e549683dc8d0139cb97670a0b536701d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 70
 WHO Prequalification Programme Training Workshop on Assessment of Quality Part of Dossier Copenhagen 19 to 22 January 2011 Dissolution case studies Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 1
WHO Prequalification Programme Training Workshop on Assessment of Quality Part of Dossier Copenhagen 19 to 22 January 2011 Dissolution case studies Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 1
 Design of session What is: § § Dissolution testing? Multi-point dissolution (dissolution profile)? Comparative dissolution? Similarity of dissolution profiles? s abs/cap t release IR Focus: Applications: § § § Pharmaceutical development Setting of dissolution specification Up-scaling and Variations In biowaiver studies (BCS-based biowaiver & additional strengths) Disintegration and dissolution API solid state properties Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 2
Design of session What is: § § Dissolution testing? Multi-point dissolution (dissolution profile)? Comparative dissolution? Similarity of dissolution profiles? s abs/cap t release IR Focus: Applications: § § § Pharmaceutical development Setting of dissolution specification Up-scaling and Variations In biowaiver studies (BCS-based biowaiver & additional strengths) Disintegration and dissolution API solid state properties Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 2
 Immediate-release (IR) dosage forms l IR dosage forms are preparations showing a release of the API(s) which is not deliberately modified by a special formulation design and/or manufacturing method (EP) § § Also called Conventional-release dosage forms Duration of the test is typically 20 to 60 minutes (USP <1092>) l The BCS introduced two specific terms § Rapidly dissolving: ≥ 85% in ≤ 30 minutes § Very rapidly dissolving: ≥ 85% in ≤ 15 minutes o In 3 BCS media (WHO BE guideline definition) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 3
Immediate-release (IR) dosage forms l IR dosage forms are preparations showing a release of the API(s) which is not deliberately modified by a special formulation design and/or manufacturing method (EP) § § Also called Conventional-release dosage forms Duration of the test is typically 20 to 60 minutes (USP <1092>) l The BCS introduced two specific terms § Rapidly dissolving: ≥ 85% in ≤ 30 minutes § Very rapidly dissolving: ≥ 85% in ≤ 15 minutes o In 3 BCS media (WHO BE guideline definition) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 3
 What is dissolution testing? It measures the portion (%) of the API 1. that has been released from tablets/capsules matrix and 2. that has dissolved in the dissolution medium during controlled testing conditions within a defined period In simple terms: § The tablet thus first disintegrates § Then the API will be able to dissolve § Slow disintegration ➜ slow dissolution Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 4
What is dissolution testing? It measures the portion (%) of the API 1. that has been released from tablets/capsules matrix and 2. that has dissolved in the dissolution medium during controlled testing conditions within a defined period In simple terms: § The tablet thus first disintegrates § Then the API will be able to dissolve § Slow disintegration ➜ slow dissolution Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 4
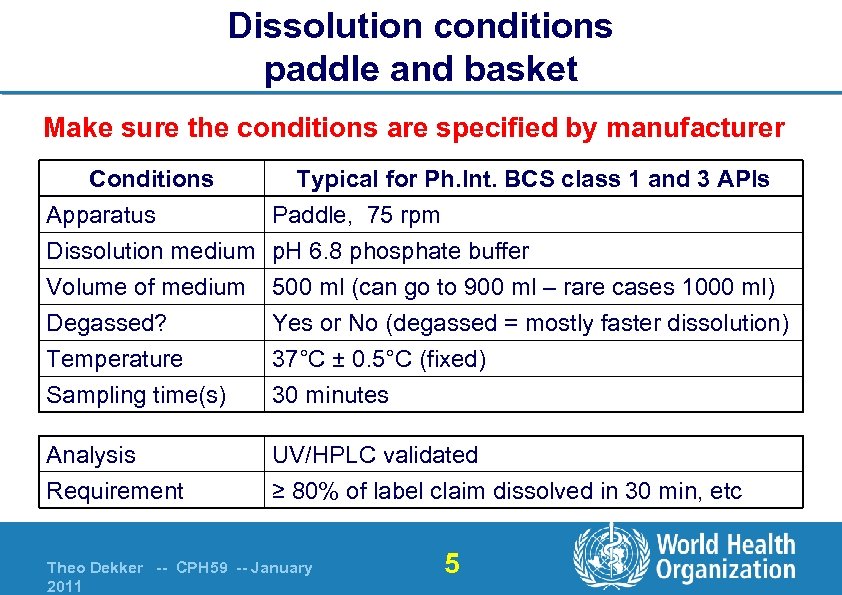 Dissolution conditions paddle and basket Make sure the conditions are specified by manufacturer Conditions Typical for Ph. Int. BCS class 1 and 3 APIs Apparatus Paddle, 75 rpm Dissolution medium p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer Volume of medium 500 ml (can go to 900 ml – rare cases 1000 ml) Degassed? Temperature Sampling time(s) Yes or No (degassed = mostly faster dissolution) 37°C ± 0. 5°C (fixed) 30 minutes Analysis UV/HPLC validated Requirement ≥ 80% of label claim dissolved in 30 min, etc Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 5
Dissolution conditions paddle and basket Make sure the conditions are specified by manufacturer Conditions Typical for Ph. Int. BCS class 1 and 3 APIs Apparatus Paddle, 75 rpm Dissolution medium p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer Volume of medium 500 ml (can go to 900 ml – rare cases 1000 ml) Degassed? Temperature Sampling time(s) Yes or No (degassed = mostly faster dissolution) 37°C ± 0. 5°C (fixed) 30 minutes Analysis UV/HPLC validated Requirement ≥ 80% of label claim dissolved in 30 min, etc Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 5
 Single point dissolution test l Simplest form of dissolution § One sample is withdrawn from the dissolution medium o Through an in-line or end-of-sampling probe filter § at a pre-determined time point and § the sample is analysed for the % API(s) dissolved y bilit o UV/VIS or HPLC most common a e/st leas P re r FP o l Result is given as e. g. tly f s Mo § 93 % in 30 minutes § No decimal is required Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 6
Single point dissolution test l Simplest form of dissolution § One sample is withdrawn from the dissolution medium o Through an in-line or end-of-sampling probe filter § at a pre-determined time point and § the sample is analysed for the % API(s) dissolved y bilit o UV/VIS or HPLC most common a e/st leas P re r FP o l Result is given as e. g. tly f s Mo § 93 % in 30 minutes § No decimal is required Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 6
 Multi-point dissolution In multipoint dissolution § multiple (≥ 3) samples are withdrawn from the dissolution medium during dissolution testing § at pre-determined time points (intervals) and § each sample is analysed for the % API dissolved A graph of % API dissolved against time = the dissolution profile Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 7
Multi-point dissolution In multipoint dissolution § multiple (≥ 3) samples are withdrawn from the dissolution medium during dissolution testing § at pre-determined time points (intervals) and § each sample is analysed for the % API dissolved A graph of % API dissolved against time = the dissolution profile Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 7
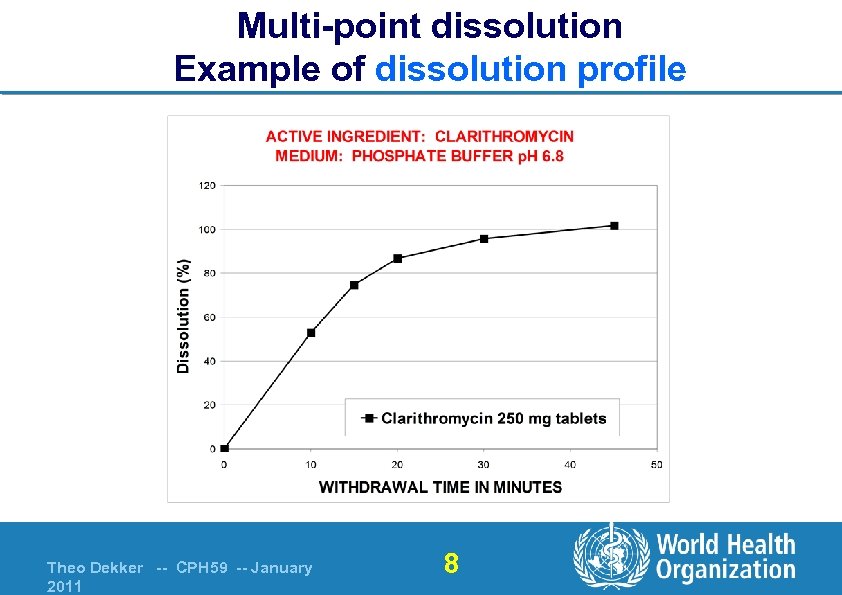 Multi-point dissolution Example of dissolution profile Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 8
Multi-point dissolution Example of dissolution profile Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 8
 Comparative dissolution testing The principle and basic requirements v Comparison of 2 or more products or batches containing the same API § by means of multipoint dissolution (comparing profiles) 1. The strength of products / batches may OR may not be the same depending on purpose of test 2. The dissolution conditions must be similar, e. g. • • Apparatus, medium, volume, rotation speed & temperature Minimize possible experimental differences in conditions 3. Samples are taken at the same time points for data comparison Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 9
