aac99a6dca4aad62f0214b495ea0bd50.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Wide Area Networks (WANs) Chapter 7
Wide Area Networks (WANs) Chapter 7
 WAN Essentials
WAN Essentials
 Figure 7 -1: Wide Area Networks (WANs) • Wide Area Networks (WANs) – Single networks that connect different sites – So Layer 1 and Layer 2 operation • WAN Purposes – Internet access (Chapter 6) – Link sites within the same corporation – Provide remote access to individuals who are off site 7 -3
Figure 7 -1: Wide Area Networks (WANs) • Wide Area Networks (WANs) – Single networks that connect different sites – So Layer 1 and Layer 2 operation • WAN Purposes – Internet access (Chapter 6) – Link sites within the same corporation – Provide remote access to individuals who are off site 7 -3
 Figure 7 -1: Wide Area Networks (WANs) • WANs are Characterized by High Cost and Low Speeds – High cost per bit transmitted compared to LANs – Consequently, lower speeds (most commonly 128 kbps to a few megabits per second) • This speed usually is aggregate throughput shared by many users – Much slower than LAN speeds (100 Mbps to 1 Gbps to the desktop) 7 -4
Figure 7 -1: Wide Area Networks (WANs) • WANs are Characterized by High Cost and Low Speeds – High cost per bit transmitted compared to LANs – Consequently, lower speeds (most commonly 128 kbps to a few megabits per second) • This speed usually is aggregate throughput shared by many users – Much slower than LAN speeds (100 Mbps to 1 Gbps to the desktop) 7 -4
 Figure 7 -1: Wide Area Networks (WANs) • Carriers – Beyond their physical premises, companies must use the services of regulated carriers for transmission • Companies do not have rights of way to lay wires beyond their premises – Customers are limited to whatever services the carriers provide – Prices for carrier services change abruptly and without technological reasons – Prices and service availability vary widely from country to country 7 -5
Figure 7 -1: Wide Area Networks (WANs) • Carriers – Beyond their physical premises, companies must use the services of regulated carriers for transmission • Companies do not have rights of way to lay wires beyond their premises – Customers are limited to whatever services the carriers provide – Prices for carrier services change abruptly and without technological reasons – Prices and service availability vary widely from country to country 7 -5
 Leased Line Networks
Leased Line Networks
 Leased Lines: Recap • Leased Line Characteristics – Point-to-point circuits – Always on – High speeds: 64 kbps (rare) to several gigabits per second – Leased for a minimum period of time – Usually offered by telephone companies 7 -7
Leased Lines: Recap • Leased Line Characteristics – Point-to-point circuits – Always on – High speeds: 64 kbps (rare) to several gigabits per second – Leased for a minimum period of time – Usually offered by telephone companies 7 -7
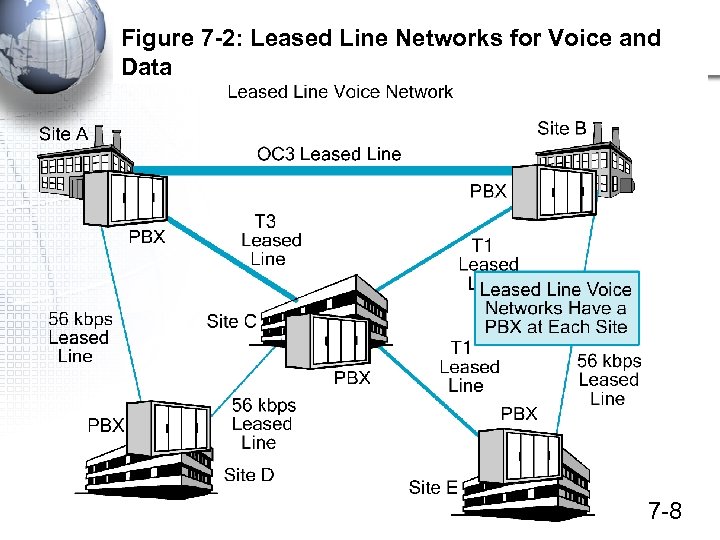 Figure 7 -2: Leased Line Networks for Voice and Data 7 -8
Figure 7 -2: Leased Line Networks for Voice and Data 7 -8
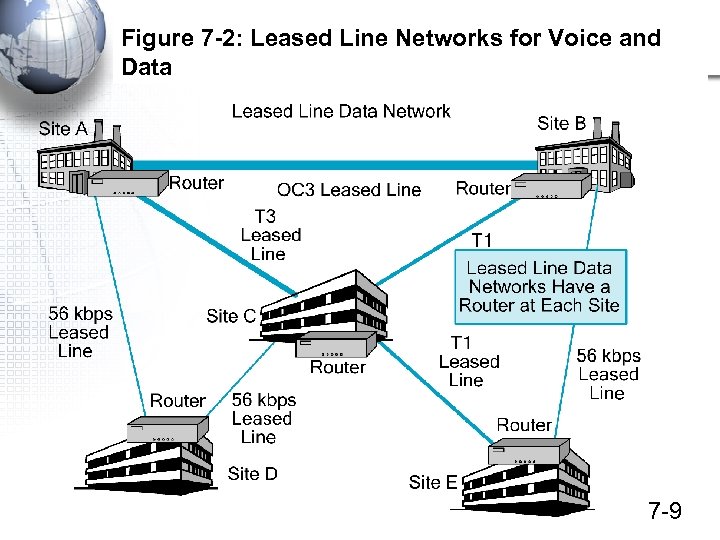 Figure 7 -2: Leased Line Networks for Voice and Data 7 -9
Figure 7 -2: Leased Line Networks for Voice and Data 7 -9
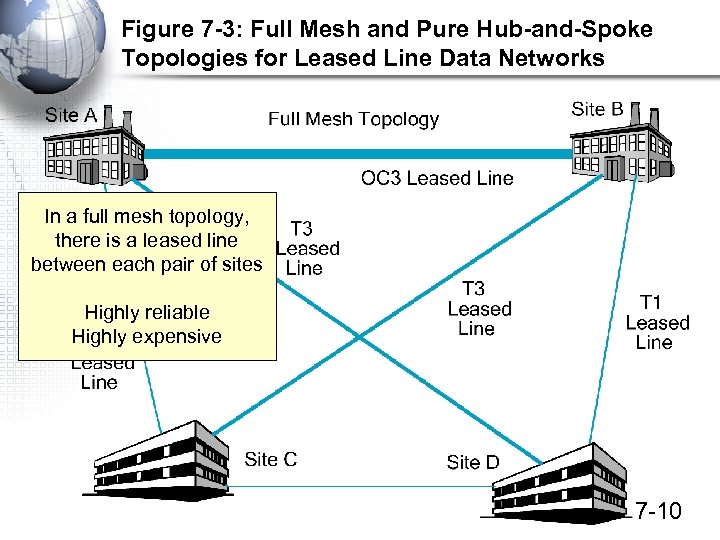 Figure 7 -3: Full Mesh and Pure Hub-and-Spoke Topologies for Leased Line Data Networks In a full mesh topology, there is a leased line between each pair of sites Highly reliable Highly expensive 7 -10
Figure 7 -3: Full Mesh and Pure Hub-and-Spoke Topologies for Leased Line Data Networks In a full mesh topology, there is a leased line between each pair of sites Highly reliable Highly expensive 7 -10
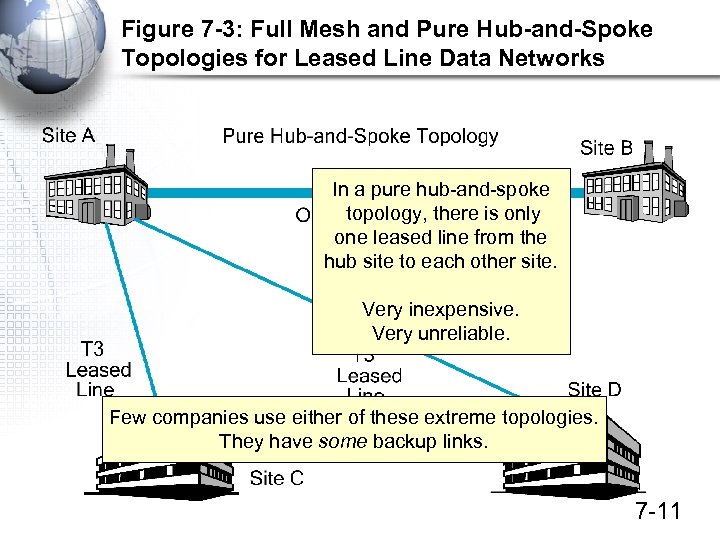 Figure 7 -3: Full Mesh and Pure Hub-and-Spoke Topologies for Leased Line Data Networks In a pure hub-and-spoke topology, there is only one leased line from the hub site to each other site. Very inexpensive. Very unreliable. Few companies use either of these extreme topologies. They have some backup links. 7 -11
Figure 7 -3: Full Mesh and Pure Hub-and-Spoke Topologies for Leased Line Data Networks In a pure hub-and-spoke topology, there is only one leased line from the hub site to each other site. Very inexpensive. Very unreliable. Few companies use either of these extreme topologies. They have some backup links. 7 -11
