52def99ee055908091f7d81ed6deec72.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 4
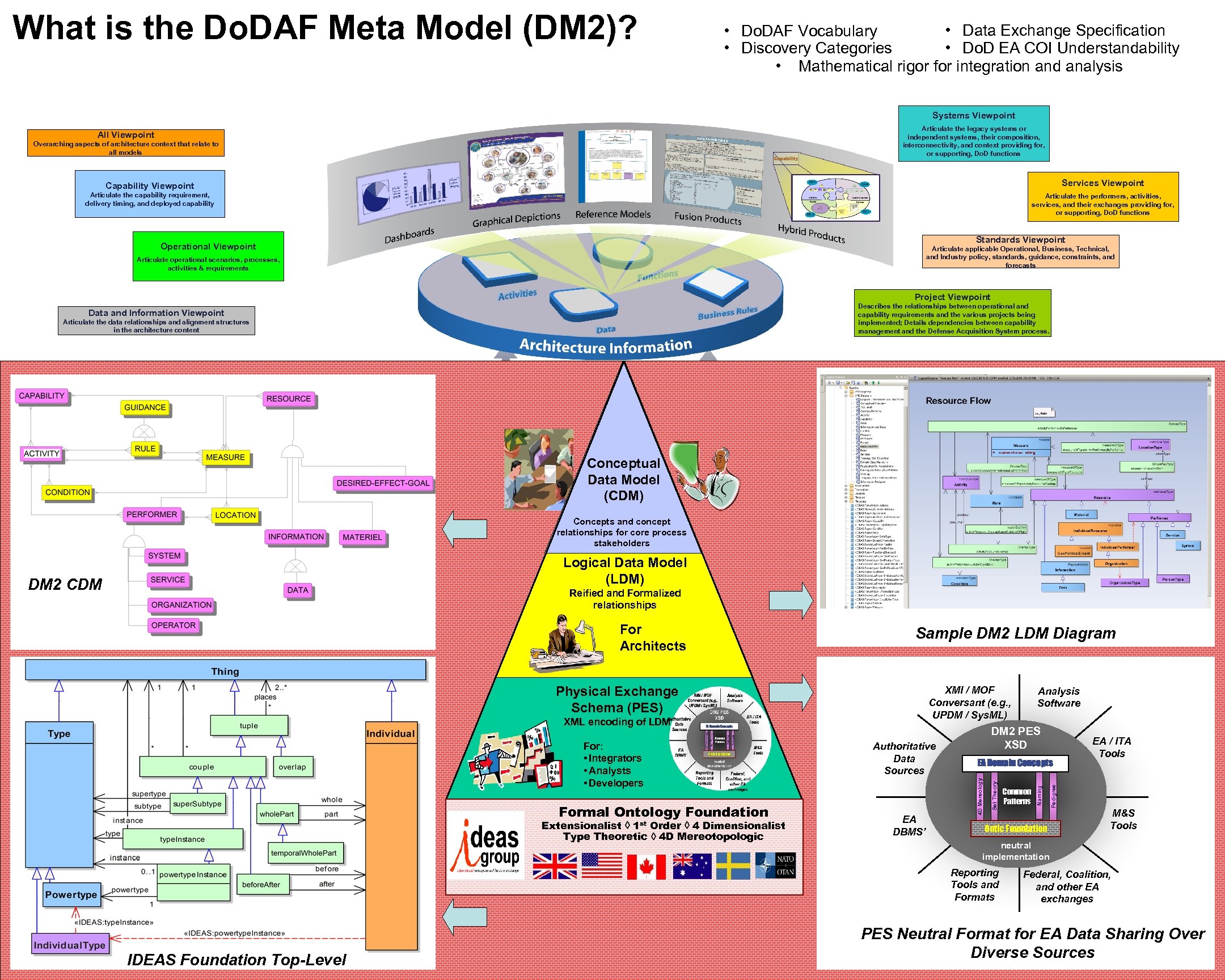 What is the Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2)? • Data Exchange Specification • Do. DAF Vocabulary • Do. D EA COI Understandability • Discovery Categories • Mathematical rigor for integration and analysis Systems Viewpoint Articulate the legacy systems or independent systems, their composition, interconnectivity, and context providing for, or supporting, Do. D functions All Viewpoint Overarching aspects of architecture context that relate to all models Capability Viewpoint Services Viewpoint Articulate the capability requirement, delivery timing, and deployed capability Articulate the performers, activities, services, and their exchanges providing for, or supporting, Do. D functions Standards Viewpoint Operational Viewpoint Articulate applicable Operational, Business, Technical, and Industry policy, standards, guidance, constraints, and forecasts Articulate operational scenarios, processes, activities & requirements Project Viewpoint Describes the relationships between operational and capability requirements and the various projects being implemented; Details dependencies between capability management and the Defense Acquisition System process. Data and Information Viewpoint Articulate the data relationships and alignment structures in the architecture content Conceptual Data Model (CDM) Concepts and concept relationships for core process stakeholders Logical Data Model (LDM) DM 2 CDM Reified and Formalized relationships Sample DM 2 LDM Diagram XMI / MOF Conversant (e. g. , UPDM / Sys. ML) Formal Ontology Foundation Extensionalist à 1 st Order à 4 Dimensionalist Type Theoretic à 4 D Mereotopologic Authoritative Data Sources EA DBMS’ EA Domain Concepts Ontic Foundation EA / ITA Tools M&S Tools neutral implementation Reporting Tools and Formats IDEAS Foundation Top-Level Common Patterns Pedigree For: • Integrators • Analysts • Developers DM 2 PES XSD Set Theory XML encoding of LDM Analysis Software Naming Physical Exchange Schema (PES) 4 D Mereology For Architects Federal, Coalition, and other EA exchanges PES Neutral Format for EA Data Sharing Over Diverse Sources
What is the Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2)? • Data Exchange Specification • Do. DAF Vocabulary • Do. D EA COI Understandability • Discovery Categories • Mathematical rigor for integration and analysis Systems Viewpoint Articulate the legacy systems or independent systems, their composition, interconnectivity, and context providing for, or supporting, Do. D functions All