88ff856f1c136b90b2771c240bca0095.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Where is South Africa? Who lived there? n Natives of South Africa – Zulus (black natives) n White Dutch migrants – Boers or Afrikaners (1650 s) – see map on A 12 n British colonists – (1790 s) n
Where is South Africa? Who lived there? n Natives of South Africa – Zulus (black natives) n White Dutch migrants – Boers or Afrikaners (1650 s) – see map on A 12 n British colonists – (1790 s) n
 Imperialism in South Africa n n n n Dutch settlers came to S. A. for better farmlands in the 1650 s. British colonization of SA began in 1790 s – why? 1. SA was ½ way point to get to India, a British colony 2. Diamonds & gold were discovered Boer Wars (1880 s-1910) – Boers vs. British 1887 – Zulu nation was defeated by British army after years of fighting Boers were defeated by 1910 giving British firm control over South Africa
Imperialism in South Africa n n n n Dutch settlers came to S. A. for better farmlands in the 1650 s. British colonization of SA began in 1790 s – why? 1. SA was ½ way point to get to India, a British colony 2. Diamonds & gold were discovered Boer Wars (1880 s-1910) – Boers vs. British 1887 – Zulu nation was defeated by British army after years of fighting Boers were defeated by 1910 giving British firm control over South Africa
 Apartheid n n n British ultimately gave control of SA to white Boers in 1940 s (after WWII) Boers fearing black control, instituted a system of racial segregation called Apartheid segregated nonwhite population & made non-whites second class citizens 1948 -1994
Apartheid n n n British ultimately gave control of SA to white Boers in 1940 s (after WWII) Boers fearing black control, instituted a system of racial segregation called Apartheid segregated nonwhite population & made non-whites second class citizens 1948 -1994
 Chinese Isolationism n n n For thousands of years, China had remained isolated from Europe & rest of world Mountains, deserts, and a series of Dynasties made that possible. China was another unexplored area that presented a financial opportunity for Europeans
Chinese Isolationism n n n For thousands of years, China had remained isolated from Europe & rest of world Mountains, deserts, and a series of Dynasties made that possible. China was another unexplored area that presented a financial opportunity for Europeans
 Opium Wars (1839 -1842) n Chinese purchased few British made goods n n Britain had a trade imbalance Britain wanted a positive balance of trade w/China During 1790’s British illegally smuggled the drug opium into China By 1830 s, millions of Chinese were addicted & buying British Opium
Opium Wars (1839 -1842) n Chinese purchased few British made goods n n Britain had a trade imbalance Britain wanted a positive balance of trade w/China During 1790’s British illegally smuggled the drug opium into China By 1830 s, millions of Chinese were addicted & buying British Opium
 Opium Wars Continued n 1839 Emp. Daoguang stated anyone using/importing opium would be executed. n China halted all trade w/ Britain, Britain responded w/ Gun Boat diplomacy – n Sending warships to threaten Chinese n BR easily defeated China between 1839 -41
Opium Wars Continued n 1839 Emp. Daoguang stated anyone using/importing opium would be executed. n China halted all trade w/ Britain, Britain responded w/ Gun Boat diplomacy – n Sending warships to threaten Chinese n BR easily defeated China between 1839 -41
 First Opium War: Battle at Sea British Warship Chinese Warships
First Opium War: Battle at Sea British Warship Chinese Warships
 Treaty of Nanjing (1842) n n n First of many unequal treaties China was forced to sign 1. China pays reparations ($$ to British for “damages”) 2. Hong Kong became a Brit. Colony (last until 1997!) 3. More Chinese ports opened to foreign trade 4. Brit. citizens living in China lived under Extraterritoriality laws – thus were immune from Chinese law
Treaty of Nanjing (1842) n n n First of many unequal treaties China was forced to sign 1. China pays reparations ($$ to British for “damages”) 2. Hong Kong became a Brit. Colony (last until 1997!) 3. More Chinese ports opened to foreign trade 4. Brit. citizens living in China lived under Extraterritoriality laws – thus were immune from Chinese law
