b8bcc9d102b95c28c2a9dd47860a2d93.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

What is Strategy 1 -

Case: IBM • At the height of its power: • 407000 employees • $6 Billion profits • Then hit problems: • 140000 employees lost jobs • $5 Billion loss • Dividends fell from $1, 21 to $0, 54 2 1 -2

3 Background • Formed 1911 • Made scales, coffee grinders, cheese slicers and clocks • 1924 changed name to IBM to focus on computing technologies • Led the world until the 1970 s in computer technology 1 -3

4 Trouble ahead • System/360 mainframes led the world but required 5 new factories • Control problems led to an increase in bureaucracy: between 1963 -1966, personnel increased by 130%, sales only 97% • Meetings and consensus created stagnation in the organisation 1 -4

5 Today? • New CEO, Louis Gerstner in 1993 • Reduced bureaucracy • Performance based pay for executives • Brought in outsiders • Moved into IT service sector 1 -5
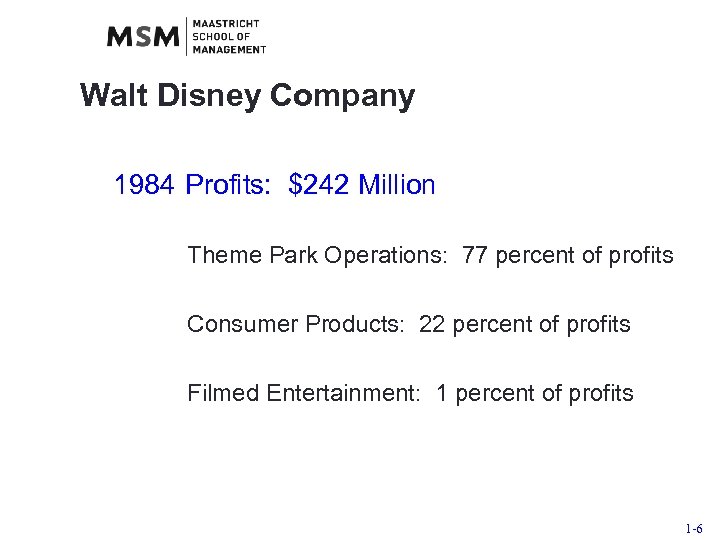
Walt Disney Company 1984 Profits: $242 Million Theme Park Operations: 77 percent of profits Consumer Products: 22 percent of profits Filmed Entertainment: 1 percent of profits 1 -6

Walt Disney Company Hired Michael Eisner - 1984 1. Increased admission prices at theme parks 1984 - $186 m 1989 - $787 m 2. Focused on movie studios (character development) 1984 - $2. 42 m 1994 - $845 m 3. Diversified into television (ABC), hotels, retail stores, sport team, cruise line, publishing, consumer products, licensing, etc. (Huey & Mc. Gowan, 1995) Market Cap: 1984 = $2 billion 1994 = $28 billion 1 -7

Definition of Strategy: A firm’s theory about how to gain competitive advantages Eisner’s theory may have been: People will pay a premium price for extraordinary entertainment. We have the necessary resources to create extraordinary entertainment. Therefore, let’s redeploy our resources in a different way and offer something extraordinary to people. 1 -8

The Strategic Management Process External Analysis Mission Strategic Choice Objectives Strategy Implementation Competitive Advantage Internal Analysis 1 -9
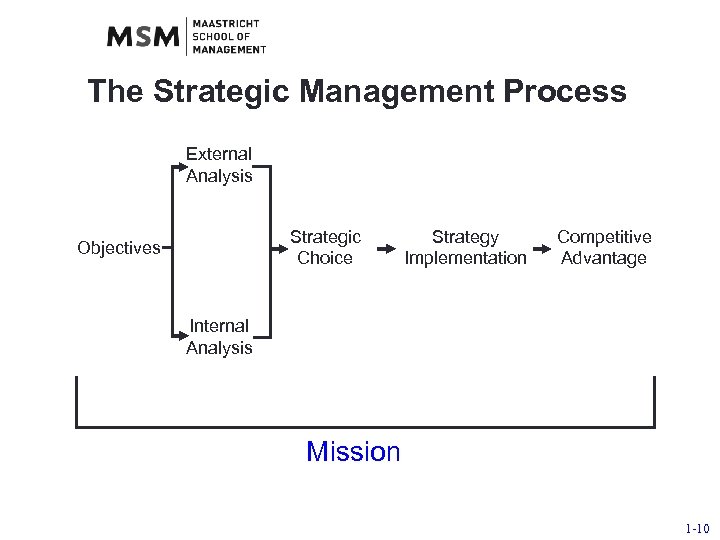
The Strategic Management Process External Analysis Strategic Choice Objectives Strategy Implementation Competitive Advantage Internal Analysis Mission 1 -10

