cac398e5cb009f8b576f74273a005d4a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51

Who should control education? Prof. Oleg Liber Institute for Educational Cybernetics University of Bolton

Education is a Human Right "Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory. Technical and professional education shall be made generally available and higher education shall be equally accessible to all on the basis of merit” Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Article 26

Education is a Human Right "The States Parties. . . recognize the right of everyone to education. . Education shall enable all persons to participate effectively in a free society, promote understanding, tolerance and friendship among. . . racial, ethnic or religious groups. . Primary education shall be compulsory and available free to all. . . Secondary education. . . including technical and vocational secondary education, shall be made generally available and accessible to all. . Higher education shall be made equally accessible to all. . “ --International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, Article 13

Shared Understanding? Primary Education: In UK ends at age 11, but in Denmark at age 16!

Shared Understanding? Secondary Education: “Secondary schools have been generally the great disappointment of the 20 th century. They have been too big, too demoralised, distanced from true learning by the national curriculum and the hurriedness and uniformity that it imparts, too restricting for young adults.

Shared Understanding? Secondary Education: “The time will come when the compulsory school age is lowered to 14 and… more teenagers averse to school will be coupled with an older person as their education companion to introduce them to learning. ” (Young, 2000)

Shared Understanding? Technical and Vocational Education …contrasted with theory and abstract conceptual knowledge, characteristic of tertiary education. i. e. not Law, Medicine, Engineering, Dentistry, Teaching, Nursing… ? Countryside Recreation & Tourism Food and Drink Heritage Management Casino Operations Management Golf and Sports Turf Management Outdoor Adventure Management

What is Education for? . . Education shall be directed to the full development of the human personality and to the strengthening of respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms. It shall promote understanding, tolerance and friendship among. . . racial or religious groups. . Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Article 26 …Education shall enable all persons to participate effectively in a free society International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, Article 13

What does Education do? …for most men the right to learn is curtailed by the obligation to attend school … attempt to expand the pedagogue's responsibility until it engulfs his pupils' lifetimes …the search for… educational webs which heighten the opportunity for each one to transform each moment of his living into one of learning, sharing, and caring. Illich (1972)

Everyone knows that… Education spending is huge in the developed world The developing world cannot match this but is forced to try The Education system reinforces the cycle of disadvantage This is systemic

The promise of the computer: 1980 “…the computer will enable us to so modify the learning environment outside the classroom that much of not all the knowledge schools presently try to teach with such pain and expense and limited success will be learned, as the child learns to talk, painlessly, successfully, and without organized instruction” Seymour Papert (1980) Mindstorms, Harvester, Brighton p. 9

The promise of the computer: 1985 Interactive content on CD ROM (or Videodisk, or CDi…) Intelligent tutoring: “the acme of all the educational media if they existed” (Laurillard 1993) The end of school? The end of courses? All we need is more computers!

Villemard postcard from 1910 depicting education in the year 2000; Bibliothèque National de France

The promise of e. Learning 1990 s The WWW Content distribution (and sharing) Online discussions Online assessment The end of the campus? VLEs (LMS) All we need is bandwidth and standards

The promise of e. Learning, 21 st C We have the technology bandwidth standards software for collaboration What’s the problem? Why is education so unchanged? Why has Lifelong learning come to mean training?

It’s the system “Study theory of a system” (Deming 2000) POSIWID – the purpose of a system is what it does (Beer 1985) “…we have forgotten that education had any other purpose than to promote growth” (Wolf 2002)

What is to be done? • Understand (model) the system • what does it do and how? • Recognise and acknowledge the importance of non-formal modes of learning • Promote and support selforganised learning • give the people the tools • Invert and find a new role for institutions • re-design the meta-system
Modelling the Education System • Beer’s Viable System • • • Model (VSM) Establish the identity (purpose) Agree recursions of the system Model each recursion Fiv e Fou r Thre e

Establishing the identity Transformation: what is being transformed? Actors: who effects the transformation? Suppliers: who supplies the inputs? Customers: who benefits? Owners: who controls the system? Interveners: who else matters? Espejo, R. (1990)

