2fa2e26162626cbb225115d838fb3d6e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 What was the Cold War? • 1946 -1991 (45 years). • Was brought about by competition between the U. S. & the Soviet Union for power and influence in the world. • * Consisted of political and economic conflict and military tensions throughout the globe.
What was the Cold War? • 1946 -1991 (45 years). • Was brought about by competition between the U. S. & the Soviet Union for power and influence in the world. • * Consisted of political and economic conflict and military tensions throughout the globe.
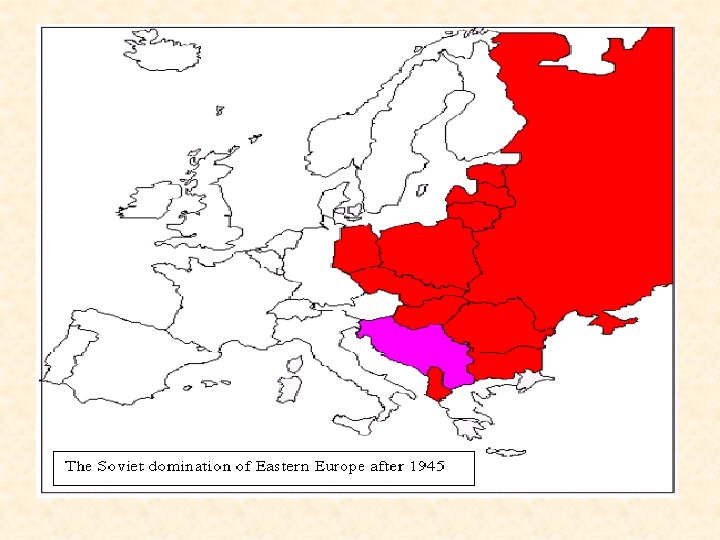
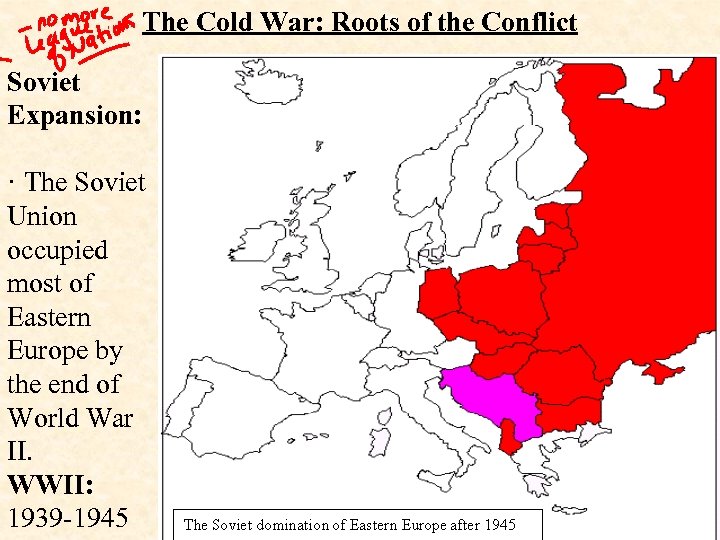 The Cold War: Roots of the Conflict Soviet Expansion: · The Soviet Union occupied most of Eastern Europe by the end of World War II. WWII: 1939 -1945
The Cold War: Roots of the Conflict Soviet Expansion: · The Soviet Union occupied most of Eastern Europe by the end of World War II. WWII: 1939 -1945
 Communism • (from Latin: communis = "common") is a socioeconomic structure and political ideology that promotes the establishment of an classless, stateless society based on common ownership and control of the means of production and property in general. • Think Marx, Lenin, Stalin, Mao, Pol-Pot
Communism • (from Latin: communis = "common") is a socioeconomic structure and political ideology that promotes the establishment of an classless, stateless society based on common ownership and control of the means of production and property in general. • Think Marx, Lenin, Stalin, Mao, Pol-Pot
 Yalta Conference 1945
Yalta Conference 1945
 Yalta Conference • FDR, Churchill & Stalin outlined the division of postwar Germany into spheres of influence and planned for the trials of war criminals.
Yalta Conference • FDR, Churchill & Stalin outlined the division of postwar Germany into spheres of influence and planned for the trials of war criminals.
