fa2a00d8b6643872662319a1906fbeee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Why do we need regional complementary currencies? -Considerations from an integrative point of view. Boulder, Naropa, March 2004 www. stefan-brunnhuber. de
Why do we need regional complementary currencies? -Considerations from an integrative point of view. Boulder, Naropa, March 2004 www. stefan-brunnhuber. de
 1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
 1. Sustainability „. . . is a development, which fulfills the present needs without risking that future generations cannot fulfill their own needs. . . “. Brundlandt-Report, UN, 1986
1. Sustainability „. . . is a development, which fulfills the present needs without risking that future generations cannot fulfill their own needs. . . “. Brundlandt-Report, UN, 1986
 1. Sustainability S=Dx. Tx. Vx. I
1. Sustainability S=Dx. Tx. Vx. I
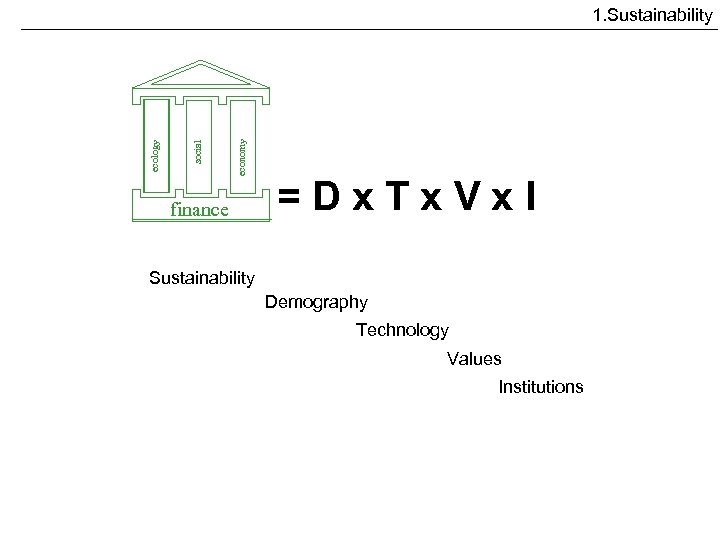 economy social ecology 1. Sustainability finance =Dx. Tx. Vx. I Sustainability Demography Technology Values Institutions
economy social ecology 1. Sustainability finance =Dx. Tx. Vx. I Sustainability Demography Technology Values Institutions
 1. Sustainability S=Dx. Tx. Vx. I Money is not a natural law, but a convention, like a marriage contract or club rules…
1. Sustainability S=Dx. Tx. Vx. I Money is not a natural law, but a convention, like a marriage contract or club rules…
 What does sustainability means from a financial perspective? 1. to achieve a long term- perspective (SHV) 2. closing the income gap (military conflicts, life expectance) 3. covering the debth load by one generation 4. tackling social issues (unemployment ect. ) 5. coping with the energy carrier (non-renewable vs. renewable)
What does sustainability means from a financial perspective? 1. to achieve a long term- perspective (SHV) 2. closing the income gap (military conflicts, life expectance) 3. covering the debth load by one generation 4. tackling social issues (unemployment ect. ) 5. coping with the energy carrier (non-renewable vs. renewable)
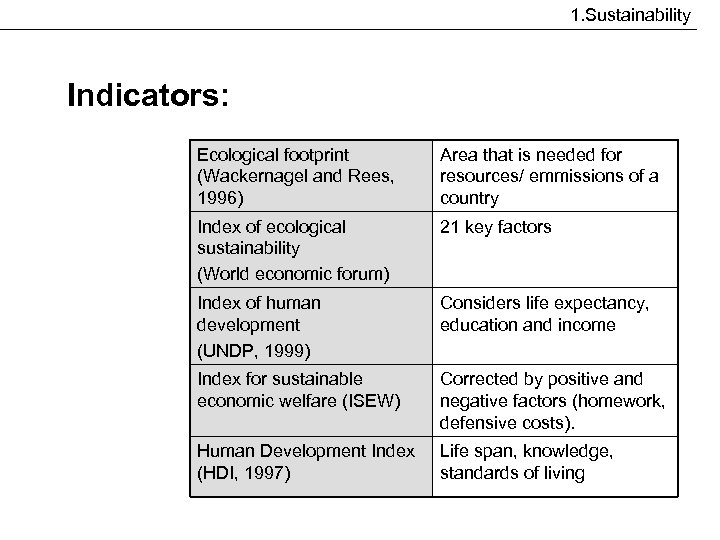 1. Sustainability Indicators: Ecological footprint (Wackernagel and Rees, 1996) Area that is needed for resources/ emmissions of a country Index of ecological sustainability (World economic forum) 21 key factors Index of human development (UNDP, 1999) Considers life expectancy, education and income Index for sustainable economic welfare (ISEW) Corrected by positive and negative factors (homework, defensive costs). Human Development Index (HDI, 1997) Life span, knowledge, standards of living
