f85b6d19eea63cae00ed6ce647e35d83.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Wireless Networks l l 1 Cellular and line telephone systems are responsible for providing coverage throughout a particular territory, called a coverage region or market The interconnection of many such systems defines a wireless network over a country or continent
Wireless Networks l l 1 Cellular and line telephone systems are responsible for providing coverage throughout a particular territory, called a coverage region or market The interconnection of many such systems defines a wireless network over a country or continent
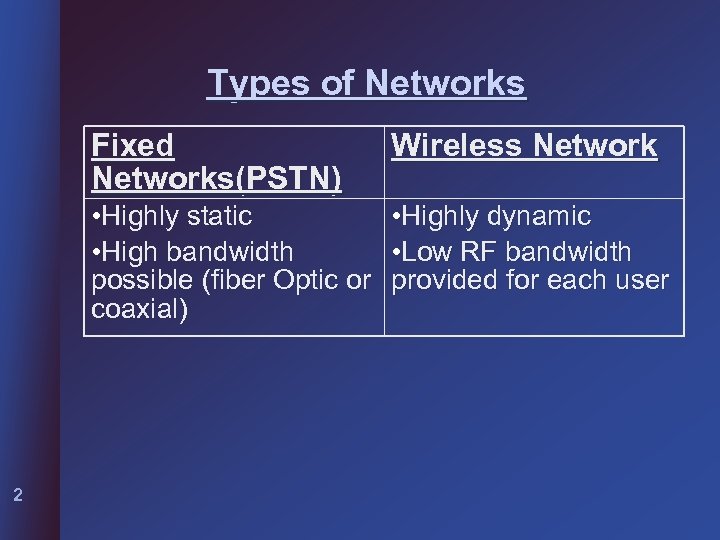 Types of Networks Fixed Networks(PSTN) Wireless Network • Highly static • Highly dynamic • High bandwidth • Low RF bandwidth possible (fiber Optic or provided for each user coaxial) 2
Types of Networks Fixed Networks(PSTN) Wireless Network • Highly static • Highly dynamic • High bandwidth • Low RF bandwidth possible (fiber Optic or provided for each user coaxial) 2
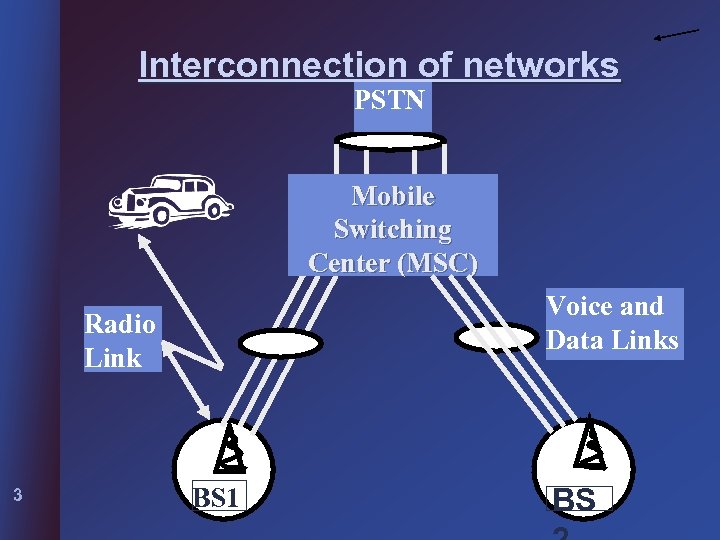 Interconnection of networks PSTN Mobile Switching Center (MSC) Voice and Data Links Radio Link 3 BS 1 BS
Interconnection of networks PSTN Mobile Switching Center (MSC) Voice and Data Links Radio Link 3 BS 1 BS
 Functions of PSTN l l l 4 l Highly integrated communications network that connects almost all of of world’s population Each country is responsible for the regulation of PSTN within it’s borders. Over time, government to private transition takes place. PSTN has a network of fixed telephone exchanges Over time, transition has occurred from manual to automatic exchanges
Functions of PSTN l l l 4 l Highly integrated communications network that connects almost all of of world’s population Each country is responsible for the regulation of PSTN within it’s borders. Over time, government to private transition takes place. PSTN has a network of fixed telephone exchanges Over time, transition has occurred from manual to automatic exchanges
 History of PSTN network l l l 5 Controlled by long distance companies like AT&T, Sprint etc. 1984 – Supreme Court issues Modified Final Judgement (MFJ) Break up of AT&T into 7 major Bell operating systems (BOCs) each with its own service region.