 United Nations • Plans were made at the Yalta Conference for a United Nations Conference to be held in San Francisco in April 1945. • The Soviet Union, under the leadership of Joseph Stalin, agreed to participate in planning the new organizations which would be known as the United Nations or UN.
United Nations • Plans were made at the Yalta Conference for a United Nations Conference to be held in San Francisco in April 1945. • The Soviet Union, under the leadership of Joseph Stalin, agreed to participate in planning the new organizations which would be known as the United Nations or UN.
 The United Nations
The United Nations
 The United Nations: Purpose • *It was established to help nations find peaceful solutions to conflicts. • Replaced the League of Nations as an international peacekeeping organization. • It has its own military unlike the League of Nations, hence it can enforce its ideology and goals.
The United Nations: Purpose • *It was established to help nations find peaceful solutions to conflicts. • Replaced the League of Nations as an international peacekeeping organization. • It has its own military unlike the League of Nations, hence it can enforce its ideology and goals.
 The United Nations: Headquarters: NYC
The United Nations: Headquarters: NYC
 The United Nations: Organization • General Assembly – *discusses world problems – Votes on actions – Controls UN budget
The United Nations: Organization • General Assembly – *discusses world problems – Votes on actions – Controls UN budget
 United Nations: Organization • Security Council: – Investigates situations that threaten peace – Sets UN policies – Works for peaceful settlement of disputes
United Nations: Organization • Security Council: – Investigates situations that threaten peace – Sets UN policies – Works for peaceful settlement of disputes
 United Nations: Organization • Secretariat: – Coordinates work of all UN agencies – Is headed by Secretary General • International Court of Justice: • helps settle legal disputes between nations • Gives legal opinions to General Assembly
United Nations: Organization • Secretariat: – Coordinates work of all UN agencies – Is headed by Secretary General • International Court of Justice: • helps settle legal disputes between nations • Gives legal opinions to General Assembly
 UN: Organization • *Trusteeship Council: – Administers territories that are not self-governing – Helps such territories work toward independence *Economic & Social Council: -promotes human rights; cooperates with member nations to improve standard of living; works for improved economic and social conditions
UN: Organization • *Trusteeship Council: – Administers territories that are not self-governing – Helps such territories work toward independence *Economic & Social Council: -promotes human rights; cooperates with member nations to improve standard of living; works for improved economic and social conditions
 UN: Declaration of Human Rights • In 1946, President Truman appointed former first lady Eleanor Roosevelt as a UN delegate, the only woman in the American delegation. • Mrs. Roosevelt’s committee authored the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, a proclamation for human rights for all people.
UN: Declaration of Human Rights • In 1946, President Truman appointed former first lady Eleanor Roosevelt as a UN delegate, the only woman in the American delegation. • Mrs. Roosevelt’s committee authored the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, a proclamation for human rights for all people.
 Cold War Foreign Policy for U. S. : Containment • American foreign policy after WWII • The determination to prevent the spread of communism in the world. • Basically to confine communism to the area in which it already existed, the Soviet Union and the Eastern European nations.
Cold War Foreign Policy for U. S. : Containment • American foreign policy after WWII • The determination to prevent the spread of communism in the world. • Basically to confine communism to the area in which it already existed, the Soviet Union and the Eastern European nations.
 • In 1946, Winston Churchill correctly warned that the Soviets were creating an “iron curtain” in Eastern Europe. Winston Churchill giving the “Iron Curtain” address at Westminster College on March 5, 1946
• In 1946, Winston Churchill correctly warned that the Soviets were creating an “iron curtain” in Eastern Europe. Winston Churchill giving the “Iron Curtain” address at Westminster College on March 5, 1946
 Winston Churchill - “The Sinews of Peace” March 5, 1946 - Westminster College, Fulton, Missouri From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia, all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and, in many cases, increasing measure of control from Moscow…. Whatever conclusions may be drawn from these facts - and facts they are - this is certainly not the Liberated Europe we fought to build up. Nor is it one which contains the essentials of permanent peace….
