a3eb7fa89986960035896b60f16a8d0f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Whole Foods Market Case Study By: Dan Mc. Lindon Kyle Mc. Daniel Jeremy Smiley Tom Anderson Ray Moorman

Whole Foods Question Key Can Whole Foods remain competitive in face of major changes in the competitive environment?
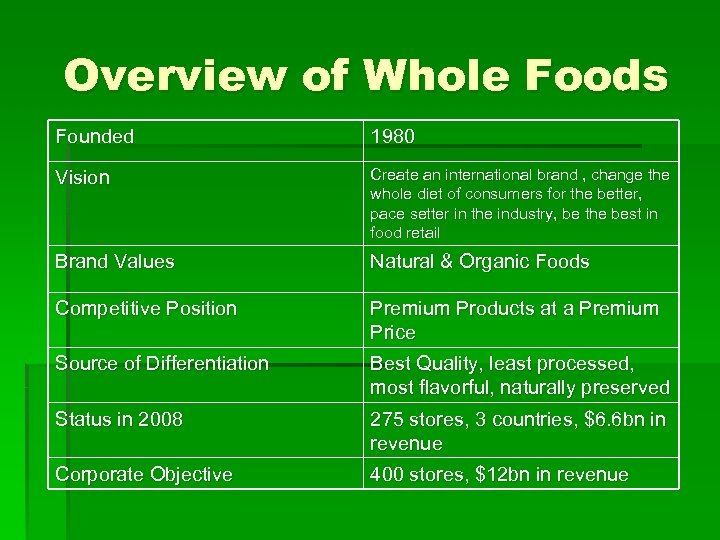
Overview of Whole Foods Founded 1980 Vision Create an international brand , change the whole diet of consumers for the better, pace setter in the industry, be the best in food retail Brand Values Natural & Organic Foods Competitive Position Premium Products at a Premium Price Source of Differentiation Best Quality, least processed, most flavorful, naturally preserved Status in 2008 275 stores, 3 countries, $6. 6 bn in revenue Corporate Objective 400 stores, $12 bn in revenue

What is changing in the external environment?
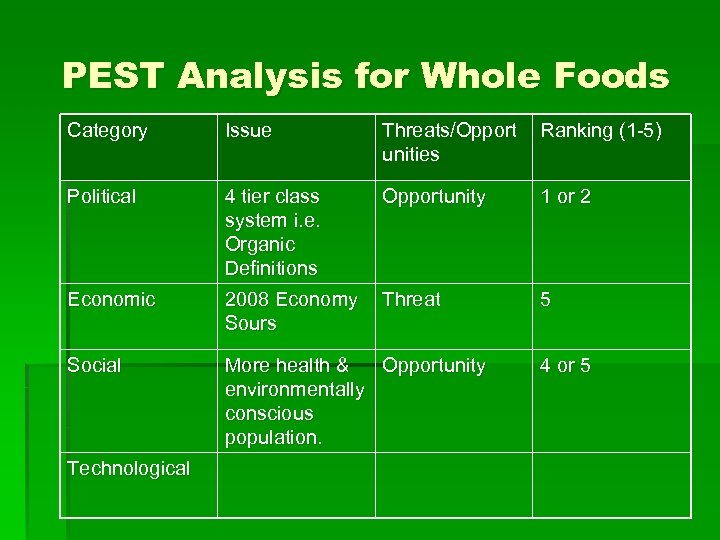
PEST Analysis for Whole Foods Category Issue Threats/Opport unities Ranking (1 -5) Political 4 tier class system i. e. Organic Definitions Opportunity 1 or 2 Economic 2008 Economy Sours Threat 5 Social More health & Opportunity environmentally conscious population. Technological 4 or 5

