54a0a777b9918dfc6758acc53b5d3eb5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64

What's Wrong with Balanced Scorecard? Some Constructive Improvements for Better Performance Management. Unicom: Performance Management and Balanced Scorecard Forum 7 December 2005, London. Updated Oct 2007 Whalley, See end slides 12. 15 Tom Gilb, Senior Partner, Result Planning Limited. Author of 'Competitive Engineering'. What are some of the weaknesses of Balanced Scorecard? How to quantify any qualitative management objective. How to quantify the impact of any strategy on any objectives? How to implement strategies evolutionarily - for early results, and for risk control. How to dynamically determine priorities quantitatively . Summary: 10 Principles for Improving Balanced Scorecard for Performance management 1 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 1

What are some of the weaknesses of Balanced Scorecard? The objectives are not clear. They are highly ambiguous They are not quantified - numeric They are not measurable - trackable The objectives do not have additional information to help us deal with them: Rationale or Justification Authority Impacts (on higher level objectives) Supported By (other objective or strategies) Stakeholders AN EXCEPTION, to some of this criticism: see slides at end, David Whalley 2 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 2

Real Examples of this problem Version 1: We are successful when we have the capability to understand the needs of the market as measured by the engagement in a consultative contribution to Our Corp. and our customers <-- OCS BSC as of June 13 200 x Version 2 OCS will ensure that all our training and development programs, job descriptions, and hiring priorities are aligned with critical knowledge, skills, and abilities needed to achieve our strategic objectives. 3 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 3

L 2 Develop competencies, technical knowledge, critical skills Gist: OCS will ensure that all our training and development programs, job descriptions, and hiring priorities are aligned with critical knowledge, skills, and abilities needed to achieve our strategic objectives. Timely alignment of development with objectives Continuing and timely evolution of KSA (Knowledge, Skills, Abilities) to meet the dynamics of the market. <--David S Assumption: leadership is a competency <-Larry Stakeholders Direct: {Operations Employees, Training & Development, HR, } Indirect: Customers Complex Objective: See detail following. Anticipation Gist: how well we foresee when what we need to build up Currency Gist: how well we have managed to keep up with our needs, avoiding shortfalls Effectiveness Gist: how good we are at successfully deploying our skills in practice Alignment Gist: how well we align our skills with real current objectives Employee Morale? ? 4 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 4

L 2: Develop competencies, technical knowledge, critical skills: A ‘COMPLEX’ OBJECTIVE Gist: OCS will ensure that all our training and development programs, job descriptions, and hiring priorities are aligned with critical knowledge, skills, and abilities needed to achieve our strategic objectives. Timely alignment of development with objectives Continuing and timely evolution of KSA (Knowledge, Skills, Abilities) to meet the dynamics of the market. <--David S Assumption: leadership is a competency <-Larry Stakeholders Direct: {Operations Employees, Training & Development, HR, } Indirect: Customers Type: Complex Objective: See detail following. Anticipation Gist: how well we foresee when what we need to build up Currency Gist: how well we have managed to keep up with our needs, avoiding shortfalls Effectiveness Gist: how good we are at successfully deploying our skills in practice Alignment Gist: how well we align our skills with real current objectives Employee Morale? ? 5 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 5

L 2: Stakeholders; a brainstormed list Employees, Training & Development Customers, communities, consumers, investors, broker dealers, governments, NGO, employees Operations employees, lenders, internal business partners, Employees, customers, OCS Leadership Customers, staff OCS leadership, employees OCS Leadership, OCS Staff, HR, Training & Development, Business Partners. DIFFERENTIALS All Competency Developers, shareholders, Jamie Gxxxx, Our Corp. (in general) 6 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 6
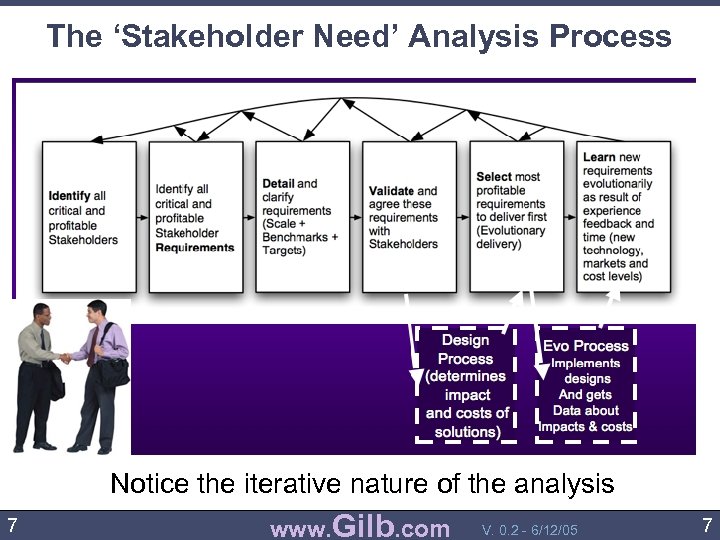
The ‘Stakeholder Need’ Analysis Process Notice the iterative nature of the analysis 7 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 7

Stakeholder Artifacts: Zachman zifa. com Data 8 Function Network People www. Gilb. com Time Motivation V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 8

L 2. Anticipation Gist: how well we foresee when & what we need to build up Stakeholders see L 2, Ops Employees Scale: % of critical actually needed CTK {Competencies, Technical Knowledge, Critical Skills} which we correctly foresaw in a timely manner as judged with hindsight. CTK: Defined as: Competencies, Technical Knowledge and Critical Skills <Meter [Monthly Report to WE] Self identification against a pre-described list of CTKs <-Larry & Team Rationale: helps individual feedback and learning Problem: is the list current needs, not the old set? > Benchmarks======== “What’s the situation? ” Our Past: Past [Competency 200 x, End May 200 x] 50% to 90% ? . <- Group guesses “ No comparable measures, these are educated guesses. ” [Federal Highways Administration, 1996]<Ray will supply> %<- Ray, Public Domain [Center for Creative Leadership, Personal Skills Measurement] ___% <--Larry See Measuring Value of human assets/Capital: Harvard, Bruce, Record <[{GE , Xerox, Motorola, FDIC Bank Examiner Program <-David Sxxxx} ? ? ? ]> Trend [End 200 z] Our Past - some % Rationale: the firm is going into markets we are not really aware of <-Larry =====Targets ==== What results do stakeholders want? ======== Ideal: 100% Wish [ End 200 q, Operations] 98% <-- David Sxx Rationale: allows us to immediately react to changes in the market. . See Objectives like {I 2, C 2} Goal [End 200 z, Our Corp. , CTKs necessary to process the current business] 100%<--Larry ======= Constraints ========= Fail [End 200 y, Operations] 80% <-- Con Assumption: if we can’t get 80% then we must question whether the strategies we are employing are any good <Con Assumption: our business is going to change steadily at 10% per year <- Con Rationale: we need 100% of CTKs necessary to process the current portfolio Note there is a method for backing into this number <-Larry Rationale: < if bad then employee dissatisfaction, losses, wasted days of training……. > <- Con Best Bank: Generic Constraint: must be better % than any other known bank Record in USA. 9 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 9