1. Sustainability Indicators: Ecological footprint (Wackernagel and Rees, 1996) Area that is needed for resources/ emmissions of a country Index of ecological sustainability (World economic forum) 21 key factors Index of human development (UNDP, 1999) Considers life expectancy, education and income Index for sustainable economic welfare (ISEW) Corrected by positive and negative factors (homework, defensive costs). Human Development Index (HDI, 1997) Life span, knowledge, standards of living
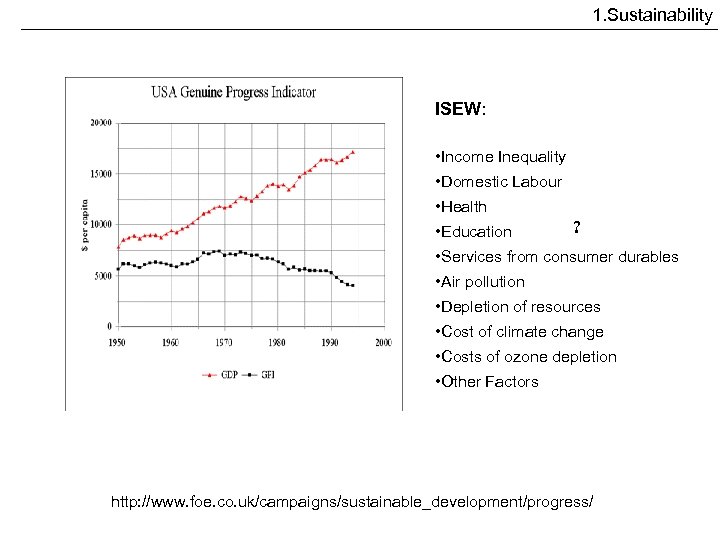 1. Sustainability ISEW: • Income Inequality • Domestic Labour • Health • Education ? • Services from consumer durables • Air pollution • Depletion of resources • Cost of climate change • Costs of ozone depletion • Other Factors http: //www. foe. co. uk/campaigns/sustainable_development/progress/
1. Sustainability ISEW: • Income Inequality • Domestic Labour • Health • Education ? • Services from consumer durables • Air pollution • Depletion of resources • Cost of climate change • Costs of ozone depletion • Other Factors http: //www. foe. co. uk/campaigns/sustainable_development/progress/
 1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
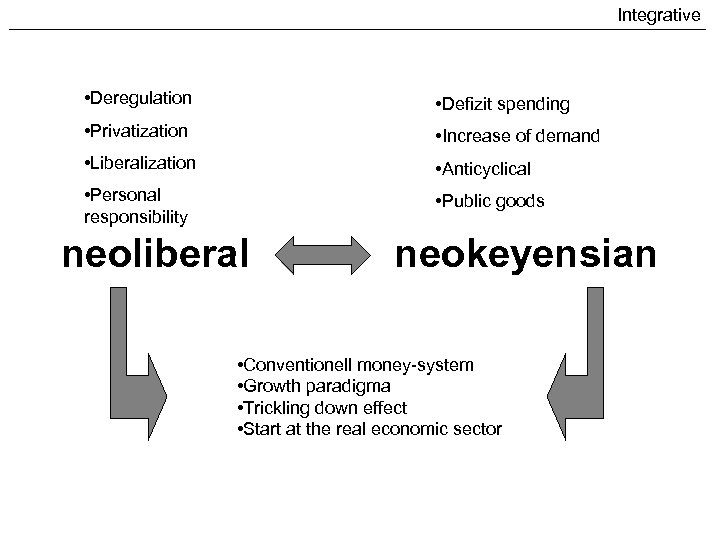 Integrative • Deregulation • Defizit spending • Privatization • Increase of demand • Liberalization • Anticyclical • Personal responsibility • Public goods neoliberal neokeyensian • Conventionell money-system • Growth paradigma • Trickling down effect • Start at the real economic sector
Integrative • Deregulation • Defizit spending • Privatization • Increase of demand • Liberalization • Anticyclical • Personal responsibility • Public goods neoliberal neokeyensian • Conventionell money-system • Growth paradigma • Trickling down effect • Start at the real economic sector
 Integrative • From inside out • Enyclopedic knowledge • Homo economicus
Integrative • From inside out • Enyclopedic knowledge • Homo economicus
 Integrative Towards an integrative approach: 1. Helicopter view 2. Less affected by the given models 3. Looking for overlooked connections 4. bring individual responsibility and public goods together F. Vester, 2002, K. Wilber, 2001
Integrative Towards an integrative approach: 1. Helicopter view 2. Less affected by the given models 3. Looking for overlooked connections 4. bring individual responsibility and public goods together F. Vester, 2002, K. Wilber, 2001
 Integrative neoliberal neokeyensian Complementary currencies as they mainly have a „built in target“ (BIT)
Integrative neoliberal neokeyensian Complementary currencies as they mainly have a „built in target“ (BIT)
