46da230943c7c65edf3328b429319154.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Why immunotherapy fails ? Stephen Durham Imperial College and Royal Brompton Hospital, London UK
Why immunotherapy fails ? Stephen Durham Imperial College and Royal Brompton Hospital, London UK
 Declaration • Research funding, consultancy and lecture fees from ALK Abello • Lecture fees from Allergy Therapeutics
Declaration • Research funding, consultancy and lecture fees from ALK Abello • Lecture fees from Allergy Therapeutics
 Why immunotherapy fails ? • • • wrong set up wrong patient wrong allergen(s) wrong dose wrong duration
Why immunotherapy fails ? • • • wrong set up wrong patient wrong allergen(s) wrong dose wrong duration
 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
 Immunotherapy clinic
Immunotherapy clinic
 Immunotherapy clinic • Leadership/organisation of allergy clinic • Staff competencies (induction/training) • Clinic facilities – bookings, observation space – storage for vaccines / skin test reagents – safety procedures – rescue equipment • Immunotherapy protocols Alvarez-Cuesta E et al Allergy 2006; 61 Suppl. 82: 1 -20
Immunotherapy clinic • Leadership/organisation of allergy clinic • Staff competencies (induction/training) • Clinic facilities – bookings, observation space – storage for vaccines / skin test reagents – safety procedures – rescue equipment • Immunotherapy protocols Alvarez-Cuesta E et al Allergy 2006; 61 Suppl. 82: 1 -20
 Staff competencies • • • Evaluation of the patients’ condition Entering data in “Immunotherapy Record Form” Injection technique Dose modification Active observation of patients Early recognition of anaphylactic reactions Treatment /monitoring of anaphylactic reactions How to perform scheduled assessments Factors determining whether to continue/stop IT Alvarez-Cuesta E et al Allergy 2006; 61 Suppl. 82: 1 -20