How to quantify any ‘qualitative’ management objective. Decompose complex objectives into elementary objectives (see example L 2 above). Define a ‘Scale’ of measure Use common sense Try Google for ideas Collect corporate Scale ideas and reuse Define a practical ‘Meter’ How to measure progress in practice Maybe several different ones for different purposes Define Numeric Points on the Scale Benchmarks (Past, Record, Trend) Constraints (Fail, Survival) Targets (Goal, Wish, Stretch, Ideal) 10 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 10

The necessity of quantifying the impact of any strategy, on any objectives? A ‘Strategy’, or ‘Means Objective’ Exists only to help you meet your strategic objectives You need to estimate the effect of these on your strategic objective Goals [wrt deadlines] This gives some indication of the expected power of the Strategy (or the Means Objective). This estimate can be used to: Prioritize strategies Decide to reformulate strategies for greater effect. Understand the value/cost ratio (profitability) of a strategy. 11 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 11

Quantified Technical Objectives that support Top Management Objectives (non confidential version UK 2005) Quantified Technical Objectives 12 www. Gilb. com Rough mapping Of impact on Top Objectives V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 12

Technical Objectives versus Strategies Value to Cost Ratio 13 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 13

Twelve Tough Questions: ‘Impact Estimation’ Simplified 1. NUMBERS Why isn’t the improvement quantified? 2. RISK What’s the risk or uncertainty and why? 3. DOUBT Are you sure? If not, why not? 4. SOURCE Where did you get that information from? How can I check it out? 5. IMPACT How does your idea affect my goals? 6. ALL CRITICAL FACTORS Did we forget anything critical? A more detailed treatment of these questions is in a paper at http: //www. gilb. com 14 7. EVIDENCE How do you know it works that way? 8. ENOUGH Have we got a complete solution? 9. PROFITABILITY FIRST Are we going to do the profitable things first? 10. COMMITMENT Who’s responsible? 11. PROOF How can we be sure the plan is working? 12. NO CURE Is it no cure, no pay? www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 14

How to implement strategies evolutionarily - for early results, and for risk control. • One useful way to implement strategies and to test the validity of a balanced scorecard is to use the “Evolutionary Result Delivery” – The project of meeting the Balanced Scorecard objectives is intentionally divided into a large number of steps ( say 50, or 2% of time to deadlines) – Each step will focus on a single objective, and a single strategy. It will deliver the strategy to stakeholders, and measure real progress – The feedback and learning will tell you if your Balanced Scorecard ideas are realistic. – It will also help to make the BSC taken more seriously – Tom Peters is one management Guru who has observed that successful improvements are evolutionary. 15 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 15
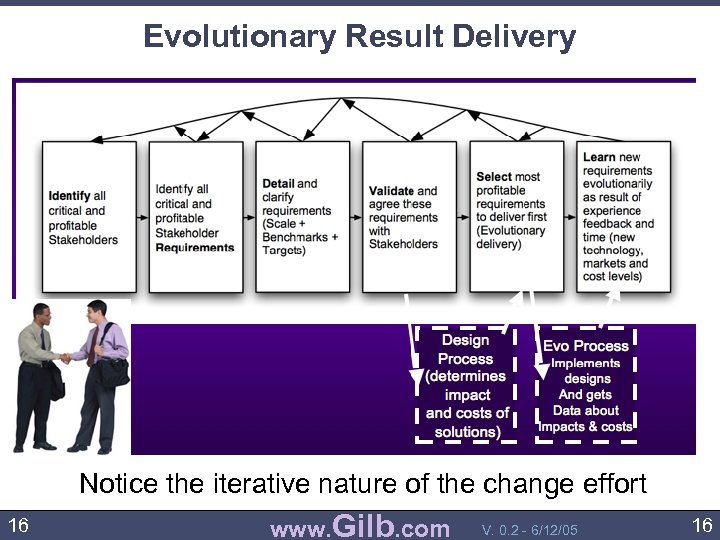
Evolutionary Result Delivery Notice the iterative nature of the change effort 16 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 16

How to dynamically determine priorities quantitatively Which BSC Objectives have priority? Or, how do we determine their priority? • ‘Priority’ is ‘claim on scarce resources’ • Priority is ‘to reach specified Goal levels on time’ • The Objectives that are farthest, Evolutionarily, from their Goal, should probably get the higher priority for remaining resources • Meeting constraints (Fail, Survival levels) is the first priority • Meeting Goal levels, then Stretch levels, then Wish are the next priorities. See: Gilb and Maier: Managing Priorities. INCOSE 2005 17 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 17

Summary: 10 Principles for Improving Balanced Scorecard for Performance management . 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Define all Objectives quantitatively Define practical short term measuring methods Analyze benchmarks before setting requirements Set constraints numerically Set targets numerically Include qualifiers for when, where, if Include supporting statements, like ‘rationale’ Include specification of stakeholders per objective Relate strategies for reaching the objective using an impact estimation 10. Try out strategies incrementally, based on highest estimated value first. 18 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 18

Practical Examples (NOT INCLUDED IN A 30 MINUTE LECTURE! JUST FOR REFERENCE From a real exercise with our client in clarifying Balanced Scorecard objectives (all company and person last names are hidden). 19 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 19

Operations Division Strategy Map Financial F 1 Reliably Manage Book of Business <- Don Miller F 2 Enable Revenue Growth <F 3 Support Housing Goals <- Con Kxxxxx Customer C 1 Become the Primary Information Source <- Cheryl C 2 C 3 C 4 Internal I 5 I 6 I 7 Learning & Growth L 1 L 2 L 3 20 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 20

C 1: Become Primary Info Source Gist: providing customers with value-added information Impacts: closer customer partnership, Corp Goal 2 (leading presence, products & markets which we do not currently serve). Owners: {Cheryl Thomas, Jeff Robertson}. Version: 21 June 200 x Stakeholders Direct: { External Customers} Indirect: Internal Customers? Assumption: Data Quality: The data timeliness, dependability, accuracy, & completeness is dealt with in other BSC Objectives and is assumed to be at appropriate levels. <-- I 1 Info Trans: Data has been translated into information <- I 6 Scale: annual % change in customer access to our information Meter [Web-available Information] % change in average return hits/data element available. Goal [End 200 q, New Customers] 20%? annual improvement “example” Goal [End 200 z, All Customers, Servicing Information] 30%? “example” 21 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 21

