7022d97e9cd6bf55d4825172dc6d5465.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 1
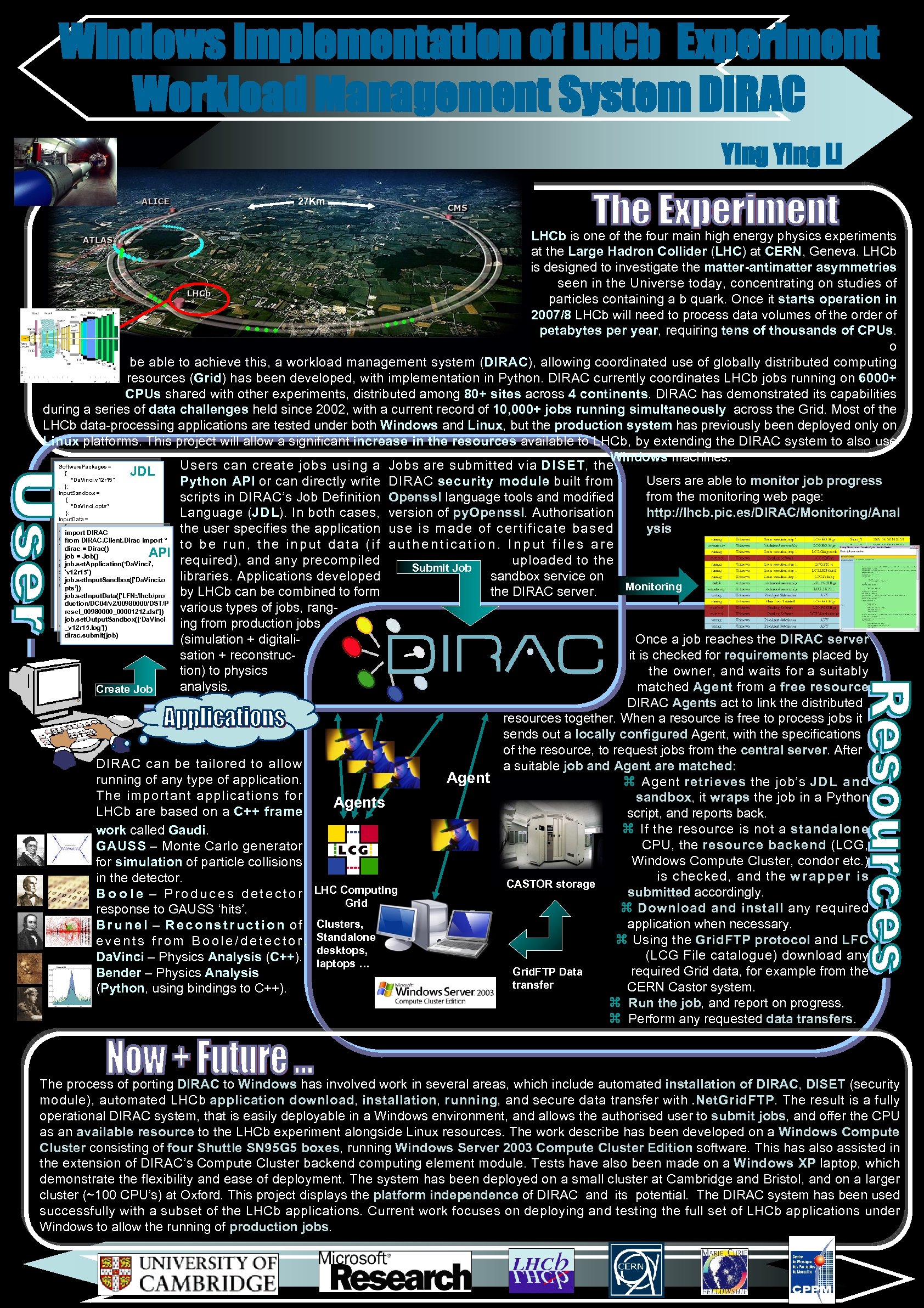
Windows Implementation of LHCb Experiment Workload Management System DIRAC Ying Li 27 Km LHCb is one of the four main high energy physics experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN, Geneva. LHCb is designed to investigate the matter-antimatter asymmetries seen in the Universe today, concentrating on studies of particles containing a b quark. Once it starts operation in 2007/8 LHCb will need to process data volumes of the order of petabytes per year, requiring tens of thousands of CPUs. T o be able to achieve this, a workload management system (DIRAC), allowing coordinated use of globally distributed computing resources (Grid) has been developed, with implementation in Python. DIRAC currently coordinates LHCb jobs running on 6000+ CPUs shared with other experiments, distributed among 80+ sites across 4 continents. DIRAC has demonstrated its capabilities during a series of data challenges held since 2002, with a current record of 10, 000+ jobs running simultaneously across the Grid. Most of the LHCb data-processing applications are tested under both Windows and Linux, but the production system has previously been deployed only on Linux platforms. This project will allow a significant increase in the resources available to LHCb, by extending the DIRAC system to also use Windows machines. Software. Packages = Users can create jobs using a Jobs are submitted via DISET, the { JDL “Da. Vinci. v 12 r 15" Users are able to monitor job progress Python API or can directly write DIRAC security module built from }; Input. Sandbox = from the monitoring web page: scripts in DIRAC’s Job Definition Openssl language tools and modified { “Da. Vinci. opts” }; http: //lhcb. pic. es/DIRAC/Monitoring/Anal Language (JDL). In both cases, version of py. Openssl. Authorisation Input. Data = { ysis the user specifies the application use is made of certificate based "LFN: /lhcb/production/DC 04/v 2/009800 import DIRAC 00/DST/Presel_00980000_00001212. dst * from DIRAC. Client. Dirac import " to be run, the input data (if authentication. Input files are dirac = Dirac() }; API job = = “Da. Vinci_1"; Job. Name. Job() required), and any precompiled uploaded to the job. set. Application(‘Da. Vinci', Owner = "ying"; Submit Job Std. Output = "std. out"; 'v 12 r 15') libraries. Applications developed sandbox service on Std. Error = "std. err"; job. set. Input. Sandbox(['Da. Vinci. o Output. Sandbox = pts’]) Monitoring { by LHCb can be combined to form the DIRAC server. job. set. Input. Data(['LFN: /lhcb/pro "std. out", duction/DC 04/v 2/00980000/DST/P "std. err", various types of jobs, rang“Da. Vinci_v 12 r 15. log” resel_00980000_00001212. dst']) }; job. set. Output. Sandbox([‘Da. Vinci Job. Type = "user"; ing from production jobs _v 12 r 15. log’]) dirac. submit(job) (simulation + digitali. Once a job reaches the DIRAC server sation + reconstrucit is checked for requirements placed by tion) to physics the owner, and waits for a suitably analysis. matched Agent from a free resource. Create Job DIRAC Agents act to link the distributed resources together. When a resource is free to process jobs it sends out a locally configured Agent, with the specifications of the resource, to request jobs from the central server. After DIRAC can be tailored to allow a suitable job and Agent are matched: Agent running of any type of application. Agent retrieves the job’s JDL and The important applications for sandbox, it wraps the job in a Python Agents LHCb are based on a C++ frame script, and reports back. If the resource is not a standalone work called Gaudi. CPU, the resource backend (LCG, GAUSS – Monte Carlo generator Windows Compute Cluster, condor etc. ) for simulation of particle collisions is checked, and the w r a p p e r i s in the detector. CASTOR storage submitted accordingly. B o o l e – P r o d u c e s d e t e c t o r LHC Computing Grid Download and install any required response to GAUSS ‘hits’. application when necessary. B r u n e l – R e c o n s t r u c t i o n o f Clusters, Using the Grid. FTP protocol and LFC e v e n t s f r o m B o o l e / d e t e c t o r. Standalone desktops, (LCG File catalogue) download any Da. Vinci – Physics Analysis (C++). laptops … Grid. FTP Data required Grid data, for example from the Bender – Physics Analysis transfer CERN Castor system. (Python, using bindings to C++). Run the job, and report on progress. Perform any requested data transfers. The process of porting DIRAC to Windows has involved work in several areas, which include automated installation of DIRAC, DISET (security module), automated LHCb application download, installation, running, and secure data transfer with. Net. Grid. FTP. The result is a fully operational DIRAC system, that is easily deployable in a Windows environment, and allows the authorised user to submit jobs, and offer the CPU as an available resource to the LHCb experiment alongside Linux resources. The work describe has been developed on a Windows Compute Cluster consisting of four Shuttle SN 95 G 5 boxes, running Windows Server 2003 Compute Cluster Edition software. This has also assisted in the extension of DIRAC’s Compute Cluster backend computing element module. Tests have also been made on a Windows XP laptop, which demonstrate the flexibility and ease of deployment. The system has been deployed on a small cluster at Cambridge and Bristol, and on a larger cluster (~100 CPU’s) at Oxford. This project displays the platform independence of DIRAC and its potential. The DIRAC system has been used successfully with a subset of the LHCb applications. Current work focuses on deploying and testing the full set of LHCb applications under Windows to allow the running of production jobs.
7022d97e9cd6bf55d4825172dc6d5465.ppt