Staff competencies • • • Evaluation of the patients’ condition Entering data in “Immunotherapy Record Form” Injection technique Dose modification Active observation of patients Early recognition of anaphylactic reactions Treatment /monitoring of anaphylactic reactions How to perform scheduled assessments Factors determining whether to continue/stop IT Alvarez-Cuesta E et al Allergy 2006; 61 Suppl. 82: 1 -20
 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
 Selection of patients for immunotherapy • Symptoms induced by allergen • Ig. E to relevant allergen (SPT/RAST) • Symptoms due to one or few allergens • No contra-indications (severe asthma, beta/blockers, inability to comply with IT)
Selection of patients for immunotherapy • Symptoms induced by allergen • Ig. E to relevant allergen (SPT/RAST) • Symptoms due to one or few allergens • No contra-indications (severe asthma, beta/blockers, inability to comply with IT)
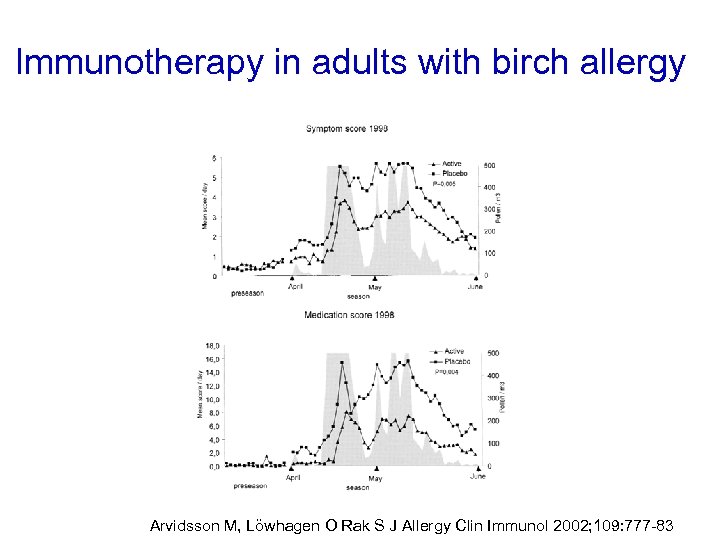 Immunotherapy in adults with birch allergy Arvidsson M, Löwhagen O Rak S J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002; 109: 777 -83
Immunotherapy in adults with birch allergy Arvidsson M, Löwhagen O Rak S J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002; 109: 777 -83
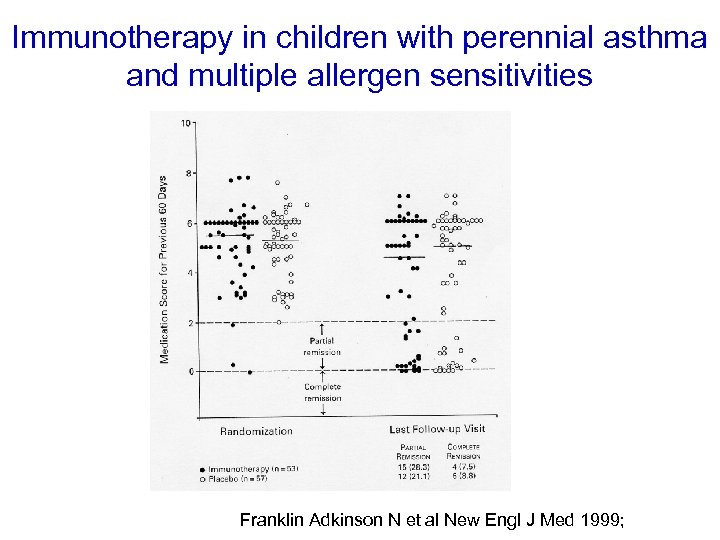 Immunotherapy in children with perennial asthma and multiple allergen sensitivities Franklin Adkinson N et al New Engl J Med 1999;
Immunotherapy in children with perennial asthma and multiple allergen sensitivities Franklin Adkinson N et al New Engl J Med 1999;
 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
 Selection of allergen extracts • Standardisation - in-house reference standards (IHRs) - units of biologic potency - major allergen content (5 -20 mcg major Ag) - recombinant allergens • Documented benefit (controlled trials) - efficacy - safety - children and adults - longterm effects
