58391c22b9a511242384a83acc2fc633.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68

 What is the Middle East ?
What is the Middle East ?
 Pair-Share • What do you think when people say the Middle East? • What images come to mind? • Why?
Pair-Share • What do you think when people say the Middle East? • What images come to mind? • Why?
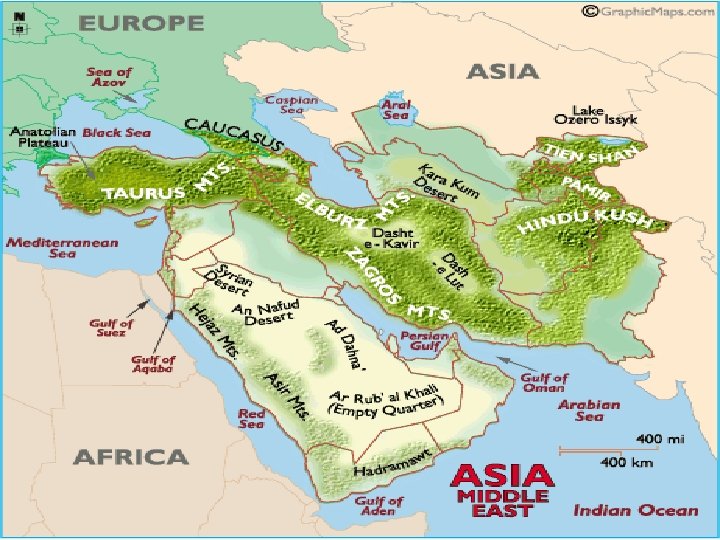
 Geography of the Middle East • The region known as the Middle East straddles three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa • It has connected major trade routes since ancient times between Europe, India, and China • People, ideas, goods, and religions have originated in and flowed through this region
Geography of the Middle East • The region known as the Middle East straddles three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa • It has connected major trade routes since ancient times between Europe, India, and China • People, ideas, goods, and religions have originated in and flowed through this region
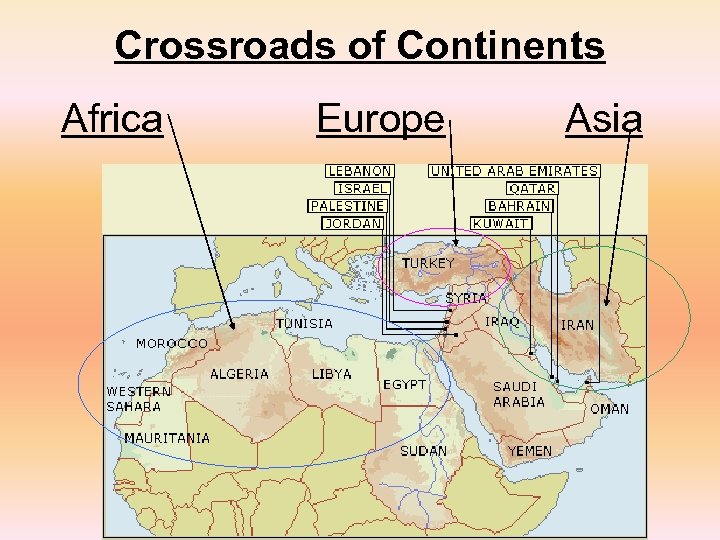 Crossroads of Continents Africa Europe Asia
Crossroads of Continents Africa Europe Asia
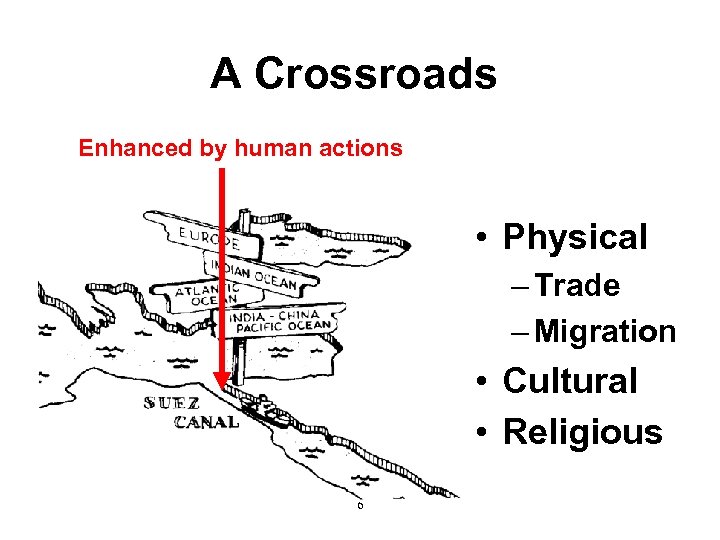 A Crossroads Enhanced by human actions • Physical – Trade – Migration • Cultural • Religious 6
A Crossroads Enhanced by human actions • Physical – Trade – Migration • Cultural • Religious 6
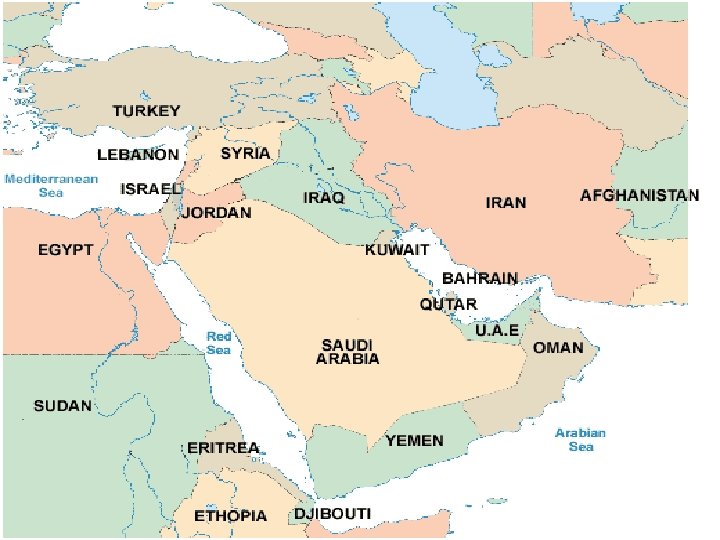
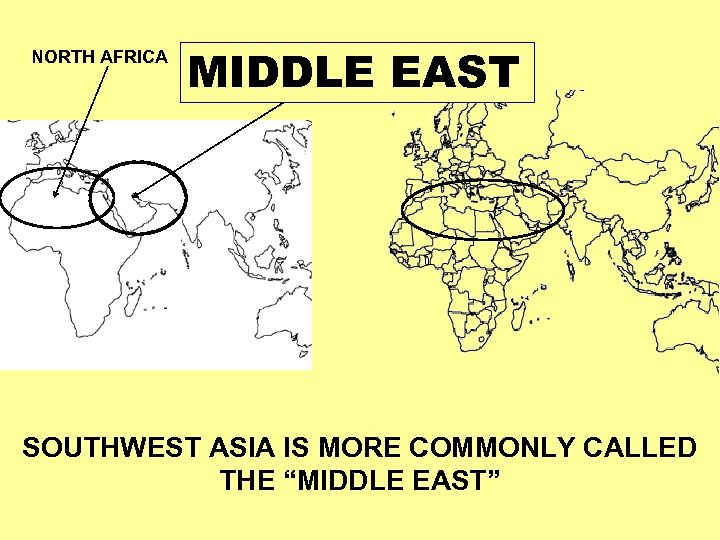 NORTH AFRICA SOUTHWEST MIDDLEASIA EAST SOUTHWEST ASIA IS MORE COMMONLY CALLED THE “MIDDLE EAST”
NORTH AFRICA SOUTHWEST MIDDLEASIA EAST SOUTHWEST ASIA IS MORE COMMONLY CALLED THE “MIDDLE EAST”
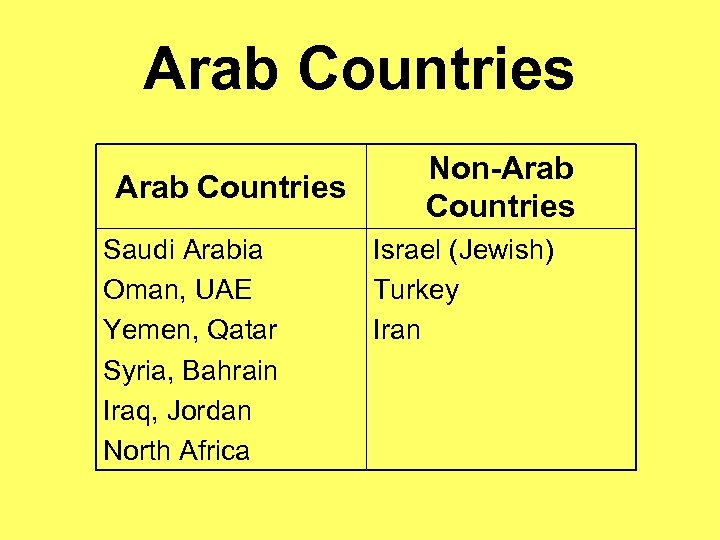 Arab Countries Saudi Arabia Oman, UAE Yemen, Qatar Syria, Bahrain Iraq, Jordan North Africa Non-Arab Countries Israel (Jewish) Turkey Iran
