d5d7a14ac608a0a670040a18160ae323.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Wireless LAN Solution & Deployment Tjie Seng, Njauw © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1
Wireless LAN Solution & Deployment Tjie Seng, Njauw © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1
 The Paradigm Shift Fixed Communications Mobile Communications © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 2
The Paradigm Shift Fixed Communications Mobile Communications © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 2
 The Paradigm Shift Fixed Work Area Work where you want! © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 3
The Paradigm Shift Fixed Work Area Work where you want! © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 3
 The Paradigm Shift Tethered Network Connection Wireless Network Connectivity Wireless LAN Products © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 4
The Paradigm Shift Tethered Network Connection Wireless Network Connectivity Wireless LAN Products © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 4
 What is a Wireless LAN? Ø Radio Frequency Technologies Ø WLANs Product Categories Ø Standards Based Technology © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 5
What is a Wireless LAN? Ø Radio Frequency Technologies Ø WLANs Product Categories Ø Standards Based Technology © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 5
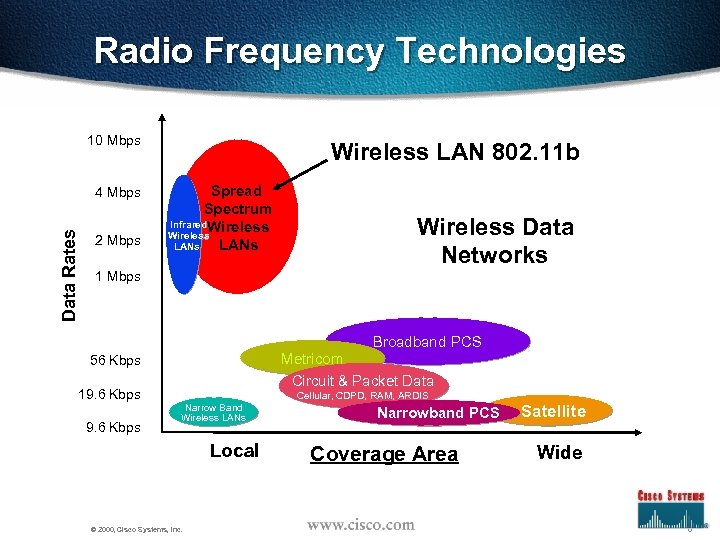 Radio Frequency Technologies 10 Mbps Data Rates 4 Mbps 2 Mbps Wireless LAN 802. 11 b Spread Spectrum Infrared. Wireless LANs Wireless Data Networks 1 Mbps Broadband PCS Metricom Circuit & Packet Data 56 Kbps 19. 6 Kbps Cellular, CDPD, RAM, ARDIS Narrow Band Wireless LANs Local © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. Narrowband PCS Coverage Area Satellite Wide 6
Radio Frequency Technologies 10 Mbps Data Rates 4 Mbps 2 Mbps Wireless LAN 802. 11 b Spread Spectrum Infrared. Wireless LANs Wireless Data Networks 1 Mbps Broadband PCS Metricom Circuit & Packet Data 56 Kbps 19. 6 Kbps Cellular, CDPD, RAM, ARDIS Narrow Band Wireless LANs Local © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. Narrowband PCS Coverage Area Satellite Wide 6
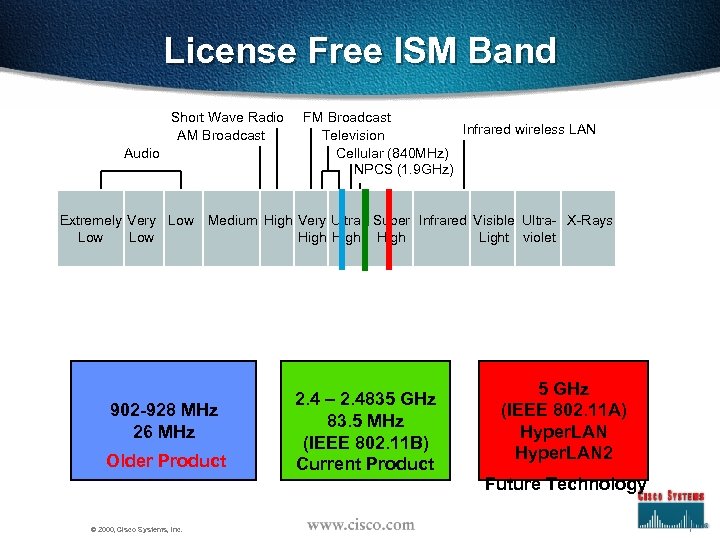 License Free ISM Band Short Wave Radio AM Broadcast Audio FM Broadcast Infrared wireless LAN Television Cellular (840 MHz) NPCS (1. 9 GHz) Extremely Very Low Medium High Very Ultra Super Infrared Visible Ultra- X-Rays Low High Light violet 902 -928 MHz 26 MHz Older Product 2. 4 – 2. 4835 GHz 83. 5 MHz (IEEE 802. 11 B) Current Product 5 GHz (IEEE 802. 11 A) Hyper. LAN 2 Future Technology © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7
