9d204b7891d9339966312173bd628d48.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 What we’ll learn üFeudalism: loose org. designed for protection b/c kings were too weak üAll were impacted by Feudalism during the Middle (Medieval) Ages üLords, vassals, knights, peasants, serfs Why? üMutual obligations were the basis of Feudalism üWhat would you do for someone who gave you land, protected you, or worked for you?
What we’ll learn üFeudalism: loose org. designed for protection b/c kings were too weak üAll were impacted by Feudalism during the Middle (Medieval) Ages üLords, vassals, knights, peasants, serfs Why? üMutual obligations were the basis of Feudalism üWhat would you do for someone who gave you land, protected you, or worked for you?
 Chapter 7. 2 Feudalism and the Manor Economy 1. Medieval society was a network of mutual obligations 2. Even Kings and nobles took vows of loyalty and service to others 3. This was part of a new political and economic system during the Middle Ages
Chapter 7. 2 Feudalism and the Manor Economy 1. Medieval society was a network of mutual obligations 2. Even Kings and nobles took vows of loyalty and service to others 3. This was part of a new political and economic system during the Middle Ages
 Feudalism and the Manor Economy 4. In the face of many invaders, this was a chaotic society b/c no rulers could control large areas 5. Much warfare and violence.
Feudalism and the Manor Economy 4. In the face of many invaders, this was a chaotic society b/c no rulers could control large areas 5. Much warfare and violence.
 Focus Q • What have you heard students say to respectfully correct each other? • When would this be appropriate? • Why don’t students do this very often?
Focus Q • What have you heard students say to respectfully correct each other? • When would this be appropriate? • Why don’t students do this very often?
 Focus Q • Page 219, “Feudalism Develops” • Bullet point notes • 1 sentence summary
Focus Q • Page 219, “Feudalism Develops” • Bullet point notes • 1 sentence summary
 How could peasant, the lowest of society, be the strong man of Medieval society?
How could peasant, the lowest of society, be the strong man of Medieval society?