Comparative dissolution testing The principle and basic requirements v Comparison of 2 or more products or batches containing the same API § by means of multipoint dissolution (comparing profiles) 1. The strength of products / batches may OR may not be the same depending on purpose of test 2. The dissolution conditions must be similar, e. g. • • Apparatus, medium, volume, rotation speed & temperature Minimize possible experimental differences in conditions 3. Samples are taken at the same time points for data comparison Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 9
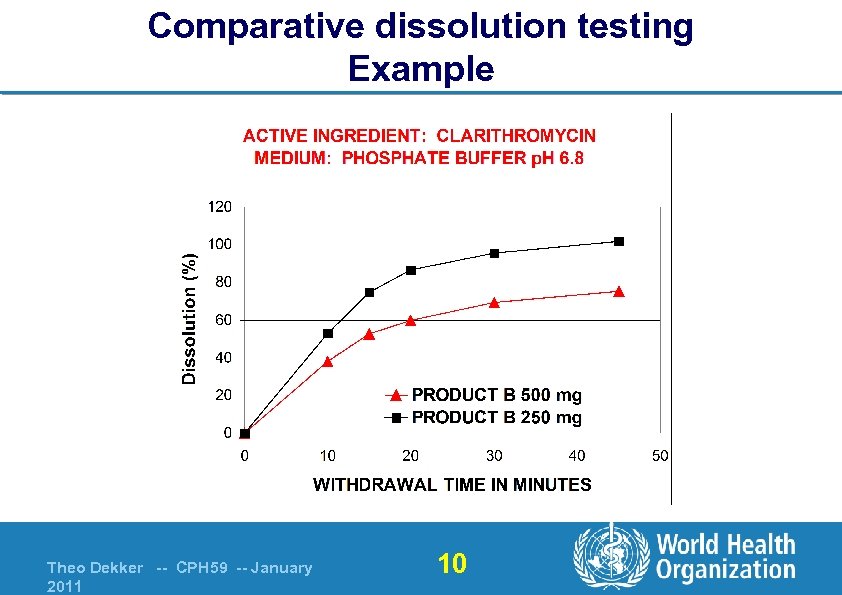 Comparative dissolution testing Example Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 10
Comparative dissolution testing Example Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 10
 Comparative dissolution testing When are dissolution profiles similar? Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 11
Comparative dissolution testing When are dissolution profiles similar? Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 11
 Comparative dissolution testing Profile similarity determination 1. If both the test and reference product show ≥ 85% dissolution within 15 minutes, § the profiles are considered to be similar o No calculations are required If this is not the case, apply point 2 (next point) 2. Calculate the f 2 value (similarity factor): § If f 2 ≥ 50 o the profiles are regarded similar o No decimal required (f 2 = 49. 51 ≡ 50) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 12
Comparative dissolution testing Profile similarity determination 1. If both the test and reference product show ≥ 85% dissolution within 15 minutes, § the profiles are considered to be similar o No calculations are required If this is not the case, apply point 2 (next point) 2. Calculate the f 2 value (similarity factor): § If f 2 ≥ 50 o the profiles are regarded similar o No decimal required (f 2 = 49. 51 ≡ 50) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 12
 Comparative dissolution testing Similarity factor f 2 n = number of time points Rt = % API dissolved of reference product at time point x Tt = % API dissolved of test product at time point x l Minimum of 3 time points (zero excluded) l 12 units (one / vessel) for each batch (for “official” purposes) l Only one measurement should be considered after the reference product has reached 85 % dissolution (or asymptote is reached) l RSD: ≤ 20% at early time point & ≤ 10% at later time points (apply with some discretion) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 13
Comparative dissolution testing Similarity factor f 2 n = number of time points Rt = % API dissolved of reference product at time point x Tt = % API dissolved of test product at time point x l Minimum of 3 time points (zero excluded) l 12 units (one / vessel) for each batch (for “official” purposes) l Only one measurement should be considered after the reference product has reached 85 % dissolution (or asymptote is reached) l RSD: ≤ 20% at early time point & ≤ 10% at later time points (apply with some discretion) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 13
 Typical mistakes Often manufacturers include the following points in the f 2 calculation l Time zero in the f 2 calculation § % dissolved = 0 at t = 0 minutes l Points beyond the reference product reaches 85% It is not according to the “rules” l What is the problem with including these points? The f 2 value will increase – may lead to false positive f 2 Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 14
Typical mistakes Often manufacturers include the following points in the f 2 calculation l Time zero in the f 2 calculation § % dissolved = 0 at t = 0 minutes l Points beyond the reference product reaches 85% It is not according to the “rules” l What is the problem with including these points? The f 2 value will increase – may lead to false positive f 2 Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 14
 Comparative dissolution testing Similarity factor f 2 Take note - apply WHO requirement in PQP: l Unfortunate differences between WHO, FDA and EMEA guidelines on determination of “dissolution last point” for f 2 calculations: Source FDA (2000) WHO (2006) EMEA (2010) Only one measurement (of both products) should be considered after: BOTH the reference AND test products have reached 85 % dissolution (or asymptote is reached) the REFERENCE product has reached 85 % dissolution (or asymptote is reached) ANY ONE of the reference OR test product has reached 85 % dissolution (or asymptote is reached) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 15
Comparative dissolution testing Similarity factor f 2 Take note - apply WHO requirement in PQP: l Unfortunate differences between WHO, FDA and EMEA guidelines on determination of “dissolution last point” for f 2 calculations: Source FDA (2000) WHO (2006) EMEA (2010) Only one measurement (of both products) should be considered after: BOTH the reference AND test products have reached 85 % dissolution (or asymptote is reached) the REFERENCE product has reached 85 % dissolution (or asymptote is reached) ANY ONE of the reference OR test product has reached 85 % dissolution (or asymptote is reached) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 15
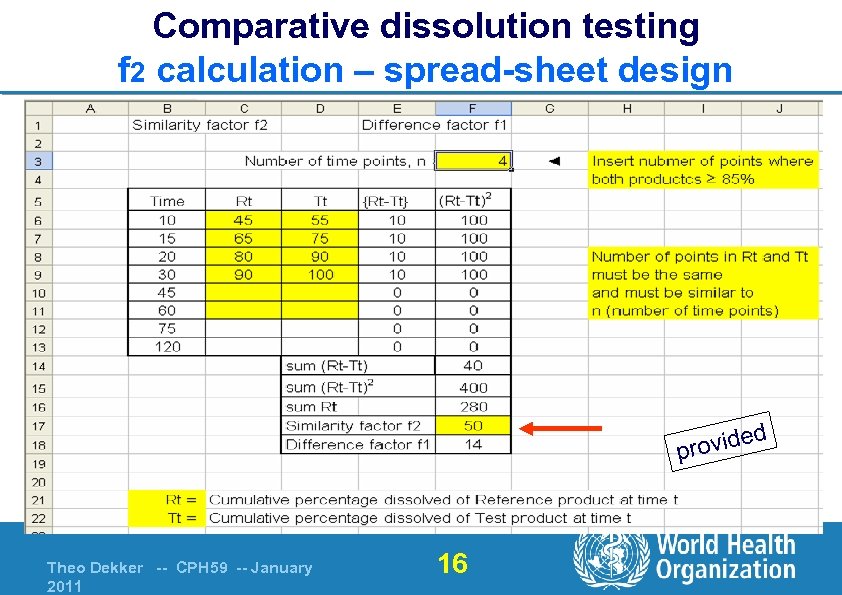 Comparative dissolution testing f 2 calculation – spread-sheet design d rovide p Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 16
Comparative dissolution testing f 2 calculation – spread-sheet design d rovide p Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 16
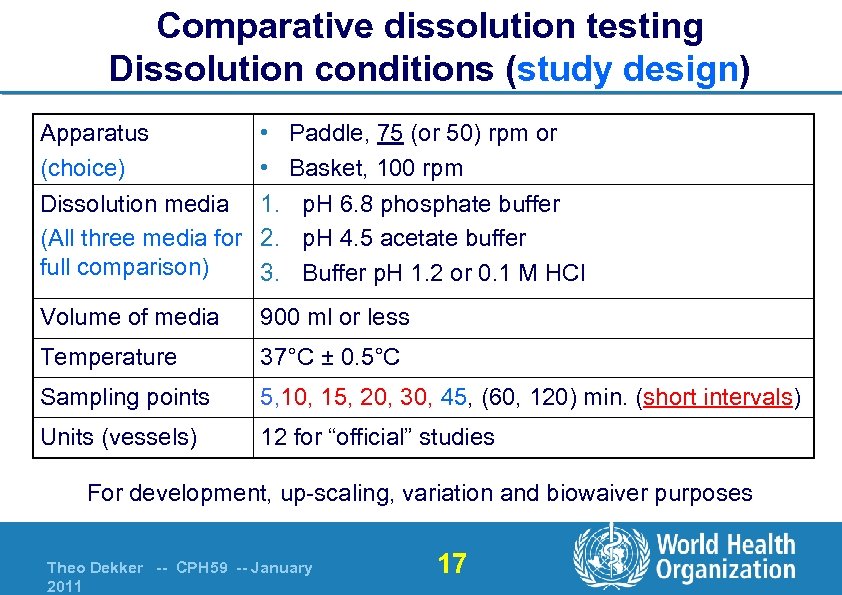 Comparative dissolution testing Dissolution conditions (study design) Apparatus (choice) Dissolution media (All three media for full comparison) • • 1. 2. 3. Volume of media 900 ml or less Temperature 37°C ± 0. 5°C Sampling points 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, (60, 120) min. (short intervals) Units (vessels) 12 for “official” studies Paddle, 75 (or 50) rpm or Basket, 100 rpm p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer p. H 4. 5 acetate buffer Buffer p. H 1. 2 or 0. 1 M HCl For development, up-scaling, variation and biowaiver purposes Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 17
Comparative dissolution testing Dissolution conditions (study design) Apparatus (choice) Dissolution media (All three media for full comparison) • • 1. 2. 3. Volume of media 900 ml or less Temperature 37°C ± 0. 5°C Sampling points 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, (60, 120) min. (short intervals) Units (vessels) 12 for “official” studies Paddle, 75 (or 50) rpm or Basket, 100 rpm p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer p. H 4. 5 acetate buffer Buffer p. H 1. 2 or 0. 1 M HCl For development, up-scaling, variation and biowaiver purposes Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 17
 Comparative dissolution testing Comparison of products / batches When are the dissolution properties of two products (batches) regarded similar? When their dissolution profiles are similar § in all three BCS media l Statements of instability or insolubility are not acceptable unless demonstrated / justified (literature also acceptable) o Assessor must query unjustified statements like this o Often the manufacturer knows submitted data might be queried… Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 18
