 Why Surface Weather Maps?
Why Surface Weather Maps?
 First Surface Weather Map
First Surface Weather Map
 The Telegraphic Communication Revolution
The Telegraphic Communication Revolution
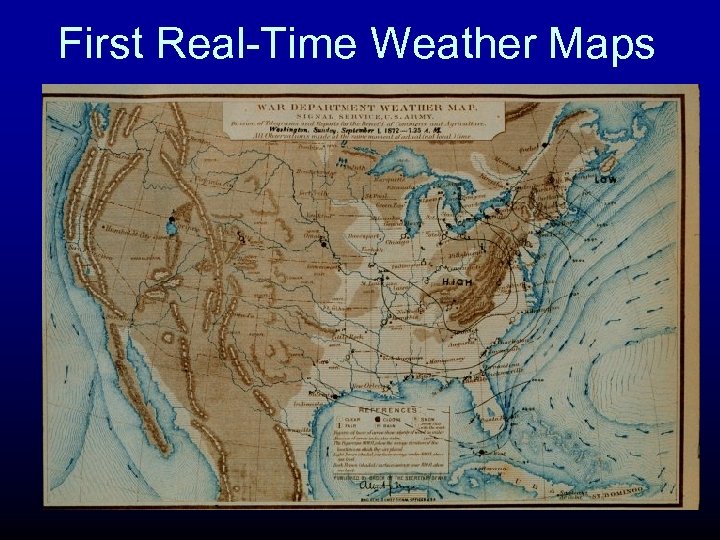 First Real-Time Weather Maps
First Real-Time Weather Maps
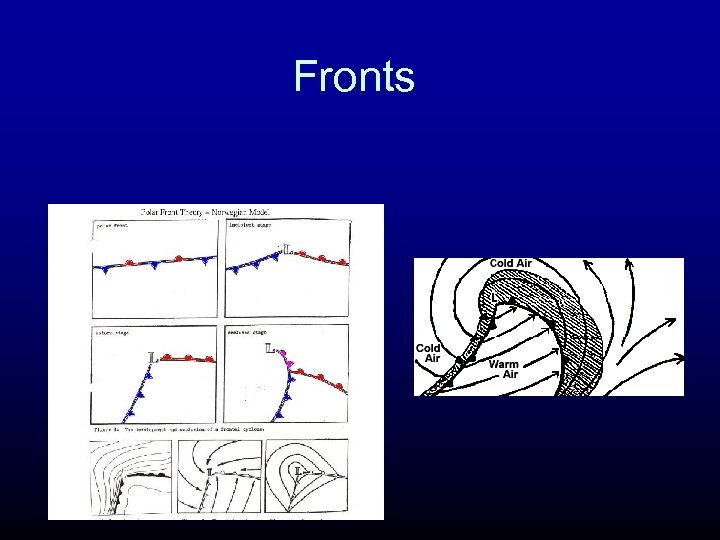 Fronts
Fronts
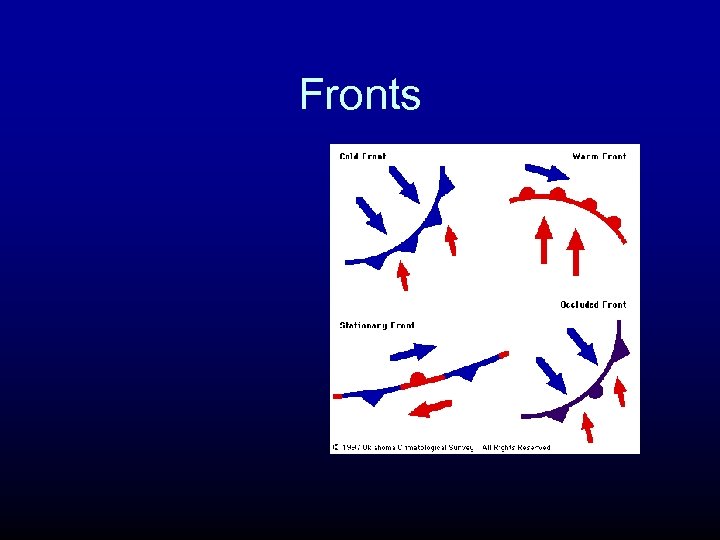 Fronts
Fronts
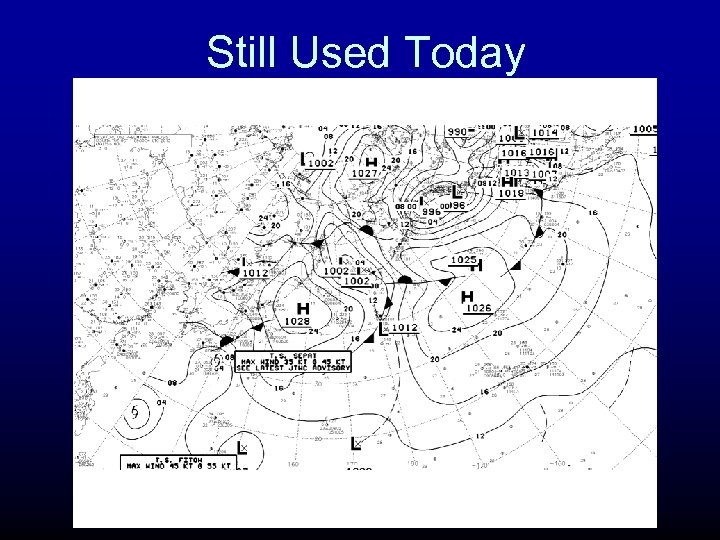 Still Used Today
Still Used Today
 What is on surface charts?
