8cf47a3ed1643f2ab7a7cb9f9cc5c2d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 What is the Greenhouse Effect? How is the temperature of the Earth maintained? What is the Carbon Cycle?
What is the Greenhouse Effect? How is the temperature of the Earth maintained? What is the Carbon Cycle?
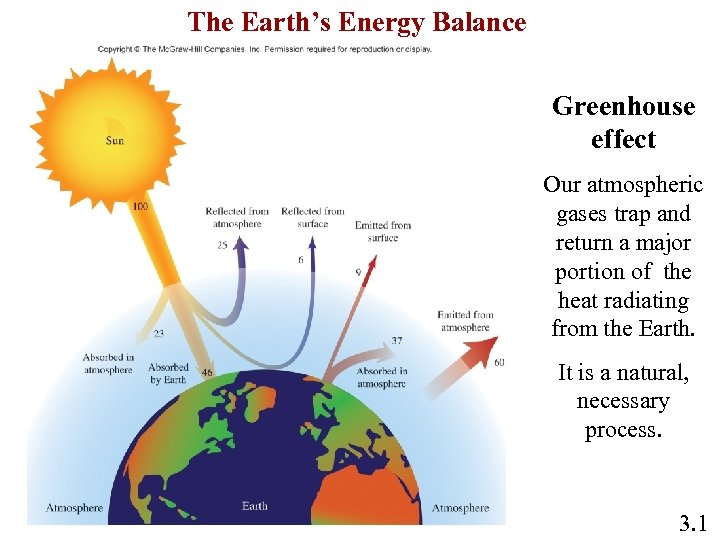 The Earth’s Energy Balance Greenhouse effect Our atmospheric gases trap and return a major portion of the heat radiating from the Earth. It is a natural, necessary process. 3. 1
The Earth’s Energy Balance Greenhouse effect Our atmospheric gases trap and return a major portion of the heat radiating from the Earth. It is a natural, necessary process. 3. 1