 1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
 3. Money system „The last beings to comprehend the nature of water, are fish“ B. Lietaer, 2000
3. Money system „The last beings to comprehend the nature of water, are fish“ B. Lietaer, 2000
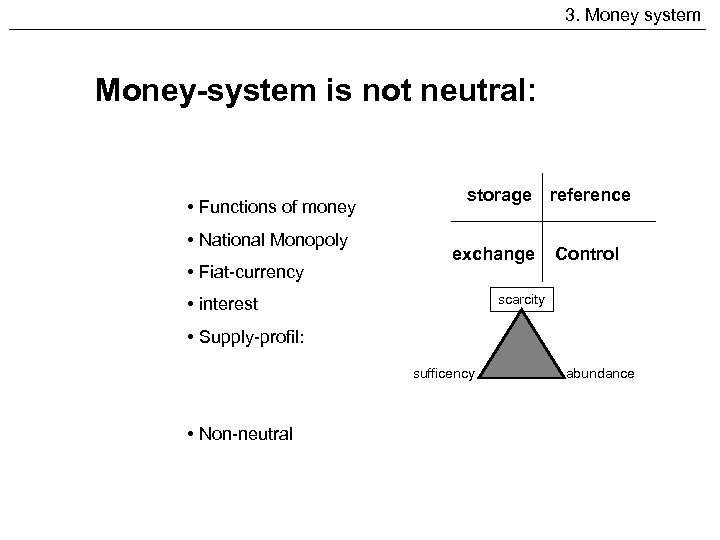 3. Money system Money-system is not neutral: • Functions of money • National Monopoly • Fiat-currency storage reference exchange Control scarcity • interest • Supply-profil: sufficency • Non-neutral abundance
3. Money system Money-system is not neutral: • Functions of money • National Monopoly • Fiat-currency storage reference exchange Control scarcity • interest • Supply-profil: sufficency • Non-neutral abundance
 3. Money system ? ? Moneysystem
3. Money system ? ? Moneysystem
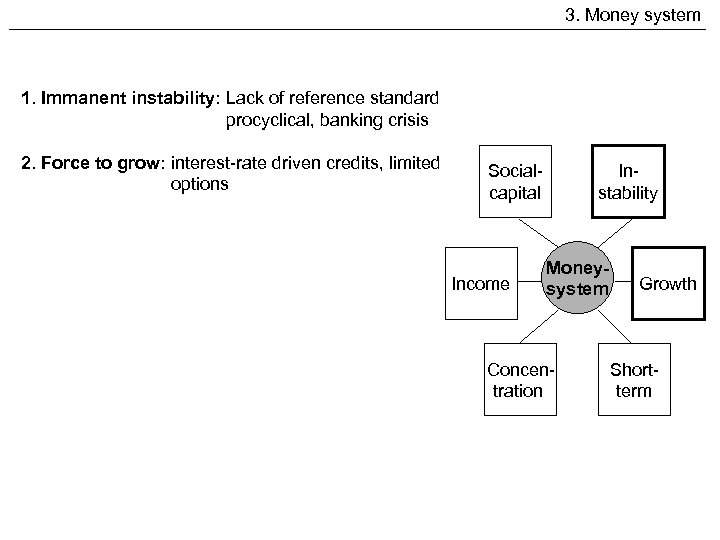 3. Money system 1. Immanent instability: Lack of reference standard procyclical, banking crisis 2. Force to grow: interest-rate driven credits, limited options Socialcapital Income Instability Moneysystem Concentration Growth Shortterm
3. Money system 1. Immanent instability: Lack of reference standard procyclical, banking crisis 2. Force to grow: interest-rate driven credits, limited options Socialcapital Income Instability Moneysystem Concentration Growth Shortterm
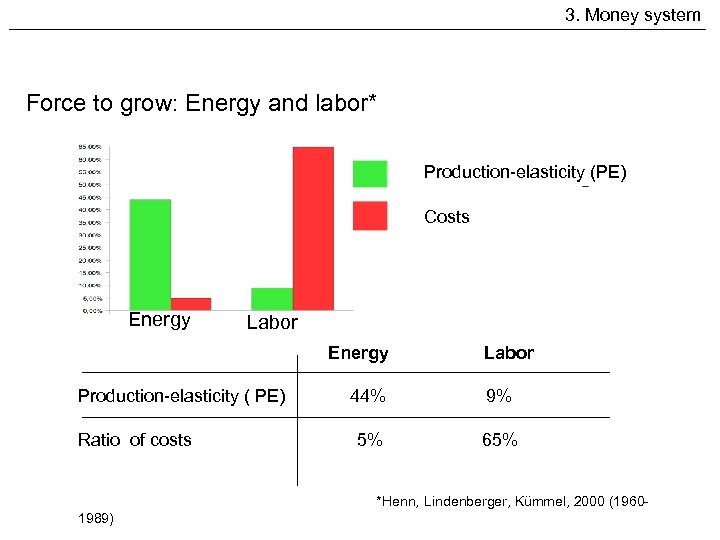 3. Money system Force to grow: Energy and labor* Production-elasticity (PE) Costs Energy Labor Energy Production-elasticity ( PE) Ratio of costs Labor 44% 9% 5% 65% *Henn, Lindenberger, Kümmel, 2000 (19601989)
3. Money system Force to grow: Energy and labor* Production-elasticity (PE) Costs Energy Labor Energy Production-elasticity ( PE) Ratio of costs Labor 44% 9% 5% 65% *Henn, Lindenberger, Kümmel, 2000 (19601989)
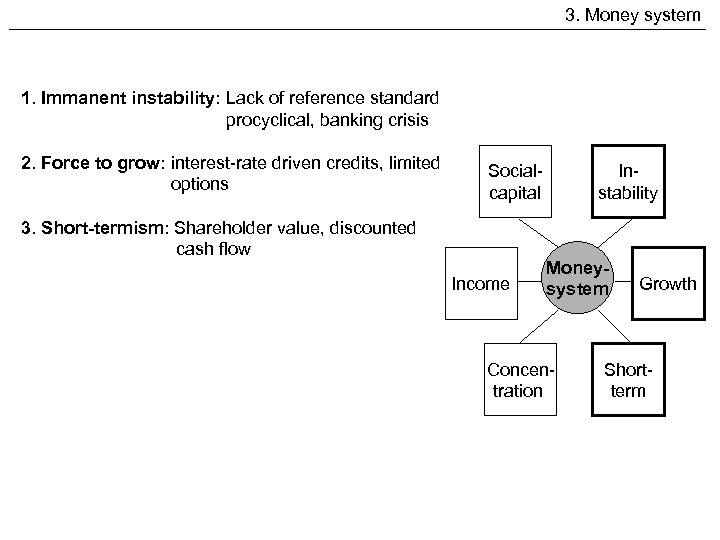 3. Money system 1. Immanent instability: Lack of reference standard procyclical, banking crisis 2. Force to grow: interest-rate driven credits, limited options Socialcapital 3. Short-termism: Shareholder value, discounted cash flow Income Instability Moneysystem Concentration Growth Shortterm
3. Money system 1. Immanent instability: Lack of reference standard procyclical, banking crisis 2. Force to grow: interest-rate driven credits, limited options Socialcapital 3. Short-termism: Shareholder value, discounted cash flow Income Instability Moneysystem Concentration Growth Shortterm
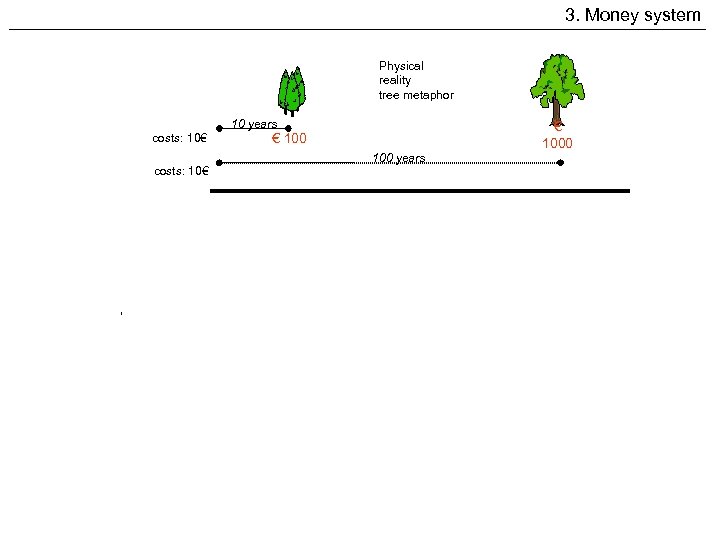 3. Money system Physical reality tree metaphor 10 years costs: 10€ 100 years costs: 10€ Currency with a positve interst rate of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: € 1000 € 100 Financial investment with interest rate € 7, 60 € 61, 39 Currency with an anchorage due of 5% per year Financial investment with anchorage due Demurrage Value calculated as from today: € 167, 02 € 168. 903, 82