Arab Countries Saudi Arabia Oman, UAE Yemen, Qatar Syria, Bahrain Iraq, Jordan North Africa Non-Arab Countries Israel (Jewish) Turkey Iran
 Ethnicities • • • Arabs Jews Turks Persians Kurds
Ethnicities • • • Arabs Jews Turks Persians Kurds
 Bodies of Water
Bodies of Water
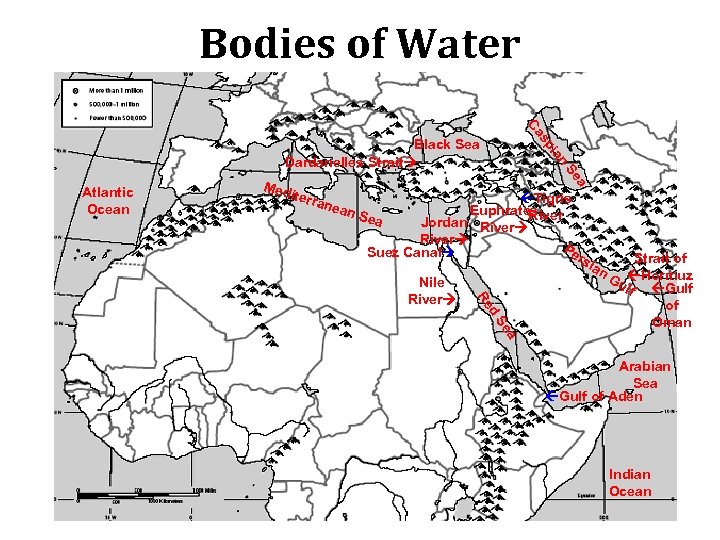 Bodies of Water Ca iterr a a Se Med an Atlantic Ocean i sp Black Sea Dardanelles Strait Tigris Euphrates n Se River a Jordan River Pe Suez Canal nea rs d Re Nile River ian a Se Strait of Gu Hormuz lf Gulf of Oman Arabian Sea Gulf of Aden Indian Ocean
Bodies of Water Ca iterr a a Se Med an Atlantic Ocean i sp Black Sea Dardanelles Strait Tigris Euphrates n Se River a Jordan River Pe Suez Canal nea rs d Re Nile River ian a Se Strait of Gu Hormuz lf Gulf of Oman Arabian Sea Gulf of Aden Indian Ocean
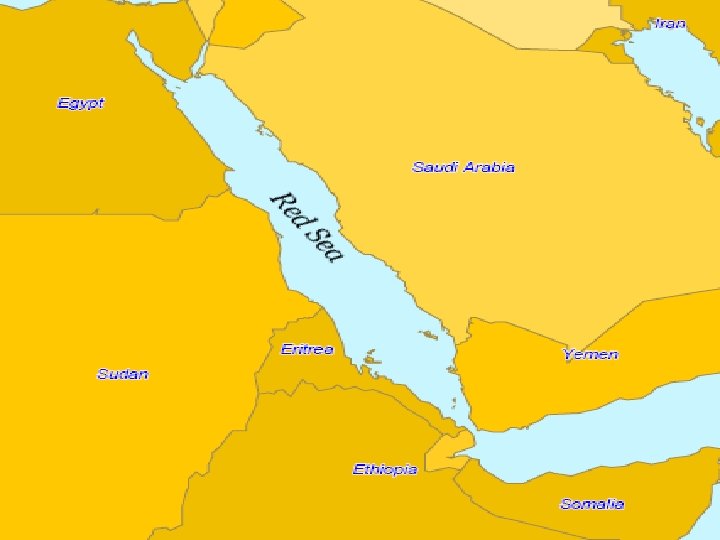
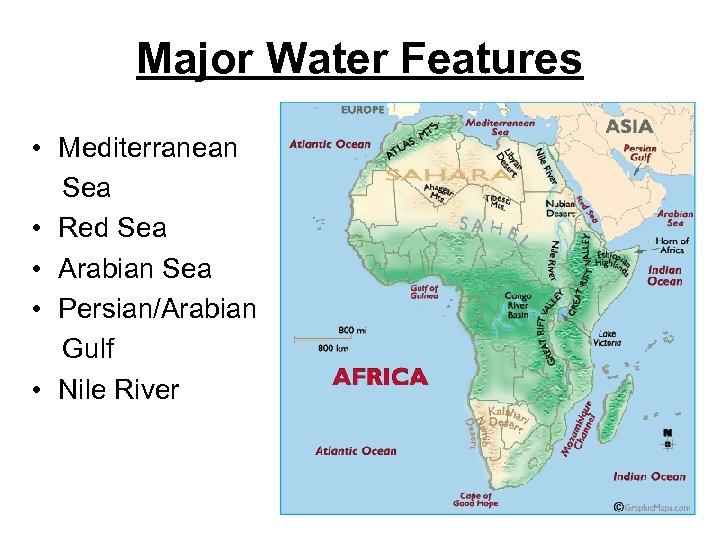 Major Water Features • Mediterranean Sea • Red Sea • Arabian Sea • Persian/Arabian Gulf • Nile River
Major Water Features • Mediterranean Sea • Red Sea • Arabian Sea • Persian/Arabian Gulf • Nile River
 Bodies of Water • Rivers & Sea – The Nile River – The Tigris & Euphrates Rivers – The Jordan River – The Red Sea • Gulfs – Persian Gulf, – Gulf of Suez, – Gulf of Aqaba
Bodies of Water • Rivers & Sea – The Nile River – The Tigris & Euphrates Rivers – The Jordan River – The Red Sea • Gulfs – Persian Gulf, – Gulf of Suez, – Gulf of Aqaba
 Bodies of Water • The countries of the Middle East have a very hot and dry climate. • Four large oceans or bodies of water border the Middle East. • Mountain ranges close to many of the coastal areas block rains coming from these bodies of water and result in much of the interior being desert. • Because there are coastal areas as well as a number of large rivers, other parts of the region have enough water to support agriculture and towns and cities of significant size.