C 2 Goal 1 of 3 % of business we want to be in compared to the business we are in. 22 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 22
![Scale’s C 2: 2 of 3 Scale: % of [defined] business we want to Scale’s C 2: 2 of 3 Scale: % of [defined] business we want to](https://present5.com/presentation/54a0a777b9918dfc6758acc53b5d3eb5/image-23.jpg)
Scale’s C 2: 2 of 3 Scale: % of [defined] business we want to be in compared to the business we are inn. Scale: Average time from we want to move into a new product until we actually start doing business with it. Scale: average time before we get positive return on investment. Scale: Average time from we move into a new product until it is built into our infrastructure. 23 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 23
![C 2 -Reach 3 of 3 Scale: % of [defined] business we want to C 2 -Reach 3 of 3 Scale: % of [defined] business we want to](https://present5.com/presentation/54a0a777b9918dfc6758acc53b5d3eb5/image-24.jpg)
C 2 -Reach 3 of 3 Scale: % of [defined] business we want to be in compared to the business we are in. Meter: compare the <list of products and volumes we want to be in> with the <list of actual> Past [MF, 6 -200 x] 90 % Past [STO, 6 -200 x] ? ? Record [Am. Ex, 6 -200 x] <- Stephanie ? ? Record [xx, 6 -200 x] <- will be collected by Ray Trend [MF, STO, 6 -200 z] ? 70% <- Stephanie ? ? Guess Fail [MF, STO, 6 -200 y] 98% <- Stephanie Goal [MF, STO, 6 -200 y] 100% <- Stephanie 24 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 24

C 4: Building Unique Value-Balanced Partnerships: Gist: Make our customers/partners profitable beyond their wildest imagination Scale: incremental US$ cost savings per year, as viewed by each Customer/Partner of choice, compared to not having a partnership agreement. Meter: internal and external reports and their validation to one another. Note: we might choose to have unique Meters for each customer. Past [Before Partnership Agreement] 0 L. N. Past [June 21, 200 x] ? S. G. Trend [ Fail [End 3 Qt, 200 x] 0 % of Past Team Goal [End 3 Qt, 200 x] +10% of Past Team 25 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 25

I 7: Manage & Strengthen Relationships w/All Constituents: Team 1 Example I 7: Manage & Strengthen Relationships w/All Constituents: Gist: Scale: perception, by those people who rely on us for support, on our ability to met or exceed Commitments. 0 being a total failure and 10 being incredibly great. Commitments: Defined: Note: Evolution of scales. <To be thrown away. > % of commitments (qualities, deliveries) met by deadlines. % of milestones or deliverables met within the deadlines. Assumption: all quality aspects of the deliveries are specified clearly and met at time of delivery. meeting commitments by deadlines Oral, implied, writing, contractually. % of operational success in meeting the changing operational dynamics # of times Oxx can meet management's … 26 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 26
![BSC [Operations]. F 1. “Reliably Manage Book of Business” Donna Keeps Official Notes (Monday BSC [Operations]. F 1. “Reliably Manage Book of Business” Donna Keeps Official Notes (Monday](https://present5.com/presentation/54a0a777b9918dfc6758acc53b5d3eb5/image-27.jpg)
BSC [Operations]. F 1. “Reliably Manage Book of Business” Donna Keeps Official Notes (Monday 19 th, 12 Noon) Stakeholders: Direct: Investors, Lenders, Operations, Business Leads, Regulators, FMIS Business Partners & Downstream Data users, Gist: Reliably Managing Book of Business To mitigate Our Corp and Investors risk of loss. Assumption: There is a Corporate level of “Risk” Objective (to be determined) which this objective will contribute to (be a ‘means objective’ to that corp objective)) Guess at Corp. Objective: “To mitigate Our Corp and Investors risk of loss”. Strategies: (only as background info here) Communicate to investors accurately about risk <- Con Accurate and timely data Reliable systems and processes Controls Scale: Operational Health Index. A weighted scale index where 100% is a perfect ops system at any stage of operational environment. Meter: gather data to calculate the Index score using whatever is the current definition of the Operational Health Index. Assumption: all components of the Index are scales for other objectives in the Balanced Scorecard <--Con ====== Benchmarks Baseline: Past [End 1999] 50% to 75% Range ? ? Assumption> <-- Cheryl, Pat & Con (65 -70) Record Trend [ End 200 q] ======Targets ===== Wish [End 200 x] [End 200 q] Stretch Fail [End 200 x] Baseline + 0%? Goal [End 200 x] Baseline + 5%? AR: [End 200 x, OHI. Application Reliability] <+1%? to whatever it is at in the OHI model> “symbolic note to show we might target individual components of the OH Index” Strategies [AR] : reduce number of CSRs <- Con ------------Book of Business: Defined As: FM assets and liabilities. Operational Health Index: OHI: {Application Reliability, Controls, Accuracy, Capacity, Customer Impact, Financial Impact, <Reconciling Items>} 27 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 27

F 1 Notes NOTE: Complex Objective: consists of Risk Forecast Reconciling Items (a symptom of a flawed process) Operational Health Index: Defined As: Several categories (see detail F 1 -1 Operational health, whole page of measures) Application Reliability Controls (Risk Management) Accuracy Capacity Customer Impact Financial Impact 28 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 28
![I 5: Manage & Improve Transaction Processing: Stakeholders: Direct: {Investors [MXX], Lenders, Operations, CIS I 5: Manage & Improve Transaction Processing: Stakeholders: Direct: {Investors [MXX], Lenders, Operations, CIS](https://present5.com/presentation/54a0a777b9918dfc6758acc53b5d3eb5/image-29.jpg)
I 5: Manage & Improve Transaction Processing: Stakeholders: Direct: {Investors [MXX], Lenders, Operations, CIS (? ), Indirect: {Regulators “ to assess safety & soundness”, Business Segments (Single & Multiple Family)}. Impacts: Corporate Goal 6 {costs, acquisitions, large quantities}, see note in slide ahead. Ambition: To reduce the real time throughput in our total (manual and automated) system for correctly handled transactions. Note: this implies that any form of continuous improvement, manual or automated, which improves speed and correctness are going to be viewed as good strategies to help meet this Objective. Note: cost reductions are implied through ’correctness’ (reduced rework) and “business process speed” Scale: Average throughput time for a correctly handled [defined type of Transaction] Note: [defined type of Transaction] includes new products Meter: <Manual samples of defined transaction types, supplemented with automatic measurements of some transaction types. > Past [Type: All] 10 days? ? ? Past [A/A] Past [Type: FRM “Fixed Rate Mortgage”, End 200 y] Goal [Type: 29 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 29

