de41e441e86dc1257d759d17e0b7a70b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 &
&
 Who Are We? KPMG Risk And Advisory Services • Manage risk in automated and financial systems • Understand risks consistent with business need • Evaluate mitigation measures consistent with business need • Recommend controls and solutions consistent with business need Carl Salmonsen • CISA • CISSP • B. S. Mgmt Sci • 14 years in IT and Information Security John Mee • CISSP • MSc Comp. Sci. • 18 years in IT and Information Security
Who Are We? KPMG Risk And Advisory Services • Manage risk in automated and financial systems • Understand risks consistent with business need • Evaluate mitigation measures consistent with business need • Recommend controls and solutions consistent with business need Carl Salmonsen • CISA • CISSP • B. S. Mgmt Sci • 14 years in IT and Information Security John Mee • CISSP • MSc Comp. Sci. • 18 years in IT and Information Security
 e. Commerce…. . . Why? • • Lower Cost Increased Efficiency Speed to Market Increased Security (huh? ? ) More Diverse Customer Base Improved Customer Service Creates New Services Physical Size and Location Don't Matter
e. Commerce…. . . Why? • • Lower Cost Increased Efficiency Speed to Market Increased Security (huh? ? ) More Diverse Customer Base Improved Customer Service Creates New Services Physical Size and Location Don't Matter
 e. Commerce High Profile Examples Amazon. com - The Internet’s largest virtual bookstore Security First National Bank - The first original virtual bank e. Trade - An online stock broker at reduced prices Wall Street Journal Interactive - An online version of the WSJ Commonalties in examples drive definition • Use of a common electronic medium • Perform commercial exchanges of value • Transaction between two entities e. Commerce
e. Commerce High Profile Examples Amazon. com - The Internet’s largest virtual bookstore Security First National Bank - The first original virtual bank e. Trade - An online stock broker at reduced prices Wall Street Journal Interactive - An online version of the WSJ Commonalties in examples drive definition • Use of a common electronic medium • Perform commercial exchanges of value • Transaction between two entities e. Commerce
 e. Commerce Emerging e. Commerce Examples Digital Content – Peer-to-Peer (starting with Napster); Apples i. Tunes Music Store, Mobile e. Commerce - Vending (and other) machine purchases Using cell phone of other specialized token or smart card (Europe), Master Card - August 28, 2003 - Master. Card International today unveiled Master. Card® Side. Card™, the stylish new payment card which features a modified design small enough to fit on a key ring. Micro. Payments – Allows Web Surfers a method to make small Purchases (under $1) for tidbits of on-line content.
e. Commerce Emerging e. Commerce Examples Digital Content – Peer-to-Peer (starting with Napster); Apples i. Tunes Music Store, Mobile e. Commerce - Vending (and other) machine purchases Using cell phone of other specialized token or smart card (Europe), Master Card - August 28, 2003 - Master. Card International today unveiled Master. Card® Side. Card™, the stylish new payment card which features a modified design small enough to fit on a key ring. Micro. Payments – Allows Web Surfers a method to make small Purchases (under $1) for tidbits of on-line content.
 Are Internet (and other) security issues overhyped? • YES • But. . there are valid concerns
Are Internet (and other) security issues overhyped? • YES • But. . there are valid concerns