Bodies of Water • The countries of the Middle East have a very hot and dry climate. • Four large oceans or bodies of water border the Middle East. • Mountain ranges close to many of the coastal areas block rains coming from these bodies of water and result in much of the interior being desert. • Because there are coastal areas as well as a number of large rivers, other parts of the region have enough water to support agriculture and towns and cities of significant size.
 The Coastline • Many Southwest Asian cities are based around ports. • These cities usually have major industries. • Ports make it easier to ship the things produced by industries. • Port cities with major industries usually pollute their water supplies. • Oil is the main export in Southwest Asia. • Huge ships and oil spills pollute the waters of the Persian Gulf.
The Coastline • Many Southwest Asian cities are based around ports. • These cities usually have major industries. • Ports make it easier to ship the things produced by industries. • Port cities with major industries usually pollute their water supplies. • Oil is the main export in Southwest Asia. • Huge ships and oil spills pollute the waters of the Persian Gulf.
 Persian Gulf • The Persian Gulf is also known as the Arabian Gulf. • The term Arabian Gulf is used by Arab countries near the Persian Gulf such as Saudi Arabia, Oman, and the U. A. E. but it is not recognized by the United Nations.
Persian Gulf • The Persian Gulf is also known as the Arabian Gulf. • The term Arabian Gulf is used by Arab countries near the Persian Gulf such as Saudi Arabia, Oman, and the U. A. E. but it is not recognized by the United Nations.
 Seas
Seas
 Red Sea • The Red Sea is connected to the Mediterranean Sea by the Suez Canal. • The Suez Canal does not have locks like the Panama Canal or the St. Lawrence Seaway because there is no change in elevation.
Red Sea • The Red Sea is connected to the Mediterranean Sea by the Suez Canal. • The Suez Canal does not have locks like the Panama Canal or the St. Lawrence Seaway because there is no change in elevation.
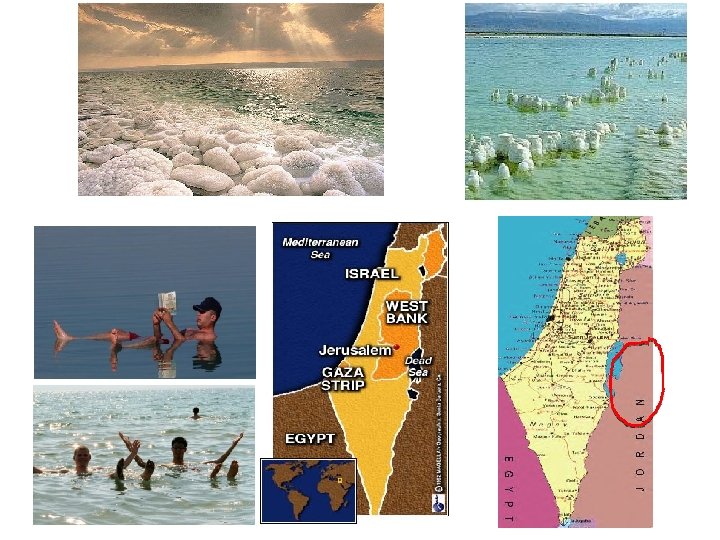
 Dead Sea • Landlocked salt lake • Lowest point on Earth- 1, 320 feet below sea level • Saltiest water in the world (33%) – So salty that only bacteria live in it – You float in the water! • Average of 330 days of full sunshine a year
Dead Sea • Landlocked salt lake • Lowest point on Earth- 1, 320 feet below sea level • Saltiest water in the world (33%) – So salty that only bacteria live in it – You float in the water! • Average of 330 days of full sunshine a year
 Black Sea • Major importance to states that fringe its coasts • Shallow near Danube Delta / exceeding 7, 000 ft. in south slopes of Pontic Mountains • Deep water ports in northern Turkey • Receiving plentiful freshwater; moderately salty • Virtually tideless • Overflows through Bosporus into Sea of Marmara and then through Dardanelles into the Aegean Sea
Black Sea • Major importance to states that fringe its coasts • Shallow near Danube Delta / exceeding 7, 000 ft. in south slopes of Pontic Mountains • Deep water ports in northern Turkey • Receiving plentiful freshwater; moderately salty • Virtually tideless • Overflows through Bosporus into Sea of Marmara and then through Dardanelles into the Aegean Sea
 Caspian Sea • Inland “sea” without outlet • The surface is 92 ft below sea level • Most of inflow from Volga • sea level dropping due to utilization of Volga and other waters for irrigation • Freight, ferries, passenger ships and fishing boats • As with Persian Gulf, tectonics that created Caspian Sea were favorable for huge accumulations of fossil fuels • Prior to 1991 negligence in protecting the environment
Caspian Sea • Inland “sea” without outlet • The surface is 92 ft below sea level • Most of inflow from Volga • sea level dropping due to utilization of Volga and other waters for irrigation • Freight, ferries, passenger ships and fishing boats • As with Persian Gulf, tectonics that created Caspian Sea were favorable for huge accumulations of fossil fuels • Prior to 1991 negligence in protecting the environment
 Straits and Waterways
Straits and Waterways
 Strategic Waterways • The Middle East has many strategic waterways, or narrow bodies of water that are important for trade or defense.
