dc63374df92a18e2b0150b3e69634e99.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Why Quantitative I-131 http: //www. med. harvard. edu/physics/Why. Quantitative. I-131_2. ppt Robert E. Zimmerman Joint Program in Nuclear Medicine Harvard Medical School Brigham & Women’s Hospital Dana Farber Cancer Institute The Children Hospital Boston MA
Why Quantitative I-131 http: //www. med. harvard. edu/physics/Why. Quantitative. I-131_2. ppt Robert E. Zimmerman Joint Program in Nuclear Medicine Harvard Medical School Brigham & Women’s Hospital Dana Farber Cancer Institute The Children Hospital Boston MA
 Reason
Reason
 I-131 • “Magic Bullet” – Very specific for thyroid mets – Usually cleared rapidly with 2 -3 day Teff – 8 day T 1/2 leaves time for to deposit its energy – 364 kev -ray allows imaging
I-131 • “Magic Bullet” – Very specific for thyroid mets – Usually cleared rapidly with 2 -3 day Teff – 8 day T 1/2 leaves time for to deposit its energy – 364 kev -ray allows imaging
 Thyroid ablation • Very effective • Doses to 6000 -20000 rads to the thyroid • Minimal dose to other organs
Thyroid ablation • Very effective • Doses to 6000 -20000 rads to the thyroid • Minimal dose to other organs
 But there are complications in some cases • • Mets in lung and resultant dose to lung tissue Dose to blood marrow Dose to salivary glands Other? – Complex distribution
But there are complications in some cases • • Mets in lung and resultant dose to lung tissue Dose to blood marrow Dose to salivary glands Other? – Complex distribution
 Goals • Limit dose to marrow to < 200 rads • Limit dose to lungs to < 2000 rads • Estimate dose to bladder, salivary glands, other organs with significant uptake
Goals • Limit dose to marrow to < 200 rads • Limit dose to lungs to < 2000 rads • Estimate dose to bladder, salivary glands, other organs with significant uptake
 Selected History • Benua 1962 based on MSK experience gives these guidelines to limit bone marrow dose : – < 200 rads to blood – < 120 m. Ci retained at 48 hr (80 m. Ci with diffuse lung mets)
Selected History • Benua 1962 based on MSK experience gives these guidelines to limit bone marrow dose : – < 200 rads to blood – < 120 m. Ci retained at 48 hr (80 m. Ci with diffuse lung mets)
 I-131 can be imaged quantitatively but. . – scatter – penetration – sensitivity – attenuation – time …all complicate the task of getting meaningful numbers
I-131 can be imaged quantitatively but. . – scatter – penetration – sensitivity – attenuation – time …all complicate the task of getting meaningful numbers