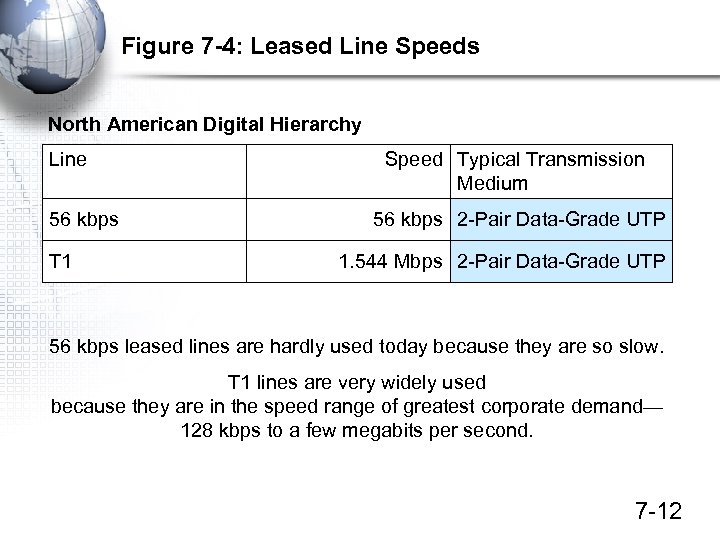 Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds North American Digital Hierarchy Line 56 kbps T 1 Speed Typical Transmission Medium 56 kbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 1. 544 Mbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 56 kbps leased lines are hardly used today because they are so slow. T 1 lines are very widely used because they are in the speed range of greatest corporate demand— 128 kbps to a few megabits per second. 7 -12
Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds North American Digital Hierarchy Line 56 kbps T 1 Speed Typical Transmission Medium 56 kbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 1. 544 Mbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 56 kbps leased lines are hardly used today because they are so slow. T 1 lines are very widely used because they are in the speed range of greatest corporate demand— 128 kbps to a few megabits per second. 7 -12
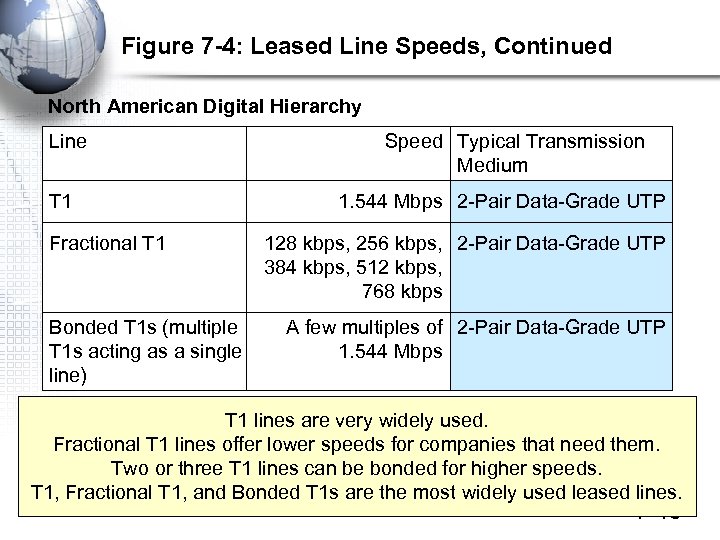 Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds, Continued North American Digital Hierarchy Line T 1 Fractional T 1 Bonded T 1 s (multiple T 1 s acting as a single line) Speed Typical Transmission Medium 1. 544 Mbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 128 kbps, 256 kbps, 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 384 kbps, 512 kbps, 768 kbps A few multiples of 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 1. 544 Mbps T 1 lines are very widely used. Fractional T 1 lines offer lower speeds for companies that need them. Two or three T 1 lines can be bonded for higher speeds. T 1, Fractional T 1, and Bonded T 1 s are the most widely used leased lines. 7 -13
Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds, Continued North American Digital Hierarchy Line T 1 Fractional T 1 Bonded T 1 s (multiple T 1 s acting as a single line) Speed Typical Transmission Medium 1. 544 Mbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 128 kbps, 256 kbps, 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 384 kbps, 512 kbps, 768 kbps A few multiples of 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 1. 544 Mbps T 1 lines are very widely used. Fractional T 1 lines offer lower speeds for companies that need them. Two or three T 1 lines can be bonded for higher speeds. T 1, Fractional T 1, and Bonded T 1 s are the most widely used leased lines. 7 -13
 Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds, Continued North American Digital Hierarchy Line T 1 T 3 Speed Typical Transmission Medium 1. 544 Mbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 44. 736 Mbps Optical Fiber The jump from T 1 to T 3 speeds is extremely large. Few firms need T 3 speeds, and they only need these speeds for some of their leased lines. Some carriers offer fractional T 3 lines to bridge the T 1 -T 3 gap. T 3 lines and all faster leased lines use optical fiber. 7 -14
Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds, Continued North American Digital Hierarchy Line T 1 T 3 Speed Typical Transmission Medium 1. 544 Mbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 44. 736 Mbps Optical Fiber The jump from T 1 to T 3 speeds is extremely large. Few firms need T 3 speeds, and they only need these speeds for some of their leased lines. Some carriers offer fractional T 3 lines to bridge the T 1 -T 3 gap. T 3 lines and all faster leased lines use optical fiber. 7 -14
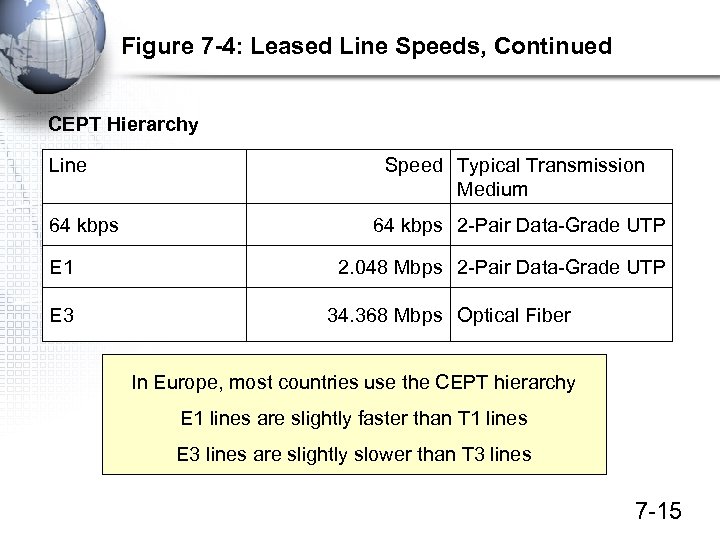 Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds, Continued CEPT Hierarchy Line 64 kbps E 1 E 3 Speed Typical Transmission Medium 64 kbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 2. 048 Mbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 34. 368 Mbps Optical Fiber In Europe, most countries use the CEPT hierarchy E 1 lines are slightly faster than T 1 lines E 3 lines are slightly slower than T 3 lines 7 -15
Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds, Continued CEPT Hierarchy Line 64 kbps E 1 E 3 Speed Typical Transmission Medium 64 kbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 2. 048 Mbps 2 -Pair Data-Grade UTP 34. 368 Mbps Optical Fiber In Europe, most countries use the CEPT hierarchy E 1 lines are slightly faster than T 1 lines E 3 lines are slightly slower than T 3 lines 7 -15