Selection of allergen extracts • Standardisation - in-house reference standards (IHRs) - units of biologic potency - major allergen content (5 -20 mcg major Ag) - recombinant allergens • Documented benefit (controlled trials) - efficacy - safety - children and adults - longterm effects
 J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 319 -25 26 centres, n=410 100, 000 SQ, 10, 000 SQ and placebo
J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 319 -25 26 centres, n=410 100, 000 SQ, 10, 000 SQ and placebo
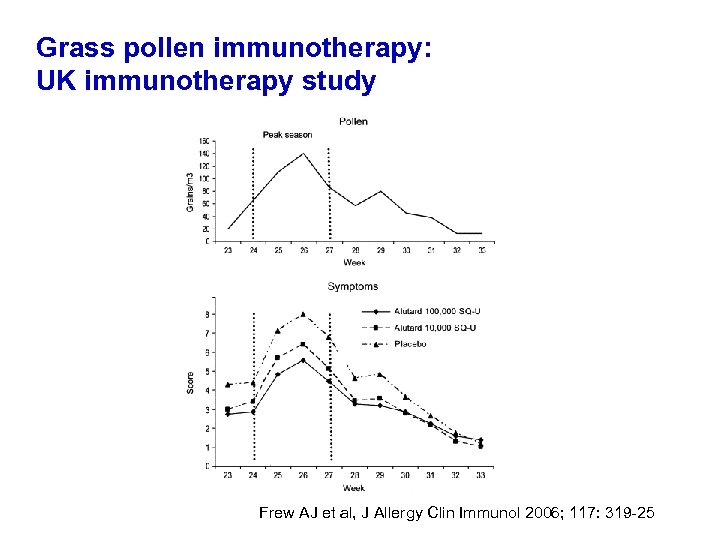 Grass pollen immunotherapy: UK immunotherapy study Frew AJ et al, J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 319 -25
Grass pollen immunotherapy: UK immunotherapy study Frew AJ et al, J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 319 -25
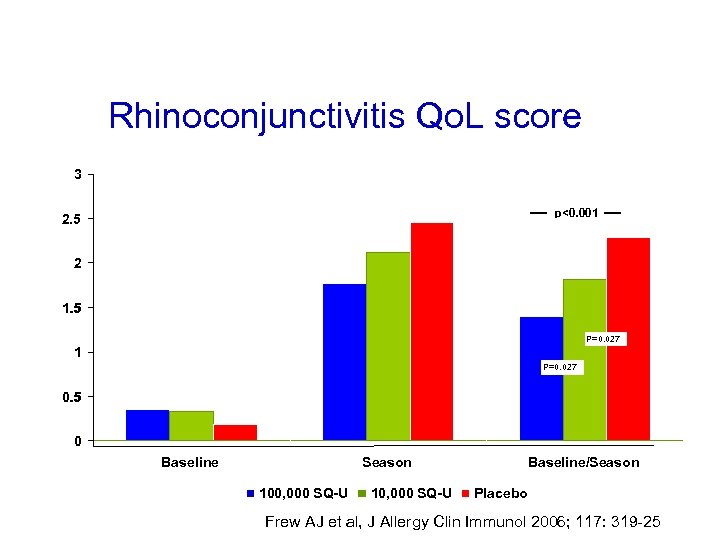 Rhinoconjunctivitis Qo. L score 3 p<0. 001 2. 5 2 1. 5 p=0. 027 P=0. 027 1 p=0. 027 P=0. 027 0. 5 0 Baseline Season 100, 000 SQ-U 10, 000 SQ-U Baseline/Season Placebo Frew AJ et al, J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 319 -25
Rhinoconjunctivitis Qo. L score 3 p<0. 001 2. 5 2 1. 5 p=0. 027 P=0. 027 1 p=0. 027 P=0. 027 0. 5 0 Baseline Season 100, 000 SQ-U 10, 000 SQ-U Baseline/Season Placebo Frew AJ et al, J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 319 -25
 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
 J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 1338 -45
J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 1338 -45
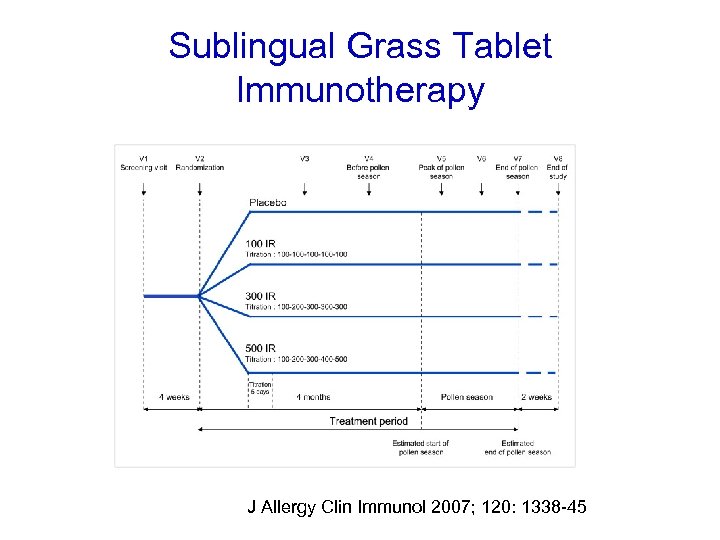 Sublingual Grass Tablet Immunotherapy J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 1338 -45
Sublingual Grass Tablet Immunotherapy J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 1338 -45