I 5 Impacts: Corporate Strategic Goals: level Goal 6 “Costs” Objective; “c. Cost reductions for the consumer, the company, and its partners” Assumption: this is the real core of goal 6, the other stuff is: a) rapid acquisition and risk assessment of customized mortgage financings through multiple channels, and b) processing of large quantities of loan and credit data on new and existing products. Assumption: 4 th implied goal is that this is an expanding universe. <-Con 30 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 30

I 5 Strategies Source: 5/25/200 x Strategy Forum <-Don M Strategies: “some expected ways to get to our goals; not final decisions” All initiatives mentioned {Axxxxxx (customer solutions project), STO {Trade support, PIGs, Factors Data Service} Efficient Infrastructure Flexible Infrastructure {comprehensive integrated end-to-end processing throughout the life cycle of a mortgage} Adequate financial controls Timely and Adequate data and information. Effective measurement and Feedback. Continually monitor and evaluate our performance. To provide a basis for continuous improvement. Eliminate Operational Redundancies. Eliminate duplication of effort. Seamless systems Integrated systems Reduce reconciliation problems. 31 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 31

BSC Objective F 3 Con Kxxxxx & Tom Gilb Tuesday June 20 th 200 x A crack was made last week at F 3 32 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 32

F 3. Community Trust Stakeholders: {Our Corp. Business Segments, Communities, Lenders, Investors, Broker Dealers}. Indirect: {Regulators, NGOs, Local and State Govt. , Realtors, Developers } Owner: Con Kxxxxx Version: June 20 th 200 x 4 pm (radical re-think as Trust rather than data quality) Specification Type: Balanced Scorecard Objective [Operations OCS]. . Supports: Corporate Objectives Goal 1 (Focused investment in under served communities, public advocacy), Many OCS Objectives. Assumption: this goal does not conflict the area of other instances outside of Operations like Our Corp. Foundation and The Housing and Community Development Division. It should complement and supplement their efforts and any practical initiatives will be co-ordinated with them to avoid any perceived conflict. Gist: To increase and maintain the trust of Our Corp. in local communities Impacts: {willingness to do business with Our Corp. , Corporate Goal 1, Affordable Housing Goal, Housing Leadership Commitment, Corporate Citizenship and Responsibility. }. Scale: % level of trust expressed and observed for Our Corp. which results from specific activities by Operations. Trust: Defined As: <willingness to possibly do business with us, or recommend us. > Benchmarks. Trust Level 200 x: Past [200 x, Underserved Community (8 instances)] ? ? Targets. Goal [200 q ] Trust Level 200 x + 20% 33 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 33

F 3: Housing Goals Data Quality Stakeholders: {Our Corp. , OFHEO, HUD, U. S. Congress, Shareholders} Owner: Con Kxxxxx Version: June 20 th 200 x 2: 40 pm Specification Type: Means Objective. Supports: Corporate Objectives Goal 1 (Leadership), Many OCS Objectives. Gist: Improve the quality of critical data Note: essentially similar to I 1 (data quality). Scale: % Fault-free data elements used to prepare critical reports. Fault-free: Defined As: the data is up-to-date, correct, complete. Benchmarks. PHG: Past [200 x, Housing Goal Data] ? ? Targets. Goal [Housing Goal Data] “ This Objective can be characterized as a complex objective” Complex Objective: “see detailed sub objectives following” Completeness Accuracy Timeliness Accessibility 34 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 34
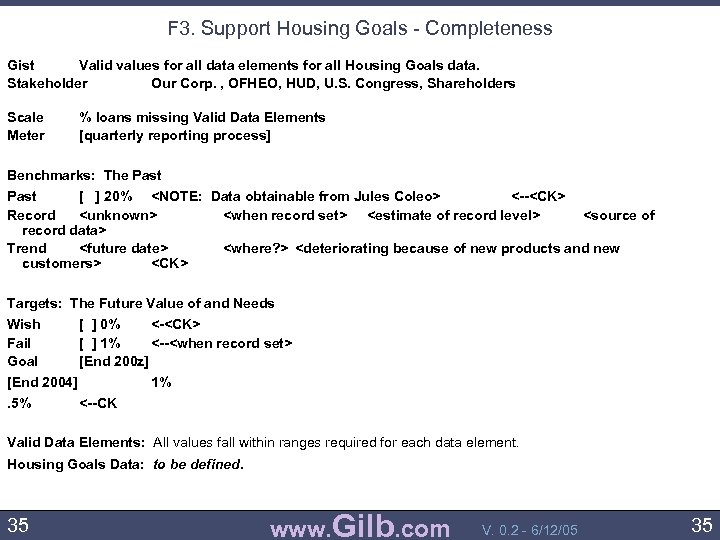
F 3. Support Housing Goals - Completeness Gist Valid values for all data elements for all Housing Goals data. Stakeholder Our Corp. , OFHEO, HUD, U. S. Congress, Shareholders Scale Meter % loans missing Valid Data Elements [quarterly reporting process] Benchmarks: The Past [ ] 20% <NOTE: Data obtainable from Jules Coleo> <--<CK> Record <unknown> <when record set> <estimate of record level> <source of record data> Trend <future date> <where? > <deteriorating because of new products and new customers> <CK> Targets: The Future Value of and Needs Wish Fail Goal [ ] 0% <-<CK> [ ] 1% <--<when record set> [End 200 z] [End 2004]. 5% 1% <--CK Valid Data Elements: All values fall within ranges required for each data element. Housing Goals Data: to be defined. 35 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 35

OBJECTIVE: F 3. Support Hxxxx Goals - Accuracy Gist Correct values for all data elements for all Hxxxx Goals data. Stakeholder Our Corp. , OFHEO, HUD, U. S. Congress, Shareholders Scale Meter % loans with Incorrect Data Elements [quarterly reporting process] Benchmarks: The Past [ ] 35% <NOTE: Data obtainable from Jules Coleo> <--<CK> Record <unknown> <when record set> <estimate of record level> <source of record data> Trend <future date> <where? > <deteriorating because of new products and new customers> <CK> Targets: The Future Value of and Needs Wish Fail Goal [ ] 1% <-<CK> [ ] 2% <--<when record set> [End 200 z] [End 2004] 1% 2% <--CK Incorrect Data Elements: All values pass relational edits for consistency and meaningfulness. Housing Goals Data: to be defined. 36 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 36

I 2 Implement Processing Solutions for All Products Con Kxxxxx w TG June 20 200 x DC 37 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 37