License Free ISM Band Short Wave Radio AM Broadcast Audio FM Broadcast Infrared wireless LAN Television Cellular (840 MHz) NPCS (1. 9 GHz) Extremely Very Low Medium High Very Ultra Super Infrared Visible Ultra- X-Rays Low High Light violet 902 -928 MHz 26 MHz Older Product 2. 4 – 2. 4835 GHz 83. 5 MHz (IEEE 802. 11 B) Current Product 5 GHz (IEEE 802. 11 A) Hyper. LAN 2 Future Technology © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 7
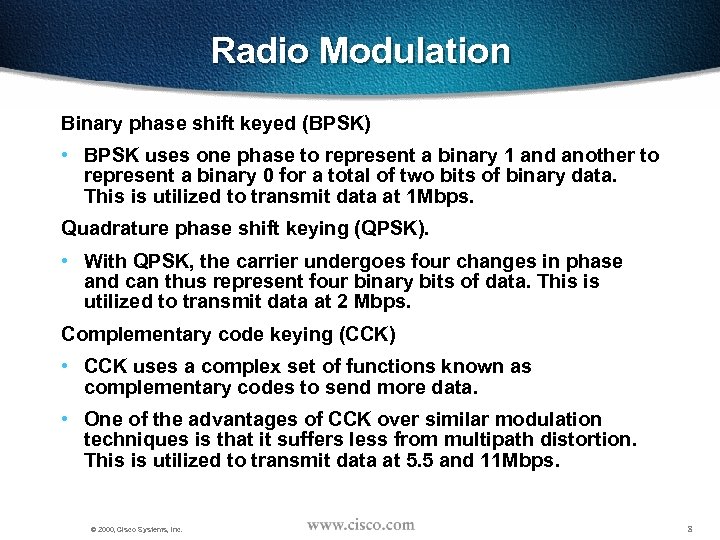 Radio Modulation Binary phase shift keyed (BPSK) • BPSK uses one phase to represent a binary 1 and another to represent a binary 0 for a total of two bits of binary data. This is utilized to transmit data at 1 Mbps. Quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK). • With QPSK, the carrier undergoes four changes in phase and can thus represent four binary bits of data. This is utilized to transmit data at 2 Mbps. Complementary code keying (CCK) • CCK uses a complex set of functions known as complementary codes to send more data. • One of the advantages of CCK over similar modulation techniques is that it suffers less from multipath distortion. This is utilized to transmit data at 5. 5 and 11 Mbps. © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 8
Radio Modulation Binary phase shift keyed (BPSK) • BPSK uses one phase to represent a binary 1 and another to represent a binary 0 for a total of two bits of binary data. This is utilized to transmit data at 1 Mbps. Quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK). • With QPSK, the carrier undergoes four changes in phase and can thus represent four binary bits of data. This is utilized to transmit data at 2 Mbps. Complementary code keying (CCK) • CCK uses a complex set of functions known as complementary codes to send more data. • One of the advantages of CCK over similar modulation techniques is that it suffers less from multipath distortion. This is utilized to transmit data at 5. 5 and 11 Mbps. © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 8
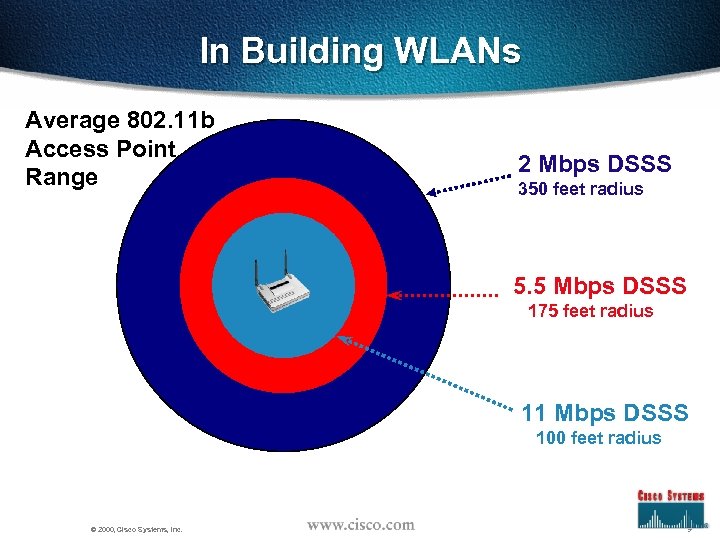 In Building WLANs Average 802. 11 b Access Point Range 2 Mbps DSSS 350 feet radius 5. 5 Mbps DSSS 175 feet radius 11 Mbps DSSS 100 feet radius © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9