Comparative dissolution testing Comparison of products / batches When are the dissolution properties of two products (batches) regarded similar? When their dissolution profiles are similar § in all three BCS media l Statements of instability or insolubility are not acceptable unless demonstrated / justified (literature also acceptable) o Assessor must query unjustified statements like this o Often the manufacturer knows submitted data might be queried… Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 18
 Profile comparison Some examples l Start the lap tops l Open the file: § Similarity factors f 2 & f 1. xls § Some of you may have other programs – use them Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 19
Profile comparison Some examples l Start the lap tops l Open the file: § Similarity factors f 2 & f 1. xls § Some of you may have other programs – use them Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 19
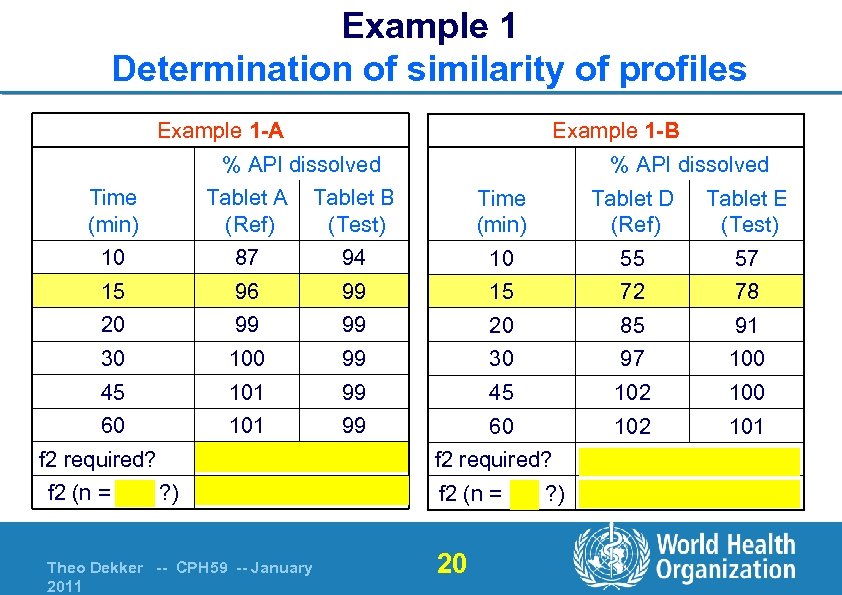 Example 1 Determination of similarity of profiles Example 1 -A Example 1 -B % API dissolved Time (min) Tablet A (Ref) Tablet B (Test) Time (min) Tablet D (Ref) Tablet E (Test) 10 87 94 10 55 57 15 96 99 15 72 78 20 99 99 20 85 91 30 100 99 30 97 100 45 101 99 45 102 100 60 101 99 60 102 101 f 2 required? f 2 (n = N/A ? ) No, ≥ 85% in 15 min profiles similar Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 f 2 required? f 2 (n = 3 ? ) 20 Yes 64 (similar)
Example 1 Determination of similarity of profiles Example 1 -A Example 1 -B % API dissolved Time (min) Tablet A (Ref) Tablet B (Test) Time (min) Tablet D (Ref) Tablet E (Test) 10 87 94 10 55 57 15 96 99 15 72 78 20 99 99 20 85 91 30 100 99 30 97 100 45 101 99 45 102 100 60 101 99 60 102 101 f 2 required? f 2 (n = N/A ? ) No, ≥ 85% in 15 min profiles similar Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 f 2 required? f 2 (n = 3 ? ) 20 Yes 64 (similar)
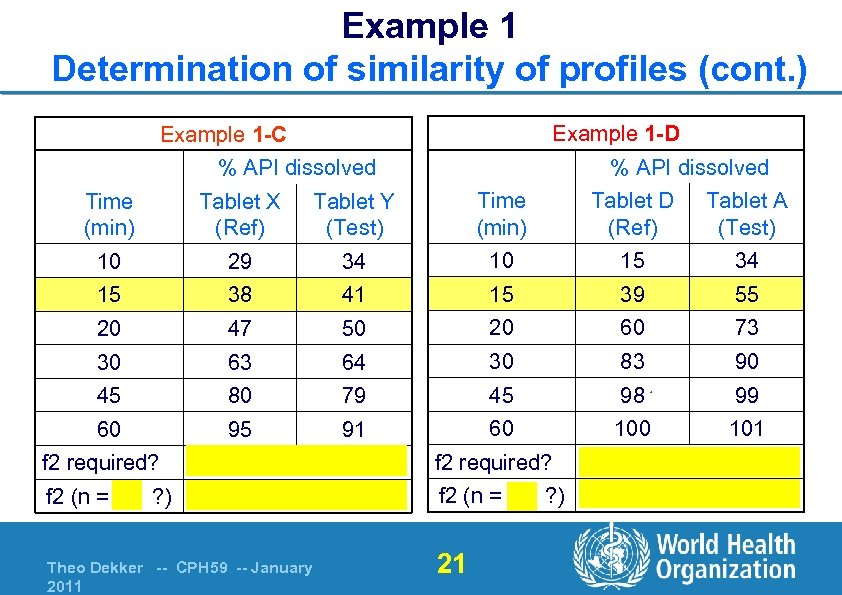 Example 1 Determination of similarity of profiles (cont. ) Example 1 -D Example 1 -C % API dissolved Time (min) Tablet X (Ref) Tablet Y (Test) Time (min) Tablet D (Ref) Tablet A (Test) 10 29 34 10 15 34 15 38 41 15 39 55 20 47 50 20 60 73 30 63 64 30 83 90 45 80 79 45 98 99 60 95 91 60 101 f 2 required? f 2 (n = 6 ? ) Yes 74 (similar) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 f 2 required? f 2 (n = 5 ? ) 21 Yes 44 (not similar)
Example 1 Determination of similarity of profiles (cont. ) Example 1 -D Example 1 -C % API dissolved Time (min) Tablet X (Ref) Tablet Y (Test) Time (min) Tablet D (Ref) Tablet A (Test) 10 29 34 10 15 34 15 38 41 15 39 55 20 47 50 20 60 73 30 63 64 30 83 90 45 80 79 45 98 99 60 95 91 60 101 f 2 required? f 2 (n = 6 ? ) Yes 74 (similar) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 f 2 required? f 2 (n = 5 ? ) 21 Yes 44 (not similar)
 Sampling intervals Why must samples be taken at short intervals for profile comparison? To prevent false positive results Test: Let us take previous example 1 -D and omit some points Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 22
Sampling intervals Why must samples be taken at short intervals for profile comparison? To prevent false positive results Test: Let us take previous example 1 -D and omit some points Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 22
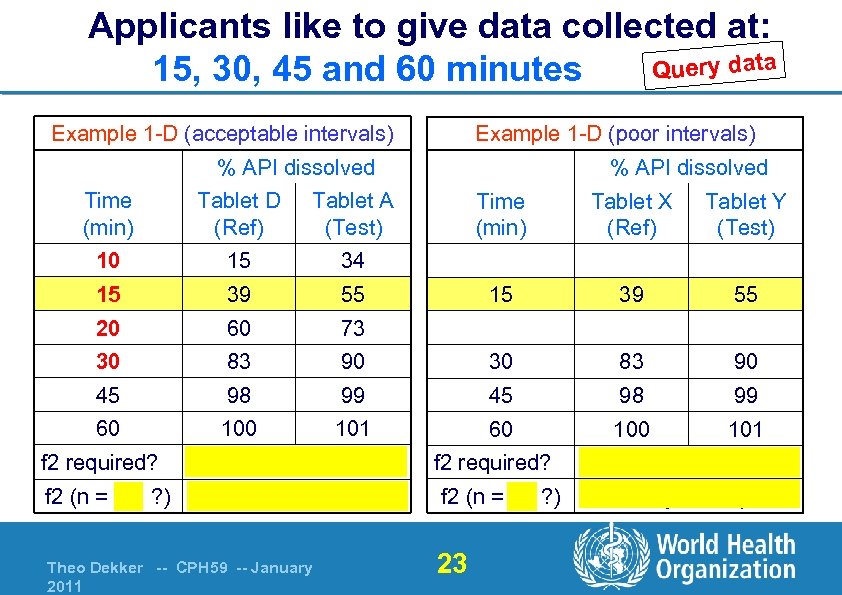 Applicants like to give data collected at: Query data 15, 30, 45 and 60 minutes Example 1 -D (acceptable intervals) Example 1 -D (poor intervals) % API dissolved Time (min) Tablet D (Ref) Tablet A (Test) 10 15 34 15 39 55 20 60 73 30 83 45 60 % API dissolved f 2 required? f 2 (n = 5 ? ) Time (min) Tablet X (Ref) Tablet Y (Test) 15 39 55 90 30 83 90 98 99 45 98 99 100 101 60 101 Yes 44 (not similar) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 f 2 required? f 2 (n = 3 ? ) 23 Yes 50 (similar)
Applicants like to give data collected at: Query data 15, 30, 45 and 60 minutes Example 1 -D (acceptable intervals) Example 1 -D (poor intervals) % API dissolved Time (min) Tablet D (Ref) Tablet A (Test) 10 15 34 15 39 55 20 60 73 30 83 45 60 % API dissolved f 2 required? f 2 (n = 5 ? ) Time (min) Tablet X (Ref) Tablet Y (Test) 15 39 55 90 30 83 90 98 99 45 98 99 100 101 60 101 Yes 44 (not similar) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 f 2 required? f 2 (n = 3 ? ) 23 Yes 50 (similar)
 Applications l Pharmaceutical development l Setting of dissolution specification l Up-scaling: biobatch to validation batches § To support any differences in formulation/processing l Variations l In biowaiver studies § BCS-based biowaiver & additional strengths l Disintegration and dissolution Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 24
Applications l Pharmaceutical development l Setting of dissolution specification l Up-scaling: biobatch to validation batches § To support any differences in formulation/processing l Variations l In biowaiver studies § BCS-based biowaiver & additional strengths l Disintegration and dissolution Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 24
 Application Pharmaceutical development Comparative dissolution integral part of § 3. 2. P. 2 Pharmaceutical Development § 3. 2. P. 2. 2. 1 Formulation Development o In vitro dissolution or drug release Comparative dissolution also applicable to 1. 3. 2. P. 2. 1. 1 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient o Intrinsic dissolution (polymorph solubility comparison) o Powder dissolution (particle size / polymorphism studies) – See rifampicin (later) 2. Development of pharmacopoeial dissolution tests Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 25
Application Pharmaceutical development Comparative dissolution integral part of § 3. 2. P. 2 Pharmaceutical Development § 3. 2. P. 2. 2. 1 Formulation Development o In vitro dissolution or drug release Comparative dissolution also applicable to 1. 3. 2. P. 2. 1. 1 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient o Intrinsic dissolution (polymorph solubility comparison) o Powder dissolution (particle size / polymorphism studies) – See rifampicin (later) 2. Development of pharmacopoeial dissolution tests Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 25
 Pharmaceutical development l Target the dissolution profiles of the comparator product § All 3 BCS media – unless justified o Some APIs are unstable in acid medium – e. g. the artemisinins § Data to be provided in dossier § Scientific approach - quality target product profile (QTPP) o Optimize chances of BE against comparator l Derive QC dissolution conditions + acceptance criteria § Product specific – discriminating power o Consult the Generic Guideline, 3. 2. P. 2. 2. 1 (in vitro dissolution) o The compendial method is not mandatory Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 26
Pharmaceutical development l Target the dissolution profiles of the comparator product § All 3 BCS media – unless justified o Some APIs are unstable in acid medium – e. g. the artemisinins § Data to be provided in dossier § Scientific approach - quality target product profile (QTPP) o Optimize chances of BE against comparator l Derive QC dissolution conditions + acceptance criteria § Product specific – discriminating power o Consult the Generic Guideline, 3. 2. P. 2. 2. 1 (in vitro dissolution) o The compendial method is not mandatory Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 26