11 Mission Statements • At X, we strive to lead in the creation, development and manufacture of the industry's most advanced information technologies, including computer systems, software, networking systems, storage devices and microelectronics. And our worldwide network of X solutions and services professionals translates these advanced technologies into business value for our customers. 1 -11

12 • We are a global family with a proud heritage, passionately committed to providing personal mobility for people around the world. We anticipate consumer needs and deliver outstanding products and services that improve people’s lives. 1 -12

The Strategic Management Process Objectives: • specific, measurable targets • the things a firm needs to ‘do’ to achieve its mission • should influence other elements in the strategic management process Example: IBM’s mission & objectives 1 -13

Current IBM Mission Statement • “At IBM, we strive to lead in the invention, development and manufacture of the industry's most advanced information technologies, including computer systems, software, storage systems and microelectronics. • We translate these advanced technologies into value for our customers through our professional solutions, services and consulting businesses worldwide. " 1 -14
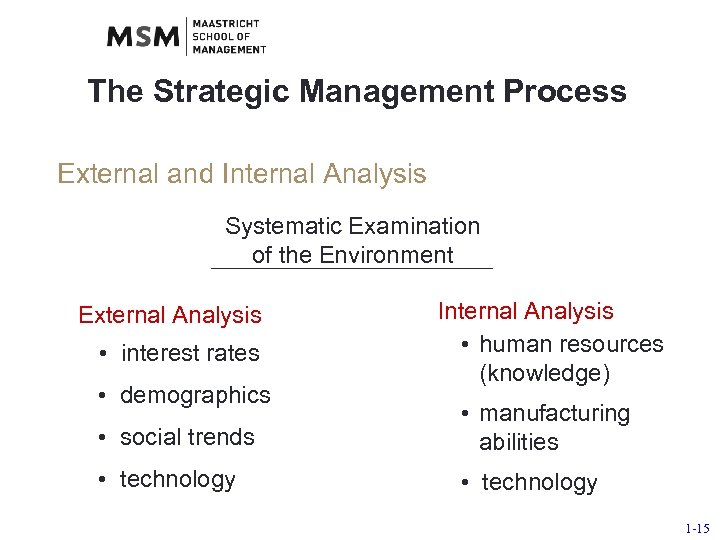
The Strategic Management Process External and Internal Analysis Systematic Examination of the Environment External Analysis • interest rates • demographics Internal Analysis • human resources (knowledge) • social trends • manufacturing abilities • technology 1 -15
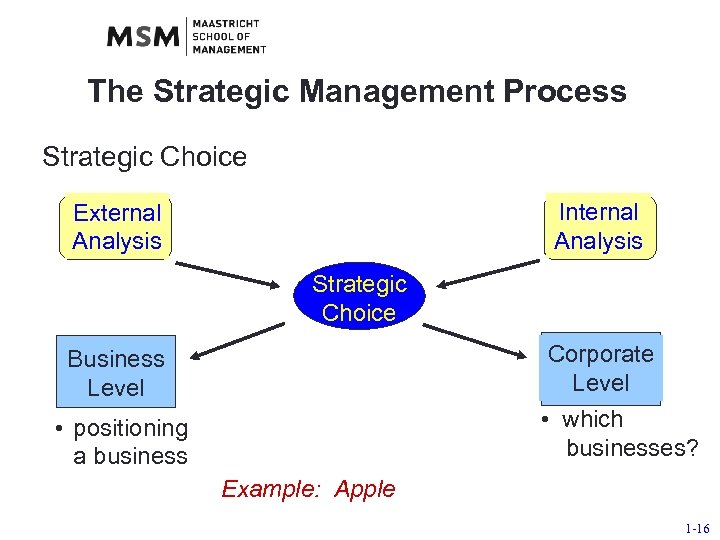
The Strategic Management Process Strategic Choice Internal Analysis External Analysis Strategic Choice Corporate Level Business Level • which businesses? • positioning a business Example: Apple 1 -16

The Strategic Management Process Strategy Implementation • how strategies are carried out • who will do what • organizational structure and control • who reports to whom • how does the firm hire, promote, pay, etc. 1 -17

