bb94cc59f014aa9c0a56179b8ca4937c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Wireless LAN Security Kim W. Tracy NEIU, University Computing k. w. tracy@ieee. org
Wireless LAN Security Kim W. Tracy NEIU, University Computing k. w. tracy@ieee. org
 Outline l l l Threats to LANs & Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Security Techniques Summary 2
Outline l l l Threats to LANs & Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Security Techniques Summary 2
 Fundamental Premise l l Security cannot be considered in isolation and to be effective must consider the entire system That is, network and LAN security must be: l Consistent with other security mechanisms l l E. g. application, data, hardware, and physical Supportive of other security mechanisms 3
Fundamental Premise l l Security cannot be considered in isolation and to be effective must consider the entire system That is, network and LAN security must be: l Consistent with other security mechanisms l l E. g. application, data, hardware, and physical Supportive of other security mechanisms 3
 Threats
Threats
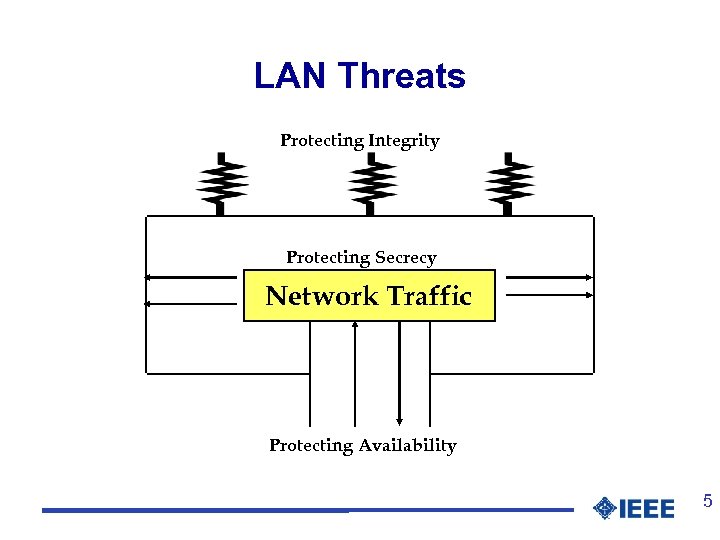 LAN Threats Protecting Integrity Protecting Secrecy Network Traffic Protecting Availability 5
LAN Threats Protecting Integrity Protecting Secrecy Network Traffic Protecting Availability 5
 Specific LAN Threats l Availability l l l Worms/Virus Do. S Errant applications creating lots of traffic/malformed traffic Authentication l Spying devices on LAN l l For example, a contractor connecting to LAN Secrecy l Sniffers being connected to the LAN to collect passwords, etc. 6
Specific LAN Threats l Availability l l l Worms/Virus Do. S Errant applications creating lots of traffic/malformed traffic Authentication l Spying devices on LAN l l For example, a contractor connecting to LAN Secrecy l Sniffers being connected to the LAN to collect passwords, etc. 6
 Authentication
Authentication
 Current State of LAN Authentication l Usually none! l l If in the building can plug in to the LAN Can cause severe problems: l l Using LAN for illegal purposes (company/person may be liable) Can more easily compromise servers l l For example, send spam from your mail servers Wireless LANs are bringing issue out 8
Current State of LAN Authentication l Usually none! l l If in the building can plug in to the LAN Can cause severe problems: l l Using LAN for illegal purposes (company/person may be liable) Can more easily compromise servers l l For example, send spam from your mail servers Wireless LANs are bringing issue out 8
 Authentication services l 802. 1 X – IEEE standard for LAN authentication l l Kerberos (closed environment) l l Can use PKI certificate-based authentication Single login (once per session) To multiple servers/domains ‘Ticket’ for each server X. 509 (open environment) l l l Based on public key infrastructure Used in SSL, IPSEC, S/MIME, SET… One-way, two-way or three-way authentication 9