 Generally accepted procedure • Dual-head planar gamma camera imaging w/standard source • ROI for selected organs • Obtain geometric mean of Ant and Post counts • Measure attenuation using gamma camera and area source (e. g. Co-57 sheet source) • Obtain blood samples to estimate marrow dose • Follow long enough (e. g 4 days) • Use MIRD dose calculation techniques
Generally accepted procedure • Dual-head planar gamma camera imaging w/standard source • ROI for selected organs • Obtain geometric mean of Ant and Post counts • Measure attenuation using gamma camera and area source (e. g. Co-57 sheet source) • Obtain blood samples to estimate marrow dose • Follow long enough (e. g 4 days) • Use MIRD dose calculation techniques
 Resource intensive • Imaging: – ~3 hr first day • Attenuation scan • 2 hr pre void scan + blood • 4 hr post void scan + blood – 1 hr day 2, 3 and 4 + bloods • • Blood samples to count ROI to draw and calculate Dosimetry calculation Dose plan
Resource intensive • Imaging: – ~3 hr first day • Attenuation scan • 2 hr pre void scan + blood • 4 hr post void scan + blood – 1 hr day 2, 3 and 4 + bloods • • Blood samples to count ROI to draw and calculate Dosimetry calculation Dose plan
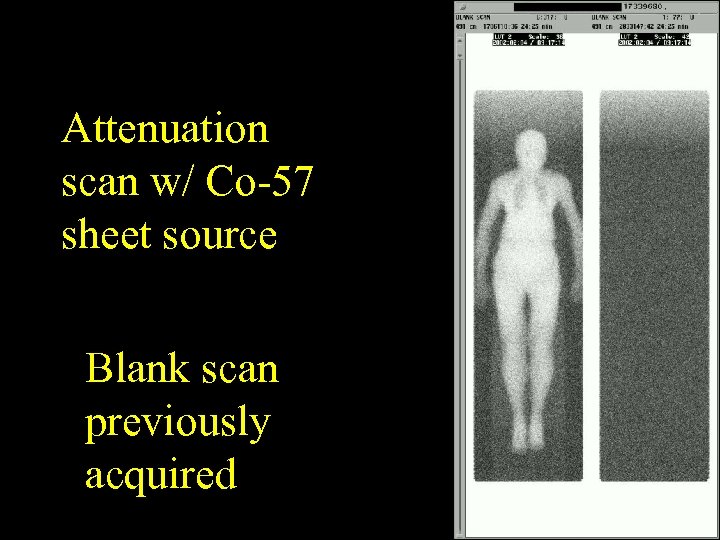 Attenuation scan w/ Co-57 sheet source Blank scan previously acquired
Attenuation scan w/ Co-57 sheet source Blank scan previously acquired
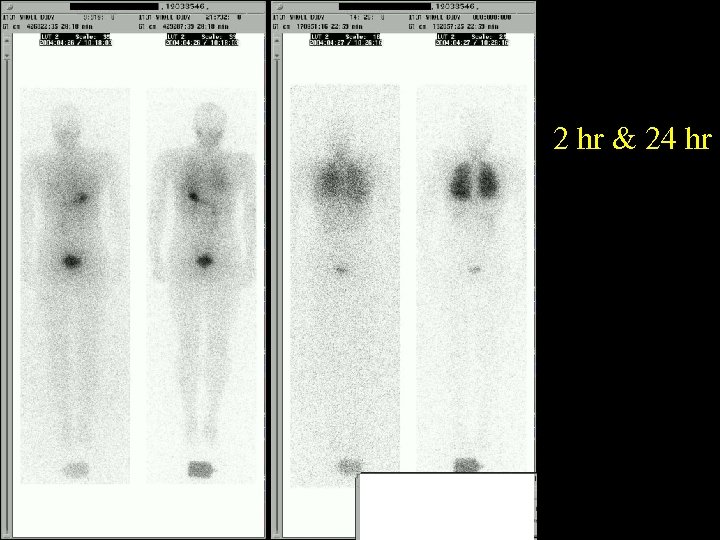 2 hr & 24 hr
2 hr & 24 hr
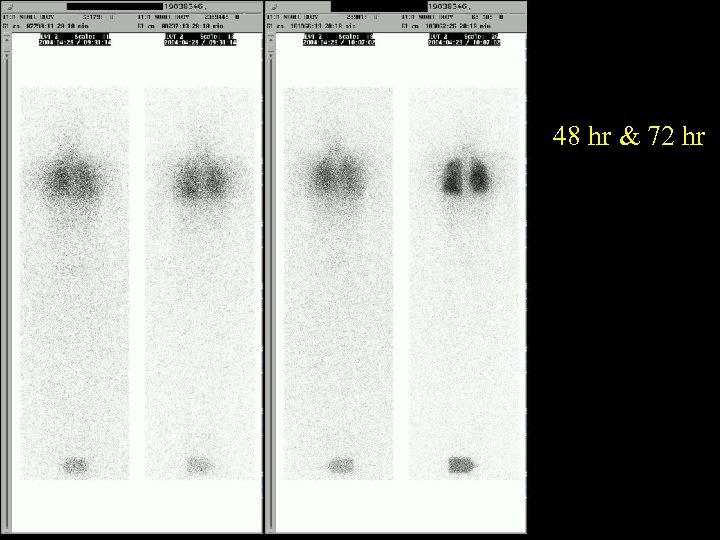 48 hr & 72 hr
48 hr & 72 hr
 Aids • MIRD – tables, models, data • MIRDOSE 1, 2, 3 by Stabin • RADAR by Stabin (http: //www. doseinfo-radar. com/RADARHome. html) • Olinda by Stabin • Nucli. Dose Erwin & Groch (includes MIRDOSE 2) • Gamma camera ROI tools • Spreadsheets
Aids • MIRD – tables, models, data • MIRDOSE 1, 2, 3 by Stabin • RADAR by Stabin (http: //www. doseinfo-radar. com/RADARHome. html) • Olinda by Stabin • Nucli. Dose Erwin & Groch (includes MIRDOSE 2) • Gamma camera ROI tools • Spreadsheets
 MIRD Medical Internal Radiation Dose Subcommittee of the Society of Nuclear Medicine
MIRD Medical Internal Radiation Dose Subcommittee of the Society of Nuclear Medicine
 • MIRD Publication - MIRD Dose Estimate Report #19: Radiation Absorbed Dose Estimates from 18 F-FDG • MIRD Publication - MIRD Supplement 1999: Foreword, MIRD Perspective, Pamphlets 14 Revised, 15, 16, and 17 • MIRD Publication - MIRD Dose Estimate Report #13: Radiation Absorbed Dose from Technetium-99 m-labeled bone imaging agents • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #11: S, Absorbed Dose per Unit Cumulated Activity for Selected Radionuclides and Organs (PART 1) • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #11: S, Absorbed Dose per Unit Cumulated Activity for Selected Radionuclides and Organs (PART 2) • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #11: S, Absorbed Dose per Unit Cumulated Activity for Selected Radionuclides and Organs (PART 3) • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #13: Specific Absorbed Fractions for Photon Sources Uniformly Distributed in the Heart Chambers and Heart Wall of Heterogeneous Phantom • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #5 Revised: Estimates of Absorbed Fractions for Monoenergetic Photon Sources Uniformly Distributed in Various Organs of a Heterogeneous Phantom
• MIRD Publication - MIRD Dose Estimate Report #19: Radiation Absorbed Dose Estimates from 18 F-FDG • MIRD Publication - MIRD Supplement 1999: Foreword, MIRD Perspective, Pamphlets 14 Revised, 15, 16, and 17 • MIRD Publication - MIRD Dose Estimate Report #13: Radiation Absorbed Dose from Technetium-99 m-labeled bone imaging agents • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #11: S, Absorbed Dose per Unit Cumulated Activity for Selected Radionuclides and Organs (PART 1) • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #11: S, Absorbed Dose per Unit Cumulated Activity for Selected Radionuclides and Organs (PART 2) • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #11: S, Absorbed Dose per Unit Cumulated Activity for Selected Radionuclides and Organs (PART 3) • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #13: Specific Absorbed Fractions for Photon Sources Uniformly Distributed in the Heart Chambers and Heart Wall of Heterogeneous Phantom • MIRD Publication - MIRD Pamphlet #5 Revised: Estimates of Absorbed Fractions for Monoenergetic Photon Sources Uniformly Distributed in Various Organs of a Heterogeneous Phantom
 MIRDOSE • A series (v 1, v 2, v 3) of software programs that ran on PCs circa 1985 -1998 by Michael Stabin then of Oak Ridge Associated Universities and Oak Ridge National Laboratories • Eventually FDA stopped distribution of the software since it was a medical device!
MIRDOSE • A series (v 1, v 2, v 3) of software programs that ran on PCs circa 1985 -1998 by Michael Stabin then of Oak Ridge Associated Universities and Oak Ridge National Laboratories • Eventually FDA stopped distribution of the software since it was a medical device!
 RADAR Web site RAdiation Dose Assessment Resource By Michael Stabin and colleagues Difficult to use for individual dosimetry.
RADAR Web site RAdiation Dose Assessment Resource By Michael Stabin and colleagues Difficult to use for individual dosimetry.
