c9e7f91f7427f9104777b49ca5bd9816.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 • What were goals of the Treaty of Versailles? • What issues emerged as the victors dealt with nations and national groups? • What were goals of the League of Nations?
• What were goals of the Treaty of Versailles? • What issues emerged as the victors dealt with nations and national groups? • What were goals of the League of Nations?
 The Creating of “NEW EUROPE” The Treaty of Versailles
The Creating of “NEW EUROPE” The Treaty of Versailles
 Pp 657 -661 (Blue Book 526 -531) • List what the Treaty of Versailles did to Germany. Is it Fair? Which is the worst one in your opinion why? • Should the US have ratified this treaty? Why/Why not?
Pp 657 -661 (Blue Book 526 -531) • List what the Treaty of Versailles did to Germany. Is it Fair? Which is the worst one in your opinion why? • Should the US have ratified this treaty? Why/Why not?
 • How did the map of Europe change from 1914 and 1919? (p RED 644 -645 and 659) Blue book p 508/512 and 527 • What were the issues with Poland, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, Ottomans, Russia, minorities in Austria-Hungary, in Danzig, the Sudeten Germans, Armenians and Kurds
• How did the map of Europe change from 1914 and 1919? (p RED 644 -645 and 659) Blue book p 508/512 and 527 • What were the issues with Poland, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, Ottomans, Russia, minorities in Austria-Hungary, in Danzig, the Sudeten Germans, Armenians and Kurds
 • Goals of League of Nations? • How accomplish goals? • How does mandate process relate to League’s goals? • Diagram the structure of the League and its relation to the World Court
• Goals of League of Nations? • How accomplish goals? • How does mandate process relate to League’s goals? • Diagram the structure of the League and its relation to the World Court
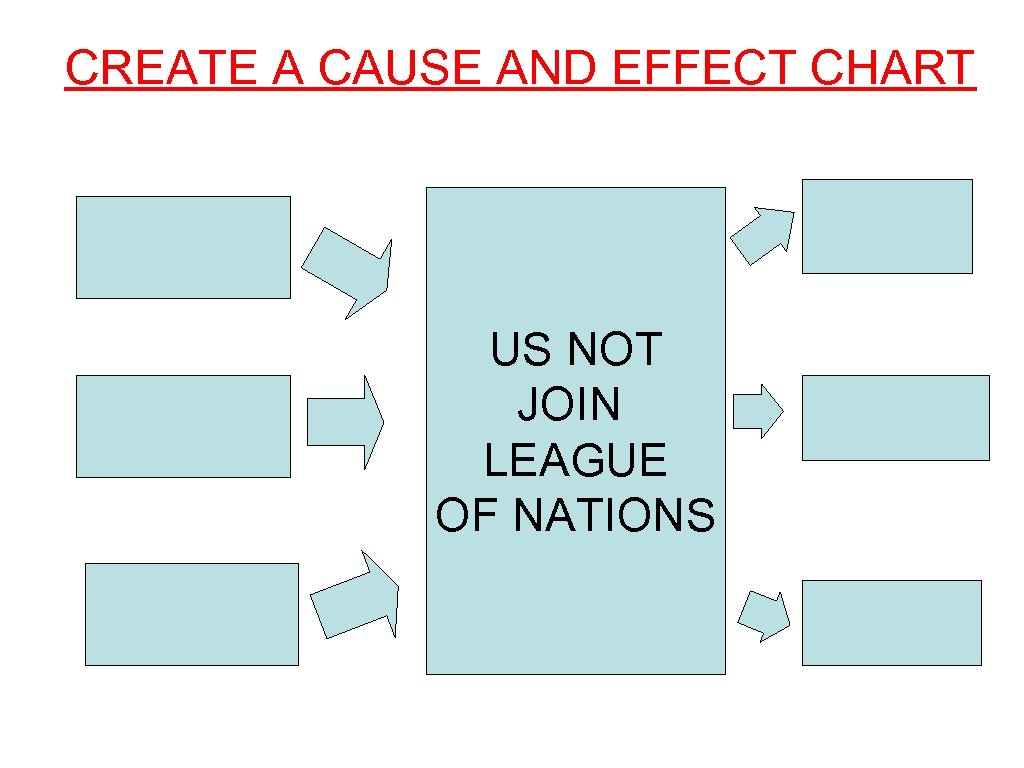 CREATE A CAUSE AND EFFECT CHART US NOT JOIN LEAGUE OF NATIONS
CREATE A CAUSE AND EFFECT CHART US NOT JOIN LEAGUE OF NATIONS
 • Using computer explore the Armenian Genocide. • • • Who is involved? Where did it take place? When did it take place? What is it? Why did it take place?
• Using computer explore the Armenian Genocide. • • • Who is involved? Where did it take place? When did it take place? What is it? Why did it take place?
