823c0e2fbd53eeeb68af12080bb8b5e2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Windows 2008 Adminstration
Windows 2008 Adminstration
 Versions • Windows 2000 pro – Supports upto 4 Gb RAM – Works with 2000 server to take advantage of ADS and intellimirror (allow users' data, software, and settings to follow them) – Upto 2 processors • Windows 2000 server – New Management tools using MMC – DHCP, DNS, IIS, Index Server, RAS, VPN – Upto 4 processors • Windows 2000 Advanced server – – Upto 8 Gb RAM Better network load balancing Clustering Upto 8 processors • Windows 2000 Datacenter – Upto 64 Gb RAM – Supports upto 32 processors
Versions • Windows 2000 pro – Supports upto 4 Gb RAM – Works with 2000 server to take advantage of ADS and intellimirror (allow users' data, software, and settings to follow them) – Upto 2 processors • Windows 2000 server – New Management tools using MMC – DHCP, DNS, IIS, Index Server, RAS, VPN – Upto 4 processors • Windows 2000 Advanced server – – Upto 8 Gb RAM Better network load balancing Clustering Upto 8 processors • Windows 2000 Datacenter – Upto 64 Gb RAM – Supports upto 32 processors
 Windows 2003 Server Systems • Standard – Upto 4 way SMP, 4 GB RAM • Enterprise – Upto 8 way SMP, 32 GB RAM, 64 -bit support • Datacenter – Upto 32 way SMP, 64 GB RAM (32 -bit versions) – Upto 128 way SMP, 512 GB RAM (64 -bit versions) • Web Edition – Primarily as IIS server for web application hosting and XML services • Small Business Server – Integrates Share. Point Services, Exchange Server 2003, ISA (Internet Security & Acceleration) server, SQL Server 2003.
Windows 2003 Server Systems • Standard – Upto 4 way SMP, 4 GB RAM • Enterprise – Upto 8 way SMP, 32 GB RAM, 64 -bit support • Datacenter – Upto 32 way SMP, 64 GB RAM (32 -bit versions) – Upto 128 way SMP, 512 GB RAM (64 -bit versions) • Web Edition – Primarily as IIS server for web application hosting and XML services • Small Business Server – Integrates Share. Point Services, Exchange Server 2003, ISA (Internet Security & Acceleration) server, SQL Server 2003.
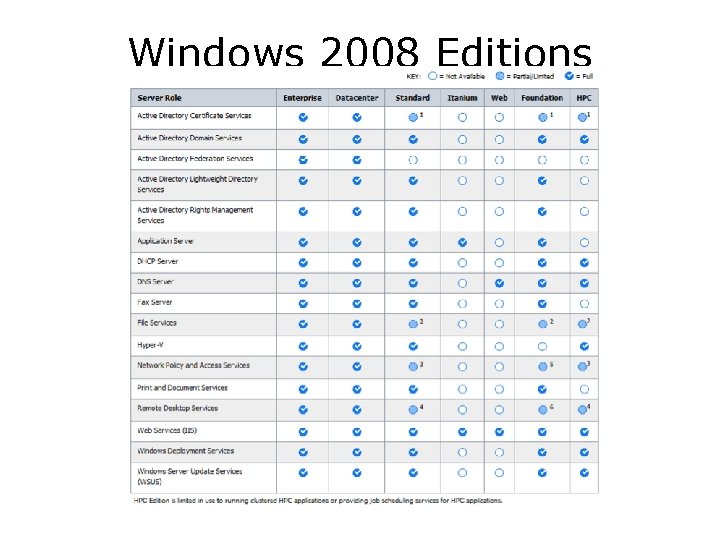 Windows 2008 Editions
Windows 2008 Editions
 Installation Preparations • HCL (hardware Compatibility List) • Gather hardware information and drivers • Start with atleast – PIII processors • (min: 133 MHz. . Good luck) – Plenty of RAM • Atleast 256 Mb – SCSI-based disk subsystem (preferable)
Installation Preparations • HCL (hardware Compatibility List) • Gather hardware information and drivers • Start with atleast – PIII processors • (min: 133 MHz. . Good luck) – Plenty of RAM • Atleast 256 Mb – SCSI-based disk subsystem (preferable)
 Pre-installation • Upgrade or Install ? • FAT or NTFS – Dual-boot (FAT) – Domain Controller (NTFS) – ADS Security features (NTFS) • Server mode: – Domain Controller • Has domain info stored in ADS • No more PDC/BDC. ADS -> Multimaster domain model – Member Server • Do not hold ADS info. – Stand-alone • Participates in a workgroup. • Licensing – Per Seat • CAL for each client computer. Not monitored by server – Per Server • CAL defines number of connections to server
Pre-installation • Upgrade or Install ? • FAT or NTFS – Dual-boot (FAT) – Domain Controller (NTFS) – ADS Security features (NTFS) • Server mode: – Domain Controller • Has domain info stored in ADS • No more PDC/BDC. ADS -> Multimaster domain model – Member Server • Do not hold ADS info. – Stand-alone • Participates in a workgroup. • Licensing – Per Seat • CAL for each client computer. Not monitored by server – Per Server • CAL defines number of connections to server
 Installing the Server • Upgrade from older versions • Prepare boot disks and install • Install from the network where files are located • Components to Install • Configuring Network connectivity