Viewpoint Overarching aspects of architecture context that relate to all models Capability Viewpoint Services Viewpoint Articulate the capability requirement, delivery timing, and deployed capability Articulate the performers, activities, services, and their exchanges providing for, or supporting, Do. D functions Standards Viewpoint Operational Viewpoint Articulate applicable Operational, Business, Technical, and Industry policy, standards, guidance, constraints, and forecasts Articulate operational scenarios, processes, activities & requirements Project Viewpoint Describes the relationships between operational and capability requirements and the various projects being implemented; Details dependencies between capability management and the Defense Acquisition System process. Data and Information Viewpoint Articulate the data relationships and alignment structures in the architecture content Conceptual Data Model (CDM) Concepts and concept relationships for core process stakeholders Logical Data Model (LDM) DM 2 CDM Reified and Formalized relationships Sample DM 2 LDM Diagram XMI / MOF Conversant (e. g. , UPDM / Sys. ML) Formal Ontology Foundation Extensionalist à 1 st Order à 4 Dimensionalist Type Theoretic à 4 D Mereotopologic Authoritative Data Sources EA DBMS’ EA Domain Concepts Ontic Foundation EA / ITA Tools M&S Tools neutral implementation Reporting Tools and Formats IDEAS Foundation Top-Level Common Patterns Pedigree For: • Integrators • Analysts • Developers DM 2 PES XSD Set Theory XML encoding of LDM Analysis Software Naming Physical Exchange Schema (PES) 4 D Mereology For Architects Federal, Coalition, and other EA exchanges PES Neutral Format for EA Data Sharing Over Diverse Sources
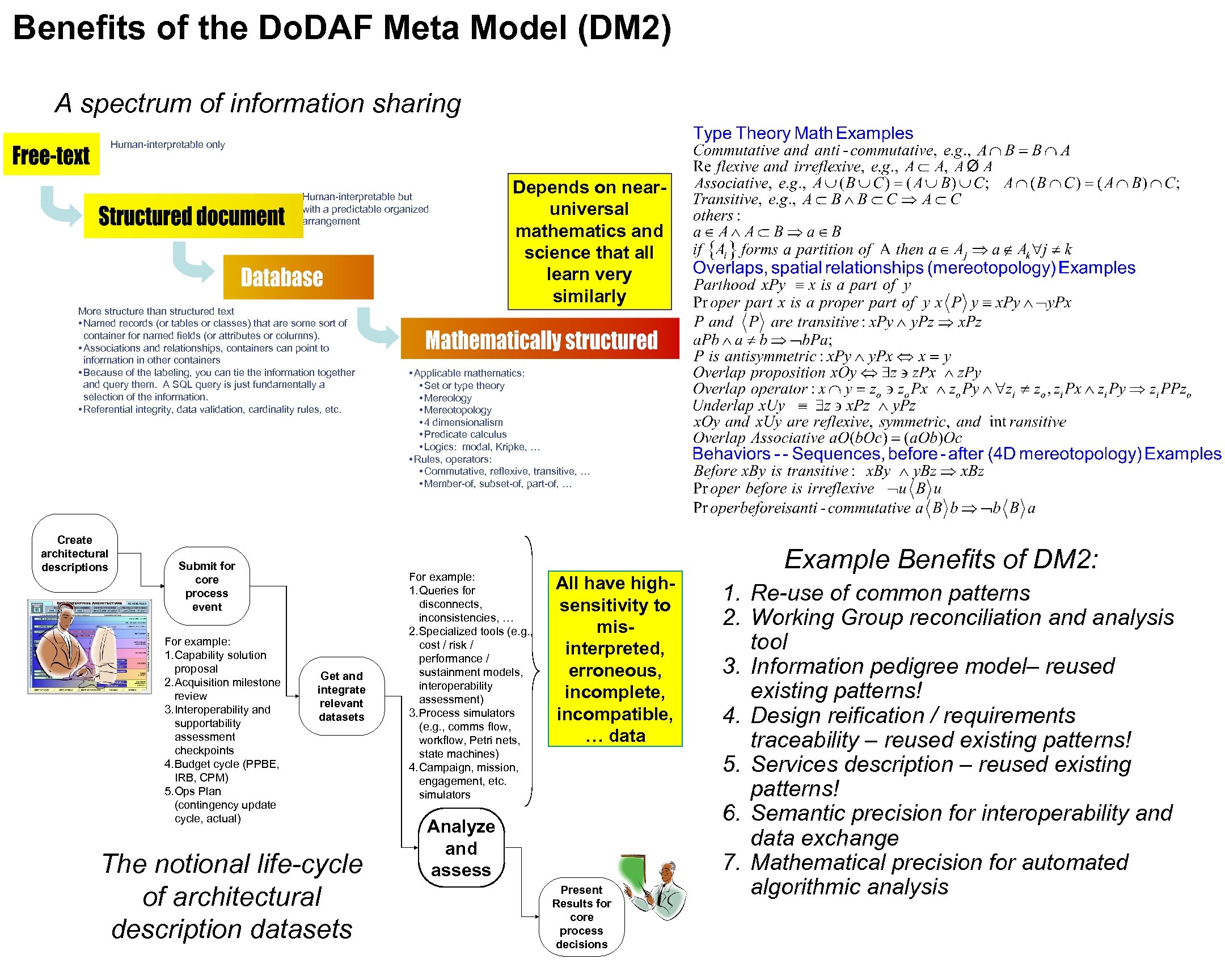 Benefits of the Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2) A spectrum of information sharing Human-interpretable only Human-interpretable but with a predictable organized arrangement More structure than structured text • Named records (or tables or classes) that are some sort of container for named fields (or attributes or columns). • Associations and relationships, containers can point to information in other containers • Because of the labeling, you can tie the information together and query them. A SQL query is just fundamentally a selection of the information. • Referential integrity, data validation, cardinality rules, etc. Create architectural descriptions Submit for core process event For example: 1. Capability solution proposal 2. Acquisition milestone review 3. Interoperability and supportability assessment checkpoints 4. Budget cycle (PPBE, IRB, CPM) 