Examples T: Learner’s ability to control their future A: Learners S: Teachers C: The population O: The community I: Other institutions – work, arts, leisure National economic growth Teachers Publishers The national economy The state Competitors
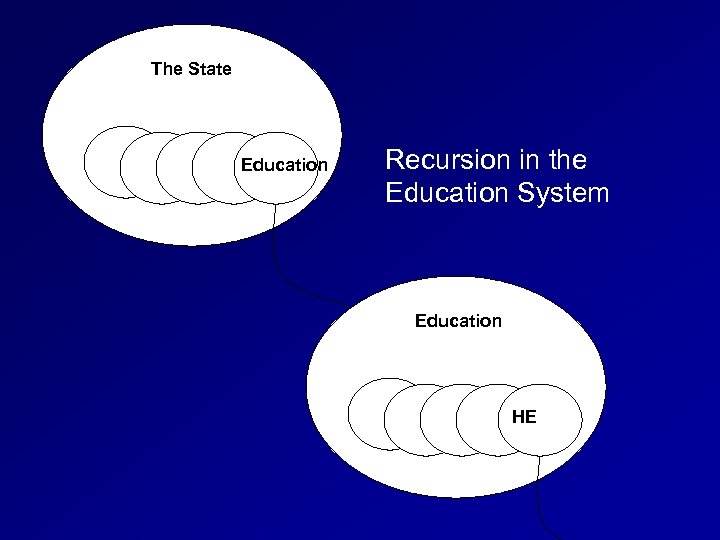
The State Education Recursion in the Education System Education HE Institution Dept State Programme Institution Dept. HE

Recursion is important “…fundamental processes are causing… loss of control… processes… are needed to contain explosive disorder. Management will need to work at the metasystemic level. We can no longer afford to tinker with the internal mechanisms of established institutions. ” Beer (1975) Platform for Change. Chichester, Wiley p. 117
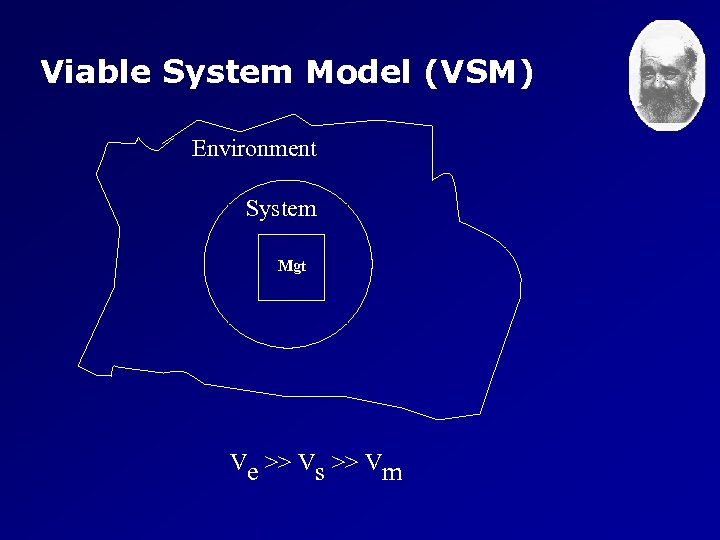
Viable System Model (VSM) Environment System Mgt Ve >> Vs >> Vm
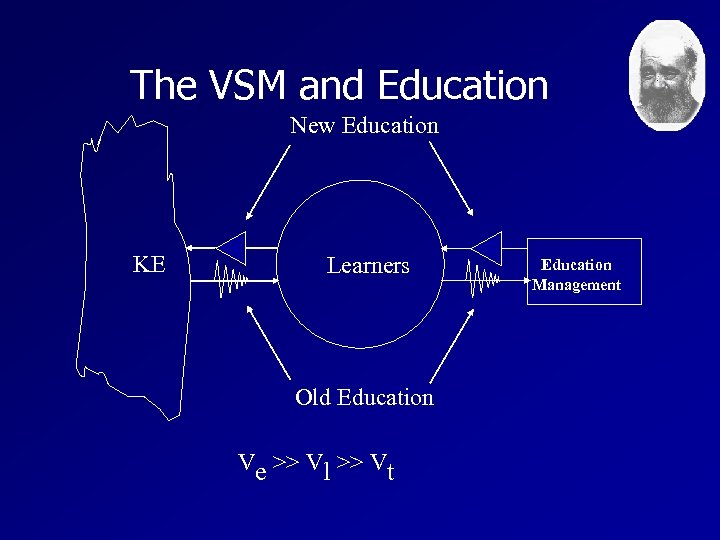
The VSM and Education New Education KE Learners Old Education Ve >> Vl >> Vt Education Management
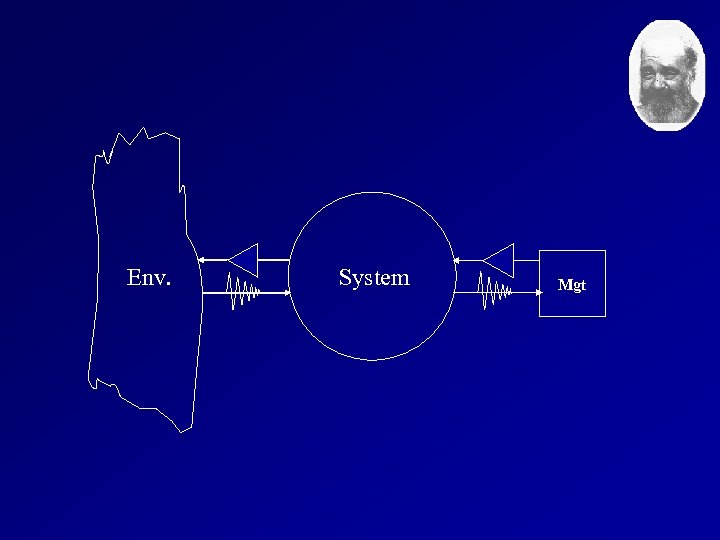
Env. System Mgt