Execution Capability (I 2) Version 13 June draft Stakeholder: {Borrower, Lender, Our Corp. , Realtor, Regulator, Investor, Broker Dealer, Core markets, Ancillary Markets}. Gist: Substantial improvement of execution capability as appropriate for various markets. <- Con Kxxxxx. Note: ‘it is about trading off scale for execution’ <--W. Exxxx Scale: Total Spread: Execution-based weighted spread across a variety of investors: the difference between the weighted average cost of funds and the weighted average yield. Meter Past Goal Note I 2 is a means strategy for F 2 38 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 38

New Markets and Products Support (I 2) Version 20 June revision Stakeholder: Gist: Direct: {Borrower, Lender, Our Corp. , Investor, Broker Dealer, }. Indirect: {Regulator, Realtor} To enhance our capability of extending our services to products and markets we do not currently serve. Authority: Corporate Goal 2 (d) “markets we do not currently serve”. Rationale: Our Division must effectively support the technical capability to serve these new markets and products. Scale: The average calendar time between request (‘concept to spec’ process) to Our Division for support in entering a new market, or delivering a new product, until successful first useful capability is operational and has been successfully used at all, when priority is highest. Note: implementation delays due to assigned low priority, and consequent lack of resource to make improvements, should not be included as a measure of Our Division capability. <-TG, agreed CK Assumption: the ‘earned value’ aspect of these changes will be covered by I 7 (or elsewhere). <--CK Meter: manual analysis/logs , by Our Division, of real requests and successful implementations. Note: 2 Q 200 x we are prototyping this meter, 3 rd. Q 200 x we will use it on past observations. <-CK ======BENCHMARKS ====== Past Support: Past [New Incremental Product] 12 Months, [New Product] 24 months, [New Business Areas] 36 months. Source CK quick approximations. New Product: Defined: something incremental, but could be really new Record [Construction to ‘Perm’(anent Loan)] 6 months <- CK[Fixed Rate Adjustable] <6 months? <-CK ask Stephanie>, Trend Note: we are improving this ability because of introduction of product pilots. <-C Kxxxxx ======= TARGETS ========= Wish “have to get better”, [New Product] 2 months <- CK, [New Market Area, New Channel Required] 6 months <-CK Fail [200 x] “sustain current performance<-CK” = Past Support, Note could change Fail if investment were made. <-CK Fail 200 q: Fail [Year 200 q] Past Support /2 Authority: Corp Goals 2 (products we do not currently serve) and 4 ( record financial performance) Stretch [200 y] = Fail 200 q, Rationale: we want to one of the corporate leaders in improving time to market <-CK Assumption: we will need to have a much better understanding of our processing baseline. Constraint: We are constrained in how much time we can cut out by the characteristics of our current core processing systems <CK Goal [Long term] <ops implementation speed is not perceived as the bottleneck> Note: this goal needs to be seen in the light of Earned Value measurement efforts, see BSC Objective I 7 <-CK Note I 2 is a ‘means strategy’ for F 2 39 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 39

I 3: Manage Operational Risk: (15 minute version) Gist: ability to identify, define, plan for and mitigate any Interesting Operational Risks. Impacts: $ value loss Interesting Operational Risks: Defined As: the internal (Operational health Index) or external risks which, when considering both probability of occurrence and potential damage, rank as most profitable to manage. Note: we have a Business Continuity Risk model in conjunction with disaster planning, which needs to be integrated into this plan. Complex Objectives Unidentified internal audit points Dollar value loss Ability to mitigate risk Exposed risk factor - business continuity 40 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 40

I 4: Support Liquidity: Owner: Win Hxxxx Version: June 21 200 x Stakeholders Direct{Tom Lxxxx (The Portfolio), Operations Services (Larry Bxxxx, others), Ops Leadership Group} Indirect: {Our Corporation, …. } Gist: maximize ability/basic capability to generate income through the acquisition and management of asset-based cash flows. SAI Units: Scale: Support Accomplishment Index: Defined As: A Our Corp. defined (Scale 0 to 100). Made up of 16 weighted factors (initiatives). Meter: Maurice Gxxx calls around monthly to gather data for this. Impacts: 3 Corporate Goals: namely 2 (28% MDO), Goal 4&3 ( $41 mill in cash products), Maintain net interest margin/? (Goal 3), MBS Volume (Goal 4) Assumptions: : I 4 A 1: We will be free to continue to build our portfolio unrestricted. <- WH I 4 A 2: We will be able to continue to offer managed cash flow products <- WH. I 4 A 3: The portfolio is going to be the primary income generator. <- WH ===== Benchmarks ======= Past [April for March 200 x] 30 SAI Units Past [May for April 200 x] 42 SAI Units Trend [End 200 x] 93 SAI Units =====Targets ======= Wish [End 200 x] 95% ± 4% <-- M & W Ideal 100 SAI Units Goal [Operations, by End 200 x] 99% <--W & M ===== Constraints ==== Fail [Operations, Anytime Rest of 200 x & on] 50 -60 SAI Units 41 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 41

I 7: Value Delivery Gist: consistently deliver specified, and Implied, critical values to stakeholders, as defined in contracts and policy documents. Owner: Stephanie Gxxx & Liz Nxxxxx Version: June 20 200 x Implied: Defined As: not specified in the project contract, but specified in writing elsewhere in Our Corp. Standards and Policies. Assumption: stakeholder requirements are not entirely fixed in the formal contract at the project beginning. There must be scope at all times throughout the development and enhancement of the systems for learning and insight as to more competitive and useful requirements to be formally specified and appropriately prioritized. <-TG Rationale: making sure that we deliver the quality and functionality is critical to our support of all stakeholder objectives Stakeholders: Direct {All Instances which OCS delivers a product to }. Indirect: All users of systems delivered or maintained by OCS Scale: % of implied (Policy) or expressed (Contract) commitments to stakeholders, which are delivered by the deadlines which are agreed and committed in writing. Meter: <manual audit of all contracts, initial report by project manager> Assumption: we can specify all critical needs and values ( like system qualities) in clear unambiguous testable and measurable ways (like Gilb methods www. gilb. com, see also Con Kxxxx’s product/value Development Methodology ). ===== Benchmarks ===== Past Record Trend =====Targets ====== Wish Must Plan Stretch Ideal 42 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 42