 Instructional Aim: How did China become a sphere of influence for the European powers? (same as Wednesday) n n n n DO NOW: 2. 12. 2015 1. Be prepared to staple your annotations to Part II scenes – make sure your name is on both 2. Continue your notes from Wednesday Behavioral Aim: SW begin working on Imperialism handout on the causes Focus Question: Why was having a favorable balance of trade important for Britain economically? CCSS. ELA-Literacy. RH. 9 -10. 1 Assignments: February Break Essays outlines = 100 points due Wed. Feb. 25 th
Instructional Aim: How did China become a sphere of influence for the European powers? (same as Wednesday) n n n n DO NOW: 2. 12. 2015 1. Be prepared to staple your annotations to Part II scenes – make sure your name is on both 2. Continue your notes from Wednesday Behavioral Aim: SW begin working on Imperialism handout on the causes Focus Question: Why was having a favorable balance of trade important for Britain economically? CCSS. ELA-Literacy. RH. 9 -10. 1 Assignments: February Break Essays outlines = 100 points due Wed. Feb. 25 th
 Sphere of Influence n n Britain’s intervention in China led other European powers to want trade access to China The U. S. was China biggest foreign trading partner and feared China would be Imperialized & divided Instead of colonization, China would have a Open Door policy where foreign countries could trade w/ China Sphere of Influence – European countries and Japan received an area of influence over China where they dictated trade, but did not directly control China
Sphere of Influence n n Britain’s intervention in China led other European powers to want trade access to China The U. S. was China biggest foreign trading partner and feared China would be Imperialized & divided Instead of colonization, China would have a Open Door policy where foreign countries could trade w/ China Sphere of Influence – European countries and Japan received an area of influence over China where they dictated trade, but did not directly control China
 Instructional Aim: How was the Boxer Rebellion a response to foreign Imperialism? n n n DO NOW: 2. 23. 2015 1. Have out your textbook to pg. 808 -809 & open to your last days notes on Chinese Imperialism Behavioral Aim: SW begin working on Imperialism handout on the causes as well as 5 theme essay outlines Essential Question: Why was having a favorable balance of trade important for Britain economically? CCSS. ELA-Literacy. RH. 9 -10. 1 Assignments: February Break Essays outlines = 100 points due Wed. Feb. 25 th
Instructional Aim: How was the Boxer Rebellion a response to foreign Imperialism? n n n DO NOW: 2. 23. 2015 1. Have out your textbook to pg. 808 -809 & open to your last days notes on Chinese Imperialism Behavioral Aim: SW begin working on Imperialism handout on the causes as well as 5 theme essay outlines Essential Question: Why was having a favorable balance of trade important for Britain economically? CCSS. ELA-Literacy. RH. 9 -10. 1 Assignments: February Break Essays outlines = 100 points due Wed. Feb. 25 th
 Questions to be answered in Notes pg. 808 -809 1. Who are the Boxers? What were the Boxers angry with? What did they do? (808 -809) n 2. How was the Boxer rebellion an example of Chinese Nationalism? (Analysis Question) n
Questions to be answered in Notes pg. 808 -809 1. Who are the Boxers? What were the Boxers angry with? What did they do? (808 -809) n 2. How was the Boxer rebellion an example of Chinese Nationalism? (Analysis Question) n
 You can work on the following assignment … 1. Theme Essay I-Charts (which are due on Wednesday) n 2. Classwork#3 Imperialism handout n Imperialism in China – 805 -809 n Imperialism in Africa – 773 -779 n
You can work on the following assignment … 1. Theme Essay I-Charts (which are due on Wednesday) n 2. Classwork#3 Imperialism handout n Imperialism in China – 805 -809 n Imperialism in Africa – 773 -779 n
 Instructional Aim: SW assess and analyze the poem The White Man’s Burden to better understand the topic of Imperialism DO NOW: 1. 8. 2013 1. Set up your notes titled “White Man’s Burden” n Behavioral Aim: SW read and paraphrase the poem “The White Man’s Burden” n Focus Question: How does the poem symbolize themes of Imperialism n CCS: 2. 1 -2. 4 World History n Assignments: HW#8 – White Man’s Burden stanza analysis n