Mgt. on. Organization
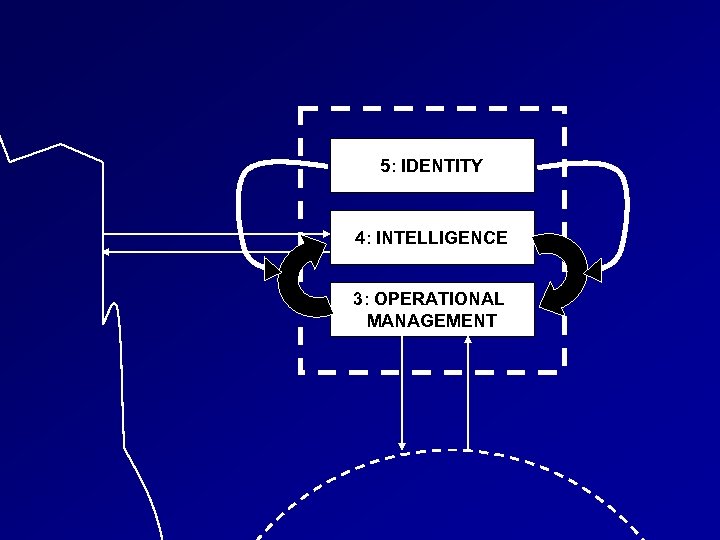
5: IDENTITY 4: INTELLIGENCE 3: OPERATIONAL MANAGEMENT
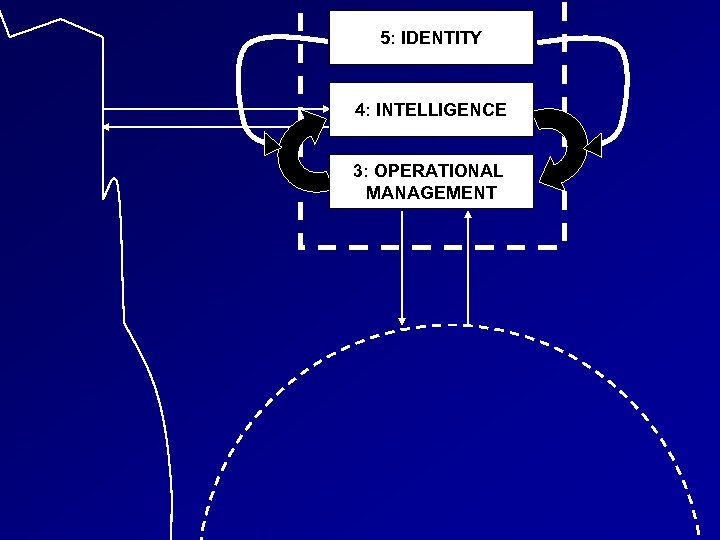
5: IDENTITY 4: INTELLIGENCE 3: OPERATIONAL MANAGEMENT
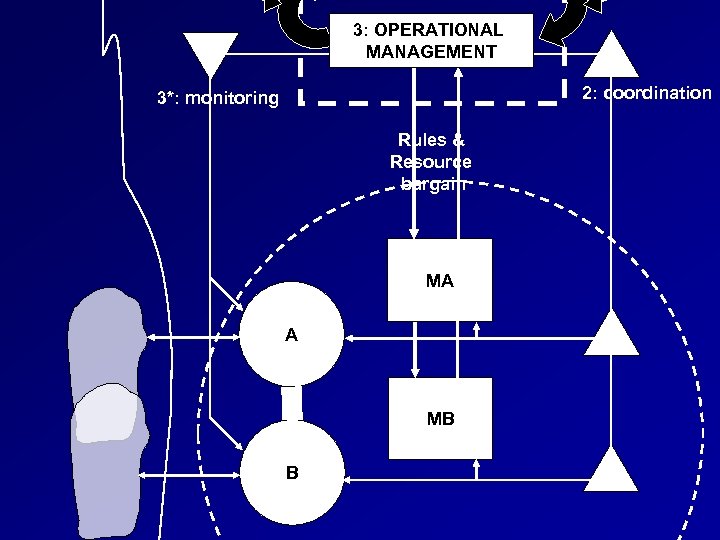