Winston Churchill - “The Sinews of Peace” March 5, 1946 - Westminster College, Fulton, Missouri From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia, all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and, in many cases, increasing measure of control from Moscow…. Whatever conclusions may be drawn from these facts - and facts they are - this is certainly not the Liberated Europe we fought to build up. Nor is it one which contains the essentials of permanent peace….
 Peep under the Iron curtain March 6, 1946
Peep under the Iron curtain March 6, 1946
 Jewish children in the Warsaw Ghetto in 1942
Jewish children in the Warsaw Ghetto in 1942
 · By 1948, every Eastern European country was under communist control. American Response: · Truman Doctrine – statement of President Truman that promised military and economic support to nations threatened by communism. Specifically: • In 1947, the U. S. gave $400 million to Greece and Turkey in order to help them put down communist revolts.
· By 1948, every Eastern European country was under communist control. American Response: · Truman Doctrine – statement of President Truman that promised military and economic support to nations threatened by communism. Specifically: • In 1947, the U. S. gave $400 million to Greece and Turkey in order to help them put down communist revolts.
 Aid for Europe: · Secretary of State George Marshall toured Western Europe and witnessed widespread homelessness and famine. Children in a London suburb, waiting outside the wreckage of what was their home. September 1940.
Aid for Europe: · Secretary of State George Marshall toured Western Europe and witnessed widespread homelessness and famine. Children in a London suburb, waiting outside the wreckage of what was their home. September 1940.
 * The U. S. gave over $12 billion in aid to European countries between 1948 and 1952, helping to improve their economies and lessen the chance of communist revolutions.
* The U. S. gave over $12 billion in aid to European countries between 1948 and 1952, helping to improve their economies and lessen the chance of communist revolutions.
 Satellite Nations • A satellite nation is a nation that appears to be sovereign, but is actually under the control of another nation. • Examples would be nations such as Hungary and Poland under the USSR. On the surface, they seemed to be independent nations, but they were actually under the control of Russia as part of the USSR. (part of the “iron curtain”)
Satellite Nations • A satellite nation is a nation that appears to be sovereign, but is actually under the control of another nation. • Examples would be nations such as Hungary and Poland under the USSR. On the surface, they seemed to be independent nations, but they were actually under the control of Russia as part of the USSR. (part of the “iron curtain”)
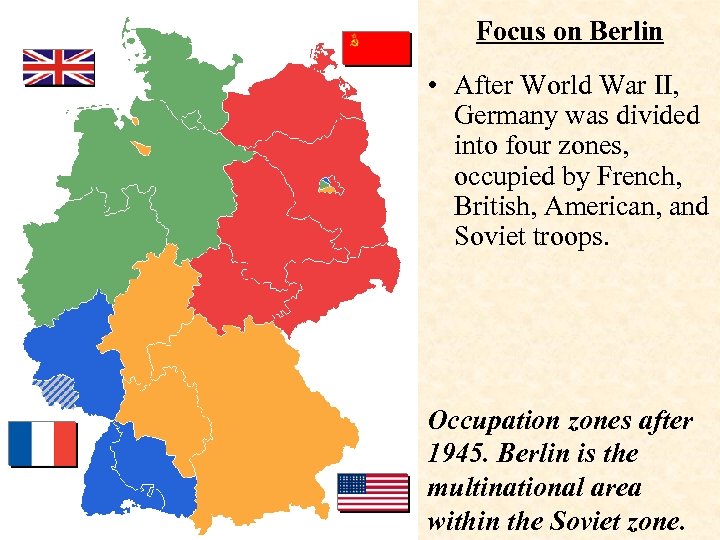 Focus on Berlin • After World War II, Germany was divided into four zones, occupied by French, British, American, and Soviet troops. Occupation zones after 1945. Berlin is the multinational area within the Soviet zone.
Focus on Berlin • After World War II, Germany was divided into four zones, occupied by French, British, American, and Soviet troops. Occupation zones after 1945. Berlin is the multinational area within the Soviet zone.