 • What were goals of the Treaty of Versailles? • What issues emerged as the victors dealt with nations and national groups? • What were goals of the League of Nations?
• What were goals of the Treaty of Versailles? • What issues emerged as the victors dealt with nations and national groups? • What were goals of the League of Nations?
 Personal Response Illustrations Questions
Personal Response Illustrations Questions
 How did life change in US after WWI? What were causes of world wide Great Depression that began in 1929? What were effects of Great Depression on world? What was New Deal and how would it change government in US?
How did life change in US after WWI? What were causes of world wide Great Depression that began in 1929? What were effects of Great Depression on world? What was New Deal and how would it change government in US?
 Great Depression WWI is over US comes out of war in better shape than other allies From 1918 -1929 US goes through economic boom US New Role We helped in the war and was involved in peace process While economy of Europe was poor US was strong After WWI Europe had trouble paying of debts US not want leadership role Pulled out of League of Nations We wanted to enjoy prosperity and be left alone
Great Depression WWI is over US comes out of war in better shape than other allies From 1918 -1929 US goes through economic boom US New Role We helped in the war and was involved in peace process While economy of Europe was poor US was strong After WWI Europe had trouble paying of debts US not want leadership role Pulled out of League of Nations We wanted to enjoy prosperity and be left alone
 Roaring Twenties A fast pace life in the US Era of Pleasure Many Changes automobile industry Commercial airlines mail first people in the 1930 Telephones Movies “Talkies” Jazz Women given the right to vote Prohibition Bootleggers
Roaring Twenties A fast pace life in the US Era of Pleasure Many Changes automobile industry Commercial airlines mail first people in the 1930 Telephones Movies “Talkies” Jazz Women given the right to vote Prohibition Bootleggers
 Cracks in the perfect world 1. Wages did not keep up with labor = could not buy all the goods being produced Profits went to stockholders or were reinvested back into the company for new machines and new factories As new machines bought = less workers hired and some were let go 2. Agriculture also suffered. High demand during war. Farmers take out loans to keep up with demand. After war demand went down. Farmers overproduce to try and pay off loans. Lead to lowering farm prices. 3. Economic Nationalism = Protective tariffs to help own countries economy
Cracks in the perfect world 1. Wages did not keep up with labor = could not buy all the goods being produced Profits went to stockholders or were reinvested back into the company for new machines and new factories As new machines bought = less workers hired and some were let go 2. Agriculture also suffered. High demand during war. Farmers take out loans to keep up with demand. After war demand went down. Farmers overproduce to try and pay off loans. Lead to lowering farm prices. 3. Economic Nationalism = Protective tariffs to help own countries economy
 High American tariffs made it difficult for countries to sell goods in our country This made it hard for them to buy American goods or pay their war debts. We then lent money to countries help them buy American goods All this did was lead them to be more in debt Reparations on Germany How will Germany pay back money to England France? How will England France pay US back if they do not get paid reparations?
High American tariffs made it difficult for countries to sell goods in our country This made it hard for them to buy American goods or pay their war debts. We then lent money to countries help them buy American goods All this did was lead them to be more in debt Reparations on Germany How will Germany pay back money to England France? How will England France pay US back if they do not get paid reparations?
 Causes of the Great Depression 1. Credit which leads to On Margin 2. Overproduction Credit US buy everything on credit (consumer goods) In the 1920's people turn to market speculation = was a risky investment Buy a stock in hope to sell it for a profit In the 1920's stock prices rose at an astronomical rate. No one could see the good times ending!!!
Causes of the Great Depression 1. Credit which leads to On Margin 2. Overproduction Credit US buy everything on credit (consumer goods) In the 1920's people turn to market speculation = was a risky investment Buy a stock in hope to sell it for a profit In the 1920's stock prices rose at an astronomical rate. No one could see the good times ending!!!