 OLINDA/EXM Organ Level INternal Dose Assessment/EXponential Modeling By Michael Stabin of Vanderbilt. Has FDA 510(k) exemption
OLINDA/EXM Organ Level INternal Dose Assessment/EXponential Modeling By Michael Stabin of Vanderbilt. Has FDA 510(k) exemption
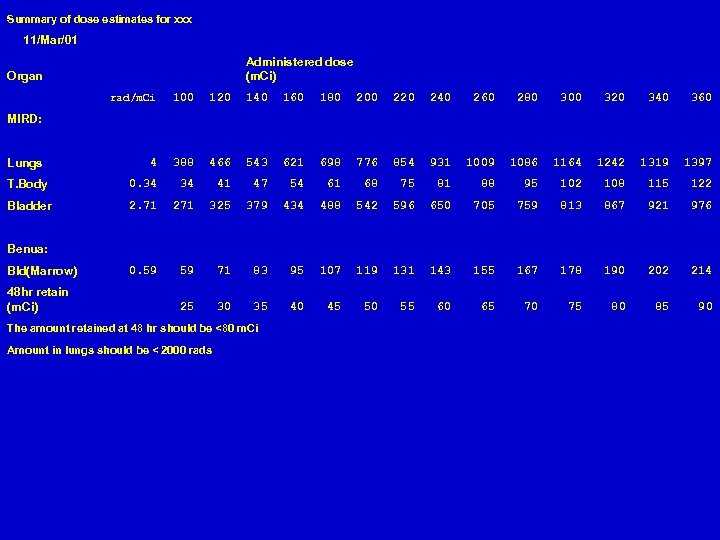 Summary of dose estimates for xxx 11/Mar/01 Administered dose (m. Ci) Organ rad/m. Ci 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260 280 300 320 340 360 4 388 466 543 621 698 776 854 931 1009 1086 1164 1242 1319 1397 T. Body 0. 34 34 41 47 54 61 68 75 81 88 95 102 108 115 122 Bladder 2. 71 271 325 379 434 488 542 596 650 705 759 813 867 921 976 0. 59 59 71 83 95 107 119 131 143 155 167 178 190 202 214 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 MIRD: Lungs Benua: Bld(Marrow) 48 hr retain (m. Ci) The amount retained at 48 hr should be <80 m. Ci Amount in lungs should be < 2000 rads
Summary of dose estimates for xxx 11/Mar/01 Administered dose (m. Ci) Organ rad/m. Ci 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260 280 300 320 340 360 4 388 466 543 621 698 776 854 931 1009 1086 1164 1242 1319 1397 T. Body 0. 34 34 41 47 54 61 68 75 81 88 95 102 108 115 122 Bladder 2. 71 271 325 379 434 488 542 596 650 705 759 813 867 921 976 0. 59 59 71 83 95 107 119 131 143 155 167 178 190 202 214 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 MIRD: Lungs Benua: Bld(Marrow) 48 hr retain (m. Ci) The amount retained at 48 hr should be <80 m. Ci Amount in lungs should be < 2000 rads
 Brigham & Women's Hospital Division of Nuclear Medicine Whole Body Dosimetry Study with 131 I Indications: Quantitative estimate of 131 I in metastases or thyroid remnants requiring complete dosimetry to protect critical organs. Patient Preparation: This exam should not be performed if the patient has had any iodine medications which will interfere with the study or any iodinated contrast media within the last 6 weeks. TSH level should be evaluated prior to radiopharmaceutical administration. Levels should be greater than 50 u. U/ml. The patient should be fasting for 1 hour prior to ingestion of the radiopharmaceutical and should not eat for at least 30 min. following. Radiopharmaceutical: 131 I solution Dose: 3 m. Ci Written directive form must be signed by Attending Physician prior to administration. Route of Administration: oral
Brigham & Women's Hospital Division of Nuclear Medicine Whole Body Dosimetry Study with 131 I Indications: Quantitative estimate of 131 I in metastases or thyroid remnants requiring complete dosimetry to protect critical organs. Patient Preparation: This exam should not be performed if the patient has had any iodine medications which will interfere with the study or any iodinated contrast media within the last 6 weeks. TSH level should be evaluated prior to radiopharmaceutical administration. Levels should be greater than 50 u. U/ml. The patient should be fasting for 1 hour prior to ingestion of the radiopharmaceutical and should not eat for at least 30 min. following. Radiopharmaceutical: 131 I solution Dose: 3 m. Ci Written directive form must be signed by Attending Physician prior to administration. Route of Administration: oral
