8cf0d901e1186cc3681e3d726259a8eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Which GPS Receiver Do I Need? Will you be… Mapping or Navigating?
Which GPS Receiver Do I Need? Will you be… Mapping or Navigating?
 “Mapping” is any activity or process that produces a graphical representation of a ground feature by means of a point, line or polygon. While mapping you may need to produce attribute data concerning the features that you are mapping. One resulting product from a mapping project is a GIS data layer or theme. If you would like to learn more about attribute feature data collection choose the “Mapping Features” button below, otherwise pick the “Continue” button. Continue Mapping Features
“Mapping” is any activity or process that produces a graphical representation of a ground feature by means of a point, line or polygon. While mapping you may need to produce attribute data concerning the features that you are mapping. One resulting product from a mapping project is a GIS data layer or theme. If you would like to learn more about attribute feature data collection choose the “Mapping Features” button below, otherwise pick the “Continue” button. Continue Mapping Features
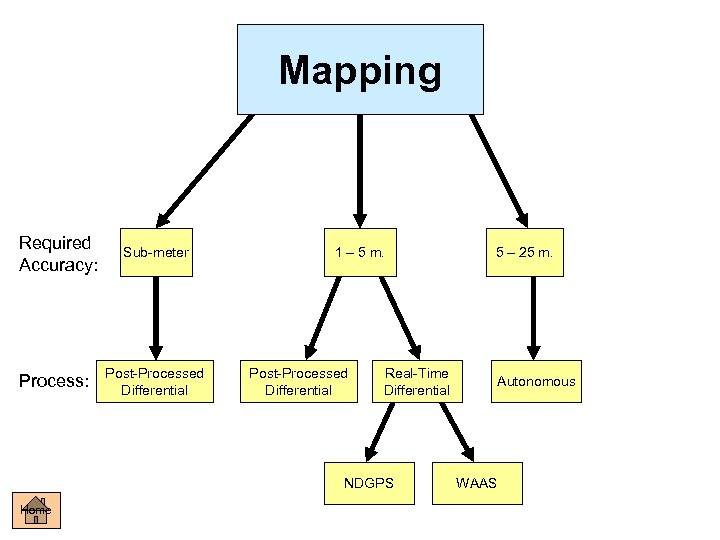 Mapping Required Accuracy: Process: Sub-meter Post-Processed Differential 1 – 5 m. Post-Processed Differential Real-Time Differential NDGPS Home 5 – 25 m. Autonomous WAAS
Mapping Required Accuracy: Process: Sub-meter Post-Processed Differential 1 – 5 m. Post-Processed Differential Real-Time Differential NDGPS Home 5 – 25 m. Autonomous WAAS
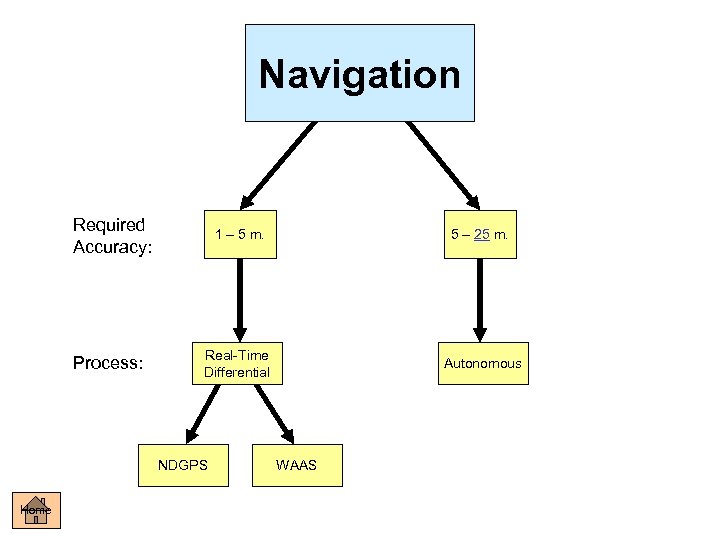 Navigation Required Accuracy: Process: 1 – 5 m. 5 – 25 m. Real-Time Differential Autonomous NDGPS Home WAAS
Navigation Required Accuracy: Process: 1 – 5 m. 5 – 25 m. Real-Time Differential Autonomous NDGPS Home WAAS
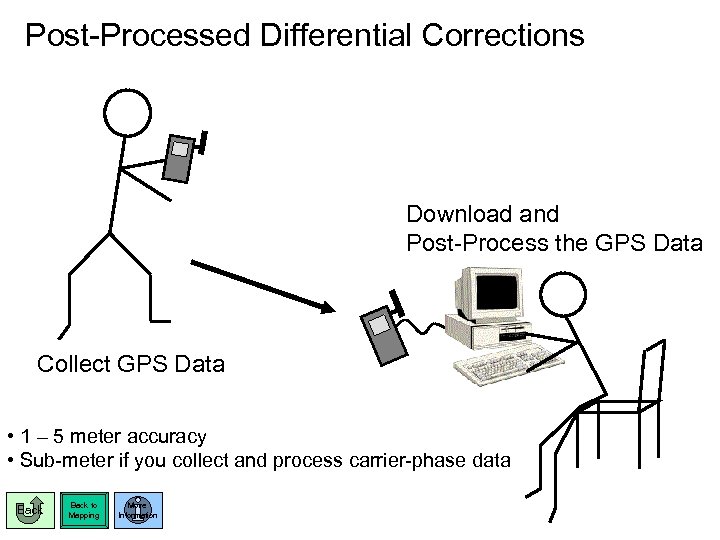 Post-Processed Differential Corrections Download and Post-Process the GPS Data Collect GPS Data • 1 – 5 meter accuracy • Sub-meter if you collect and process carrier-phase data Back to Mapping More Information
Post-Processed Differential Corrections Download and Post-Process the GPS Data Collect GPS Data • 1 – 5 meter accuracy • Sub-meter if you collect and process carrier-phase data Back to Mapping More Information
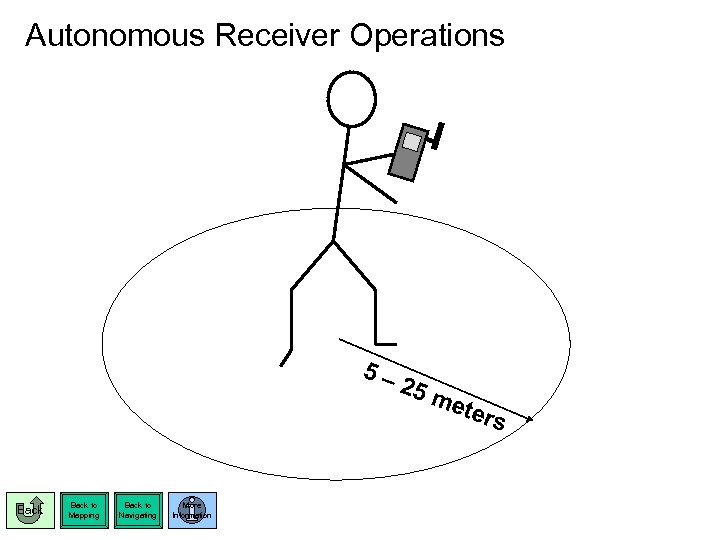 Autonomous Receiver Operations 5– Back to Mapping Back to Navigating More Information 25 m ete rs
Autonomous Receiver Operations 5– Back to Mapping Back to Navigating More Information 25 m ete rs
 Real-time Differential Corrections 1– 1– 5 m ete rs NDGPS Back to Mapping Back to Navigating More Information 5 m ete rs WAAS
Real-time Differential Corrections 1– 1– 5 m ete rs NDGPS Back to Mapping Back to Navigating More Information 5 m ete rs WAAS
 Post-Processed Differential Corrections Examples of Receivers: • Trimble XR and XRS Series (~ $10, 000) • Trimble Geo. Explorer CE XT (~ $6, 000) • Garmin Receiver with Rhino™ Data Collection and Post-processing Software (~$1500) Back to Mapping Back to Navigating