3. Money system Physical reality tree metaphor 10 years costs: 10€ 100 years costs: 10€ Currency with a positve interst rate of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: € 1000 € 100 Financial investment with interest rate € 7, 60 € 61, 39 Currency with an anchorage due of 5% per year Financial investment with anchorage due Demurrage Value calculated as from today: € 167, 02 € 168. 903, 82
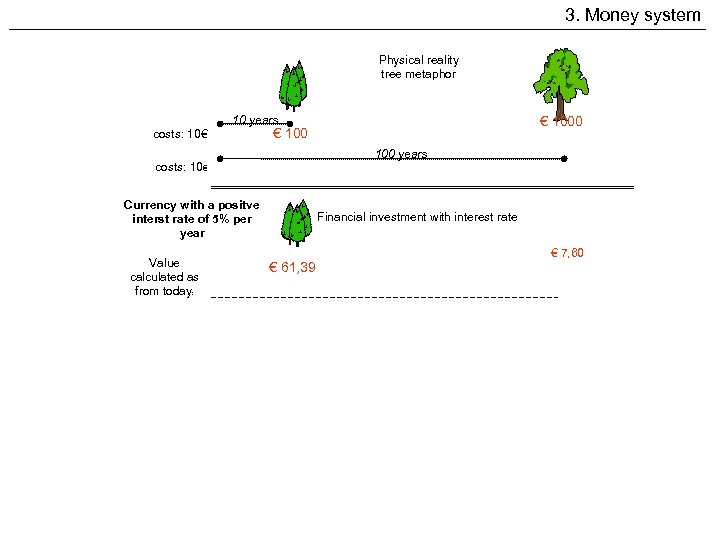 3. Money system Physical reality tree metaphor 10 years costs: 10€ € 1000 € 100 years costs: 10€ Currency with a positve interst rate of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: Financial investment with interest rate € 7, 60 € 61, 39 Currency with an anchorage due of 5% per year Financial investment with anchorage due Demurrage Value calculated as from today: € 167, 02 € 168. 903, 82
3. Money system Physical reality tree metaphor 10 years costs: 10€ € 1000 € 100 years costs: 10€ Currency with a positve interst rate of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: Financial investment with interest rate € 7, 60 € 61, 39 Currency with an anchorage due of 5% per year Financial investment with anchorage due Demurrage Value calculated as from today: € 167, 02 € 168. 903, 82
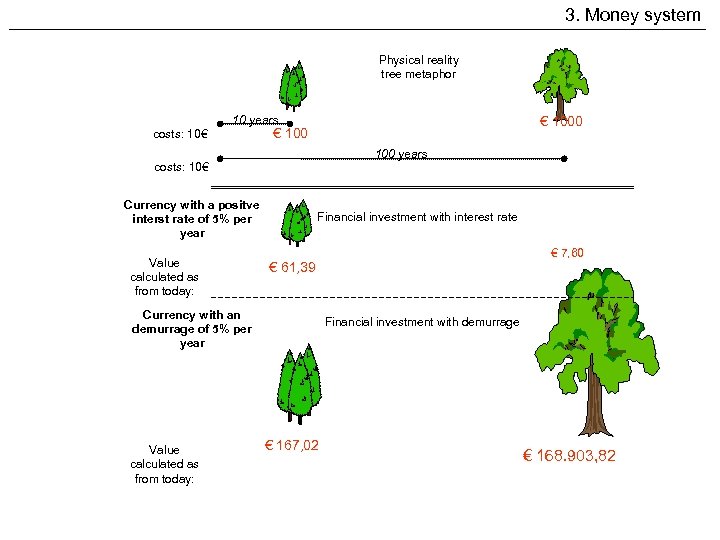 3. Money system Physical reality tree metaphor 10 years costs: 10€ € 1000 € 100 years costs: 10€ Currency with a positve interst rate of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: Financial investment with interest rate Currency with an demurrage of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: € 7, 60 € 61, 39 Financial investment with demurrage € 167, 02 € 168. 903, 82
3. Money system Physical reality tree metaphor 10 years costs: 10€ € 1000 € 100 years costs: 10€ Currency with a positve interst rate of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: Financial investment with interest rate Currency with an demurrage of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: € 7, 60 € 61, 39 Financial investment with demurrage € 167, 02 € 168. 903, 82
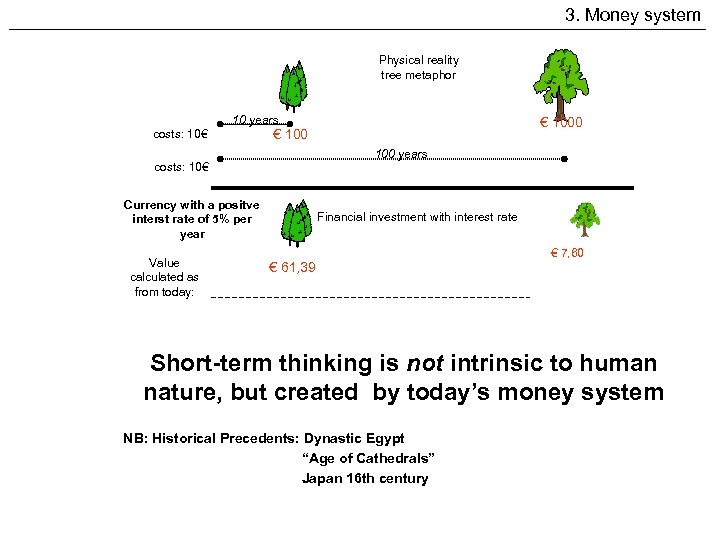 3. Money system Physical reality tree metaphor 10 years costs: 10€ 100 years costs: 10€ Currency with a positve interst rate of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: Currency with an demurrage of 5% per year € 1000 € 100 Financial investment with interest rate € 7, 60 € 61, 39 Financial investment with demurrage Short-term thinking is not intrinsic to human nature, but created by today’s money system NB: Historical Precedents: Dynastic Egypt € 167, 02 Value “Age of Cathedrals” calculated as Japan 16 th century from today: € 168. 903, 82