3: OPERATIONAL MANAGEMENT 2: coordination 3*: monitoring Rules & Resource bargain MA A MB B
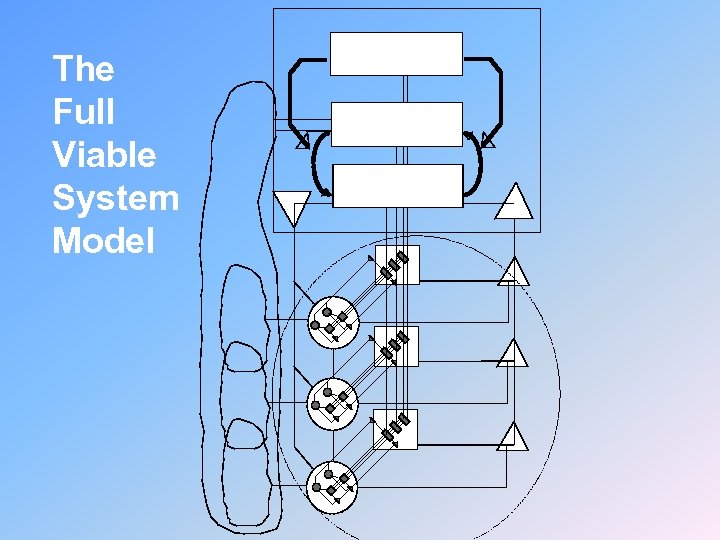
The Full Viable System Model Five 5. Policy Four 4. Strategy Three 3. Control
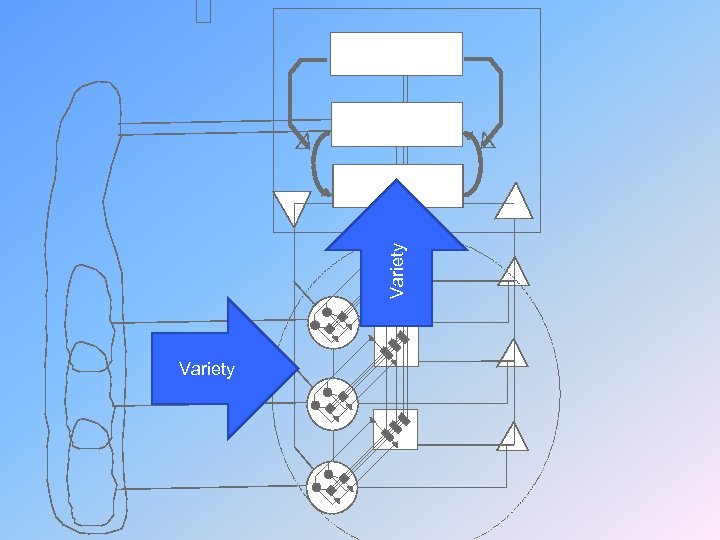
Five 5. Policy Four 4. Strategy Variety Three 3. Control Variety