 Risks! Traditional Risks • • • Lack of Privacy or Confidentiality Transaction Integrity False Identification of Transaction Participants Inability to Prove Transactions Occurred False Storefronts
Risks! Traditional Risks • • • Lack of Privacy or Confidentiality Transaction Integrity False Identification of Transaction Participants Inability to Prove Transactions Occurred False Storefronts
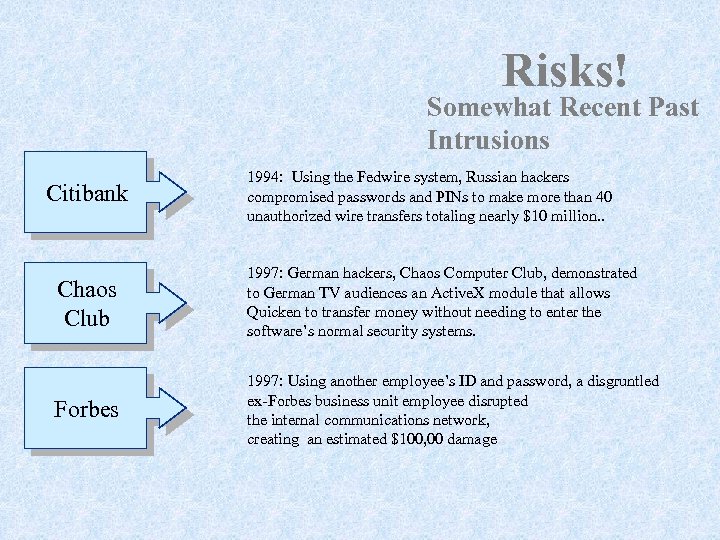 Risks! Somewhat Recent Past Intrusions Citibank 1994: Using the Fedwire system, Russian hackers compromised passwords and PINs to make more than 40 unauthorized wire transfers totaling nearly $10 million. . Chaos Club 1997: German hackers, Chaos Computer Club, demonstrated to German TV audiences an Active. X module that allows Quicken to transfer money without needing to enter the software’s normal security systems. Forbes 1997: Using another employee’s ID and password, a disgruntled ex-Forbes business unit employee disrupted the internal communications network, creating an estimated $100, 00 damage
Risks! Somewhat Recent Past Intrusions Citibank 1994: Using the Fedwire system, Russian hackers compromised passwords and PINs to make more than 40 unauthorized wire transfers totaling nearly $10 million. . Chaos Club 1997: German hackers, Chaos Computer Club, demonstrated to German TV audiences an Active. X module that allows Quicken to transfer money without needing to enter the software’s normal security systems. Forbes 1997: Using another employee’s ID and password, a disgruntled ex-Forbes business unit employee disrupted the internal communications network, creating an estimated $100, 00 damage
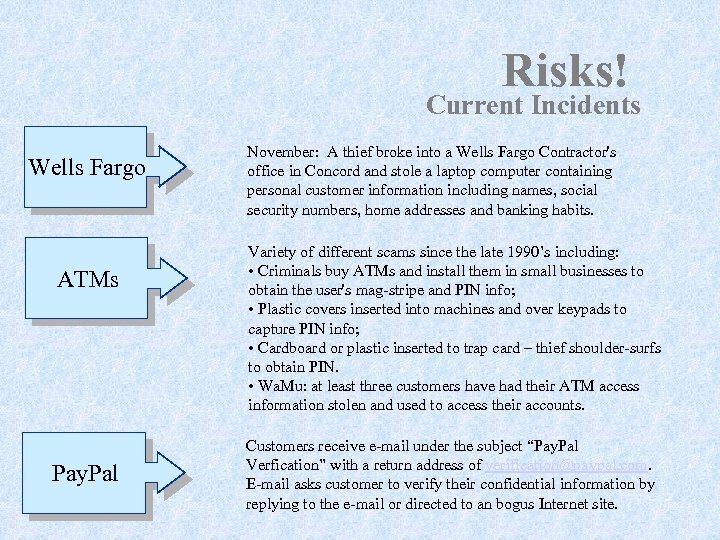 Risks! Current Incidents Wells Fargo ATMs Pay. Pal November: A thief broke into a Wells Fargo Contractor's office in Concord and stole a laptop computer containing personal customer information including names, social security numbers, home addresses and banking habits. Variety of different scams since the late 1990’s including: • Criminals buy ATMs and install them in small businesses to obtain the user's mag-stripe and PIN info; • Plastic covers inserted into machines and over keypads to capture PIN info; • Cardboard or plastic inserted to trap card – thief shoulder-surfs to obtain PIN. • Wa. Mu: at least three customers have had their ATM access information stolen and used to access their accounts. Customers receive e-mail under the subject “Pay. Pal Verfication” with a return address of verification@paypal. com. E-mail asks customer to verify their confidential information by replying to the e-mail or directed to an bogus Internet site.
Risks! Current Incidents Wells Fargo ATMs Pay. Pal November: A thief broke into a Wells Fargo Contractor's office in Concord and stole a laptop computer containing personal customer information including names, social security numbers, home addresses and banking habits. Variety of different scams since the late 1990’s including: • Criminals buy ATMs and install them in small businesses to obtain the user's mag-stripe and PIN info; • Plastic covers inserted into machines and over keypads to capture PIN info; • Cardboard or plastic inserted to trap card – thief shoulder-surfs to obtain PIN. • Wa. Mu: at least three customers have had their ATM access information stolen and used to access their accounts. Customers receive e-mail under the subject “Pay. Pal Verfication” with a return address of verification@paypal. com. E-mail asks customer to verify their confidential information by replying to the e-mail or directed to an bogus Internet site.