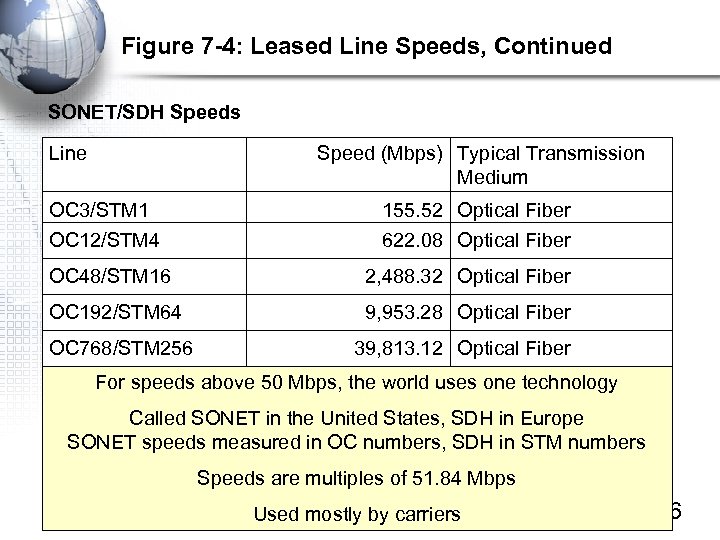 Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds, Continued SONET/SDH Speeds Line Speed (Mbps) Typical Transmission Medium OC 3/STM 1 155. 52 Optical Fiber OC 12/STM 4 622. 08 Optical Fiber OC 48/STM 16 2, 488. 32 Optical Fiber OC 192/STM 64 9, 953. 28 Optical Fiber OC 768/STM 256 39, 813. 12 Optical Fiber For speeds above 50 Mbps, the world uses one technology Called SONET in the United States, SDH in Europe SONET speeds measured in OC numbers, SDH in STM numbers Speeds are multiples of 51. 84 Mbps Used mostly by carriers 7 -16
Figure 7 -4: Leased Line Speeds, Continued SONET/SDH Speeds Line Speed (Mbps) Typical Transmission Medium OC 3/STM 1 155. 52 Optical Fiber OC 12/STM 4 622. 08 Optical Fiber OC 48/STM 16 2, 488. 32 Optical Fiber OC 192/STM 64 9, 953. 28 Optical Fiber OC 768/STM 256 39, 813. 12 Optical Fiber For speeds above 50 Mbps, the world uses one technology Called SONET in the United States, SDH in Europe SONET speeds measured in OC numbers, SDH in STM numbers Speeds are multiples of 51. 84 Mbps Used mostly by carriers 7 -16
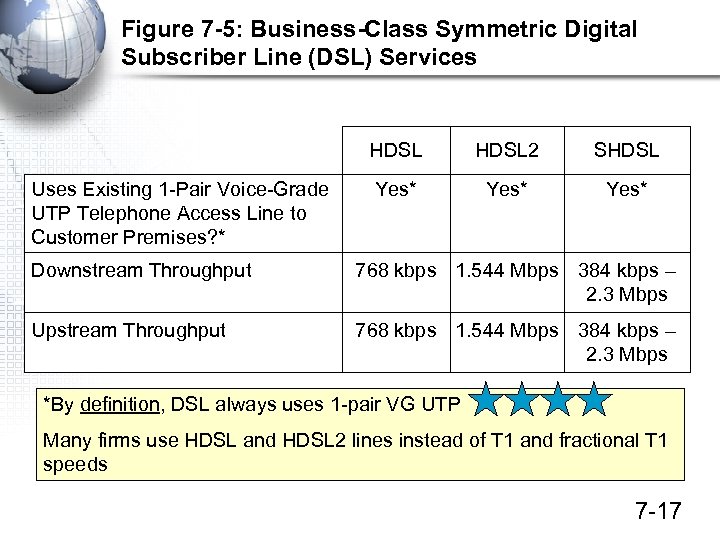 Figure 7 -5: Business-Class Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Services HDSL Uses Existing 1 -Pair Voice-Grade UTP Telephone Access Line to Customer Premises? * HDSL 2 SHDSL Yes* Downstream Throughput 768 kbps 1. 544 Mbps 384 kbps – 2. 3 Mbps Upstream Throughput 768 kbps 1. 544 Mbps 384 kbps – 2. 3 Mbps *By definition, DSL always uses 1 -pair VG UTP Many firms use HDSL and HDSL 2 lines instead of T 1 and fractional T 1 speeds 7 -17
Figure 7 -5: Business-Class Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Services HDSL Uses Existing 1 -Pair Voice-Grade UTP Telephone Access Line to Customer Premises? * HDSL 2 SHDSL Yes* Downstream Throughput 768 kbps 1. 544 Mbps 384 kbps – 2. 3 Mbps Upstream Throughput 768 kbps 1. 544 Mbps 384 kbps – 2. 3 Mbps *By definition, DSL always uses 1 -pair VG UTP Many firms use HDSL and HDSL 2 lines instead of T 1 and fractional T 1 speeds 7 -17
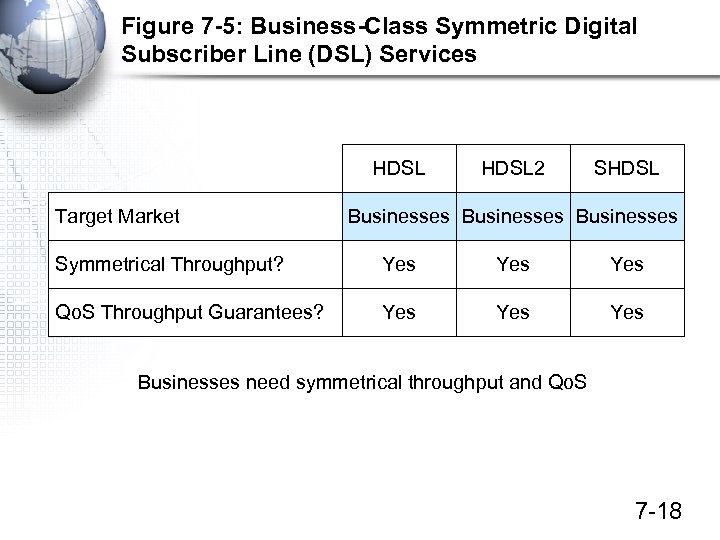 Figure 7 -5: Business-Class Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Services HDSL Target Market HDSL 2 SHDSL Businesses Symmetrical Throughput? Yes Yes Qo. S Throughput Guarantees? Yes Yes Businesses need symmetrical throughput and Qo. S 7 -18
Figure 7 -5: Business-Class Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Services HDSL Target Market HDSL 2 SHDSL Businesses Symmetrical Throughput? Yes Yes Qo. S Throughput Guarantees? Yes Yes Businesses need symmetrical throughput and Qo. S 7 -18
 Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs)
Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs)
 Figure 7 -6: Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) • Recap: Leased Line Data Networks – Use many leased lines, which must span long distances between sites – This is very expensive – Company must design and operate its leased line network • Public Switched Data Networks – Carrier does more of the operational and management work – Total cost of technology, service, and management usually lower than leased line networks 7 -20
Figure 7 -6: Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) • Recap: Leased Line Data Networks – Use many leased lines, which must span long distances between sites – This is very expensive – Company must design and operate its leased line network • Public Switched Data Networks – Carrier does more of the operational and management work – Total cost of technology, service, and management usually lower than leased line networks 7 -20
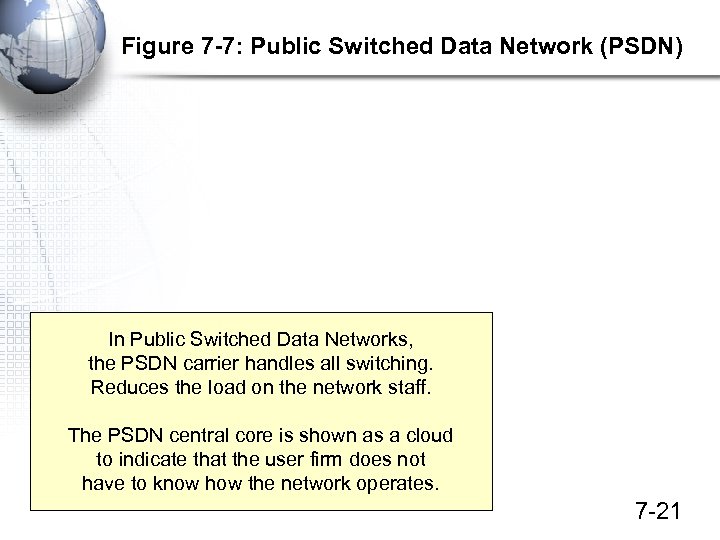 Figure 7 -7: Public Switched Data Network (PSDN) In Public Switched Data Networks, the PSDN carrier handles all switching. Reduces the load on the network staff. The PSDN central core is shown as a cloud to indicate that the user firm does not have to know how the network operates. 7 -21
Figure 7 -7: Public Switched Data Network (PSDN) In Public Switched Data Networks, the PSDN carrier handles all switching. Reduces the load on the network staff. The PSDN central core is shown as a cloud to indicate that the user firm does not have to know how the network operates. 7 -21