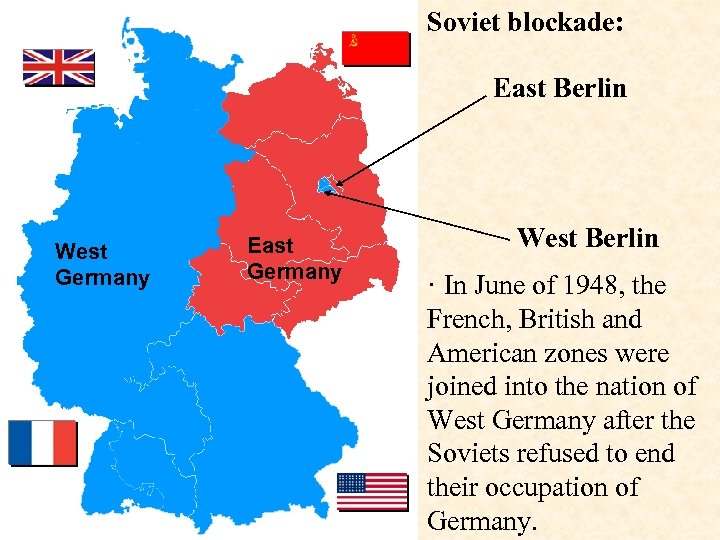 Soviet blockade: East Berlin West Germany East Germany West Berlin · In June of 1948, the French, British and American zones were joined into the nation of West Germany after the Soviets refused to end their occupation of Germany.
Soviet blockade: East Berlin West Germany East Germany West Berlin · In June of 1948, the French, British and American zones were joined into the nation of West Germany after the Soviets refused to end their occupation of Germany.
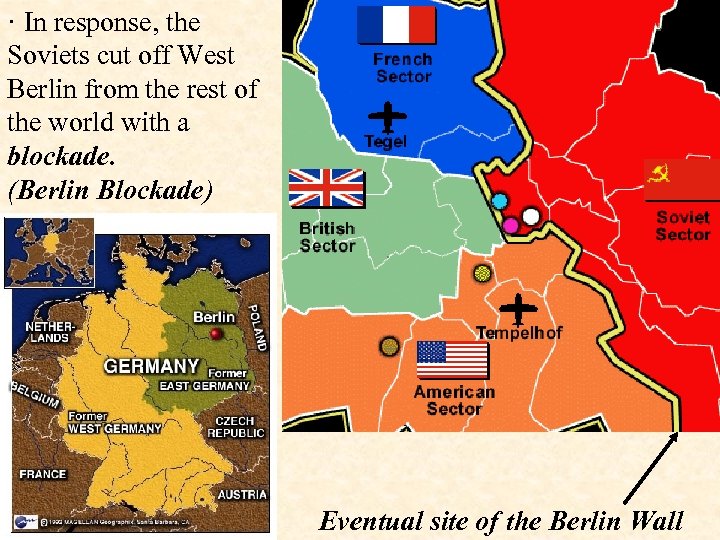 · In response, the Soviets cut off West Berlin from the rest of the world with a blockade. (Berlin Blockade) Eventual site of the Berlin Wall
· In response, the Soviets cut off West Berlin from the rest of the world with a blockade. (Berlin Blockade) Eventual site of the Berlin Wall
 A huge airlift: · President Truman decided to avoid the blockade by flying in food and other supplies to the needy people of West Berlin. · At times, over 5, 000 tons of supplies arrived daily.
A huge airlift: · President Truman decided to avoid the blockade by flying in food and other supplies to the needy people of West Berlin. · At times, over 5, 000 tons of supplies arrived daily.
 Berlin Airlift Supplies
Berlin Airlift Supplies
 Germany remains divided: · In May of 1949, Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union ended the blockade. · The Soviet zone of Germany, including East Berlin, became known as the nation of East Germany.
Germany remains divided: · In May of 1949, Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union ended the blockade. · The Soviet zone of Germany, including East Berlin, became known as the nation of East Germany.

 The Berlin Airlift • The U. S. , GB, and France would not back down. • A year later, on May 12, 1949, the Soviets recognized their defeat in the area and ended the blockade. • West Germany was given full sovereignty (freedom) East Germany remained under Russian control. • Construction of the Berlin Wall began in August of 1961.
The Berlin Airlift • The U. S. , GB, and France would not back down. • A year later, on May 12, 1949, the Soviets recognized their defeat in the area and ended the blockade. • West Germany was given full sovereignty (freedom) East Germany remained under Russian control. • Construction of the Berlin Wall began in August of 1961.