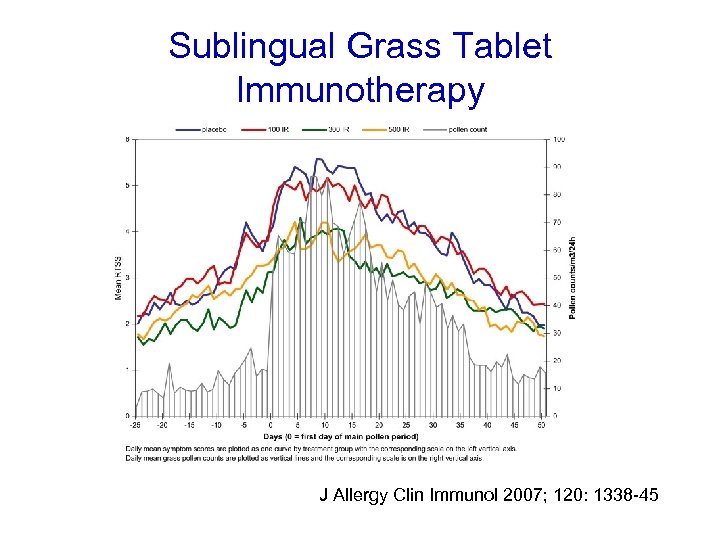 Sublingual Grass Tablet Immunotherapy J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 1338 -45
Sublingual Grass Tablet Immunotherapy J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 1338 -45
 Randomised DBPC trial (n=855). 3 doses v placebo • 2, 500 SQ-T • 25, 000 SQ-T • 75, 000 SQ-T Once daily 8 weeks pre-season and continued throughout season
Randomised DBPC trial (n=855). 3 doses v placebo • 2, 500 SQ-T • 25, 000 SQ-T • 75, 000 SQ-T Once daily 8 weeks pre-season and continued throughout season
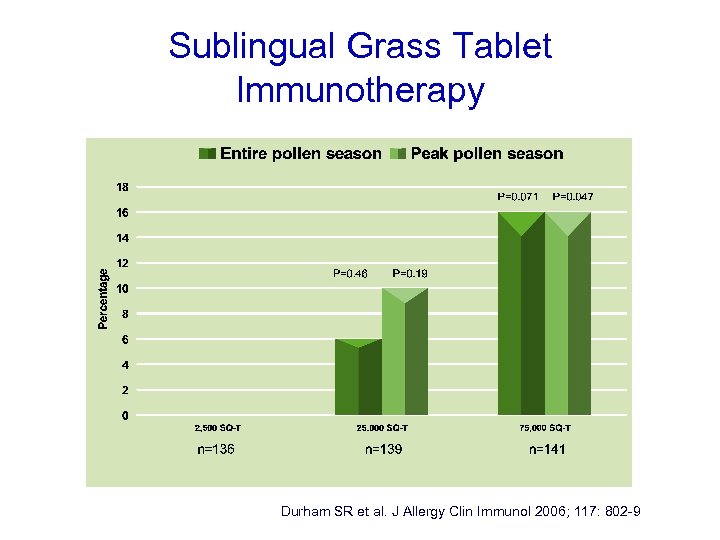 Sublingual Grass Tablet Immunotherapy Durham SR et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 802 -9
Sublingual Grass Tablet Immunotherapy Durham SR et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 802 -9
 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration
 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration - efficacy - tolerance
Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration - efficacy - tolerance
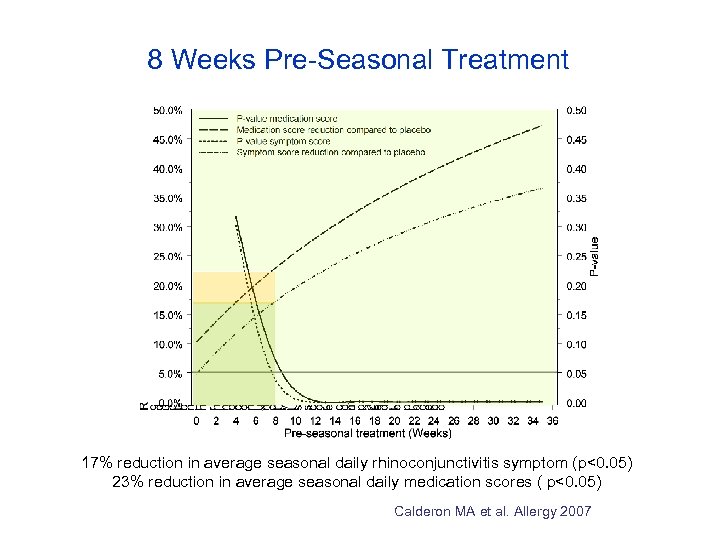 8 Weeks Pre-Seasonal Treatment 17% reduction in average seasonal daily rhinoconjunctivitis symptom (p<0. 05) 23% reduction in average seasonal daily medication scores ( p<0. 05) Calderon MA et al. Allergy 2007
8 Weeks Pre-Seasonal Treatment 17% reduction in average seasonal daily rhinoconjunctivitis symptom (p<0. 05) 23% reduction in average seasonal daily medication scores ( p<0. 05) Calderon MA et al. Allergy 2007
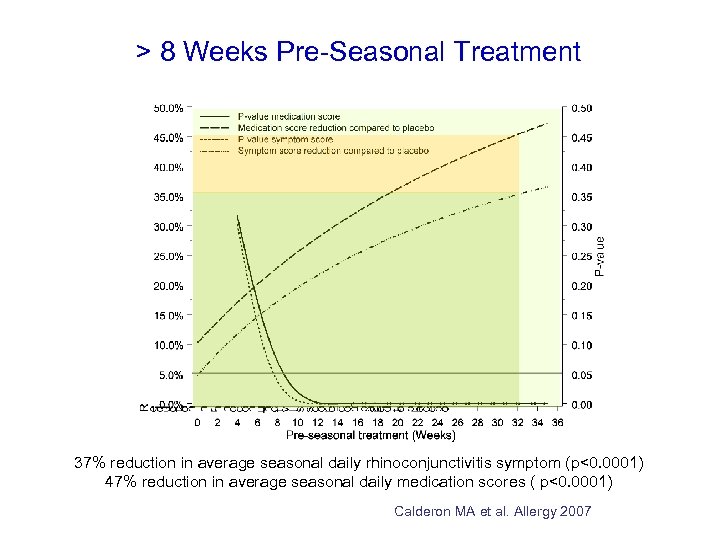 > 8 Weeks Pre-Seasonal Treatment 37% reduction in average seasonal daily rhinoconjunctivitis symptom (p<0. 0001) 47% reduction in average seasonal daily medication scores ( p<0. 0001) Calderon MA et al. Allergy 2007