The Strategic Management Process Strategy Implementation • every strategic choice has strategy implementation implications • strategy implementation is just as important as strategy formulation A Strategy Is Only As Good As Its Implementation Example: Napoleon’s invasion of Russia 1 -18
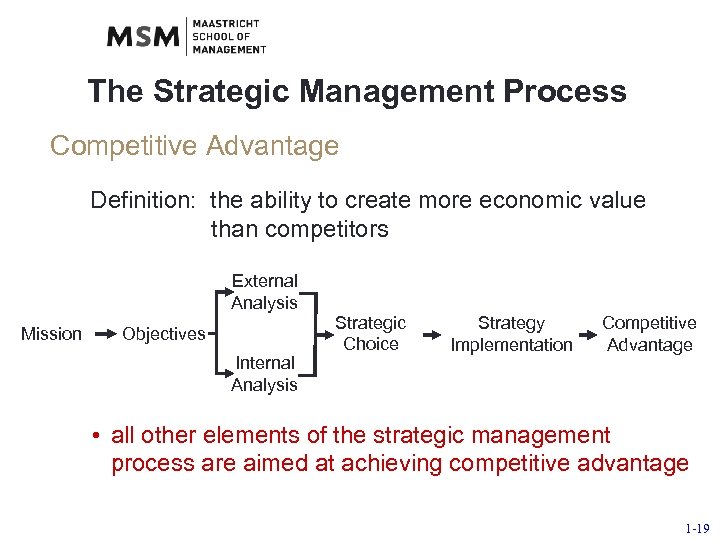
The Strategic Management Process Competitive Advantage Definition: the ability to create more economic value than competitors External Analysis Mission Objectives Internal Analysis Strategic Choice Strategy Implementation Competitive Advantage • all other elements of the strategic management process are aimed at achieving competitive advantage 1 -19

Competitive Advantage The Ability to Create More Economic Value Than Competitors • there must be something different about a firm’s offering vis-à-vis competitors’ offerings • if all firms’ strategies were the same, no firm would have a competitive advantage • competitive advantage is the result of doing something different and/or better than competitors 1 -20

Competitive Advantage Two Types of Difference 1) Preference for the firm’s output • people choose the firm’s output over others’ • people are willing to pay a premium Example: Mercedes 2) Cost advantage vis-à-vis competitors • lower costs of production/distribution Example: Ryan. Air 1 -21

Competitive Advantage The Strategic Management Process External Analysis Internal Analysis Strategic Choice Strategy Competitive Implementation Advantage • identify and exploit differences that may lead to competitive advantage Example: Apple’s i. Pod 1 -22
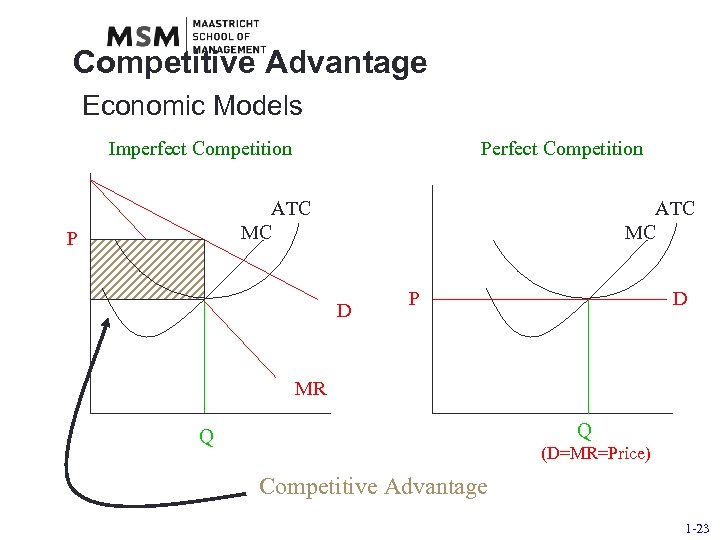
Competitive Advantage Economic Models Imperfect Competition Perfect Competition ATC MC P ATC MC D P D MR Q Q (D=MR=Price) Competitive Advantage 1 -23

Competitive Advantage Temporary & Sustainable • competitive advantage typically results in high profits • profits attract competition • competition limits the duration of competitive advantage in most cases Therefore, • most competitive advantage is temporary • competitors imitate the advantage or offer something better 1 -24

Competitive Advantage Temporary & Sustainable Some competitive advantages are sustainable if: • competitors are unable to imitate the source of advantage • no one conceives of a better offering Of course, • in time, even sustainable competitive advantage may be lost 1 -25

Competitive Advantage Competitive Parity • the firm’s offerings are ‘average’ • people do not have a preference for the firm’s offering • the firm does not have a cost advantage over others • some things that may lead to competitive parity may still be critical to success (e. g. , telephones) 1 -26

Competitive Advantage Competitive Disadvantage • people may have an aversion to the firm’s offering • the firm may have a cost disadvantage • a firm may have outdated technology/equipment • a firm may have a negative reputation Example: Mc. Donalds 1 -27