 Risks! Future Risks • Dramatic growth in B-B, B-C, and B-E • Internet terminals in stores, airports, bars • Self-Checkout stands In Short. Anything that contains personal information Such as a magnetic strip on a card • Driver's License • Credit Card • ATM Card • Medical Provider Cards
Risks! Future Risks • Dramatic growth in B-B, B-C, and B-E • Internet terminals in stores, airports, bars • Self-Checkout stands In Short. Anything that contains personal information Such as a magnetic strip on a card • Driver's License • Credit Card • ATM Card • Medical Provider Cards
 Where is the threat coming from? Disgruntled/Former Employees Competitors Hackers Foreign Governments Crooks MY NETWORK
Where is the threat coming from? Disgruntled/Former Employees Competitors Hackers Foreign Governments Crooks MY NETWORK
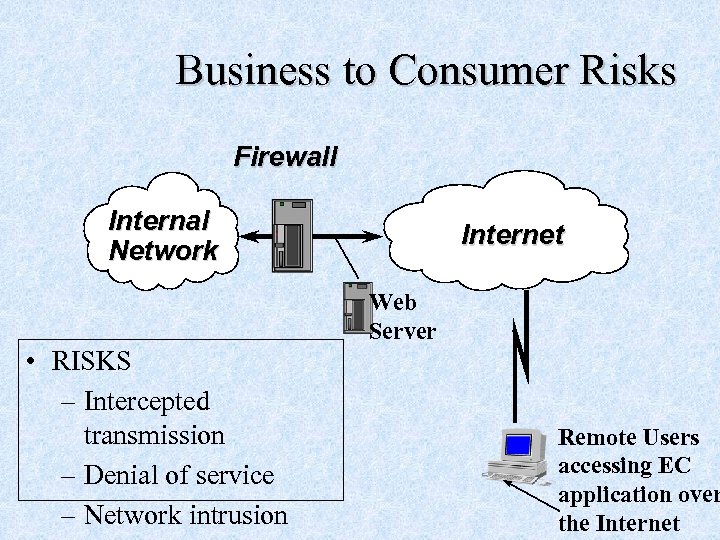 Business to Consumer Risks Firewall Internal Network Internet Web Server • RISKS – Intercepted transmission – Denial of service – Network intrusion Remote Users accessing EC application over the Internet
Business to Consumer Risks Firewall Internal Network Internet Web Server • RISKS – Intercepted transmission – Denial of service – Network intrusion Remote Users accessing EC application over the Internet
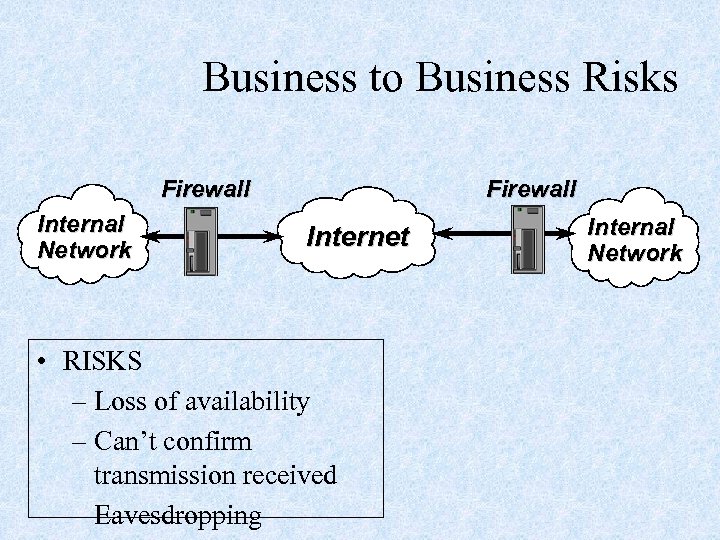 Business to Business Risks Firewall Internal Network Firewall Internet • RISKS – Loss of availability – Can’t confirm transmission received – Eavesdropping Internal Network
Business to Business Risks Firewall Internal Network Firewall Internet • RISKS – Loss of availability – Can’t confirm transmission received – Eavesdropping Internal Network
 Potential Business Impact • • Public Embarrassment / Image Compromised Confidential Information Compromised Integrity Of Information Disruption of Services (System / Network Outages) • Fraud or Theft of Services • Financial Liability • Criminal Liability Under State or Federal Laws
Potential Business Impact • • Public Embarrassment / Image Compromised Confidential Information Compromised Integrity Of Information Disruption of Services (System / Network Outages) • Fraud or Theft of Services • Financial Liability • Criminal Liability Under State or Federal Laws
 How Do You Implement Adequate Security?
How Do You Implement Adequate Security?