What are the changes in demand?
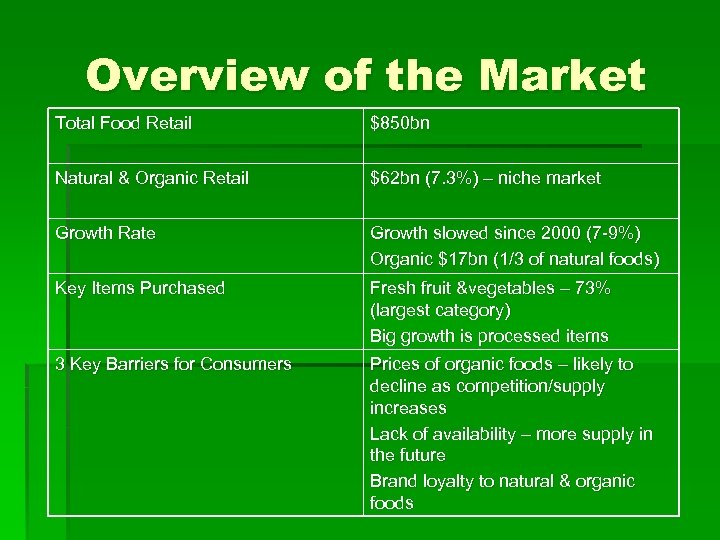
Overview of the Market Total Food Retail $850 bn Natural & Organic Retail $62 bn (7. 3%) – niche market Growth Rate Growth slowed since 2000 (7 -9%) Organic $17 bn (1/3 of natural foods) Key Items Purchased Fresh fruit &vegetables – 73% (largest category) Big growth is processed items 3 Key Barriers for Consumers Prices of organic foods – likely to decline as competition/supply increases Lack of availability – more supply in the future Brand loyalty to natural & organic foods
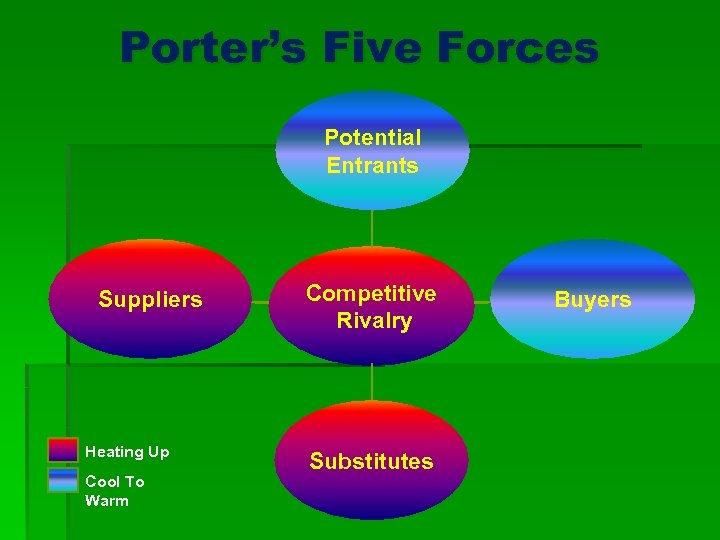
Porter’s Five Forces Potential Entrants Suppliers Heating Up Cool To Warm Competitive Rivalry Substitutes Buyers
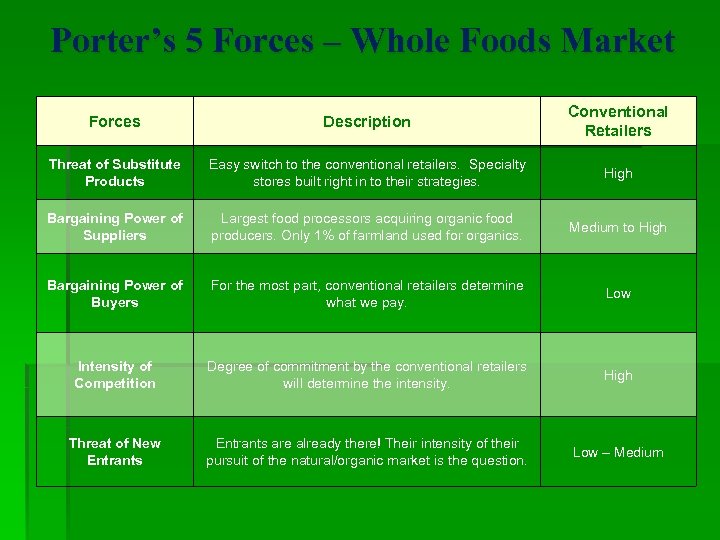
Porter’s 5 Forces – Whole Foods Market Forces Description Conventional Retailers Threat of Substitute Products Easy switch to the conventional retailers. Specialty stores built right in to their strategies. High Bargaining Power of Suppliers Largest food processors acquiring organic food producers. Only 1% of farmland used for organics. Medium to High Bargaining Power of Buyers For the most part, conventional retailers determine what we pay. Low Intensity of Competition Degree of commitment by the conventional retailers will determine the intensity. High Threat of New Entrants are already there! Their intensity of their pursuit of the natural/organic market is the question. Low – Medium
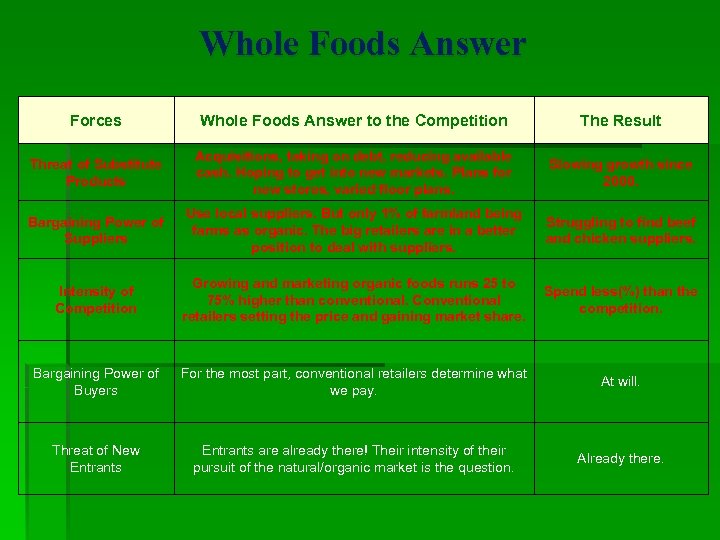
Whole Foods Answer Forces Whole Foods Answer to the Competition The Result Threat of Substitute Products Acquisitions, taking on debt, reducing available cash. Hoping to get into new markets. Plans for new stores, varied floor plans. Slowing growth since 2000. Bargaining Power of Suppliers Use local suppliers. But only 1% of farmland being farms as organic. The big retailers are in a better position to deal with suppliers. Struggling to find beef and chicken suppliers. Intensity of Competition Growing and marketing organic foods runs 25 to 75% higher than conventional. Conventional retailers setting the price and gaining market share. Spend less(%) than the competition. Bargaining Power of Buyers For the most part, conventional retailers determine what we pay. At will. Threat of New Entrants are already there! Their intensity of their pursuit of the natural/organic market is the question. Already there.