In Building WLANs Average 802. 11 b Access Point Range 2 Mbps DSSS 350 feet radius 5. 5 Mbps DSSS 175 feet radius 11 Mbps DSSS 100 feet radius © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 9
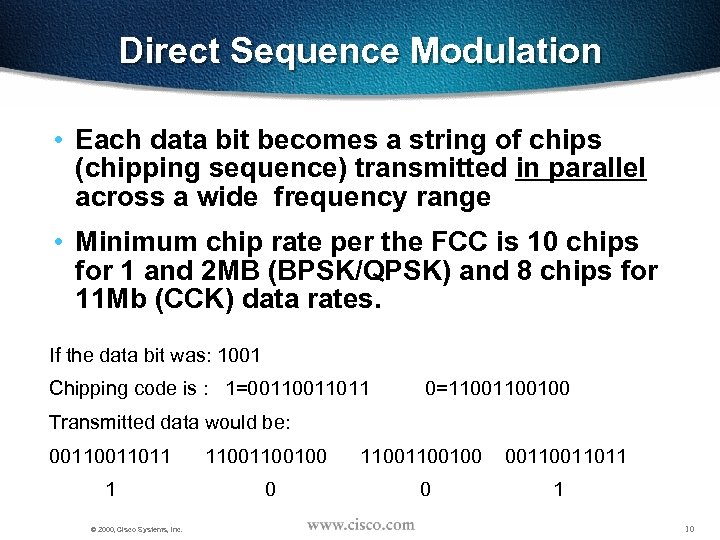 Direct Sequence Modulation • Each data bit becomes a string of chips (chipping sequence) transmitted in parallel across a wide frequency range • Minimum chip rate per the FCC is 10 chips for 1 and 2 MB (BPSK/QPSK) and 8 chips for 11 Mb (CCK) data rates. If the data bit was: 1001 Chipping code is : 1=0011011 0=1100100 Transmitted data would be: 0011011 11001100100 1 0 0 © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 0011011 1 10
Direct Sequence Modulation • Each data bit becomes a string of chips (chipping sequence) transmitted in parallel across a wide frequency range • Minimum chip rate per the FCC is 10 chips for 1 and 2 MB (BPSK/QPSK) and 8 chips for 11 Mb (CCK) data rates. If the data bit was: 1001 Chipping code is : 1=0011011 0=1100100 Transmitted data would be: 0011011 11001100100 1 0 0 © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 0011011 1 10
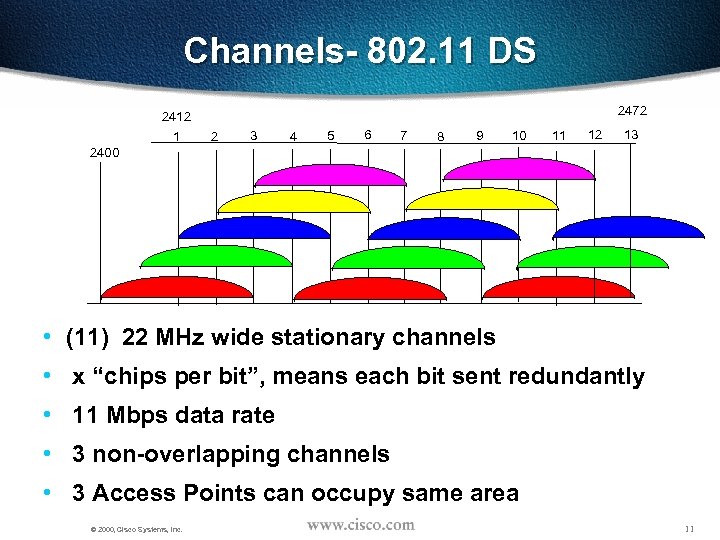 Channels- 802. 11 DS 2472 2412 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 2400 • (11) 22 MHz wide stationary channels • x “chips per bit”, means each bit sent redundantly • 11 Mbps data rate • 3 non-overlapping channels • 3 Access Points can occupy same area © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 11
Channels- 802. 11 DS 2472 2412 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 2400 • (11) 22 MHz wide stationary channels • x “chips per bit”, means each bit sent redundantly • 11 Mbps data rate • 3 non-overlapping channels • 3 Access Points can occupy same area © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 11
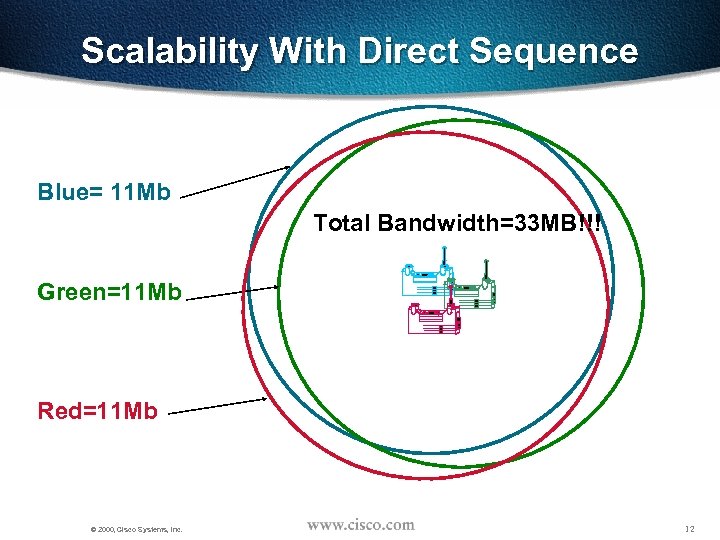 Scalability With Direct Sequence Blue= 11 Mb Total Bandwidth=33 MB!!! Green=11 Mb Red=11 Mb © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 12
Scalability With Direct Sequence Blue= 11 Mb Total Bandwidth=33 MB!!! Green=11 Mb Red=11 Mb © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 12
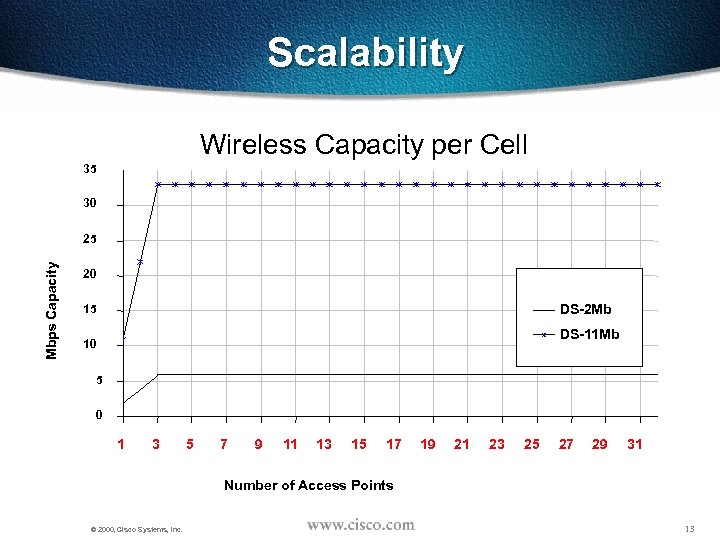 Scalability Wireless Capacity per Cell 35 30 Mbps Capacity 25 20 DS-2 Mb 15 DS-11 Mb 10 5 0 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 Number of Access Points © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 13