Strategic Waterways • The Middle East has many strategic waterways, or narrow bodies of water that are important for trade or defense.
 Bosporus and Dardanelles • The Bosporus and Dardanelles connect the Black Sea with the Mediterranean Sea. • Made up of the Dardanelles, the Bosporus, and the Sea of Marmara • The Bosporus splits the country of Turkey into two parts: Small part in Europe, Small part in Europe • Istanbul is an important city because it is located on the Bosporus and controls this important trade route. • The Asian part of Turkey includes the large peninsula called Anatolia.
Bosporus and Dardanelles • The Bosporus and Dardanelles connect the Black Sea with the Mediterranean Sea. • Made up of the Dardanelles, the Bosporus, and the Sea of Marmara • The Bosporus splits the country of Turkey into two parts: Small part in Europe, Small part in Europe • Istanbul is an important city because it is located on the Bosporus and controls this important trade route. • The Asian part of Turkey includes the large peninsula called Anatolia.
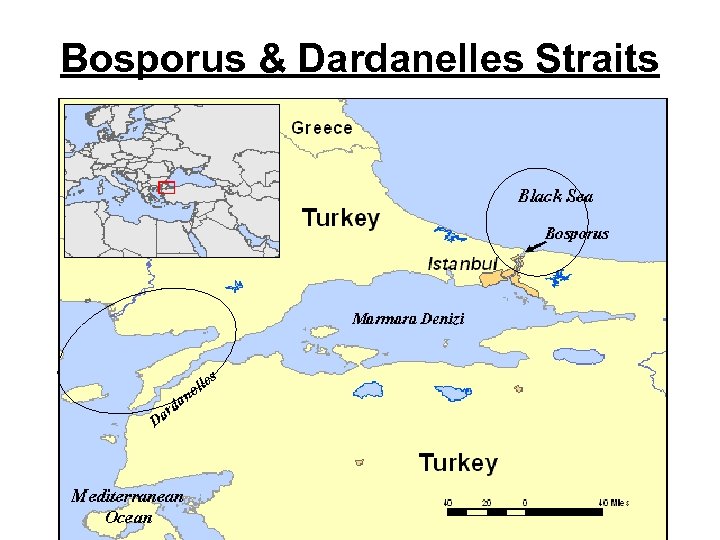 Bosporus & Dardanelles Straits
Bosporus & Dardanelles Straits
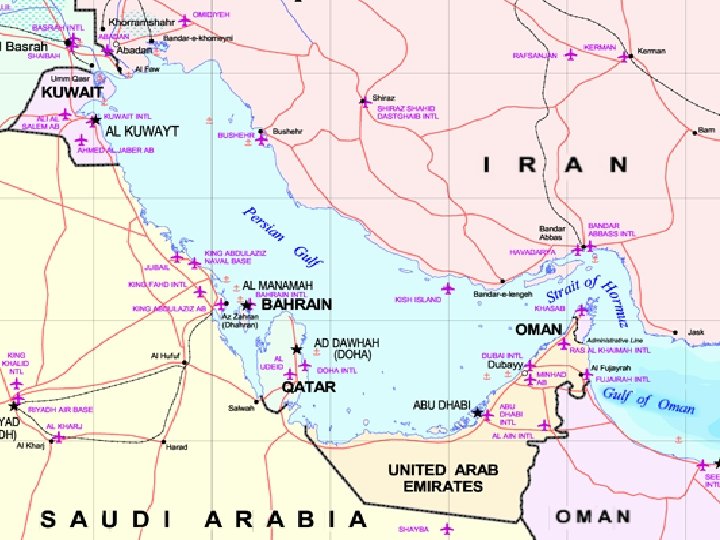
 Strait of Hormuz • The Strait of Hormuz connects the Persian Gulf with the Arabian Sea. • Iran is on one side of the strait and the U. A. E. and Oman are on the other side. • The strait is important because most of the oil in the world must be transported from the Persian Gulf to world markets.
Strait of Hormuz • The Strait of Hormuz connects the Persian Gulf with the Arabian Sea. • Iran is on one side of the strait and the U. A. E. and Oman are on the other side. • The strait is important because most of the oil in the world must be transported from the Persian Gulf to world markets.
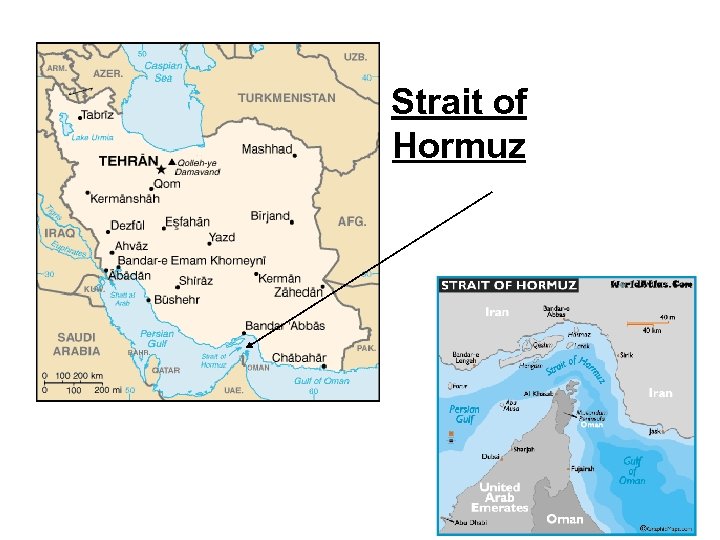 Strait of Hormuz
Strait of Hormuz
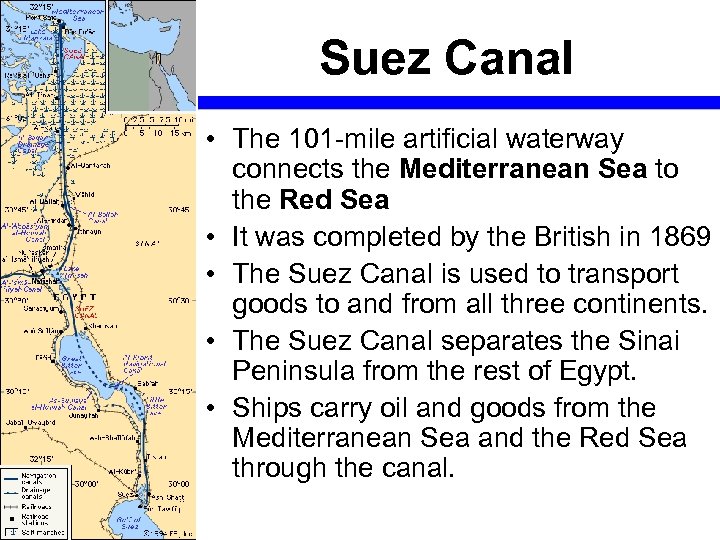 Suez Canal • The 101 -mile artificial waterway connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea • It was completed by the British in 1869 • The Suez Canal is used to transport goods to and from all three continents. • The Suez Canal separates the Sinai Peninsula from the rest of Egypt. • Ships carry oil and goods from the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea through the canal.