What is on surface charts?
 Surface Observations are plotted using the station model
Surface Observations are plotted using the station model
 Station Model
Station Model
 Practice
Practice
 Pressure Change over the Past 3 hr
Pressure Change over the Past 3 hr
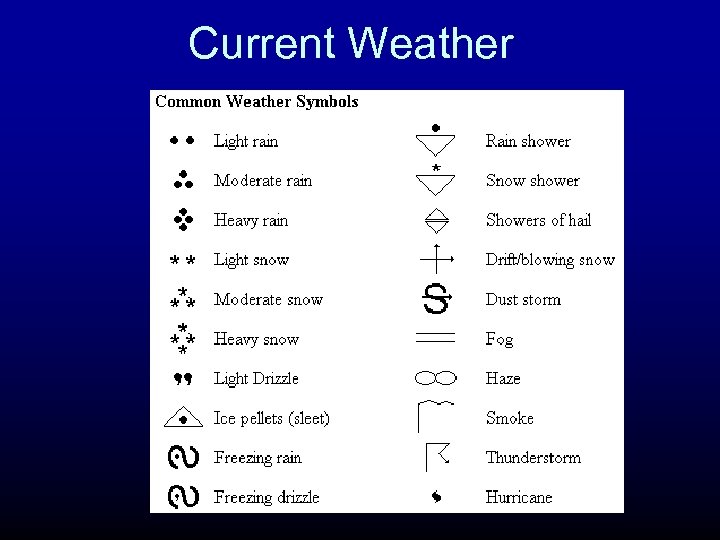 Current Weather
Current Weather
 Sky Coverage
Sky Coverage
 Sky Obscured…you are in cloud
Sky Obscured…you are in cloud
 Wind Pennants
Wind Pennants
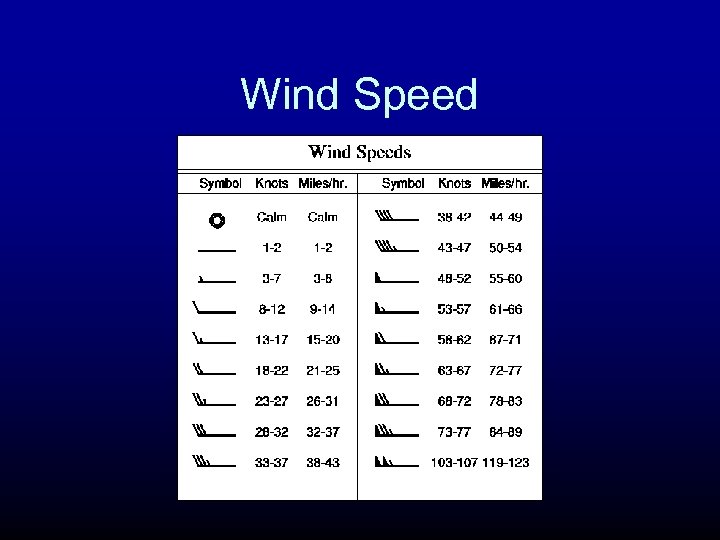 Wind Speed
Wind Speed
 You need to be able to read the station models
You need to be able to read the station models
 What kind of observations are plotted on surface charts?
What kind of observations are plotted on surface charts?
 Drifting Buoys
Drifting Buoys
 Isobars of sea level pressure are found on station map
Isobars of sea level pressure are found on station map
 Why use sea level pressure rather than station pressure— the pressure at the elevation of the barometer?
