402f4b1faa380cce5fea846c13cd250b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Who Are the Users and What Are Their Expectations? * Aspects of Academic Bibliographies Anikó Dudás, Ph. D Hungary Bibliography in the Digital Age IFLA Satellite Meeting National Library of Poland, Warsaw, 9 August 2012
Who Are the Users and What Are Their Expectations? * Aspects of Academic Bibliographies Anikó Dudás, Ph. D Hungary Bibliography in the Digital Age IFLA Satellite Meeting National Library of Poland, Warsaw, 9 August 2012
 Presentation Outline 1. 2. Users of NBs and their expectations: Hungarian Academic Publication and Citation Database (MTMT) Sources (respecting disc fileds of Humanities and Social Sciences) 3. Special MTMT data elements in comparison with data used in standard bib description
Presentation Outline 1. 2. Users of NBs and their expectations: Hungarian Academic Publication and Citation Database (MTMT) Sources (respecting disc fileds of Humanities and Social Sciences) 3. Special MTMT data elements in comparison with data used in standard bib description
 1. Hungarian Academic Publication and Citation Database (MTMT) l bibliographical data of researchers’, professors’ publications and citations
1. Hungarian Academic Publication and Citation Database (MTMT) l bibliographical data of researchers’, professors’ publications and citations
 Publication Based on l l l Citation Bibliographical data But the database itself is not a universal bibliograpy system Focuces particularly on • Hungarica data – restricted to the publications of contemporary, learned „Hungarus” authors • Personal and institutional research publication output • Citations should be collected as well
Publication Based on l l l Citation Bibliographical data But the database itself is not a universal bibliograpy system Focuces particularly on • Hungarica data – restricted to the publications of contemporary, learned „Hungarus” authors • Personal and institutional research publication output • Citations should be collected as well
 Some specific expectations • • up-to-date register of publications & citations data-entering is carried out by registered users (researchers) and operators authentic, verified a tool for monitoring and mapping Hungarian research publication output display options: by persons, institutions (affiliation must be attached) and so many other views serves as a basic bibliometric aid data should be re-usable in R&D information systems Bibliography Commettee is responsible for metadata improvements
Some specific expectations • • up-to-date register of publications & citations data-entering is carried out by registered users (researchers) and operators authentic, verified a tool for monitoring and mapping Hungarian research publication output display options: by persons, institutions (affiliation must be attached) and so many other views serves as a basic bibliometric aid data should be re-usable in R&D information systems Bibliography Commettee is responsible for metadata improvements
 A personal publication list
A personal publication list
 Display options
Display options
 MTMT: detailed citation list
MTMT: detailed citation list
 MTMT: some figures l l Launched in 2009 (by bringing together several STM databases) Members are: • Independent individuals • Persons affiliated with organizations: • research institutions of HAS • most outstanding research universities • other universities • colleges, hospitals • government bodies • for-profit organizations are interested as well