History of PSTN network l l l 5 Controlled by long distance companies like AT&T, Sprint etc. 1984 – Supreme Court issues Modified Final Judgement (MFJ) Break up of AT&T into 7 major Bell operating systems (BOCs) each with its own service region.
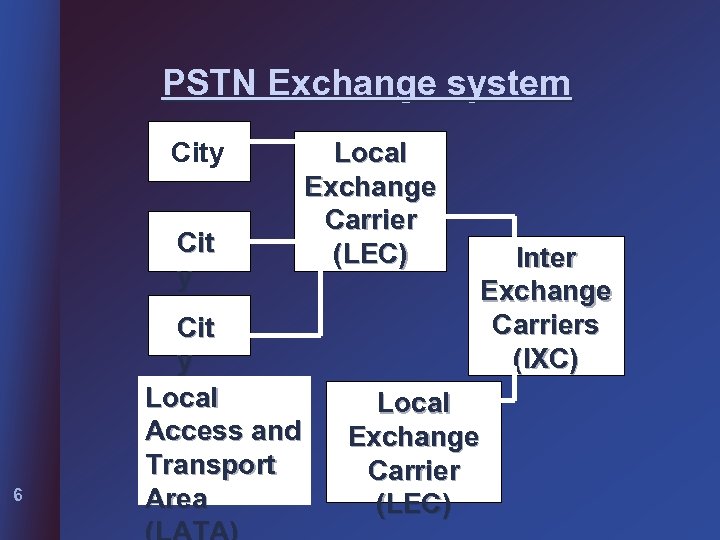 PSTN Exchange system City Cit y 6 Cit y Local Access and Transport Area Local Exchange Carrier (LEC) Inter Exchange Carriers (IXC) Local Exchange Carrier (LEC)
PSTN Exchange system City Cit y 6 Cit y Local Access and Transport Area Local Exchange Carrier (LEC) Inter Exchange Carriers (IXC) Local Exchange Carrier (LEC)
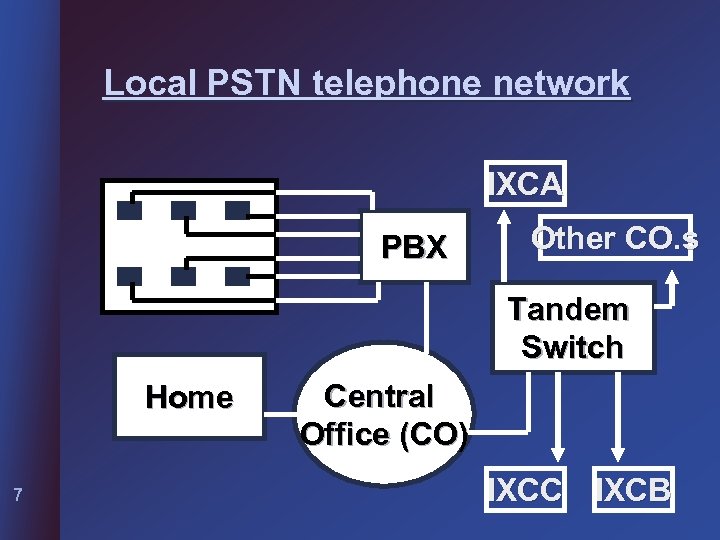 Local PSTN telephone network IXCA PBX Other CO. s Tandem Switch Home 7 Central Office (CO) IXCC IXCB
Local PSTN telephone network IXCA PBX Other CO. s Tandem Switch Home 7 Central Office (CO) IXCC IXCB
 Wireless Networks l l 8 Wireless Networks are extremely complex, unlike static local, fixed telephone networks. Wireless networks requires air interface between base stations and randomly spaced subscribers Complex propagation media MSC must eventually provide connection to PSTN and other MSCs
Wireless Networks l l 8 Wireless Networks are extremely complex, unlike static local, fixed telephone networks. Wireless networks requires air interface between base stations and randomly spaced subscribers Complex propagation media MSC must eventually provide connection to PSTN and other MSCs
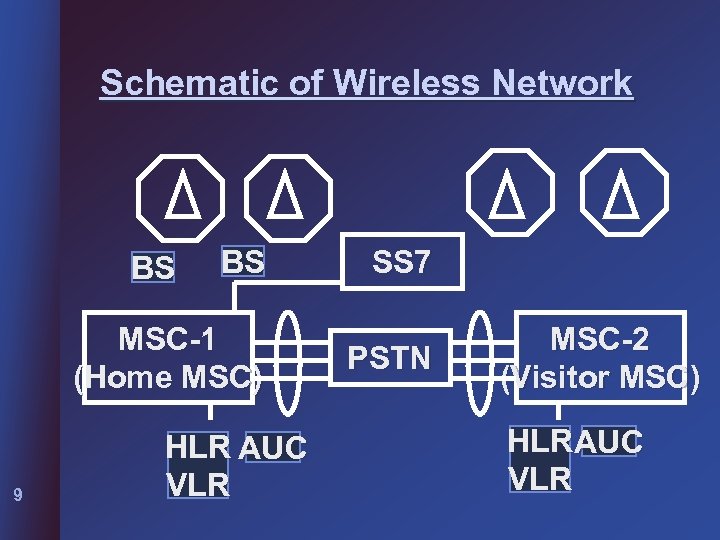 Schematic of Wireless Network BS BS MSC-1 (Home MSC) 9 HLR AUC VLR SS 7 PSTN MSC-2 (Visitor MSC) HLR AUC VLR
Schematic of Wireless Network BS BS MSC-1 (Home MSC) 9 HLR AUC VLR SS 7 PSTN MSC-2 (Visitor MSC) HLR AUC VLR
 Wireless network comparison 10 First, second and third generations l Modulation techniques (Analog, Digital, Spread Spectrum) l Switching (channel) techniques (Circuit switching, packet switching) l Signaling (control) techniques (in-band, CCS) l Practical systems (USDC, GSM, CDMA) l Network capabilities
Wireless network comparison 10 First, second and third generations l Modulation techniques (Analog, Digital, Spread Spectrum) l Switching (channel) techniques (Circuit switching, packet switching) l Signaling (control) techniques (in-band, CCS) l Practical systems (USDC, GSM, CDMA) l Network capabilities
 First Generation Networks l l l 11 Analog Technology -FM modulation AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone Services) – in U. S. Mobile Terminals Base Stations MSCs PSTN is separate network from the signalling network
First Generation Networks l l l 11 Analog Technology -FM modulation AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone Services) – in U. S. Mobile Terminals Base Stations MSCs PSTN is separate network from the signalling network