 On Margin Investors borrowed money to buy stocks Only collateral used was the stock itself People would only put down 10% the value of the stock This meant that you would buy $1, 000 worth of stock with only 10% down, or $100. When the stock price went up you sell stock and pay off debt If stock price fell no way to pay it back and no way for bank to get any money back
On Margin Investors borrowed money to buy stocks Only collateral used was the stock itself People would only put down 10% the value of the stock This meant that you would buy $1, 000 worth of stock with only 10% down, or $100. When the stock price went up you sell stock and pay off debt If stock price fell no way to pay it back and no way for bank to get any money back
 Overproduction To meet the demand for goods in the 1920's factories overproduced When there was more goods than demand the prices fell. CRASH OF 1929 October 29, 1929 = Black Tuesday Panic selling of stocks 16 million shares dumped on the market in one day Prices fell People try to sell their stocks No one buys stocks One week lose 30 billion ($ 377, 587, 032, 777. 41)
Overproduction To meet the demand for goods in the 1920's factories overproduced When there was more goods than demand the prices fell. CRASH OF 1929 October 29, 1929 = Black Tuesday Panic selling of stocks 16 million shares dumped on the market in one day Prices fell People try to sell their stocks No one buys stocks One week lose 30 billion ($ 377, 587, 032, 777. 41)
 Crash of 1929 Stocks became worthless Peoples money vanished $26 million lost Banks began to call loans Loans not paid lead to banks closing Thousands of banks closed People that had money in those banks lost their money
Crash of 1929 Stocks became worthless Peoples money vanished $26 million lost Banks began to call loans Loans not paid lead to banks closing Thousands of banks closed People that had money in those banks lost their money
 Great Depression Economies around the world slowed down 30 million workers around the world were unemployed Germany stopped paying reparations Allies stopped paying the US Prices were very low but people did not have enough money to buy anything
Great Depression Economies around the world slowed down 30 million workers around the world were unemployed Germany stopped paying reparations Allies stopped paying the US Prices were very low but people did not have enough money to buy anything
 Responses to Great Depression US continued Economic Nationalism, raise tariffs even higher and cut off loans to Europe Germany and Austria tried to form a custom union but World Court banned it England tried to lower tariffs within whole empire France struggled with economy lead to three government changes in 1933 In Germany the Weimar Republic was dismantled
Responses to Great Depression US continued Economic Nationalism, raise tariffs even higher and cut off loans to Europe Germany and Austria tried to form a custom union but World Court banned it England tried to lower tariffs within whole empire France struggled with economy lead to three government changes in 1933 In Germany the Weimar Republic was dismantled
 The US was behind other countries in the area of social legislation President Herbert Hoover believed that "prosperity was around the corner"
The US was behind other countries in the area of social legislation President Herbert Hoover believed that "prosperity was around the corner"
 Franklin Delano Roosevelt 1933 elected New Deal - government gave money for food, shelter, and clothing. Also set up program of public works. Changes in the banking and Stock Market Social Security Act = unemployment and retirement instituted Minimum wage created and 40 hour work week Government pay farmers to grow certain crops to help soil TVA = Tennessee Valley Authority = series of dams to produce cheap electricity FDIC = Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
Franklin Delano Roosevelt 1933 elected New Deal - government gave money for food, shelter, and clothing. Also set up program of public works. Changes in the banking and Stock Market Social Security Act = unemployment and retirement instituted Minimum wage created and 40 hour work week Government pay farmers to grow certain crops to help soil TVA = Tennessee Valley Authority = series of dams to produce cheap electricity FDIC = Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation

 New Deal lead government of the US to be more involved in the peoples lives than in time in the history of the US The only way out of the Great Depression for the US was when the US mobilized its industry for WWII!!!!!!
New Deal lead government of the US to be more involved in the peoples lives than in time in the history of the US The only way out of the Great Depression for the US was when the US mobilized its industry for WWII!!!!!!
 The rise of Totalitarian Rulers
The rise of Totalitarian Rulers
 WHAT IS THE WORLD LIKE POST WWI? • WHAT IS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DEMOCRACY AND DICTATORSHIP? • WHAT WOULD LEAD PEOPLE TO ACCEPT TOTALITARIAN RULE?
WHAT IS THE WORLD LIKE POST WWI? • WHAT IS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DEMOCRACY AND DICTATORSHIP? • WHAT WOULD LEAD PEOPLE TO ACCEPT TOTALITARIAN RULE?
 Italy post WWI Italy after WWI = BAD depression Treaty of Versailles Rise of Benito Mussolini socialist school teacher arrested for vagrancy editor of socialist newspaper arrest for pacifist propaganda in 1911 1914 against war then changed his mind (kicked out of socialist party) founded Fasci d'Azione Rivoluzionaria (pro war group) wounded in grenade practice 1919 founded Fasci de Combattimento (political party) lead to the formation of Fascism
Italy post WWI Italy after WWI = BAD depression Treaty of Versailles Rise of Benito Mussolini socialist school teacher arrested for vagrancy editor of socialist newspaper arrest for pacifist propaganda in 1911 1914 against war then changed his mind (kicked out of socialist party) founded Fasci d'Azione Rivoluzionaria (pro war group) wounded in grenade practice 1919 founded Fasci de Combattimento (political party) lead to the formation of Fascism

 Fascism 1. Strong Leader 2. Strong nationalism 3. Hatred of democracy 4. Hatred of socialism and communism 5. Use of Symbols 6. Use of Violence 7. Use of propaganda 8. Strong armed forces 9. Control of all aspects of life and work Why people accept this?
Fascism 1. Strong Leader 2. Strong nationalism 3. Hatred of democracy 4. Hatred of socialism and communism 5. Use of Symbols 6. Use of Violence 7. Use of propaganda 8. Strong armed forces 9. Control of all aspects of life and work Why people accept this?