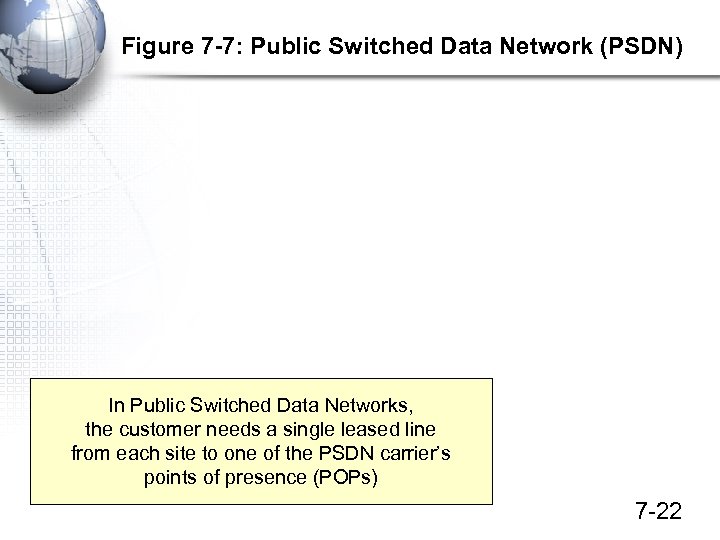 Figure 7 -7: Public Switched Data Network (PSDN) In Public Switched Data Networks, the customer needs a single leased line from each site to one of the PSDN carrier’s points of presence (POPs) 7 -22
Figure 7 -7: Public Switched Data Network (PSDN) In Public Switched Data Networks, the customer needs a single leased line from each site to one of the PSDN carrier’s points of presence (POPs) 7 -22
 Leased Lines in PSDNs • A company has ten sites • It wants to use a PSDN • Will it need leased lines even if it is using a PDSN? • How many leased lines will it need? • Between what two locations will each leased line go? 7 -23
Leased Lines in PSDNs • A company has ten sites • It wants to use a PSDN • Will it need leased lines even if it is using a PDSN? • How many leased lines will it need? • Between what two locations will each leased line go? 7 -23
 Figure 7 -6: PSDNs • Service Level Agreements (SLAs) – Guarantees for services – Throughput, availability, latency, error rate, etc. – An SLA might guarantee a latency of no more than 100 ms 99. 99 percent of the time • SLA guarantees no worse than a certain worst-case level of performance 7 -24
Figure 7 -6: PSDNs • Service Level Agreements (SLAs) – Guarantees for services – Throughput, availability, latency, error rate, etc. – An SLA might guarantee a latency of no more than 100 ms 99. 99 percent of the time • SLA guarantees no worse than a certain worst-case level of performance 7 -24
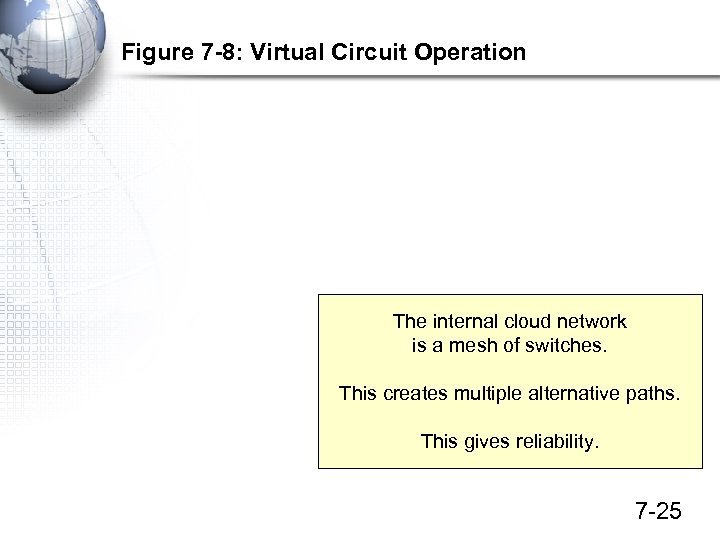 Figure 7 -8: Virtual Circuit Operation The internal cloud network is a mesh of switches. This creates multiple alternative paths. This gives reliability. 7 -25
Figure 7 -8: Virtual Circuit Operation The internal cloud network is a mesh of switches. This creates multiple alternative paths. This gives reliability. 7 -25
 Figure 7 -8: Virtual Circuit Operation Mesh switching is slow because each switch must evaluate available alternative paths and select the best one. This creates expensive switching. 7 -26
Figure 7 -8: Virtual Circuit Operation Mesh switching is slow because each switch must evaluate available alternative paths and select the best one. This creates expensive switching. 7 -26
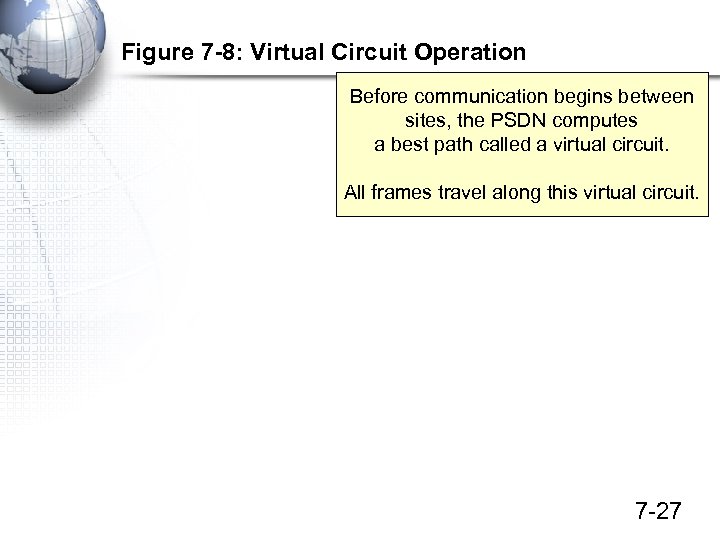 Figure 7 -8: Virtual Circuit Operation Before communication begins between sites, the PSDN computes a best path called a virtual circuit. All frames travel along this virtual circuit. 7 -27
Figure 7 -8: Virtual Circuit Operation Before communication begins between sites, the PSDN computes a best path called a virtual circuit. All frames travel along this virtual circuit. 7 -27
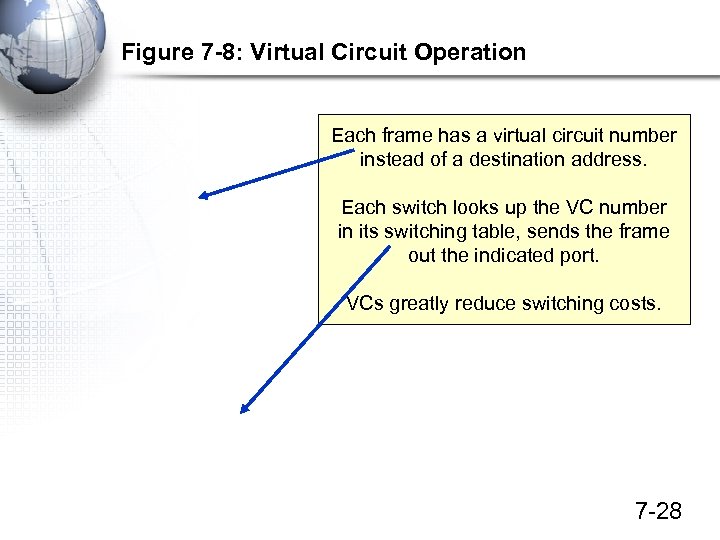 Figure 7 -8: Virtual Circuit Operation Each frame has a virtual circuit number instead of a destination address. Each switch looks up the VC number in its switching table, sends the frame out the indicated port. VCs greatly reduce switching costs. 7 -28
Figure 7 -8: Virtual Circuit Operation Each frame has a virtual circuit number instead of a destination address. Each switch looks up the VC number in its switching table, sends the frame out the indicated port. VCs greatly reduce switching costs. 7 -28
 Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) Frame Relay ATM Metropolitan Area Ethernet Carrier IP Networks
Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) Frame Relay ATM Metropolitan Area Ethernet Carrier IP Networks
 Figure 7 -9: Frame Relay • Frame Relay is the Most Popular PSDN Service Today – 56 kbps to 40 Mbps – This fits the range of greatest corporate demand for WAN speed – Usually less expensive than a network of leased lines – Grew rapidly in the 1990 s, to be come equal to leased line WANs in terms of market share (about 40%) – Carriers have raised prices, reducing growth 7 -30
Figure 7 -9: Frame Relay • Frame Relay is the Most Popular PSDN Service Today – 56 kbps to 40 Mbps – This fits the range of greatest corporate demand for WAN speed – Usually less expensive than a network of leased lines – Grew rapidly in the 1990 s, to be come equal to leased line WANs in terms of market share (about 40%) – Carriers have raised prices, reducing growth 7 -30