 Functions of MSC l l Maintains mobile related information and handoff control l 12 Provides overall System control for each region Performs all call processing; billing; fraud detection within the market
Functions of MSC l l Maintains mobile related information and handoff control l 12 Provides overall System control for each region Performs all call processing; billing; fraud detection within the market
 Wireless component linkages l l 13 Base station to Mobile user : Analog speech, low rate data Data transmission between BS – user RVC RCC FVC FCC Base station - MSC: 9600 B/S Data Link MSC - PSTN Landline Trunked lines and Tandem Switch
Wireless component linkages l l 13 Base station to Mobile user : Analog speech, low rate data Data transmission between BS – user RVC RCC FVC FCC Base station - MSC: 9600 B/S Data Link MSC - PSTN Landline Trunked lines and Tandem Switch
 IS-41 Network Protocol l l 14 l Network protocol standard to allow automatic registration of roamers – inter-operator roaming Allow MSCs of different service providers to pass information about subscribers to other MSCs on demand HLR – Home Location Register – real time user list VLR – Visitor Location Register AUC – Authentication Center
IS-41 Network Protocol l l 14 l Network protocol standard to allow automatic registration of roamers – inter-operator roaming Allow MSCs of different service providers to pass information about subscribers to other MSCs on demand HLR – Home Location Register – real time user list VLR – Visitor Location Register AUC – Authentication Center
 Roaming process l l 15 l Mobile periodically keys up and transmits identity information which allows MSC to constantly update it’s customer list. The registration command is sent in over control channels at 5 -10 minute intervals MIN – Mobile Identification Number (Telephone No. ) ESN – Electronic Serial Number
Roaming process l l 15 l Mobile periodically keys up and transmits identity information which allows MSC to constantly update it’s customer list. The registration command is sent in over control channels at 5 -10 minute intervals MIN – Mobile Identification Number (Telephone No. ) ESN – Electronic Serial Number
 Registration l l l 16 l By comparing MIN of roaming subscriber with HLR database, the MSC identifies roamers MSC sends registration request over landline signaling network to subscriber’s home MSC Home MSC validates roamer’s MIN and ESN and returns a customer profile to visited MSC Home and visitor MSC update their HLR and VLR
Registration l l l 16 l By comparing MIN of roaming subscriber with HLR database, the MSC identifies roamers MSC sends registration request over landline signaling network to subscriber’s home MSC Home MSC validates roamer’s MIN and ESN and returns a customer profile to visited MSC Home and visitor MSC update their HLR and VLR