 Fascism compare/contrast to communism (p 679) Mussolini gains power first soldiers and upset nationalist Fascist grow with anti communism lower class promise economy improvement anti communist Blackshirts = Thugs
Fascism compare/contrast to communism (p 679) Mussolini gains power first soldiers and upset nationalist Fascist grow with anti communism lower class promise economy improvement anti communist Blackshirts = Thugs
 With collapse of world economy People believed capitialism and democracy run its course New totalitarian ruler to bring order 1921 Mussolini voted into parliament 1922 March on Rome (fear of Communist Revolution) country out of control Victor Emmanuel III made Mussolini Premier
With collapse of world economy People believed capitialism and democracy run its course New totalitarian ruler to bring order 1921 Mussolini voted into parliament 1922 March on Rome (fear of Communist Revolution) country out of control Victor Emmanuel III made Mussolini Premier
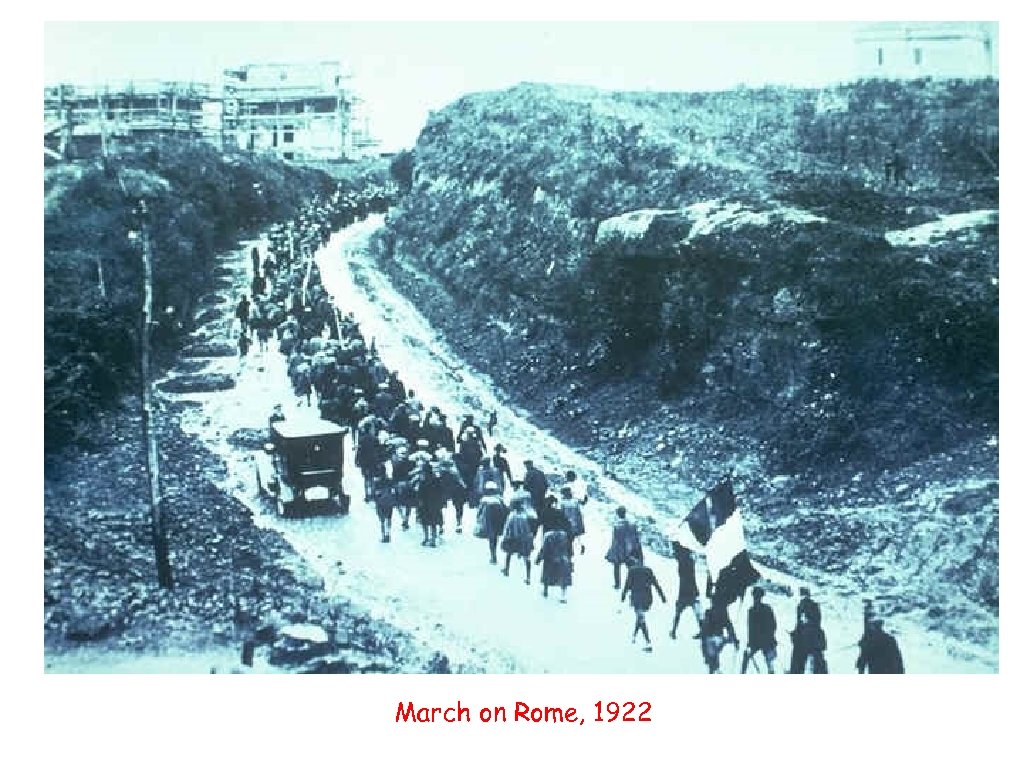 March on Rome, 1922
March on Rome, 1922
 Destroyed Democracy fascist party rises in power "IL Duce" 1925 opposition to Mussolini took over press disbanded many freedoms = speech, trial, assembly & strike secret police force = OVRA The Organizzazione per la Vigilanza e la Repressione dell'Antifascismo ("Organization for Vigilance and Repression of Anti-Fascism") head of several parts of government and Fascist party All teacher swear an oath newspaper editors chosen by Mussolini himself creation of Corporatist State = government control all professions
Destroyed Democracy fascist party rises in power "IL Duce" 1925 opposition to Mussolini took over press disbanded many freedoms = speech, trial, assembly & strike secret police force = OVRA The Organizzazione per la Vigilanza e la Repressione dell'Antifascismo ("Organization for Vigilance and Repression of Anti-Fascism") head of several parts of government and Fascist party All teacher swear an oath newspaper editors chosen by Mussolini himself creation of Corporatist State = government control all professions

 Things he did to strengthen Italy and his control 1. strengthen army and navy 2. "Win the battle of Motherhood" 3. "Railroads run on time" 4. "Mussolini is always right" By 1930's three governments in Europe Democracy, Communism and Fascism
Things he did to strengthen Italy and his control 1. strengthen army and navy 2. "Win the battle of Motherhood" 3. "Railroads run on time" 4. "Mussolini is always right" By 1930's three governments in Europe Democracy, Communism and Fascism
 GERMANY POST WWI November 1918 Weimar Republic dominated by Socialist and Jewish citizens Many Germans hate new republic signed Treaty of Versailles unemployment high = 1929 1. 3 million 1933 6 million inflation high =1918 4 German dollar to one dollar 1923 January 17, 972 to one 1923 November 4, 200, 000, 000 to one
GERMANY POST WWI November 1918 Weimar Republic dominated by Socialist and Jewish citizens Many Germans hate new republic signed Treaty of Versailles unemployment high = 1929 1. 3 million 1933 6 million inflation high =1918 4 German dollar to one dollar 1923 January 17, 972 to one 1923 November 4, 200, 000, 000 to one

 Revolts in Germany One new Political party was German Workers Party One of the first recruits was Adolf Hitler change named to National Socialist German Workers Party = Nazi Party Came up with 25 points of the party
Revolts in Germany One new Political party was German Workers Party One of the first recruits was Adolf Hitler change named to National Socialist German Workers Party = Nazi Party Came up with 25 points of the party