Competitive Advantage Measuring Competitive Advantage Superior Economic Performance Is Viewed as Evidence of Competitive Advantage • it is rather easy to see the evidence of competitive advantage • measuring the source of the advantage per se is typically impossible • it’s difficult to ‘measure’ technology 1 -28

Competitive Advantage Measuring Competitive Advantage Two Classes of Measures: 1) Accounting Measures • ROA, Profit Margin, ROE, etc. that exceed industry averages 2) Economic Measures • earning a return in excess of the cost of capital 1 -29
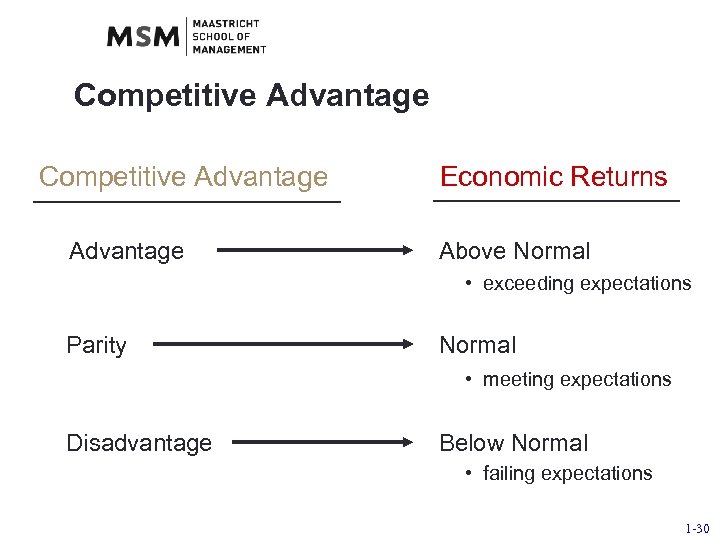
Competitive Advantage Economic Returns Above Normal • exceeding expectations Parity Normal • meeting expectations Disadvantage Below Normal • failing expectations 1 -30

Competitive Advantage & The Strategic Management Process Emergent vs. Intended Strategies • the strategic management process leads managers to intended strategies However, • conditions often change or new information becomes available • managers respond adopt emergent strategies Example: Honda Motorcycles 1 -31

The Strategic Management Process Summary Firms could achieve competitive parity and survive • they would face a flat demand curve • their cost structure would be the industry average • they would need to adapt their strategy over time just to survive • they would fail if they didn’t adapt their strategy 1 -32

The Strategic Management Process Summary This course is not about mere survival, it is about thriving—achieving competitive advantage • the strategic management process helps managers achieve competitive advantage • competitive advantage depends on differences • strategy is about discovering and exploiting these differences 1 -33
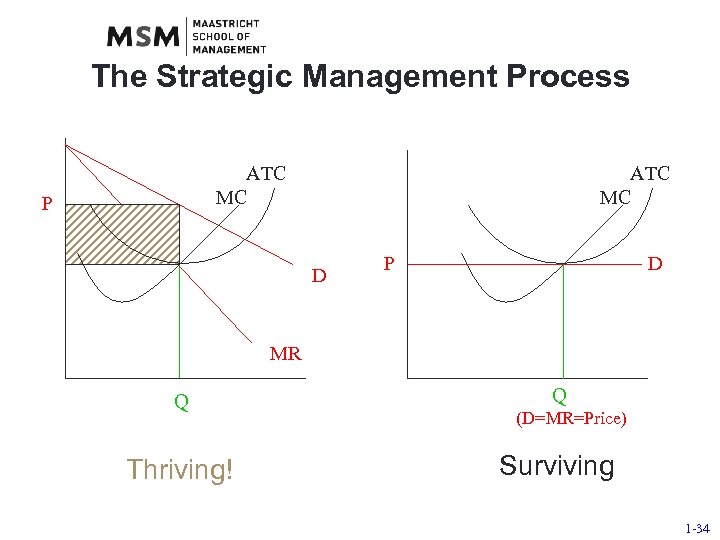
The Strategic Management Process ATC MC P ATC MC D P D MR Q Thriving! Q (D=MR=Price) Surviving 1 -34

Samsung China • Describe the Chinese macro environment in 1995. • What are the main characteristics of the Chinese colour television market? • What changes were taking place in the Korean market? How was this affecting Korean firms? • Describe Samsung’s strategy in the US. Why did they take this strategy? • What is Samsung’s competitive advantage? • What are the entry options open to Samsung? What are the main issues? • What would you recommend to Samsung? 1 -35
b8bcc9d102b95c28c2a9dd47860a2d93.ppt