Scalability Wireless Capacity per Cell 35 30 Mbps Capacity 25 20 DS-2 Mb 15 DS-11 Mb 10 5 0 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 Number of Access Points © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 13
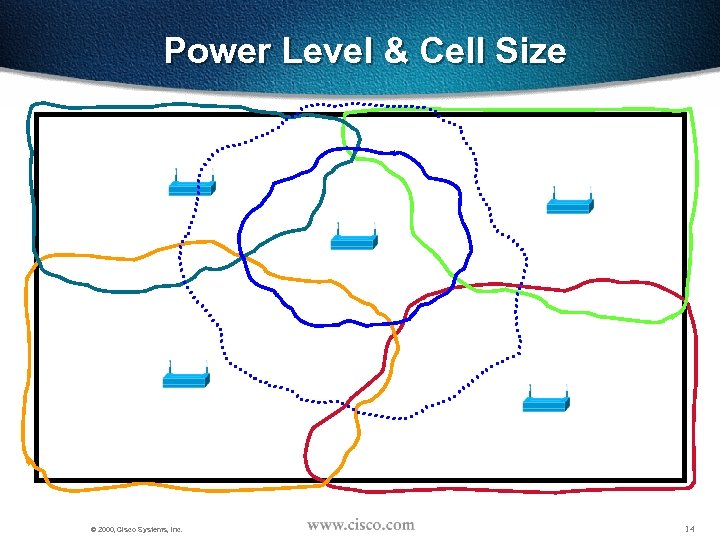 Power Level & Cell Size © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 14
Power Level & Cell Size © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 14
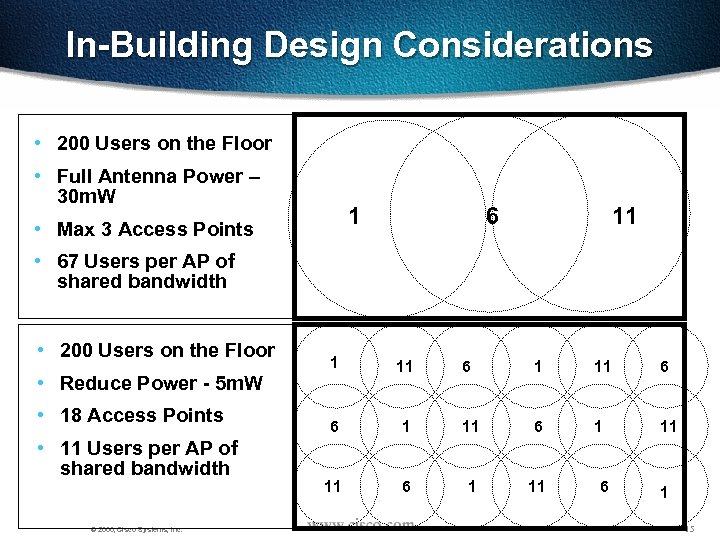 In-Building Design Considerations • 200 Users on the Floor • Full Antenna Power – 30 m. W 1 • Max 3 Access Points 6 11 • 67 Users per AP of shared bandwidth • 200 Users on the Floor • Reduce Power - 5 m. W • 18 Access Points • 11 Users per AP of shared bandwidth © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 11 6 6 1 11 11 6 1 15
In-Building Design Considerations • 200 Users on the Floor • Full Antenna Power – 30 m. W 1 • Max 3 Access Points 6 11 • 67 Users per AP of shared bandwidth • 200 Users on the Floor • Reduce Power - 5 m. W • 18 Access Points • 11 Users per AP of shared bandwidth © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 11 6 6 1 11 11 6 1 15
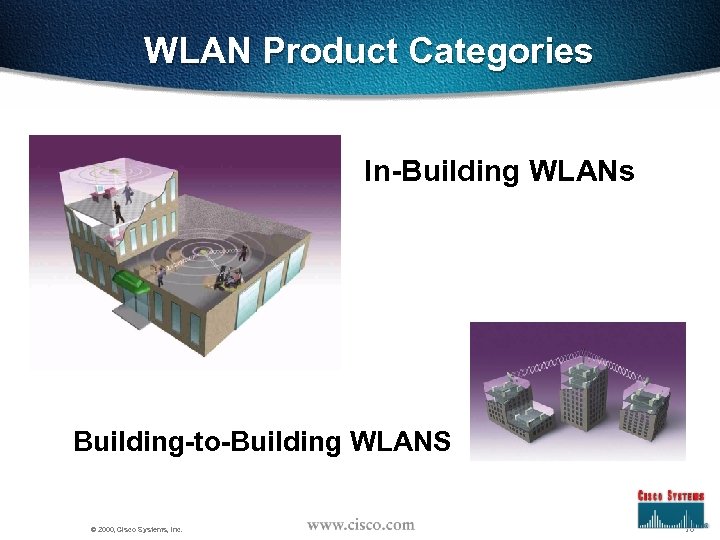 WLAN Product Categories In-Building WLANs Building-to-Building WLANS © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 16
WLAN Product Categories In-Building WLANs Building-to-Building WLANS © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 16
 In-Building WLAN Components Ethernet Backbone Internet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 17
In-Building WLAN Components Ethernet Backbone Internet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 17
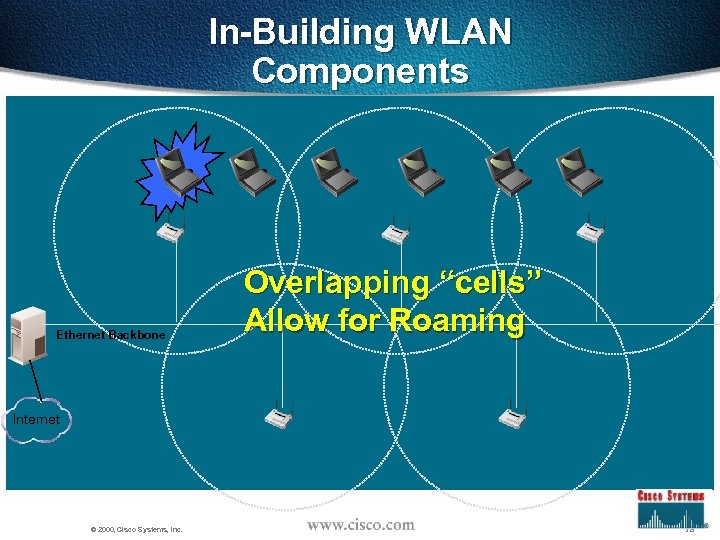 In-Building WLAN Components Ethernet Backbone Overlapping “cells” Allow for Roaming Internet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 18
In-Building WLAN Components Ethernet Backbone Overlapping “cells” Allow for Roaming Internet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 18
 In-Building WLAN Components Ethernet Backbone Internet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 19
In-Building WLAN Components Ethernet Backbone Internet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 19
 In-Building WLAN Components Ethernet Backbone Internet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 20
In-Building WLAN Components Ethernet Backbone Internet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 20