3. Money system Physical reality tree metaphor 10 years costs: 10€ 100 years costs: 10€ Currency with a positve interst rate of 5% per year Value calculated as from today: Currency with an demurrage of 5% per year € 1000 € 100 Financial investment with interest rate € 7, 60 € 61, 39 Financial investment with demurrage Short-term thinking is not intrinsic to human nature, but created by today’s money system NB: Historical Precedents: Dynastic Egypt € 167, 02 Value “Age of Cathedrals” calculated as Japan 16 th century from today: € 168. 903, 82
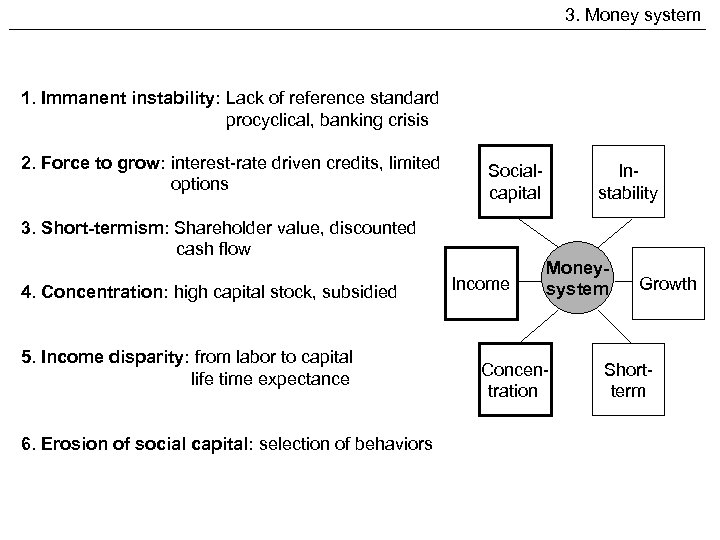 3. Money system 1. Immanent instability: Lack of reference standard procyclical, banking crisis 2. Force to grow: interest-rate driven credits, limited options Socialcapital 3. Short-termism: Shareholder value, discounted cash flow 4. Concentration: high capital stock, subsidied 5. Income disparity: from labor to capital life time expectance 6. Erosion of social capital: selection of behaviors Income Instability Moneysystem Concentration Growth Shortterm
3. Money system 1. Immanent instability: Lack of reference standard procyclical, banking crisis 2. Force to grow: interest-rate driven credits, limited options Socialcapital 3. Short-termism: Shareholder value, discounted cash flow 4. Concentration: high capital stock, subsidied 5. Income disparity: from labor to capital life time expectance 6. Erosion of social capital: selection of behaviors Income Instability Moneysystem Concentration Growth Shortterm
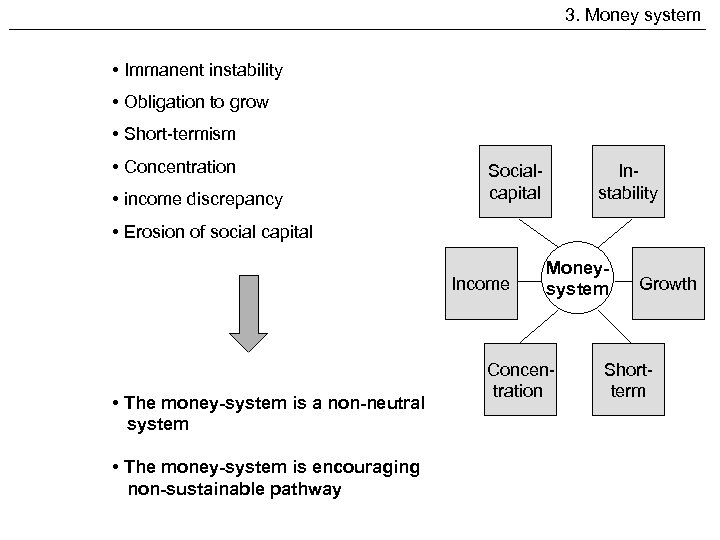 3. Money system • Immanent instability • Obligation to grow • Short-termism • Concentration • income discrepancy Socialcapital Instability • Erosion of social capital Income • The money-system is a non-neutral system • The money-system is encouraging non-sustainable pathway Moneysystem Concentration Growth Shortterm
3. Money system • Immanent instability • Obligation to grow • Short-termism • Concentration • income discrepancy Socialcapital Instability • Erosion of social capital Income • The money-system is a non-neutral system • The money-system is encouraging non-sustainable pathway Moneysystem Concentration Growth Shortterm
 1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