5. Ops Plan (contingency update cycle, actual) Get and integrate relevant datasets The notional life-cycle of architectural description datasets Depends on nearuniversal mathematics and science that all learn very similarly • Applicable mathematics: • Set or type theory • Mereology • Mereotopology • 4 dimensionalism • Predicate calculus • Logics: modal, Kripke, … • Rules, operators: • Commutative, reflexive, transitive, … • Member-of, subset-of, part-of, … For example: 1. Queries for disconnects, inconsistencies, … 2. Specialized tools (e. g. , cost / risk / performance / sustainment models, interoperability assessment) 3. Process simulators (e. g. , comms flow, workflow, Petri nets, state machines) 4. Campaign, mission, engagement, etc. simulators All have highsensitivity to misinterpreted, erroneous, incomplete, incompatible, … data Analyze and assess Present Results for core process decisions Example Benefits of DM 2: 1. Re-use of common patterns 2. Working Group reconciliation and analysis tool 3. Information pedigree model– reused existing patterns! 4. Design reification / requirements traceability – reused existing patterns! 5. Services description – reused existing patterns! 6. Semantic precision for interoperability and data exchange 7. Mathematical precision for automated algorithmic analysis
Benefits of the Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2) A spectrum of information sharing Human-interpretable only Human-interpretable but with a predictable organized arrangement More structure than structured text • Named records (or tables or classes) that are some sort of container for named fields (or attributes or columns). • Associations and relationships, containers can point to information in other containers • Because of the labeling, you can tie the information together and query them. A SQL query is just fundamentally a selection of the information. • Referential integrity, data validation, cardinality rules, etc. Create architectural descriptions Submit for core process event For example: 1. Capability solution proposal 2. Acquisition milestone review 3. Interoperability and supportability assessment checkpoints 4. Budget cycle (PPBE, IRB, CPM) 5. Ops Plan (contingency update cycle, actual) Get and integrate relevant datasets The notional life-cycle of architectural description datasets Depends on nearuniversal mathematics and science that all learn very similarly • Applicable mathematics: • Set or type theory • Mereology • Mereotopology • 4 dimensionalism • Predicate calculus • Logics: modal, Kripke, … • Rules, operators: • Commutative, reflexive, transitive, … • Member-of, subset-of, part-of, … For