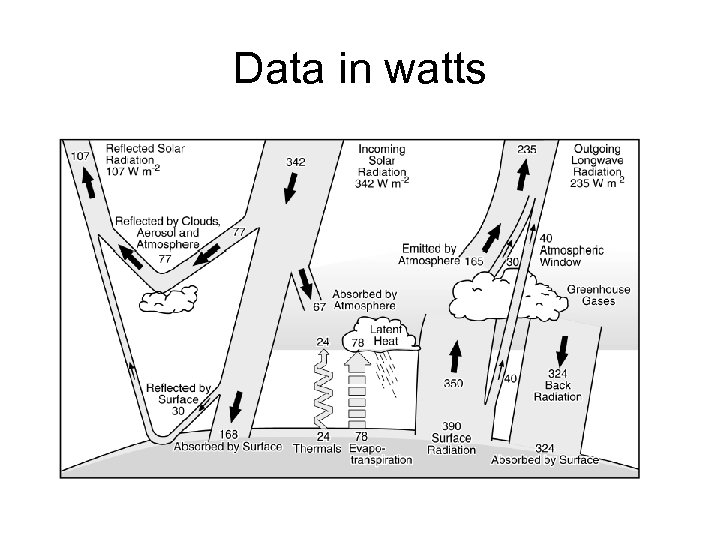 Data in watts
Data in watts
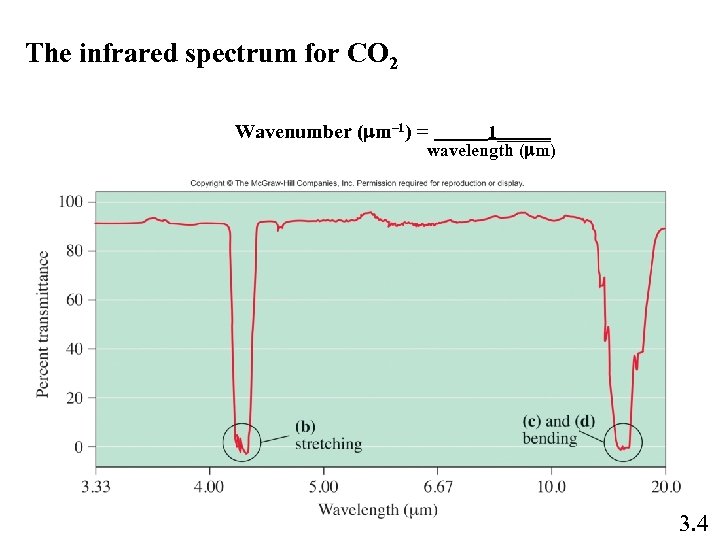 The infrared spectrum for CO 2 Wavenumber (mm– 1) = 1______ wavelength (mm) 3. 4
The infrared spectrum for CO 2 Wavenumber (mm– 1) = 1______ wavelength (mm) 3. 4
 Climate Forcing/Feedback How does Earth stay Comfortable for Us? • Gaia Hypothesis – Biological and Physical Processes Produce Homeostasis • Negative is Good – Feedback control • Positive is Bad – Oscillate out of control
Climate Forcing/Feedback How does Earth stay Comfortable for Us? • Gaia Hypothesis – Biological and Physical Processes Produce Homeostasis • Negative is Good – Feedback control • Positive is Bad – Oscillate out of control