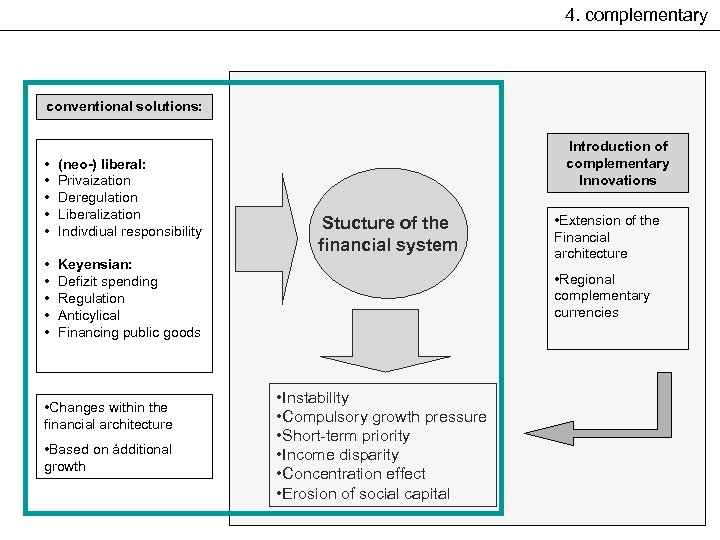 4. complementary conventional solutions: • • • (neo-) liberal: Privaization Deregulation Liberalization Indivdiual responsibility • • • Introduction of complementary Innovations Keyensian: Defizit spending Regulation Anticylical Financing public goods • Changes within the financial architecture • Based on ádditional growth Stucture of the financial system • Extension of the Financial architecture • Regional complementary currencies • Instability • Compulsory growth pressure • Short-term priority • Income disparity • Concentration effect • Erosion of social capital
4. complementary conventional solutions: • • • (neo-) liberal: Privaization Deregulation Liberalization Indivdiual responsibility • • • Introduction of complementary Innovations Keyensian: Defizit spending Regulation Anticylical Financing public goods • Changes within the financial architecture • Based on ádditional growth Stucture of the financial system • Extension of the Financial architecture • Regional complementary currencies • Instability • Compulsory growth pressure • Short-term priority • Income disparity • Concentration effect • Erosion of social capital
 4. complementary - REGIONAL COMPLEMENTARY CURRENCIESRegion: Currency: Complementary: Regional complementary currency:
4. complementary - REGIONAL COMPLEMENTARY CURRENCIESRegion: Currency: Complementary: Regional complementary currency:
 4. complementary Definition: Region: geographic area where people tend to identify with; between global and local neighborhood (10. 000 – 5 Mill. )
4. complementary Definition: Region: geographic area where people tend to identify with; between global and local neighborhood (10. 000 – 5 Mill. )
 4. complementary Definition: Currency: „… is a convention, an agreement of a community to use something as a medium of exchange“ B. Lietaer, 2001
4. complementary Definition: Currency: „… is a convention, an agreement of a community to use something as a medium of exchange“ B. Lietaer, 2001
 4. complementary Definition: Complementary: - Found in different disciplines (physics: Pauli, Heisenberg, psychology: C. G. Jung, Weizsäcker, Uexkuell, DNA-coding) General issues: Continuity and stability, semantic and syntax, content and form ect. Act as a “medium of exchange” in addition to the given system Not linked causally to each other, but run parallel and depend on each other Necessary to balance the whole system To match unused resources and unmeet needs
4. complementary Definition: Complementary: - Found in different disciplines (physics: Pauli, Heisenberg, psychology: C. G. Jung, Weizsäcker, Uexkuell, DNA-coding) General issues: Continuity and stability, semantic and syntax, content and form ect. Act as a “medium of exchange” in addition to the given system Not linked causally to each other, but run parallel and depend on each other Necessary to balance the whole system To match unused resources and unmeet needs