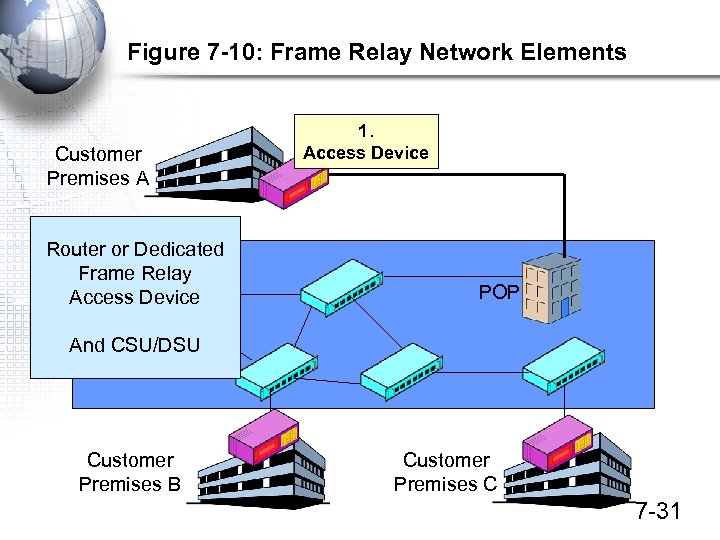 Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements Customer Premises A Router or Dedicated Switch Frame Relay Access Device 1. Access Device POP And CSU/DSU Customer Premises B Customer Premises C 7 -31
Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements Customer Premises A Router or Dedicated Switch Frame Relay Access Device 1. Access Device POP And CSU/DSU Customer Premises B Customer Premises C 7 -31
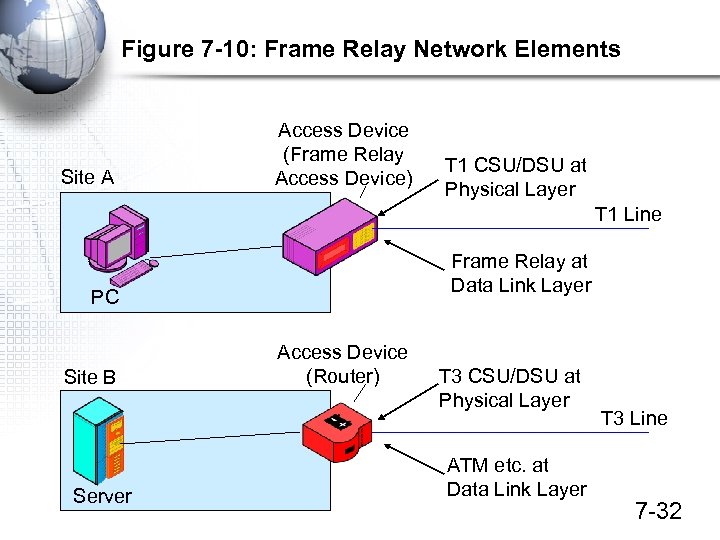 Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements Site A Access Device (Frame Relay Access Device) T 1 CSU/DSU at Physical Layer T 1 Line Frame Relay at Data Link Layer PC Site B Server Access Device (Router) T 3 CSU/DSU at Physical Layer ATM etc. at Data Link Layer T 3 Line 7 -32
Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements Site A Access Device (Frame Relay Access Device) T 1 CSU/DSU at Physical Layer T 1 Line Frame Relay at Data Link Layer PC Site B Server Access Device (Router) T 3 CSU/DSU at Physical Layer ATM etc. at Data Link Layer T 3 Line 7 -32
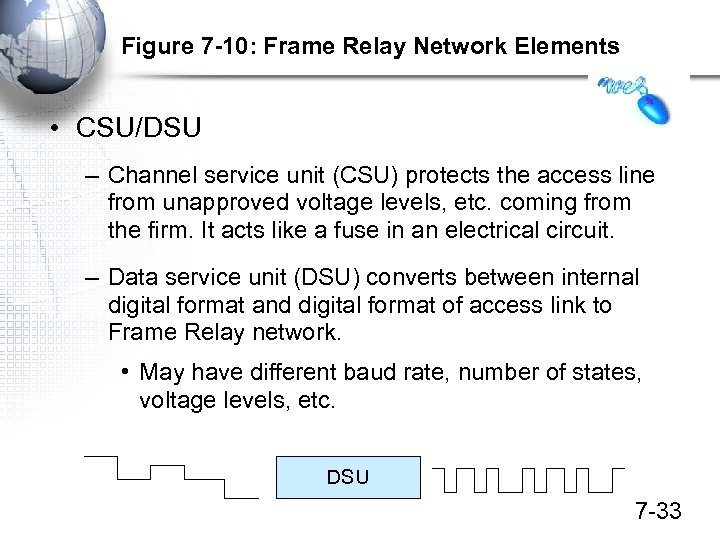 Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements • CSU/DSU – Channel service unit (CSU) protects the access line from unapproved voltage levels, etc. coming from the firm. It acts like a fuse in an electrical circuit. – Data service unit (DSU) converts between internal digital format and digital format of access link to Frame Relay network. • May have different baud rate, number of states, voltage levels, etc. DSU 7 -33
Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements • CSU/DSU – Channel service unit (CSU) protects the access line from unapproved voltage levels, etc. coming from the firm. It acts like a fuse in an electrical circuit. – Data service unit (DSU) converts between internal digital format and digital format of access link to Frame Relay network. • May have different baud rate, number of states, voltage levels, etc. DSU 7 -33
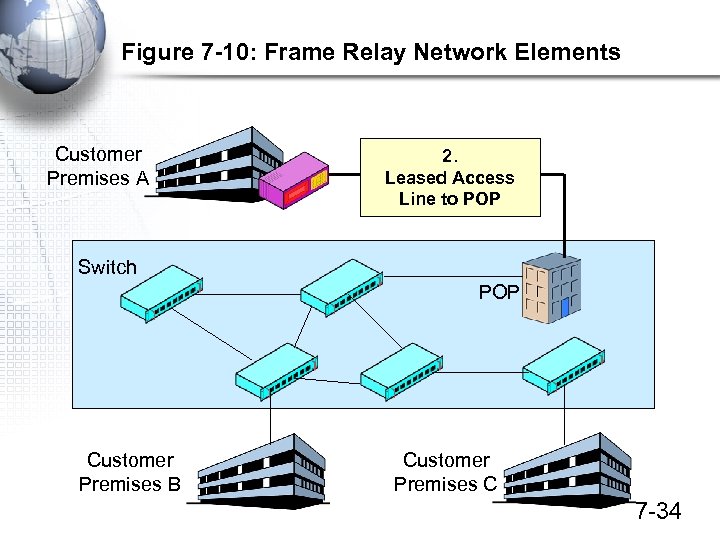 Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements Customer Premises A 2. Leased Access Line to POP Switch POP Customer Premises B Customer Premises C 7 -34
Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements Customer Premises A 2. Leased Access Line to POP Switch POP Customer Premises B Customer Premises C 7 -34
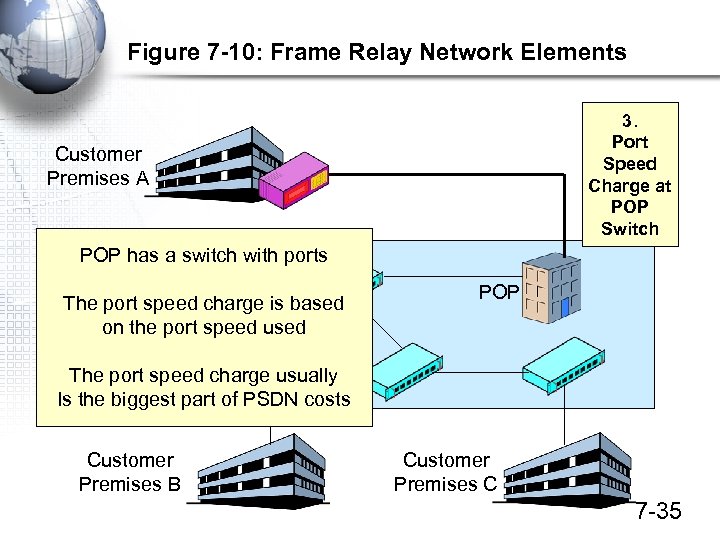 Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements 3. Port Speed Charge at POP Switch Customer Premises A POP has a switch with ports Switch The port speed charge is based on the port speed used POP The port speed charge usually Is the biggest part of PSDN costs Customer Premises B Customer Premises C 7 -35
Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements 3. Port Speed Charge at POP Switch Customer Premises A POP has a switch with ports Switch The port speed charge is based on the port speed used POP The port speed charge usually Is the biggest part of PSDN costs Customer Premises B Customer Premises C 7 -35
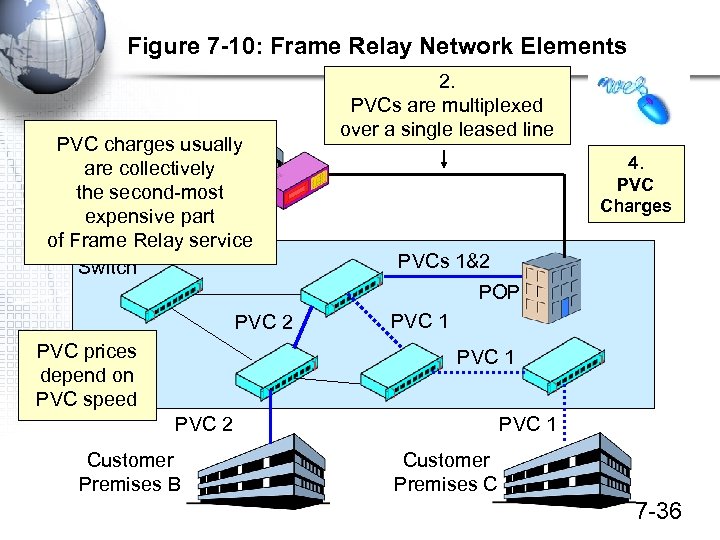 Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements PVC charges usually Customer are collectively Premises A the second-most expensive part of Frame Relay service Switch 2. PVCs are multiplexed over a single leased line 4. PVC Charges PVCs 1&2 POP PVC 2 PVC prices depend on PVC speed PVC 1 PVC 2 Customer Premises B PVC 1 Customer Premises C 7 -36
Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements PVC charges usually Customer are collectively Premises A the second-most expensive part of Frame Relay service Switch 2. PVCs are multiplexed over a single leased line 4. PVC Charges PVCs 1&2 POP PVC 2 PVC prices depend on PVC speed PVC 1 PVC 2 Customer Premises B PVC 1 Customer Premises C 7 -36
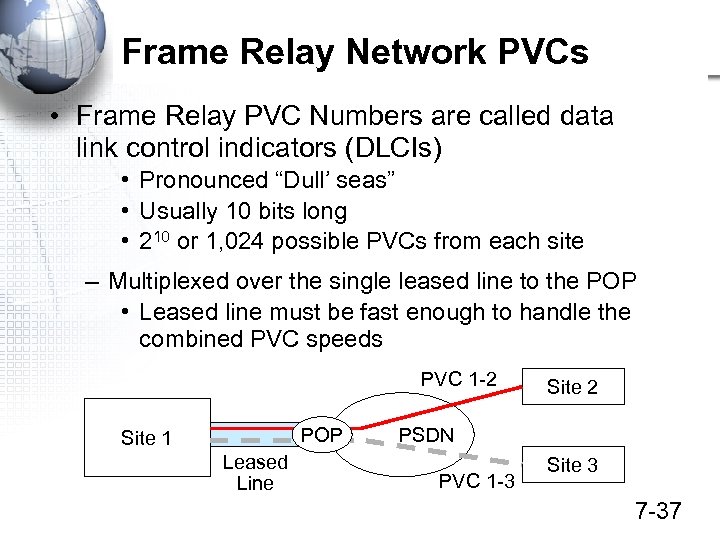 Frame Relay Network PVCs • Frame Relay PVC Numbers are called data link control indicators (DLCIs) • Pronounced “Dull’ seas” • Usually 10 bits long • 210 or 1, 024 possible PVCs from each site – Multiplexed over the single leased line to the POP • Leased line must be fast enough to handle the combined PVC speeds PVC 1 -2 POP Site 1 Leased Line Site 2 PSDN PVC 1 -3 Site 3 7 -37