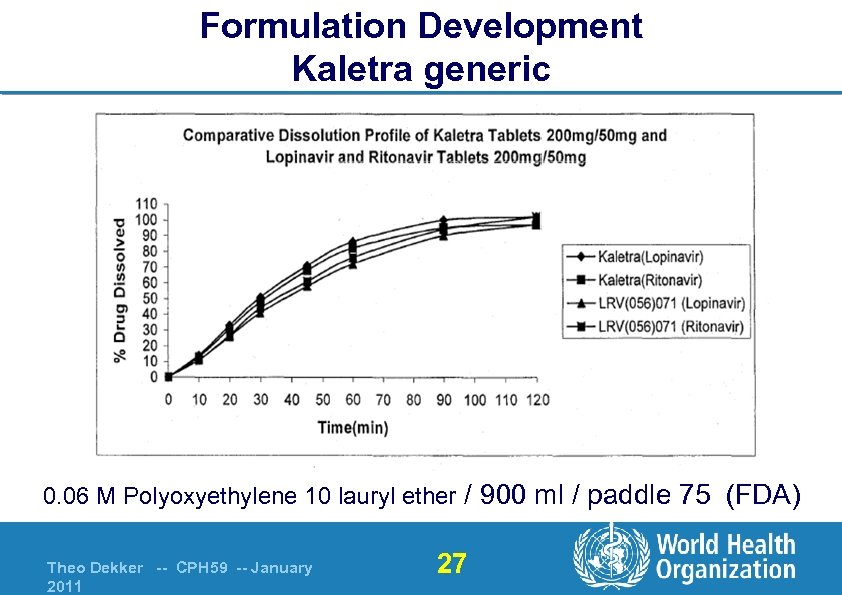 Formulation Development Kaletra generic 0. 06 M Polyoxyethylene 10 lauryl ether / 900 ml / paddle 75 (FDA) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 27
Formulation Development Kaletra generic 0. 06 M Polyoxyethylene 10 lauryl ether / 900 ml / paddle 75 (FDA) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 27
 Application Scale-up and variations l Scale up: biobatch to proposed production batches § To demonstrate in vitro similarity of such batches o This is considered essential for retention of efficacy o To support any differences in formulation/processing l Post-approval variation applications § A requirement of a particular variation (against biobatch) o Similar to scale-up o Consult WHO’s Variation Guide Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 28
Application Scale-up and variations l Scale up: biobatch to proposed production batches § To demonstrate in vitro similarity of such batches o This is considered essential for retention of efficacy o To support any differences in formulation/processing l Post-approval variation applications § A requirement of a particular variation (against biobatch) o Similar to scale-up o Consult WHO’s Variation Guide Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 28
 Application Biowaivers There are 2 types of biowaivers 1. BCS-based biowaivers (surrogate for BE studies) § Selectively applied in PQP 2. Additional strength biowaivers § Generally applied in PQP On PQP website you can find the § § § PQP specific guides o Referring to WHO main guideline on BE Templates for applications / assessments Applicant must also provide a study protocol Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 29
Application Biowaivers There are 2 types of biowaivers 1. BCS-based biowaivers (surrogate for BE studies) § Selectively applied in PQP 2. Additional strength biowaivers § Generally applied in PQP On PQP website you can find the § § § PQP specific guides o Referring to WHO main guideline on BE Templates for applications / assessments Applicant must also provide a study protocol Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 29
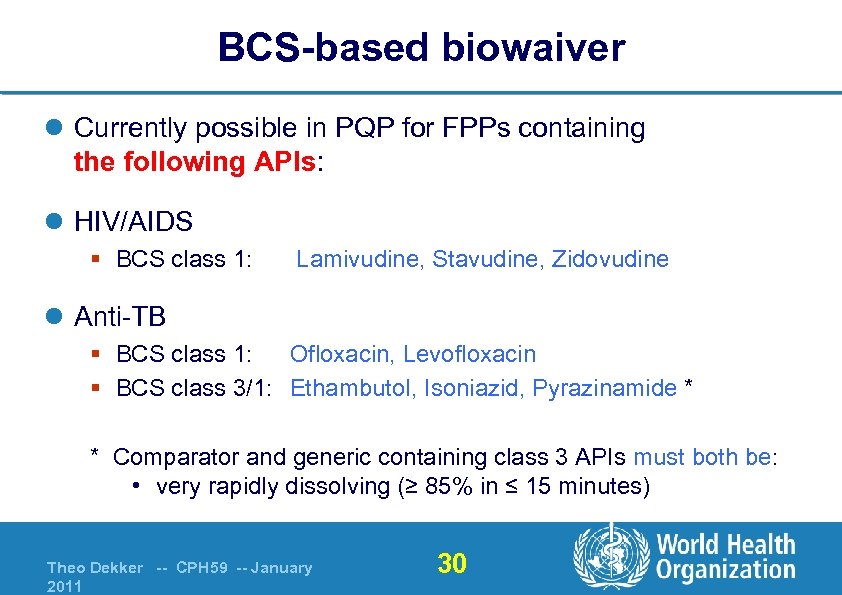 BCS-based biowaiver l Currently possible in PQP for FPPs containing the following APIs: l HIV/AIDS § BCS class 1: Lamivudine, Stavudine, Zidovudine l Anti-TB § BCS class 1: Ofloxacin, Levofloxacin § BCS class 3/1: Ethambutol, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide * * Comparator and generic containing class 3 APIs must both be: • very rapidly dissolving (≥ 85% in ≤ 15 minutes) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 30
BCS-based biowaiver l Currently possible in PQP for FPPs containing the following APIs: l HIV/AIDS § BCS class 1: Lamivudine, Stavudine, Zidovudine l Anti-TB § BCS class 1: Ofloxacin, Levofloxacin § BCS class 3/1: Ethambutol, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide * * Comparator and generic containing class 3 APIs must both be: • very rapidly dissolving (≥ 85% in ≤ 15 minutes) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 30
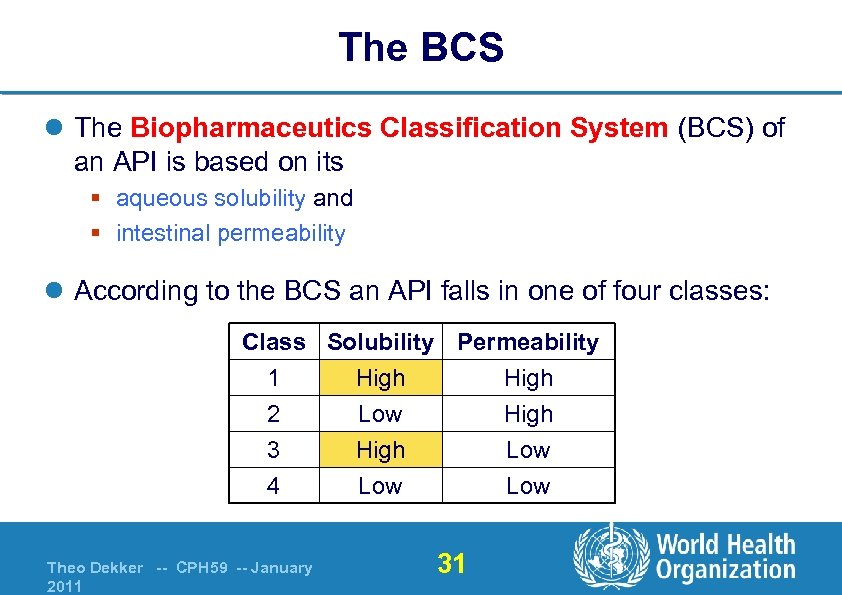 The BCS l The Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) of an API is based on its § aqueous solubility and § intestinal permeability l According to the BCS an API falls in one of four classes: Class Solubility Permeability 1 High 2 Low High 3 High Low 4 Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 Low 31
The BCS l The Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) of an API is based on its § aqueous solubility and § intestinal permeability l According to the BCS an API falls in one of four classes: Class Solubility Permeability 1 High 2 Low High 3 High Low 4 Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 Low 31
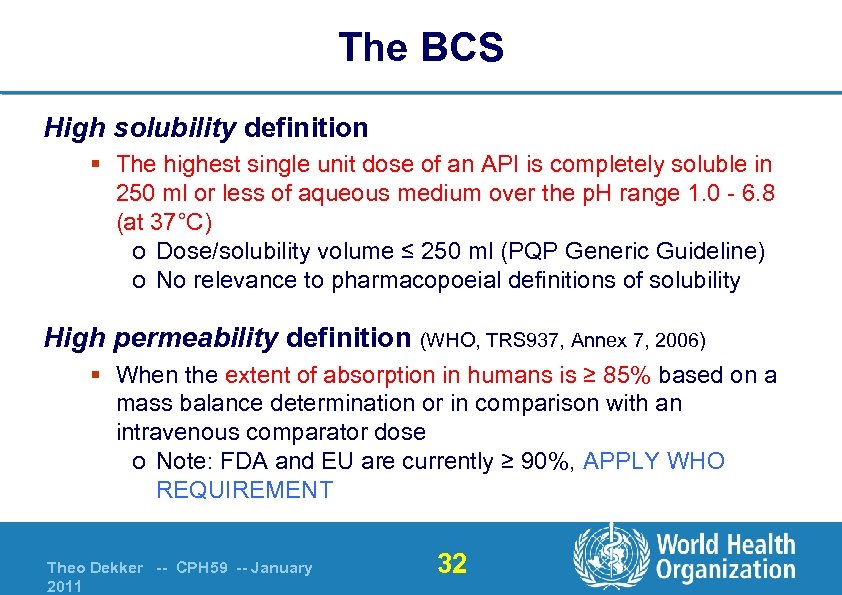 The BCS High solubility definition § The highest single unit dose of an API is completely soluble in 250 ml or less of aqueous medium over the p. H range 1. 0 - 6. 8 (at 37°C) o Dose/solubility volume ≤ 250 ml (PQP Generic Guideline) o No relevance to pharmacopoeial definitions of solubility High permeability definition (WHO, TRS 937, Annex 7, 2006) § When the extent of absorption in humans is ≥ 85% based on a mass balance determination or in comparison with an intravenous comparator dose o Note: FDA and EU are currently ≥ 90%, APPLY WHO REQUIREMENT Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 32
The BCS High solubility definition § The highest single unit dose of an API is completely soluble in 250 ml or less of aqueous medium over the p. H range 1. 0 - 6. 8 (at 37°C) o Dose/solubility volume ≤ 250 ml (PQP Generic Guideline) o No relevance to pharmacopoeial definitions of solubility High permeability definition (WHO, TRS 937, Annex 7, 2006) § When the extent of absorption in humans is ≥ 85% based on a mass balance determination or in comparison with an intravenous comparator dose o Note: FDA and EU are currently ≥ 90%, APPLY WHO REQUIREMENT Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 32
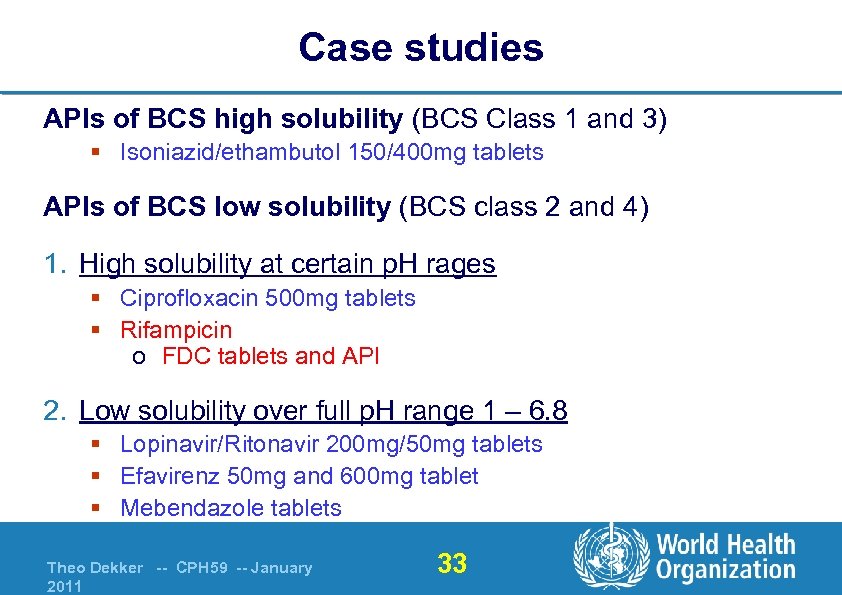 Case studies APIs of BCS high solubility (BCS Class 1 and 3) § Isoniazid/ethambutol 150/400 mg tablets APIs of BCS low solubility (BCS class 2 and 4) 1. High solubility at certain p. H rages § Ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablets § Rifampicin o FDC tablets and API 2. Low solubility over full p. H range 1 – 6. 8 § Lopinavir/Ritonavir 200 mg/50 mg tablets § Efavirenz 50 mg and 600 mg tablet § Mebendazole tablets Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 33
Case studies APIs of BCS high solubility (BCS Class 1 and 3) § Isoniazid/ethambutol 150/400 mg tablets APIs of BCS low solubility (BCS class 2 and 4) 1. High solubility at certain p. H rages § Ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablets § Rifampicin o FDC tablets and API 2. Low solubility over full p. H range 1 – 6. 8 § Lopinavir/Ritonavir 200 mg/50 mg tablets § Efavirenz 50 mg and 600 mg tablet § Mebendazole tablets Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 33
 Ph. Int. test method development Isoniazid/Ethambutol tablets § Strength: 150 mg/400 mg l No innovator/comparator product § Method development based on commercial samples l The APIs are both Class 3/1 § Highly soluble across p. H 1 – 6. 8 § Thus buffer p. H 6. 8 was selected as first choice § Expect APIs in one sample to show similar profiles o Amazingly so Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 34
Ph. Int. test method development Isoniazid/Ethambutol tablets § Strength: 150 mg/400 mg l No innovator/comparator product § Method development based on commercial samples l The APIs are both Class 3/1 § Highly soluble across p. H 1 – 6. 8 § Thus buffer p. H 6. 8 was selected as first choice § Expect APIs in one sample to show similar profiles o Amazingly so Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 34
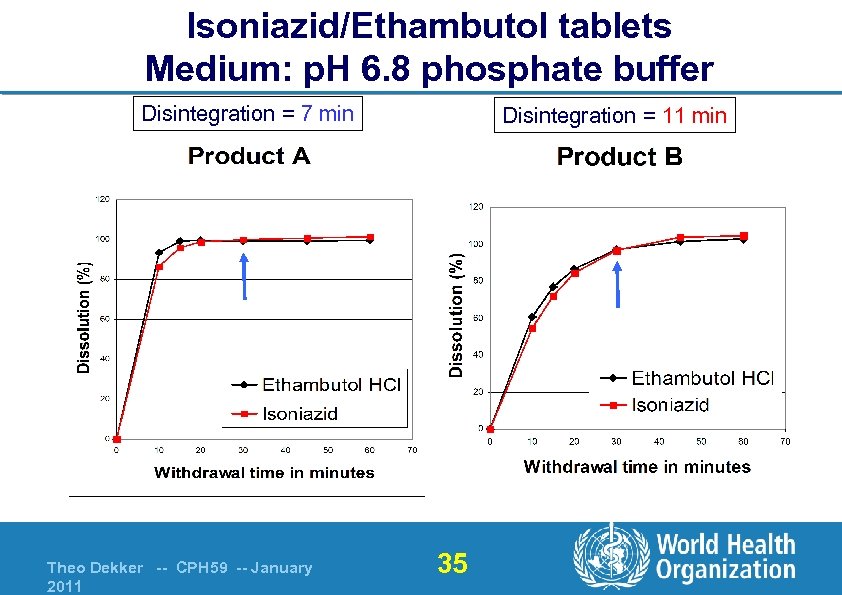 Isoniazid/Ethambutol tablets Medium: p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer Disintegration = 7 min Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 Disintegration = 11 min 35
Isoniazid/Ethambutol tablets Medium: p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer Disintegration = 7 min Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 Disintegration = 11 min 35