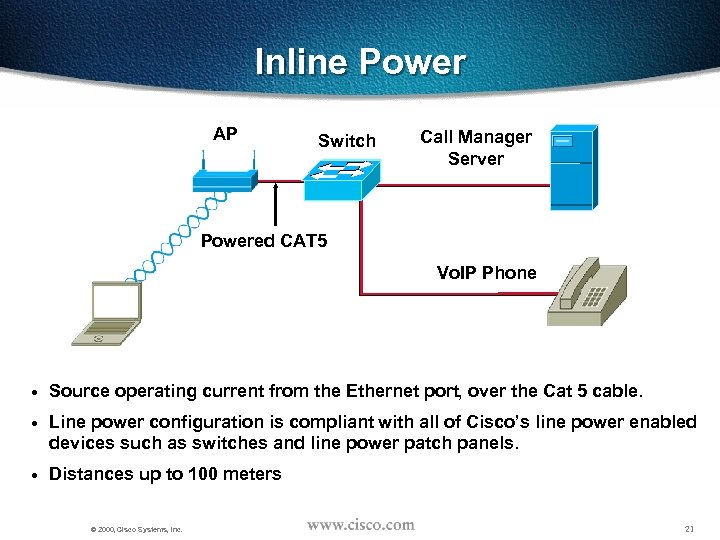 Inline Power AP Switch Call Manager Server Powered CAT 5 Vo. IP Phone · Source operating current from the Ethernet port, over the Cat 5 cable. · Line power configuration is compliant with all of Cisco’s line power enabled devices such as switches and line power patch panels. · Distances up to 100 meters © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 21
Inline Power AP Switch Call Manager Server Powered CAT 5 Vo. IP Phone · Source operating current from the Ethernet port, over the Cat 5 cable. · Line power configuration is compliant with all of Cisco’s line power enabled devices such as switches and line power patch panels. · Distances up to 100 meters © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 21
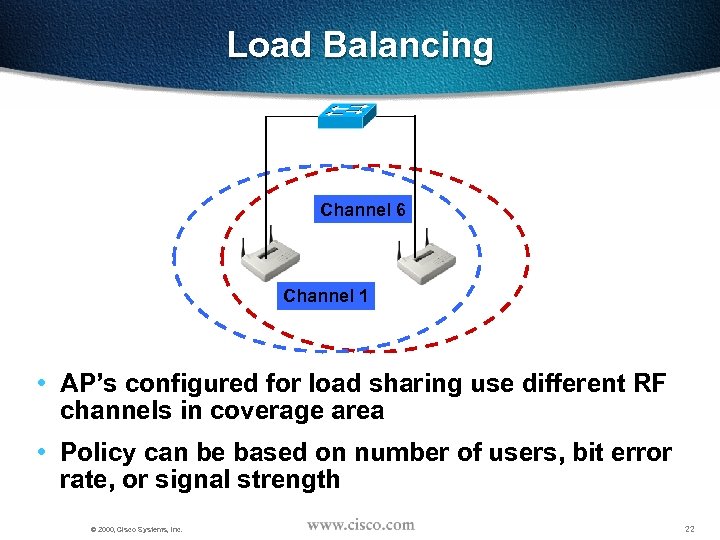 Load Balancing Channel 6 Channel 1 • AP’s configured for load sharing use different RF channels in coverage area • Policy can be based on number of users, bit error rate, or signal strength © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 22
Load Balancing Channel 6 Channel 1 • AP’s configured for load sharing use different RF channels in coverage area • Policy can be based on number of users, bit error rate, or signal strength © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 22
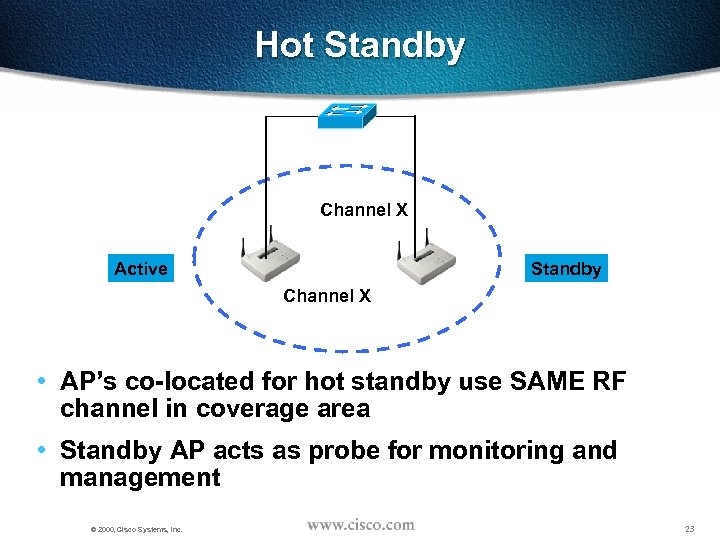 Hot Standby Channel X Active Standby Channel X • AP’s co-located for hot standby use SAME RF channel in coverage area • Standby AP acts as probe for monitoring and management © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 23
Hot Standby Channel X Active Standby Channel X • AP’s co-located for hot standby use SAME RF channel in coverage area • Standby AP acts as probe for monitoring and management © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 23
 Security Considerations (*#&$*( #(*&$*(#$ #)($__%# #$#% © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. Encryption or WEP 40 -Bit 128 -Bit 24
Security Considerations (*#&$*( #(*&$*(#$ #)($__%# #$#% © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. Encryption or WEP 40 -Bit 128 -Bit 24
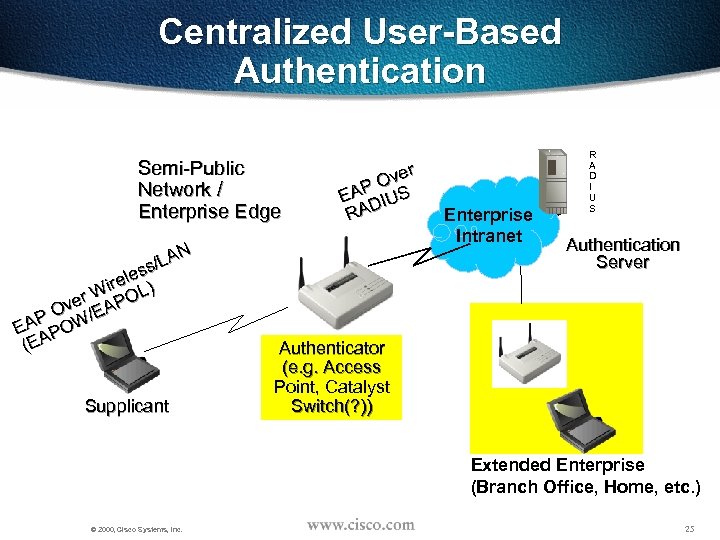 Centralized User-Based Authentication Semi-Public Network / Enterprise Edge N /LA ss ele ) ir r W POL e Ov /EA POW (EA Supplicant r Ove EAP IUS RAD Enterprise Intranet R A D I U S Authentication Server Authenticator (e. g. Access Point, Catalyst Switch(? )) Extended Enterprise (Branch Office, Home, etc. ) © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 25