 Security methodology • Proper security must provide the appropriate assurance that in any transaction: • Both parties are identified and authenticated • Both parties can only perform the actions they are supposed to • The transaction information is correct/unaltered • The transaction is kept confidential
Security methodology • Proper security must provide the appropriate assurance that in any transaction: • Both parties are identified and authenticated • Both parties can only perform the actions they are supposed to • The transaction information is correct/unaltered • The transaction is kept confidential
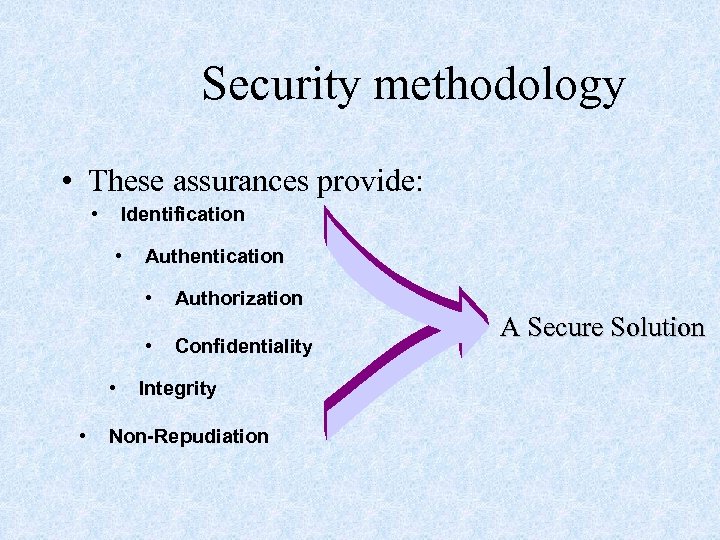 Security methodology • These assurances provide: • Identification • Authentication • • Authorization Confidentiality Integrity Non-Repudiation A Secure Solution
Security methodology • These assurances provide: • Identification • Authentication • • Authorization Confidentiality Integrity Non-Repudiation A Secure Solution
 The EC Security Toolkit • • • Firewalls Strong authentication Public key technology Secure Protocols Virtual Private Networks General system security
The EC Security Toolkit • • • Firewalls Strong authentication Public key technology Secure Protocols Virtual Private Networks General system security
 The EC Security Toolkit • Firewalls • • • Strong authentication Public key technology Secure Protocols Virtual Private Networks General system security
The EC Security Toolkit • Firewalls • • • Strong authentication Public key technology Secure Protocols Virtual Private Networks General system security
 Firewall Solutions • Functions of a Firewall – Between a trusted and untrusted network – Controls traffic based on service, source, destination, user ID – Deny everything that is not specifically allowed
Firewall Solutions • Functions of a Firewall – Between a trusted and untrusted network – Controls traffic based on service, source, destination, user ID – Deny everything that is not specifically allowed
 The EC Security Toolkit • Firewalls • Strong authentication • • Public key technology Secure Protocols Virtual Private Networks General system security
The EC Security Toolkit • Firewalls • Strong authentication • • Public key technology Secure Protocols Virtual Private Networks General system security
 Strong Authentication • What you know, what you have, what you are (where you are? ) • Uses two of the above • Several main types – Time based tokens – Challenge response – Public key (client side certificates) – Smart card based
Strong Authentication • What you know, what you have, what you are (where you are? ) • Uses two of the above • Several main types – Time based tokens – Challenge response – Public key (client side certificates) – Smart card based
 Leading Authentication Examples • IDs & Passwords – Benefits: Users are comfortable – Risks: Easily compromised or cracked! • Digital Certificates – Benefits: Can be invisible to the user – Risks: Require infrastructure, trust hierarchy • Smartcards – Benefits: Strong link back to specific user – Risks: Deploying readers, inconvenient for user
Leading Authentication Examples • IDs & Passwords – Benefits: Users are comfortable – Risks: Easily compromised or cracked! • Digital Certificates – Benefits: Can be invisible to the user – Risks: Require infrastructure, trust hierarchy • Smartcards – Benefits: Strong link back to specific user – Risks: Deploying readers, inconvenient for user
