Bee define object is responsible of determining the nature of the device (Coordinator / FFD or RFD) in the network, commencing and replying to binding requests and ensuring a secure relationship between devices. - The user-defined application refers to the end device that conforms to the Zig. Bee Standard.
Wireless Personal Area Networks 1 - Network and Application Support layer - APS sub-layer responsible for maintaining tables that enable matching between two devices and communication among them, discovery, identify other devices that operate in the operating space of any device. - Zig. Bee define object is responsible of determining the nature of the device (Coordinator / FFD or RFD) in the network, commencing and replying to binding requests and ensuring a secure relationship between devices. - The user-defined application refers to the end device that conforms to the Zig. Bee Standard.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks 2 - Media access control (MAC) layer - permits use of several topologies without introducing complexity and is meant to work with large numbers of devices. 3 – Physical (PHY) layer - accommodates high levels of integration - enable cheaper implementations
Wireless Personal Area Networks 2 - Media access control (MAC) layer - permits use of several topologies without introducing complexity and is meant to work with large numbers of devices. 3 – Physical (PHY) layer - accommodates high levels of integration - enable cheaper implementations
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Zig. Bee Devices 1 – Zig. Bee Coordinator node (only one, act as a router to other networks, it is designed to store information about the network). 2 – The Full Function Device (intermediary router transmitting data from other devices). 3 – The Reduced Function Device (it is just capable to talk in the network).
Wireless Personal Area Networks Zig. Bee Devices 1 – Zig. Bee Coordinator node (only one, act as a router to other networks, it is designed to store information about the network). 2 – The Full Function Device (intermediary router transmitting data from other devices). 3 – The Reduced Function Device (it is just capable to talk in the network).
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Zig. Bee Applications 1. Embedded in consumer electronics. 2. Home and building automation and security systems. 3. Industrial controls. 4. PC peripherals. 5. Medical and industrial sensor applications. 6. Toys and games and similar applications.
Wireless Personal Area Networks Zig. Bee Applications 1. Embedded in consumer electronics. 2. Home and building automation and security systems. 3. Industrial controls. 4. PC peripherals. 5. Medical and industrial sensor applications. 6. Toys and games and similar applications.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Comparison of Bluetooth and Zig. Bee Bluetooth Zig. Bee Transmission Scheme FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) DHSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum) Modulation GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying) QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) or BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) Frequency Band 2. 