Installing the Server • Upgrade from older versions • Prepare boot disks and install • Install from the network where files are located • Components to Install • Configuring Network connectivity
 Configuring Client • Creating user account • Creating Shared folders – Everyone full control (default) • Permissions on shared folders • Client Configuration – Use ‘Client for Microsoft networks’ – Select ‘log on to NT domain’ and type the domain name. • Log in as user on client – Browse the network to see the server and the ADS – If server does not show up, use ‘find computer’ option to detect the newly installed server.
Configuring Client • Creating user account • Creating Shared folders – Everyone full control (default) • Permissions on shared folders • Client Configuration – Use ‘Client for Microsoft networks’ – Select ‘log on to NT domain’ and type the domain name. • Log in as user on client – Browse the network to see the server and the ADS – If server does not show up, use ‘find computer’ option to detect the newly installed server.
 Server Administration • Security vs. Productivity • User accounts – Unique SID (Security ID) across space & time • No two users will ever have the same SID, even it a user is deleted and recreated – Creating, modifying and deleting users • User Groups – Members inherit permissions – Groups can be members of groups • Creating a hierarchy of group permissions
Server Administration • Security vs. Productivity • User accounts – Unique SID (Security ID) across space & time • No two users will ever have the same SID, even it a user is deleted and recreated – Creating, modifying and deleting users • User Groups – Members inherit permissions – Groups can be members of groups • Creating a hierarchy of group permissions
 • Two types: Groups – Built-In • Fixed and cannot be deleted. Has pre-assigned set of permissions. P: 291 • Cannot be made members of other groups – Other groups you create can be added. • To disable – remove all members – User-defined • Administrator definable group objects. • Scope: – Universal » Exits thro’ the org (made of many individual domains) » Can contain members from any other domain – Global » Contains members only from one domain. » Can assign permissions across multiple domains. – Domain local » Exists only within a single domain • Groups – Security – Distribution » Only to maintain distribution lists. Has no security impact. » For email apps (Exchange 2000).
• Two types: Groups – Built-In • Fixed and cannot be deleted. Has pre-assigned set of permissions. P: 291 • Cannot be made members of other groups – Other groups you create can be added. • To disable – remove all members – User-defined • Administrator definable group objects. • Scope: – Universal » Exits thro’ the org (made of many individual domains) » Can contain members from any other domain – Global » Contains members only from one domain. » Can assign permissions across multiple domains. – Domain local » Exists only within a single domain • Groups – Security – Distribution » Only to maintain distribution lists. Has no security impact. » For email apps (Exchange 2000).
 Shared folders • Drives and folder shares – Both NTFS and FAT – Permissions on folder/files within share that are separate from permission on share itself • NTFS only. • Most restrictive permissions apply for shared folders. – R&d group has ‘R’ on folder ‘test’ – R&d has ‘Ch’ on subfolder within test. – Effective for R&d is ‘R’ – most restrictive Users receive permission based on the groups of which they are members and these are cumulative – file systems – Jdoe has ‘R’. Jdoe is member of ‘emp’ with ‘Ch’. – Jdoe’s cumulative is ‘RCh’ • NO ACCESS/DENY overrides everything.