How the Education System attenuates variety: knowledge Implied stability of knowledge Knowledge divided into academic subjects Institutions into subject based departments Subjects into courses Courses have linear curricula Curricula into lessons

How the Education System attenuates complexity: institutions & people Sectors are similar Institutions are similar People are similar grouped by ‘ability’ attend lessons learn content tested on content before they can move to the next course
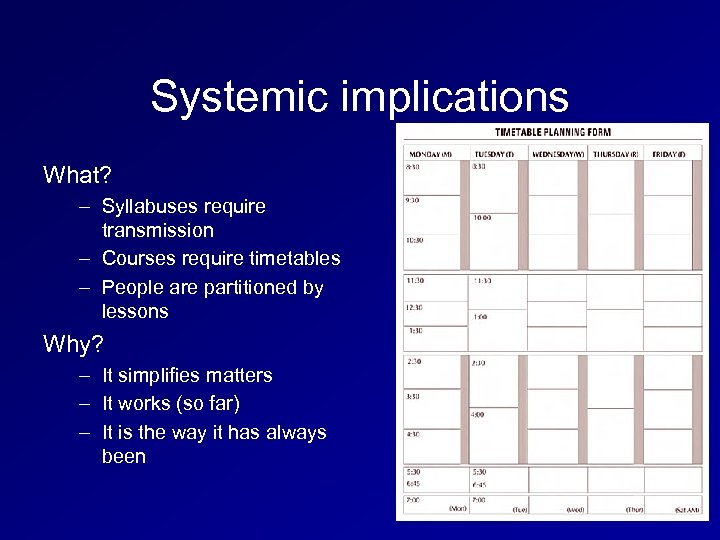
Systemic implications What? – Syllabuses require transmission – Courses require timetables – People are partitioned by lessons Why? – – – It simplifies matters It works (so far) It is the way it has always been

Pedagogic limitations People have unique histories, aptitudes and desires People have different learning approaches People have different time availability Designed for transmission of pre-defined content Difficult to organise – – – Individualised learning Small group learning Problem based learning

The costs of traditional education Difficult to develop process skills Team skills, problem solving skills, creative skills, conversational and social skills Overspecialisation No space for polymaths
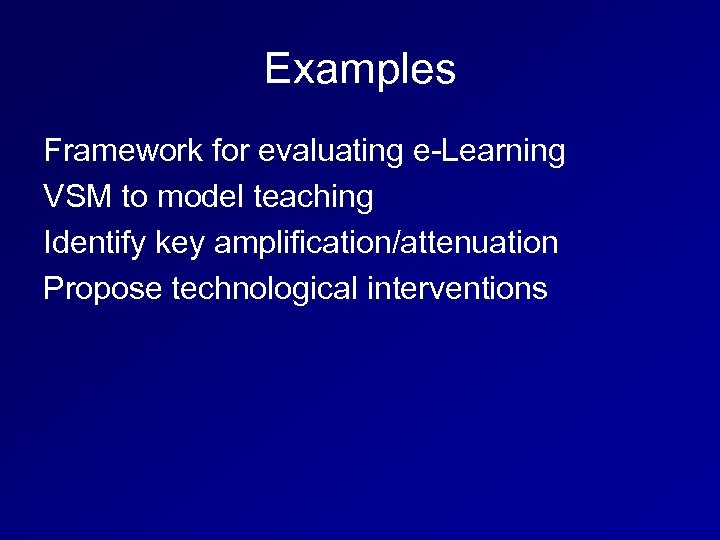
Examples Framework for evaluating e-Learning VSM to model teaching Identify key amplification/attenuation Propose technological interventions
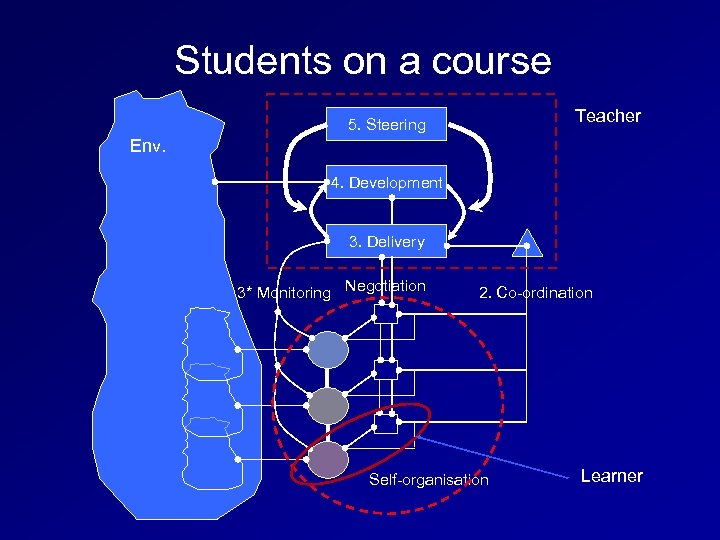
Students on a course Teacher 5. Steering Env. 4. Development 3. Delivery 3* Monitoring Negotiation 2. Co-ordination Self-organisation Learner