 Focus Q Make a chart showing the responsibilities of Lords and Vassals according to 7. 2 worksheet.
Focus Q Make a chart showing the responsibilities of Lords and Vassals according to 7. 2 worksheet.
 Focus Q: Wed. , October 2 • Who is the warrior class in our society? Are they respected? How do they get their training? • Where are today’s castles? Who lives there? What do they do for a living?
Focus Q: Wed. , October 2 • Who is the warrior class in our society? Are they respected? How do they get their training? • Where are today’s castles? Who lives there? What do they do for a living?
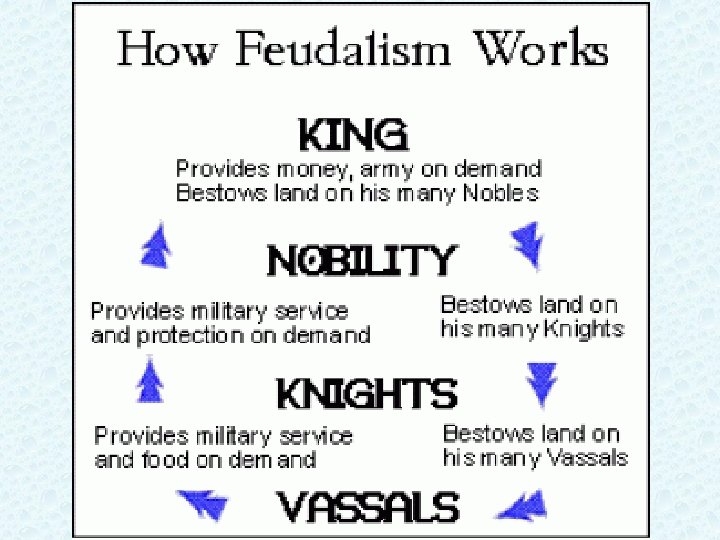
 **Feudalism** Develops 1. In the face of invasions, Kings and Emperors needed a *plan for protection*, a political and economic structure 2. Powerful local lords divided their land with lesser lords (vassals) 3. Vassals pledged loyalty and military service to the greater lord
**Feudalism** Develops 1. In the face of invasions, Kings and Emperors needed a *plan for protection*, a political and economic structure 2. Powerful local lords divided their land with lesser lords (vassals) 3. Vassals pledged loyalty and military service to the greater lord
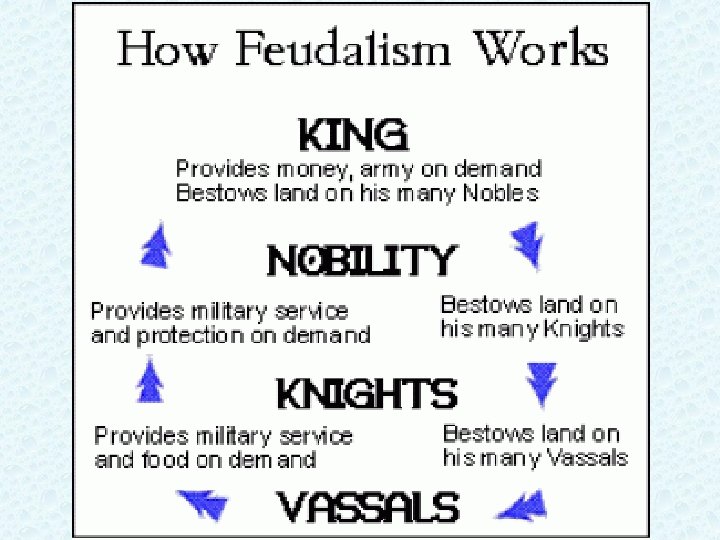
 Mutual Obligations 1. Pol/econ relationship btwn lords and vassals was based on exchange of land for military service and loyalty 2. This was very important b/c warfare was a way of life
Mutual Obligations 1. Pol/econ relationship btwn lords and vassals was based on exchange of land for military service and loyalty 2. This was very important b/c warfare was a way of life
 Lords grants vassal a *FIEF (estate, land)* –Fiefs include serfs, towns, buildings 2. Lord promises to protect his vassal 1.
Lords grants vassal a *FIEF (estate, land)* –Fiefs include serfs, towns, buildings 2. Lord promises to protect his vassal 1.
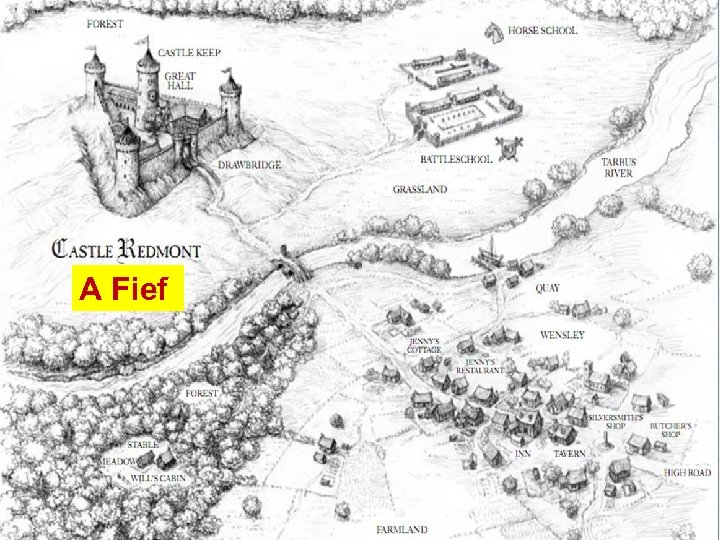 A Fief
A Fief
 *Vassals* pledges to his lord 1. **loyalty 2. 40 days of military service** 3. $ and advice This was a warrior society.
*Vassals* pledges to his lord 1. **loyalty 2. 40 days of military service** 3. $ and advice This was a warrior society.