Plan focus on Gist/Scale initially, other detail later Example of Complex Objective L 1 (Build and refine strategic alignment) Stakeholders: Direct: Operations Employees Indirect: Corporate partners Gist: Having well-aligned Operations Goals which deliver planned measured contributions to targeted Corporate Goals. Assumption: this process will aid the learning and growth perspective, and empower employees to execute plans which contribute to corporate goals. Complex Objective: {Alignment, Contribution} Alignment Gist: high degree of alignment of Operation’s Objectives with targeted Corporate Objectives Scale: % of formal top level BSC Objectives which are intended to contribute to one or more Corporate level Goals and other Top Level Ends: Defined As: any missions, strategies, goals, objectives, projects, by whatever name, which are initiated outside of Operations, which Operations can potentially contribute to. Contribution Gist: maximum delivery to the Aligned (with Corp. ) Operation’s Objectives planned levels Scale: % of Corporate Aligned Goals Planned level which are met on time. Strategies: IA: Individual Alignment of Employee Goals to Operations Goals (in progress now). L&G: Learning and growth mechanisms for individuals and group. Impacts: Some Corporate Goals and some corporate ends 43 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 43

L 2: Currency Stakeholders: O leadership, O EE’s, T+D, <Product Development>. Gist: how well have we managed to deliver. CTKC’s to keep up with market needs. Scale: % of <Critical> CTKC; s delivered by Date Needed (in order to continuously satisfy market). Meter [Monthly Report to WE] Self-identification against a list of CTKC’s required to support growing product line + book of business. =====Benchmarks ======= Past [? , ? ] 70%? <--Guess “was DSI, etc. outsourced due to lack of CTKC’s in-house” Rationale: 50% of business analyst positions filled by externals to make up for in-house CTKC’s deficiency <--RK Record ? ? Trend [? , ? ] <75% (down arrow symbol =? ? TG) Rationale: Complex new products do not fit in core systems/processes. Rationale: not familiar with new markets. =====Targets ======== Wish [End 200 z] 98% <- MS, RK, FD Stretch Goal [End 200 q] <90%> Rationale: need CTKC’s to support product growth. ======= Constraints ===== Fail [End 200 q] <85%> Rationale: Ops ability to assimilate new business is critical to achieve EPS (Earnings Per Share) target. 44 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 44

Culture Capability (L 3) Stakeholders: {Chairman? , <His VPs? >, Bill Exxxxx (Sr. VP), …. } Gist: world class culture. Note: probably complex objective but now! Scale: Average speed of adaptation to [defined classes of Change] for a defined class of [Employee] to a defined [Degree]. Meter <how to track this in practice. ======= Benchmarks====== Past Trend Record ======Targets====== Goal [Change = Technological, Employee = Manager, Degree = Reasonable] 1 year Goal [Change = Ideological, Employee = Top Manager, Degree = Fanatic] 3 months, 45 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 45

Data Quality (I 1) Stakeholders Gist Complex Objective: Currency (detailed next slide) Availability These 3 were not detailed here Completeness Accuracy 46 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 46

Data Quality. Currency Gist: hugely better than we are today in currency. Do absolute!! <- WE Stakeholders………. Scale: time delay between real events (‘moved’, ‘paid’) which updated things, and when we have the information correctly available for our practical use. Meter < pick a set of loans as as sample> <--CK ==== Benchmarks ===== Past: 60 -180 days <- Con Kxxxxx Trend Record ==== Targets ====== Wish <real time> Fail <worse better? ? > Goal [Payments, End 200 y ] 1 day <- CK [All Critical Data, End 200 q] < 1 hour <- TG swag All Critical Data: Defined As: { Payments, Defaults, Postal Addresses} 47 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 47

Execution Capability (I 2) Stakeholder: {Borrower, Lender, Our Corp. , Realtor, Regulator, Investor, Broker Dealer, Core markets, Ancillary Markets}. Gist: Substantial improvement of execution capability as appropriate for various markets. <- Con Kxxxxx. Note: ‘it is about trading off scale for execution’ <--W. Exxxxx Scale: Total Spread: Execution-based weighted spread across a variety of investors: the difference between the weighted average cost of funds and the weighted average yield. Meter Past Goal 48 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 48

L 2. Effectiveness Gist: how good we are at successfully deploying our skills in practice Stakeholders: O EE’s, Customers, Product Development Scale: % of new product development that is turned down because of lack of CTKC about how to develop the product. Meter: feedback from Product Development and O EE’s. Past [Operation Employees, 6/200 x] ? ? 20%± 20 <- Marty wild guess Record [? ? ? ] ? ? ? Trend [200 q] 20% <- Marty Guess Fail [200 q] =Past [6/200 x] Goal [200 y] 15 <- Team Goal [200 z] 10 <- Team Goal [200 q] 5 <- Team Wish [200 q] 0 -1 <- Team Assumption: Requests that are coming out of product is reasonable and rational. <Larry Assumption: List of leadership qualities that are identified by the Office of the Chair is higher order than L 2 <- Larry 49 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 49
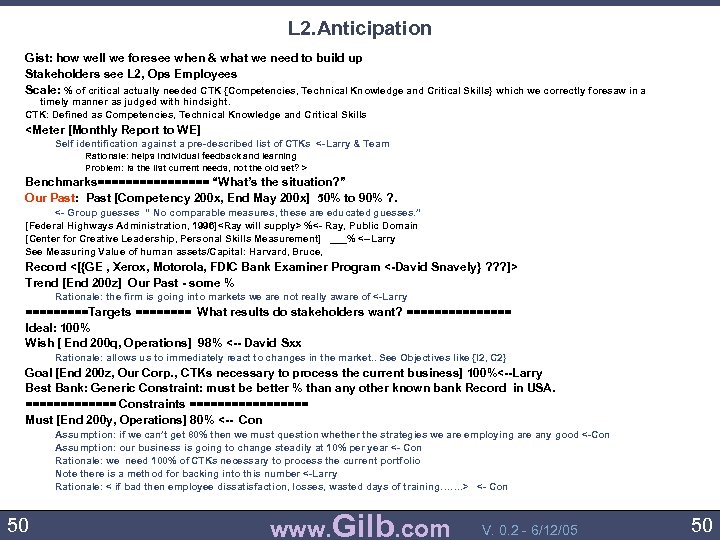
L 2. Anticipation Gist: how well we foresee when & what we need to build up Stakeholders see L 2, Ops Employees Scale: % of critical actually needed CTK {Competencies, Technical Knowledge and Critical Skills} which we correctly foresaw in a timely manner as judged with hindsight. CTK: Defined as Competencies, Technical Knowledge and Critical Skills <Meter [Monthly Report to WE] Self identification against a pre-described list of CTKs <-Larry & Team Rationale: helps individual feedback and learning Problem: is the list current needs, not the old set? > Benchmarks======== “What’s the situation? ” Our Past: Past [Competency 200 x, End May 200 x] 50% to 90% ? . <- Group guesses “ No comparable measures, these are educated guesses. ” [Federal Highways Administration, 1996]<Ray will supply> %<- Ray, Public Domain [Center for Creative Leadership, Personal Skills Measurement] ___% <--Larry See Measuring Value of human assets/Capital: Harvard, Bruce, Record <[{GE , Xerox, Motorola, FDIC Bank Examiner Program <-David Snavely} ? ? ? ]> Trend [End 200 z] Our Past - some % Rationale: the firm is going into markets we are not really aware of <-Larry =====Targets ==== What results do stakeholders want? ======== Ideal: 100% Wish [ End 200 q, Operations] 98% <-- David Sxx Rationale: allows us to immediately react to changes in the market. . See Objectives like {I 2, C 2} Goal [End 200 z, Our Corp. , CTKs necessary to process the current business] 100%<--Larry Best Bank: Generic Constraint: must be better % than any other known bank Record in USA. ======= Constraints ========= Must [End 200 y, Operations] 80% <-- Con Assumption: if we can’t get 80% then we must question whether the strategies we are employing are any good <-Con Assumption: our business is going to change steadily at 10% per year <- Con Rationale: we need 100% of CTKs necessary to process the current portfolio Note there is a method for backing into this number <-Larry Rationale: < if bad then employee dissatisfaction, losses, wasted days of training……. > <- Con 50 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 50