Instructional Aim: SW assess and analyze the poem The White Man’s Burden to better understand the topic of Imperialism DO NOW: 1. 8. 2013 1. Set up your notes titled “White Man’s Burden” n Behavioral Aim: SW read and paraphrase the poem “The White Man’s Burden” n Focus Question: How does the poem symbolize themes of Imperialism n CCS: 2. 1 -2. 4 World History n Assignments: HW#8 – White Man’s Burden stanza analysis n
 The White Man’s Burden by Rudyard Kipling n Popular poem published in 1899 at a time when the U. S was debating whether to become an imperial power after Spanish American War n n Cuba, PR, Philippines, & Guam Poem is from White American/European perspective Poem was originally written to explain why Whites needed to imperialize & why it was their duty to improve the condition of the natives. Yet, many criticized poem as an excuse to justify control of native lands through military & economic means
The White Man’s Burden by Rudyard Kipling n Popular poem published in 1899 at a time when the U. S was debating whether to become an imperial power after Spanish American War n n Cuba, PR, Philippines, & Guam Poem is from White American/European perspective Poem was originally written to explain why Whites needed to imperialize & why it was their duty to improve the condition of the natives. Yet, many criticized poem as an excuse to justify control of native lands through military & economic means
 Group Work n Work together to summarize each stanza of the poem (2 sentences) n List two lines that you felt were significant to the stanza You and your group should use dictionaries and work cooperatively to summarize all SEVEN stanzas n Stanza#1 n
Group Work n Work together to summarize each stanza of the poem (2 sentences) n List two lines that you felt were significant to the stanza You and your group should use dictionaries and work cooperatively to summarize all SEVEN stanzas n Stanza#1 n
 Example of HW#8 Stanza#1 Summary – __________ n __________________ n Two Lines - _____________ n __________________ n
Example of HW#8 Stanza#1 Summary – __________ n __________________ n Two Lines - _____________ n __________________ n
 Instructional Aim: Why was India such a valuable colony to the British colonial system? n n n n DO NOW: 2. 24. 2015 1. Set up your notes titled “Imperialism in India” 2. Open your textbook to pg. 791 Behavioral Aim: SW use their notes to complete their charts on Imperialism Essential Question: What was the purpose of restricting the Indian economy for Britain? CCSS. ELA-Literacy. RH. 9 -10. 1 Assignments: February Break Essays outlines = 100 points due Wed. Feb. 25 th
Instructional Aim: Why was India such a valuable colony to the British colonial system? n n n n DO NOW: 2. 24. 2015 1. Set up your notes titled “Imperialism in India” 2. Open your textbook to pg. 791 Behavioral Aim: SW use their notes to complete their charts on Imperialism Essential Question: What was the purpose of restricting the Indian economy for Britain? CCSS. ELA-Literacy. RH. 9 -10. 1 Assignments: February Break Essays outlines = 100 points due Wed. Feb. 25 th
 Britain’s Jewel in the Crown pg. 791 Read Pg. 791 – Britain’s “Jewel in the Crown” n 1. What made India the “Jewel in the British Crown”? In essence, why was India important to the British, especially economically? n
Britain’s Jewel in the Crown pg. 791 Read Pg. 791 – Britain’s “Jewel in the Crown” n 1. What made India the “Jewel in the British Crown”? In essence, why was India important to the British, especially economically? n
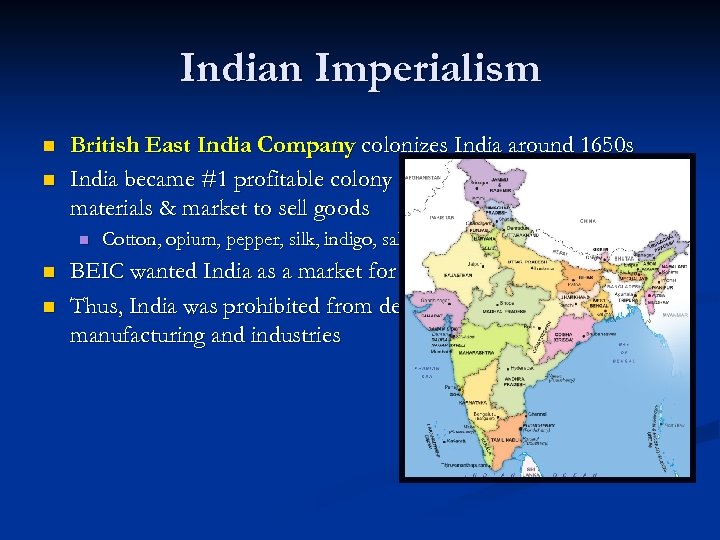 Indian Imperialism n n British East India Company colonizes India around 1650 s India became #1 profitable colony for BEIC due to its raw materials & market to sell goods n n n Cotton, opium, pepper, silk, indigo, saltpeter, coffee, & tea BEIC wanted India as a market for their finished goods Thus, India was prohibited from developing their own manufacturing and industries
Indian Imperialism n n British East India Company colonizes India around 1650 s India became #1 profitable colony for BEIC due to its raw materials & market to sell goods n n n Cotton, opium, pepper, silk, indigo, saltpeter, coffee, & tea BEIC wanted India as a market for their finished goods Thus, India was prohibited from developing their own manufacturing and industries
 Egypt’s Suez Canal n n Why would Britain want control of the Canal? How would this benefit them?