 l l l 17 SS 7 (Signaling System 7) Process Switch controlled services for users Call return, call formatting, repeat dialing, call block, call tracing, caller ID 800 Series - Toll free access to calling party –paid by service subscriber Alternated Billing Service and line information database (ADB/LIDB) Enables calling party to bill a call to a personal number (third party number, calling card or collect call) from any number
l l l 17 SS 7 (Signaling System 7) Process Switch controlled services for users Call return, call formatting, repeat dialing, call block, call tracing, caller ID 800 Series - Toll free access to calling party –paid by service subscriber Alternated Billing Service and line information database (ADB/LIDB) Enables calling party to bill a call to a personal number (third party number, calling card or collect call) from any number
 Functioning Of SS 7 l l 18 MSC controls the switching and billing functions and interacts with PSTN to transfer between global grid and its cluster of base stations MSC uses the SS 7 signaling network for location validation and call delivery to its users which are roaming and relies on several information databases
Functioning Of SS 7 l l 18 MSC controls the switching and billing functions and interacts with PSTN to transfer between global grid and its cluster of base stations MSC uses the SS 7 signaling network for location validation and call delivery to its users which are roaming and relies on several information databases
 Switching in Networks l l MSC dedicates a voice channel connection between base station and PSTN for duration of cell phone call l 19 First generation Circuit Switching As calls are initiated and completed, different radio circuits and dedicated PSTN voice circuits are switched in and out to handle traffic
Switching in Networks l l MSC dedicates a voice channel connection between base station and PSTN for duration of cell phone call l 19 First generation Circuit Switching As calls are initiated and completed, different radio circuits and dedicated PSTN voice circuits are switched in and out to handle traffic
 Properties of circuit switching l l 20 Wireless data networks are not well supported by circuit switching, due to their short, bursty transmissions => often, time required to establish a circuit exceeds the duration of data transmission. Circuit switching is best suited for dedicated voice-only traffic, or for instances where data is continuously sent over long periods of time.
Properties of circuit switching l l 20 Wireless data networks are not well supported by circuit switching, due to their short, bursty transmissions => often, time required to establish a circuit exceeds the duration of data transmission. Circuit switching is best suited for dedicated voice-only traffic, or for instances where data is continuously sent over long periods of time.