Frame Relay Network PVCs • Frame Relay PVC Numbers are called data link control indicators (DLCIs) • Pronounced “Dull’ seas” • Usually 10 bits long • 210 or 1, 024 possible PVCs from each site – Multiplexed over the single leased line to the POP • Leased line must be fast enough to handle the combined PVC speeds PVC 1 -2 POP Site 1 Leased Line Site 2 PSDN PVC 1 -3 Site 3 7 -37
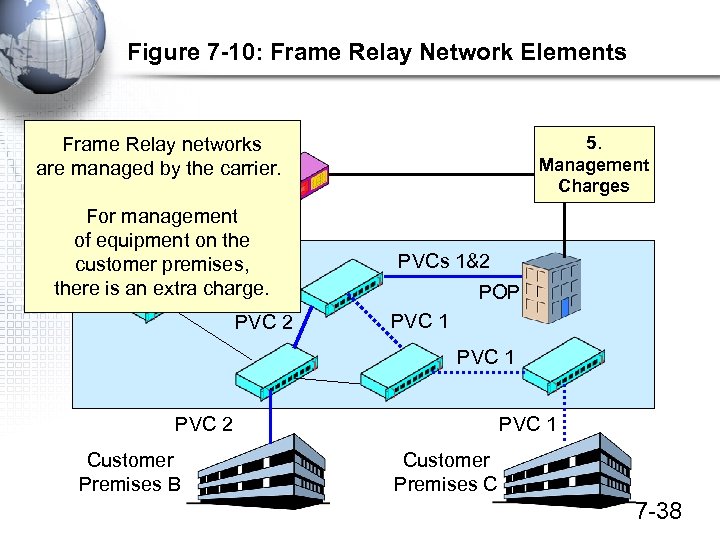 Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements 5. Management Charges Frame Relay networks Customer are managed by the carrier. Premises A For management of equipment on the customer premises, Switch there is an extra charge. PVC 2 PVCs 1&2 POP PVC 1 PVC 2 Customer Premises B PVC 1 Customer Premises C 7 -38
Figure 7 -10: Frame Relay Network Elements 5. Management Charges Frame Relay networks Customer are managed by the carrier. Premises A For management of equipment on the customer premises, Switch there is an extra charge. PVC 2 PVCs 1&2 POP PVC 1 PVC 2 Customer Premises B PVC 1 Customer Premises C 7 -38
 Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) Frame Relay ATM Metropolitan Area Ethernet Carrier IP Networks
Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) Frame Relay ATM Metropolitan Area Ethernet Carrier IP Networks
 Figure 7 -11: ATM • ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) is a another PSDN • ATM Provides Speeds Greater than Frame Relay Can Provide – One megabit per second to several gigabits per second • Not a Competitor for Frame Relay – Most carriers offer both FR and ATM – Sell based on the customer’s speed range needs – May even interconnect the two services 7 -40
Figure 7 -11: ATM • ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) is a another PSDN • ATM Provides Speeds Greater than Frame Relay Can Provide – One megabit per second to several gigabits per second • Not a Competitor for Frame Relay – Most carriers offer both FR and ATM – Sell based on the customer’s speed range needs – May even interconnect the two services 7 -40
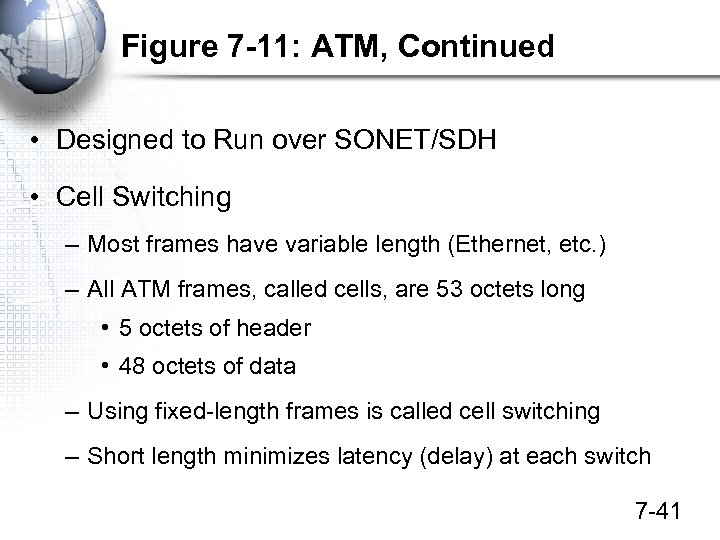 Figure 7 -11: ATM, Continued • Designed to Run over SONET/SDH • Cell Switching – Most frames have variable length (Ethernet, etc. ) – All ATM frames, called cells, are 53 octets long • 5 octets of header • 48 octets of data – Using fixed-length frames is called cell switching – Short length minimizes latency (delay) at each switch 7 -41
Figure 7 -11: ATM, Continued • Designed to Run over SONET/SDH • Cell Switching – Most frames have variable length (Ethernet, etc. ) – All ATM frames, called cells, are 53 octets long • 5 octets of header • 48 octets of data – Using fixed-length frames is called cell switching – Short length minimizes latency (delay) at each switch 7 -41
 Figure 7 -11: ATM, Continued • ATM Has Strong Quality of Service (Qo. S) Guarantees for Voice Traffic – Not surprising because ATM was created for the PSTN’s transport core • For pure data transmission, however, ATM usually does NOT provide Qo. S guarantees!! • Manageability, Complexity, and Cost – Very strong management tools for large networks (designed for the PSTN) – Too complex and expensive for most firms – Not thriving in the marketplace 7 -42
Figure 7 -11: ATM, Continued • ATM Has Strong Quality of Service (Qo. S) Guarantees for Voice Traffic – Not surprising because ATM was created for the PSTN’s transport core • For pure data transmission, however, ATM usually does NOT provide Qo. S guarantees!! • Manageability, Complexity, and Cost – Very strong management tools for large networks (designed for the PSTN) – Too complex and expensive for most firms – Not thriving in the marketplace 7 -42
 Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) Frame Relay ATM Metropolitan Area Ethernet Carrier IP Networks
Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) Frame Relay ATM Metropolitan Area Ethernet Carrier IP Networks
 Figure 7 -12: Metropolitan Area Ethernet • Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) – MANs are carrier networks that are limited to a large urban area and its suburbs – Metropolitan area Ethernet (metro Ethernet) is available for this niche – New but growing very rapidly 7 -44