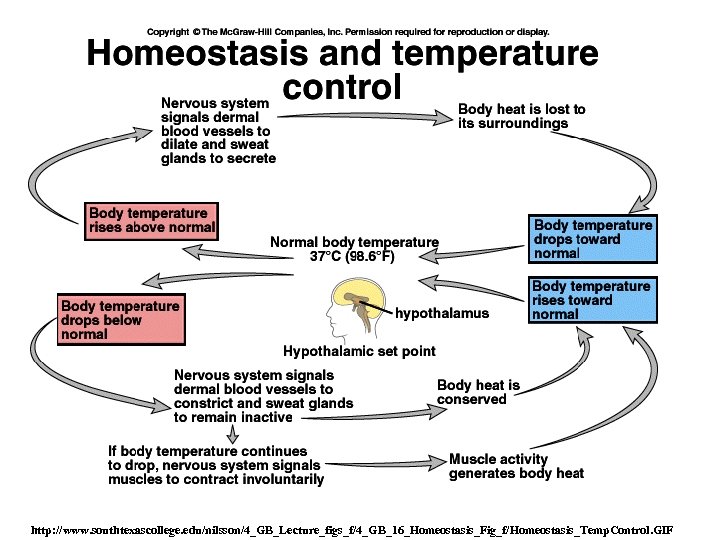 http: //www. southtexascollege. edu/nilsson/4_GB_Lecture_figs_f/4_GB_16_Homeostasis_Fig_f/Homeostasis_Temp. Control. GIF
http: //www. southtexascollege. edu/nilsson/4_GB_Lecture_figs_f/4_GB_16_Homeostasis_Fig_f/Homeostasis_Temp. Control. GIF
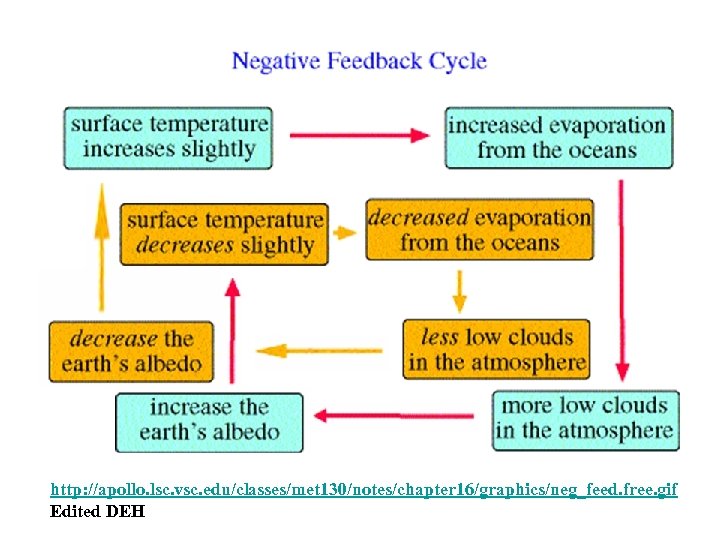 http: //apollo. lsc. vsc. edu/classes/met 130/notes/chapter 16/graphics/neg_feed. free. gif Edited DEH
http: //apollo. lsc. vsc. edu/classes/met 130/notes/chapter 16/graphics/neg_feed. free. gif Edited DEH
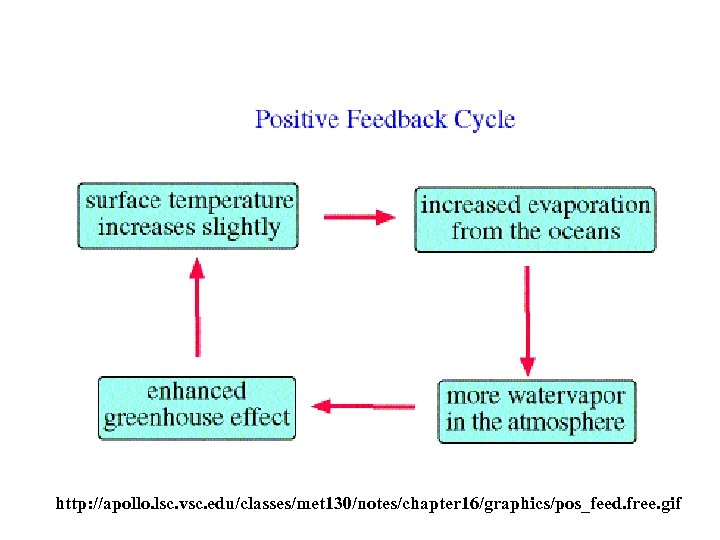 http: //apollo. lsc. vsc. edu/classes/met 130/notes/chapter 16/graphics/pos_feed. free. gif
http: //apollo. lsc. vsc. edu/classes/met 130/notes/chapter 16/graphics/pos_feed. free. gif