Why use sea level pressure rather than station pressure— the pressure at the elevation of the barometer?
 Terrain effects on pressure would swamp the meteorological signal
Terrain effects on pressure would swamp the meteorological signal
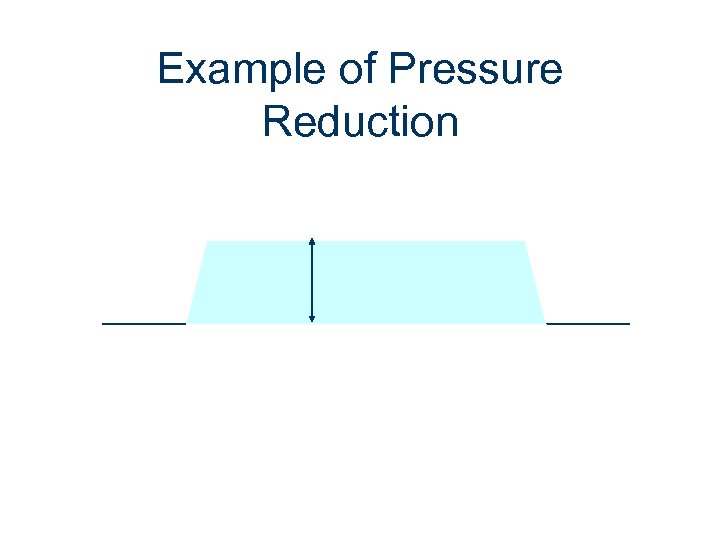 Example of Pressure Reduction
Example of Pressure Reduction
 Pressure Reduction
Pressure Reduction
 Once the analysis is done, put on H’s and L’s
Once the analysis is done, put on H’s and L’s
 Winds and pressure
Winds and pressure
 Will explain why in a few weeks
Will explain why in a few weeks
 In the northern hemisphere winds tend to blow countclockwise around lows and clockwise around highs (opposite in the southern hemisphere)
In the northern hemisphere winds tend to blow countclockwise around lows and clockwise around highs (opposite in the southern hemisphere)
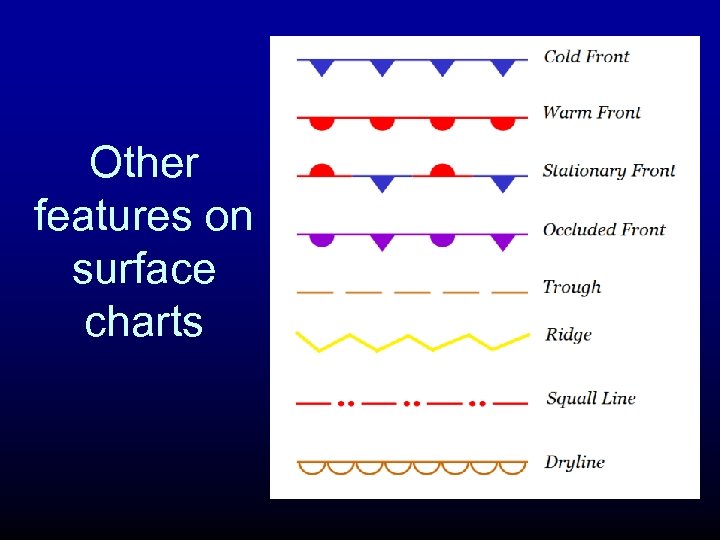 Other features on surface charts
Other features on surface charts
 What are fronts?
What are fronts?