MTMT: some figures l l Launched in 2009 (by bringing together several STM databases) Members are: • Independent individuals • Persons affiliated with organizations: • research institutions of HAS • most outstanding research universities • other universities • colleges, hospitals • government bodies • for-profit organizations are interested as well
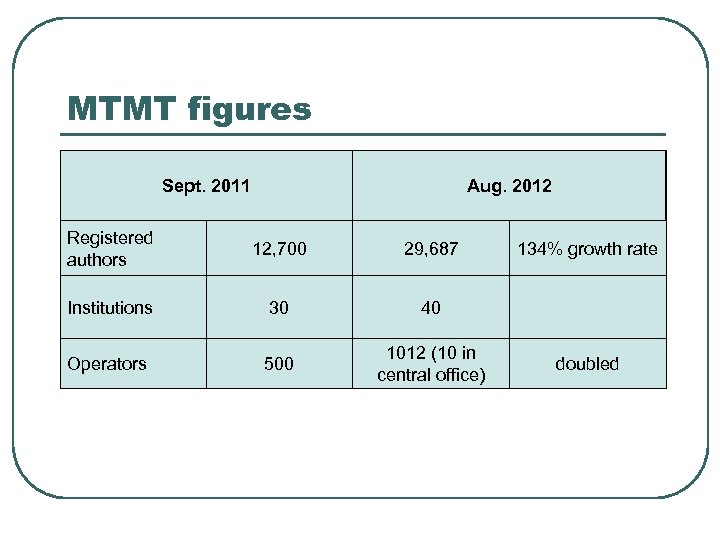 MTMT figures Sept. 2011 Aug. 2012 Registered authors 12, 700 29, 687 Institutions 30 40 Operators 500 1012 (10 in central office) 134% growth rate doubled
MTMT figures Sept. 2011 Aug. 2012 Registered authors 12, 700 29, 687 Institutions 30 40 Operators 500 1012 (10 in central office) 134% growth rate doubled
 Number of publications and citations (Aug. 2012) Number of publication records Number of citation records Articles 387, 573 Dependent citations 455, 428 Books 96, 597 Independent citations 2, 076, 772 Book chapters 111, 705 Not marked Patents 3, 170 Dissertations 5, 916 Other works 70, 497 Publications in total 833, 504 Citations in total 104, 778 2, 636978
Number of publications and citations (Aug. 2012) Number of publication records Number of citation records Articles 387, 573 Dependent citations 455, 428 Books 96, 597 Independent citations 2, 076, 772 Book chapters 111, 705 Not marked Patents 3, 170 Dissertations 5, 916 Other works 70, 497 Publications in total 833, 504 Citations in total 104, 778 2, 636978
 Growth rate: C: 40% P: 26%
Growth rate: C: 40% P: 26%
 Ratio of publication types Data are not limited solely to scholarly works and to „soft” disciplines
Ratio of publication types Data are not limited solely to scholarly works and to „soft” disciplines
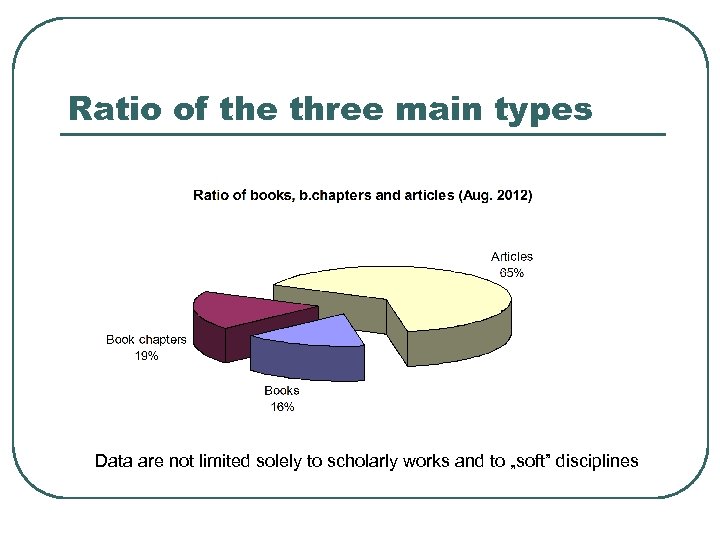 Ratio of the three main types Data are not limited solely to scholarly works and to „soft” disciplines
Ratio of the three main types Data are not limited solely to scholarly works and to „soft” disciplines
 PPCU FH – local database (2010) Data are limited to scholarly works; „soft” fields More than half appear in books
PPCU FH – local database (2010) Data are limited to scholarly works; „soft” fields More than half appear in books
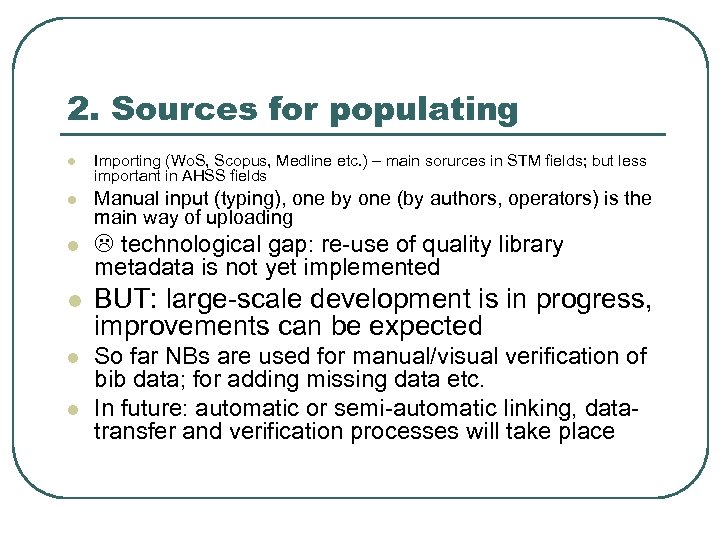 2. Sources for populating l Importing (Wo. S, Scopus, Medline etc. ) – main sorurces in STM fields; but less important in AHSS fields l Manual input (typing), one by one (by authors, operators) is the main way of uploading l technological gap: re-use of quality library metadata is not yet implemented l BUT: large-scale development is in progress, improvements can be expected l So far NBs are used for manual/visual verification of bib data; for adding missing data etc. In future: automatic or semi-automatic linking, datatransfer and verification processes will take place l
2. Sources for populating l Importing (Wo. S, Scopus, Medline etc. ) – main sorurces in STM fields; but less important in AHSS fields l Manual input (typing), one by one (by authors, operators) is the main way of uploading l technological gap: re-use of quality library metadata is not yet implemented l BUT: large-scale development is in progress, improvements can be expected l So far NBs are used for manual/visual verification of bib data; for adding missing data etc. In future: automatic or semi-automatic linking, datatransfer and verification processes will take place l
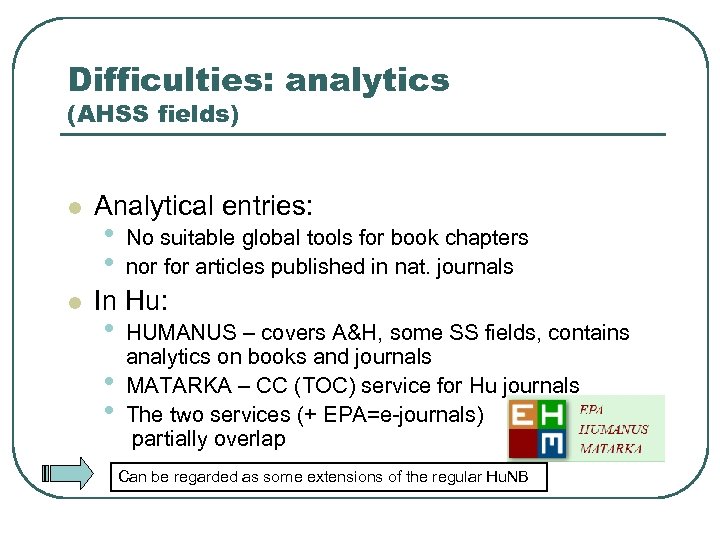 Difficulties: analytics (AHSS fields) l l Analytical entries: • • No suitable global tools for book chapters nor for articles published in nat. journals In Hu: • • • HUMANUS – covers A&H, some SS fields, contains analytics on books and journals MATARKA – CC (TOC) service for Hu journals The two services (+ EPA=e-journals) partially overlap Can be regarded as some extensions of the regular Hu. NB