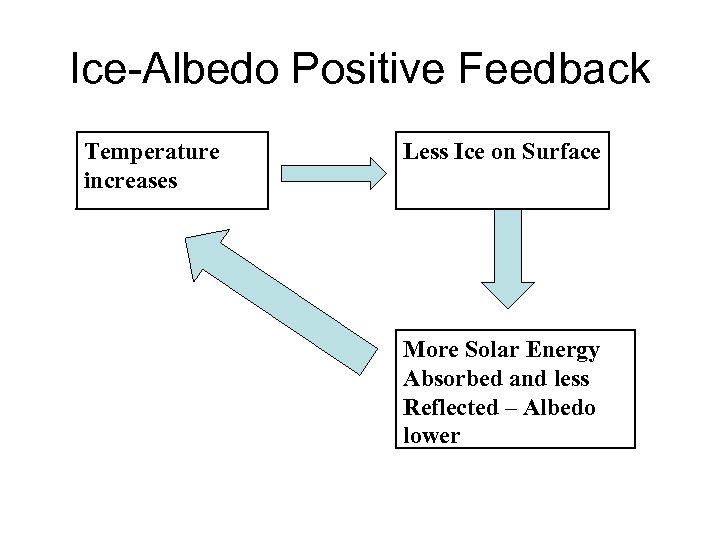 Ice-Albedo Positive Feedback Temperature increases Less Ice on Surface More Solar Energy Absorbed and less Reflected – Albedo lower
Ice-Albedo Positive Feedback Temperature increases Less Ice on Surface More Solar Energy Absorbed and less Reflected – Albedo lower
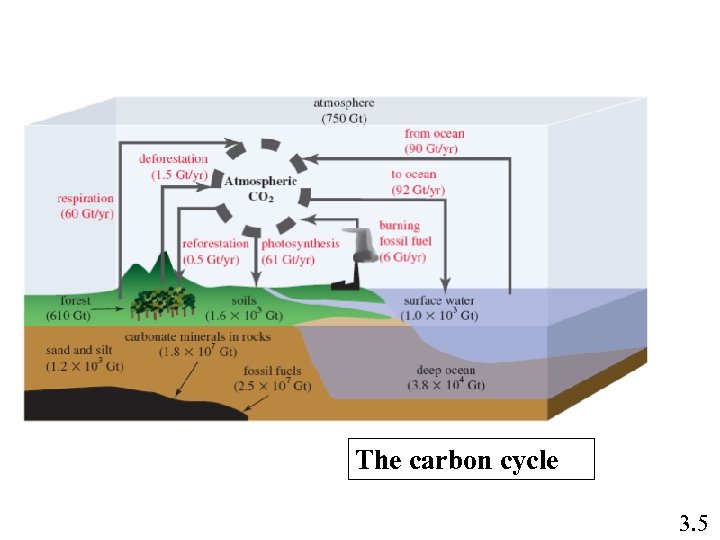 The carbon cycle 3. 5
The carbon cycle 3. 5
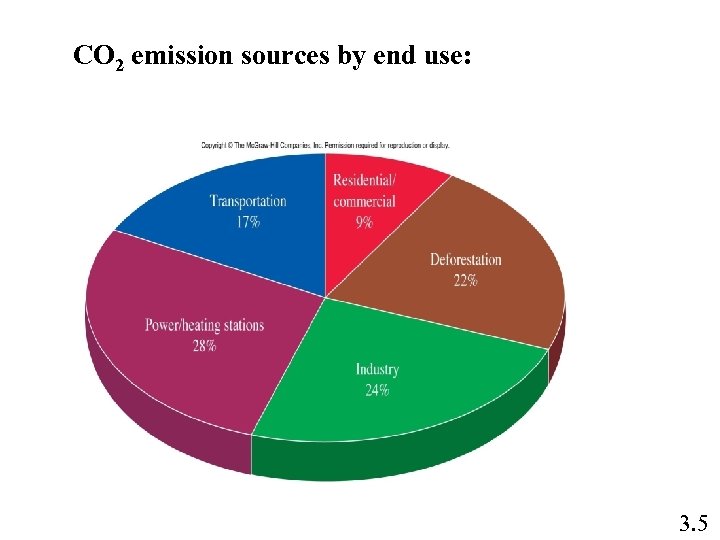 CO 2 emission sources by end use: 3. 5
CO 2 emission sources by end use: 3. 5
 Ways to reduce CO 2 Emissions • Where is the Biggest Target? • Where are the Easy Targets?
Ways to reduce CO 2 Emissions • Where is the Biggest Target? • Where are the Easy Targets?