Centralized User-Based Authentication Semi-Public Network / Enterprise Edge N /LA ss ele ) ir r W POL e Ov /EA POW (EA Supplicant r Ove EAP IUS RAD Enterprise Intranet R A D I U S Authentication Server Authenticator (e. g. Access Point, Catalyst Switch(? )) Extended Enterprise (Branch Office, Home, etc. ) © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 25
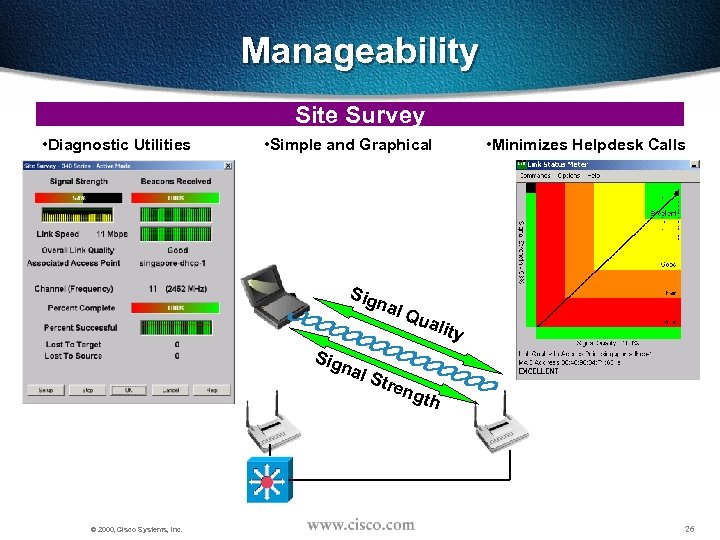 Manageability Site Survey • Diagnostic Utilities • Simple and Graphical Sig nal • Minimizes Helpdesk Calls Qua lity Stre ngt h © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 26
Manageability Site Survey • Diagnostic Utilities • Simple and Graphical Sig nal • Minimizes Helpdesk Calls Qua lity Stre ngt h © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 26
 In Building Site Survey © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 27
In Building Site Survey © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 27
 Wireless Bridges • Decreases Implementation Costs A Fraction the Cost of Trenching • High Speed Connections Greater Bandwidth than T 1 Lines • Eliminates Recurring Charges No Monthly Leased Line Fees • Reduces Installation Delays No Right of Way or Permits Required, Installation in an Afternoon • Makes Physical Barriers Irrelevant Bypass Lakes, Rivers, Freeways, Railroads © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 28
Wireless Bridges • Decreases Implementation Costs A Fraction the Cost of Trenching • High Speed Connections Greater Bandwidth than T 1 Lines • Eliminates Recurring Charges No Monthly Leased Line Fees • Reduces Installation Delays No Right of Way or Permits Required, Installation in an Afternoon • Makes Physical Barriers Irrelevant Bypass Lakes, Rivers, Freeways, Railroads © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 28
 Wireless Antennas Bridges Mast Mount High Gain Yagi Mast Solid Dish Omni Directional 8 d. Bi 5. 2 d. Bi 13. 5 d. Bi 21 d. Bi 60 H 55 V 360 H 7 V 30 H 25 V 12. 4 H 12. 4 V 2. 0 Miles 5000’ 4. 6 Miles 6. 5 Miles 25 Miles 3390’ 1580’ 1. 4 Miles 2 Miles 11. 5 Miles 3’ 3’ 1’ 1. 5’ 2’ Patch Wall Mast Mount Type Gain Beam Width Approximate Range at 2 Mbps Approximate Range at 11 Mbps Cable Length © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. Directional 29
Wireless Antennas Bridges Mast Mount High Gain Yagi Mast Solid Dish Omni Directional 8 d. Bi 5. 2 d. Bi 13. 5 d. Bi 21 d. Bi 60 H 55 V 360 H 7 V 30 H 25 V 12. 4 H 12. 4 V 2. 0 Miles 5000’ 4. 6 Miles 6. 5 Miles 25 Miles 3390’ 1580’ 1. 4 Miles 2 Miles 11. 5 Miles 3’ 3’ 1’ 1. 5’ 2’ Patch Wall Mast Mount Type Gain Beam Width Approximate Range at 2 Mbps Approximate Range at 11 Mbps Cable Length © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. Directional 29