Changes in the Competitive Landscape Should they really welcome competition? § Local, regional, independent, national, and specialty stores are all competitors. § CEO say it is a gateway for customers to try natural/organic foods or opportunity for the competition? Take a look at Store Sales Growth 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 14. 9% 12. 8% 11. 0% 7. 1% ? ? ? Sales growth has been cut in half since 2004!
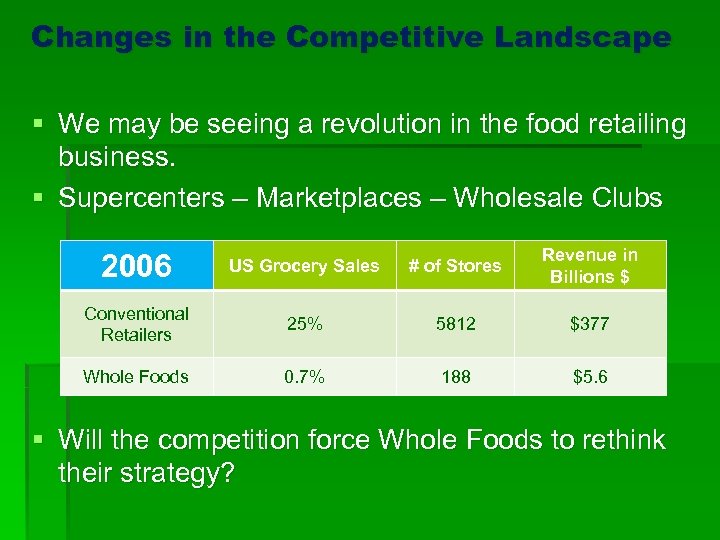
Changes in the Competitive Landscape § We may be seeing a revolution in the food retailing business. § Supercenters – Marketplaces – Wholesale Clubs 2006 US Grocery Sales # of Stores Revenue in Billions $ Conventional Retailers 25% 5812 $377 Whole Foods 0. 7% 188 $5. 6 § Will the competition force Whole Foods to rethink their strategy?