Authentication services l 802. 1 X – IEEE standard for LAN authentication l l Kerberos (closed environment) l l Can use PKI certificate-based authentication Single login (once per session) To multiple servers/domains ‘Ticket’ for each server X. 509 (open environment) l l l Based on public key infrastructure Used in SSL, IPSEC, S/MIME, SET… One-way, two-way or three-way authentication 9
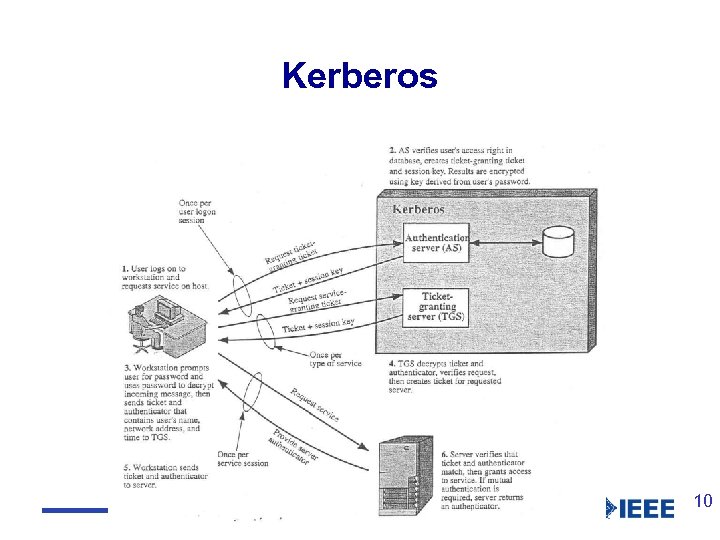 Kerberos 10
Kerberos 10
![X. 509 Authentication A One-way authentication B [Ta, Ra, B, Ekpub. B(Kab) ] sgn. X. 509 Authentication A One-way authentication B [Ta, Ra, B, Ekpub. B(Kab) ] sgn.](https://present5.com/presentation/bb94cc59f014aa9c0a56179b8ca4937c/image-11.jpg) X. 509 Authentication A One-way authentication B [Ta, Ra, B, Ekpub. B(Kab) ] sgn. A Two-way authentication [Tb, Rb, A, Ra, Ekpub. A(Kab) ] sgn. B [Ta, Ra, B, Ekpub. B(Kab) ] sgn. A [Tb, Rb, A, Ra, Ekpub. A(Kab) ] sgn. B Three-way authentication [Rb] sgn. A 11
X. 509 Authentication A One-way authentication B [Ta, Ra, B, Ekpub. B(Kab) ] sgn. A Two-way authentication [Tb, Rb, A, Ra, Ekpub. A(Kab) ] sgn. B [Ta, Ra, B, Ekpub. B(Kab) ] sgn. A [Tb, Rb, A, Ra, Ekpub. A(Kab) ] sgn. B Three-way authentication [Rb] sgn. A 11
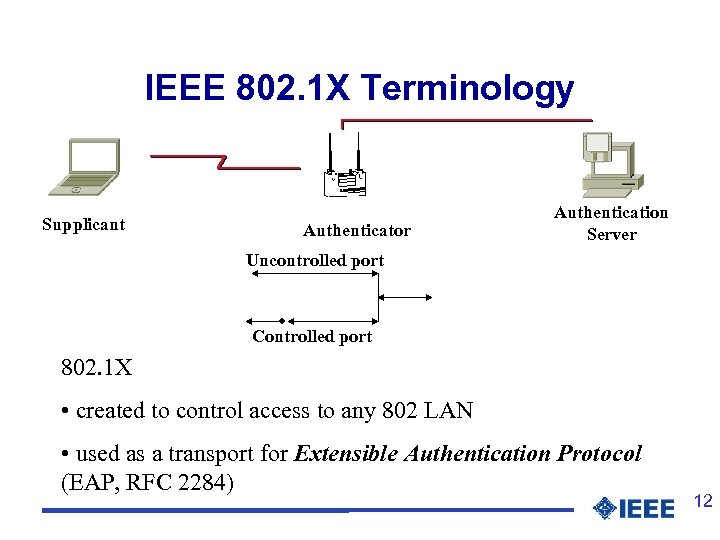 IEEE 802. 1 X Terminology Supplicant Authenticator Authentication Server Uncontrolled port Controlled port 802. 1 X • created to control access to any 802 LAN • used as a transport for Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP, RFC 2284) 12
IEEE 802. 1 X Terminology Supplicant Authenticator Authentication Server Uncontrolled port Controlled port 802. 1 X • created to control access to any 802 LAN • used as a transport for Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP, RFC 2284) 12
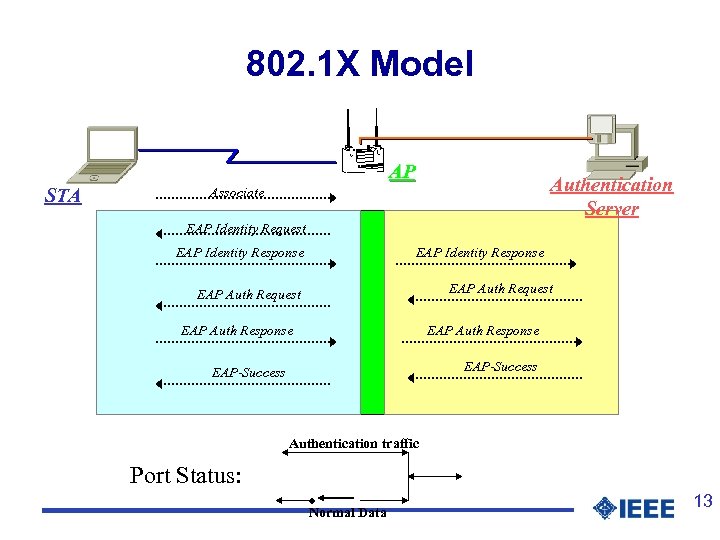 802. 1 X Model AP STA Authentication Server Associate EAP Identity Request EAP Identity Response EAP Auth Request EAP Auth Response EAP-Success Authentication traffic Port Status: Normal Data 13
802. 1 X Model AP STA Authentication Server Associate EAP Identity Request EAP Identity Response EAP Auth Request EAP Auth Response EAP-Success Authentication traffic Port Status: Normal Data 13
 Wireless LAN Security
Wireless LAN Security
 Introduction l 802. 11 standard specifies the operating parameters of wireless local area networks (WLAN) l l History: 802. 11, b, a, g, i Minimal security in early versions Original architecture not well suited for modern security needs 802. 11 i attempts to address security issues with WLANs 15
Introduction l 802. 11 standard specifies the operating parameters of wireless local area networks (WLAN) l l History: 802. 11, b, a, g, i Minimal security in early versions Original architecture not well suited for modern security needs 802. 11 i attempts to address security issues with WLANs 15