 l l 21 Second Generation Wireless Networks Employ digital modulation and have advanced call processing capabilities. Examples: o Global system for Mobile (GSM) o DECT (Digital European Cordless Telephone) o Cordless Telephone (CT 2) -British system o JDC – Japanese Digital Cellular system
l l 21 Second Generation Wireless Networks Employ digital modulation and have advanced call processing capabilities. Examples: o Global system for Mobile (GSM) o DECT (Digital European Cordless Telephone) o Cordless Telephone (CT 2) -British system o JDC – Japanese Digital Cellular system
 Packet Switching network l l 22 Second generation switching network Packet Switching (or virtual switching) implements connectionless services for large number of data users, who remain virtually connected Packet switching breaks each message into smaller units for transmission and recovery When a message is broken into packets, control information is added to each packet to provide source/
Packet Switching network l l 22 Second generation switching network Packet Switching (or virtual switching) implements connectionless services for large number of data users, who remain virtually connected Packet switching breaks each message into smaller units for transmission and recovery When a message is broken into packets, control information is added to each packet to provide source/
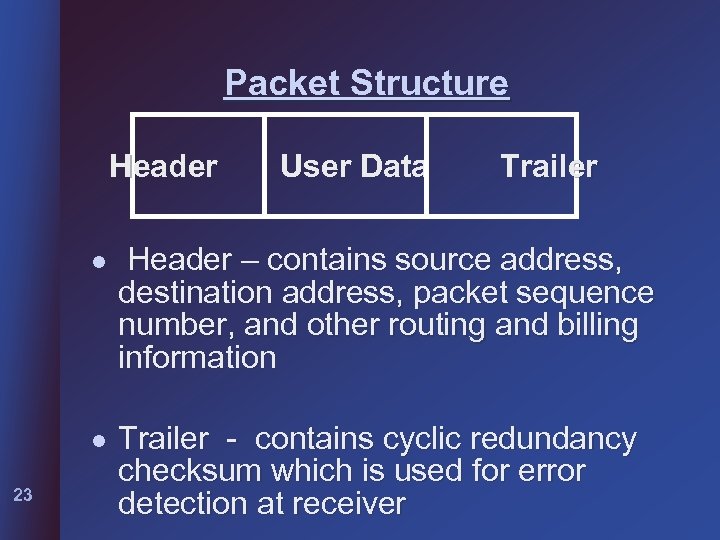 Packet Structure Header User Data Trailer l l 23 Header – contains source address, destination address, packet sequence number, and other routing and billing information Trailer - contains cyclic redundancy checksum which is used for error detection at receiver
Packet Structure Header User Data Trailer l l 23 Header – contains source address, destination address, packet sequence number, and other routing and billing information Trailer - contains cyclic redundancy checksum which is used for error detection at receiver
 Packet Switching properties l l l 24 Packet switching is also called Packet Radio (PR) when used by a wireless link Provides excellent channel efficiency for data transmission, since the channel is utilized only when sending or receiving bursts of information X 25 is widely used packet radio protocol – developed by CCITT (ITU-T) International Telecommunication Union.
Packet Switching properties l l l 24 Packet switching is also called Packet Radio (PR) when used by a wireless link Provides excellent channel efficiency for data transmission, since the channel is utilized only when sending or receiving bursts of information X 25 is widely used packet radio protocol – developed by CCITT (ITU-T) International Telecommunication Union.
 Second Generation Wireless Networks… l l l 25 New network architectures that reduce burden of MSC - BSC (base station controller) inserted between several base stations and MSC All systems are digital voice coding and employ digital modulation Systems employ common channel signaling for simultaneous voice and control information
Second Generation Wireless Networks… l l l 25 New network architectures that reduce burden of MSC - BSC (base station controller) inserted between several base stations and MSC All systems are digital voice coding and employ digital modulation Systems employ common channel signaling for simultaneous voice and control information
 Advances in Second Generation Networks l l l 26 While 1 st generation systems were primarily designed for voice, second generation networks provide paging, facsimile and high –data rate network access Handoff is mobile-controlled. MAHO(Mobile assisted Handoff) The mobile units in this generation perform functions like received power reporting, adjacent base station scanning, data encoding
Advances in Second Generation Networks l l l 26 While 1 st generation systems were primarily designed for voice, second generation networks provide paging, facsimile and high –data rate network access Handoff is mobile-controlled. MAHO(Mobile assisted Handoff) The mobile units in this generation perform functions like received power reporting, adjacent base station scanning, data encoding
 Common Channel Signaling (CCS) l l l 27 Second generation signaling network Digital Technique that provides simultaneous transmission of user data, signaling data and other related traffic through a network. [Mobile <> BS <> MSC <>MSC ] Uses out of band signaling channels which separate the network data from the user (voice or data) on the same channel or using TDM.