Suez Canal • The 101 -mile artificial waterway connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea • It was completed by the British in 1869 • The Suez Canal is used to transport goods to and from all three continents. • The Suez Canal separates the Sinai Peninsula from the rest of Egypt. • Ships carry oil and goods from the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea through the canal.
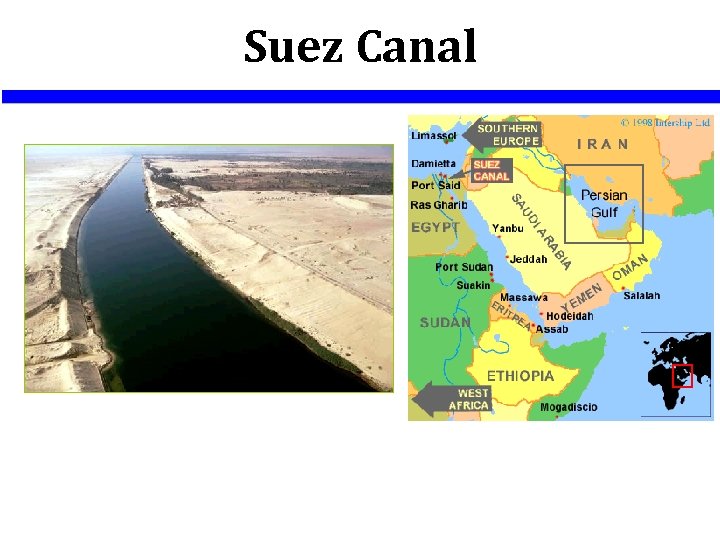 Suez Canal
Suez Canal
 Pair-Share • If you had to explain to your parents about the water features of the Middle East, how would you summarize it for them? • Why?
Pair-Share • If you had to explain to your parents about the water features of the Middle East, how would you summarize it for them? • Why?
 Rivers
Rivers
 The Rivers • There are very few major rivers in the region • The Tigris, Euphrates, and Nile rivers are the longest and most powerful • These rivers run through just a few countries of the entire region • Rivers are the main source of water for drinking and for power in many Southwest Asian countries – Countries without major rivers must also find other ways to generate electricity
The Rivers • There are very few major rivers in the region • The Tigris, Euphrates, and Nile rivers are the longest and most powerful • These rivers run through just a few countries of the entire region • Rivers are the main source of water for drinking and for power in many Southwest Asian countries – Countries without major rivers must also find other ways to generate electricity
 The Mighty Nile
The Mighty Nile
 The Mighty Nile River • THE WORLD’S LONGEST RIVER with 4, 240 miles, draining one tenth of Africa • The Nile gets its name from the Greek word "Nelios", meaning River Valley • Formed by union of Blue Nile and White Nile • The Nile and its tributaries flow though nine countries (flowing north) • Its source: The White Nile: Lake Victoria, Uganda • The Blue Nile: Lake Tana, Ethiopia. • Masses of water traverse the full width of the Sahara Desert! • White Nile from Lake Victoria into Sudd, joining Blue Nile (from Lake Tana) at Khartoum • Blue Nile is fed by monsoon rains of Ethiopian Plateau • Fluctuations of Blue Nile formerly led to famous floods in Egypt • Series of 5 cataracts / creation of the delta • Delta Egypt
The Mighty Nile River • THE WORLD’S LONGEST RIVER with 4, 240 miles, draining one tenth of Africa • The Nile gets its name from the Greek word "Nelios", meaning River Valley • Formed by union of Blue Nile and White Nile • The Nile and its tributaries flow though nine countries (flowing north) • Its source: The White Nile: Lake Victoria, Uganda • The Blue Nile: Lake Tana, Ethiopia. • Masses of water traverse the full width of the Sahara Desert! • White Nile from Lake Victoria into Sudd, joining Blue Nile (from Lake Tana) at Khartoum • Blue Nile is fed by monsoon rains of Ethiopian Plateau • Fluctuations of Blue Nile formerly led to famous floods in Egypt • Series of 5 cataracts / creation of the delta • Delta Egypt
 The Mighty Nile River Continued… • Water has been the key to life in this arid environment, since the beginning of time. • The Nile is an example of an exotic river because it receives its water as runoff in humid regions or from highland zones and then flows across large expanses of desert before reaching the Mediterranean Sea. • Along 2% of the Egyptian territory (Nile Valley and Delta) live more than 95% of the Egyptian population (72, 100, 000 in 2003). 95% OF THE PEOPLE LIVE IN 5% OF THE LAND • Other examples of exotic river systems are the Tigris. Euphrates system and the Jordan River.
The Mighty Nile River Continued… • Water has been the key to life in this arid environment, since the beginning of time. • The Nile is an example of an exotic river because it receives its water as runoff in humid regions or from highland zones and then flows across large expanses of desert before reaching the Mediterranean Sea. • Along 2% of the Egyptian territory (Nile Valley and Delta) live more than 95% of the Egyptian population (72, 100, 000 in 2003). 95% OF THE PEOPLE LIVE IN 5% OF THE LAND • Other examples of exotic river systems are the Tigris. Euphrates system and the Jordan River.
 The Mighty Nile River Continued… • Empties into the Mediterranean Sea • The land along the Nile is very fertile. • Floods on the river deposit silt, or finely ground fertile soil, all along the river. • Before it reaches the sea, the Nile fans out into a huge fertile delta. • Completion of Aswan High Dam in 1971 greatly altered the rivers regime (Lake Nasser) • The Aswan High Dam controls flooding on the Nile. • Because of the lack of silt, farmers need to use fertilizer to grow crops.
The Mighty Nile River Continued… • Empties into the Mediterranean Sea • The land along the Nile is very fertile. • Floods on the river deposit silt, or finely ground fertile soil, all along the river. • Before it reaches the sea, the Nile fans out into a huge fertile delta. • Completion of Aswan High Dam in 1971 greatly altered the rivers regime (Lake Nasser) • The Aswan High Dam controls flooding on the Nile. • Because of the lack of silt, farmers need to use fertilizer to grow crops.