 Point Four Program • • A foreign aid program begun by President Truman for extending U. S. economic and technical assistance to less developed nations. • FYI: Truman(1945 -1953) Presidency-Dem
Point Four Program • • A foreign aid program begun by President Truman for extending U. S. economic and technical assistance to less developed nations. • FYI: Truman(1945 -1953) Presidency-Dem
 North Atlantic Treaty Organization • NATO • A military alliance of the nations of Western Europe, the U. S. & Canada
North Atlantic Treaty Organization • NATO • A military alliance of the nations of Western Europe, the U. S. & Canada
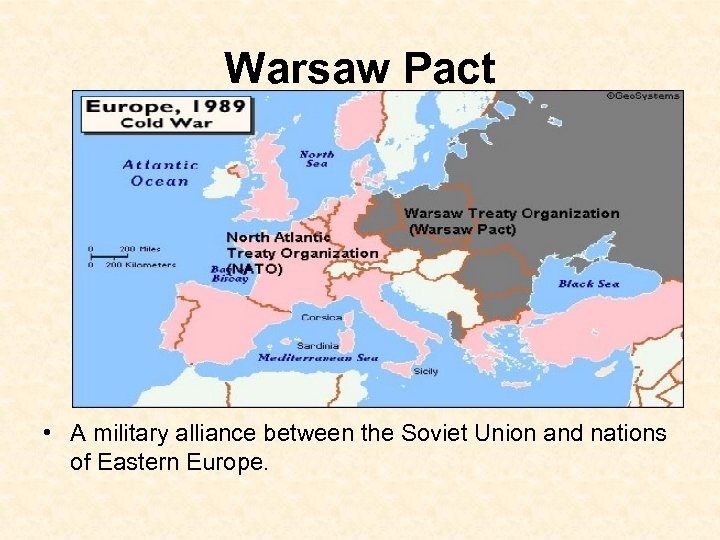 Warsaw Pact • A military alliance between the Soviet Union and nations of Eastern Europe.
Warsaw Pact • A military alliance between the Soviet Union and nations of Eastern Europe.
 European Union: EU • The economic organization of European nations designed to increase the economic power of Europe in the world economy
European Union: EU • The economic organization of European nations designed to increase the economic power of Europe in the world economy
 The Euro: A form of common currency • Approximately: • US Dollar(s) = 0. 7227 Euro(s) • 1 EUR = 1. 3837 USD • The euro was launched on 1 January 1999 as an electronic currency and became legal tender on 1 January 2002,
The Euro: A form of common currency • Approximately: • US Dollar(s) = 0. 7227 Euro(s) • 1 EUR = 1. 3837 USD • The euro was launched on 1 January 1999 as an electronic currency and became legal tender on 1 January 2002,
 The Cold War: 1945 -1990 • CONTAINMENT IN ASIA – Quick review: During WWII which Asian country was our enemy? China was an ally. • JAPAN (Remember Pearl Harbor & Japanese internment camps? Korematsu vs. U. S) After WW II: Japan becomes an ally and China becomes the enemy! (Mao Zedong-Communist Leader in China)
The Cold War: 1945 -1990 • CONTAINMENT IN ASIA – Quick review: During WWII which Asian country was our enemy? China was an ally. • JAPAN (Remember Pearl Harbor & Japanese internment camps? Korematsu vs. U. S) After WW II: Japan becomes an ally and China becomes the enemy! (Mao Zedong-Communist Leader in China)
 Containment in Asia • U. S. was alarmed by China’s communist led country • U. S. had overseen the initial rebuilding of postwar Japan and had helped put a new constitutional democracy in place. • Support for Japan was now seen as a way of offsetting communist China’s influence in Asia.
Containment in Asia • U. S. was alarmed by China’s communist led country • U. S. had overseen the initial rebuilding of postwar Japan and had helped put a new constitutional democracy in place. • Support for Japan was now seen as a way of offsetting communist China’s influence in Asia.