Post-Processed Differential Corrections Examples of Receivers: • Trimble XR and XRS Series (~ $10, 000) • Trimble Geo. Explorer CE XT (~ $6, 000) • Garmin Receiver with Rhino™ Data Collection and Post-processing Software (~$1500) Back to Mapping Back to Navigating
 Autonomous Receiver Operations Examples of Receivers: • Trimble XR and XRS Series (~ $10, 000) • Trimble Geo. Explorer CE XT (~ $6, 000) • CSI Mini. Max (~ $2500) • Garmins (~ $100 - $1000) • Magellans (~ $100 - $3000) Back to Mapping Back to Navigating
Autonomous Receiver Operations Examples of Receivers: • Trimble XR and XRS Series (~ $10, 000) • Trimble Geo. Explorer CE XT (~ $6, 000) • CSI Mini. Max (~ $2500) • Garmins (~ $100 - $1000) • Magellans (~ $100 - $3000) Back to Mapping Back to Navigating
 Real-time Differential Corrections Examples of Receivers: • Trimble XR and XRS Series (~ $10, 000) • Trimble Geo. Explorer CE XT (~ $6, 000) • CSI Mini. Max (~ $2500) • Garmins (~ $200 - $1500) • Magellans (~ $200 - $3000) Back to Mapping Back to Navigating
Real-time Differential Corrections Examples of Receivers: • Trimble XR and XRS Series (~ $10, 000) • Trimble Geo. Explorer CE XT (~ $6, 000) • CSI Mini. Max (~ $2500) • Garmins (~ $200 - $1500) • Magellans (~ $200 - $3000) Back to Mapping Back to Navigating
 Sub-meter Considerations: • • • Back Expensive 10 minute (or more) approximate occupation time Used primarily for point positioning
Sub-meter Considerations: • • • Back Expensive 10 minute (or more) approximate occupation time Used primarily for point positioning
 1 – 5 Meter Accuracy Considerations: • • Back Post-processed option is more expensive than real-time Real-time may not be available or practical for operations
1 – 5 Meter Accuracy Considerations: • • Back Post-processed option is more expensive than real-time Real-time may not be available or practical for operations
 Autonomous ( 6 – 25 m. ) Considerations: • • Back Can be very inexpensive Will not meet most requirements for mapping
Autonomous ( 6 – 25 m. ) Considerations: • • Back Can be very inexpensive Will not meet most requirements for mapping
 Nationwide Differential GPS Service Considerations: • • • More expensive than WAAS since an additional receiver is required Is usually (but not always) slightly more accurate than WAAS Is not line-of-sight. It can be used in the trees and in terrain that WAAS cannot Coast Guard NDGPS Website: http: //www. navcen. uscg. gov/dgps/Default. htm Back More Information
Nationwide Differential GPS Service Considerations: • • • More expensive than WAAS since an additional receiver is required Is usually (but not always) slightly more accurate than WAAS Is not line-of-sight. It can be used in the trees and in terrain that WAAS cannot Coast Guard NDGPS Website: http: //www. navcen. uscg. gov/dgps/Default. htm Back More Information