Figure 7 -12: Metropolitan Area Ethernet • Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) – MANs are carrier networks that are limited to a large urban area and its suburbs – Metropolitan area Ethernet (metro Ethernet) is available for this niche – New but growing very rapidly 7 -44
 Figure 7 -12: Metro Ethernet, Cont. • Attractions of Metropolitan Area Ethernet – Very Low Prices Compared to Frame Relay and ATM – High Speeds: Tens of megabits per second – Familiar Technology for the Networking Staff • No need to learn a new technology – Rapid Provisioning • Setting up service to a customer • Changing the service (adding more capacity) 7 -45
Figure 7 -12: Metro Ethernet, Cont. • Attractions of Metropolitan Area Ethernet – Very Low Prices Compared to Frame Relay and ATM – High Speeds: Tens of megabits per second – Familiar Technology for the Networking Staff • No need to learn a new technology – Rapid Provisioning • Setting up service to a customer • Changing the service (adding more capacity) 7 -45
 Figure 7 -12: Metro Ethernet, Cont. • Carrier Class Service – Basic Ethernet standards are insufficient for large wide area networks – Quality of service and management tools must be developed – The goal: provide carrier class services that are sufficient for customers 7 -46
Figure 7 -12: Metro Ethernet, Cont. • Carrier Class Service – Basic Ethernet standards are insufficient for large wide area networks – Quality of service and management tools must be developed – The goal: provide carrier class services that are sufficient for customers 7 -46
 Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) Frame Relay ATM Metropolitan Area Ethernet Carrier IP Networks
Public Switched Data Networks (PSDNs) Frame Relay ATM Metropolitan Area Ethernet Carrier IP Networks
 Carrier IP Networks • Some Carriers Now Offer IP Networks – Essentially, private internets – Operate at Layer 3 instead of at Layers 1 and 2, like Frame Relay, ATM, and Ethernet – Use TCP/IP standards – Operated entirely by the carrier, so no overload in the Internet backbone from connected carries – Access is not open to everyone, so security is enhanced – Also called Private IP Networks 7 -48
Carrier IP Networks • Some Carriers Now Offer IP Networks – Essentially, private internets – Operate at Layer 3 instead of at Layers 1 and 2, like Frame Relay, ATM, and Ethernet – Use TCP/IP standards – Operated entirely by the carrier, so no overload in the Internet backbone from connected carries – Access is not open to everyone, so security is enhanced – Also called Private IP Networks 7 -48
 Carrier IP Networks • Other Advantages – Allow companies to use familiar IP technology – Mature management and control standards – Carrier can manage everything if the customer desires that (and will pay) – Offer Vo. IP as well as data—convergence to reduce technology and management costs • Growing Rapidly – Carriers may soon force Frame Relay users to switch to carrier IP service 7 -49
Carrier IP Networks • Other Advantages – Allow companies to use familiar IP technology – Mature management and control standards – Carrier can manage everything if the customer desires that (and will pay) – Offer Vo. IP as well as data—convergence to reduce technology and management costs • Growing Rapidly – Carriers may soon force Frame Relay users to switch to carrier IP service 7 -49
 Virtual Private Network (VPNs)
Virtual Private Network (VPNs)
 Figure 7 -13: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) • Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) – Virtual private networks (VPN) use the Internet with added security for data transmission • The Attractions of Internet Transmission – Lowest cost per bit transmitted – Universal access to communication partners (Everybody uses the Internet) 7 -51
Figure 7 -13: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) • Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) – Virtual private networks (VPN) use the Internet with added security for data transmission • The Attractions of Internet Transmission – Lowest cost per bit transmitted – Universal access to communication partners (Everybody uses the Internet) 7 -51