 802. 11 b l Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) l Confidentiality l Encryption l l l Access Control l l 40 -bit keys (increased to 104 -bit by WEP 2) Based on RC 4 algorithm Shared key authentication + Encryption Data Integrity l Integrity checksum computed for all messages 16
802. 11 b l Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) l Confidentiality l Encryption l l l Access Control l l 40 -bit keys (increased to 104 -bit by WEP 2) Based on RC 4 algorithm Shared key authentication + Encryption Data Integrity l Integrity checksum computed for all messages 16
 802. 11 b l Vulnerabilities in WEP l Poorly implemented encryption l l Key reuse, small keys, no keyed MIC Weak authentication No key management No interception detection 17
802. 11 b l Vulnerabilities in WEP l Poorly implemented encryption l l Key reuse, small keys, no keyed MIC Weak authentication No key management No interception detection 17
 802. 11 b l Successful attacks on 802. 11 b l l l Key recovery - Air. Snort Man-in-the-middle Denial of service Authentication forging Known plaintext Known ciphertext 18
802. 11 b l Successful attacks on 802. 11 b l l l Key recovery - Air. Snort Man-in-the-middle Denial of service Authentication forging Known plaintext Known ciphertext 18
 802. 11 i l Security Specifications l Improved Encryption l l l CCMP (AES), TKIP, WRAP 2 -way authentication Key management Ad-hoc network support Improved security architecture 19
802. 11 i l Security Specifications l Improved Encryption l l l CCMP (AES), TKIP, WRAP 2 -way authentication Key management Ad-hoc network support Improved security architecture 19
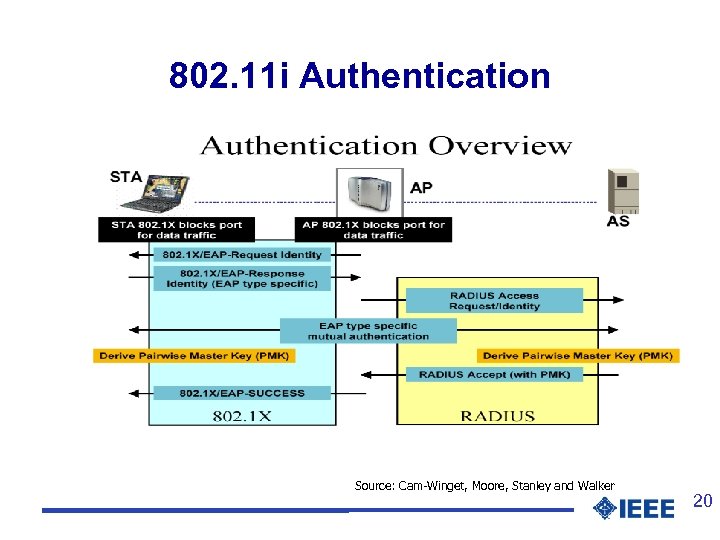 802. 11 i Authentication Source: Cam-Winget, Moore, Stanley and Walker 20
802. 11 i Authentication Source: Cam-Winget, Moore, Stanley and Walker 20
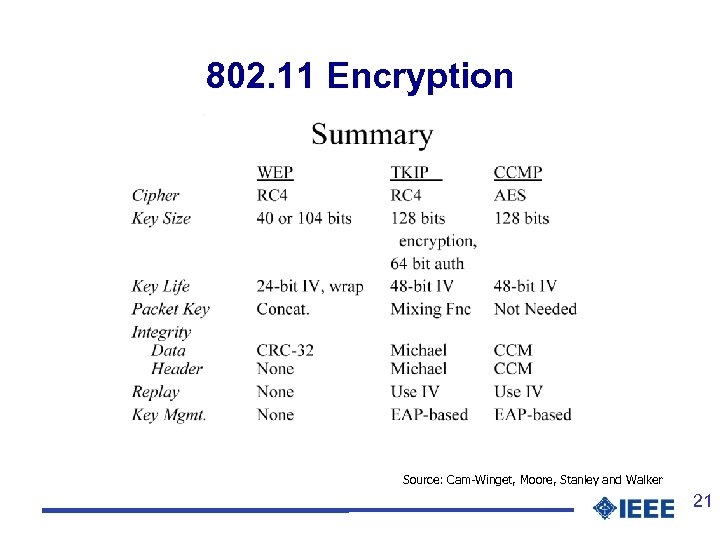 802. 11 Encryption Source: Cam-Winget, Moore, Stanley and Walker 21
802. 11 Encryption Source: Cam-Winget, Moore, Stanley and Walker 21
 802. 11 i – Potential Weaknesses l Hardware requirements l Hardware upgrade needed for AES support l l l Authentication server needed for 2 -way authentication Complexity l l Strength of TKIP and Wrap questionable in the long term The more complex a system is, the more likely it may contain an undetected backdoor Patchwork nature of “fixing” 802. 11 b 22
802. 11 i – Potential Weaknesses l Hardware requirements l Hardware upgrade needed for AES support l l l Authentication server needed for 2 -way authentication Complexity l l Strength of TKIP and Wrap questionable in the long term The more complex a system is, the more likely it may contain an undetected backdoor Patchwork nature of “fixing” 802. 11 b 22