example: 1. Queries for disconnects, inconsistencies, … 2. Specialized tools (e. g. , cost / risk / performance / sustainment models, interoperability assessment) 3. Process simulators (e. g. , comms flow, workflow, Petri nets, state machines) 4. Campaign, mission, engagement, etc. simulators All have highsensitivity to misinterpreted, erroneous, incomplete, incompatible, … data Analyze and assess Present Results for core process decisions Example Benefits of DM 2: 1. Re-use of common patterns 2. Working Group reconciliation and analysis tool 3. Information pedigree model– reused existing patterns! 4. Design reification / requirements traceability – reused existing patterns! 5. Services description – reused existing patterns! 6. Semantic precision for interoperability and data exchange 7. Mathematical precision for automated algorithmic analysis
 How to Implement the Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2) Join the DM 2 Working Group! • DM 2 WG open to all • Collaboration Site • Business rules, e. g. , 1. –Aggregation and subtype rules • Coordination with many other groups, e. g. , –Controlled vocabulary –Data models –Vendors and implementers –Software and systems organizations 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. Current baseline CDM, LDM, and PES files and documentation 2. Working copy 3. IDEAS model and profile 4. Folders with: 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. Outreach and Tutorial Onsites -- Mike. Wayson@osd. mil ‾ WG information ‾ References and research ‾ Tutorials and briefings 5. Next meeting info 6. Links to IDEAS & BORO IDEAS Partial Bibliography 1. 2. 3. DM 2 Description Documents Berger, Peter L, and Thomas Luckmann; The Social Construction of Reality; Doubleday & Company, Garden City, New York; 1966. Casati, Roberto, and Achille C Varzi; Holes and other Superficialities; The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts; 1995. Casati, Roberto, and Achille C Varzi; Parts and Places: The Structure of Spatial Representation; The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts; 1999. Clark, Bowman L; “Individuals and Points”; Notre Dame Journal of Formal Logic, Vol. 26; 1985. Coquand, Thierry; “Type Theory”; Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy; 2006. Davenport, Thomas H, and Laurence Prusak; Working Knowlege: How Organizations Manage What They Know; Harvard Business School Press, Boston, Massachusetts; 1998. Gilbert, Margaret; On Social Facts; Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey; 1992. Grenon, Pierre, and Barry Smith; “The Cornucopia of Formal-Ontological