 Ways to reduce CO 2 Emissions Power Sector • Energy Efficiency – use less • Switch from Coal to Natural Gas -50% red. • Renewable Energy – Solar electric – Solar Thermal – Wind – driven by solar heating of earth – Hydropower – related to solar – Bio. Fuels – solar energy capture • Plant based • Algae based
Ways to reduce CO 2 Emissions Power Sector • Energy Efficiency – use less • Switch from Coal to Natural Gas -50% red. • Renewable Energy – Solar electric – Solar Thermal – Wind – driven by solar heating of earth – Hydropower – related to solar – Bio. Fuels – solar energy capture • Plant based • Algae based
 Combined Heat and Power • Use “waste heat” • 90 -95% total efficiency 1/3 the CO 2 • Over 200 College and University systems – Yale 60 Megawatt – Electricity – Steam and hot water
Combined Heat and Power • Use “waste heat” • 90 -95% total efficiency 1/3 the CO 2 • Over 200 College and University systems – Yale 60 Megawatt – Electricity – Steam and hot water
 How do scientists study climate? • • Collect data, historical and paleo. Consider physical mechanisms at work Develop models and test them Limitations of science – Can’t prove a positive – Eliminate possibilities – What remains is accepted
How do scientists study climate? • • Collect data, historical and paleo. Consider physical mechanisms at work Develop models and test them Limitations of science – Can’t prove a positive – Eliminate possibilities – What remains is accepted
 Why is there still a ? • Correlation does not PROVE Causation • Climate Models (GCM’s) Still Imperfect – Cloud Impacts Undertain • Wishful Thinking
Why is there still a ? • Correlation does not PROVE Causation • Climate Models (GCM’s) Still Imperfect – Cloud Impacts Undertain • Wishful Thinking
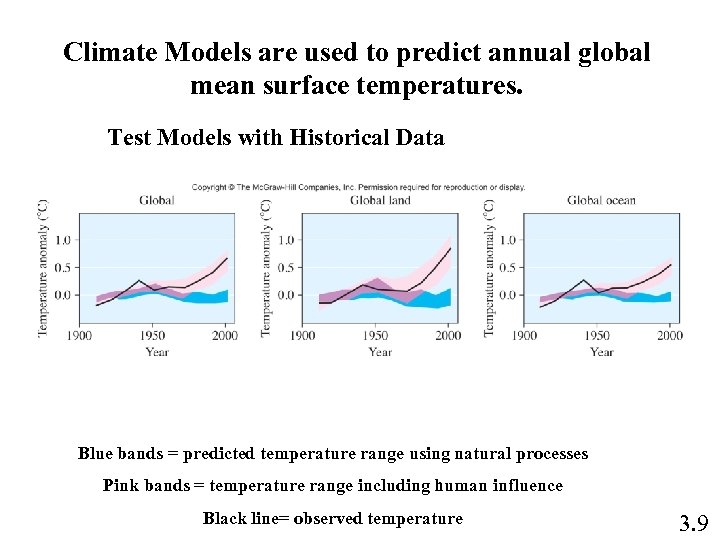 Climate Models are used to predict annual global mean surface temperatures. Test Models with Historical Data Blue bands = predicted temperature range using natural processes Pink bands = temperature range including human influence Black line= observed temperature 3. 9
Climate Models are used to predict annual global mean surface temperatures. Test Models with Historical Data Blue bands = predicted temperature range using natural processes Pink bands = temperature range including human influence Black line= observed temperature 3. 9
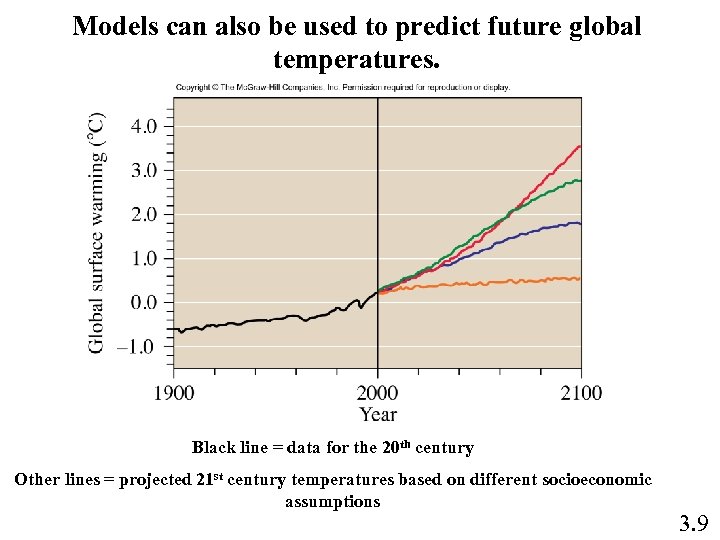 Models can also be used to predict future global temperatures. Black line = data for the 20 th century Other lines = projected 21 st century temperatures based on different socioeconomic assumptions 3. 9
Models can also be used to predict future global temperatures. Black line = data for the 20 th century Other lines = projected 21 st century temperatures based on different socioeconomic assumptions 3. 9