 A Structured Society Monarchs…. powerful lords (dukes, counts) ………. . Vassals had…. vassals…. . hmmm…. 1. So sometimes a man was a lord and a vassal 2. Vassals often had fiefs (estates) from more than 1 lord 3. It got complex…. . but you usually had a liege lord to whom you owed your 1 st loyalty
A Structured Society Monarchs…. powerful lords (dukes, counts) ………. . Vassals had…. vassals…. . hmmm…. 1. So sometimes a man was a lord and a vassal 2. Vassals often had fiefs (estates) from more than 1 lord 3. It got complex…. . but you usually had a liege lord to whom you owed your 1 st loyalty
 Medieval Castles video • United Streaming • “World History: The Medieval Era” • Segments 1 -4 look good – #1 Life in a Castle – relationships
Medieval Castles video • United Streaming • “World History: The Medieval Era” • Segments 1 -4 look good – #1 Life in a Castle – relationships
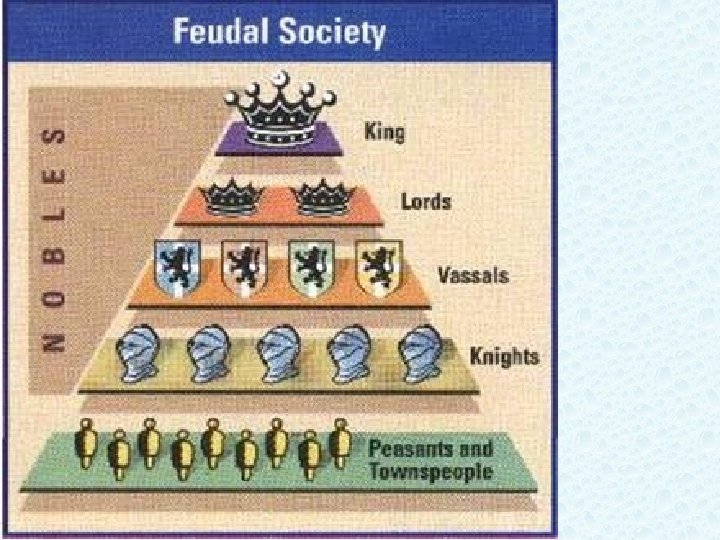
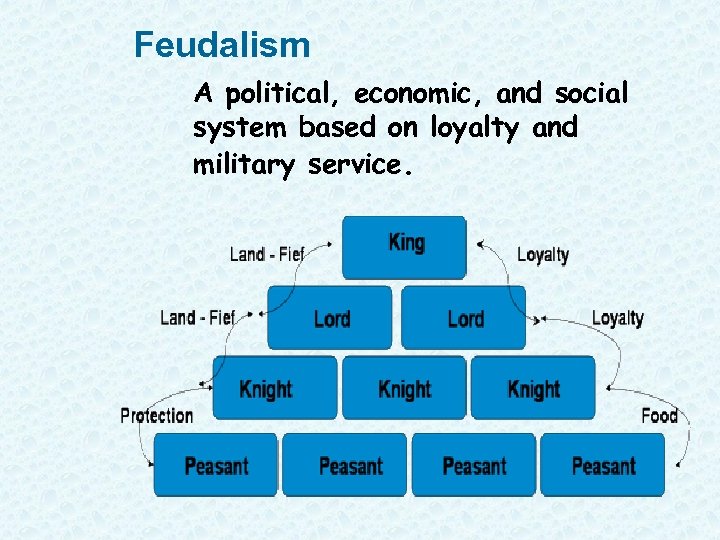 Feudalism A political, economic, and social system based on loyalty and military service.
Feudalism A political, economic, and social system based on loyalty and military service.