Relations”; Dialectica. Vol. 58; 2004 Grenon, Pierre, and Barry Smith; “Snap and Span: Toward Dynamic Spatial Ontology”; Spatial Cognition and Computation; Lawrence Erlbaum Assosiates, Inc, Leipzig, Germany. Hacking, Ian; Historical Ontology; Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts; 2002. Hawley, Katherine; How Things Persist; Oxford University Press, Oxford; 2001 Janssen, Terry, et al; A Multi- INT Sematic Reasoning Framework for Intelligence Analysis Support Kay, Paul; “Taxonomy and Semantic Contrast”; Language; Vols. 47, number 4; University of California, Berkeley, CA, 1971. Kempson, Ruth M; Semantic Theory; Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; 1977. Levinson, Stephen C; Pragmatics; Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; 1984. Lyons, John; Language, Meaning, & Context; Fontana Paperbacks, Great Britain; 1981. Nerlich, Graham; The Shape of Space; Second ed; Cambridge University Press, New York, NY; 1994. Partee, Barbara H, Alice Ter Meulen, and Robert E Wall; Mathematical Methods in Linguistics, Vol. 30; Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht; 1990. Partridge, Chris; Business Objects: Re-Engineering for Re-Use; The Boro Centre; 2005. Potter, Michael; Set Theory and its Philosophy; Oxford University Press, Oxford; 2004. Pulman, S G; Word Meaning and Belief; Ed. James R Hurford and John A Hawkins; Croom Helm Linguistics Series; Billing & Sons Limited, Great Britain; 1983. Sider, Theodore; Four Dimensionalism: An Ontology of Persistence and Time; Oxford University Press, Oxford; 2001. Simons, Peter; Parts: A Study in Ontology; Oxford University Press, Oxford; 1987. Smith, Barry; “Against Fantology”; Experience and Analysis; By M E Reicher and J C Marek; 2005. Smith, Barry; “The Basic Tools of Formal Ontology”; Formal Ontology in Information Systems; IOS Press, Amsterdam; Frontiers in Artifitial Intellegence and Applications; 1998 Smith, Barry; “Mereotopology: A Theory of Parts and Boundaries”; Data and Knowledge Engineering; Department of Philosophy, Buffalo, New York; 1996. Smith, Barry, and David M Mark; “Do Mountains Exist? Toward an Ontology of Landforms. ” Enviorment & Planning B (Planning and Design); National Center for Geographic Information and Analysis, Buffalo, New York; 2009. Stein, Lynn Andrea; “Imagination and Situated Cognition”; Thinking about Android Epistemology; Ed. Kenneth M Ford, Clark Glymour, and Partick J Hayes; AAAI Press, Menlo Park; 2006. Other ontology resources: IDEAS Group, BORO, Matthew West, Model. Futures, Barry Smith / NCOR