 Imaging: 1. WB Blank scan with 57 Co sheet source: Use acquisition protocol BWH WB Co-57 Blank Scan. Prior to radiopharmaceutical administration a 57 Co WB blank scan must be performed. Mark the table for patient re-positioning for all imaging sessions by placing a piece of tape on the table corresponding to the location of the top of the patient’s head. Place 57 Co sheet source on detector 2 of e. cam or MS 2 with high energy collimators in place. Use both detectors and peak for 57 Co. Do blank scan with no patient on table starting where top of head will be located to end of feet. 2. WB transmission scan is be performed next. Use acquisition protocol BWH Co-57 Transmission Scan. Leave the 57 Co sheet source on detector 2. Place the patient on table at location of tape. Do anterior WB sweep from head to toe for 20 min. (8 cm/min). 3. Administer the radiopharmaceutical. The patient must not void between administration and first imaging session. 4. Prepare standard of 50 -100 Ci of I-131 in 250 ml tissue culture flask. Label flask with name, time, date and activity. 5. Use acquisition protocol BWH I 131 WB scan. Perform WB sweep anterior/posterior 60 -120 minutes post administration of I-131. Scan for 20 min. (8 cm/min) and include standard in field of view (e. g. between feet or lower legs). 6. Repeat WB sweeps at 24, 48 and 72 hours post administration of 131 I. Increase imaging time at later time points to 40 min (16 cm/min) and include standard in all imaging sessions. 7. Spot views of head and neck may be required by Nuclear Med physician. 8. Draw 2 cc of blood at each imaging session, excluding transmission session. Record name of patient, time and date of blood drawing on each tube and on patient jacket. All samples will be counted on the last day of imaging. 9. Processing using Nuclidose on ICON/IDL system will be done by the physicist. ROIs corresponding to each source organ will be drawn. Time activity curves will be obtained. Dose calculations will be performed to obtain rads/m. Ci. Adapted from CH protocol REZ 5 Dec 2000
Imaging: 1. WB Blank scan with 57 Co sheet source: Use acquisition protocol BWH WB Co-57 Blank Scan. Prior to radiopharmaceutical administration a 57 Co WB blank scan must be performed. Mark the table for patient re-positioning for all imaging sessions by placing a piece of tape on the table corresponding to the location of the top of the patient’s head. Place 57 Co sheet source on detector 2 of e. cam or MS 2 with high energy collimators in place. Use both detectors and peak for 57 Co. Do blank scan with no patient on table starting where top of head will be located to end of feet. 2. WB transmission scan is be performed next. Use acquisition protocol BWH Co-57 Transmission Scan. Leave the 57 Co sheet source on detector 2. Place the patient on table at location of tape. Do anterior WB sweep from head to toe for 20 min. (8 cm/min). 3. Administer the radiopharmaceutical. The patient must not void between administration and first imaging session. 4. Prepare standard of 50 -100 Ci of I-131 in 250 ml tissue culture flask. Label flask with name, time, date and activity. 5. Use acquisition protocol BWH I 131 WB scan. Perform WB sweep anterior/posterior 60 -120 minutes post administration of I-131. Scan for 20 min. (8 cm/min) and include standard in field of view (e. g. between feet or lower legs). 6. Repeat WB sweeps at 24, 48 and 72 hours post administration of 131 I. Increase imaging time at later time points to 40 min (16 cm/min) and include standard in all imaging sessions. 7. Spot views of head and neck may be required by Nuclear Med physician. 8. Draw 2 cc of blood at each imaging session, excluding transmission session. Record name of patient, time and date of blood drawing on each tube and on patient jacket. All samples will be counted on the last day of imaging. 9. Processing using Nuclidose on ICON/IDL system will be done by the physicist. ROIs corresponding to each source organ will be drawn. Time activity curves will be obtained. Dose calculations will be performed to obtain rads/m. Ci. Adapted from CH protocol REZ 5 Dec 2000