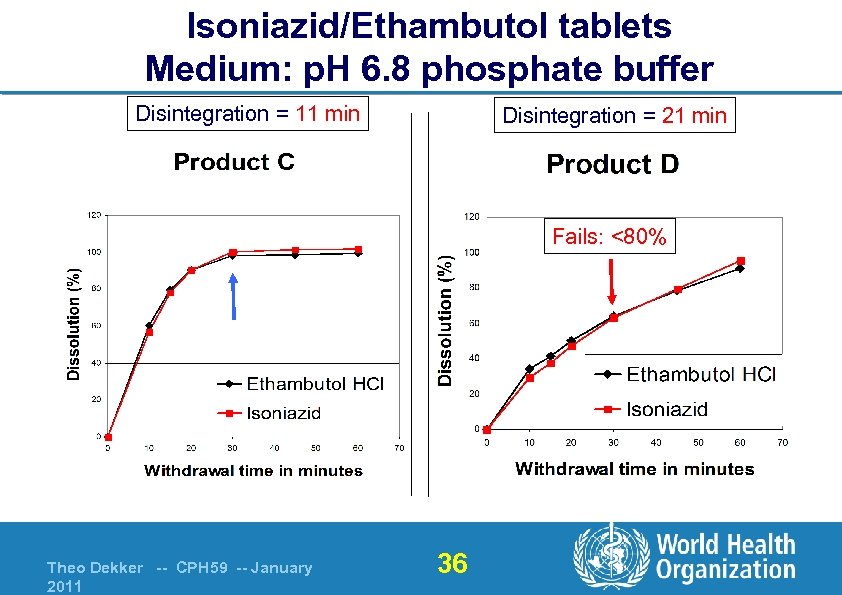 Isoniazid/Ethambutol tablets Medium: p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer Disintegration = 11 min Disintegration = 21 min Fails: <80% Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 36
Isoniazid/Ethambutol tablets Medium: p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer Disintegration = 11 min Disintegration = 21 min Fails: <80% Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 36
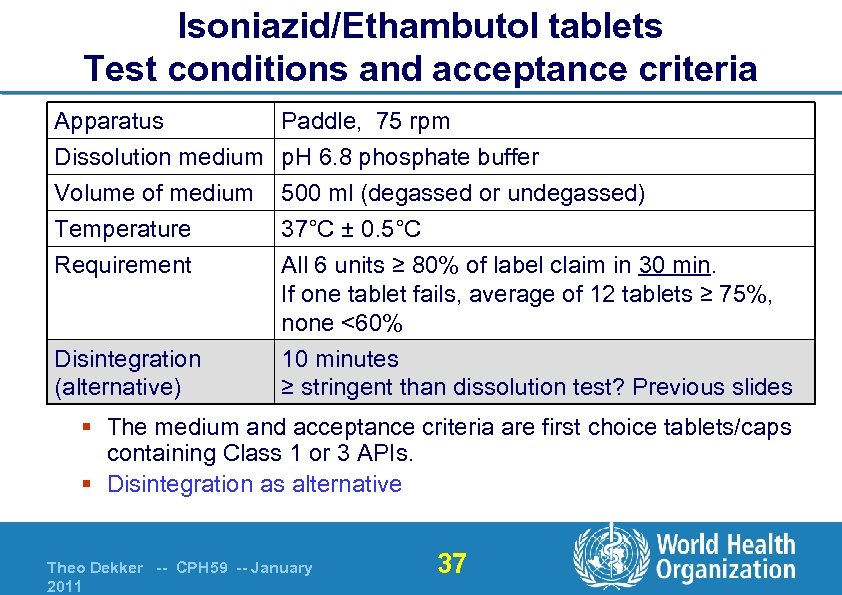 Isoniazid/Ethambutol tablets Test conditions and acceptance criteria Apparatus Dissolution medium Volume of medium Temperature Paddle, 75 rpm p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer 500 ml (degassed or undegassed) 37°C ± 0. 5°C Requirement All 6 units ≥ 80% of label claim in 30 min. If one tablet fails, average of 12 tablets ≥ 75%, none <60% 10 minutes ≥ stringent than dissolution test? Previous slides Disintegration (alternative) § The medium and acceptance criteria are first choice tablets/caps containing Class 1 or 3 APIs. § Disintegration as alternative Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 37
Isoniazid/Ethambutol tablets Test conditions and acceptance criteria Apparatus Dissolution medium Volume of medium Temperature Paddle, 75 rpm p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer 500 ml (degassed or undegassed) 37°C ± 0. 5°C Requirement All 6 units ≥ 80% of label claim in 30 min. If one tablet fails, average of 12 tablets ≥ 75%, none <60% 10 minutes ≥ stringent than dissolution test? Previous slides Disintegration (alternative) § The medium and acceptance criteria are first choice tablets/caps containing Class 1 or 3 APIs. § Disintegration as alternative Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 37
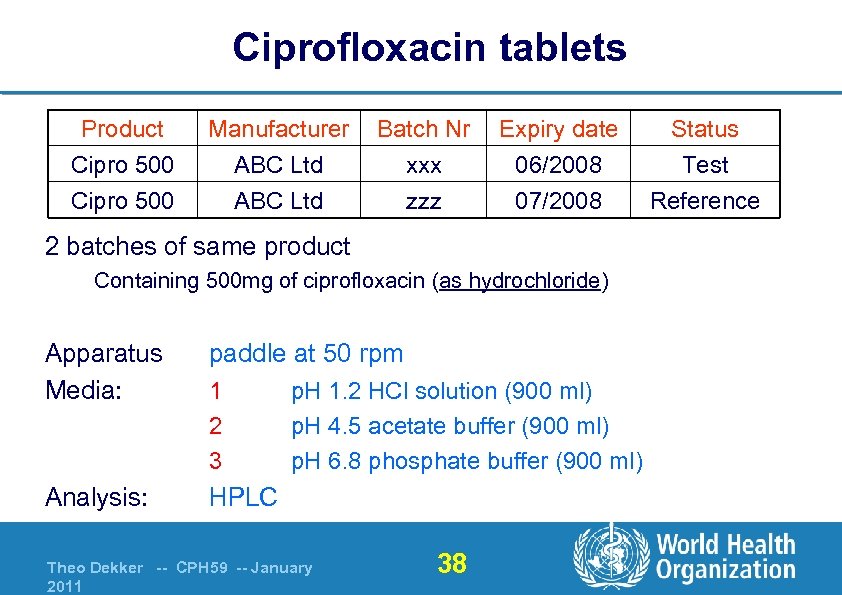 Ciprofloxacin tablets Product Cipro 500 Manufacturer ABC Ltd Batch Nr xxx zzz Expiry date 06/2008 07/2008 2 batches of same product Containing 500 mg of ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride) Apparatus Media: paddle at 50 rpm Analysis: HPLC 1 2 3 p. H 1. 2 HCl solution (900 ml) p. H 4. 5 acetate buffer (900 ml) p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer (900 ml) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 38 Status Test Reference
Ciprofloxacin tablets Product Cipro 500 Manufacturer ABC Ltd Batch Nr xxx zzz Expiry date 06/2008 07/2008 2 batches of same product Containing 500 mg of ciprofloxacin (as hydrochloride) Apparatus Media: paddle at 50 rpm Analysis: HPLC 1 2 3 p. H 1. 2 HCl solution (900 ml) p. H 4. 5 acetate buffer (900 ml) p. H 6. 8 phosphate buffer (900 ml) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 38 Status Test Reference
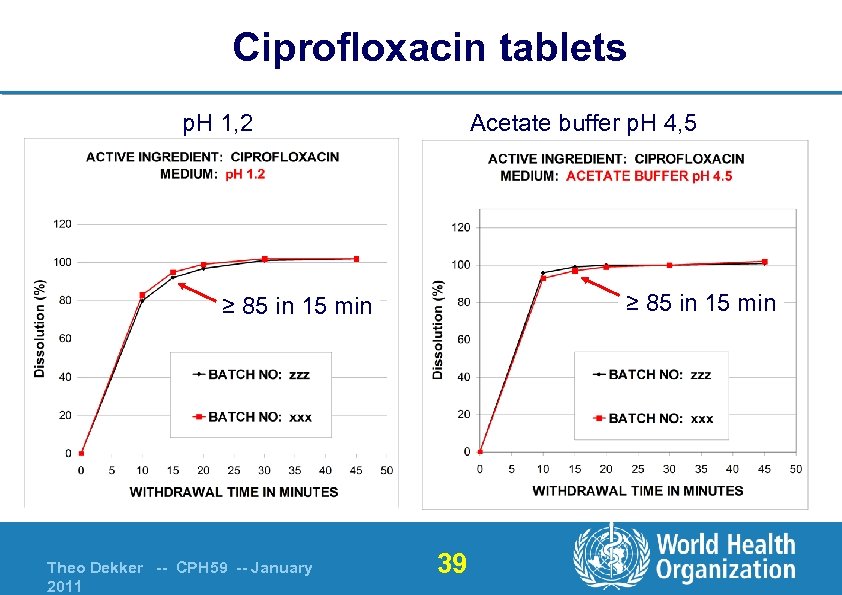 Ciprofloxacin tablets p. H 1, 2 Acetate buffer p. H 4, 5 ≥ 85 in 15 min Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 39
Ciprofloxacin tablets p. H 1, 2 Acetate buffer p. H 4, 5 ≥ 85 in 15 min Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 39
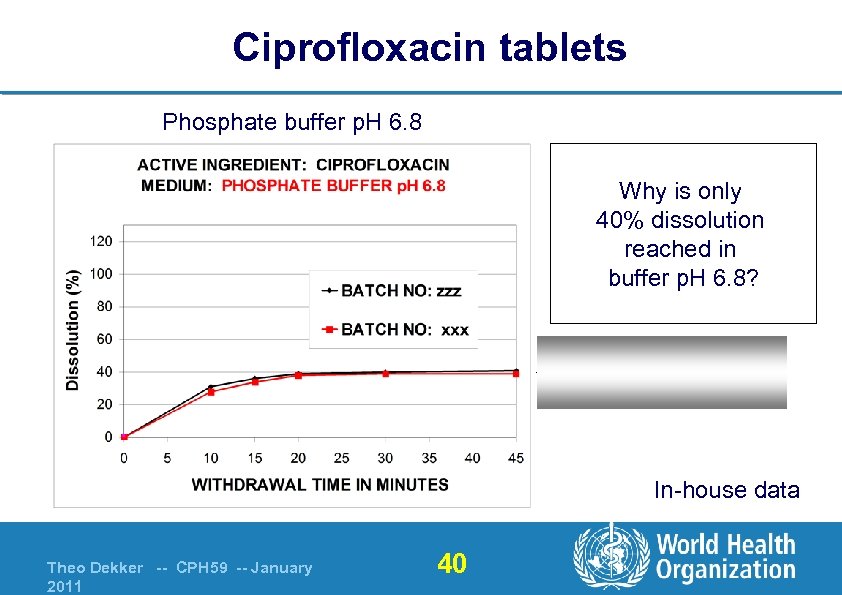 Ciprofloxacin tablets Phosphate buffer p. H 6. 8 Why is only 40% dissolution reached in buffer p. H 6. 8? Asymptote (saturated) In-house data Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 40
Ciprofloxacin tablets Phosphate buffer p. H 6. 8 Why is only 40% dissolution reached in buffer p. H 6. 8? Asymptote (saturated) In-house data Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 40
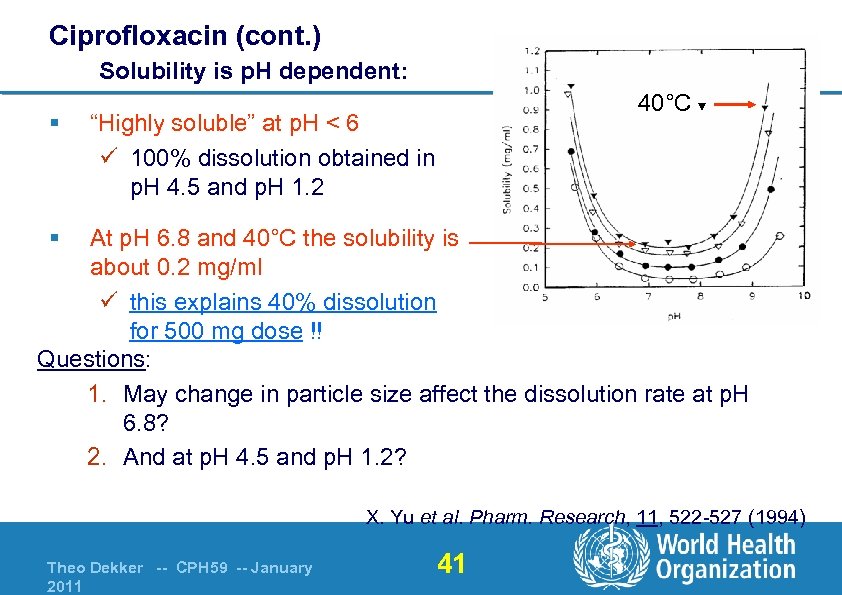 Ciprofloxacin (cont. ) Solubility is p. H dependent: § 40°C ▼ “Highly soluble” at p. H < 6 ü 100% dissolution obtained in p. H 4. 5 and p. H 1. 2 § At p. H 6. 8 and 40°C the solubility is about 0. 2 mg/ml ü this explains 40% dissolution for 500 mg dose !! Questions: 1. May change in particle size affect the dissolution rate at p. H 6. 8? 2. And at p. H 4. 5 and p. H 1. 2? X. Yu et al. Pharm. Research, 11, 522 -527 (1994) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 41
Ciprofloxacin (cont. ) Solubility is p. H dependent: § 40°C ▼ “Highly soluble” at p. H < 6 ü 100% dissolution obtained in p. H 4. 5 and p. H 1. 2 § At p. H 6. 8 and 40°C the solubility is about 0. 2 mg/ml ü this explains 40% dissolution for 500 mg dose !! Questions: 1. May change in particle size affect the dissolution rate at p. H 6. 8? 2. And at p. H 4. 5 and p. H 1. 2? X. Yu et al. Pharm. Research, 11, 522 -527 (1994) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 41
 Ciprofloxacin tablets QC method – acceptance criteria From data 1. Buffer p. H 6. 8 = not useable for quality control § Far from sink conditions 2. p. H 1. 2 or p. H 4. 5 = suitable (900 ml) § § paddle 50 rpm 80% (Q) in 20 minutes considered as product specific / tight USP monograph § § § 900 ml 0. 01 N hydrochloric acid paddle 50 rpm 80% (Q) in 30 minutes Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 42
Ciprofloxacin tablets QC method – acceptance criteria From data 1. Buffer p. H 6. 8 = not useable for quality control § Far from sink conditions 2. p. H 1. 2 or p. H 4. 5 = suitable (900 ml) § § paddle 50 rpm 80% (Q) in 20 minutes considered as product specific / tight USP monograph § § § 900 ml 0. 01 N hydrochloric acid paddle 50 rpm 80% (Q) in 30 minutes Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 42
 Special case Rifampicin FDC products containing rifampicin § § Class 2 API BCS low solubility o At higher p. H (highly soluble in buffer p. H 1. 2) 1. WHO recommendation for dissolution test § Rifampicin as “marker” 2. Polymorphism and particle size § § Intrinsic dissolution Powder dissolution Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 43
Special case Rifampicin FDC products containing rifampicin § § Class 2 API BCS low solubility o At higher p. H (highly soluble in buffer p. H 1. 2) 1. WHO recommendation for dissolution test § Rifampicin as “marker” 2. Polymorphism and particle size § § Intrinsic dissolution Powder dissolution Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 43
 TB FDC IR tablets Recommendation l For conventional immediate release TB fixed-dose combination tablets containing rifampicin WHO recommends: § Rifampicin could serve as the marker for dissolution testing in the relevant FDCs, as it is the least soluble substance. o WHO Technical Report Series 937, page 8 l The applicant would need justification § (at least 3 batches) in support of a specification where only rifampicin would be included in the specifications. Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 44
TB FDC IR tablets Recommendation l For conventional immediate release TB fixed-dose combination tablets containing rifampicin WHO recommends: § Rifampicin could serve as the marker for dissolution testing in the relevant FDCs, as it is the least soluble substance. o WHO Technical Report Series 937, page 8 l The applicant would need justification § (at least 3 batches) in support of a specification where only rifampicin would be included in the specifications. Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 44
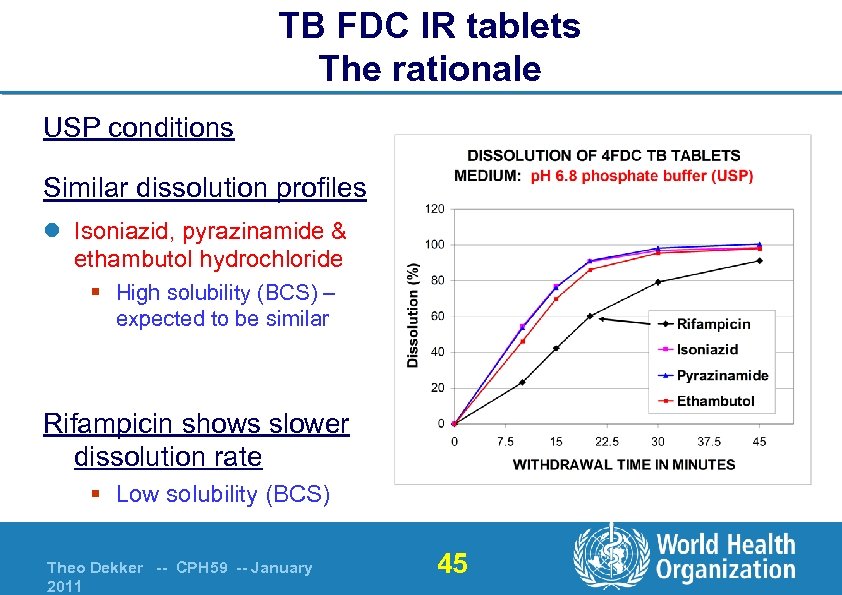 TB FDC IR tablets The rationale USP conditions Similar dissolution profiles l Isoniazid, pyrazinamide & ethambutol hydrochloride § High solubility (BCS) – expected to be similar Rifampicin shows slower dissolution rate § Low solubility (BCS) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 45