Proposed criteria 3. How does negotiation of learning take place? 2. How can a unit of learning be structured sequentially and / or hierarchically over time? What facilities are there to organise learners in a variety of ways in the module (whole group, small groups, individuals)? 3*. What facilities are there to monitor the success of the unit of learning as it runs? What can learners do on their own, outside of the purview of the teacher? 4. To what extent is it possible for the teacher to adapt the module structure once teaching is underway? Britain & Liber (2004) A Framework for pedagogical evaluation of Virtual Learning Environments. JISC Report http: //www. jisc. ac. uk/uploaded_documents/VLE%20 Full%20 Report%2006. doc

Example Personal Learning Environments Start with the whole person as a viable system Identify where new technological interventions can help amplify Join up fragments
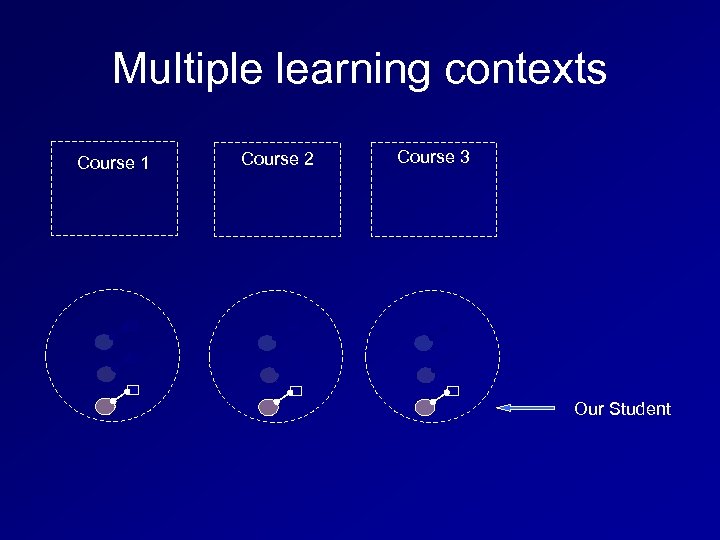
Multiple learning contexts Course 1 Course 2 Course 3 Our Student

Joining up the fragments
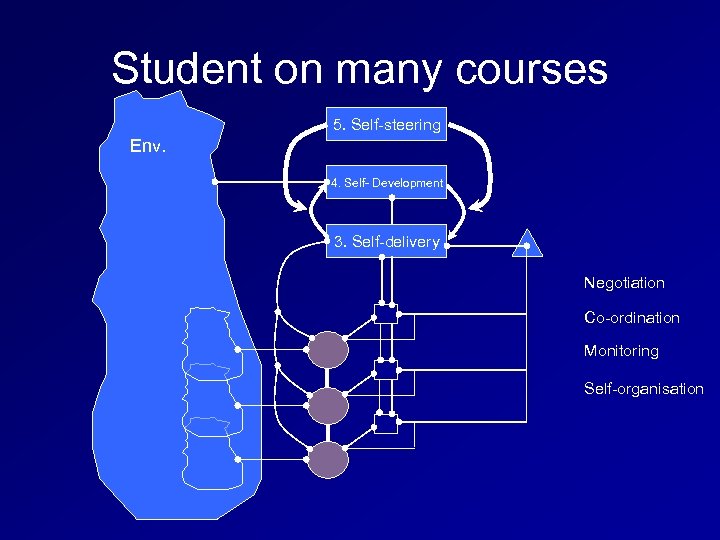
Student on many courses 5. Self-steering Env. 4. Self- Development 3. Self-delivery Negotiation Co-ordination Monitoring Self-organisation