> 8 Weeks Pre-Seasonal Treatment 37% reduction in average seasonal daily rhinoconjunctivitis symptom (p<0. 0001) 47% reduction in average seasonal daily medication scores ( p<0. 0001) Calderon MA et al. Allergy 2007
 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration - efficacy - tolerance (persistent efficacy after withdrawal)
Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration - efficacy - tolerance (persistent efficacy after withdrawal)
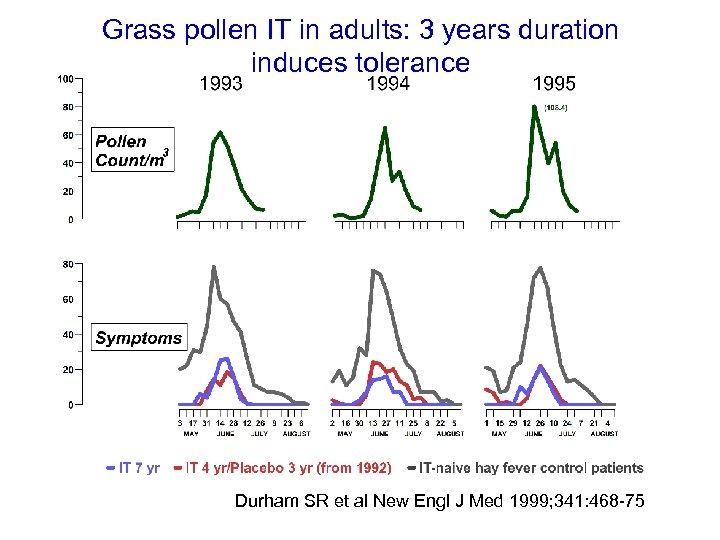 Grass pollen IT in adults: 3 years duration induces tolerance Durham SR et al New Engl J Med 1999; 341: 468 -75
Grass pollen IT in adults: 3 years duration induces tolerance Durham SR et al New Engl J Med 1999; 341: 468 -75
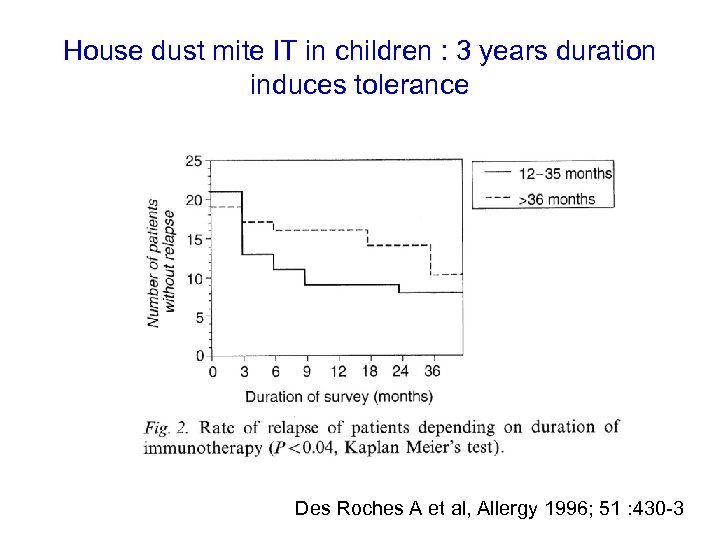 House dust mite IT in children : 3 years duration induces tolerance Des Roches A et al, Allergy 1996; 51 : 430 -3
House dust mite IT in children : 3 years duration induces tolerance Des Roches A et al, Allergy 1996; 51 : 430 -3
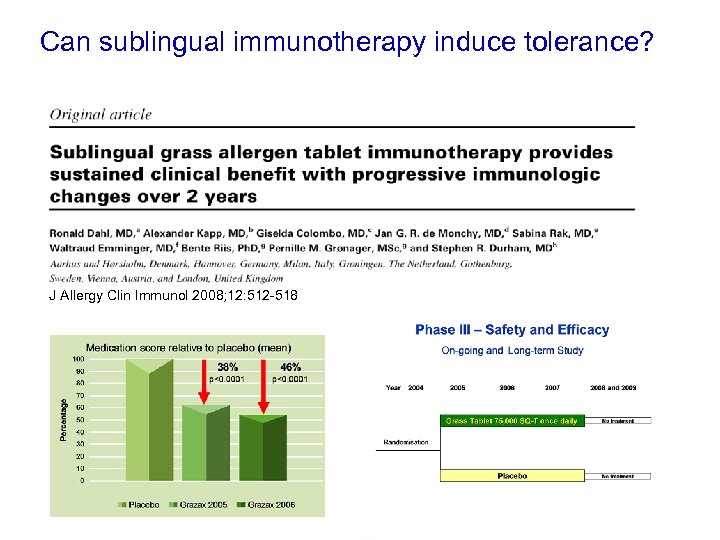 Can sublingual immunotherapy induce tolerance? J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 12: 512 -518
Can sublingual immunotherapy induce tolerance? J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 12: 512 -518
 Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration - efficacy - tolerance
Why immunotherapy succeeds ? • • • right set up right patient right allergen(s) right dose right duration - efficacy - tolerance
 Why immunotherapy fails? • • • wrong set up wrong patient wrong allergen(s) wrong dose wrong duration - no efficacy - no tolerance
Why immunotherapy fails? • • • wrong set up wrong patient wrong allergen(s) wrong dose wrong duration - no efficacy - no tolerance
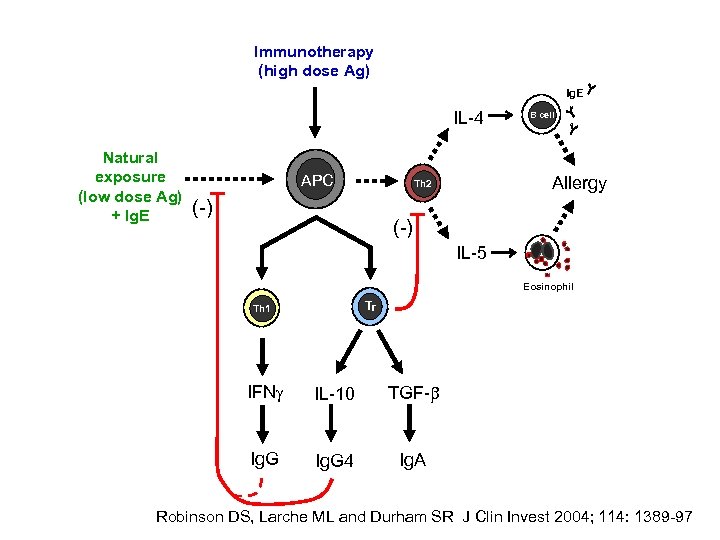 Immunotherapy (high dose Ag) Ig. E IL-4 Natural exposure (low dose Ag) + Ig. E APC Allergy Th 2 (-) B cell (-) IL-5 Eosinophil Tr Th 1 IFNg IL-10 TGF-b Ig. G 4 Ig. A Robinson DS, Larche ML and Durham SR J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1389 -97
