50c216981521aa8059c50b7ddcf2a589.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 WHO International Clinical Trial Registry Platform A. Metin Gülmezoglu Project Coordinator Department of Reproductive Health and Research World Health Organization
WHO International Clinical Trial Registry Platform A. Metin Gülmezoglu Project Coordinator Department of Reproductive Health and Research World Health Organization
 Why Registration o Fulfill ethical obligation to participants, the public o Address problem of publication bias o Contribute to development of unbiased systematic reviews o Advance science more quickly n Speed disclosure of results n Increase effectiveness of research funding n Increase participation by patients, doctors, researchers o Increase transparency of information about trials n Reduce over-reporting & ambiguity
Why Registration o Fulfill ethical obligation to participants, the public o Address problem of publication bias o Contribute to development of unbiased systematic reviews o Advance science more quickly n Speed disclosure of results n Increase effectiveness of research funding n Increase participation by patients, doctors, researchers o Increase transparency of information about trials n Reduce over-reporting & ambiguity
 Trials Registration - History o Historical calls for registration of human research; early small registers o Multiple studies establishing publication bias o Recent proliferation of local and specialty registers o Support from journal editors o AMA statement of support o NY Attorney General suit & disclosure settlement o Plans for industry trials registration o Support from speakers at Mexico City Joint plenary
Trials Registration - History o Historical calls for registration of human research; early small registers o Multiple studies establishing publication bias o Recent proliferation of local and specialty registers o Support from journal editors o AMA statement of support o NY Attorney General suit & disclosure settlement o Plans for industry trials registration o Support from speakers at Mexico City Joint plenary
 People have suffered and resources have been wasted because disappointing results of research have not been reported.
People have suffered and resources have been wasted because disappointing results of research have not been reported.
 Biased under-reporting of research is ethically and scientifically unacceptable, and it should be outlawed. Information about ongoing research should be registered prospectively and publicly. Sir Iain Chalmers, November 2004, Mexico City
Biased under-reporting of research is ethically and scientifically unacceptable, and it should be outlawed. Information about ongoing research should be registered prospectively and publicly. Sir Iain Chalmers, November 2004, Mexico City
 WHO involvement o October 2003 London n Dr JW Lee discusses WHO's role in global health systems research – trial registration is highlighted o April 2004 London stakeholder/funder discussion n Registration will benefit informed decisions o April 2004 WHO registers its trials via ISRCTN
WHO involvement o October 2003 London n Dr JW Lee discusses WHO's role in global health systems research – trial registration is highlighted o April 2004 London stakeholder/funder discussion n Registration will benefit informed decisions o April 2004 WHO registers its trials via ISRCTN
 WHO involvement
WHO involvement
 Why WHO? o Global, neutral body o Role in setting norms and standards o Contribute to capacity building o Accountable to member states
Why WHO? o Global, neutral body o Role in setting norms and standards o Contribute to capacity building o Accountable to member states
 Stakeholders’ Meeting October 2004 at Rockefeller Foundation o WHO o Medical journal editors o Research sponsors (industry/government/foundations) o Research investigators o Cochrane Collaboration o Regulators/government n US, Canada, UK, Germany n Office of NY State Attorney General o ISRCTN & Meta. Register; Clinical. Trials. gov
Stakeholders’ Meeting October 2004 at Rockefeller Foundation o WHO o Medical journal editors o Research sponsors (industry/government/foundations) o Research investigators o Cochrane Collaboration o Regulators/government n US, Canada, UK, Germany n Office of NY State Attorney General o ISRCTN & Meta. Register; Clinical. Trials. gov
 Statement of NY stakeholders: Need for global approach to trials registration o Unambiguous identification of trials o Consensus needed on which trials; data; timing and disclosure of results o One-stop search portal; publicly available o System that is simple, effective, efficient o Capacity built where appropriate (cont’d)