Self management Negotiating Learning: Steering Coordinating courses: Development Env. – Commitments to different activities – Managing time, scheduling, resources, materials, colleagues, reading, activities, making overall sense Delivery Monitoring: – Am I making progress on each course as I expected? - reflection Self-organised collaboration – Finding synergy between courses & activities Development: – New courses? New materials? New colleagues? Where next? PDP
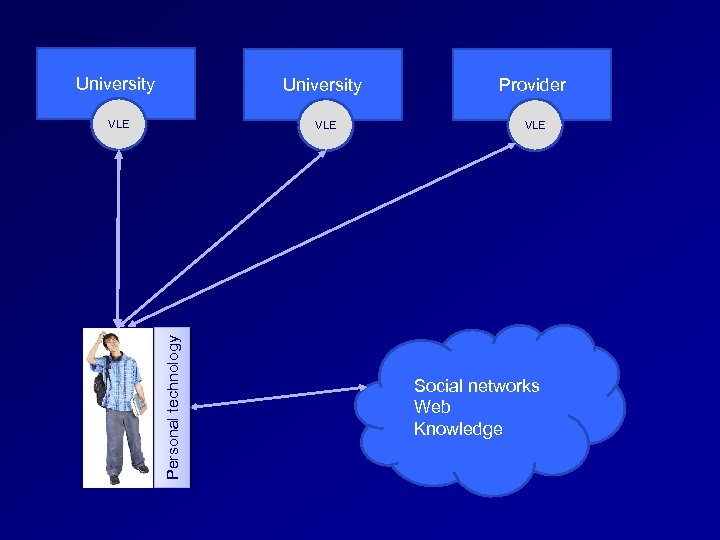
University Provider VLE VLE Personal technology University Social networks Web Knowledge
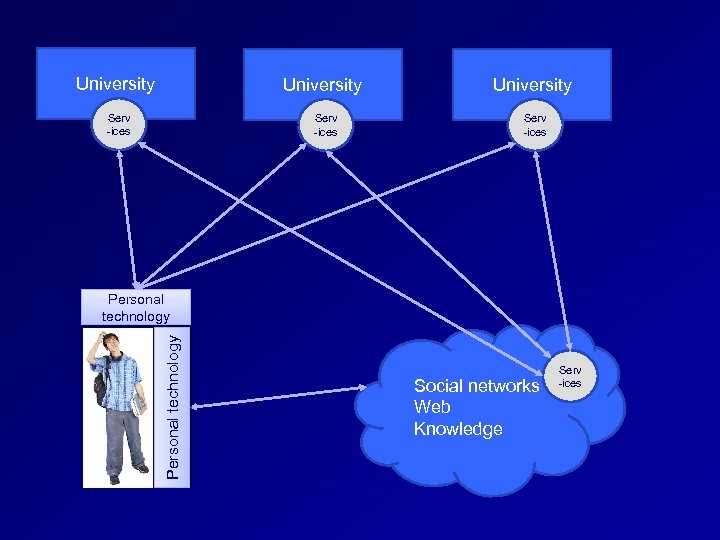
University Serv -ices Personal technology Social networks Web Knowledge Serv -ices

Real Possibilities? University as service? Customers or apprentices? Separate teaching and certification? different products Encourage and nurture inquiry Inquiry-based learning at the workplace Ensure high level interoperability provide information, not tools Use models and real data to manage our work no more blame Co-educate

Universities and students Are learners part of the institution? Is the learners part of the institution’s environment? Are institutions part of the learners’ environments? Are all these “true”? How do they affect the design of technical systems?

Challenge for institutions What is their purpose given modern information environment? Re-think education – all recursions Make lifelong learning real Promote and facilitate selforganised learning Institutional inversion (Illich)

Alternatives Full deschooling? 100% self organised online Resourced how? The digerati New elites… same elites? Return to participative education - WEA State operate as metasystem Democratic control over our futures

“We are plagued by misconceptions about learning that stem from thinking that schooling is synonymous with education” (p 162) Gordon Pask (1982) Microman. London, Century The daunting challenge of achieving a sustainable society in the coming decades demands a wholesale and urgent reorientation of educational vision and practice. Sterling, S. (2004). Whole systems thinking as a basis for paradigm change in education: Explorations in the context of sustainability. Ph. D. thesis, University of Bath. Retrieved February 28, 2005 from http: //www. bath. ac. uk/cree/sterling. htm.
cac398e5cb009f8b576f74273a005d4a.ppt