Immunotherapy (high dose Ag) Ig. E IL-4 Natural exposure (low dose Ag) + Ig. E APC Allergy Th 2 (-) B cell (-) IL-5 Eosinophil Tr Th 1 IFNg IL-10 TGF-b Ig. G 4 Ig. A Robinson DS, Larche ML and Durham SR J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1389 -97
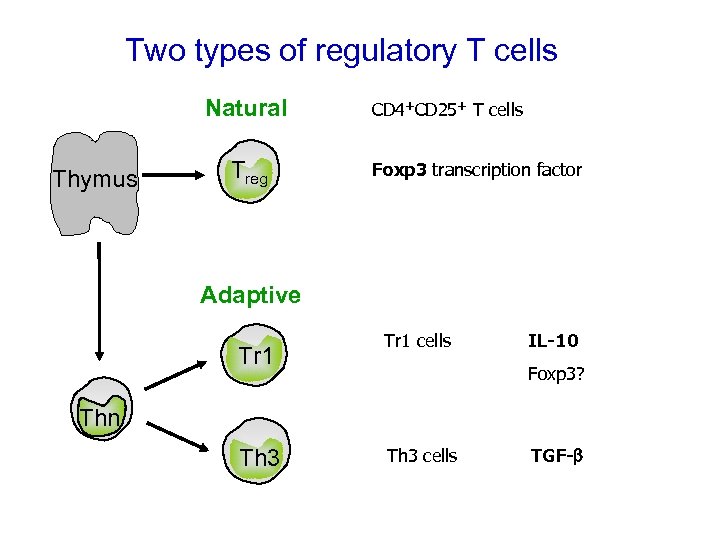 Two types of regulatory T cells Natural Thymus Treg CD 4+CD 25+ T cells Foxp 3 transcription factor Adaptive Tr 1 cells IL-10 Foxp 3? Thn Th 3 cells TGF-b
Two types of regulatory T cells Natural Thymus Treg CD 4+CD 25+ T cells Foxp 3 transcription factor Adaptive Tr 1 cells IL-10 Foxp 3? Thn Th 3 cells TGF-b
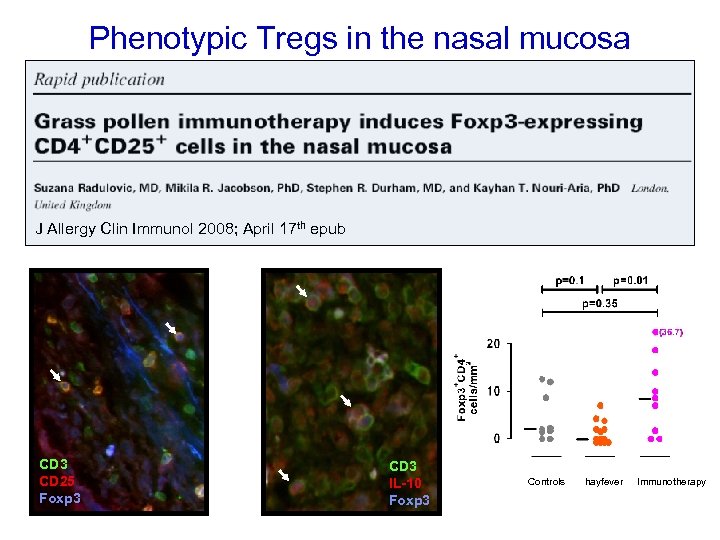 Phenotypic Tregs in the nasal mucosa J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; April 17 th epub CD 3 CD 25 Foxp 3 CD 3 IL-10 Foxp 3 Controls hayfever Immunotherapy
Phenotypic Tregs in the nasal mucosa J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; April 17 th epub CD 3 CD 25 Foxp 3 CD 3 IL-10 Foxp 3 Controls hayfever Immunotherapy
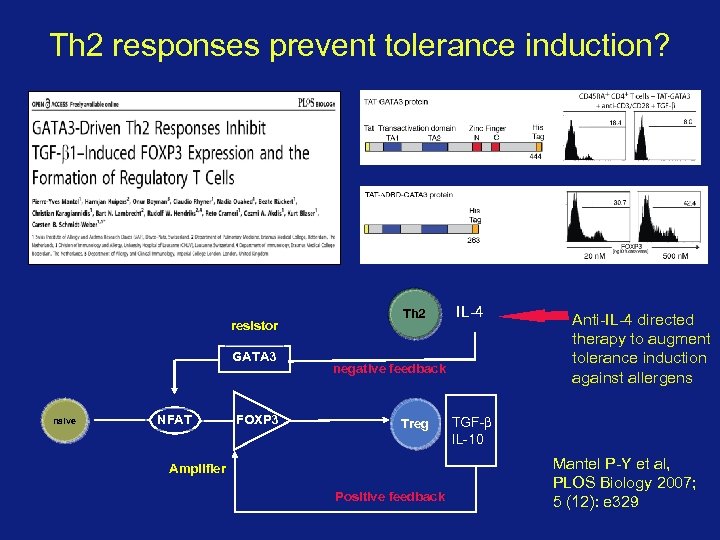 Th 2 responses prevent tolerance induction? resistor GATA 3 naive NFAT FOXP 3 Th 2 IL-4 negative feedback Treg Amplifier Positive feedback TGF-β, IL-10 TGF-b IL-27 IL-10 IL-35 Anti-IL-4 directed therapy to augment tolerance induction against allergens Mantel P-Y et al, PLOS Biology 2007; 5 (12): e 329
Th 2 responses prevent tolerance induction? resistor GATA 3 naive NFAT FOXP 3 Th 2 IL-4 negative feedback Treg Amplifier Positive feedback TGF-β, IL-10 TGF-b IL-27 IL-10 IL-35 Anti-IL-4 directed therapy to augment tolerance induction against allergens Mantel P-Y et al, PLOS Biology 2007; 5 (12): e 329
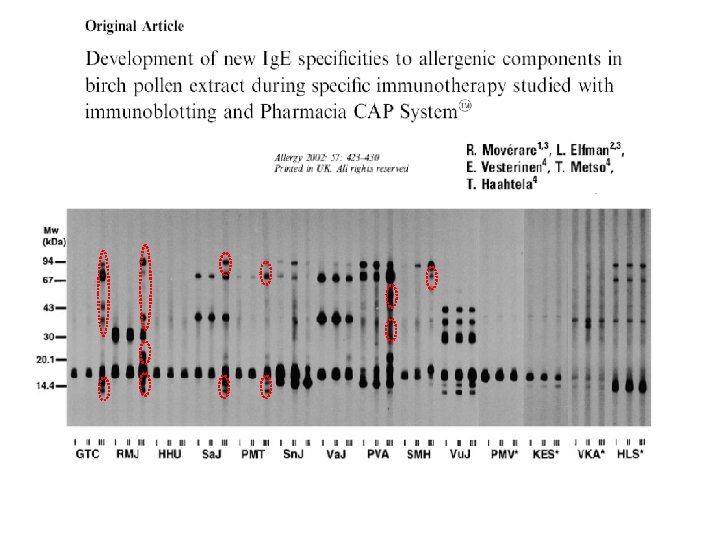
 Can we predict success or failure of immunotherapy?