How to Implement the Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2) Join the DM 2 Working Group! • DM 2 WG open to all • Collaboration Site • Business rules, e. g. , 1. –Aggregation and subtype rules • Coordination with many other groups, e. g. , –Controlled vocabulary –Data models –Vendors and implementers –Software and systems organizations 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. Current baseline CDM, LDM, and PES files and documentation 2. Working copy 3. IDEAS model and profile 4. Folders with: 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. Outreach and Tutorial Onsites -- Mike. Wayson@osd. mil ‾ WG information ‾ References and research ‾ Tutorials and briefings 5. Next meeting info 6. Links to IDEAS & BORO IDEAS Partial Bibliography 1. 2. 3. DM 2 Description Documents Berger, Peter L, and Thomas Luckmann; The Social Construction of Reality; Doubleday & Company, Garden City, New York; 1966. Casati, Roberto, and Achille C Varzi; Holes and other Superficialities; The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts; 1995. Casati, Roberto, and Achille C Varzi; Parts and Places: The Structure of Spatial Representation; The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts; 1999. Clark, Bowman L; “Individuals and Points”; Notre Dame Journal of Formal Logic, Vol. 26; 1985. Coquand, Thierry; “Type Theory”; Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy; 2006. Davenport, Thomas H, and Laurence Prusak; Working Knowlege: How Organizations Manage What They Know; Harvard Business School Press, Boston, Massachusetts; 1998. Gilbert, Margaret; On Social Facts; Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey; 1992. Grenon, Pierre, and Barry Smith; “The Cornucopia of Formal-Ontological Relations”; Dialectica. Vol. 58; 2004 Grenon, Pierre, and Barry Smith; “Snap and Span: Toward Dynamic Spatial Ontology”; Spatial Cognition and Computation; Lawrence Erlbaum Assosiates, Inc, Leipzig, Germany. Hacking, Ian; Historical Ontology; Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts; 2002. Hawley, Katherine; How Things Persist; Oxford University Press, Oxford; 2001 Janssen, Terry, et al; A Multi- INT Sematic Reasoning Framework for Intelligence Analysis Support Kay, Paul; “Taxonomy and Semantic Contrast”; Language; Vols. 47, number 4; University of California, Berkeley, CA, 1971. Kempson, Ruth M; Semantic Theory; Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; 1977. Levinson, Stephen C; Pragmatics; Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; 1984. Lyons, John; Language, Meaning, & Context; Fontana Paperbacks, Great Britain; 1981. Nerlich, Graham; The Shape of Space; Second ed; Cambridge University Press, New York, NY; 1994. Partee, Barbara