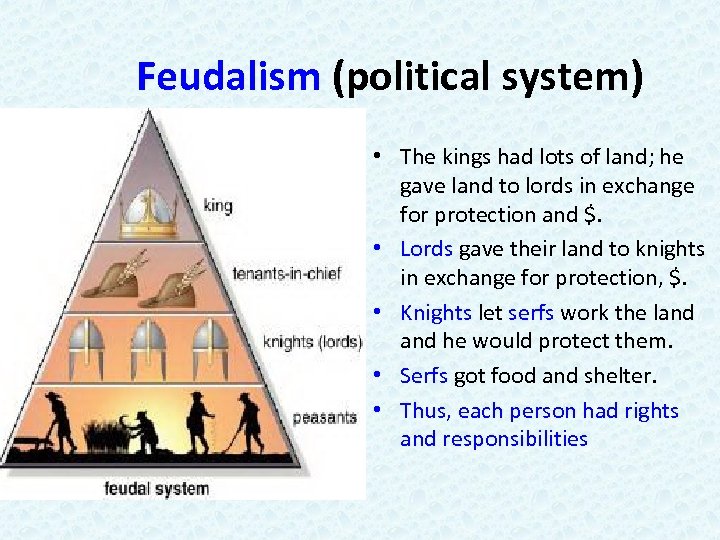 Feudalism (political system) • The kings had lots of land; he gave land to lords in exchange for protection and $. • Lords gave their land to knights in exchange for protection, $. • Knights let serfs work the land he would protect them. • Serfs got food and shelter. • Thus, each person had rights and responsibilities
Feudalism (political system) • The kings had lots of land; he gave land to lords in exchange for protection and $. • Lords gave their land to knights in exchange for protection, $. • Knights let serfs work the land he would protect them. • Serfs got food and shelter. • Thus, each person had rights and responsibilities
 Just for laughs…… • Baseball is wrong……. . man with 4 balls cannot walk. • Mr. Win says…. man who stand on toilet is high on pot
Just for laughs…… • Baseball is wrong……. . man with 4 balls cannot walk. • Mr. Win says…. man who stand on toilet is high on pot
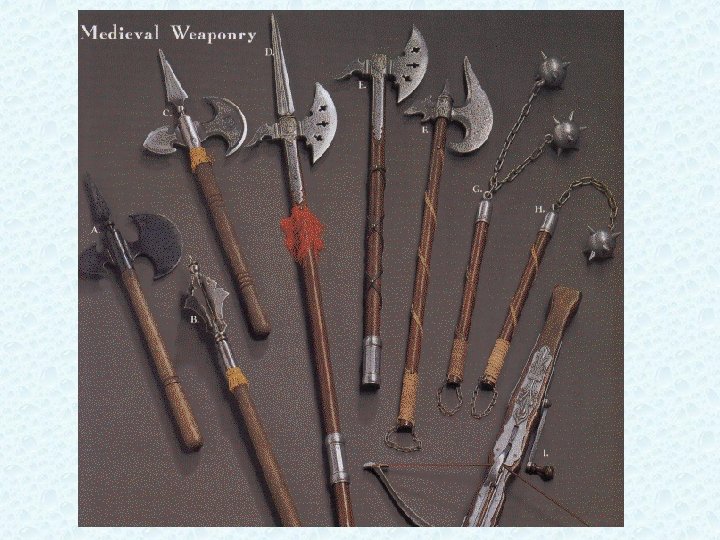
 Knights and Warfare If you were going to be a Knight, at age 7 sent away to your father’s lord for training • Ride, fight, keep armor and weapons in shape • Strict discipline • Usually fought on horseback w/swords, lances, axes, armor, shields
