 Wire Media: UTP • Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) – Ordinary copper wire – Twisted several times per inch to reduce interference – Pair of wires needed for a complete electrical signal – Unshielded: nothing but plastic coating • No protection from interference
Wire Media: UTP • Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) – Ordinary copper wire – Twisted several times per inch to reduce interference – Pair of wires needed for a complete electrical signal – Unshielded: nothing but plastic coating • No protection from interference
 Wire Media: UTP • Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) – Business telephone wiring traditionally comes in 4 -pair UTP wire bundles – Used in LAN wiring to use existing building wiring technology
Wire Media: UTP • Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) – Business telephone wiring traditionally comes in 4 -pair UTP wire bundles – Used in LAN wiring to use existing building wiring technology
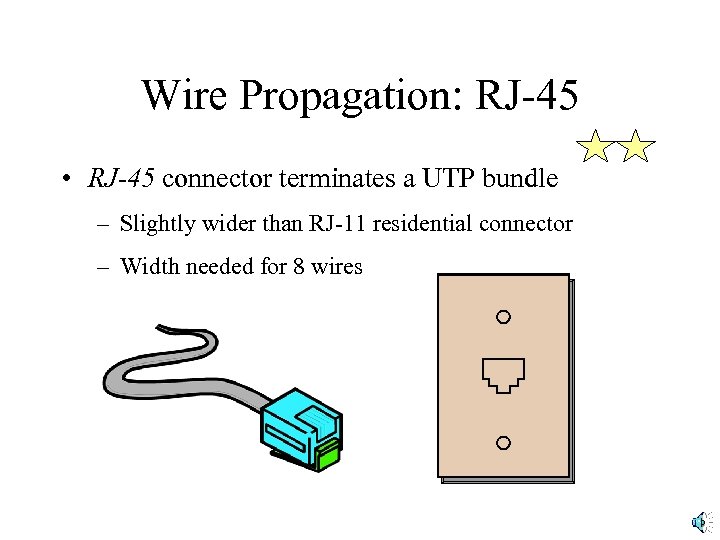 Wire Propagation: RJ-45 • RJ-45 connector terminates a UTP bundle – Slightly wider than RJ-11 residential connector – Width needed for 8 wires
Wire Propagation: RJ-45 • RJ-45 connector terminates a UTP bundle – Slightly wider than RJ-11 residential connector – Width needed for 8 wires
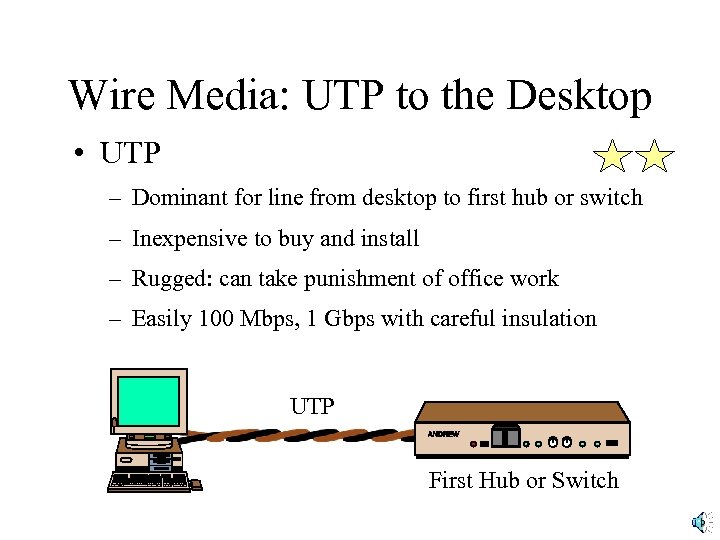 Wire Media: UTP to the Desktop • UTP – Dominant for line from desktop to first hub or switch – Inexpensive to buy and install – Rugged: can take punishment of office work – Easily 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps with careful insulation UTP First Hub or Switch
Wire Media: UTP to the Desktop • UTP – Dominant for line from desktop to first hub or switch – Inexpensive to buy and install – Rugged: can take punishment of office work – Easily 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps with careful insulation UTP First Hub or Switch