 Adolf Hitler Failed to enter art school Fought in WWI Blamed Jews for loss of WWI Nazi gains support = France and Belgium marched in to land to settle reparation problem 1923 lead Munich Putsch spent time in prison Mein Kampf (my Struggle) National Socialism Racsism “create living space” = Poland Russia Strong government under Hitler Got out and started politicking talked about treaty, reparations, loss of land unemployment ect Nazi gains more support
Adolf Hitler Failed to enter art school Fought in WWI Blamed Jews for loss of WWI Nazi gains support = France and Belgium marched in to land to settle reparation problem 1923 lead Munich Putsch spent time in prison Mein Kampf (my Struggle) National Socialism Racsism “create living space” = Poland Russia Strong government under Hitler Got out and started politicking talked about treaty, reparations, loss of land unemployment ect Nazi gains more support
 Made promises 1. Repeal Treaty of Versailles 2. Build armaments 3. Regain lost land 4. Rebuild German empire(3 rd Reich) 5. Protect vs communism 6. Bring back the Aryan Race to supremacy
Made promises 1. Repeal Treaty of Versailles 2. Build armaments 3. Regain lost land 4. Rebuild German empire(3 rd Reich) 5. Protect vs communism 6. Bring back the Aryan Race to supremacy
 RISE TO POWER 1930 Nazis increased in popularity won seats in Parliament = 1928 won 12 ranked 9 th 1930 won 107 ranked 2 nd 1932 won 230 ranked 1 st 1933 Hitler appointed Chancellor by President Paul Von Hindenberg Used Stormtroops(Brownshirts) to intimidate 1933 Reichstag set on fire Hitler given power to deal with "Threat" Could do things without parliaments OK 1934 Hindenberg died Hitler combined both offices Dictatorship in place one country one people one leader
RISE TO POWER 1930 Nazis increased in popularity won seats in Parliament = 1928 won 12 ranked 9 th 1930 won 107 ranked 2 nd 1932 won 230 ranked 1 st 1933 Hitler appointed Chancellor by President Paul Von Hindenberg Used Stormtroops(Brownshirts) to intimidate 1933 Reichstag set on fire Hitler given power to deal with "Threat" Could do things without parliaments OK 1934 Hindenberg died Hitler combined both offices Dictatorship in place one country one people one leader
 1934 Nuremberg rally
1934 Nuremberg rally
 Nazi Germany lowered unemployment 1933 = 6 million 1939 = 301, 900 Der Fuhrer Police state = Gestapo report on each other even children sent people away Banned opposition = one political party in Germany Killed allies = Night of the Long Knives brownshirts = SA Took over schools = teach Nazi doctrine Propaganda = Germans convinced everything good due to Hitler
Nazi Germany lowered unemployment 1933 = 6 million 1939 = 301, 900 Der Fuhrer Police state = Gestapo report on each other even children sent people away Banned opposition = one political party in Germany Killed allies = Night of the Long Knives brownshirts = SA Took over schools = teach Nazi doctrine Propaganda = Germans convinced everything good due to Hitler
 Set up concentration camps Systematic limitation of Civil Right of Jews Public humiliation Ghettos Star of David 1938 Kristallnacht =Night of Broken Glass Rearmed in private until 1935 then went public 1936 = sent troops into Rhineland Allies do nothing 1936 signed alliance with Italy (ROMEBERLIN AXIS)
Set up concentration camps Systematic limitation of Civil Right of Jews Public humiliation Ghettos Star of David 1938 Kristallnacht =Night of Broken Glass Rearmed in private until 1935 then went public 1936 = sent troops into Rhineland Allies do nothing 1936 signed alliance with Italy (ROMEBERLIN AXIS)
 you likewise in the beginning was the Word
you likewise in the beginning was the Word
 • Why did Italy and Germany embrace totalitarian rule? • Would they have done it without Mussolini and Hitler?