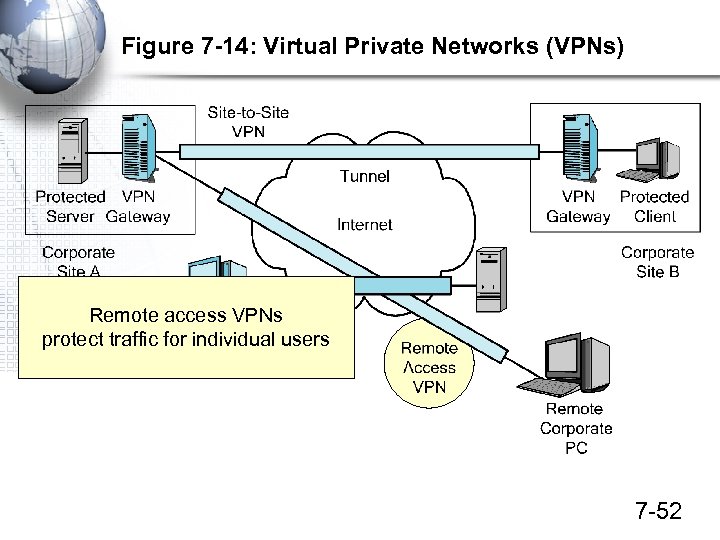 Figure 7 -14: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Remote access VPNs protect traffic for individual users 7 -52
Figure 7 -14: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Remote access VPNs protect traffic for individual users 7 -52
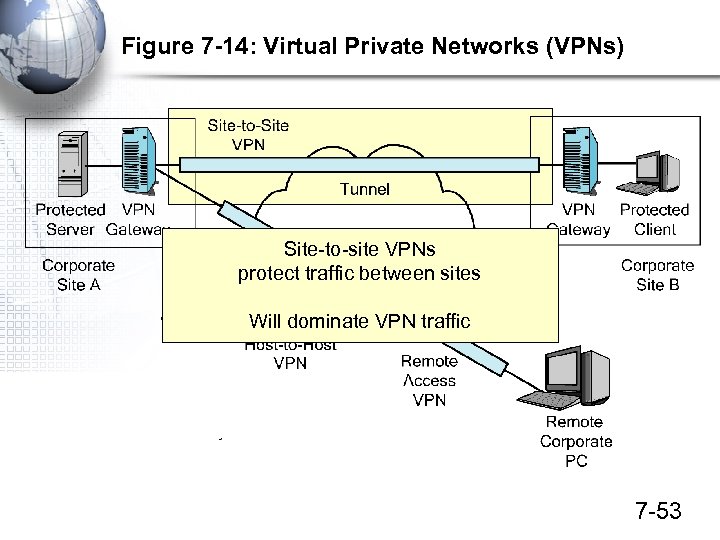 Figure 7 -14: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Site-to-site VPNs protect traffic between sites Will dominate VPN traffic 7 -53
Figure 7 -14: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) Site-to-site VPNs protect traffic between sites Will dominate VPN traffic 7 -53
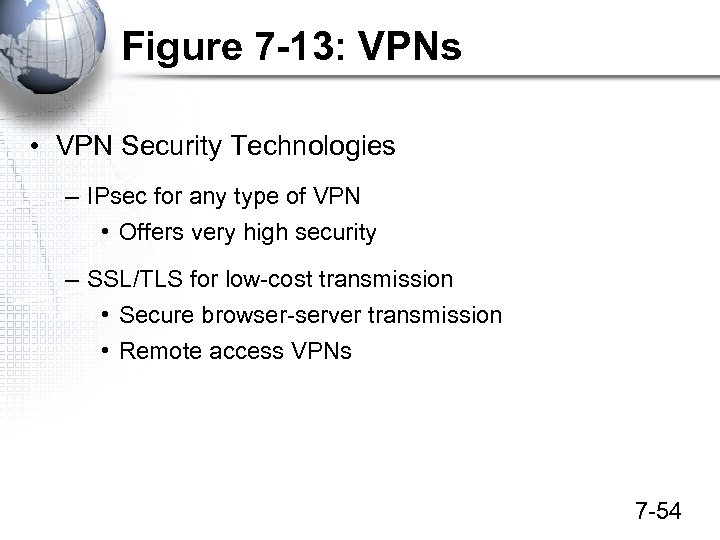 Figure 7 -13: VPNs • VPN Security Technologies – IPsec for any type of VPN • Offers very high security – SSL/TLS for low-cost transmission • Secure browser-server transmission • Remote access VPNs 7 -54
Figure 7 -13: VPNs • VPN Security Technologies – IPsec for any type of VPN • Offers very high security – SSL/TLS for low-cost transmission • Secure browser-server transmission • Remote access VPNs 7 -54
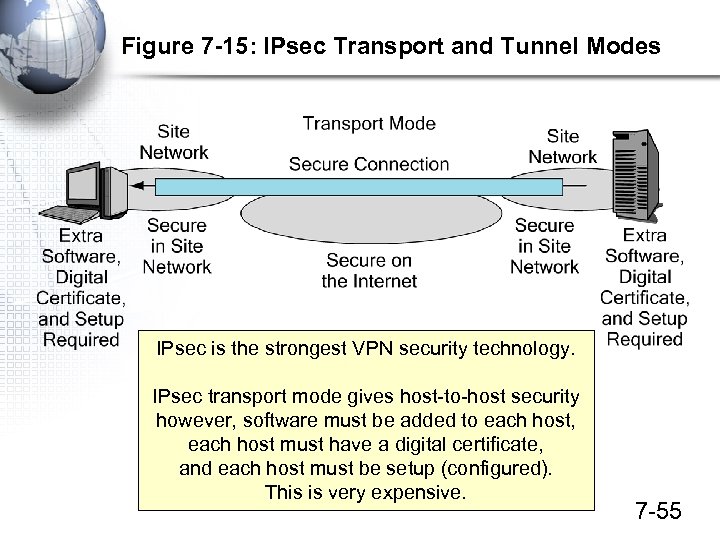 Figure 7 -15: IPsec Transport and Tunnel Modes IPsec is the strongest VPN security technology. IPsec transport mode gives host-to-host security however, software must be added to each host, each host must have a digital certificate, and each host must be setup (configured). This is very expensive. 7 -55
Figure 7 -15: IPsec Transport and Tunnel Modes IPsec is the strongest VPN security technology. IPsec transport mode gives host-to-host security however, software must be added to each host, each host must have a digital certificate, and each host must be setup (configured). This is very expensive. 7 -55
 Figure 7 -15: IPsec Transport and Tunnel Modes In IPsec tunnel mode, there is only security over the Internet between IPsec gateways at each site No security within sites, but no software, setup or certificates on the individual hosts Inexpensive compared to transport mode 7 -56
Figure 7 -15: IPsec Transport and Tunnel Modes In IPsec tunnel mode, there is only security over the Internet between IPsec gateways at each site No security within sites, but no software, setup or certificates on the individual hosts Inexpensive compared to transport mode 7 -56
 Figure 7 -16: SSL/TLS for Browser–Webserver Communication IPsec works at the internet layer. SSL/TLS works at the transport layer. Only protects SSL/TLS-aware applications. This primarily means HTTP. SSL/TLS is built into every browser and webserver. 7 -57
Figure 7 -16: SSL/TLS for Browser–Webserver Communication IPsec works at the internet layer. SSL/TLS works at the transport layer. Only protects SSL/TLS-aware applications. This primarily means HTTP. SSL/TLS is built into every browser and webserver. 7 -57
 Figure 7 -17: SSL/TLS with a Gateway SSL/TLS gateways turn SSL/TLS into a remote access VPN technology, Gives access to multiple internal webservers. Can “webify” some other applications for viewing on browsers as webpages. Can give access to other servers. 7 -58
Figure 7 -17: SSL/TLS with a Gateway SSL/TLS gateways turn SSL/TLS into a remote access VPN technology, Gives access to multiple internal webservers. Can “webify” some other applications for viewing on browsers as webpages. Can give access to other servers. 7 -58
 SSL/TLS Versus IPsec • SSL/TLS – Limited to remote access VPNs – Only moderately strong security – Harder to use with many applications • IPsec – – Offers stronger security than SSL/TLS Both remote access and site-to-site VPNs Costly to set up in the stronger transport mode Economically attractive for site-to-site VPNs in tunnel mode 7 -59
SSL/TLS Versus IPsec • SSL/TLS – Limited to remote access VPNs – Only moderately strong security – Harder to use with many applications • IPsec – – Offers stronger security than SSL/TLS Both remote access and site-to-site VPNs Costly to set up in the stronger transport mode Economically attractive for site-to-site VPNs in tunnel mode 7 -59
 Figure 7 -18: Market Perspective • Rapid Growth – VPNs – Carrier IP networks – Metro Ethernet • Stagnant – Leased line networks – Frame Relay – ATM 7 -60
Figure 7 -18: Market Perspective • Rapid Growth – VPNs – Carrier IP networks – Metro Ethernet • Stagnant – Leased line networks – Frame Relay – ATM 7 -60