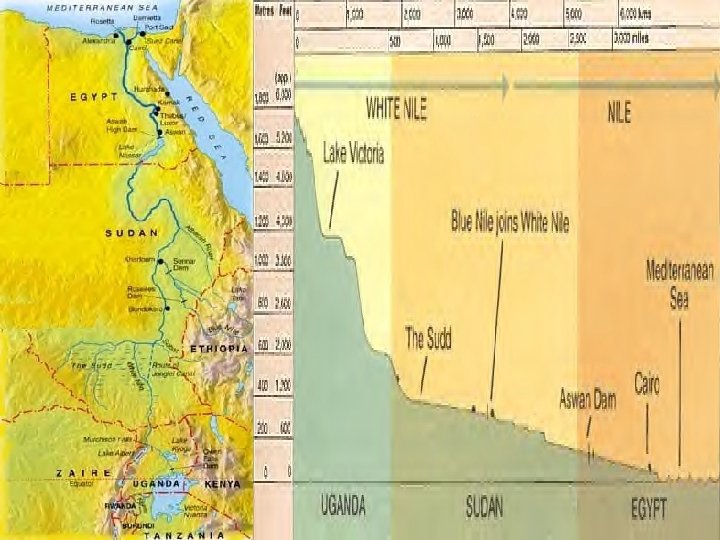
 Egypt: The “Gift of the Nile” Nile Delta Annual Nile Flooding
Egypt: The “Gift of the Nile” Nile Delta Annual Nile Flooding
 Everyday Activities on the Nile • • Tourism Farming Fishing Sometimes you’ll even see crocodiles!
Everyday Activities on the Nile • • Tourism Farming Fishing Sometimes you’ll even see crocodiles!
 Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
 Tigris and Euphrates • Both come from eastern Anatolian Highlands in Turkey and enter Gulf through Shatt al-Arab • They lose water as the cross flat deserts and their waters are diverted for irrigation • 90% of actual water is flow from runoff in Turkey • Euphrates is longer, but Tigris carries 25% more water • Increasing diversion of Euphrates by Turkey and Syria • Diversion of Tigris waters via Lake Tharthar to Euphrates • Iraq’s “third river” from Baghdad to Basrah (in 1992)
Tigris and Euphrates • Both come from eastern Anatolian Highlands in Turkey and enter Gulf through Shatt al-Arab • They lose water as the cross flat deserts and their waters are diverted for irrigation • 90% of actual water is flow from runoff in Turkey • Euphrates is longer, but Tigris carries 25% more water • Increasing diversion of Euphrates by Turkey and Syria • Diversion of Tigris waters via Lake Tharthar to Euphrates • Iraq’s “third river” from Baghdad to Basrah (in 1992)
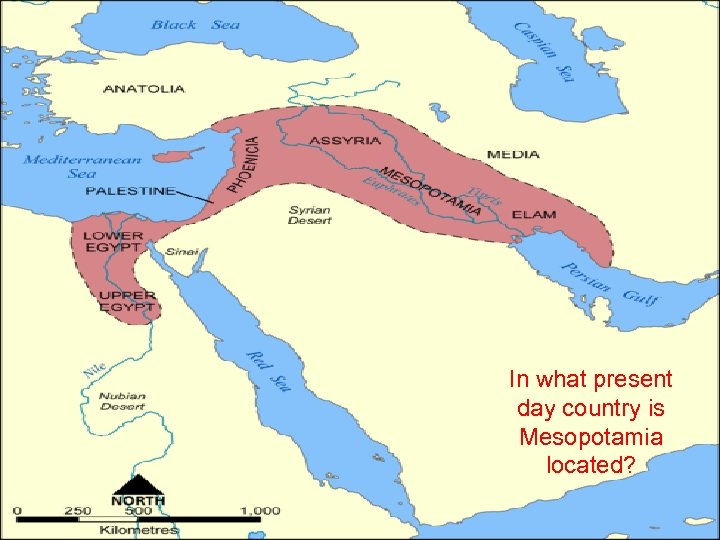 1. What two rivers run through the Fertile Crescent? 2. Which two river valley civilizations are shown on this map? In what present day country is Mesopotamia located?
1. What two rivers run through the Fertile Crescent? 2. Which two river valley civilizations are shown on this map? In what present day country is Mesopotamia located?
 Mesopotamia – The Land Between Two Rivers • Mesopotamia was a place where many cities began to grow • As its name suggests, Mesopotamia was located between two rivers. • The two rivers were the Tigris River and the Euphrates River. • Mesopotamia was located in the Middle East, and surrounded by desert. (what is now Iraq) • People came to Mesopotamia because the soil between the two rivers was very fertile. • Mesopotamia was part of a larger region called the Fertile Crescent.
Mesopotamia – The Land Between Two Rivers • Mesopotamia was a place where many cities began to grow • As its name suggests, Mesopotamia was located between two rivers. • The two rivers were the Tigris River and the Euphrates River. • Mesopotamia was located in the Middle East, and surrounded by desert. (what is now Iraq) • People came to Mesopotamia because the soil between the two rivers was very fertile. • Mesopotamia was part of a larger region called the Fertile Crescent.
 The Fertile Crescent • Arc-shaped region that stretches from the Tigris and Euphrates river valley to the Persian Gulf • Very fertile soil, where civilization started • Is prone to flooding • Constantly invaded by foreign powers throughout history: – Sumerians-Hittites-Assyrians-Babylonians. Persians-Greeks-Parthians-Romans-Arabs. Ottomans- British and French-United States • The shape is somewhat similar to a crescent (think of a crescent roll, or a crescent-shaped moon).
The Fertile Crescent • Arc-shaped region that stretches from the Tigris and Euphrates river valley to the Persian Gulf • Very fertile soil, where civilization started • Is prone to flooding • Constantly invaded by foreign powers throughout history: – Sumerians-Hittites-Assyrians-Babylonians. Persians-Greeks-Parthians-Romans-Arabs. Ottomans- British and French-United States • The shape is somewhat similar to a crescent (think of a crescent roll, or a crescent-shaped moon).
 The Cradle of Civilization • Mesopotamia is located in the Middle East, which is located in Southwest Asia. • As we’ve discussed before, the first civilizations and examples of writing were found in Southwest Asia. These things began in Mesopotamia. • When a newborn baby begins life, he or she is placed in a cradle. • Mesopotamia is called the cradle of civilization because the first civilizations began there, about 5, 500 years ago in 3500 B. C.
The Cradle of Civilization • Mesopotamia is located in the Middle East, which is located in Southwest Asia. • As we’ve discussed before, the first civilizations and examples of writing were found in Southwest Asia. These things began in Mesopotamia. • When a newborn baby begins life, he or she is placed in a cradle. • Mesopotamia is called the cradle of civilization because the first civilizations began there, about 5, 500 years ago in 3500 B. C.