• Why did Italy and Germany embrace totalitarian rule? • Would they have done it without Mussolini and Hitler?
 Soviet Russian Dictatorship Civil War Policy of War Communism 1921 faced economic problems Lenin = New Economic Policy allow for private ownership of some businesses
Soviet Russian Dictatorship Civil War Policy of War Communism 1921 faced economic problems Lenin = New Economic Policy allow for private ownership of some businesses
 The NEP restored some prosperity to Russia. But to many of us this prosperity was distasteful. . . We felt ourselves sinking into the bog, paralyzed, corrupted. . . There was gambling, drunkenness, and all the filth of former times. Classes were reborn in front of our very eyes. . Serge was a Bolshevik, remembering the NEP There wasn’t any food in the country. We were down to a little bread each. Then suddenly they started the NEP. Cafes opened. Factories went back into private hands. It was Capitalism. In my eyes it was the very thing I had been fighting against. . . Most people supported Lenin, other said he was wrong, and many tore up their party membership cards. » Nikolai Izatchik, a Bolshevik, remembering the NEP Economy improved except agriculture Collective farms •
The NEP restored some prosperity to Russia. But to many of us this prosperity was distasteful. . . We felt ourselves sinking into the bog, paralyzed, corrupted. . . There was gambling, drunkenness, and all the filth of former times. Classes were reborn in front of our very eyes. . Serge was a Bolshevik, remembering the NEP There wasn’t any food in the country. We were down to a little bread each. Then suddenly they started the NEP. Cafes opened. Factories went back into private hands. It was Capitalism. In my eyes it was the very thing I had been fighting against. . . Most people supported Lenin, other said he was wrong, and many tore up their party membership cards. » Nikolai Izatchik, a Bolshevik, remembering the NEP Economy improved except agriculture Collective farms •
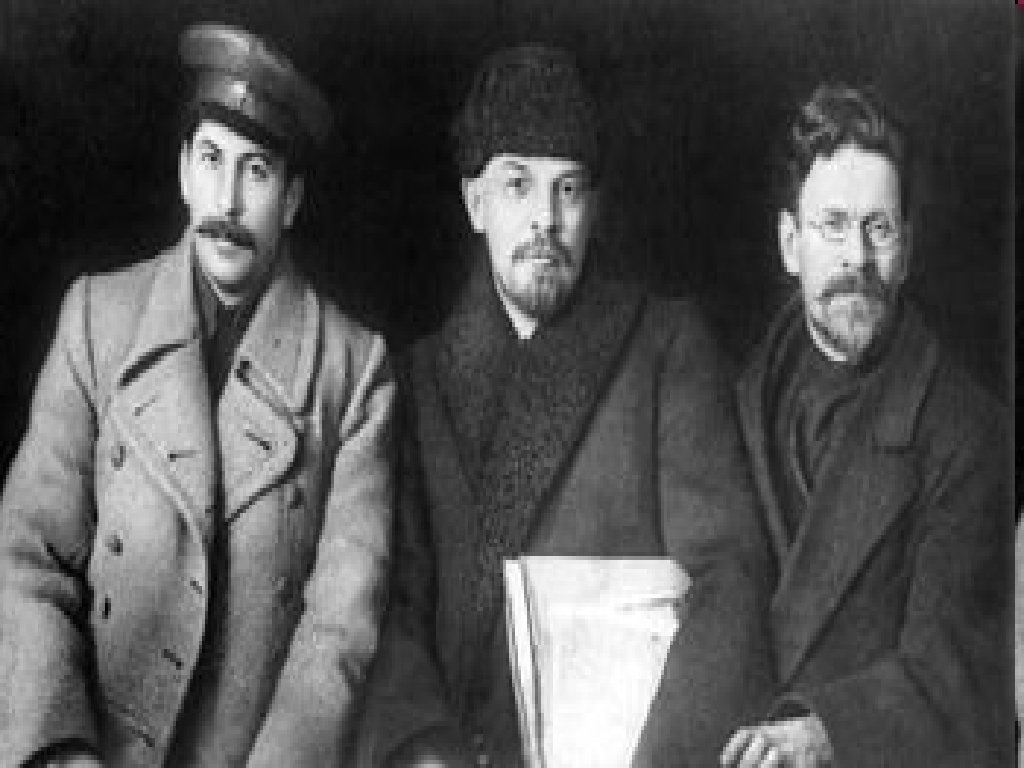


 Lenin died in 1924 I am not sure that Comrade Stalin will always use his power properly. Comrade Trotsky, on the other hand, is distinguished by his outstanding ability. Lenin's Will (1923). Competition between Joseph Stalin and Leon Trotsky Stalin a leader of party believed in socialism in one country first Trotsky founder of Red Army believed in World Wide socialist revolution
Lenin died in 1924 I am not sure that Comrade Stalin will always use his power properly. Comrade Trotsky, on the other hand, is distinguished by his outstanding ability. Lenin's Will (1923). Competition between Joseph Stalin and Leon Trotsky Stalin a leader of party believed in socialism in one country first Trotsky founder of Red Army believed in World Wide socialist revolution
 Plans of Stalin 1928 ended NEP Reinstitude Command economy "We must make good distance in ten years. Either we do it or we shall be crushed. "- Joseph Stalin Start Five year plan modern nation no consumer goods Forced collectives 2 nd Five year plans heavy industry less food and consumer goods
Plans of Stalin 1928 ended NEP Reinstitude Command economy "We must make good distance in ten years. Either we do it or we shall be crushed. "- Joseph Stalin Start Five year plan modern nation no consumer goods Forced collectives 2 nd Five year plans heavy industry less food and consumer goods

 Stalin's Russia 1. Police state = NKVD (Peoples Commissariat for International Affairs) 2. Disestablished religion = Atheism preached 3. "Social Realism" 4. Put power in the Politburo Stalin controlled Politburo 5. Purges 1. 2. 3.