 4. complementary Definition: Regional complementary currencies: „medium of exchange that mets regional unmet needs and unused sources and operates parallel to the conventional system“.
4. complementary Definition: Regional complementary currencies: „medium of exchange that mets regional unmet needs and unused sources and operates parallel to the conventional system“.
 4. complementary Complementary solutions: • (regional) complementary currencies Principles: • interest-free • mutual credits of real goods and services • cooperation and peer control • sufficient supply • chaordic-Principle
4. complementary Complementary solutions: • (regional) complementary currencies Principles: • interest-free • mutual credits of real goods and services • cooperation and peer control • sufficient supply • chaordic-Principle
 4. complementary Basic Goals of complementary currencies: 1. partial decoupling from the globalization 2. financial liquidity for the region 3. „Built-in-target“: stabil and more sustainable 4. empowering the region (diversity, visibility) 5. Human resources are encouraged (social capital)
4. complementary Basic Goals of complementary currencies: 1. partial decoupling from the globalization 2. financial liquidity for the region 3. „Built-in-target“: stabil and more sustainable 4. empowering the region (diversity, visibility) 5. Human resources are encouraged (social capital)
 1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
1. Sustainability 2. Towards an integrative approach 3. The money-system 4. Regional complementary currencies 5. Time for a change
 5. Time for a change S=Dx. Tx. Vx. I Regional complementary currencies can produce indirect susstainable feed back loops……
5. Time for a change S=Dx. Tx. Vx. I Regional complementary currencies can produce indirect susstainable feed back loops……
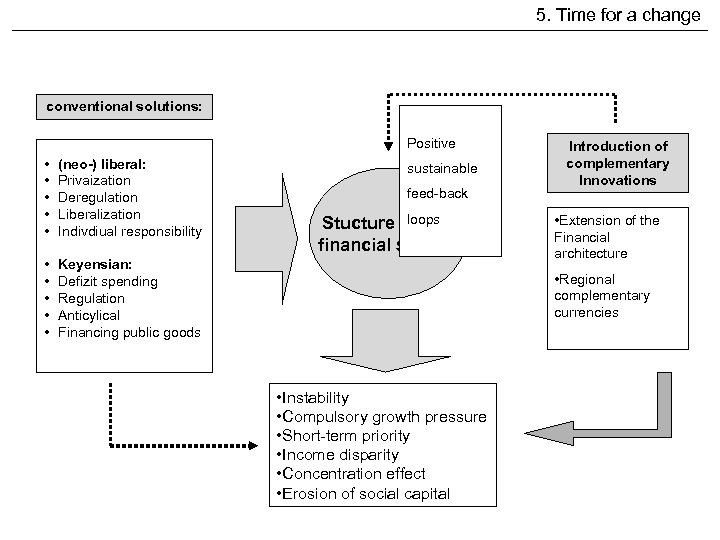 5. Time for a change conventional solutions: Positive • • • (neo-) liberal: Privaization Deregulation Liberalization Indivdiual responsibility • • • Keyensian: Defizit spending Regulation Anticylical Financing public goods sustainable feed-back loops Stucture of the financial system Introduction of complementary Innovations • Extension of the Financial architecture • Regional complementary currencies • Instability • Compulsory growth pressure • Short-term priority • Income disparity • Concentration effect • Erosion of social capital