4 GHz, 915 MHz, 868 MHz Raw Data Bit Rate 1 Mbps 250 Kbps, 40 Kbps, or 20 Kbps (depends on frequency band) Power Output Maximum 100 m. W, 2. 5 m. W, or 1 m. W, depending on class Maximum capability 0. 5 m. W; maximum as allowed by local regulations Network Topology Master-Slave 8 active nodes Star or Peer-Peer 255 active nodes
Wireless Personal Area Networks Comparison of Bluetooth and Zig. Bee Bluetooth Zig. Bee Transmission Scheme FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) DHSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum) Modulation GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying) QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) or BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying) Frequency Band 2. 4 GHz, 915 MHz, 868 MHz Raw Data Bit Rate 1 Mbps 250 Kbps, 40 Kbps, or 20 Kbps (depends on frequency band) Power Output Maximum 100 m. W, 2. 5 m. W, or 1 m. W, depending on class Maximum capability 0. 5 m. W; maximum as allowed by local regulations Network Topology Master-Slave 8 active nodes Star or Peer-Peer 255 active nodes
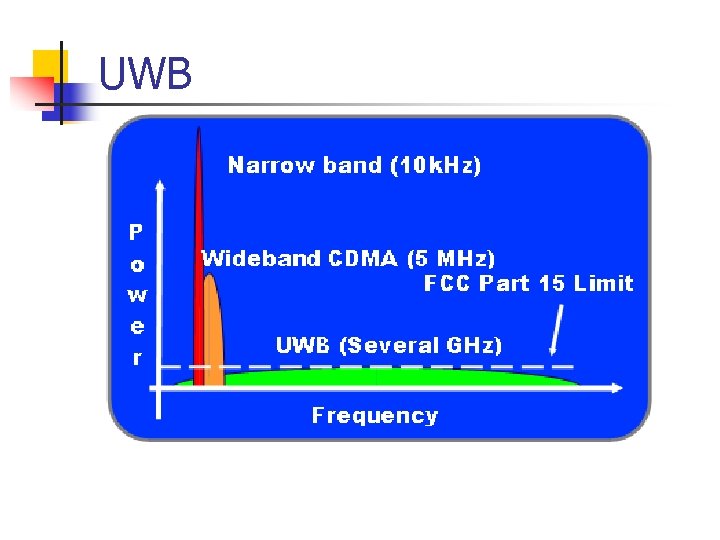
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Ultra wideband Specifications Ultra Wideband enables movement of massive files at high data rates over short distance. • High Data Rate (200 Mbps within 10 m). • Extremely low transmission energy ( less than 1 m. W). • Low cost. • Extremely difficult to intercept
Wireless Personal Area Networks Ultra wideband Specifications Ultra Wideband enables movement of massive files at high data rates over short distance. • High Data Rate (200 Mbps within 10 m). • Extremely low transmission energy ( less than 1 m. W). • Low cost. • Extremely difficult to intercept
 UWB
UWB
 UWB Applications
UWB Applications
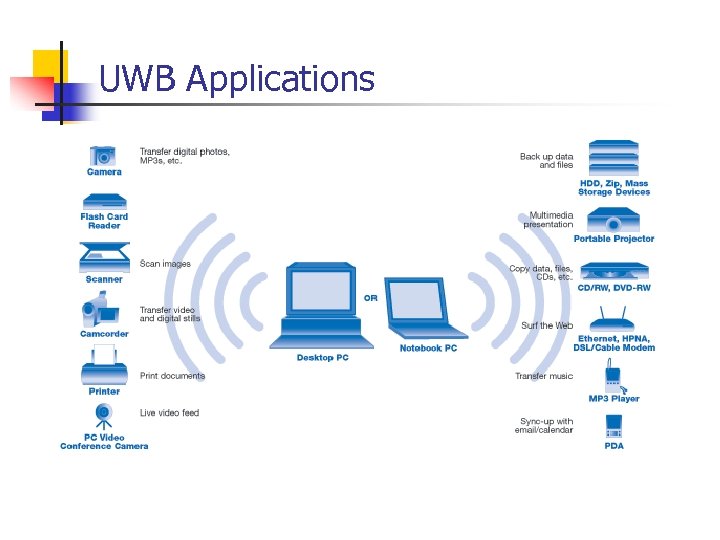
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Ultra wideband Applications 1. Short-distance applications (PC Peripherals). 2. short-range indoor application 3. applications with high data rate requirement (Wireless Monitors, Camcorders & Wireless Printing).
Wireless Personal Area Networks Ultra wideband Applications 1. Short-distance applications (PC Peripherals). 2. short-range indoor application 3. applications with high data rate requirement (Wireless Monitors, Camcorders & Wireless Printing).
 Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology RFID – Radio Frequency Identification - The concept is that a query is sent out over a radio wave and a subsequent reply is received. - Its used in supply chain management (just-in-time inventory, reducing theft and fraud, and improving the type and quantity of product marketing information). - its also used in tracking systems. - It was invented in 1948 and in commercial applications since 1980.
Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology RFID – Radio Frequency Identification - The concept is that a query is sent out over a radio wave and a subsequent reply is received. - Its used in supply chain management (just-in-time inventory, reducing theft and fraud, and improving the type and quantity of product marketing information). - its also used in tracking systems. - It was invented in 1948 and in commercial applications since 1980.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology RFID components: - Tag (Passive tag, Active tag). - Reader with antenna (Fixed or mobile) - Communications protocol suite. - Communications network - Database. Reference: http: //www. dataflows. com/RFID_Overview. shtml
Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology RFID components: - Tag (Passive tag, Active tag). - Reader with antenna (Fixed or mobile) - Communications protocol suite. - Communications network - Database. Reference: http: //www. dataflows. com/RFID_Overview. shtml
 Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology Tag (Passive tag, Active tag): - Tags can be either Class o (Read only) or Class 1 (Read/Write). - Reader (or the active tag) initiates the communication via a radio signal to enable the tag to answer with a return radio signal carrying information regarding the item. - Electronic Product Code (EPC) is used to uniquely identified an item. - In the future there will be more information tracked via EPC by using EPC Information Services (EPCIS).
Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology Tag (Passive tag, Active tag): - Tags can be either Class o (Read only) or Class 1 (Read/Write). - Reader (or the active tag) initiates the communication via a radio signal to enable the tag to answer with a return radio signal carrying information regarding the item. - Electronic Product Code (EPC) is used to uniquely identified an item. - In the future there will be more information tracked via EPC by using EPC Information Services (EPCIS).
 Wireless Personal Area Networks Example of transmitted information: Current: - This is where I originated: “manufacturing source” - This is what I am “a specific pallet carrying boxes of paper towels” or - This is what I am “a specific box of paper towels” Future: - This is my rout tracking: “my mode of transportation, my origination point, my arrival and departure time and location of every stop along the way, and the time I arrived at this final destination point” - This is my purchase and restocking information: “I was purchased by so and so, on this date and at this price, and now I have left the building – please restock this item”
Wireless Personal Area Networks Example of transmitted information: Current: - This is where I originated: “manufacturing source” - This is what I am “a specific pallet carrying boxes of paper towels” or - This is what I am “a specific box of paper towels” Future: - This is my rout tracking: “my mode of transportation, my origination point, my arrival and departure time and location of every stop along the way, and the time I arrived at this final destination point” - This is my purchase and restocking information: “I was purchased by so and so, on this date and at this price, and now I have left the building – please restock this item”
 Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology Reader with antenna: - Reader has a distance range to query tag’s information. - Readers vary in their capabilities such as how many tags a reader can capture within a specific time period, filtering and communicating with a product database. - Number of readers and their placement in the physical facility is a challenge.
Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology Reader with antenna: - Reader has a distance range to query tag’s information. - Readers vary in their capabilities such as how many tags a reader can capture within a specific time period, filtering and communicating with a product database. - Number of readers and their placement in the physical facility is a challenge.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology Communications protocol suite : - Physical Layer (describes the specific radio frequencies and whether tags and reader are communicating in half or full duplex mode). - On data-link layer Slotted Aloha scheme is used. - Application Level Events (ALE) standard defined to support collection of event data coming from readers. - Reader Protocol (RP) standard is defined to specify how readers capture and communicate event data from tags. - Communications between readers and in-house database are up to individual implementations.
Wireless Personal Area Networks RFID Technology Communications protocol suite : - Physical Layer (describes the specific radio frequencies and whether tags and reader are communicating in half or full duplex mode). - On data-link layer Slotted Aloha scheme is used. - Application Level Events (ALE) standard defined to support collection of event data coming from readers. - Reader Protocol (RP) standard is defined to specify how readers capture and communicate event data from tags. - Communications between readers and in-house database are up to individual implementations.