Egypt’s Suez Canal n n Why would Britain want control of the Canal? How would this benefit them?
 Sepoy Rebellion (1857) n n n Sepoys were Indian soldiers in British army Many were angry with terms of service & pay ***Many Hindus & Muslim refused to use gun cartridges because they were greased w/ pork & beef fat
Sepoy Rebellion (1857) n n n Sepoys were Indian soldiers in British army Many were angry with terms of service & pay ***Many Hindus & Muslim refused to use gun cartridges because they were greased w/ pork & beef fat
 Sepoy Rebellion - 1857 n n Rebellion breaks out when Sepoys were arrested for not accepting gun cartridges However, Indians were divided over their loyalties to the British Rebellion was put down & British took control of India by 1858 Indian nationalism grew & a desire for independence!
Sepoy Rebellion - 1857 n n Rebellion breaks out when Sepoys were arrested for not accepting gun cartridges However, Indians were divided over their loyalties to the British Rebellion was put down & British took control of India by 1858 Indian nationalism grew & a desire for independence!
 Group work Pg. 792 Pros & Cons of British rule in India n Positives n Negatives
Group work Pg. 792 Pros & Cons of British rule in India n Positives n Negatives
 British in India n n n Pro’s of British Rule Laid Democratic foundations Created civil service that hired Indians based on merit, not Caste Built infrastructure – roads, bridges, RRs, telegraph lines. Also built colleges and schools Con’s of British Rule Didn’t let Indians develop own Economy n n n Mercantilist exploitation prevented Indian manufacturing to develop Indians forced to buy British goods and supply raw materials Caste System persisted culturally
British in India n n n Pro’s of British Rule Laid Democratic foundations Created civil service that hired Indians based on merit, not Caste Built infrastructure – roads, bridges, RRs, telegraph lines. Also built colleges and schools Con’s of British Rule Didn’t let Indians develop own Economy n n n Mercantilist exploitation prevented Indian manufacturing to develop Indians forced to buy British goods and supply raw materials Caste System persisted culturally
 February Break Assignment (100 points) n n Full Introduction For each your body paragraph outlines: of n n Full Topic Sentence Bullet point 6 -8 points you will be making n n Details/Examples/Facts Include a full concluding sentence Provide a Conclusion Must be at least ONE page FRONT & BACK to bottom
February Break Assignment (100 points) n n Full Introduction For each your body paragraph outlines: of n n Full Topic Sentence Bullet point 6 -8 points you will be making n n Details/Examples/Facts Include a full concluding sentence Provide a Conclusion Must be at least ONE page FRONT & BACK to bottom
 Pages in the textbook Britain & India – 791 -795 n Imperialism in China – 805 -809 n Imperialism in Africa – 773 -779 n Japan – 810 -813 n
Pages in the textbook Britain & India – 791 -795 n Imperialism in China – 805 -809 n Imperialism in Africa – 773 -779 n Japan – 810 -813 n
 Model for your intro 1. BPS – state theme of the essay and how it has occurred in history n 2. Narrow to your topics – state your topics that relate to theme n 3. Direction (thesis) – look at the last trigger word in the task and make a statement based on it. n n Ex. Assess the long term impact of this imperialist movement
Model for your intro 1. BPS – state theme of the essay and how it has occurred in history n 2. Narrow to your topics – state your topics that relate to theme n 3. Direction (thesis) – look at the last trigger word in the task and make a statement based on it. n n Ex. Assess the long term impact of this imperialist movement
 Model for each essay outline n n Introduction – written in full (follow 3 step format) BP 1 - topic ONE (topic sentence) n n BP 2 - topic TWO (topic sentence) n n Topic sentence 6 -8 bullet points Concluding sentence Topic sentence 6 -8 Bullet points Concluding sentence Conclusion – written in full – restate thesis argument about your topics
Model for each essay outline n n Introduction – written in full (follow 3 step format) BP 1 - topic ONE (topic sentence) n n BP 2 - topic TWO (topic sentence) n n Topic sentence 6 -8 bullet points Concluding sentence Topic sentence 6 -8 Bullet points Concluding sentence Conclusion – written in full – restate thesis argument about your topics