L 2. Alignment Gist: how well we align our skills with real current objectives Stakeholders: Apps, Employees, Corporate leadership, New product Development People. Scale: % CTKS (skills) actually needed as compared to what we have identified as the base skills going forward. Meter: feedback from your stakeholders as of the validity of the CTKS Note: other suggested scales: % difference between real skills needed in the field and our skills 51 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 51

L 2 Stakeholders opinions Employees, Training & Development Customers, communities, consumers, investors, broker dealers, governments, NGO, employees Operations employees, lenders, internal business partners, Employees, customers, OCS Leadership Customers, staff OCS leadership, employees OCS Leadership, OCS Staff, HR, Training & Development, Business Partners. DIFFERENTIALS All Competency Developers, shareholders, Jamie Gxxx, Our Corp. (in general) 52 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 52

Scale: % of critical actually needed CTK {Competencies, Technical Knowledge and Critical Skills} which we correctly foresaw in a timely manner as judged with hindsight. Past [Competency 200 x, End May 200 x] ? ? An example of different people’s estimates of the PAST Level Measurement was not relative to the market 50% <--Con 42% 50% 80% <-Marty 90% <-WE Reason: “we trained in 90% required skills and 100% of the people went through it. ” 75% <-Al 65% <-Angela 50% <-- Cheryl 70% <-- Maurice 75% <- Donna 80% <--Ray 53 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 53

Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In Outsourcing Dave Whalley. Commercial Consultant. Co-operative Financial Services. IS Development & Delivery. Miller St 7 th Floor. Tel: 0161 903 3631 Email: David. Whalley@cfs. co. uk Talk Held UK Software management Association 17 Oct 2007
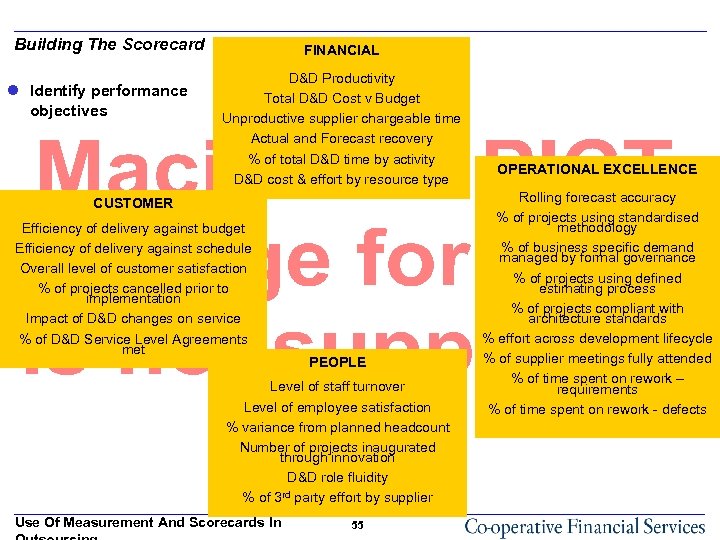
Building The Scorecard l Identify performance objectives FINANCIAL D&D Productivity Total D&D Cost v Budget Unproductive supplier chargeable time Actual and Forecast recovery % of total D&D time by activity D&D cost & effort by resource type CUSTOMER Efficiency of delivery against budget Efficiency of delivery against schedule Overall level of customer satisfaction % of projects cancelled prior to implementation Impact of D&D changes on service % of D&D Service Level Agreements met PEOPLE Level of staff turnover Level of employee satisfaction % variance from planned headcount Number of projects inaugurated through innovation D&D role fluidity % of 3 rd party effort by supplier Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In 55 OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE Rolling forecast accuracy % of projects using standardised methodology % of business specific demand managed by formal governance % of projects using defined estimating process % of projects compliant with architecture standards % effort across development lifecycle % of supplier meetings fully attended % of time spent on rework – requirements % of time spent on rework - defects
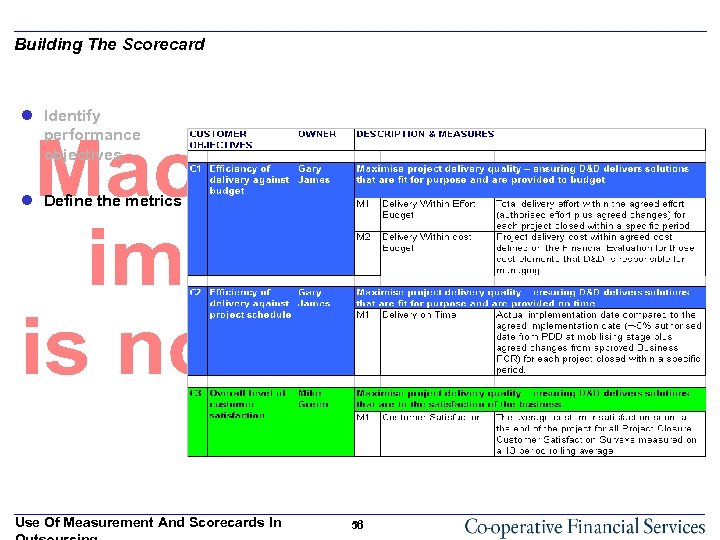
Building The Scorecard l Identify performance objectives l Define the metrics Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In 56
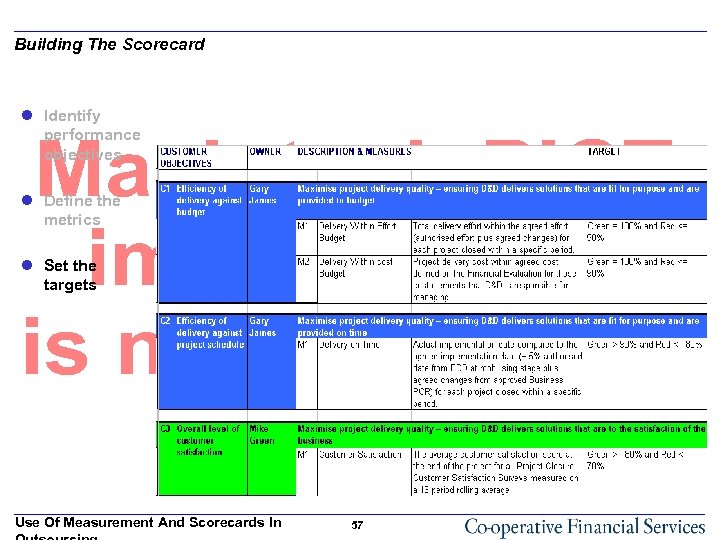
Building The Scorecard l Identify performance objectives l Define the metrics l Set the targets Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In 57