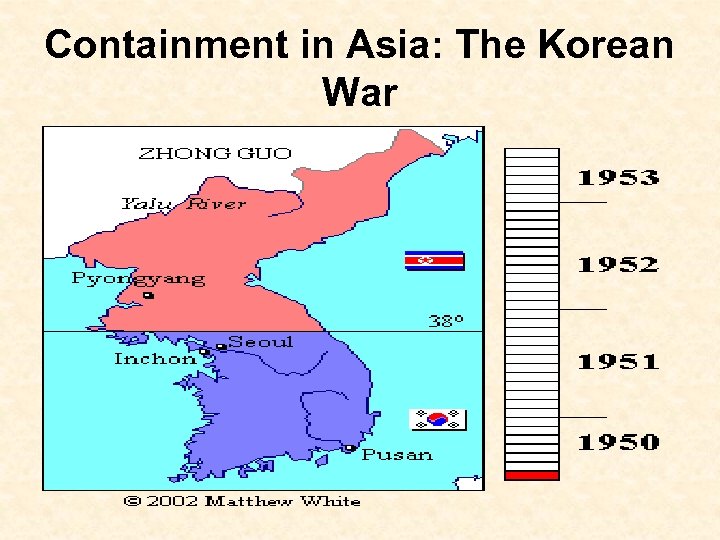 Containment in Asia: The Korean War
Containment in Asia: The Korean War
 The Korean War: 1950 -1953 • During WWII Korea had been occupied by Japan. • At the end of the War Korea was divided along the 38 th parallel or line of latitude. • The northern zone=Soviet Union influence • The southern zone=U. S. influence
The Korean War: 1950 -1953 • During WWII Korea had been occupied by Japan. • At the end of the War Korea was divided along the 38 th parallel or line of latitude. • The northern zone=Soviet Union influence • The southern zone=U. S. influence
 The Fighting Begins: The Korean War • North Korea invaded South Korea in 1950 in an attempt to unify the country. • President Truman responded to this invasion by committing American troops to major involvement in the Korean conflict. • Ever see M. A. S. H. the movie or tv series? (Mobile Army Surgical Hospital) 1970’s
The Fighting Begins: The Korean War • North Korea invaded South Korea in 1950 in an attempt to unify the country. • President Truman responded to this invasion by committing American troops to major involvement in the Korean conflict. • Ever see M. A. S. H. the movie or tv series? (Mobile Army Surgical Hospital) 1970’s
 Mac. Arthur in Command! • Mac. Arthur was in charge of the United Nations' fight to repel and defeat the aggressor. • Disagreements over the objectives & military strategies with Truman. • President recalled him and dismissed him from command.
Mac. Arthur in Command! • Mac. Arthur was in charge of the United Nations' fight to repel and defeat the aggressor. • Disagreements over the objectives & military strategies with Truman. • President recalled him and dismissed him from command.
 The Korean War & Containment • The policy of containment took a different course with American involvement in the Korean conflict. • Early containment efforts focused primarily on economic aid programs. (Truman Doc, Marshall plan) • With the Korean War the U. S. now showed it’s willingness to undertake military action to contain communism • Experiences in Korea were a warming of future global confrontations between democratic and communist opponents.
The Korean War & Containment • The policy of containment took a different course with American involvement in the Korean conflict. • Early containment efforts focused primarily on economic aid programs. (Truman Doc, Marshall plan) • With the Korean War the U. S. now showed it’s willingness to undertake military action to contain communism • Experiences in Korea were a warming of future global confrontations between democratic and communist opponents.
 The Cold War At Home • Second Red Scare: Fear of communism spreading in the U. S. – When was the first Red Scare? – Palmer Raids: • This fear led some Americans to take actions that violated the civil rights of others. • Quick review: » WWI : ________v U. S. WWII: _________v. U. S.
The Cold War At Home • Second Red Scare: Fear of communism spreading in the U. S. – When was the first Red Scare? – Palmer Raids: • This fear led some Americans to take actions that violated the civil rights of others. • Quick review: » WWI : ________v U. S. WWII: _________v. U. S.
 Cold War At Home: HUAC • 1938: The House Un-American Activities Committee was created to investigate communist activity in the U. S. • It operated for more than 30 years. • Its well-publicized probe of the movie industry (Hollywood) in the 40’s and 50’s led to the blacklisting or cutting off from employment of many actors, writers and directors.