Knights and Warfare If you were going to be a Knight, at age 7 sent away to your father’s lord for training • Ride, fight, keep armor and weapons in shape • Strict discipline • Usually fought on horseback w/swords, lances, axes, armor, shields
 What is happening?
What is happening?
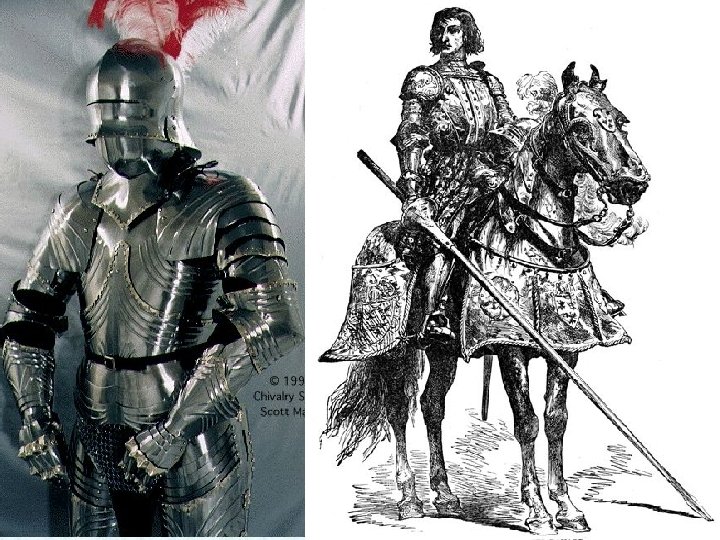
 Knights on Horseback A lance
Knights on Horseback A lance

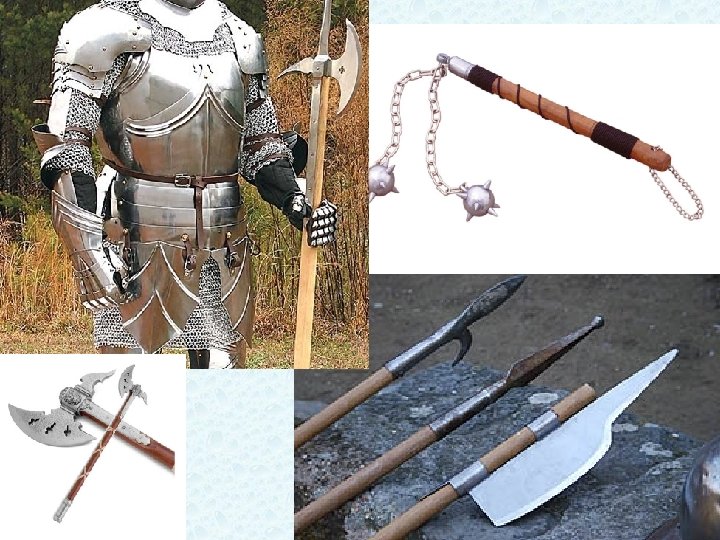
 Morning Star
Morning Star
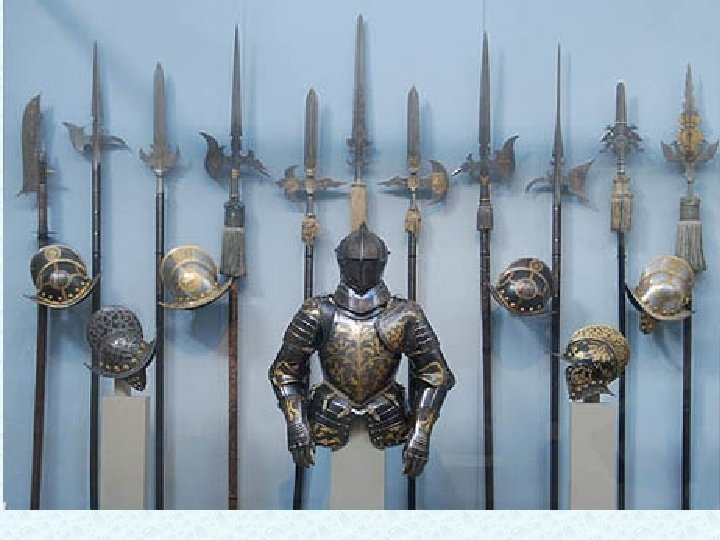



 Castles and Defense 1. Powerful lords fortified their homes more and more 2. Were homes and fortresses 3. Castles often had a strategic position at harbors, river crossings, mountain passes
Castles and Defense 1. Powerful lords fortified their homes more and more 2. Were homes and fortresses 3. Castles often had a strategic position at harbors, river crossings, mountain passes
 Castles and Defense 1. By 1100, the richest had stone castles w/high walls, towers, drawbridges and moat 2. Knights who protected it lived there 3. Peasants moved in in times of war
Castles and Defense 1. By 1100, the richest had stone castles w/high walls, towers, drawbridges and moat 2. Knights who protected it lived there 3. Peasants moved in in times of war
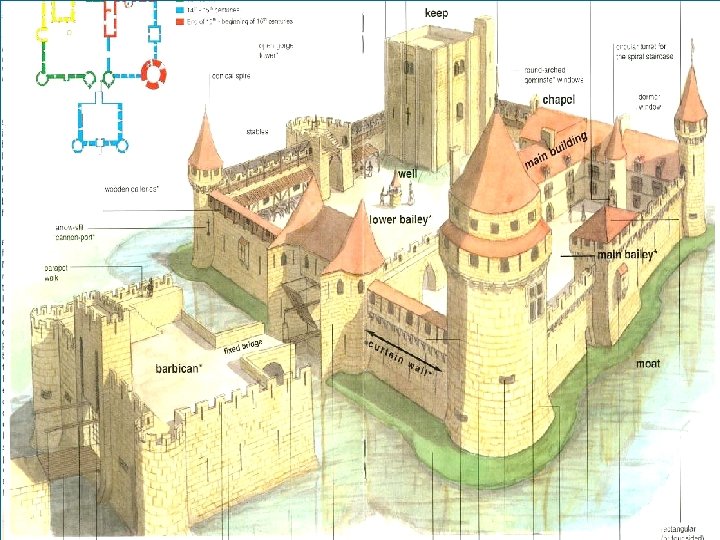 Parts of a Medieval Castle
Parts of a Medieval Castle
 Castles!