Difficulties: analytics (AHSS fields) l l Analytical entries: • • No suitable global tools for book chapters nor for articles published in nat. journals In Hu: • • • HUMANUS – covers A&H, some SS fields, contains analytics on books and journals MATARKA – CC (TOC) service for Hu journals The two services (+ EPA=e-journals) partially overlap Can be regarded as some extensions of the regular Hu. NB
 Difficulties: citation level (AHSS fields) l l l Discovering, collecting and filling in citations – lies upon the shoulders of the researchers One need much time Some help: scholar. google; Google Scholar Citation Initiatives for national citation indexes (Serbia; India – restricted; HU – pilot project) Developing a useful joint service would be welcome to facilitate recording citations
Difficulties: citation level (AHSS fields) l l l Discovering, collecting and filling in citations – lies upon the shoulders of the researchers One need much time Some help: scholar. google; Google Scholar Citation Initiatives for national citation indexes (Serbia; India – restricted; HU – pilot project) Developing a useful joint service would be welcome to facilitate recording citations
 3. MTMT data elements – characteristics Name: traced in the case of a registered person; otherwise uncontrolled Name (from authority file), AAP Affiliation Taxonomies: (1) Form; (2) Genre; (3) Character by intended audience
3. MTMT data elements – characteristics Name: traced in the case of a registered person; otherwise uncontrolled Name (from authority file), AAP Affiliation Taxonomies: (1) Form; (2) Genre; (3) Character by intended audience

 Adding authors, authorship information (in bib record) MTMT controlled name (attached from authority file) Name (whatever form) << names from external sources are coming over here Authorship portion Affiliations • Relator terms are used instead of the statement of responsibility • Number of attached authors are not limited • All authors and corporate collaborators can be listed but are not displayed in default setting
Adding authors, authorship information (in bib record) MTMT controlled name (attached from authority file) Name (whatever form) << names from external sources are coming over here Authorship portion Affiliations • Relator terms are used instead of the statement of responsibility • Number of attached authors are not limited • All authors and corporate collaborators can be listed but are not displayed in default setting
 Affiliation On personal level On publication level (two inst. are sharing the same publ. )
Affiliation On personal level On publication level (two inst. are sharing the same publ. )
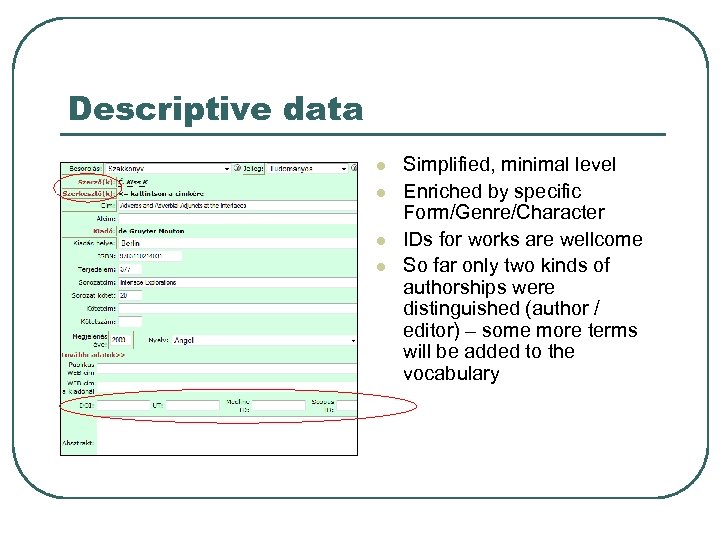 Descriptive data l l Simplified, minimal level Enriched by specific Form/Genre/Character IDs for works are wellcome So far only two kinds of authorships were distinguished (author / editor) – some more terms will be added to the vocabulary
Descriptive data l l Simplified, minimal level Enriched by specific Form/Genre/Character IDs for works are wellcome So far only two kinds of authorships were distinguished (author / editor) – some more terms will be added to the vocabulary
 Types of authorships Authorships English Hungarian Author Szerző Editor Relator terms Szerkesztő Other authorships Editor of critical edition Kritikai kiadás készítője Editor of primary source edition Forráskiadás készítője Text editor Szöveggondozó Translator Fordító Other contributor roles Egyéb közreműködő Subtypes of ‘Other contributor roles' Compiler Válogatta Compiler of the bibliography A bibliográfiát gondozta Collector Gyűjtötte Collaborator in editing Sajtó alá rendezte Interviewee Az interjút adta