 The EC Security Toolkit • Firewalls • Strong authentication • Public key technology • Secure Protocols • Virtual Private Networks • General system security
The EC Security Toolkit • Firewalls • Strong authentication • Public key technology • Secure Protocols • Virtual Private Networks • General system security
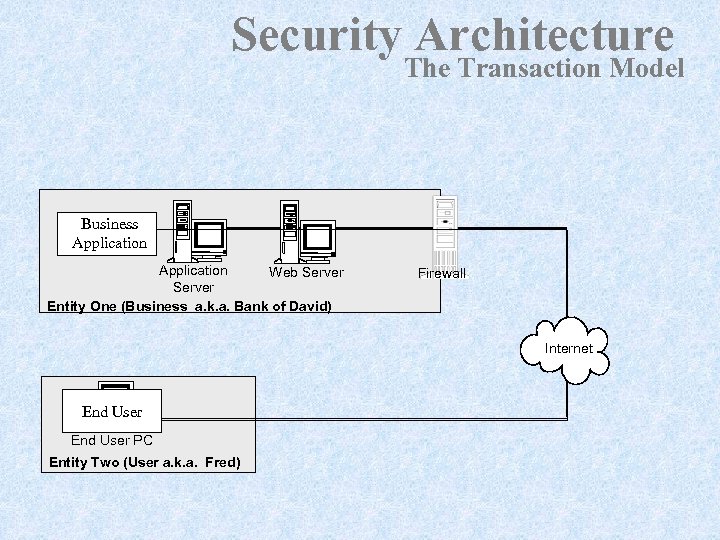 Security Architecture The Transaction Model Business Application Web Server Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Firewall Internet End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred)
Security Architecture The Transaction Model Business Application Web Server Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Firewall Internet End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred)
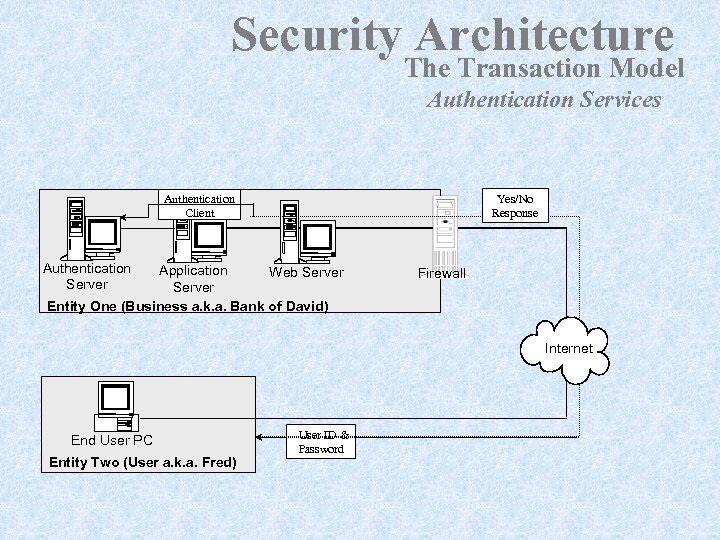 Security Architecture The Transaction Model Authentication Services Yes/No Response Authentication Client Authentication Server Application Web Server Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Firewall Internet End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) User ID & Password
Security Architecture The Transaction Model Authentication Services Yes/No Response Authentication Client Authentication Server Application Web Server Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Firewall Internet End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) User ID & Password
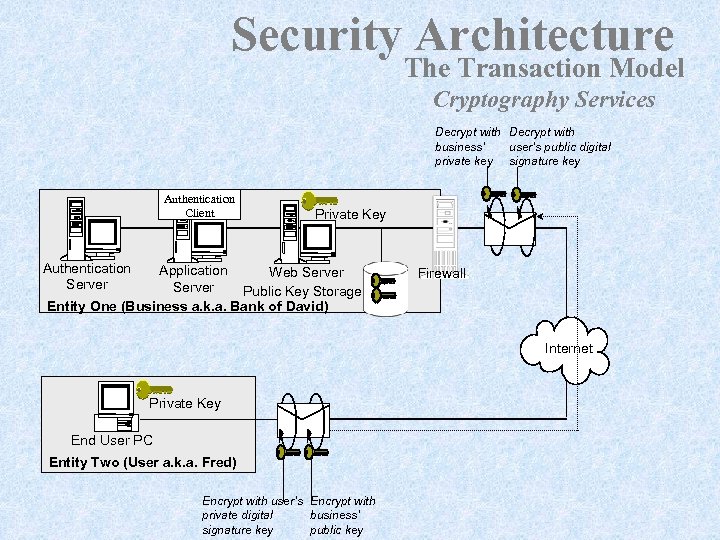 Security Architecture The Transaction Model Cryptography Services Decrypt with business’ user’s public digital private key signature key Authentication Client Private Key Authentication Server Application Web Server Public Key Storage Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Firewall Internet Private Key End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) Encrypt with user’s Encrypt with private digital business’ signature key public key
Security Architecture The Transaction Model Cryptography Services Decrypt with business’ user’s public digital private key signature key Authentication Client Private Key Authentication Server Application Web Server Public Key Storage Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Firewall Internet Private Key End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) Encrypt with user’s Encrypt with private digital business’ signature key public key
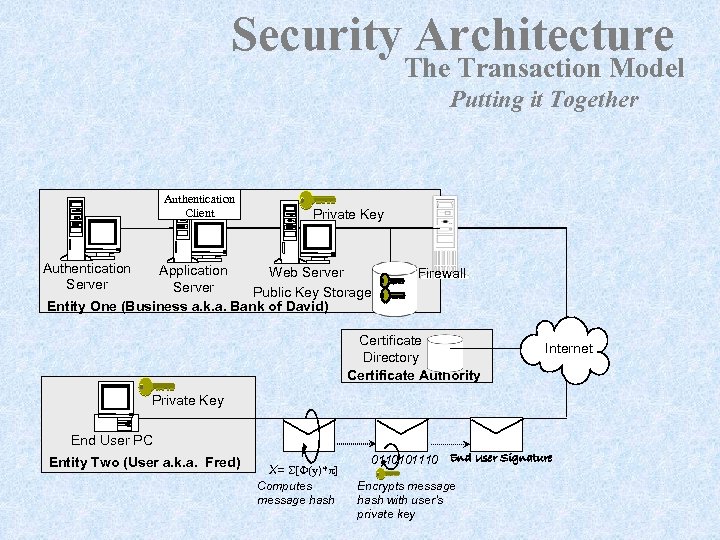 Security Architecture The Transaction Model Putting it Together Authentication Client Private Key Authentication Server Application Web Server Public Key Storage Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Firewall Certificate Directory Certificate Authority Internet Private Key End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) X= S[F(y)*p] Computes message hash 0110101110 End User Signature Encrypts message hash with user’s private key
Security Architecture The Transaction Model Putting it Together Authentication Client Private Key Authentication Server Application Web Server Public Key Storage Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Firewall Certificate Directory Certificate Authority Internet Private Key End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) X= S[F(y)*p] Computes message hash 0110101110 End User Signature Encrypts message hash with user’s private key