Stalin's Russia 1. Police state = NKVD (Peoples Commissariat for International Affairs) 2. Disestablished religion = Atheism preached 3. "Social Realism" 4. Put power in the Politburo Stalin controlled Politburo 5. Purges 1. 2. 3.
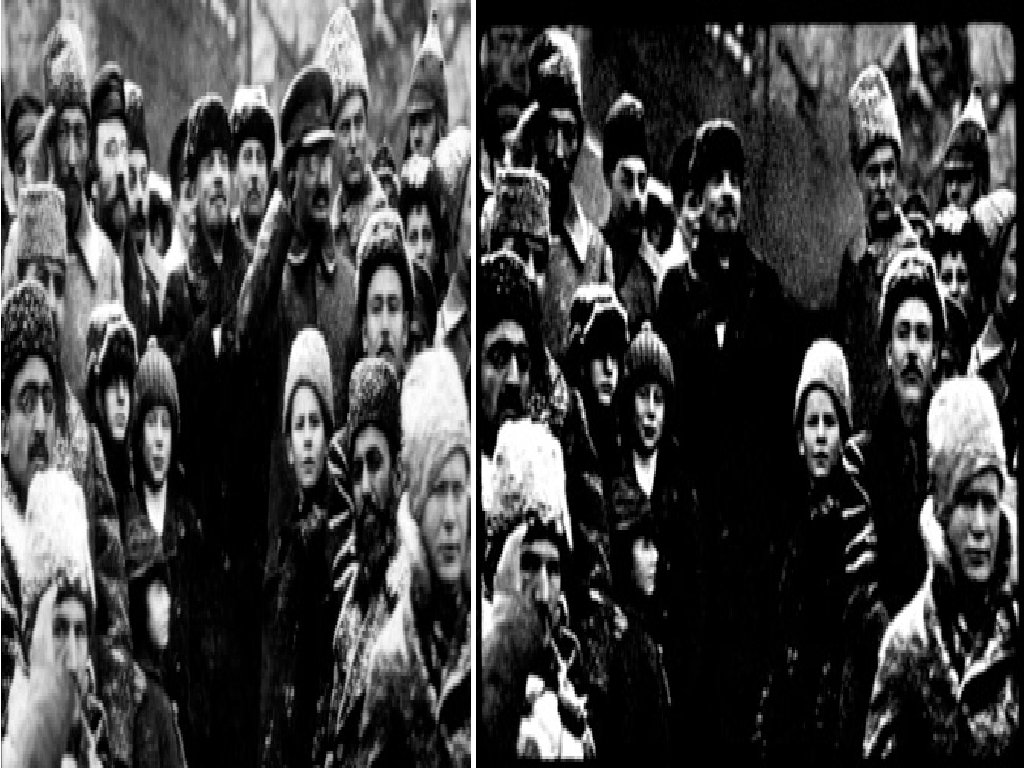
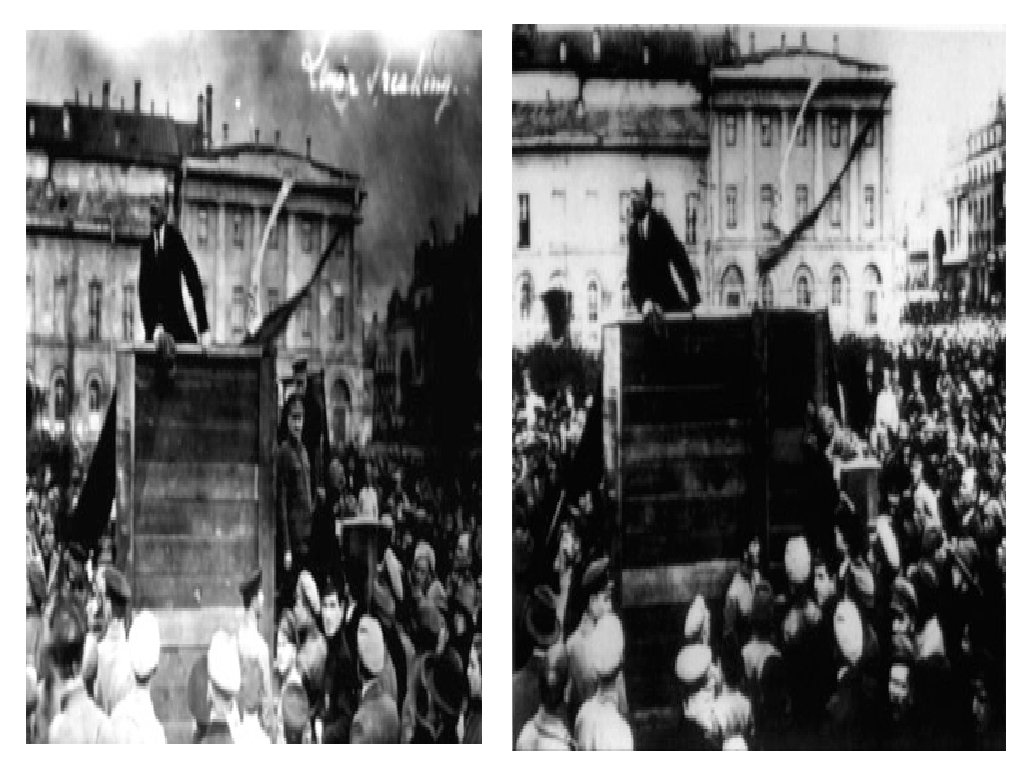