 Instructional Aim: How and why did Japan become an imperial power? n n n n DO NOW: 2. 14. 2014 1. Be prepared to hand in HW#2 (if you were absent Thurs) 2. Set up your notes titled “Imperialism in Japan” Behavioral Aim: SW analyze a map an answer questions on why Japan became an imperial power Focus Question: How did Japan’s geography play a role in it becoming an imperial power? CCS: 2. 1 -2. 4 World History Assignments: February break – Essay outline due Tues. 2/25
Instructional Aim: How and why did Japan become an imperial power? n n n n DO NOW: 2. 14. 2014 1. Be prepared to hand in HW#2 (if you were absent Thurs) 2. Set up your notes titled “Imperialism in Japan” Behavioral Aim: SW analyze a map an answer questions on why Japan became an imperial power Focus Question: How did Japan’s geography play a role in it becoming an imperial power? CCS: 2. 1 -2. 4 World History Assignments: February break – Essay outline due Tues. 2/25
 Japanese Imperialism n n n Like China, Japan had isolated itself since the 1600 s & had largely refused to participate in trade with outside world By 1850, Japan was unindustrialized & largely rural 1854 – U. S. sent Commodore Matthew Perry to force open trade with Japanese Shogun signed the Treaty of Kanagawa signed (1854) Treaty opened several port cities to trade Other European powers signed similar treaties
Japanese Imperialism n n n Like China, Japan had isolated itself since the 1600 s & had largely refused to participate in trade with outside world By 1850, Japan was unindustrialized & largely rural 1854 – U. S. sent Commodore Matthew Perry to force open trade with Japanese Shogun signed the Treaty of Kanagawa signed (1854) Treaty opened several port cities to trade Other European powers signed similar treaties
 Modernization of Japan n n Many Japanese were angry with foreign treaties 1867 – Tokogawa Shogunate ends it reign Japanese Emperor Mutsuhito took control of country & began process to modernize & industrialize Musuhito took name Meiji Emperor Mutsuhito later Meiji
Modernization of Japan n n Many Japanese were angry with foreign treaties 1867 – Tokogawa Shogunate ends it reign Japanese Emperor Mutsuhito took control of country & began process to modernize & industrialize Musuhito took name Meiji Emperor Mutsuhito later Meiji
 Meiji Restoration n n n 1867 -1912: Period under Emperor Meiji, that modernized Japan into an industrialized power Meiji sends Japanese officials to industrialized nations (GB, USA, GR) to get ideas 1. From GB – a modern navy 2. From USA – a modern public education system 3. From GR – a modern army & strong central gov’t = Mass Industrialization: Factories, 1000’s of miles of s RRs, modern military & navy, Coal use grow
Meiji Restoration n n n 1867 -1912: Period under Emperor Meiji, that modernized Japan into an industrialized power Meiji sends Japanese officials to industrialized nations (GB, USA, GR) to get ideas 1. From GB – a modern navy 2. From USA – a modern public education system 3. From GR – a modern army & strong central gov’t = Mass Industrialization: Factories, 1000’s of miles of s RRs, modern military & navy, Coal use grow
 Modernization of Japan n Japan lacked many natural resources – especially coal! Looked to colonize Korea, but China & Russia but opposed intervention Sino-Japanese War 1894 -1895 Japan defeated China for n n n Russo-Japanese War 1904 -1905 ends in Japanese victory Japan then takes Manchuria away from Russians n n Japan wins control of Korea, but angers Russia Historic victory? Japan becomes world power in Asia
Modernization of Japan n Japan lacked many natural resources – especially coal! Looked to colonize Korea, but China & Russia but opposed intervention Sino-Japanese War 1894 -1895 Japan defeated China for n n n Russo-Japanese War 1904 -1905 ends in Japanese victory Japan then takes Manchuria away from Russians n n Japan wins control of Korea, but angers Russia Historic victory? Japan becomes world power in Asia
 Instructional Aim: SW review the major concepts, terms, and themes from Imperialism n n n n DO NOW: 2. 24. 2014 1. Hand in CW#3 chart on Imperialism essay 2. Set up your notes titled “Imperialism Review” Behavioral Aim: SW review their notes from the topics on Imperialism Focus Question: How was each specific place imperialized? CCS: 2. 1 -2. 4 World History Assignments: Essay outline due Tues. 2/25 Quiz on Imperialism Tuesday