 No Control over WLAN? l l Often you want to connect to a wireless LAN over which you have no control Options: l l If you can, connect securely (WPA 2, 802. 11 i, etc. ) If unsecured, connect to your secure systems securely: l l VPN – Virtual Private Network SSL connections to secure systems Be careful not to expose passwords Watch for direct attacks on untrusted networks 23
No Control over WLAN? l l Often you want to connect to a wireless LAN over which you have no control Options: l l If you can, connect securely (WPA 2, 802. 11 i, etc. ) If unsecured, connect to your secure systems securely: l l VPN – Virtual Private Network SSL connections to secure systems Be careful not to expose passwords Watch for direct attacks on untrusted networks 23
 WLAN Security - Going Forward l l 802. 11 i appears to be a significant improvement over 802. 11 b from a security standpoint Vendors are nervous about implementing 802. 11 i protocols due to how quickly WEP was compromised after its release Only time will tell how effective 802. 11 i actually will be Wireless networks will not be completely secure until the standards that specify them are designed from the beginning with security in mind 24
WLAN Security - Going Forward l l 802. 11 i appears to be a significant improvement over 802. 11 b from a security standpoint Vendors are nervous about implementing 802. 11 i protocols due to how quickly WEP was compromised after its release Only time will tell how effective 802. 11 i actually will be Wireless networks will not be completely secure until the standards that specify them are designed from the beginning with security in mind 24
 Summary l l Wireless LAN Security is not independent of the greater network security and system security Threats to the Wireless LAN are largely in terms of being available and in providing a means to attack systems on the network l That is, not many folks attack routers (yet) 25
Summary l l Wireless LAN Security is not independent of the greater network security and system security Threats to the Wireless LAN are largely in terms of being available and in providing a means to attack systems on the network l That is, not many folks attack routers (yet) 25
 References l l ftp: //ftp. prenhall. com/pub/esm/web_marketing /ptr/pfleeger/ch 07. pdf - Charles & Shari Pfleeger’s chapter on network security http: //www. gocsi. com/forms/fbi/pdf. jhtml - To request the Computer Security Institute/FBI yearly survey results (widely referenced) 26
References l l ftp: //ftp. prenhall. com/pub/esm/web_marketing /ptr/pfleeger/ch 07. pdf - Charles & Shari Pfleeger’s chapter on network security http: //www. gocsi. com/forms/fbi/pdf. jhtml - To request the Computer Security Institute/FBI yearly survey results (widely referenced) 26