 Definition A front is a boundary between air of relatively uniform warm air and a zone in which temperatures cools rapidly
Definition A front is a boundary between air of relatively uniform warm air and a zone in which temperatures cools rapidly
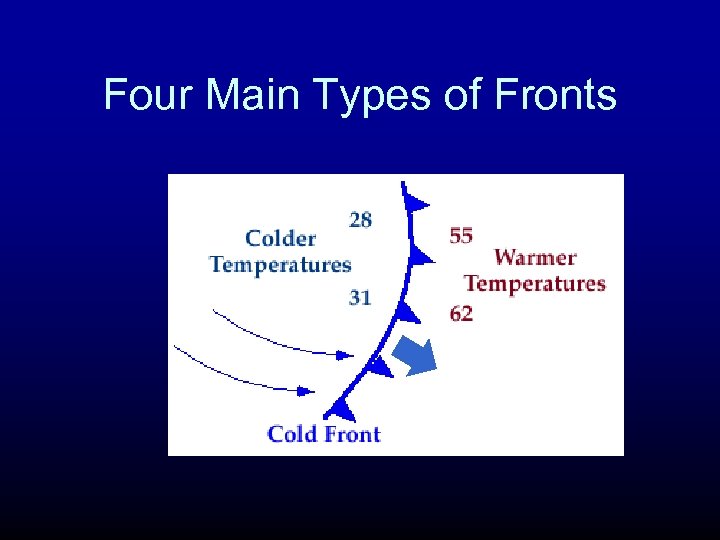 Four Main Types of Fronts
Four Main Types of Fronts
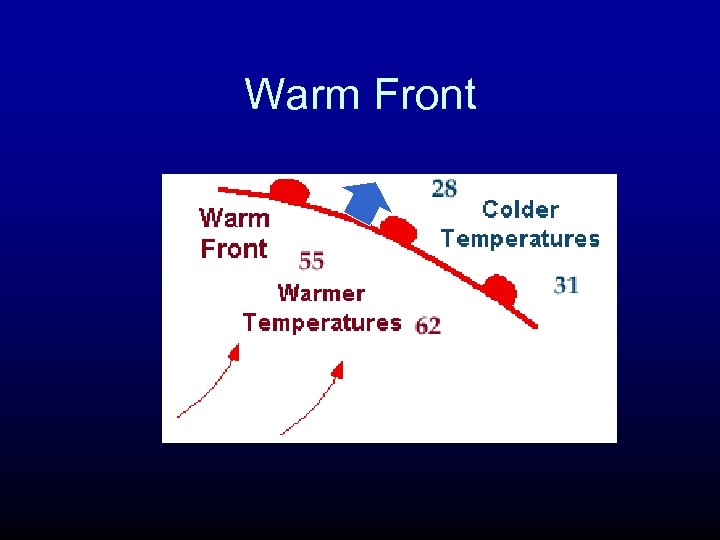 Warm Front
Warm Front
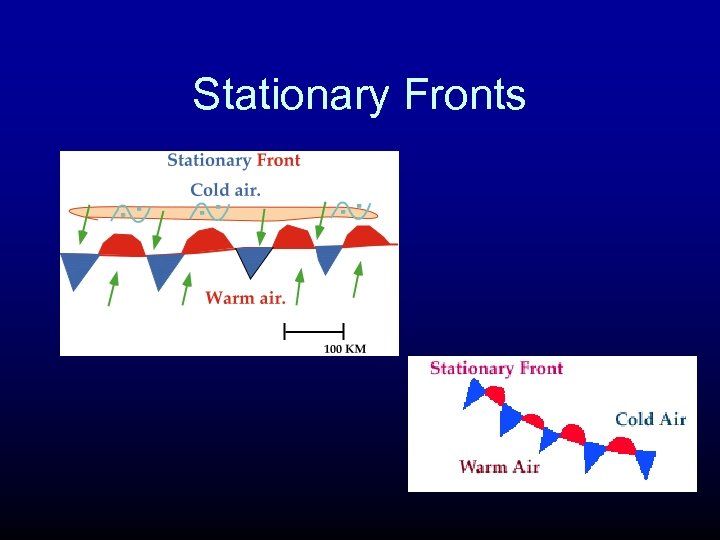 Stationary Fronts
Stationary Fronts
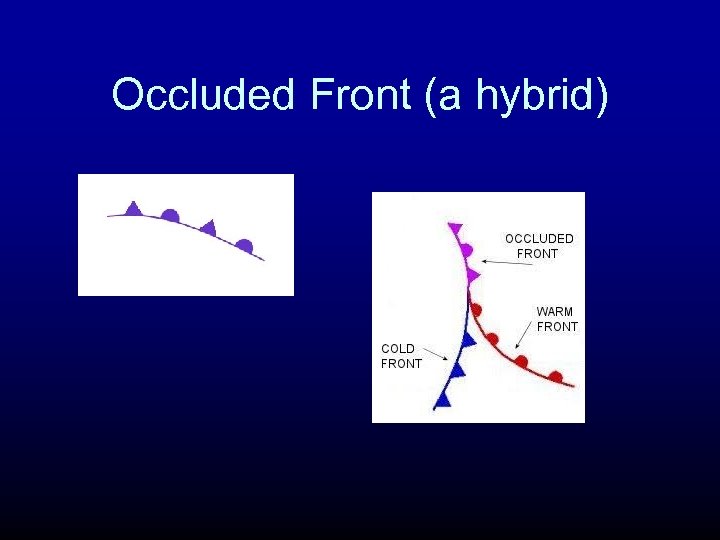 Occluded Front (a hybrid)
Occluded Front (a hybrid)