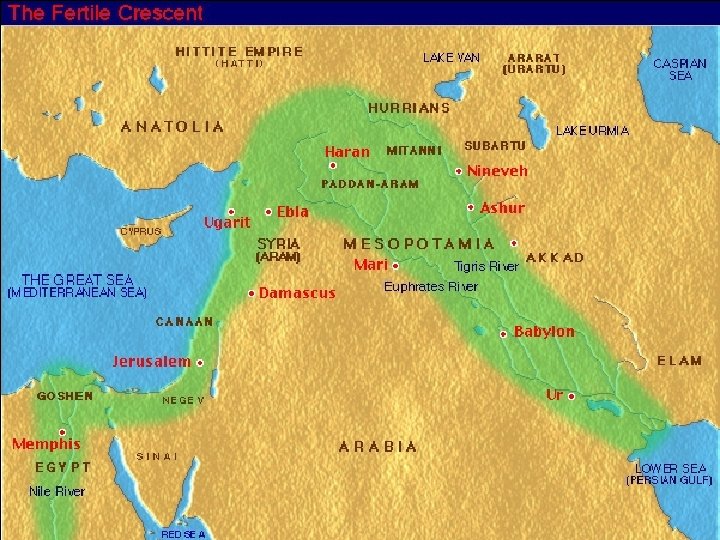
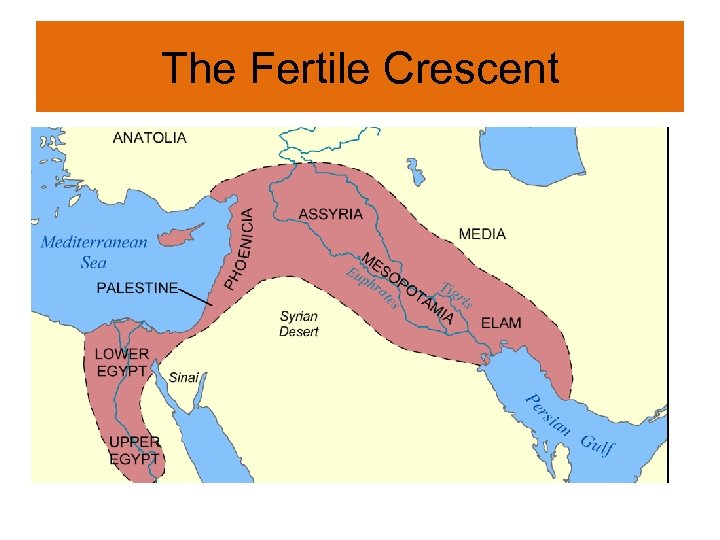 The Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent
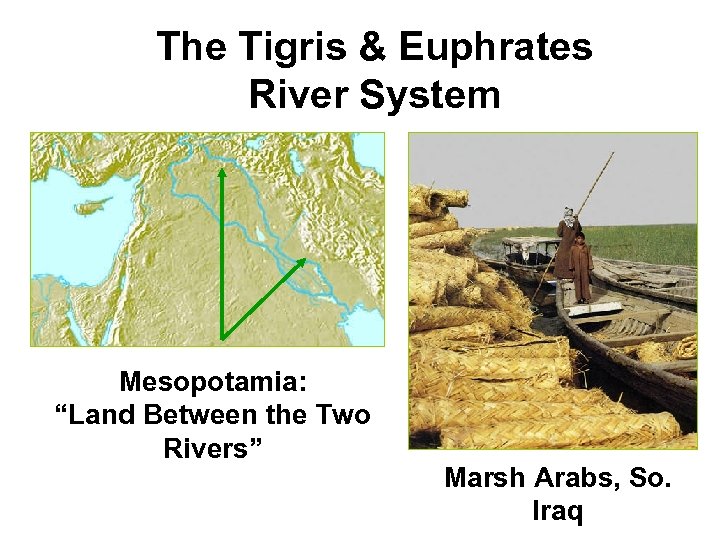 The Tigris & Euphrates River System Mesopotamia: “Land Between the Two Rivers” Marsh Arabs, So. Iraq
The Tigris & Euphrates River System Mesopotamia: “Land Between the Two Rivers” Marsh Arabs, So. Iraq
 Dust Storms Along the Tigris-Euphrates Flood Plains
Dust Storms Along the Tigris-Euphrates Flood Plains
 Jordan River
Jordan River
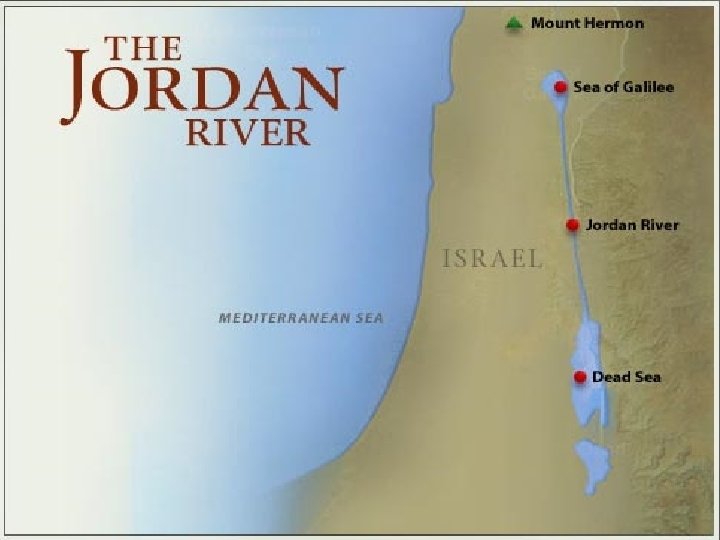
 Jordan River • The Jordan River begins in Syria and flows south through Israel and Jordan. • The river empties into a large lake called the Dead Sea. • The Jordan River provides water for both Jordan and Israel. • In the 1960’s, the Arab nations tried to divert water away from Israel by cutting off the supply of the Jordan River. • Because Israel controls Golan Heights, Jordan was unable to carry out this plan.
Jordan River • The Jordan River begins in Syria and flows south through Israel and Jordan. • The river empties into a large lake called the Dead Sea. • The Jordan River provides water for both Jordan and Israel. • In the 1960’s, the Arab nations tried to divert water away from Israel by cutting off the supply of the Jordan River. • Because Israel controls Golan Heights, Jordan was unable to carry out this plan.