Tactical Scorecard Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In 58
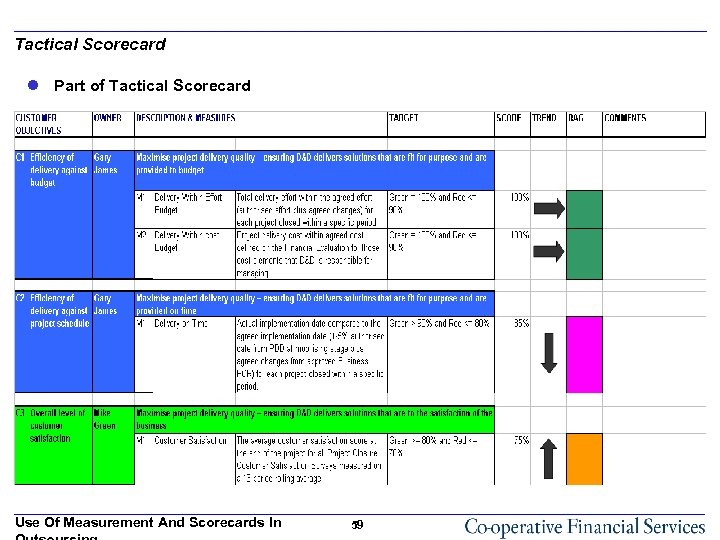
Tactical Scorecard l Part of Tactical Scorecard Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In 59

Strategic Scorecard Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In 60
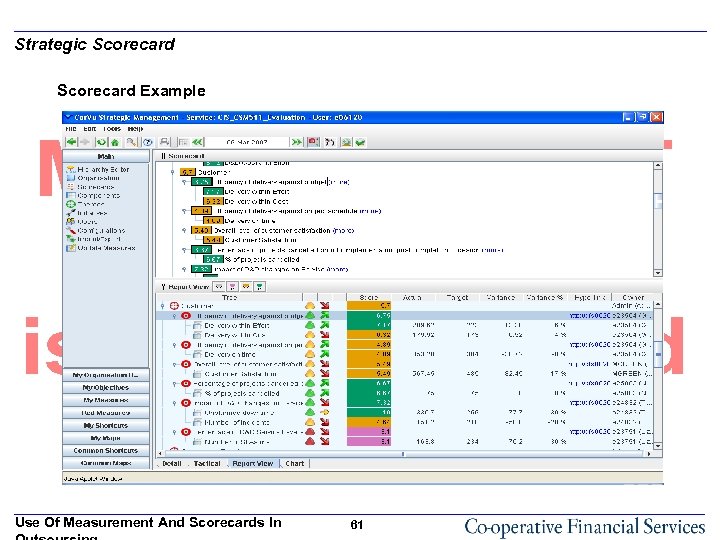
Strategic Scorecard Example Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In 61
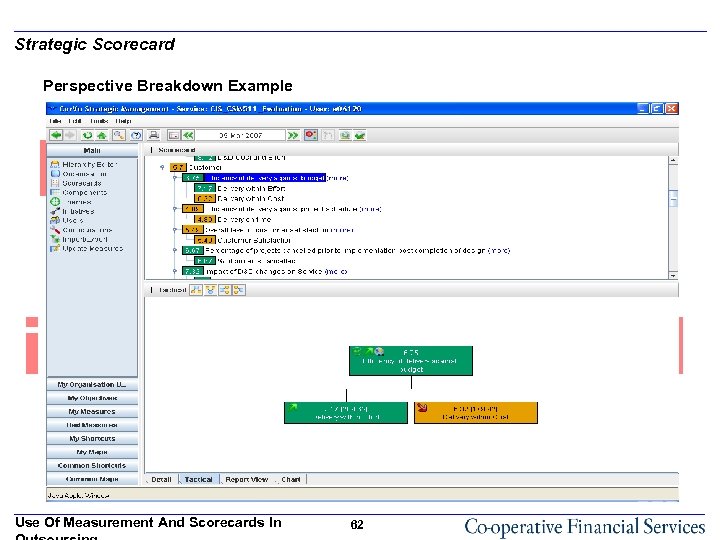
Strategic Scorecard Perspective Breakdown Example Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In 62
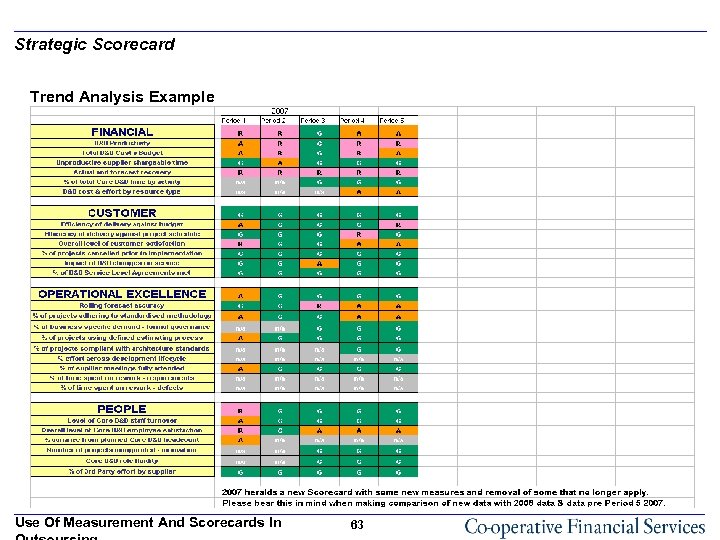
Strategic Scorecard Trend Analysis Example Use Of Measurement And Scorecards In 63

Last slide 64 www. Gilb. com V. 0. 2 - 6/12/05 64
54a0a777b9918dfc6758acc53b5d3eb5.ppt