 Wide Area Augmentation System Considerations: • • • Less expensive than NDGPS because no additional receiver is needed. GPS receiver must be WAAS enabled No wires Limited to line of sight operations to geo-stationary satellite parked over equator Unreliable in many field operating environments Usually less accurate than NDGPS Department of Transportation WAAS Website: http: //gps. faa. gov/programs/waas/howitworks. htm Back More Information
Wide Area Augmentation System Considerations: • • • Less expensive than NDGPS because no additional receiver is needed. GPS receiver must be WAAS enabled No wires Limited to line of sight operations to geo-stationary satellite parked over equator Unreliable in many field operating environments Usually less accurate than NDGPS Department of Transportation WAAS Website: http: //gps. faa. gov/programs/waas/howitworks. htm Back More Information
 Mapping Features: There are basically two options for collecting attributes in the field: • Trimble equipment with Terra. Sync or Arc. PAD • Data collection software such as ESRI’s Arc. PAD on a PDA plugged into any GPS receiver. Each has advantages and disadvantages. Pick the “More Information” button for additional info. Back to Mapping More Information
Mapping Features: There are basically two options for collecting attributes in the field: • Trimble equipment with Terra. Sync or Arc. PAD • Data collection software such as ESRI’s Arc. PAD on a PDA plugged into any GPS receiver. Each has advantages and disadvantages. Pick the “More Information” button for additional info. Back to Mapping More Information
 Trimble Equipment: • Geo. Explorer XT is relatively small and self-contained • Trimble XR and XRS are highly accurate and reliable • Pathfinder Office Software is powerful and feature packed • Expensive ($6000 - $10, 000) Note: If you use Arc. PAD and want to do post-processed differential corrections then you must buy “GPS Correct” software (~$500) from Trimble. Geo. Explorer XT Back to Mapping More Information Trimble XR More Information at Trimble’s website: http: //www. trimble. com
Trimble Equipment: • Geo. Explorer XT is relatively small and self-contained • Trimble XR and XRS are highly accurate and reliable • Pathfinder Office Software is powerful and feature packed • Expensive ($6000 - $10, 000) Note: If you use Arc. PAD and want to do post-processed differential corrections then you must buy “GPS Correct” software (~$500) from Trimble. Geo. Explorer XT Back to Mapping More Information Trimble XR More Information at Trimble’s website: http: //www. trimble. com
 PDA with Data Collection Software: • Flexible solution • Wide range of related costs ($250 - $6000) depends on selected hardware and software • Can be very powerful and feature packed ERSI’s Arc. PAD Back to Mapping
PDA with Data Collection Software: • Flexible solution • Wide range of related costs ($250 - $6000) depends on selected hardware and software • Can be very powerful and feature packed ERSI’s Arc. PAD Back to Mapping