Castles!
 English Castle
English Castle
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 French Castle
French Castle
 Catapult or Trebuchet Feudal Warfare!!!! Lances Siege Tower
Catapult or Trebuchet Feudal Warfare!!!! Lances Siege Tower
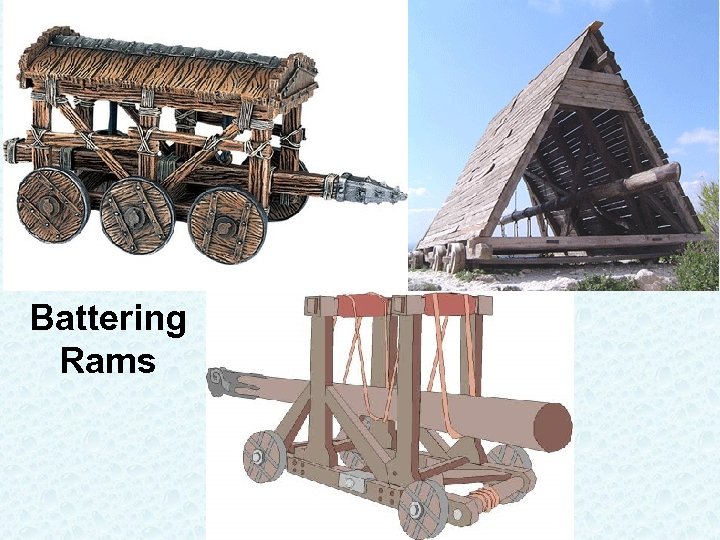 Battering Rams
Battering Rams
 Trebuchets were used to hurl all sorts of objects at the enemy. **Catapults could hurl 600 pound objects over 1000 feet**
Trebuchets were used to hurl all sorts of objects at the enemy. **Catapults could hurl 600 pound objects over 1000 feet**
 What got hurled? Stones Sharp wooden poles and darts Fire Casks of Burning Tar Burning Sand ( this became trapped inside armor ) Pots of Greek Fire Dung Dead, sometime mutilated, bodies Disease ridden bodies Body parts Dead animals Any rotting matter Quicklime
What got hurled? Stones Sharp wooden poles and darts Fire Casks of Burning Tar Burning Sand ( this became trapped inside armor ) Pots of Greek Fire Dung Dead, sometime mutilated, bodies Disease ridden bodies Body parts Dead animals Any rotting matter Quicklime
 Noblewomen: Restrictions and Power 1. When husband/father off fighting, she took over 2. Supervised vassals, managed household, did agricultural and medical tasks, might even go to war 3. 4. Rights of inheritance limited, land usually went to oldest son Widows kept their land
Noblewomen: Restrictions and Power 1. When husband/father off fighting, she took over 2. Supervised vassals, managed household, did agricultural and medical tasks, might even go to war 3. 4. Rights of inheritance limited, land usually went to oldest son Widows kept their land
 Noblewomen: Restrictions and Power 1. 2. Sent to friend/relatives for training Spin and weave, supervise servants, some learned to read and write 3. Have lots of babies, support husband
Noblewomen: Restrictions and Power 1. 2. Sent to friend/relatives for training Spin and weave, supervise servants, some learned to read and write 3. Have lots of babies, support husband
 Chivalry: A Code of Honor and Behavior
Chivalry: A Code of Honor and Behavior