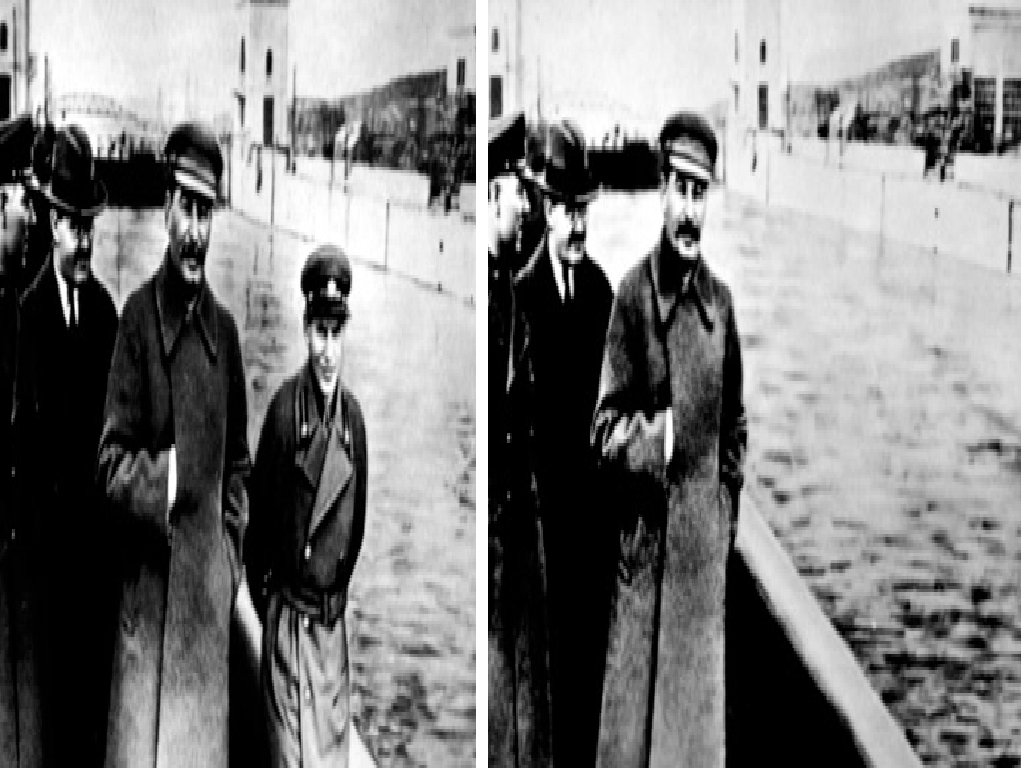




 Comintern Soviets want acceptance Soviets want revolutions around the world against capitalist Leads to fear, suspicion and hostility
Comintern Soviets want acceptance Soviets want revolutions around the world against capitalist Leads to fear, suspicion and hostility