Shared folders • Drives and folder shares – Both NTFS and FAT – Permissions on folder/files within share that are separate from permission on share itself • NTFS only. • Most restrictive permissions apply for shared folders. – R&d group has ‘R’ on folder ‘test’ – R&d has ‘Ch’ on subfolder within test. – Effective for R&d is ‘R’ – most restrictive Users receive permission based on the groups of which they are members and these are cumulative – file systems – Jdoe has ‘R’. Jdoe is member of ‘emp’ with ‘Ch’. – Jdoe’s cumulative is ‘RCh’ • NO ACCESS/DENY overrides everything.
 Permissions • Rules: – When shared folder permissions conflict with file or folder permissions, the most restrictive one always win. – File System Permissions are cumulative, taking into account permissions assigned to users and groups as well as files and folders. – When permission conflict occurs, the NO ACCESS permission always win. • Default: – Everyone has read permissions. – More restrictive rights assigned to sub folders.
Permissions • Rules: – When shared folder permissions conflict with file or folder permissions, the most restrictive one always win. – File System Permissions are cumulative, taking into account permissions assigned to users and groups as well as files and folders. – When permission conflict occurs, the NO ACCESS permission always win. • Default: – Everyone has read permissions. – More restrictive rights assigned to sub folders.
 Mapping Network drives • To view shared folders – Use Network neighborhood or My network places. • To simulate disk drive (mapping) – Right click and choose Map Network drive – DOS Command line • Net use drive_letter: UNC_for_share (universal naming convention) • Net use g: \server_nameshared_folder_name
Mapping Network drives • To view shared folders – Use Network neighborhood or My network places. • To simulate disk drive (mapping) – Right click and choose Map Network drive – DOS Command line • Net use drive_letter: UNC_for_share (universal naming convention) • Net use g: \server_nameshared_folder_name
 What is Printing really. • Print job: – Binary data send from a n/w w/k to a n/w printer. – W/k responsible formatting the data • print drivers • Different from OS to OS – Jobs sent to n/w through captured ports. • N/w client s/w redirects printer port (LPT 1) to the n/w printer. – Jobs stored in queues. • Managed as FIFO. – Print servers • Forwards jobs from print queue to the actual printer. App: -> OS -> print driver (formatting) -> n/w client sends to captured port -> print queue -> print server -> printer.
What is Printing really. • Print job: – Binary data send from a n/w w/k to a n/w printer. – W/k responsible formatting the data • print drivers • Different from OS to OS – Jobs sent to n/w through captured ports. • N/w client s/w redirects printer port (LPT 1) to the n/w printer. – Jobs stored in queues. • Managed as FIFO. – Print servers • Forwards jobs from print queue to the actual printer. App: -> OS -> print driver (formatting) -> n/w client sends to captured port -> print queue -> print server -> printer.
 Windows 2 k 3 printer setup • Add printer to printer folder – Choose sharing • Options: – Printer pooling: • High-throughput requirements. • Set of identical printers, connected to single queue, appearing as one printer. • First available printer services the job. – Permissions from the security tab. • Three types – Print, Manage Printers & Manage Documents – 2 k 3 Server can store print drivers for different OS/platforms. • Distributed and installed the first time client computers use the printer.
Windows 2 k 3 printer setup • Add printer to printer folder – Choose sharing • Options: – Printer pooling: • High-throughput requirements. • Set of identical printers, connected to single queue, appearing as one printer. • First available printer services the job. – Permissions from the security tab. • Three types – Print, Manage Printers & Manage Documents – 2 k 3 Server can store print drivers for different OS/platforms. • Distributed and installed the first time client computers use the printer.