What is Whole Foods Strategy? § § § Marketing Growth Operational

Marketing Strategy § Product § High Quality Natural and Organic Food and nonfood items § Offerings vary based on store size and tastes of local clientele § Exotic offerings and product variety § Ex) Japanese eggplant, 40 cheeses, 20 coffees § Private label products § Emphasis on perishables (fruits/veg. , bakery goods, meat, seafood) – 67 % of sales

Marketing Strategy § Price § Goal is competitive price at highest quality § Organic foods are 25 – 75% more costly to grow and market § Price and Quality are competing forces § Whole Foods chooses to focus on Quality, therefore prices are higher than conventional grocers

Marketing Strategy § Place § No standard store design. Layout customized for site and product mix. § Colorful, inviting, fun § Gathering place to learn, interact, eat, and grocery shop § Presentation § Highly regarded food displays, cleanliness, wide aisles

Marketing Strategy § Promotion § Primarily rely on word-of-mouth recommendations § 0. 5% of revenue spent on advertising § Most marketing spend is for in-store signage and events § Store personnel is knowledgeable and personable

Growth Strategy § New stores and acquisitions of small owner-managed chains in desirable markets § Ideal store size is 45, 000 – 60, 000 sq. ft.

Operational Strategy § Team-based management of store operations § Many personnel, merchandising, and operating decisions made at store level § Buying responsibility at the national and regional levels for volume discounts § Own and operate many distribution centers: 2 for produce, 9 bake houses, 5 commissary kitchens for prepared food, and a central coffee roaster

What are the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for Whole Foods?
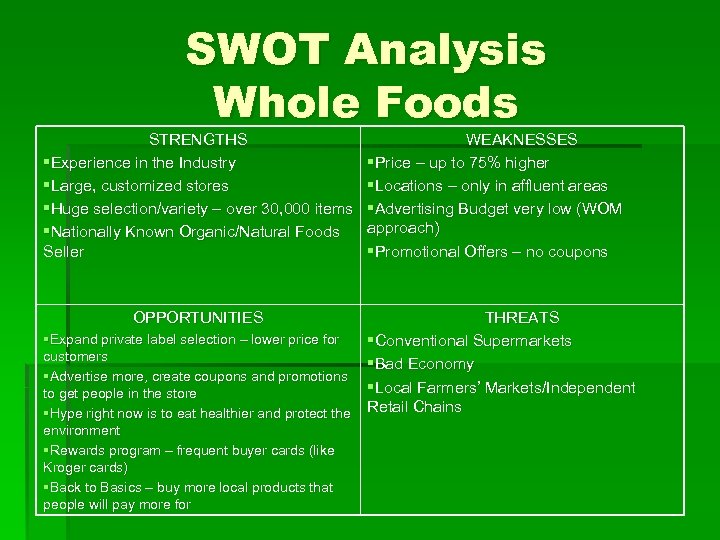
SWOT Analysis Whole Foods STRENGTHS §Experience in the Industry §Large, customized stores §Huge selection/variety – over 30, 000 items §Nationally Known Organic/Natural Foods Seller OPPORTUNITIES WEAKNESSES §Price – up to 75% higher §Locations – only in affluent areas §Advertising Budget very low (WOM approach) §Promotional Offers – no coupons THREATS §Expand private label selection – lower price for §Conventional Supermarkets customers §Bad Economy §Advertise more, create coupons and promotions §Local Farmers’ Markets/Independent to get people in the store §Hype right now is to eat healthier and protect the Retail Chains environment §Rewards program – frequent buyer cards (like Kroger cards) §Back to Basics – buy more local products that people will pay more for

What are the future challenges for Whole Foods?

Future Challenges § Conventional Grocery Stores over saturate Market & offer Organic & Natural Foods § Convince new customers to shop at WF rather then more convenient stores § Pricing – being able to compete against the conventional grocery chains § Getting more people in the store

Recommendations for Whole Foods Market

Recommendations § Lower Price to Compete with Grocery Stores § Add a customer rewards program for frequent buyers § Mail coupons to customers § Expand Private Label Selection § Lowers mfg costs, could offer discounts to customer for using WF brand products

Recommendations § Personalize Service at WF § 3 days after purchase, email Thank You cards to customers after purchases § 7 days after purchase, email 10% coupon to use on next purchase § Email recipes § Advertise, Advertise § Mail fliers to local zip codes – show locally grown foods, classes offered, items on sale, coupons

Recommendations § Catering § Offer catering to local businesses & events § Do Not Buy Wild Oats § Halt expansion until WF builds up more cash § Focus on profitable stores and use that philosophy to improve unprofitable stores
a3eb7fa89986960035896b60f16a8d0f.ppt