Types of authorships Authorships English Hungarian Author Szerző Editor Relator terms Szerkesztő Other authorships Editor of critical edition Kritikai kiadás készítője Editor of primary source edition Forráskiadás készítője Text editor Szöveggondozó Translator Fordító Other contributor roles Egyéb közreműködő Subtypes of ‘Other contributor roles' Compiler Válogatta Compiler of the bibliography A bibliográfiát gondozta Collector Gyűjtötte Collaborator in editing Sajtó alá rendezte Interviewee Az interjút adta
 Character of the work (according to the intended audience) Academic Of public interest Popular science Educational
Character of the work (according to the intended audience) Academic Of public interest Popular science Educational
 Form/genre controlled vocabulary l Used to distinguish and classify research publication products l Bibliography Committee has finished recently the harmonization, simplification of descriptors Term list includes descriptors for: l l • • Published academic works Art works (artistic, technical) Patents (Protection forms) Dissertations Implementation of the revised set of descriptors is expected in autumn
Form/genre controlled vocabulary l Used to distinguish and classify research publication products l Bibliography Committee has finished recently the harmonization, simplification of descriptors Term list includes descriptors for: l l • • Published academic works Art works (artistic, technical) Patents (Protection forms) Dissertations Implementation of the revised set of descriptors is expected in autumn
 Form/genre controlled vocabulary (types of publications) l l l Term list contains appr. 70 descriptors Different types might be credited or waived in evaluation processes They might be given different credit points Descriptor (English) Also includes Descriptor (Hungarian) Also includes (Hungarian) Academic writing Study, Academic paper Szaktanulmány Műelemzés Essay Esszé Foreword, Afterword Introduction, Preface Előszó, utószó Bevezetés Review Book review, Discussion note, Critical notice Recenzió/kritika Bírálat, Tanulmány-kritika, Arts criticism Art review Műkritika Edition of primary sources Text edition, Publication, translation of sources with commentary Forráskiadás Types of book chapters (a small detail) Szövegkiadás, Forrás kommentált fordítása
Form/genre controlled vocabulary (types of publications) l l l Term list contains appr. 70 descriptors Different types might be credited or waived in evaluation processes They might be given different credit points Descriptor (English) Also includes Descriptor (Hungarian) Also includes (Hungarian) Academic writing Study, Academic paper Szaktanulmány Műelemzés Essay Esszé Foreword, Afterword Introduction, Preface Előszó, utószó Bevezetés Review Book review, Discussion note, Critical notice Recenzió/kritika Bírálat, Tanulmány-kritika, Arts criticism Art review Műkritika Edition of primary sources Text edition, Publication, translation of sources with commentary Forráskiadás Types of book chapters (a small detail) Szövegkiadás, Forrás kommentált fordítása
 Special metadata requirements for journals So far: l Impact factors by years l Peer reviewed/not pr l These are rather standards suitable for STM fields There is a need for developing other methods for verification the real scientific/scholarly nature of a publication. Linking to NB Periodicals would be essential.