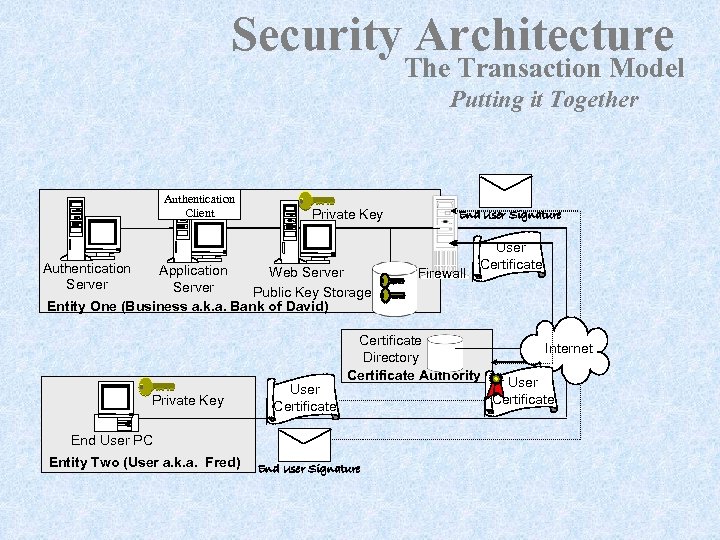 Security Architecture The Transaction Model Putting it Together Authentication Client Private Key Authentication Server Application Web Server Public Key Storage Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Private Key User Certificate Firewall User Certificate Directory Certificate Authority End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) End User Signature Internet User Certificate
Security Architecture The Transaction Model Putting it Together Authentication Client Private Key Authentication Server Application Web Server Public Key Storage Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) Private Key User Certificate Firewall User Certificate Directory Certificate Authority End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) End User Signature Internet User Certificate
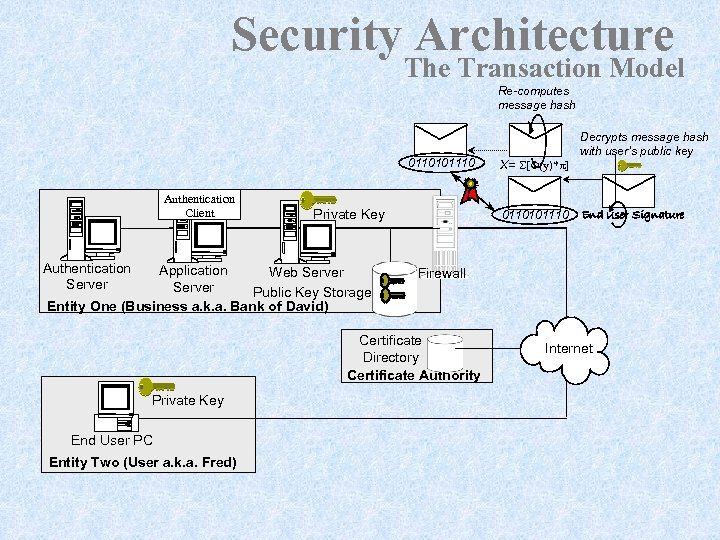 Security Architecture The Transaction Model Re-computes message hash 0110101110 Authentication Client Authentication Server Private Key Application Web Server Public Key Storage Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) 0110101110 End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) End User Signature Firewall Certificate Directory Certificate Authority Private Key X= S[F(y)*p] Decrypts message hash with user’s public key Internet
Security Architecture The Transaction Model Re-computes message hash 0110101110 Authentication Client Authentication Server Private Key Application Web Server Public Key Storage Entity One (Business a. k. a. Bank of David) 0110101110 End User PC Entity Two (User a. k. a. Fred) End User Signature Firewall Certificate Directory Certificate Authority Private Key X= S[F(y)*p] Decrypts message hash with user’s public key Internet
 The EC Security Toolkit • Firewalls • Strong authentication • Public key technology • Secure Protocols • Virtual Private Networks • General system security
The EC Security Toolkit • Firewalls • Strong authentication • Public key technology • Secure Protocols • Virtual Private Networks • General system security
 Secure Protocols ä S-HTTP ä security enhanced version of the HTTP protocol ä wraps entire message in a secure envelope ä SSL ä secures the channel with session keys ä provides data encryption, server and client ä authentication in version 3 ä SET ä provides authentication and encryption for credit ä card transactions
Secure Protocols ä S-HTTP ä security enhanced version of the HTTP protocol ä wraps entire message in a secure envelope ä SSL ä secures the channel with session keys ä provides data encryption, server and client ä authentication in version 3 ä SET ä provides authentication and encryption for credit ä card transactions
 The EC Security Toolkit • • Firewalls Strong authentication Public key technology Secure Protocols • Virtual Private Networks • General system security
The EC Security Toolkit • • Firewalls Strong authentication Public key technology Secure Protocols • Virtual Private Networks • General system security
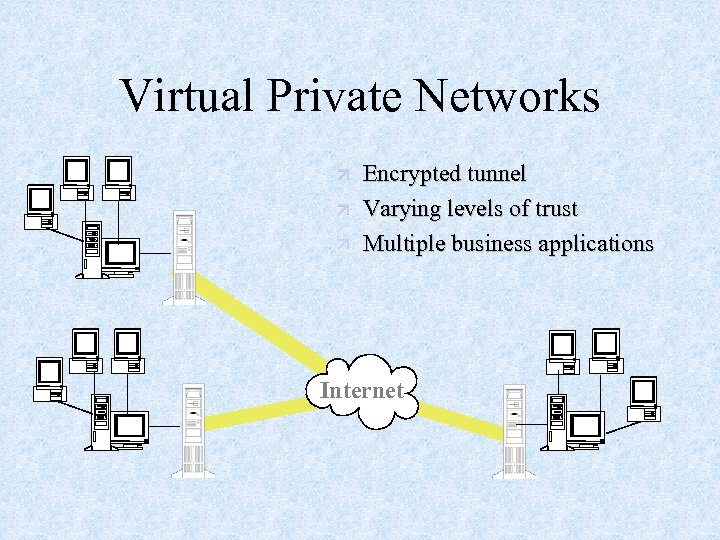 Virtual Private Networks ä ä ä Encrypted tunnel Varying levels of trust Multiple business applications Internet
Virtual Private Networks ä ä ä Encrypted tunnel Varying levels of trust Multiple business applications Internet
 The EC Security Toolkit • • • Firewalls Strong authentication Public key technology Secure Protocols Virtual Private Networks • General system security