TB FDC IR tablets The rationale USP conditions Similar dissolution profiles l Isoniazid, pyrazinamide & ethambutol hydrochloride § High solubility (BCS) – expected to be similar Rifampicin shows slower dissolution rate § Low solubility (BCS) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 45
 Rifampicin solid state properties Rifampicin shows polymorphism § But pharmacopoeias do not mention it – or specify a form l Forms I (stable) and II (metastable) + amorphous § Form II (and mixtures? ) mainly in current FPPs ? ? ? § Both API forms in commerce (also as uncontrolled mixtures) Rifampicin is known for § Variable bioavailability of FDCs o Is this due to polymorphism? y soon be PQP ma Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 46 ble th this pro wi onfronted c m
Rifampicin solid state properties Rifampicin shows polymorphism § But pharmacopoeias do not mention it – or specify a form l Forms I (stable) and II (metastable) + amorphous § Form II (and mixtures? ) mainly in current FPPs ? ? ? § Both API forms in commerce (also as uncontrolled mixtures) Rifampicin is known for § Variable bioavailability of FDCs o Is this due to polymorphism? y soon be PQP ma Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 46 ble th this pro wi onfronted c m
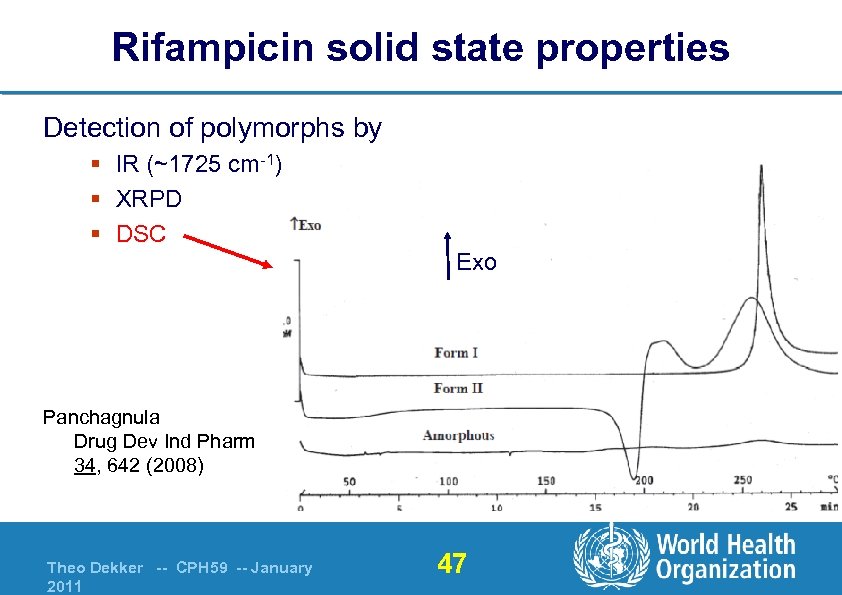 Rifampicin solid state properties Detection of polymorphs by § IR (~1725 cm-1) § XRPD § DSC Exo Panchagnula Drug Dev Ind Pharm 34, 642 (2008) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 47
Rifampicin solid state properties Detection of polymorphs by § IR (~1725 cm-1) § XRPD § DSC Exo Panchagnula Drug Dev Ind Pharm 34, 642 (2008) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 47
 Rifampicin solid state properties Powder dissolution Special method: l No excipients in test – only API material § No influence of matrix / excipients l To prevent agglomeration or floating of particles § API material + small glass beads in 2 ml dissolution medium. Vortex 1 minute. Transfer to the dissolution medium. l Method and data in: § Agrawal, …, Panchagnula. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 22, 127 (2004) § Initially developed by Prof A P Lötter, from our laboratory Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 48
Rifampicin solid state properties Powder dissolution Special method: l No excipients in test – only API material § No influence of matrix / excipients l To prevent agglomeration or floating of particles § API material + small glass beads in 2 ml dissolution medium. Vortex 1 minute. Transfer to the dissolution medium. l Method and data in: § Agrawal, …, Panchagnula. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 22, 127 (2004) § Initially developed by Prof A P Lötter, from our laboratory Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 48
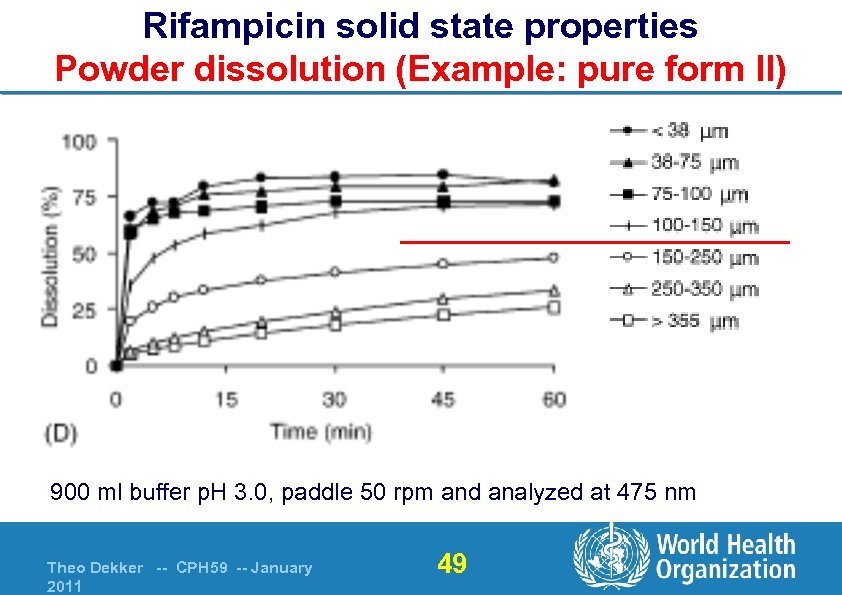 Rifampicin solid state properties Powder dissolution (Example: pure form II) 900 ml buffer p. H 3. 0, paddle 50 rpm and analyzed at 475 nm Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 49
Rifampicin solid state properties Powder dissolution (Example: pure form II) 900 ml buffer p. H 3. 0, paddle 50 rpm and analyzed at 475 nm Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 49
 Rifampicin solid state properties Powder dissolution Dissolution rate of rifampicin powder is 1. Not significantly affected by the polymorphic form § § Polymorphism seems to have no significant in vitro effect o Supported by intrinsic dissolution data (in publication) Bioavailability ? ? 2. Significantly affected by particle size § § < 100 µm → high rate, irrespective of form > 100 µm → reduced (significantly) dissolution rate l What is in it for the evaluator ? § Particle size distribution is important for rifampicin !!! Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 50
Rifampicin solid state properties Powder dissolution Dissolution rate of rifampicin powder is 1. Not significantly affected by the polymorphic form § § Polymorphism seems to have no significant in vitro effect o Supported by intrinsic dissolution data (in publication) Bioavailability ? ? 2. Significantly affected by particle size § § < 100 µm → high rate, irrespective of form > 100 µm → reduced (significantly) dissolution rate l What is in it for the evaluator ? § Particle size distribution is important for rifampicin !!! Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 50
 Powder dissolution Comments An important tool for studying dissolution behaviour of APIs of low solubility according to the BCS l Polymorphic forms § Supplemented by intrinsic dissolution l Particle size differences l More than often polymorphism and particle size are mixed up in development studies § Study polymorphs? Then particle size should be constant § Excellent example by Panchagnula to separate the variables Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 51
Powder dissolution Comments An important tool for studying dissolution behaviour of APIs of low solubility according to the BCS l Polymorphic forms § Supplemented by intrinsic dissolution l Particle size differences l More than often polymorphism and particle size are mixed up in development studies § Study polymorphs? Then particle size should be constant § Excellent example by Panchagnula to separate the variables Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 51
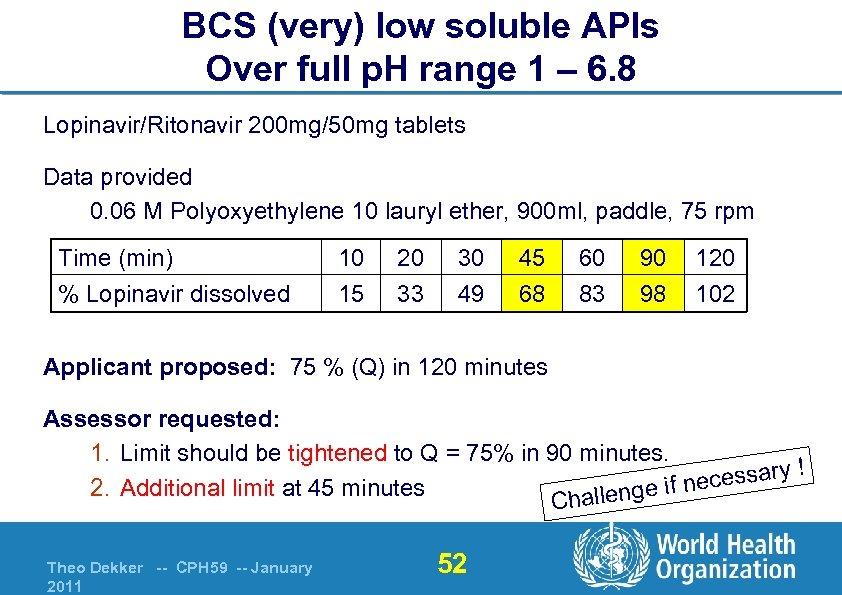 BCS (very) low soluble APIs Over full p. H range 1 – 6. 8 Lopinavir/Ritonavir 200 mg/50 mg tablets Data provided 0. 06 M Polyoxyethylene 10 lauryl ether, 900 ml, paddle, 75 rpm Time (min) % Lopinavir dissolved 10 15 20 33 30 49 45 68 60 83 90 98 120 102 Applicant proposed: 75 % (Q) in 120 minutes Assessor requested: 1. Limit should be tightened to Q = 75% in 90 minutes. essary ! ec 2. Additional limit at 45 minutes lenge if n Chal Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 52
BCS (very) low soluble APIs Over full p. H range 1 – 6. 8 Lopinavir/Ritonavir 200 mg/50 mg tablets Data provided 0. 06 M Polyoxyethylene 10 lauryl ether, 900 ml, paddle, 75 rpm Time (min) % Lopinavir dissolved 10 15 20 33 30 49 45 68 60 83 90 98 120 102 Applicant proposed: 75 % (Q) in 120 minutes Assessor requested: 1. Limit should be tightened to Q = 75% in 90 minutes. essary ! ec 2. Additional limit at 45 minutes lenge if n Chal Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 52
 BCS (very) low soluble APIs Examples of APIs of BCS low solubility over p. H 1 – 6. 8 Lopinavir, Ritonavir, Lumefantrine, Efavirenz Be careful when assessing l Surfactants (about 0. 25% to max. 2%) are normally added to increase solubility of BCS low soluble APIs § E. g. SLS (SDS), benzalkonium chloride, polysorbate 80 § Too much surfactant may result in BCS high solubility!! o Then discrimination power may be lost o Solubility should be determined using different surfactant concentrations / different surfactants § API particle size distribution specification very important § Can be very difficult to assess Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 53