Statement of NY stakeholders: Need for global approach to trials registration o Unambiguous identification of trials o Consensus needed on which trials; data; timing and disclosure of results o One-stop search portal; publicly available o System that is simple, effective, efficient o Capacity built where appropriate (cont’d)
 Statement of NY stakeholders (cont’d): WHO should establish formal process o Appropriate governance; broad collaborative process o Existing structures leveraged; need for any new structures identified o WHO mindful of ICMJE deadline
Statement of NY stakeholders (cont’d): WHO should establish formal process o Appropriate governance; broad collaborative process o Existing structures leveraged; need for any new structures identified o WHO mindful of ICMJE deadline
 Ministerial Summit – Mexico City November 2004 o The Ministerial Summit on Health Research urges the WHO to work with stakeholders in developing a global system for trials registration n Ensuring unambiguous identification of trials n Achieving consensus on which trials; data; timing and disclosure of results n Creating a one-stop public search portal n Building on existing efforts n Building capacity where needed o The Summit urges international funders to support initiative to enable launch of portal by 2006
Ministerial Summit – Mexico City November 2004 o The Ministerial Summit on Health Research urges the WHO to work with stakeholders in developing a global system for trials registration n Ensuring unambiguous identification of trials n Achieving consensus on which trials; data; timing and disclosure of results n Creating a one-stop public search portal n Building on existing efforts n Building capacity where needed o The Summit urges international funders to support initiative to enable launch of portal by 2006
 Three Tracks I. Substantive Standards / Principles n Major issues (e. g. , registration scope, disclosure standards) n High-level review of technical implementation against standards II. Technical Implementation n IT structure, adaptable operating procedures n Ongoing financial / sourcing model III. Start-Up Funding
Three Tracks I. Substantive Standards / Principles n Major issues (e. g. , registration scope, disclosure standards) n High-level review of technical implementation against standards II. Technical Implementation n IT structure, adaptable operating procedures n Ongoing financial / sourcing model III. Start-Up Funding
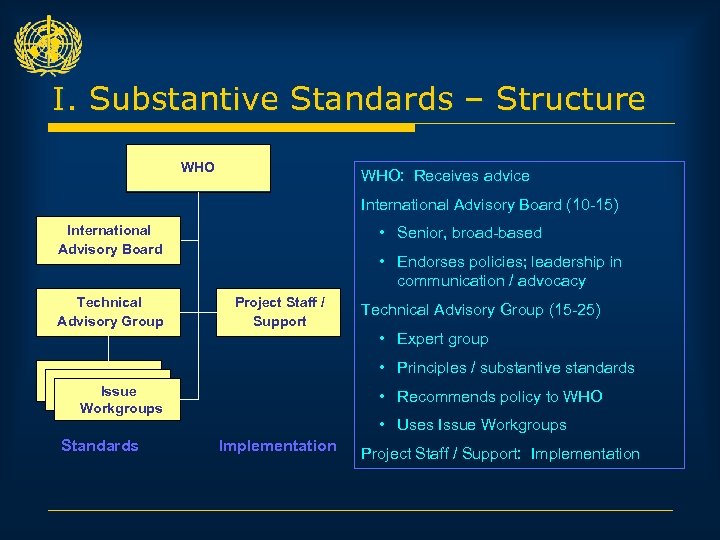 I. Substantive Standards – Structure WHO: Receives advice International Advisory Board (10 -15) International Advisory Board Technical Advisory Group • Senior, broad-based • Endorses policies; leadership in communication / advocacy Project Staff / Support Technical Advisory Group (15 -25) • Expert group • Principles / substantive standards Issue Workgroups Standards • Recommends policy to WHO • Uses Issue Workgroups Implementation Project Staff / Support: Implementation
I. Substantive Standards – Structure WHO: Receives advice International Advisory Board (10 -15) International Advisory Board Technical Advisory Group • Senior, broad-based • Endorses policies; leadership in communication / advocacy Project Staff / Support Technical Advisory Group (15 -25) • Expert group • Principles / substantive standards Issue Workgroups Standards • Recommends policy to WHO • Uses Issue Workgroups Implementation Project Staff / Support: Implementation
 I. Principles Discussion in NY: General Agreements & Issues Component Portal Registration Scope Content • Unique ID • Descriptors • Updates General Agreement Requires Discussion • One-stop global search; free access to all; basic implementation in 2005 • Include randomized controlled trials (RCT “tbd” = to be defined) • Whether to include all trials (possibly different standards for early trials) • Unambiguous ID (unique & exclusive) • Minimum data set (tbd); searchable fields • “Significant” changes / EC approval (tbd) • Whether to include detailed info, protocol Timing • Register before enrolling first participant Access to Data • General data available to all Compliance Results Scope • Ethics Committee is potential key Content • Final registration info; links to pubs & data Timing • Trials supporting approved interventions • Whether to limit access to detailed data • Need EC input; role of laws / regulations • Whether to disclose all registered trials • Whether to disclose protocol(s) • After trial completion or after approval? (of specific indication or any indication? )