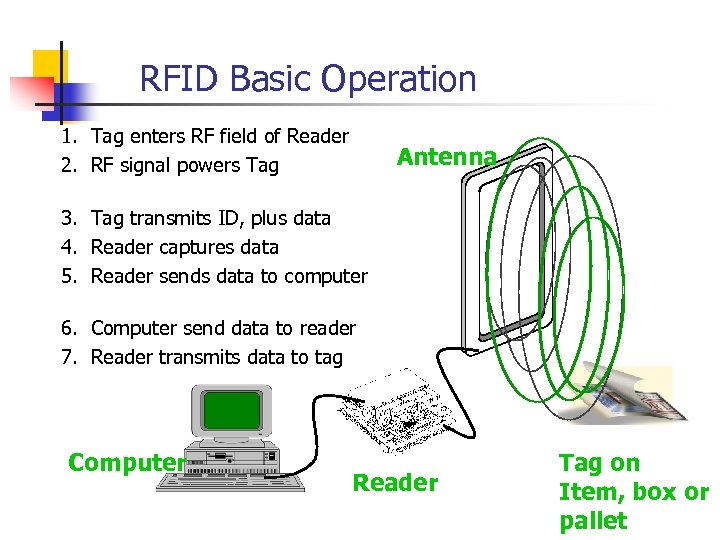 RFID Basic Operation 1. Tag enters RF field of Reader 2. RF signal powers Tag Antenna 3. Tag transmits ID, plus data 4. Reader captures data 5. Reader sends data to computer 6. Computer send data to reader 7. Reader transmits data to tag Computer Reader Tag on Item, box or pallet
RFID Basic Operation 1. Tag enters RF field of Reader 2. RF signal powers Tag Antenna 3. Tag transmits ID, plus data 4. Reader captures data 5. Reader sends data to computer 6. Computer send data to reader 7. Reader transmits data to tag Computer Reader Tag on Item, box or pallet
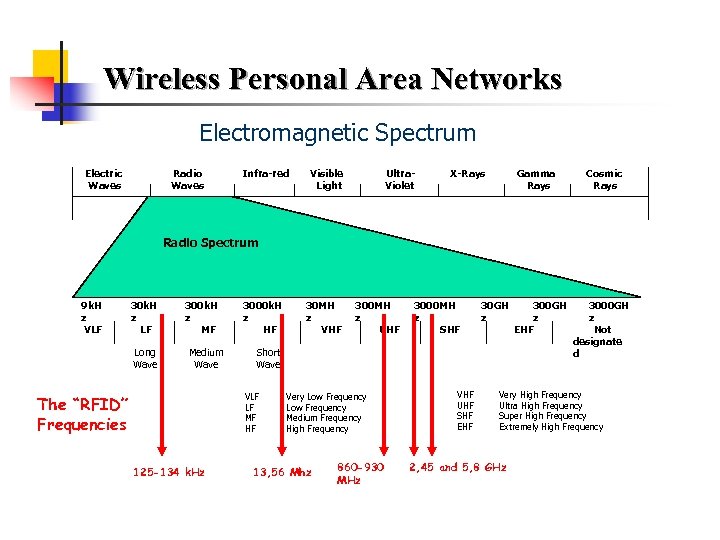 Wireless Personal Area Networks Electromagnetic Spectrum Electric Waves Radio Waves Infra-red Visible Light Ultra. Violet X-Rays Gamma Rays Cosmic Rays Radio Spectrum 9 k. H z VLF 30 k. H z LF Long Wave 300 k. H z MF Medium Wave 3000 k. H z HF 125 -134 k. Hz 300 MH z UHF 3000 MH z SHF 30 GH z Short Wave VLF LF MF HF The “RFID” Frequencies 30 MH z VHF Very Low Frequency Medium Frequency High Frequency 13, 56 Mhz 860 -930 MHz VHF UHF SHF EHF 300 GH z EHF 3000 GH z Not designate d Very High Frequency Ultra High Frequency Super High Frequency Extremely High Frequency 2, 45 and 5, 8 GHz
Wireless Personal Area Networks Electromagnetic Spectrum Electric Waves Radio Waves Infra-red Visible Light Ultra. Violet X-Rays Gamma Rays Cosmic Rays Radio Spectrum 9 k. H z VLF 30 k. H z LF Long Wave 300 k. H z MF Medium Wave 3000 k. H z HF 125 -134 k. Hz 300 MH z UHF 3000 MH z SHF 30 GH z Short Wave VLF LF MF HF The “RFID” Frequencies 30 MH z VHF Very Low Frequency Medium Frequency High Frequency 13, 56 Mhz 860 -930 MHz VHF UHF SHF EHF 300 GH z EHF 3000 GH z Not designate d Very High Frequency Ultra High Frequency Super High Frequency Extremely High Frequency 2, 45 and 5, 8 GHz
 Wireless Personal Area Networks NFC Technology NFC – Near Field Communications - NFC is a set of standards for smart-phones or whatever to establish communication with each other by bringing them into close together (0 -5 centimetres). - NFC operates at 13. 56 MHz - NFC rates ranging from 106 Kbps – 424 Kbps. - NFC involves an initiator and a target.