The EC Security Toolkit • • • Firewalls Strong authentication Public key technology Secure Protocols Virtual Private Networks • General system security
 Traditional Security • • • Host security Secure applications / programming Network security / partitioning Physical security Policies, procedures, guidelines, standards
Traditional Security • • • Host security Secure applications / programming Network security / partitioning Physical security Policies, procedures, guidelines, standards
 Some Common Mistakes • • Waiting too late to consider security Don’t analyze business risks Give security to junior member on team Pick a solution when you don’t understand the technology • Ignore operating system level security • Thinking IDs and passwords are enough
Some Common Mistakes • • Waiting too late to consider security Don’t analyze business risks Give security to junior member on team Pick a solution when you don’t understand the technology • Ignore operating system level security • Thinking IDs and passwords are enough
 Legislative Considerations • SB 1386 • HIPAA • Graham Leach Bliley
Legislative Considerations • SB 1386 • HIPAA • Graham Leach Bliley
 SB 1386 - Breach Notification Law • Any agency or entity that owns or licenses computerized data that includes personal information • shall disclose any breach of the security of the system following discovery or notification of the breach in the security of the data • to any resident of California whose unencrypted personal information was, or is reasonably believed to have been, acquired by an unauthorized person
SB 1386 - Breach Notification Law • Any agency or entity that owns or licenses computerized data that includes personal information • shall disclose any breach of the security of the system following discovery or notification of the breach in the security of the data • to any resident of California whose unencrypted personal information was, or is reasonably believed to have been, acquired by an unauthorized person
 SB 1386 - Personal Information Defined • individual's first name or first initial and last name in combination with any one or more of the following data elements, when either the name or the data elements are not encrypted: – Social security number – Driver's license number or California Identification Card number. – Account number, credit or debit card number, in combination with any required security code, access code, or password that would permit access to an individual's financial account
SB 1386 - Personal Information Defined • individual's first name or first initial and last name in combination with any one or more of the following data elements, when either the name or the data elements are not encrypted: – Social security number – Driver's license number or California Identification Card number. – Account number, credit or debit card number, in combination with any required security code, access code, or password that would permit access to an individual's financial account
 SB 1386 - Penalties • 1798. 84: – (a) Any customer injured by a violation of this title may institute a civil action to recover damages. – (b) Any business that violates, proposes to violate, or has violated this title may be enjoined. – (c) The rights and remedies available under this section are cumulative to each other and to any other rights and remedies available under law.