 *Chivalry*: Romance and Reality 1. **Code of conduct for Knights** 2. In theory…. . Fight fair, brave, loyal, true to your word, protect the weak (peasants, women), put women on a pedestal 3. Applied to other knights, not commoners 4. Few knights lived up to these ideals 5. **troubadours: wandering musicians who sang about Knights great deeds**
*Chivalry*: Romance and Reality 1. **Code of conduct for Knights** 2. In theory…. . Fight fair, brave, loyal, true to your word, protect the weak (peasants, women), put women on a pedestal 3. Applied to other knights, not commoners 4. Few knights lived up to these ideals 5. **troubadours: wandering musicians who sang about Knights great deeds**
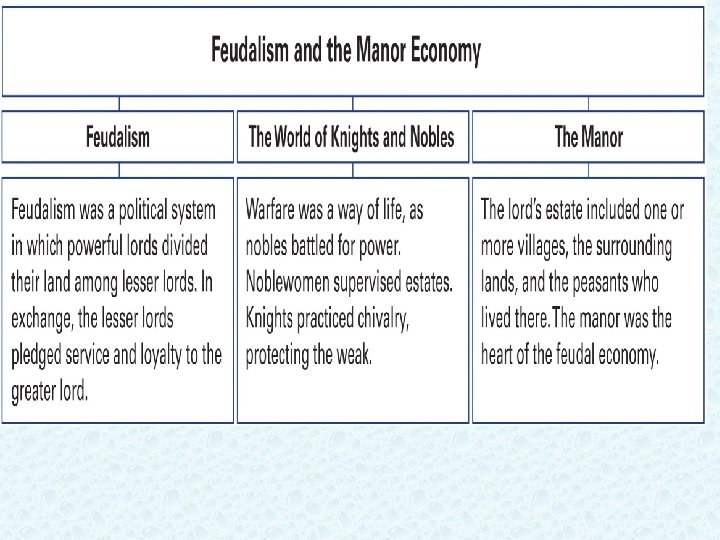 Ch 7. 2
Ch 7. 2
 Manors support Feudalism Manors: heart of feudal economy 1. Was the lord’s estate 2. Peasants were a majority of pop. , lived and worked on manor 3. Most peasants were SERFS 4. **serfs: stayed on land for life, sold with the land**, not free, couldn’t leave w/o permission, --The lowest of the low
Manors support Feudalism Manors: heart of feudal economy 1. Was the lord’s estate 2. Peasants were a majority of pop. , lived and worked on manor 3. Most peasants were SERFS 4. **serfs: stayed on land for life, sold with the land**, not free, couldn’t leave w/o permission, --The lowest of the low
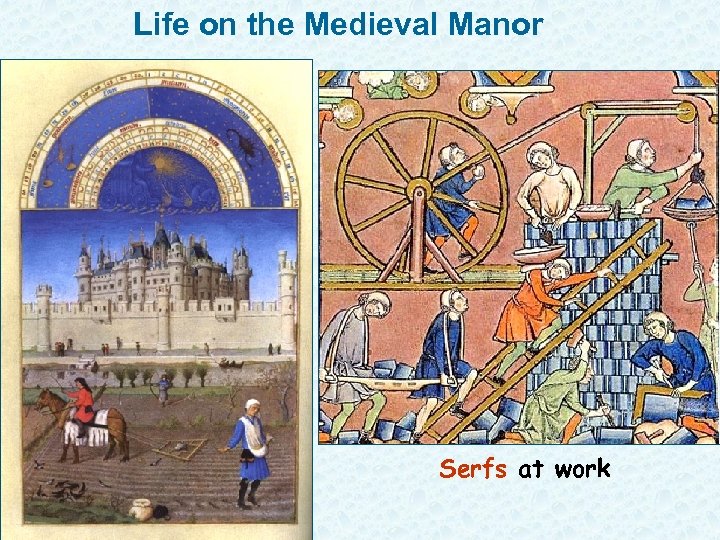 Life on the Medieval Manor Serfs at work
Life on the Medieval Manor Serfs at work
 Lords & Peasants: Mutual Obligations **Peasants—econ. backbone of society** 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Work several day/wk. on the lord’s land Repaired his roads, bridges, fences Had to ask permission to marry Paid a fee to inherit their father’s land Paid fee to use grist (grain) mill No $, paid in honey, cheese, eggs, grain, etc. --bartering
Lords & Peasants: Mutual Obligations **Peasants—econ. backbone of society** 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Work several day/wk. on the lord’s land Repaired his roads, bridges, fences Had to ask permission to marry Paid a fee to inherit their father’s land Paid fee to use grist (grain) mill No $, paid in honey, cheese, eggs, grain, etc. --bartering
 Lords & Peasants: Mutual Obligations 1. Peasants farmed some land for themselves 2. Entitled to lord’s protection 3. Couldn’t leave, couldn’t be forced off manor 4. In theory, guaranteed food, housing, land