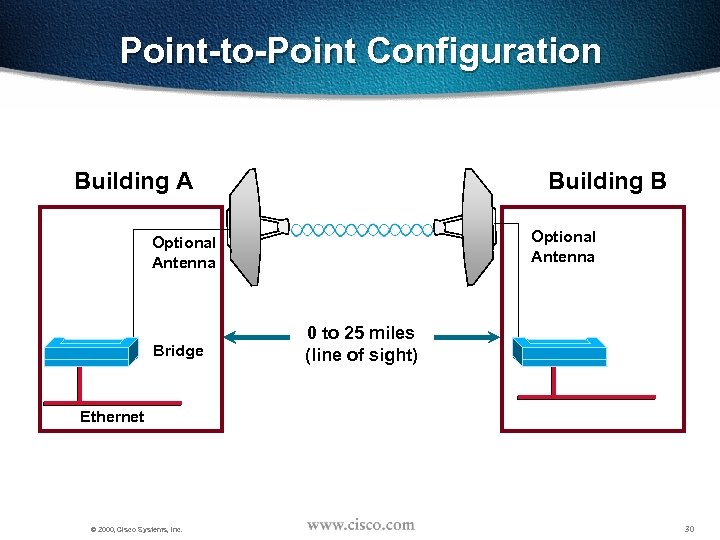 Point-to-Point Configuration Building A Building B Optional Antenna Bridge 0 to 25 miles (line of sight) Ethernet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 30
Point-to-Point Configuration Building A Building B Optional Antenna Bridge 0 to 25 miles (line of sight) Ethernet © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 30
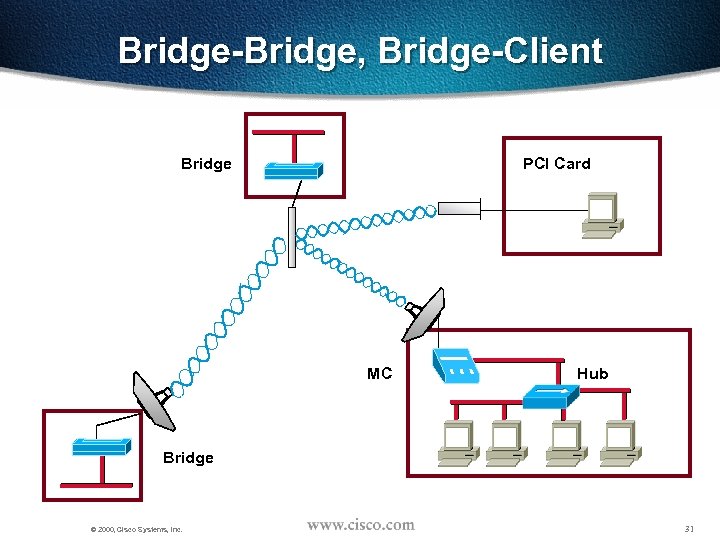 Bridge-Bridge, Bridge-Client Bridge PCI Card MC Hub Bridge © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 31
Bridge-Bridge, Bridge-Client Bridge PCI Card MC Hub Bridge © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 31
 Outdoor Path Considerations • Radio line of sight • Earth bulge • Fresnel Zone • Antenna and cabling • Data rate © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 32
Outdoor Path Considerations • Radio line of sight • Earth bulge • Fresnel Zone • Antenna and cabling • Data rate © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 32
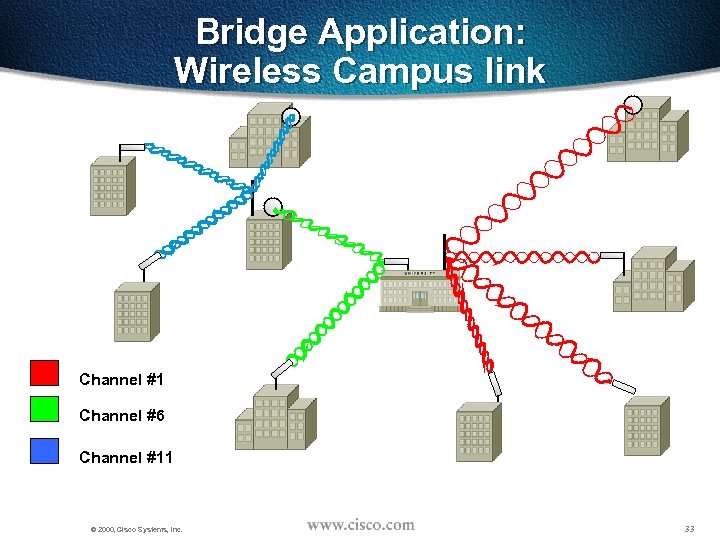 Bridge Application: Wireless Campus link Channel #1 Channel #6 Channel #11 © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 33
Bridge Application: Wireless Campus link Channel #1 Channel #6 Channel #11 © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 33
 IEEE 802. 11 A Move Toward Standardization! • A very high-performance WLAN system Efficient MAC and high-quality radio 802. 11 products perform better than proprietary systems Client interoperability • WEP standard privacy and authentication • Standards-based migration path for system growth • The IEEE 802. 11 (July 1997) for 1 and 2 Mb DSSS • The IEEE 802. 11 b (Sept 1999) for 11 Mb DSSS © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 34
IEEE 802. 11 A Move Toward Standardization! • A very high-performance WLAN system Efficient MAC and high-quality radio 802. 11 products perform better than proprietary systems Client interoperability • WEP standard privacy and authentication • Standards-based migration path for system growth • The IEEE 802. 11 (July 1997) for 1 and 2 Mb DSSS • The IEEE 802. 11 b (Sept 1999) for 11 Mb DSSS © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 34