BCS (very) low soluble APIs Examples of APIs of BCS low solubility over p. H 1 – 6. 8 Lopinavir, Ritonavir, Lumefantrine, Efavirenz Be careful when assessing l Surfactants (about 0. 25% to max. 2%) are normally added to increase solubility of BCS low soluble APIs § E. g. SLS (SDS), benzalkonium chloride, polysorbate 80 § Too much surfactant may result in BCS high solubility!! o Then discrimination power may be lost o Solubility should be determined using different surfactant concentrations / different surfactants § API particle size distribution specification very important § Can be very difficult to assess Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 53
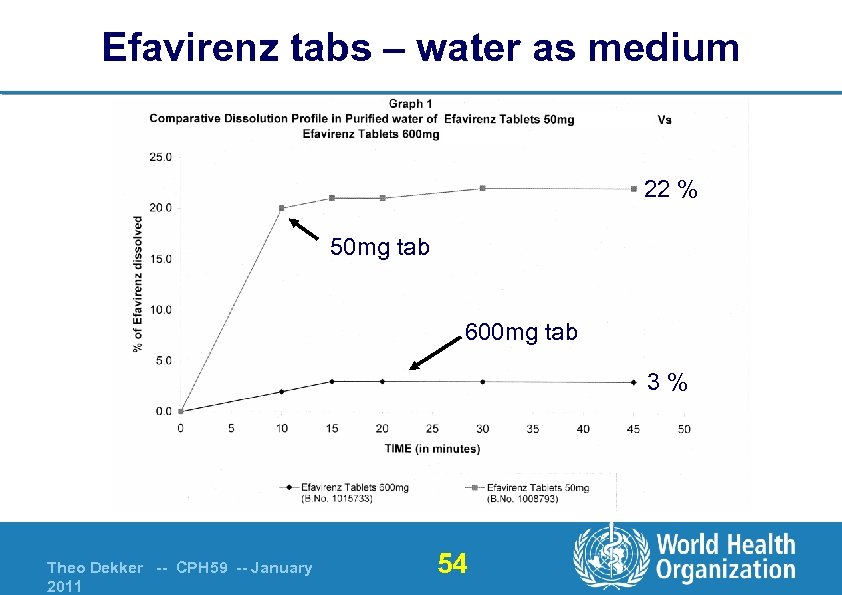 Efavirenz tabs – water as medium 22 % 50 mg tab 600 mg tab 3% Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 54
Efavirenz tabs – water as medium 22 % 50 mg tab 600 mg tab 3% Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 54
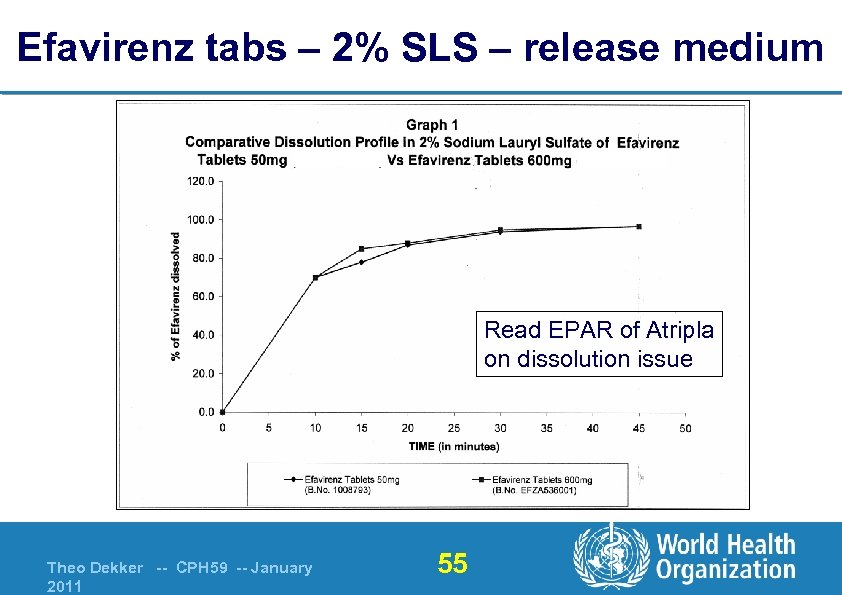 Efavirenz tabs – 2% SLS – release medium Read EPAR of Atripla on dissolution issue Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 55
Efavirenz tabs – 2% SLS – release medium Read EPAR of Atripla on dissolution issue Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 55
 Efavirenz tablets The profiles in 2% SLS are similar § For 50 mg tablets vs 600 mg tablets l Without SLS it shows huge differences in dissolution rate l Would 2% SLS medium detect particle size differences between tablet batches? § Hardly so if the 50 mg and 600 mg shows similar profiles § Better rely on particle size distribution control of the API batches o And that accounts for all APIs with low solubility over the full p. H range 1 to 6. 8 e ake not T Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 56
Efavirenz tablets The profiles in 2% SLS are similar § For 50 mg tablets vs 600 mg tablets l Without SLS it shows huge differences in dissolution rate l Would 2% SLS medium detect particle size differences between tablet batches? § Hardly so if the 50 mg and 600 mg shows similar profiles § Better rely on particle size distribution control of the API batches o And that accounts for all APIs with low solubility over the full p. H range 1 to 6. 8 e ake not T Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 56
 Mebendazole (chewable) tablets Ph. Int. API monograph (revised) § Additional information. Mebendazole exhibits polymorphism. The polymorph specified in the monograph (form C) corresponds to the crystal form of mebendazole RS (IR test) FPP monograph § Manufacture. The formulation, manufacturing process and product packaging of Chewable mebendazole tablets are designed and controlled so as to minimize the conversion of the polymorphic form of mebendazole from C to A. They ensure that, at any stage of the life-cycle of the product, when tested by a suitable method such as infrared spectrometry or X-ray powder diffractometry, the mebendazole in the tablets is predominantly in the form of polymorph C. Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 57
Mebendazole (chewable) tablets Ph. Int. API monograph (revised) § Additional information. Mebendazole exhibits polymorphism. The polymorph specified in the monograph (form C) corresponds to the crystal form of mebendazole RS (IR test) FPP monograph § Manufacture. The formulation, manufacturing process and product packaging of Chewable mebendazole tablets are designed and controlled so as to minimize the conversion of the polymorphic form of mebendazole from C to A. They ensure that, at any stage of the life-cycle of the product, when tested by a suitable method such as infrared spectrometry or X-ray powder diffractometry, the mebendazole in the tablets is predominantly in the form of polymorph C. Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 57
 Mebendazole (chewable) tablets Ph. Int. Accelerated products subjected to accelerated conditions l Some products showed change from polymorph form C to A over the period of 6 months § Detection: IR and XRPD § Form C = metastable l The polymorphic change is clearly shown by dissolution, due to solubility difference between forms C and A § 900 ml 0. 1 N HCl (paddle 75 rpm) § USP: 900 ml 0. 1 N HCl + 1%SLS (paddle 75 rpm) M. Brits et al. J. Pharm. Sci. , p 1 (2009) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 58
Mebendazole (chewable) tablets Ph. Int. Accelerated products subjected to accelerated conditions l Some products showed change from polymorph form C to A over the period of 6 months § Detection: IR and XRPD § Form C = metastable l The polymorphic change is clearly shown by dissolution, due to solubility difference between forms C and A § 900 ml 0. 1 N HCl (paddle 75 rpm) § USP: 900 ml 0. 1 N HCl + 1%SLS (paddle 75 rpm) M. Brits et al. J. Pharm. Sci. , p 1 (2009) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 58
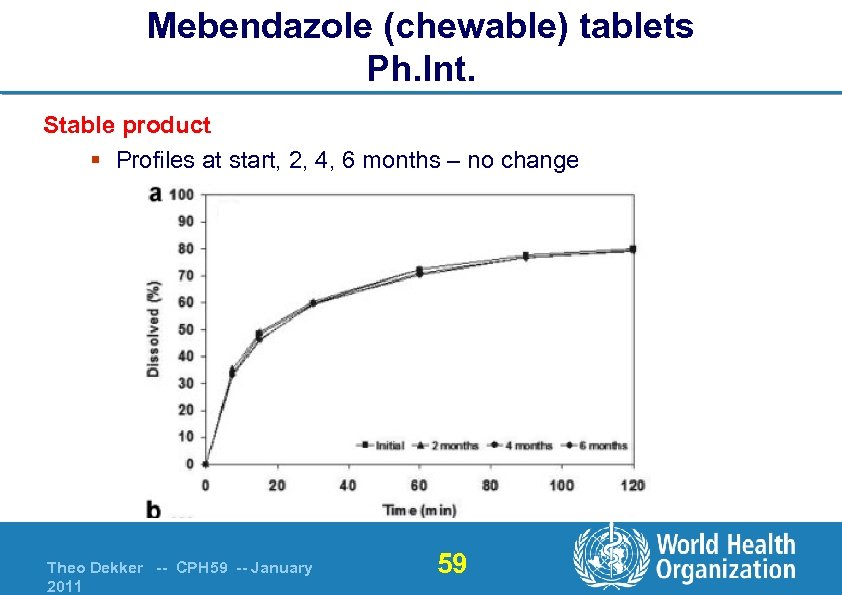 Mebendazole (chewable) tablets Ph. Int. Stable product § Profiles at start, 2, 4, 6 months – no change Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 59
Mebendazole (chewable) tablets Ph. Int. Stable product § Profiles at start, 2, 4, 6 months – no change Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 59
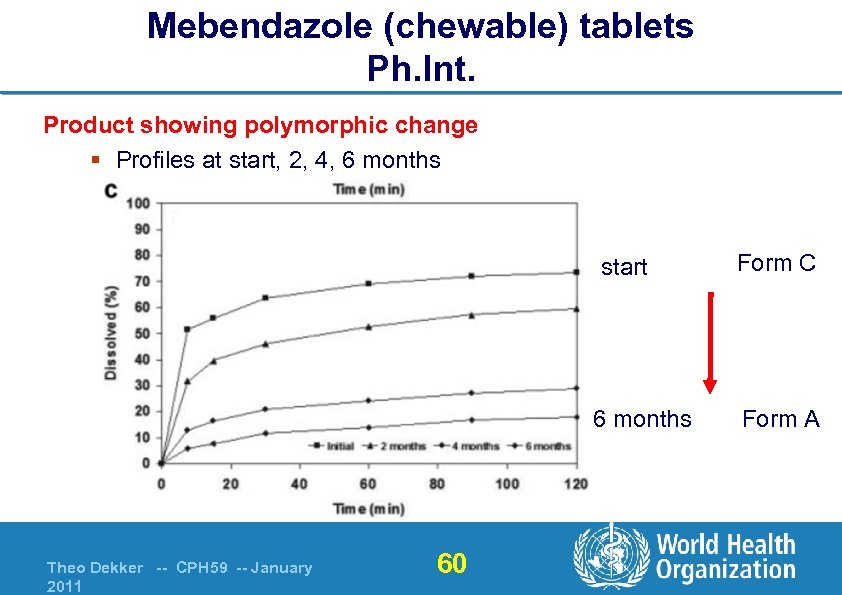 Mebendazole (chewable) tablets Ph. Int. Product showing polymorphic change § Profiles at start, 2, 4, 6 months start 6 months Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 60 Form C Form A
Mebendazole (chewable) tablets Ph. Int. Product showing polymorphic change § Profiles at start, 2, 4, 6 months start 6 months Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 60 Form C Form A
 Some practical matters Evaluators should be aware of 1. Coning (heap formation) in dissolution vessel 2. Dissolution results > than assay ? ? § Do not query to easily 3. Filtration of dissolution samples 4. Chewable tablets 5. Disintegration may replace dissolution as release test § § BCS Class 1 and 3 APIs / very rapidly dissolving tabs/caps Consult ICH Q 6 A Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 61
Some practical matters Evaluators should be aware of 1. Coning (heap formation) in dissolution vessel 2. Dissolution results > than assay ? ? § Do not query to easily 3. Filtration of dissolution samples 4. Chewable tablets 5. Disintegration may replace dissolution as release test § § BCS Class 1 and 3 APIs / very rapidly dissolving tabs/caps Consult ICH Q 6 A Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 61
 Practical matters Coning / Heap formation Coning (heap formation) in dissolution vessel l With paddle speed = 50 rpm l This may slow down (suppress) the dissolution l Affects some products l WHO avoids this by paddle 75 rpm in BE guide & Ph. Int. § Thus avoiding possible product-to-product variable due to hydrodynamics Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 62
Practical matters Coning / Heap formation Coning (heap formation) in dissolution vessel l With paddle speed = 50 rpm l This may slow down (suppress) the dissolution l Affects some products l WHO avoids this by paddle 75 rpm in BE guide & Ph. Int. § Thus avoiding possible product-to-product variable due to hydrodynamics Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 62
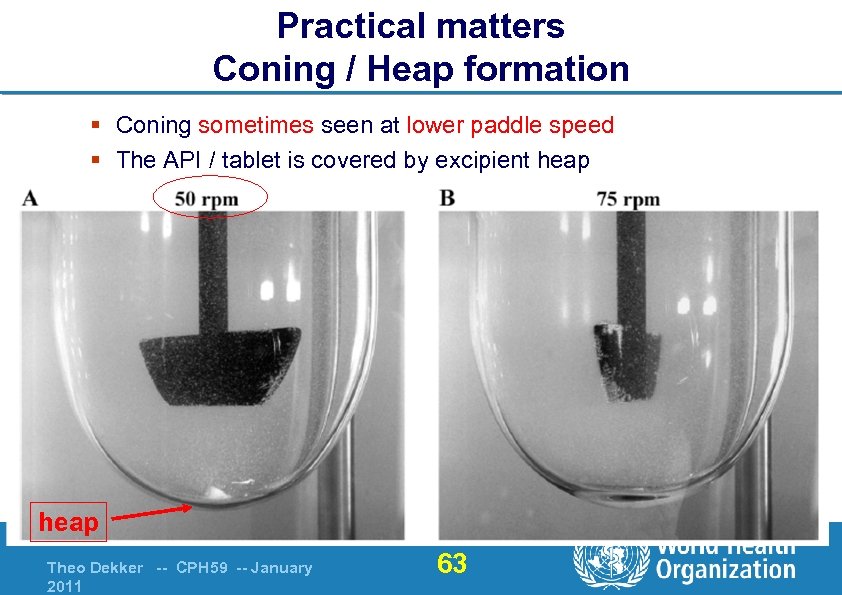 Practical matters Coning / Heap formation § Coning sometimes seen at lower paddle speed § The API / tablet is covered by excipient heap Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 63