H, Alice Ter Meulen, and Robert E Wall; Mathematical Methods in Linguistics, Vol. 30; Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht; 1990. Partridge, Chris; Business Objects: Re-Engineering for Re-Use; The Boro Centre; 2005. Potter, Michael; Set Theory and its Philosophy; Oxford University Press, Oxford; 2004. Pulman, S G; Word Meaning and Belief; Ed. James R Hurford and John A Hawkins; Croom Helm Linguistics Series; Billing & Sons Limited, Great Britain; 1983. Sider, Theodore; Four Dimensionalism: An Ontology of Persistence and Time; Oxford University Press, Oxford; 2001. Simons, Peter; Parts: A Study in Ontology; Oxford University Press, Oxford; 1987. Smith, Barry; “Against Fantology”; Experience and Analysis; By M E Reicher and J C Marek; 2005. Smith, Barry; “The Basic Tools of Formal Ontology”; Formal Ontology in Information Systems; IOS Press, Amsterdam; Frontiers in Artifitial Intellegence and Applications; 1998 Smith, Barry; “Mereotopology: A Theory of Parts and Boundaries”; Data and Knowledge Engineering; Department of Philosophy, Buffalo, New York; 1996. Smith, Barry, and David M Mark; “Do Mountains Exist? Toward an Ontology of Landforms. ” Enviorment & Planning B (Planning and Design); National Center for Geographic Information and Analysis, Buffalo, New York; 2009. Stein, Lynn Andrea; “Imagination and Situated Cognition”; Thinking about Android Epistemology; Ed. Kenneth M Ford, Clark Glymour, and Partick J Hayes; AAAI Press, Menlo Park; 2006. Other ontology resources: IDEAS Group, BORO, Matthew West, Model. Futures, Barry Smith / NCOR
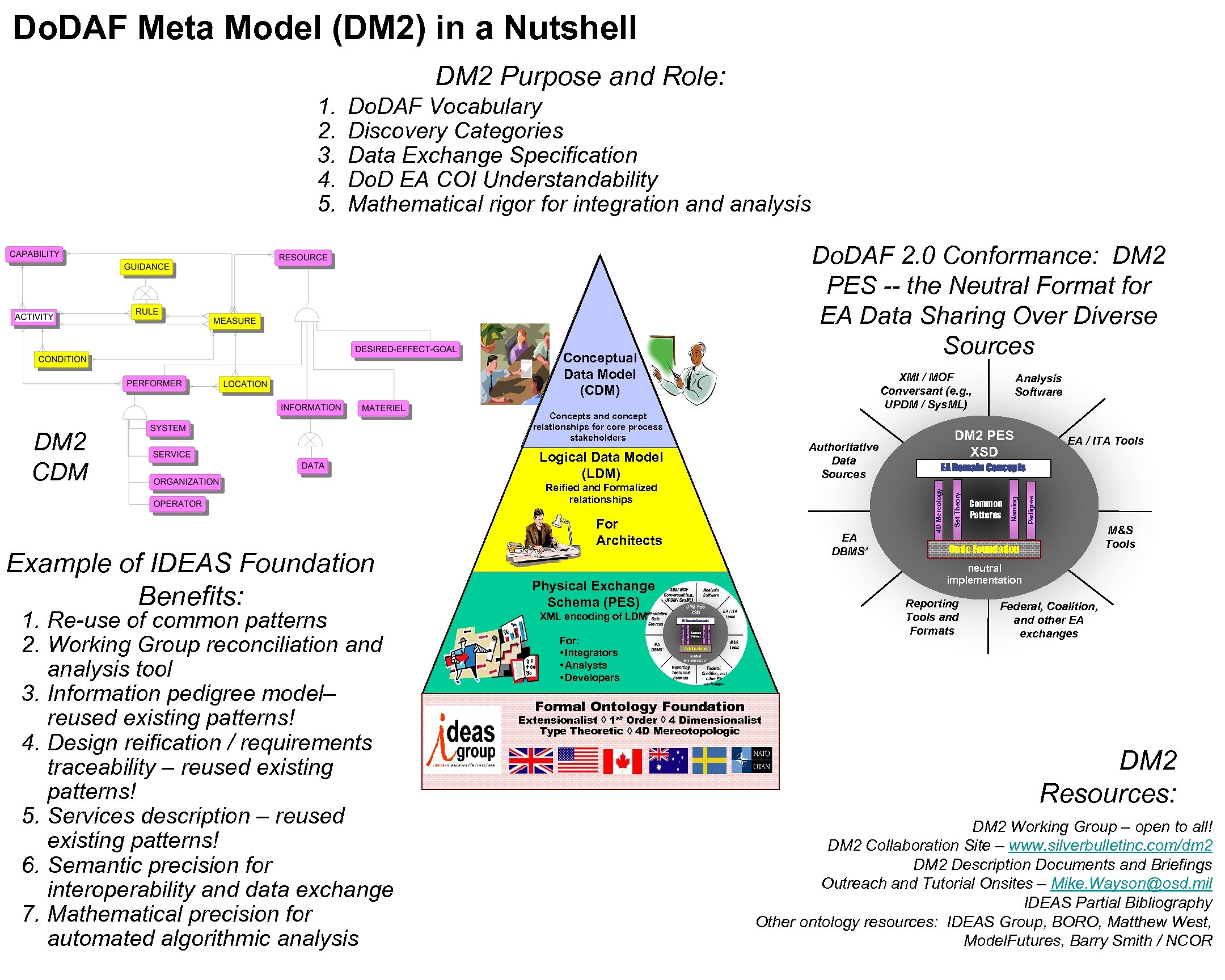 Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2) in a Nutshell DM 2 Purpose and Role: Do. DAF Vocabulary Discovery Categories Data Exchange Specification Do. D EA COI Understandability Mathematical rigor for integration and analysis Do. DAF 2. 0 Conformance: DM 2 PES -- the Neutral Format for EA Data Sharing Over Diverse Sources Example of IDEAS Foundation Benefits: 1. Re-use of common patterns 2. Working Group reconciliation and analysis tool 3. Information pedigree model– reused existing patterns! 4. Design reification / requirements traceability – reused existing patterns! 5. Services description – reused existing patterns! 