 WI-FI Certification • WECA certifies Interoperability between products. • This provides assurance to customers of migration and integration options. • Certified products can be found at http: //www. wirelessethernet. org/ © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 35
WI-FI Certification • WECA certifies Interoperability between products. • This provides assurance to customers of migration and integration options. • Certified products can be found at http: //www. wirelessethernet. org/ © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 35
 Soo… What’s Next. . © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 36
Soo… What’s Next. . © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 36
 Internet Mobile Office • Broadband solution for the mobile business professional that combines all of the following: Wired and wireless connectivity Broadband speeds when on the move Access to critical business applications Secure, end-to-end VPN access Nationwide and international coverage Consolidated billing across service providers Access to localized content © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 37
Internet Mobile Office • Broadband solution for the mobile business professional that combines all of the following: Wired and wireless connectivity Broadband speeds when on the move Access to critical business applications Secure, end-to-end VPN access Nationwide and international coverage Consolidated billing across service providers Access to localized content © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 37
 Bringing Mobile Offices to Mobile Professionals Enterprise Customers © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 38
Bringing Mobile Offices to Mobile Professionals Enterprise Customers © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 38
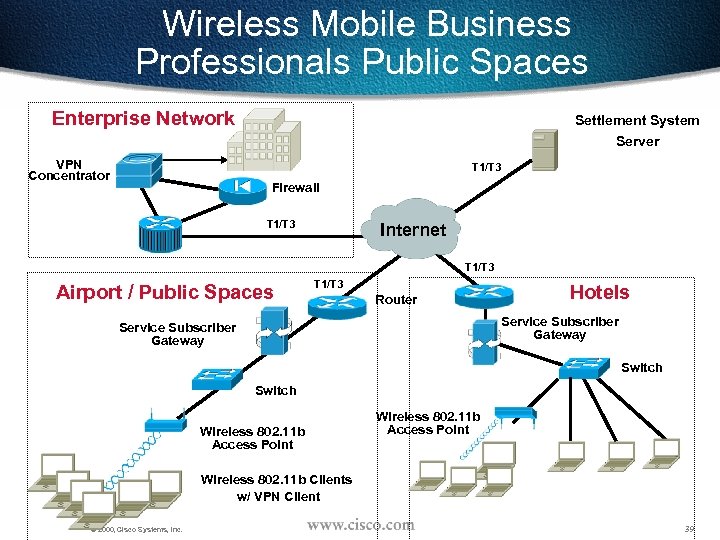 Wireless Mobile Business Professionals Public Spaces Enterprise Network Settlement System Server VPN Concentrator T 1/T 3 Firewall T 1/T 3 Internet T 1/T 3 Airport / Public Spaces T 1/T 3 Router Hotels Service Subscriber Gateway Switch Wireless 802. 11 b Access Point Wireless 802. 11 b Clients w/ VPN Client © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 39
Wireless Mobile Business Professionals Public Spaces Enterprise Network Settlement System Server VPN Concentrator T 1/T 3 Firewall T 1/T 3 Internet T 1/T 3 Airport / Public Spaces T 1/T 3 Router Hotels Service Subscriber Gateway Switch Wireless 802. 11 b Access Point Wireless 802. 11 b Clients w/ VPN Client © 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 39