Can we predict success or failure of immunotherapy?
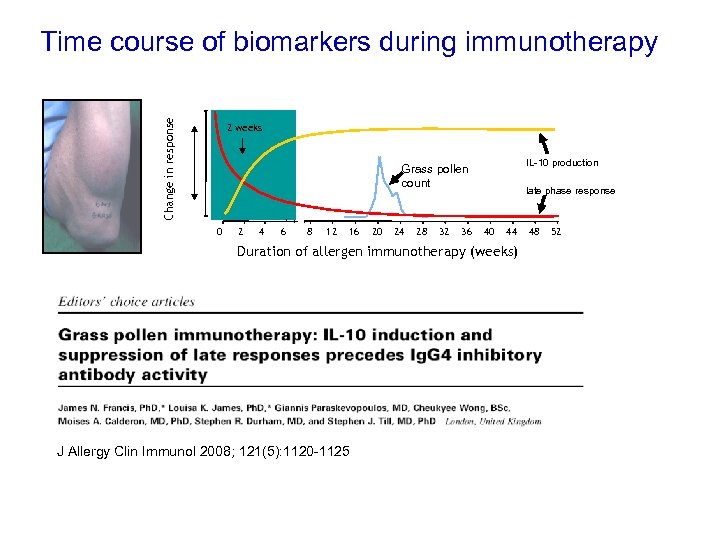 Change in response Time course of biomarkers during immunotherapy 2 weeks IL-10 production Grass pollen count 0 2 4 6 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 late phase response 40 44 Duration of allergen immunotherapy (weeks) J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121(5): 1120 -1125 48 52
Change in response Time course of biomarkers during immunotherapy 2 weeks IL-10 production Grass pollen count 0 2 4 6 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 late phase response 40 44 Duration of allergen immunotherapy (weeks) J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121(5): 1120 -1125 48 52
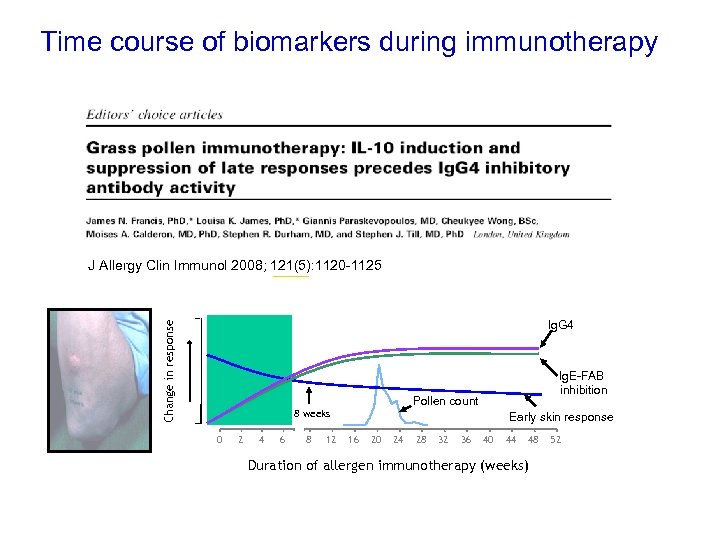 Time of biomarkers during immunotherapy Time course of changes in IL-10 and Ig. G-associated inhibitory activity Change in response Late allergen-induced Skin Response 4 weeks Grass Pollen season 0 2 4 6 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 52 Duration of allergen immunotherapy (weeks) late phase J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121(5): 1120 -1125 response Change in response Ig. G 4 Pollen count 8 weeks 0 2 4 6 8 12 Ig. E-FAB inhibition Early skin response 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 Duration of allergen immunotherapy (weeks) 52
Time of biomarkers during immunotherapy Time course of changes in IL-10 and Ig. G-associated inhibitory activity Change in response Late allergen-induced Skin Response 4 weeks Grass Pollen season 0 2 4 6 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 52 Duration of allergen immunotherapy (weeks) late phase J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121(5): 1120 -1125 response Change in response Ig. G 4 Pollen count 8 weeks 0 2 4 6 8 12 Ig. E-FAB inhibition Early skin response 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 Duration of allergen immunotherapy (weeks) 52