Cold War At Home: HUAC • 1938: The House Un-American Activities Committee was created to investigate communist activity in the U. S. • It operated for more than 30 years. • Its well-publicized probe of the movie industry (Hollywood) in the 40’s and 50’s led to the blacklisting or cutting off from employment of many actors, writers and directors.
 Civil Rights are limited in times of war or threat! • The Smith Act: 1940 – Overthrowing the U. S. gov’t or associating with groups that called for such an action is illegal. – Dennis v. U. S. : the Supreme Court upheld the Smith Act – Watkins v. U. S: HUAC can’t punish witnesses who refused to cooperate with its investigations. – Yates v. U. S. : Smith Act only applies to those that teach or advocate the direct action to overthrow the government.
Civil Rights are limited in times of war or threat! • The Smith Act: 1940 – Overthrowing the U. S. gov’t or associating with groups that called for such an action is illegal. – Dennis v. U. S. : the Supreme Court upheld the Smith Act – Watkins v. U. S: HUAC can’t punish witnesses who refused to cooperate with its investigations. – Yates v. U. S. : Smith Act only applies to those that teach or advocate the direct action to overthrow the government.
 The Loyalty Review Board: • In 1947 Truman fueled anticommunist feelings by ordering a board to conduct security checks on thousands of government employees. • Those whose loyalty was considered doubtful were dismissed. • Ex. Robert Oppenheimer: led research on Atomic bomb voiced opposition to building the second more destructive hydrogen bomb govn’t hearing about his loyalty. clearance removed barred from govn’t research
The Loyalty Review Board: • In 1947 Truman fueled anticommunist feelings by ordering a board to conduct security checks on thousands of government employees. • Those whose loyalty was considered doubtful were dismissed. • Ex. Robert Oppenheimer: led research on Atomic bomb voiced opposition to building the second more destructive hydrogen bomb govn’t hearing about his loyalty. clearance removed barred from govn’t research
 The HISS Case: • The Alger Hiss case led many Americans to believe that there was a reason to fear that there were communists in the gov’t. • In 1948, Hiss, a former adviser to President Roosevelt, was charged with having been a Communist spy during the 1930 s. • He denied this, but a young Republican committee member, Richard Nixon, pursed the investigation and convicted Hiss on perjury charges.
The HISS Case: • The Alger Hiss case led many Americans to believe that there was a reason to fear that there were communists in the gov’t. • In 1948, Hiss, a former adviser to President Roosevelt, was charged with having been a Communist spy during the 1930 s. • He denied this, but a young Republican committee member, Richard Nixon, pursed the investigation and convicted Hiss on perjury charges.
 The Rosenberg Case: 1950 • Ethel and Julius Rosenberg were charged with giving atomic secrets to the Soviets during WWII. • Convicted of espionage. • Sentenced to death. • Executed in 1953
The Rosenberg Case: 1950 • Ethel and Julius Rosenberg were charged with giving atomic secrets to the Soviets during WWII. • Convicted of espionage. • Sentenced to death. • Executed in 1953
 Mc. Carthyism • Senator Joseph Mc. Carthy began his own hunt for communists • In 1950, Mc. Carthy charged he had a list of State Department employees known as communists • Mc. Carthy made bold accusations without any evidence. • This tactic is now coined as “Mc. Carthyism”
Mc. Carthyism • Senator Joseph Mc. Carthy began his own hunt for communists • In 1950, Mc. Carthy charged he had a list of State Department employees known as communists • Mc. Carthy made bold accusations without any evidence. • This tactic is now coined as “Mc. Carthyism”
 Mc. Carthy’s Fall • He televised investigations into the unfounded charges who he thought were communist in the government. • Public support quickly faded and the Senate eventually denounced him. • The fall of Mc. Carthy ended the red scare of the 1950’s (don’t forget about the Red Scare of the 1920’s due to the Bolshevik Revolution)
Mc. Carthy’s Fall • He televised investigations into the unfounded charges who he thought were communist in the government. • Public support quickly faded and the Senate eventually denounced him. • The fall of Mc. Carthy ended the red scare of the 1950’s (don’t forget about the Red Scare of the 1920’s due to the Bolshevik Revolution)