SB 1386 - Penalties • 1798. 84: – (a) Any customer injured by a violation of this title may institute a civil action to recover damages. – (b) Any business that violates, proposes to violate, or has violated this title may be enjoined. – (c) The rights and remedies available under this section are cumulative to each other and to any other rights and remedies available under law.
 Legislative Considerations • SB 1386 • HIPAA • Graham Leach Bliley
Legislative Considerations • SB 1386 • HIPAA • Graham Leach Bliley
 Health Information Portability and Accountability Act • HIPAA requires the development of comprehensive security programs to protect healthcare data. n Public Law 104 -191, August 21, 1996 n Amends Internal Revenue Service Code of 1986 n Guarantees Health Coverage When Job Changes n Intended to Reduce Fraud and Abuse (Medicare/Medicaid) n Preempts State Laws Unless More Stringent
Health Information Portability and Accountability Act • HIPAA requires the development of comprehensive security programs to protect healthcare data. n Public Law 104 -191, August 21, 1996 n Amends Internal Revenue Service Code of 1986 n Guarantees Health Coverage When Job Changes n Intended to Reduce Fraud and Abuse (Medicare/Medicaid) n Preempts State Laws Unless More Stringent
 HIPAA Summary • Administrative Simplification - Establishes national standards for: – Electronic (EDI) transactions; – Identifiers such as provider, payer and employer; and – Improved efficiency of processing health care information. • Privacy - Protect patient data from inappropriate disclosure or use. – Require consent to use protected health information for treatment, payment and operations for healthcare; – Allow health information to be disclosed without patient authorization for certain purposes (such as research, public health and oversight) but only under defined circumstances; – Require written authorization for use and disclosure of health information for other purposes; – Create a set of fair information practices to inform patients how their information is used and disclosed, ensure they have access to information about them; and • Security - Establish safeguards around patient information systems preventing unauthorized access. – Administrative procedures; – Physical safeguards;
HIPAA Summary • Administrative Simplification - Establishes national standards for: – Electronic (EDI) transactions; – Identifiers such as provider, payer and employer; and – Improved efficiency of processing health care information. • Privacy - Protect patient data from inappropriate disclosure or use. – Require consent to use protected health information for treatment, payment and operations for healthcare; – Allow health information to be disclosed without patient authorization for certain purposes (such as research, public health and oversight) but only under defined circumstances; – Require written authorization for use and disclosure of health information for other purposes; – Create a set of fair information practices to inform patients how their information is used and disclosed, ensure they have access to information about them; and • Security - Establish safeguards around patient information systems preventing unauthorized access. – Administrative procedures; – Physical safeguards;
 Legislative Controls and Remedies • SB 1386 • HIPAA • Gramm-Leach Bliley
Legislative Controls and Remedies • SB 1386 • HIPAA • Gramm-Leach Bliley
 GLB Summary • In 1999 Congress enacted the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLB), significantly revising the way in which the financial services industry is regulated. GLB includes measures to protect the privacy of personal nonpublic information collected and used by financial service providers. – Notice to customers by the firm of its policies and practices regarding nonpublic information; – Permission for customers to "Opt Out" of disclosure by the firm of information to certain nonaffiliated third parties; – Limitations on disclosure by the firm to third parties, and various exceptions to the limitations; and – Review and maintenance of safeguards to maintain the security of customer information.
GLB Summary • In 1999 Congress enacted the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLB), significantly revising the way in which the financial services industry is regulated. GLB includes measures to protect the privacy of personal nonpublic information collected and used by financial service providers. – Notice to customers by the firm of its policies and practices regarding nonpublic information; – Permission for customers to "Opt Out" of disclosure by the firm of information to certain nonaffiliated third parties; – Limitations on disclosure by the firm to third parties, and various exceptions to the limitations; and – Review and maintenance of safeguards to maintain the security of customer information.
 Closing Comments • Good security solutions are available; the key is applying them • Public perception will change over time • Need to focus on business risks
Closing Comments • Good security solutions are available; the key is applying them • Public perception will change over time • Need to focus on business risks



