 What is IPM? It is application of interconnected set of principles and methods to minimize the problem caused by insects, diseases, weeds and others agricultural pests. IPM Techniques Includes Pest protection technique. Pest monitoring methods Bio-control methods Pest resistant plant varieties Pest attractants and repellants Use of Bio-pesticides Synthetic organic pesticides Weather data for prediction of Cultural practices in cultivation pest attack
What is IPM? It is application of interconnected set of principles and methods to minimize the problem caused by insects, diseases, weeds and others agricultural pests. IPM Techniques Includes Pest protection technique. Pest monitoring methods Bio-control methods Pest resistant plant varieties Pest attractants and repellants Use of Bio-pesticides Synthetic organic pesticides Weather data for prediction of Cultural practices in cultivation pest attack
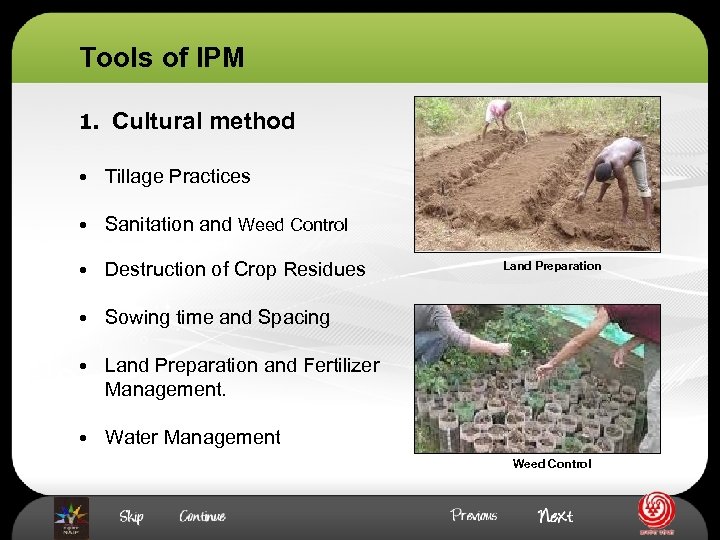 Tools of IPM 1. Cultural method • Tillage Practices • Sanitation and Weed Control • Destruction of Crop Residues Land Preparation • Sowing time and Spacing • Land Preparation and Fertilizer Management. • Water Management Weed Control
Tools of IPM 1. Cultural method • Tillage Practices • Sanitation and Weed Control • Destruction of Crop Residues Land Preparation • Sowing time and Spacing • Land Preparation and Fertilizer Management. • Water Management Weed Control
 1. Cultural method • Pest Resistant Varieties Rice: IR-20, Vani Cultivar resistant to Leaf hopper. Mango: Baneshan, Neeleshan Cultivar resistant to Leaf Hoppers. Tomato: BT-1, T-32, T-27 Cultivar resistant to Fruit borer. j. Crop Rotation Rice- Legume- Vegetables Sugarcane/ Chilies- Tobacco k. Use of Trap Crop Main Crop Trap crop Cucurbit Sun hemp Vegetable Marigold (Rice gall midge) (White ants) Pest Fruit Fly Nematode
1. Cultural method • Pest Resistant Varieties Rice: IR-20, Vani Cultivar resistant to Leaf hopper. Mango: Baneshan, Neeleshan Cultivar resistant to Leaf Hoppers. Tomato: BT-1, T-32, T-27 Cultivar resistant to Fruit borer. j. Crop Rotation Rice- Legume- Vegetables Sugarcane/ Chilies- Tobacco k. Use of Trap Crop Main Crop Trap crop Cucurbit Sun hemp Vegetable Marigold (Rice gall midge) (White ants) Pest Fruit Fly Nematode
 2. Mechanical Methods Insects are directly hit by mechanical devices and lifecycle is hampered • Hand picking • Beating and hooking • Sieving and winnowing • Clipping • Using nets and bag nets • Swatting and crushing • Brushing and sweeping • Burning, Flooding and draining Flooding Practice to Control Pest