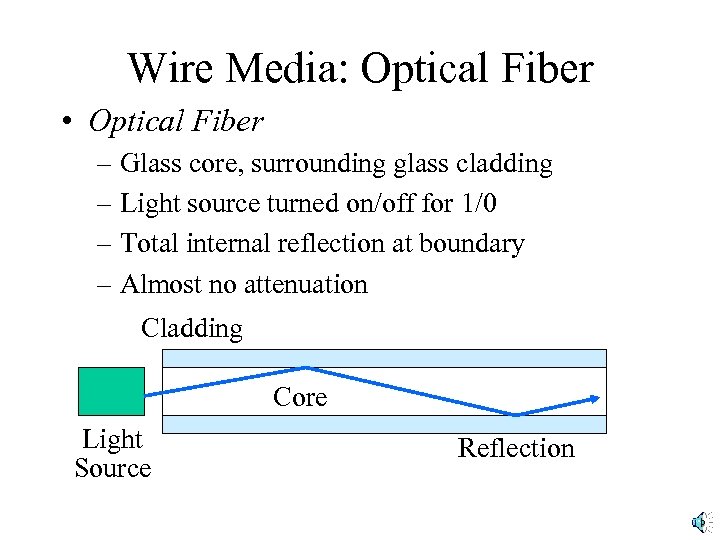 Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Optical Fiber – Glass core, surrounding glass cladding – Light source turned on/off for 1/0 – Total internal reflection at boundary – Almost no attenuation Cladding Core Light Source Reflection
Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Optical Fiber – Glass core, surrounding glass cladding – Light source turned on/off for 1/0 – Total internal reflection at boundary – Almost no attenuation Cladding Core Light Source Reflection
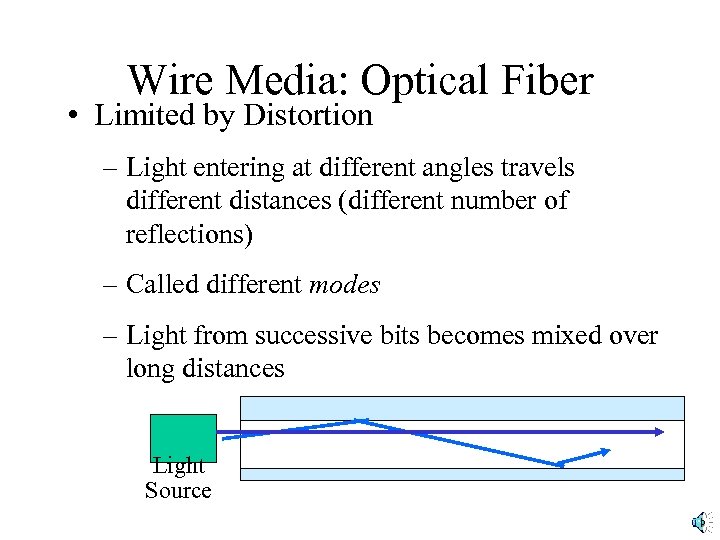 Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Limited by Distortion – Light entering at different angles travels different distances (different number of reflections) – Called different modes – Light from successive bits becomes mixed over long distances Light Source
Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Limited by Distortion – Light entering at different angles travels different distances (different number of reflections) – Called different modes – Light from successive bits becomes mixed over long distances Light Source
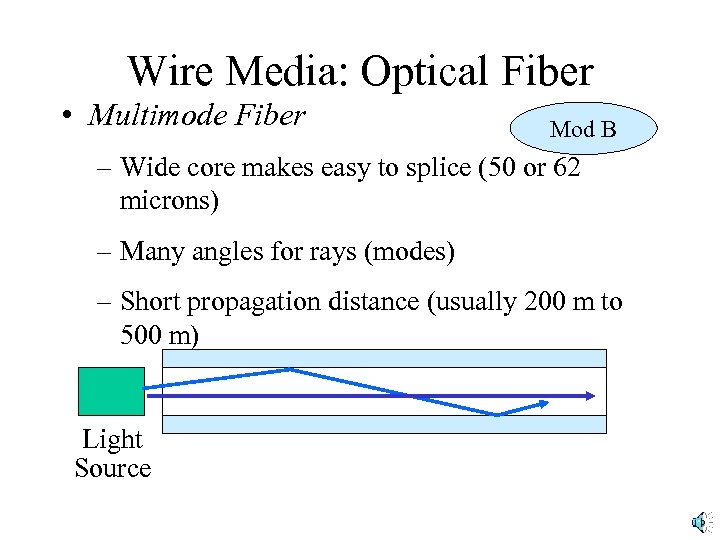 Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Multimode Fiber Mod B – Wide core makes easy to splice (50 or 62 microns) – Many angles for rays (modes) – Short propagation distance (usually 200 m to 500 m) Light Source
Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Multimode Fiber Mod B – Wide core makes easy to splice (50 or 62 microns) – Many angles for rays (modes) – Short propagation distance (usually 200 m to 500 m) Light Source
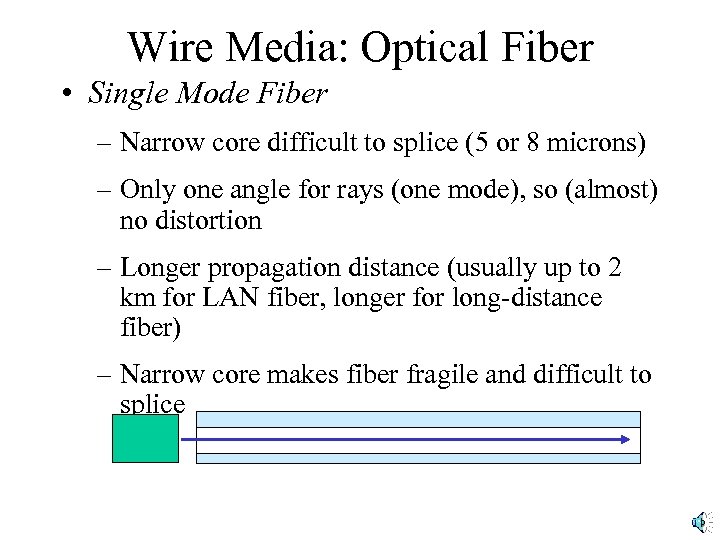 Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Single Mode Fiber – Narrow core difficult to splice (5 or 8 microns) – Only one angle for rays (one mode), so (almost) no distortion – Longer propagation distance (usually up to 2 km for LAN fiber, longer for long-distance fiber) – Narrow core makes fiber fragile and difficult to splice
Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Single Mode Fiber – Narrow core difficult to splice (5 or 8 microns) – Only one angle for rays (one mode), so (almost) no distortion – Longer propagation distance (usually up to 2 km for LAN fiber, longer for long-distance fiber) – Narrow core makes fiber fragile and difficult to splice
 Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Optical Fiber – High speeds over long distances • 200 m to 2 km – Costs more than UTP, but worth it on long runs – Good for all links between hubs and switches within and between buildings in a site network Optical Fiber
Wire Media: Optical Fiber • Optical Fiber – High speeds over long distances • 200 m to 2 km – Costs more than UTP, but worth it on long runs – Good for all links between hubs and switches within and between buildings in a site network Optical Fiber
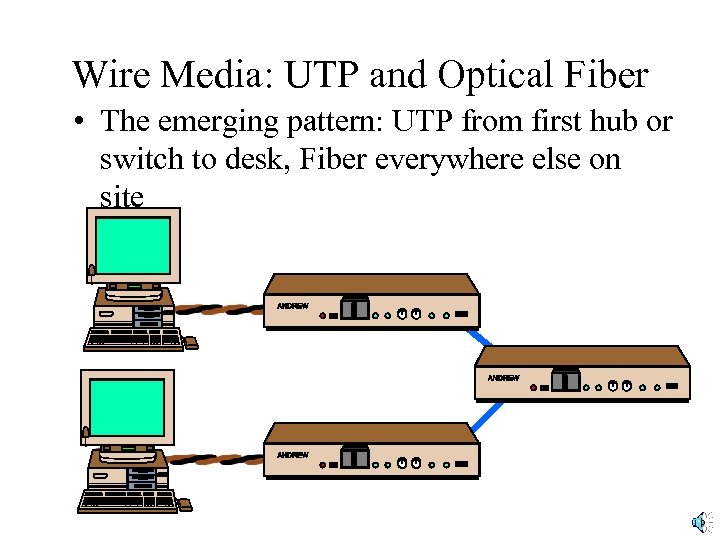 Wire Media: UTP and Optical Fiber • The emerging pattern: UTP from first hub or switch to desk, Fiber everywhere else on site
Wire Media: UTP and Optical Fiber • The emerging pattern: UTP from first hub or switch to desk, Fiber everywhere else on site
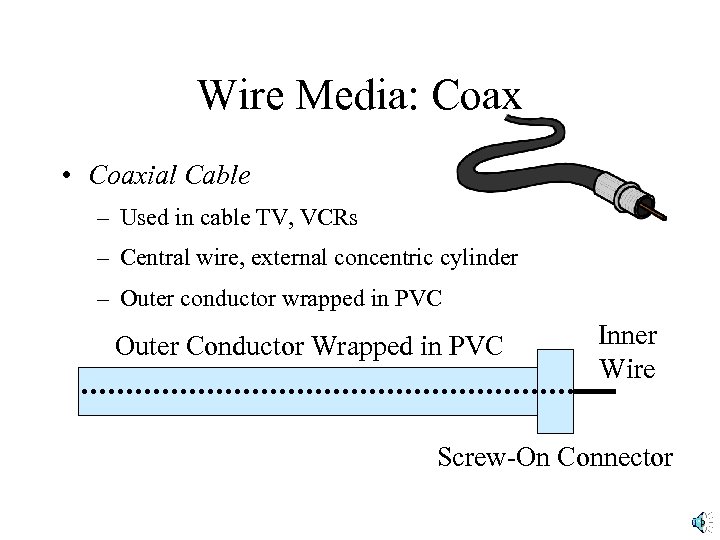 Wire Media: Coax • Coaxial Cable – Used in cable TV, VCRs – Central wire, external concentric cylinder – Outer conductor wrapped in PVC Outer Conductor Wrapped in PVC Inner Wire Screw-On Connector
Wire Media: Coax • Coaxial Cable – Used in cable TV, VCRs – Central wire, external concentric cylinder – Outer conductor wrapped in PVC Outer Conductor Wrapped in PVC Inner Wire Screw-On Connector
 Wire Media: Coaxial Cable • Coaxial Cable – Installed widely today in old 10 Mbps Ethernet LANs – Not being used in new installations • Optical fiber more cost-effective for long links • UTP more cost-effective for desktop links
Wire Media: Coaxial Cable • Coaxial Cable – Installed widely today in old 10 Mbps Ethernet LANs – Not being used in new installations • Optical fiber more cost-effective for long links • UTP more cost-effective for desktop links