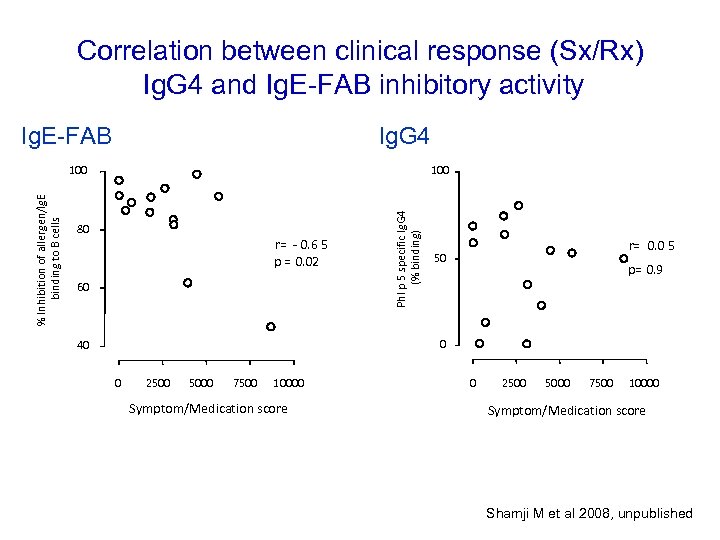 Correlation between clinical response (Sx/Rx) Ig. G 4 and Ig. E-FAB inhibitory activity Ig. E-FAB Ig. G 4 100 80 r= - 0. 6 5 p = 0. 02 60 Phl p 5 specific Ig. G 4 (% binding) % Inhibition of allergen/Ig. E binding to B cells 100 r= 0. 0 5 50 p= 0. 9 0 40 0 2500 5000 7500 10000 Symptom/Medication score Shamji M et al 2008, unpublished
Correlation between clinical response (Sx/Rx) Ig. G 4 and Ig. E-FAB inhibitory activity Ig. E-FAB Ig. G 4 100 80 r= - 0. 6 5 p = 0. 02 60 Phl p 5 specific Ig. G 4 (% binding) % Inhibition of allergen/Ig. E binding to B cells 100 r= 0. 0 5 50 p= 0. 9 0 40 0 2500 5000 7500 10000 Symptom/Medication score Shamji M et al 2008, unpublished
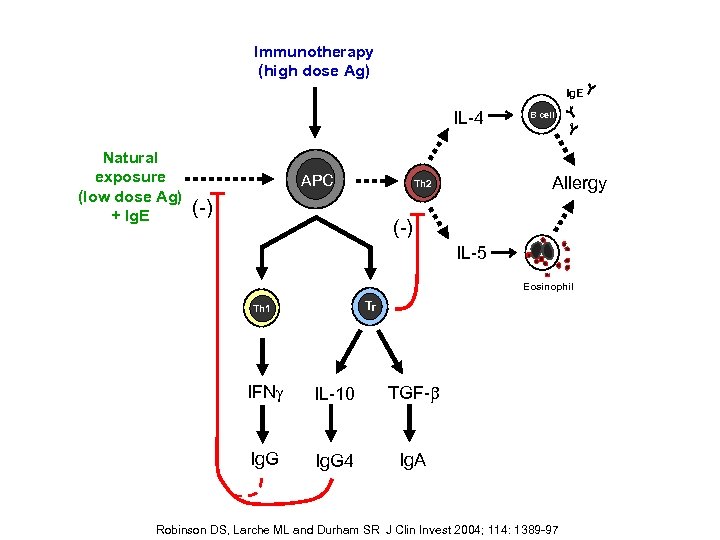 Immunotherapy (high dose Ag) Ig. E IL-4 Natural exposure (low dose Ag) + Ig. E APC Allergy Th 2 (-) B cell (-) IL-5 Eosinophil Tr Th 1 IFNg IL-10 TGF-b Ig. G 4 Ig. A Robinson DS, Larche ML and Durham SR J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1389 -97
Immunotherapy (high dose Ag) Ig. E IL-4 Natural exposure (low dose Ag) + Ig. E APC Allergy Th 2 (-) B cell (-) IL-5 Eosinophil Tr Th 1 IFNg IL-10 TGF-b Ig. G 4 Ig. A Robinson DS, Larche ML and Durham SR J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1389 -97
 Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Imperial College and Royal Brompton Hospital, London, UK M Calderon D R Wilson C Pilette S Radulovic K T Nouri-Aria M R Jacobson J N Francis M Shamji G Paraskavopoulos L Wilcock C Schmidt-Weber S J Till
Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Imperial College and Royal Brompton Hospital, London, UK M Calderon D R Wilson C Pilette S Radulovic K T Nouri-Aria M R Jacobson J N Francis M Shamji G Paraskavopoulos L Wilcock C Schmidt-Weber S J Till