I. Principles Discussion in NY: General Agreements & Issues Component Portal Registration Scope Content • Unique ID • Descriptors • Updates General Agreement Requires Discussion • One-stop global search; free access to all; basic implementation in 2005 • Include randomized controlled trials (RCT “tbd” = to be defined) • Whether to include all trials (possibly different standards for early trials) • Unambiguous ID (unique & exclusive) • Minimum data set (tbd); searchable fields • “Significant” changes / EC approval (tbd) • Whether to include detailed info, protocol Timing • Register before enrolling first participant Access to Data • General data available to all Compliance Results Scope • Ethics Committee is potential key Content • Final registration info; links to pubs & data Timing • Trials supporting approved interventions • Whether to limit access to detailed data • Need EC input; role of laws / regulations • Whether to disclose all registered trials • Whether to disclose protocol(s) • After trial completion or after approval? (of specific indication or any indication? )
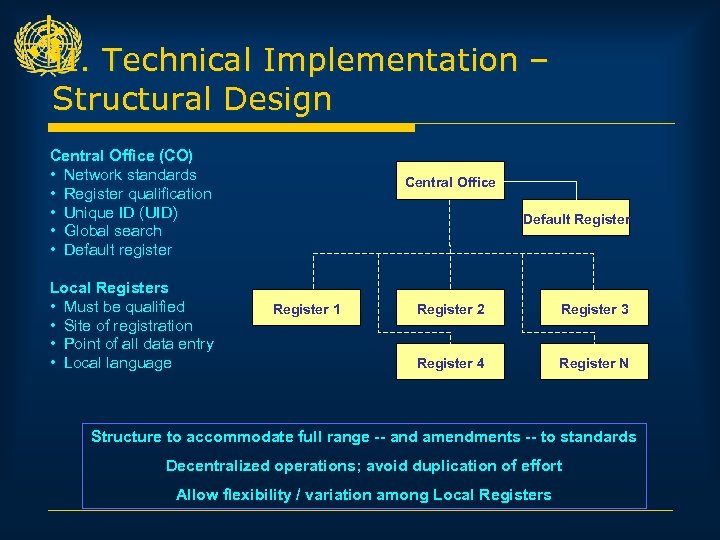 II. Technical Implementation – Structural Design Central Office (CO) • Network standards • Register qualification • Unique ID (UID) • Global search • Default register Local Registers • Must be qualified • Site of registration • Point of all data entry • Local language Central Office Default Register 1 Register 2 Register 3 Register 4 Register N Structure to accommodate full range -- and amendments -- to standards Decentralized operations; avoid duplication of effort Allow flexibility / variation among Local Registers
II. Technical Implementation – Structural Design Central Office (CO) • Network standards • Register qualification • Unique ID (UID) • Global search • Default register Local Registers • Must be qualified • Site of registration • Point of all data entry • Local language Central Office Default Register 1 Register 2 Register 3 Register 4 Register N Structure to accommodate full range -- and amendments -- to standards Decentralized operations; avoid duplication of effort Allow flexibility / variation among Local Registers
 II. Technical Implementation – Key Process Concepts o. Qualification: Central Office (CO) “qualifies” limited number of local registers, provides contractual procedures / technical specs o. Local Registration: A qualified (or default) register collects all data in local language, uses CO search tool to verify no existing Unique ID (UID), and transmits Standard Registration Data in English o. Unique ID: CO verifies / stores in Central File, and then generates / transmits UID to local register (ideally, fully automated in both directions) o. Search: CO search engine works with Standard Registration Data in Central File (may have distributed solution) o. Self-Financed: Ongoing costs of CO / standards covered by nominal fee, collected by local register at time of data transmission (can share) o. Results: At trial completion, results link added to Central File o. Outsourcing: May outsource technical components, but not control
II. Technical Implementation – Key Process Concepts o. Qualification: Central Office (CO) “qualifies” limited number of local registers, provides contractual procedures / technical specs o. Local Registration: A qualified (or default) register collects all data in local language, uses CO search tool to verify no existing Unique ID (UID), and transmits Standard Registration Data in English o. Unique ID: CO verifies / stores in Central File, and then generates / transmits UID to local register (ideally, fully automated in both directions) o. Search: CO search engine works with Standard Registration Data in Central File (may have distributed solution) o. Self-Financed: Ongoing costs of CO / standards covered by nominal fee, collected by local register at time of data transmission (can share) o. Results: At trial completion, results link added to Central File o. Outsourcing: May outsource technical components, but not control
 III. Start-Up Funding o. Start-Up Costs: to set up the project, Secretariat n In-Kind Funding: travel, meetings n Hard Dollar Funding: Will need to secure modest contributions from variety of stakeholders, beneficiaries, foundations o. Maintenance costs: work towards a self-funding. automated system
III. Start-Up Funding o. Start-Up Costs: to set up the project, Secretariat n In-Kind Funding: travel, meetings n Hard Dollar Funding: Will need to secure modest contributions from variety of stakeholders, beneficiaries, foundations o. Maintenance costs: work towards a self-funding. automated system
 Proposed Timing – Set Dates o. Standards Track: n March/April – TAG Meeting n May/June? – IAB Meeting o. Technical Implementation Track: n Present architecture to TAG for review / feedback o. Funding Track: n Begin now; look to finish by May
Proposed Timing – Set Dates o. Standards Track: n March/April – TAG Meeting n May/June? – IAB Meeting o. Technical Implementation Track: n Present architecture to TAG for review / feedback o. Funding Track: n Begin now; look to finish by May
 Thank you!
Thank you!