Lords & Peasants: Mutual Obligations 1. Peasants farmed some land for themselves 2. Entitled to lord’s protection 3. Couldn’t leave, couldn’t be forced off manor 4. In theory, guaranteed food, housing, land
 Self-Sufficient World 1. Manor was self-sufficient 2. Peasants produce most things they need – Food, clothing, simple furniture and tools 3. Cottages and huts, water mill, church, lord’s manor house, fields, pastures (animals), meadows (hay) 4. Forest reserved for the lord
Self-Sufficient World 1. Manor was self-sufficient 2. Peasants produce most things they need – Food, clothing, simple furniture and tools 3. Cottages and huts, water mill, church, lord’s manor house, fields, pastures (animals), meadows (hay) 4. Forest reserved for the lord
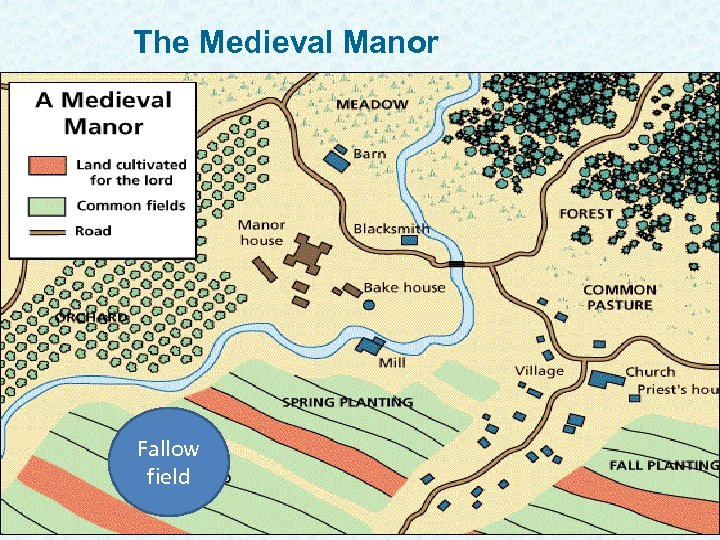 The Medieval Manor Fallow field
The Medieval Manor Fallow field
 Peasant Life…in a word…. HARSH 1. Work long hrs. —sunup to sundown 2. Hunger was common, esp. late winter—waiting for next crop 3. **Disease killed many—few lived beyond 35** 4. Ate black bread and veggies: cabbage, onions, turnips—little meat
Peasant Life…in a word…. HARSH 1. Work long hrs. —sunup to sundown 2. Hunger was common, esp. late winter—waiting for next crop 3. **Disease killed many—few lived beyond 35** 4. Ate black bread and veggies: cabbage, onions, turnips—little meat
 • • Peasant Life…in a word…. HARSH Poachers got severe punishment Family and animals lived in same hut. . aaah Celebrated marriages, births Got 1 week off at Easter, Christmas
• • Peasant Life…in a word…. HARSH Poachers got severe punishment Family and animals lived in same hut. . aaah Celebrated marriages, births Got 1 week off at Easter, Christmas
 Left side: Coat of Arms—Who am I? 1. Make a coat of arms that includes: ü 4 pictures of your values, beliefs, or principles üA caption explaining each value üA family motto: guiding principle
Left side: Coat of Arms—Who am I? 1. Make a coat of arms that includes: ü 4 pictures of your values, beliefs, or principles üA caption explaining each value üA family motto: guiding principle
 Summarize • • On focus Q page 3 things you learned I wonder…… Reminds me of……
Summarize • • On focus Q page 3 things you learned I wonder…… Reminds me of……