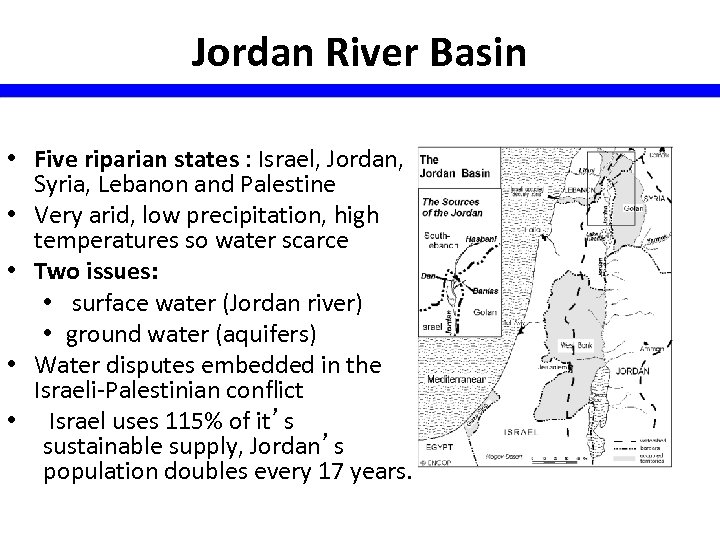 Jordan River Basin • Five riparian states : Israel, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon and Palestine • Very arid, low precipitation, high temperatures so water scarce • Two issues: • surface water (Jordan river) • ground water (aquifers) • Water disputes embedded in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict • Israel uses 115% of it’s sustainable supply, Jordan’s population doubles every 17 years.
Jordan River Basin • Five riparian states : Israel, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon and Palestine • Very arid, low precipitation, high temperatures so water scarce • Two issues: • surface water (Jordan river) • ground water (aquifers) • Water disputes embedded in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict • Israel uses 115% of it’s sustainable supply, Jordan’s population doubles every 17 years.
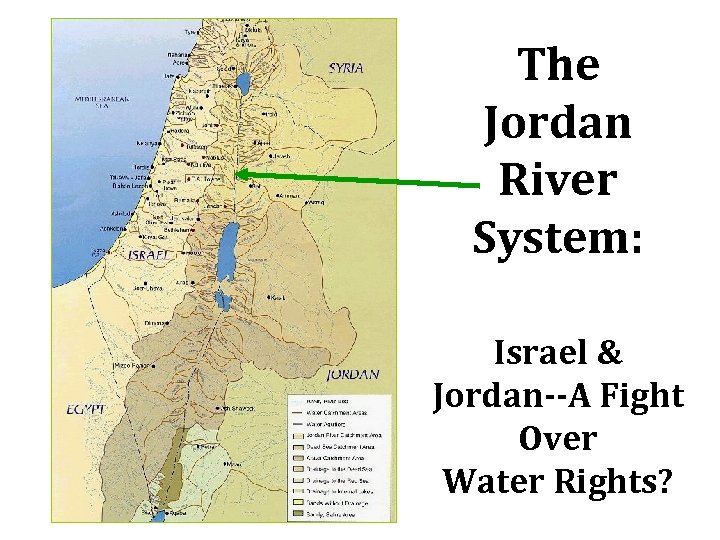 The Jordan River System: Israel & Jordan--A Fight Over Water Rights?
The Jordan River System: Israel & Jordan--A Fight Over Water Rights?
 The Jordan River Source • There are 5 countries entitled to a share of the available resource. – Jordan, Syria, Israel, Palestine and Lebanon. • Obviously politics and border issues continue to play a role in the division. • It is “agreed” that approximately 1200 million m 3 is the total “sustainable” shared abstraction. Most recent plans refer back to the • Johnston Plan (1955) which allocated this resource as follows Jordan: 720 mcm Israel: 400 mcm Syria: 132 mcm Lebanon: 35 mcm • Palestine's share was to be part of Jordan’s. – WHICH LEADS TO PROBLEMS 56% 31% 10. 3% 2. 7%
The Jordan River Source • There are 5 countries entitled to a share of the available resource. – Jordan, Syria, Israel, Palestine and Lebanon. • Obviously politics and border issues continue to play a role in the division. • It is “agreed” that approximately 1200 million m 3 is the total “sustainable” shared abstraction. Most recent plans refer back to the • Johnston Plan (1955) which allocated this resource as follows Jordan: 720 mcm Israel: 400 mcm Syria: 132 mcm Lebanon: 35 mcm • Palestine's share was to be part of Jordan’s. – WHICH LEADS TO PROBLEMS 56% 31% 10. 3% 2. 7%
 The Jordan River Source • Current abstraction from the Jordan river is unsustainable. • The Palestinian share is zero. • In 1967 all farms and lands along this traditionally rich farming area were confiscated. • Today the banks of the Jordan river are a closed military zone.
The Jordan River Source • Current abstraction from the Jordan river is unsustainable. • The Palestinian share is zero. • In 1967 all farms and lands along this traditionally rich farming area were confiscated. • Today the banks of the Jordan river are a closed military zone.

 Wadis and Oasis
Wadis and Oasis
 Wadis • Wadis § dry stream/riverbed that fill with water only after rainfall in a desert or steppe region. • A wadis is a dry riverbed in a desert that fills up when it rains.
Wadis • Wadis § dry stream/riverbed that fill with water only after rainfall in a desert or steppe region. • A wadis is a dry riverbed in a desert that fills up when it rains.
 Wadis – Instant Springs
Wadis – Instant Springs
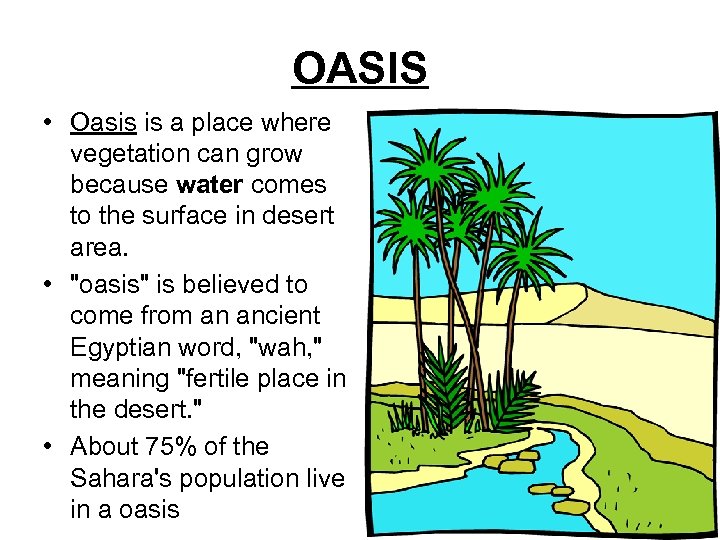 OASIS • Oasis is a place where vegetation can grow because water comes to the surface in desert area. • "oasis" is believed to come from an ancient Egyptian word, "wah, " meaning "fertile place in the desert. " • About 75% of the Sahara's population live in a oasis
OASIS • Oasis is a place where vegetation can grow because water comes to the surface in desert area. • "oasis" is believed to come from an ancient Egyptian word, "wah, " meaning "fertile place in the desert. " • About 75% of the Sahara's population live in a oasis
 Pair-Share • Based upon what we have learned about the freshwater rivers of the Middle East, summarize the top THREE water issues. • Explain.
Pair-Share • Based upon what we have learned about the freshwater rivers of the Middle East, summarize the top THREE water issues. • Explain.