Practical matters Coning / Heap formation § Coning sometimes seen at lower paddle speed § The API / tablet is covered by excipient heap Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 63
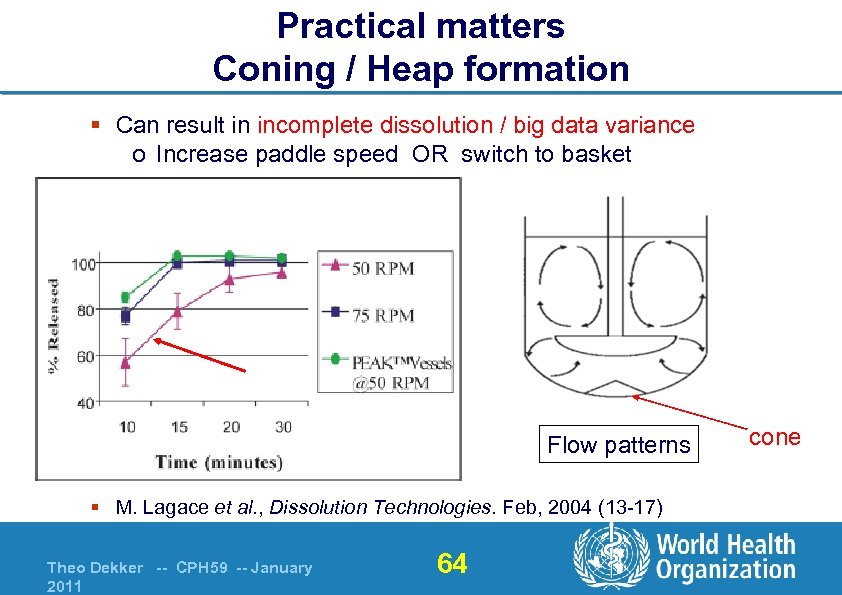 Practical matters Coning / Heap formation § Can result in incomplete dissolution / big data variance o Increase paddle speed OR switch to basket Flow patterns § M. Lagace et al. , Dissolution Technologies. Feb, 2004 (13 -17) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 64 cone
Practical matters Coning / Heap formation § Can result in incomplete dissolution / big data variance o Increase paddle speed OR switch to basket Flow patterns § M. Lagace et al. , Dissolution Technologies. Feb, 2004 (13 -17) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 64 cone
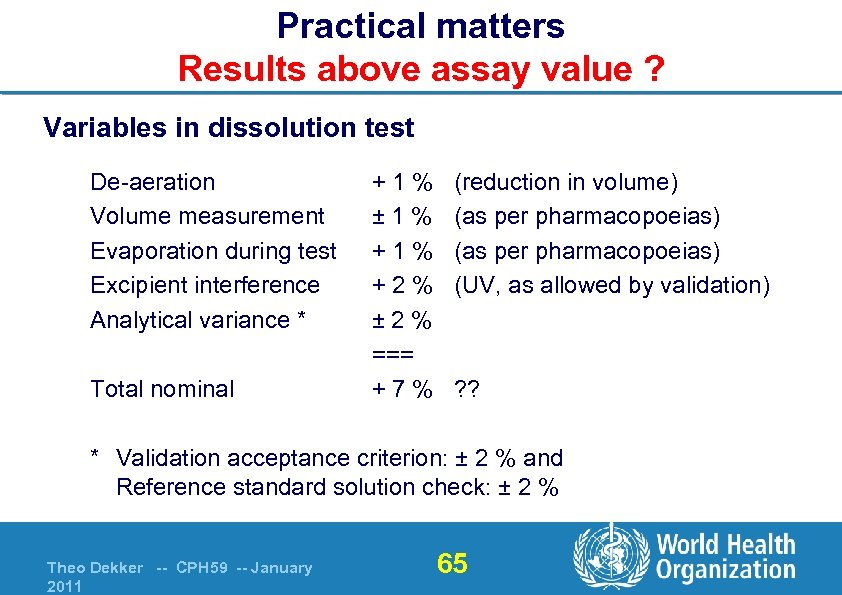 Practical matters Results above assay value ? Variables in dissolution test De-aeration Volume measurement Evaporation during test Excipient interference Analytical variance * Total nominal +1% ± 1% +2% ± 2% === +7% (reduction in volume) (as per pharmacopoeias) (UV, as allowed by validation) ? ? * Validation acceptance criterion: ± 2 % and Reference standard solution check: ± 2 % Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 65
Practical matters Results above assay value ? Variables in dissolution test De-aeration Volume measurement Evaporation during test Excipient interference Analytical variance * Total nominal +1% ± 1% +2% ± 2% === +7% (reduction in volume) (as per pharmacopoeias) (UV, as allowed by validation) ? ? * Validation acceptance criterion: ± 2 % and Reference standard solution check: ± 2 % Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 65
 Practical matters Filtration of dissolution samples Check during assessment: 1. Dissolution samples should be filtered immediately § § § To stop dissolution Through in-line filter or filter at tip of sampling probe Unless otherwise validated 2. Adsorption of the API(s) onto the filter needs to be evaluated (validated) § § § Important for low dose tablets/capsules Ideally no absorption should occur Discard first portion filtered (saturation of filter) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 66
Practical matters Filtration of dissolution samples Check during assessment: 1. Dissolution samples should be filtered immediately § § § To stop dissolution Through in-line filter or filter at tip of sampling probe Unless otherwise validated 2. Adsorption of the API(s) onto the filter needs to be evaluated (validated) § § § Important for low dose tablets/capsules Ideally no absorption should occur Discard first portion filtered (saturation of filter) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 66
 Practical matters Chewable tablets should have a dissolution / disintegration requirement § because they might be swallowed by a patient without proper chewing (FDA’s BA and BE studies, March 2003) Examples: § Didanosine tablets (chewable/dispersible) § Mebendazole tablets (USP) § Chewable mebendazole tablets Ph. Int. (adopted) o The designation on the container should state that the tablets may be chewed, swallowed whole or crushed and mixed with food or liquid… Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 67
Practical matters Chewable tablets should have a dissolution / disintegration requirement § because they might be swallowed by a patient without proper chewing (FDA’s BA and BE studies, March 2003) Examples: § Didanosine tablets (chewable/dispersible) § Mebendazole tablets (USP) § Chewable mebendazole tablets Ph. Int. (adopted) o The designation on the container should state that the tablets may be chewed, swallowed whole or crushed and mixed with food or liquid… Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 67
 Guidelines l Multisource (generic) pharmaceutical products: guidelines on registration requirements to establish interchangeability § Paragraph 9: In vitro testing (dissolution) § WHO Technical Report Series 937, Annex 7 (2006) § Main guideline for biowaivers l US-FDA. Waiver of In Vivo Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms Based on a Biopharmaceutics Classification System (August 2008) l EMEA. Guideline on the investigation of bioequivalence § CPMP/EWP/QWP/1401/98 Rev. 1/ Corr ** (Jan 2010) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 68
Guidelines l Multisource (generic) pharmaceutical products: guidelines on registration requirements to establish interchangeability § Paragraph 9: In vitro testing (dissolution) § WHO Technical Report Series 937, Annex 7 (2006) § Main guideline for biowaivers l US-FDA. Waiver of In Vivo Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms Based on a Biopharmaceutics Classification System (August 2008) l EMEA. Guideline on the investigation of bioequivalence § CPMP/EWP/QWP/1401/98 Rev. 1/ Corr ** (Jan 2010) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 68
 Guidelines PQP specific (on website): l Recommendations for conducting and assessing comparative dissolution profiles Appendix 1 to: § Guideline on submission of documentation for a multisource (generic) finished pharmaceutical product (FPP): quality part o (Generic guideline) l General notes on Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS)based biowaiver applications (2/2009) l Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS)-based biowaiver applications: anti-tuberculosis medicines (2/2009) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 69
Guidelines PQP specific (on website): l Recommendations for conducting and assessing comparative dissolution profiles Appendix 1 to: § Guideline on submission of documentation for a multisource (generic) finished pharmaceutical product (FPP): quality part o (Generic guideline) l General notes on Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS)based biowaiver applications (2/2009) l Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS)-based biowaiver applications: anti-tuberculosis medicines (2/2009) Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 69
 Closing remarks l l Comparative dissolution plays an important role in: § product development § Up-scaling: biobatch to production batches § setting of dissolution specifications § BCS-based and additional strength biowaivers § post-approval changes (variations) § API solid state properties Assessors should § understand multipoint / comparative dissolution requirements o be able to determine similarity of profiles o be able to assess release dissolution specifications o know how to assess development and biowaiver data o know when and how disintegration can replace dissolution Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 70
Closing remarks l l Comparative dissolution plays an important role in: § product development § Up-scaling: biobatch to production batches § setting of dissolution specifications § BCS-based and additional strength biowaivers § post-approval changes (variations) § API solid state properties Assessors should § understand multipoint / comparative dissolution requirements o be able to determine similarity of profiles o be able to assess release dissolution specifications o know how to assess development and biowaiver data o know when and how disintegration can replace dissolution Theo Dekker -- CPH 59 -- January 2011 70