 Limitations of Models • Assume linear change • Assume same mechanisms of climate continue to function • Role of clouds not known with certainty • Polar Vortex Collapse • Gulf Stream (Thermo-haline circulation) • Air Transport in Troposphere – Convection cell position
Limitations of Models • Assume linear change • Assume same mechanisms of climate continue to function • Role of clouds not known with certainty • Polar Vortex Collapse • Gulf Stream (Thermo-haline circulation) • Air Transport in Troposphere – Convection cell position
 Kyoto Protocol – 1997 Conference • Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) certified the scientific basis of the greenhouse effect. • Kyoto Protocol established goals to stabilize and reduce atmospheric greenhouse gases. • Emission targets set to reduce emissions of six greenhouse gases from 1990 levels. (CO 2, CH 4, NO, HFCs, PFCs, and SF 6) • Trading of emission credits allowed. 3. 11
Kyoto Protocol – 1997 Conference • Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) certified the scientific basis of the greenhouse effect. • Kyoto Protocol established goals to stabilize and reduce atmospheric greenhouse gases. • Emission targets set to reduce emissions of six greenhouse gases from 1990 levels. (CO 2, CH 4, NO, HFCs, PFCs, and SF 6) • Trading of emission credits allowed. 3. 11
 The Kyoto mechanisms • Emissions trading – known as “the carbon market" • Clean development mechanism (CDM) – Polluters can reduce emissions in developing countries and get credit. • Joint implementation (JI). – Eg. USA could buy forests in Brazil and get credit for carbon sinks
The Kyoto mechanisms • Emissions trading – known as “the carbon market" • Clean development mechanism (CDM) – Polluters can reduce emissions in developing countries and get credit. • Joint implementation (JI). – Eg. USA could buy forests in Brazil and get credit for carbon sinks
 The Kyoto mechanisms • • Registry System – Record transactions Annual Reports Compliance System Adaptation Fund – Money to help poor countries adapt to Climate Change
The Kyoto mechanisms • • Registry System – Record transactions Annual Reports Compliance System Adaptation Fund – Money to help poor countries adapt to Climate Change
 Where are we today? (2009) • Copenhagen Meeting – Kyoto expires in 2012 – Kyoto goals not met – US, China, India, and Australia never signed – Need to move forward with new agreement – Can the US-China-India- and Australia join? • Meeting begins with real optimism!
Where are we today? (2009) • Copenhagen Meeting – Kyoto expires in 2012 – Kyoto goals not met – US, China, India, and Australia never signed – Need to move forward with new agreement – Can the US-China-India- and Australia join? • Meeting begins with real optimism!
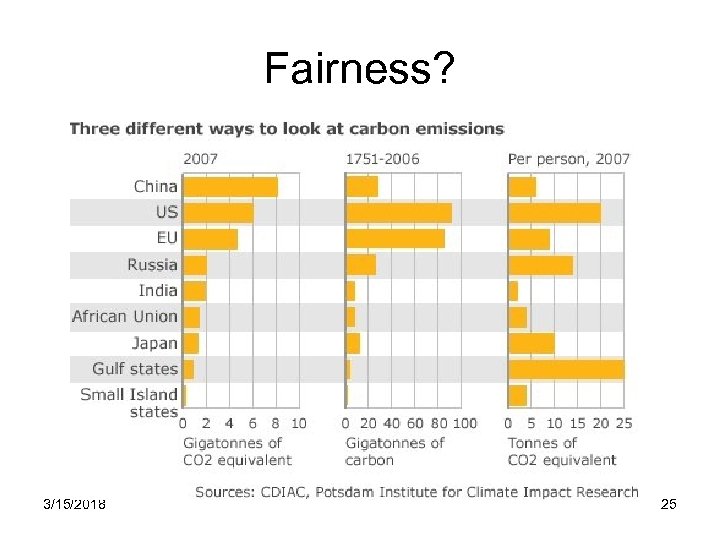 Fairness? 3/15/2018 25
Fairness? 3/15/2018 25