5. Time for a change conventional solutions: Positive • • • (neo-) liberal: Privaization Deregulation Liberalization Indivdiual responsibility • • • Keyensian: Defizit spending Regulation Anticylical Financing public goods sustainable feed-back loops Stucture of the financial system Introduction of complementary Innovations • Extension of the Financial architecture • Regional complementary currencies • Instability • Compulsory growth pressure • Short-term priority • Income disparity • Concentration effect • Erosion of social capital
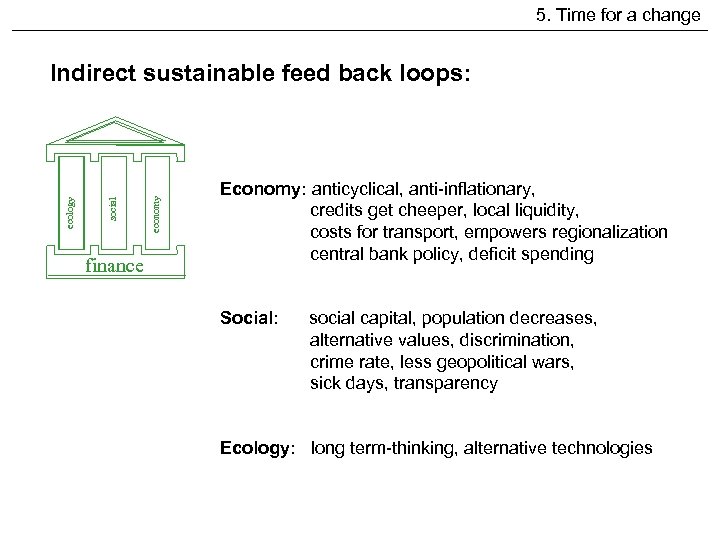 5. Time for a change finance economy social ecology Indirect sustainable feed back loops: Economy: anticyclical, anti-inflationary, credits get cheeper, local liquidity, costs for transport, empowers regionalization central bank policy, deficit spending Social: social capital, population decreases, alternative values, discrimination, crime rate, less geopolitical wars, sick days, transparency Ecology: long term-thinking, alternative technologies
5. Time for a change finance economy social ecology Indirect sustainable feed back loops: Economy: anticyclical, anti-inflationary, credits get cheeper, local liquidity, costs for transport, empowers regionalization central bank policy, deficit spending Social: social capital, population decreases, alternative values, discrimination, crime rate, less geopolitical wars, sick days, transparency Ecology: long term-thinking, alternative technologies
 5. Time for a change What`s the case for business? 1. High fixed and low marginal costs 2. Added value > marginal costs of an additional costumer 3. For example: airlines, hotels, movies, restaurants 4. Unused resources and unmet needs
5. Time for a change What`s the case for business? 1. High fixed and low marginal costs 2. Added value > marginal costs of an additional costumer 3. For example: airlines, hotels, movies, restaurants 4. Unused resources and unmet needs
 5. Time for a change What`s the case for public financing? 1. cost – benefit analysis: factor 3 -7 2. Increase of „social capital“ in the region 3. Decrease of public costs 4. f. ex. : social costs, sick days, crime rate,
5. Time for a change What`s the case for public financing? 1. cost – benefit analysis: factor 3 -7 2. Increase of „social capital“ in the region 3. Decrease of public costs 4. f. ex. : social costs, sick days, crime rate,
 5. Time for a change Our future economy Money and sustainability The overlooked connections www. stefan-brunnhuber. de www. futuremoney. de
5. Time for a change Our future economy Money and sustainability The overlooked connections www. stefan-brunnhuber. de www. futuremoney. de