Instructional Aim: SW review the major concepts, terms, and themes from Imperialism n n n n DO NOW: 2. 24. 2014 1. Hand in CW#3 chart on Imperialism essay 2. Set up your notes titled “Imperialism Review” Behavioral Aim: SW review their notes from the topics on Imperialism Focus Question: How was each specific place imperialized? CCS: 2. 1 -2. 4 World History Assignments: Essay outline due Tues. 2/25 Quiz on Imperialism Tuesday
 Copy down these concepts/terms n n n n Berlin Conference Boer/Afrikaners & Zulus Opium Wars Balance of Trade Gun Boat Diplomacy Treaty of Nanjing Boxer Rebellion n n Suez Canal Commodore M. Perry T. of Kanagawa Meiji Restoration Sepoy Rebellion Know for your quiz
Copy down these concepts/terms n n n n Berlin Conference Boer/Afrikaners & Zulus Opium Wars Balance of Trade Gun Boat Diplomacy Treaty of Nanjing Boxer Rebellion n n Suez Canal Commodore M. Perry T. of Kanagawa Meiji Restoration Sepoy Rebellion Know for your quiz
 Review of Imperialism n n 1. Man-made waterway that connected Med. Sea to Red Sea and made travel shorter for British ships to India 2. Tell me TWO reasons Japan became an imperial power? 3. Period in Japanese history where emperor returned to power and Japan began to modernize 4. Uprising in China in 1900 where common folk attempted to siege European section of Beijing, but was crushed.
Review of Imperialism n n 1. Man-made waterway that connected Med. Sea to Red Sea and made travel shorter for British ships to India 2. Tell me TWO reasons Japan became an imperial power? 3. Period in Japanese history where emperor returned to power and Japan began to modernize 4. Uprising in China in 1900 where common folk attempted to siege European section of Beijing, but was crushed.
 Review of Imperialism n n 5. The British used this strategy to intimidate the Chinese. They sent war ships and threatened destruction of Chinese cities 6. These wars were fought over the right to open up trade in China. 7. In 1884/85 European leaders met to partition Africa into colonies and avoid war over the continent 8. This was a historic war because it was the first time a non-European power defeated a European power. It also opened up Korea & China to colonization
Review of Imperialism n n 5. The British used this strategy to intimidate the Chinese. They sent war ships and threatened destruction of Chinese cities 6. These wars were fought over the right to open up trade in China. 7. In 1884/85 European leaders met to partition Africa into colonies and avoid war over the continent 8. This was a historic war because it was the first time a non-European power defeated a European power. It also opened up Korea & China to colonization
 Oral History Project – Due Tuesday Feb. 28, 2012 n 1. Selecting your subject & typing out your 35 questions (HW#1) n n 2. Conducting your interview n n n Person should be at least 60 yrs. of age Select a place & time to interview your subject Avoid yes or no questions and use follow up questions to get more out of your subject Ask questions that your subject would be comfortable answering, be sensitive Transcript – document all answers to your questions. Must be typed 3 page Essay – see handout instructions
Oral History Project – Due Tuesday Feb. 28, 2012 n 1. Selecting your subject & typing out your 35 questions (HW#1) n n 2. Conducting your interview n n n Person should be at least 60 yrs. of age Select a place & time to interview your subject Avoid yes or no questions and use follow up questions to get more out of your subject Ask questions that your subject would be comfortable answering, be sensitive Transcript – document all answers to your questions. Must be typed 3 page Essay – see handout instructions
 Example of a Transcript Q 1: When was the first time you saw a television? n A 1: The first time I remember a TV, I think was in 1953 when I was 10 yrs old. It was a black and white box. n Q 2: What were your favorite television shows? n A 2: We watched the Jack Benny Show n
Example of a Transcript Q 1: When was the first time you saw a television? n A 1: The first time I remember a TV, I think was in 1953 when I was 10 yrs old. It was a black and white box. n Q 2: What were your favorite television shows? n A 2: We watched the Jack Benny Show n