 Backups • Making regular and reliable backups • Not just files – Files have attribute bits that define permissions, owners, backup status
Backups • Making regular and reliable backups • Not just files – Files have attribute bits that define permissions, owners, backup status
 Types of Backup • File/Directory: Selected files and directories • Full / Image: Everything including programs and settings • Shadow: make a copy to another location when the user makes changes • Incremental: – backup includes all the files that have changed since the last backup • Differential: – those files changed since the last full backup, so any changed file appears only on one differential backup. • Daily: – all files modified on a given day
Types of Backup • File/Directory: Selected files and directories • Full / Image: Everything including programs and settings • Shadow: make a copy to another location when the user makes changes • Incremental: – backup includes all the files that have changed since the last backup • Differential: – those files changed since the last full backup, so any changed file appears only on one differential backup. • Daily: – all files modified on a given day
 Backup strategies – Many different Possibilities: • One possible method is Normal full backup once a week and differential every night – Requires only two tapes for restore – Requires more media • Normal Full once a week and incremental every night. – Requires multiple tapes to restore – Requires less media
Backup strategies – Many different Possibilities: • One possible method is Normal full backup once a week and differential every night – Requires only two tapes for restore – Requires more media • Normal Full once a week and incremental every night. – Requires multiple tapes to restore – Requires less media
 Backup in win 2 k 3 • Not the best program. • Third party software preferable – Symantec, Arc. Serve, Backup Exec, etc. – Added functionalities • Manager tape libraries, media pools • Win 2 k 3 program helps – Backup files, restore and prepare for system state rebuilt in case of catastrophes – Backup/restore to/from: • Network, commercial backup sites, Tapes, Optimal • Continuous Data Protection (CDP) – Real time back to another site
Backup in win 2 k 3 • Not the best program. • Third party software preferable – Symantec, Arc. Serve, Backup Exec, etc. – Added functionalities • Manager tape libraries, media pools • Win 2 k 3 program helps – Backup files, restore and prepare for system state rebuilt in case of catastrophes – Backup/restore to/from: • Network, commercial backup sites, Tapes, Optimal • Continuous Data Protection (CDP) – Real time back to another site
 Backup Management Policies • Backup creation policies – What to backup, how frequently, etc. • Restoration and Retention policies – Restoration test, audit – How long to retain • Media Storage Location policies – Legal requirements on how certain type of data is stored
Backup Management Policies • Backup creation policies – What to backup, how frequently, etc. • Restoration and Retention policies – Restoration test, audit – How long to retain • Media Storage Location policies – Legal requirements on how certain type of data is stored
 Server 2003 Services • Important windows 2003 services – DHCP • Defines scope (range) of ip to be allocated – Fixed ip – servers – DHCP – clients, printers • DNS – Create domains (info 472. info. net) and subdomains (accounting. info 472. info. net) – Multiple servers can be used to manage separate portions of the DNS namespace (zone) – Integral part of ADS • RRAS – Access to n/w resources through dialup/ISN using modems (RAS) – RRAS for VPN through secure tunnels
Server 2003 Services • Important windows 2003 services – DHCP • Defines scope (range) of ip to be allocated – Fixed ip – servers – DHCP – clients, printers • DNS – Create domains (info 472. info. net) and subdomains (accounting. info 472. info. net) – Multiple servers can be used to manage separate portions of the DNS namespace (zone) – Integral part of ADS • RRAS – Access to n/w resources through dialup/ISN using modems (RAS) – RRAS for VPN through secure tunnels
 • IIS More win 2 k 3 services – Provides web, FTP, SMTP, NNTP services • Unix/DOS-style ftp sites, web services with front page extensions, mail protocols, NNTP usenet news groups • Cluster services: – Combine servers into clusters • Load balancing – Share tcp/ip based services (web) • Fail over – Share common disk array, server takes over control of services when other server fails • Terminal Services: – Virtual windows machines • Clients connecting and running applications of server as if they were local apps. • One powerful server and software for all users. • Remote management of server
• IIS More win 2 k 3 services – Provides web, FTP, SMTP, NNTP services • Unix/DOS-style ftp sites, web services with front page extensions, mail protocols, NNTP usenet news groups • Cluster services: – Combine servers into clusters • Load balancing – Share tcp/ip based services (web) • Fail over – Share common disk array, server takes over control of services when other server fails • Terminal Services: – Virtual windows machines • Clients connecting and running applications of server as if they were local apps. • One powerful server and software for all users. • Remote management of server