Common Channel Signaling (CCS) l l l 27 Second generation signaling network Digital Technique that provides simultaneous transmission of user data, signaling data and other related traffic through a network. [Mobile <> BS <> MSC <>MSC ] Uses out of band signaling channels which separate the network data from the user (voice or data) on the same channel or using TDM.
 Advantages of CCS l l 28 Advantage – high speed signaling (50 kbps –Mbps) is not limited by low speed voice data (20 bps – 20 kbps) Substantial increase in the number of users
Advantages of CCS l l 28 Advantage – high speed signaling (50 kbps –Mbps) is not limited by low speed voice data (20 bps – 20 kbps) Substantial increase in the number of users
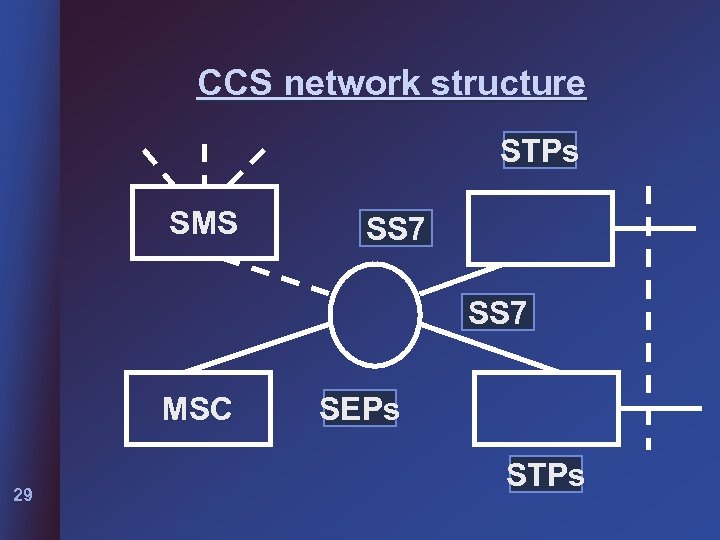 CCS network structure STPs SMS SS 7 MSC 29 SEPs STPs
CCS network structure STPs SMS SS 7 MSC 29 SEPs STPs
 CCS network components l l l 30 CCS network architecture is composed of geographically distributed central switching offices. Service Management system (SMS) Switching end points (SEPs) Signaling transfer points(STPs) Database service management system(DBAS)
CCS network components l l l 30 CCS network architecture is composed of geographically distributed central switching offices. Service Management system (SMS) Switching end points (SEPs) Signaling transfer points(STPs) Database service management system(DBAS)
 Third Generation Wireless Networks l 31 Aim is to provide a single set of standards that can meet a wide range of wireless applications, and provide universal access around the globe => voice, data and video
Third Generation Wireless Networks l 31 Aim is to provide a single set of standards that can meet a wide range of wireless applications, and provide universal access around the globe => voice, data and video
 Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) l l 32 Parallel worldwide network for CCS signaling traffic that can be used to either route traffic on PSTN or provide new services between network nodes and end users ISDN has 2 types of channels: o Information bearing channels called Bearer channels (B channels) – 64 kbps o Out of band signaling channels, called data channels (D channels)
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) l l 32 Parallel worldwide network for CCS signaling traffic that can be used to either route traffic on PSTN or provide new services between network nodes and end users ISDN has 2 types of channels: o Information bearing channels called Bearer channels (B channels) – 64 kbps o Out of band signaling channels, called data channels (D channels)
 Broadband ISDN (B-ISDN) l l 33 End user applications require greater bandwidth for computer systems and video imaging Based on asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) technology which allows packet switching – 100 Gbps
Broadband ISDN (B-ISDN) l l 33 End user applications require greater bandwidth for computer systems and video imaging Based on asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) technology which allows packet switching – 100 Gbps
 Future Wireless Networks l l 34 Based on B-ISDN to provide access to information networks such as Internet and other public and private databases PCS - Personal Communication System PCN - Personal Communication Network International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT – 2000)
Future Wireless Networks l l 34 Based on B-ISDN to provide access to information networks such as Internet and other public and private databases PCS - Personal Communication System PCN - Personal Communication Network International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT – 2000)