6. Semantic precision for interoperability and data exchange 7. Mathematical precision for automated algorithmic analysis Authoritative Data Sources Logical Data Model (LDM) Reified and Formalized relationships For Architects EA DBMS’ Analysis Software DM 2 PES XSD EA / ITA Tools EA Domain Concepts Common Patterns Naming Concepts and concept relationships for core process stakeholders Set Theory DM 2 CDM XMI / MOF Conversant (e. g. , UPDM / Sys. ML) Pedigree Conceptual Data Model (CDM) 4 D Mereology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. M&S Tools Ontic Foundation neutral implementation Physical Exchange Schema (PES) Reporting Tools and Formats XML encoding of LDM For: • Integrators • Analysts • Developers Federal, Coalition, and other EA exchanges Formal Ontology Foundation Extensionalist à 1 st Order à 4 Dimensionalist Type Theoretic à 4 D Mereotopologic DM 2 Resources: DM 2 Working Group – open to all! DM 2 Collaboration Site – www. silverbulletinc. com/dm 2 DM 2 Description Documents and Briefings Outreach and Tutorial Onsites – Mike. Wayson@osd. mil IDEAS Partial Bibliography Other ontology resources: IDEAS Group, BORO, Matthew West, Model. Futures, Barry Smith / NCOR
Do. DAF Meta Model (DM 2) in a Nutshell DM 2 Purpose and Role: Do. DAF Vocabulary Discovery Categories Data Exchange Specification Do. D EA COI Understandability Mathematical rigor for integration and analysis Do. DAF 2. 0 Conformance: DM 2 PES -- the Neutral Format for EA Data Sharing Over Diverse Sources Example of IDEAS Foundation Benefits: 1. Re-use of common patterns 2. Working Group reconciliation and analysis tool 3. Information pedigree model– reused existing patterns! 4. Design reification / requirements traceability – reused existing patterns! 5. Services description – reused existing patterns! 6. Semantic precision for interoperability and data exchange 7. Mathematical precision for automated algorithmic analysis Authoritative Data Sources Logical Data Model (LDM) Reified and Formalized relationships For Architects EA DBMS’ Analysis Software DM 2 PES XSD EA / ITA Tools EA Domain Concepts Common Patterns Naming Concepts and concept relationships for core process stakeholders Set Theory DM 2 CDM XMI / MOF Conversant (e. g. , UPDM / Sys. ML) Pedigree Conceptual Data Model (CDM) 4 D Mereology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. M&S Tools Ontic Foundation neutral implementation Physical Exchange Schema (PES) Reporting Tools and Formats XML encoding of LDM For: • Integrators • Analysts • Developers Federal, Coalition, and other EA exchanges Formal Ontology Foundation Extensionalist à 1 st Order à 4 Dimensionalist Type Theoretic à 4 D Mereotopologic DM 2 Resources: DM 2 Working Group – open to all! DM 2 Collaboration Site – www. silverbulletinc. com/dm 2 DM 2 Description Documents and Briefings Outreach and Tutorial Onsites – Mike. Wayson@osd. mil IDEAS Partial Bibliography Other ontology resources: IDEAS Group, BORO, Matthew West, Model. Futures, Barry Smith / NCOR