Special metadata requirements for journals So far: l Impact factors by years l Peer reviewed/not pr l These are rather standards suitable for STM fields There is a need for developing other methods for verification the real scientific/scholarly nature of a publication. Linking to NB Periodicals would be essential.
 Bibliometric implementations l l Automated counting, sorting of publications and citations Summarizing IF values Hirsch index Display options for bibliometric data are available
Bibliometric implementations l l Automated counting, sorting of publications and citations Summarizing IF values Hirsch index Display options for bibliometric data are available
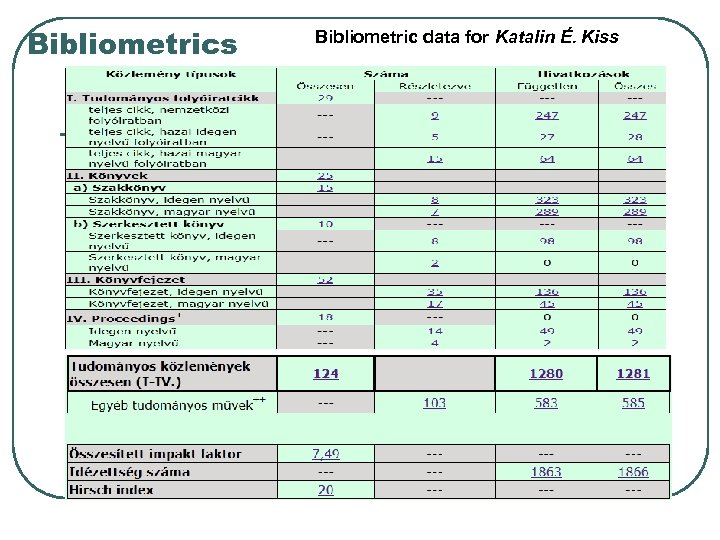 Bibliometrics Bibliometric data for Katalin É. Kiss
Bibliometrics Bibliometric data for Katalin É. Kiss
 Why to be interlinked with NBs? l Data creation and processing: re-using qualitative processing and authentic data from NBs l Analytical entries (tables of contents) can be also usable l Verification (standard, permanent links, data linking, Verification open identifiers are significant) In turn, NBs can benefit from the early stages of metadata life-cycle – data often appear first in MTMT, swift data can be re-used, completed, enriched Specific metadata added by users and/or operators of the academic bibliography can enrich the NB. l l
Why to be interlinked with NBs? l Data creation and processing: re-using qualitative processing and authentic data from NBs l Analytical entries (tables of contents) can be also usable l Verification (standard, permanent links, data linking, Verification open identifiers are significant) In turn, NBs can benefit from the early stages of metadata life-cycle – data often appear first in MTMT, swift data can be re-used, completed, enriched Specific metadata added by users and/or operators of the academic bibliography can enrich the NB. l l
 Who Are the Users and What Are Their Expectations? * Aspects of Academic Bibliographies www. mtmt. hu Anikó Dudás, Ph. D Hungary Bibliography in the Digital Age IFLA Satellite Meeting National Library of Poland, Warsaw, 9 August 2012
Who Are the Users and What Are Their Expectations? * Aspects of Academic Bibliographies www. mtmt. hu Anikó Dudás, Ph. D Hungary Bibliography in the Digital Age IFLA Satellite Meeting National Library of Poland, Warsaw, 9 August 2012