Wireless Personal Area Networks NFC Technology NFC – Near Field Communications - NFC is a set of standards for smart-phones or whatever to establish communication with each other by bringing them into close together (0 -5 centimetres). - NFC operates at 13. 56 MHz - NFC rates ranging from 106 Kbps – 424 Kbps. - NFC involves an initiator and a target.
 Wireless Personal Area Networks NFC Technology There are two NFC operational modes: 1 - Passive communication mode: The initiator device provides a carrier fields and the target device answers by modulating the existing field. 2 - Active communication mode: Both initiator and target device communicate by alternately generating their own fields.
Wireless Personal Area Networks NFC Technology There are two NFC operational modes: 1 - Passive communication mode: The initiator device provides a carrier fields and the target device answers by modulating the existing field. 2 - Active communication mode: Both initiator and target device communicate by alternately generating their own fields.
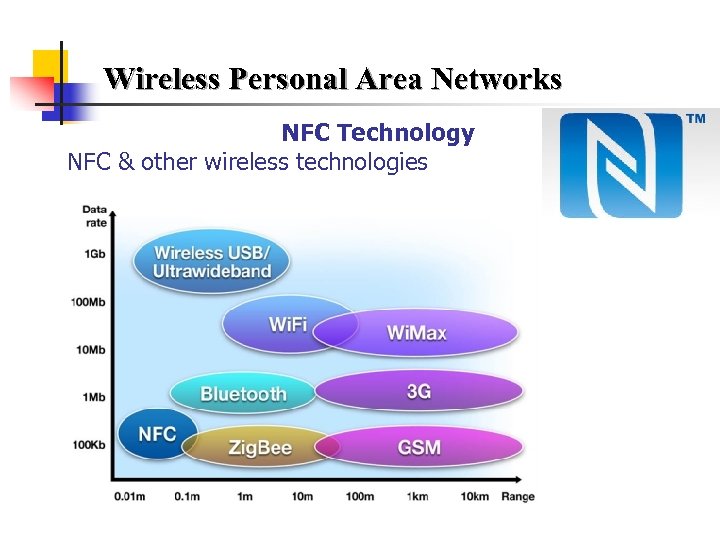 Wireless Personal Area Networks NFC Technology NFC & other wireless technologies
Wireless Personal Area Networks NFC Technology NFC & other wireless technologies
 Wireless Personal Area Networks NFC use examples: NFC Technology • Paying by mobile devices like cell phones • Credit card integration into a mobile device • Electronic ticketing for transport usage • Personal electronic document • Download of data from kiosks such as railway time table • Flight and hotel booking • Music and photos download from camera, cell phones, multimedia readers • Connections P 2 P (peer to peer) for an easy information transmission between wireless devices.
Wireless Personal Area Networks NFC use examples: NFC Technology • Paying by mobile devices like cell phones • Credit card integration into a mobile device • Electronic ticketing for transport usage • Personal electronic document • Download of data from kiosks such as railway time table • Flight and hotel booking • Music and photos download from camera, cell phones, multimedia readers • Connections P 2 P (peer to peer) for an easy information transmission between wireless devices.