2. Mechanical Methods Insects are directly hit by mechanical devices and lifecycle is hampered • Hand picking • Beating and hooking • Sieving and winnowing • Clipping • Using nets and bag nets • Swatting and crushing • Brushing and sweeping • Burning, Flooding and draining Flooding Practice to Control Pest
 3. Physical Methods • Sound: Ultrasonic waves • Heat and Radiation • Cold and Moisture • Light: light trap • Air Pressure: increasing Carbon di-oxide in store house Light Trap
3. Physical Methods • Sound: Ultrasonic waves • Heat and Radiation • Cold and Moisture • Light: light trap • Air Pressure: increasing Carbon di-oxide in store house Light Trap
 4. Chemical Method a. Use of Botanical Insecticides Pyrethrin from Chrysanthemum Rotenone from Derris elliptica Azadirachtin from Neem Nicotine from Tobacco
4. Chemical Method a. Use of Botanical Insecticides Pyrethrin from Chrysanthemum Rotenone from Derris elliptica Azadirachtin from Neem Nicotine from Tobacco
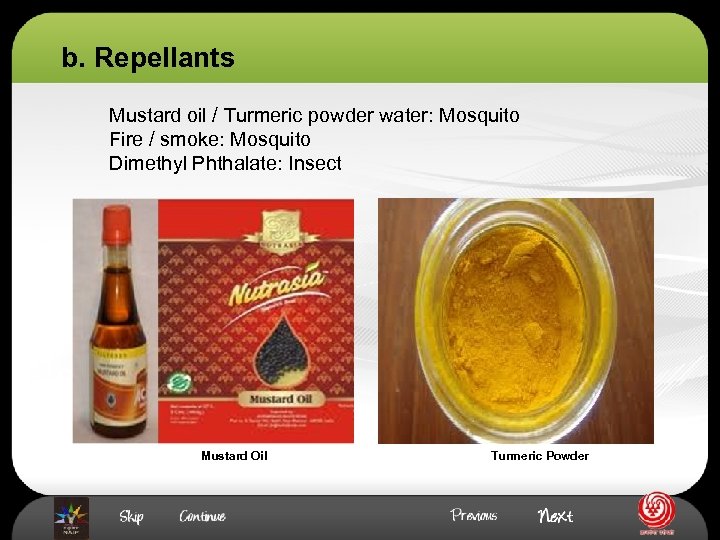 b. Repellants Mustard oil / Turmeric powder water: Mosquito Fire / smoke: Mosquito Dimethyl Phthalate: Insect Mustard Oil Turmeric Powder
b. Repellants Mustard oil / Turmeric powder water: Mosquito Fire / smoke: Mosquito Dimethyl Phthalate: Insect Mustard Oil Turmeric Powder
 c. Insect Growth Regulators Examples: Diflubenzuron, Triflumuron, Azadirachtin, etc. d. Chemical Insecticide
c. Insect Growth Regulators Examples: Diflubenzuron, Triflumuron, Azadirachtin, etc. d. Chemical Insecticide
 e. Insect Attractant Allomones: Ants, bees and beetles. Kairomones: Hymenoptera Pheromones: Noctuidera, Lepidoptera, Homoptera, etc. Natural Food Lures: Floral scents: Nectar Feeding Pest Essential oils: Phytophagus Insect Decomposing products: Scavengers Pheromone Trap f. New Generation Chemicals Neonicotinoides Avermectins Formamidines Pyrrole Nereistoxin Quinazoline
e. Insect Attractant Allomones: Ants, bees and beetles. Kairomones: Hymenoptera Pheromones: Noctuidera, Lepidoptera, Homoptera, etc. Natural Food Lures: Floral scents: Nectar Feeding Pest Essential oils: Phytophagus Insect Decomposing products: Scavengers Pheromone Trap f. New Generation Chemicals Neonicotinoides Avermectins Formamidines Pyrrole Nereistoxin Quinazoline
 5. Biological Methods a. Predator: Birds, Snakes and other Reptiles b. Parasitoids: Trichogramma, Cotesia, Isotima, etc. c. Pathogens i. Ingested microbes: • Bacteria: Bacillus, Psedomonas, etc. • Viruses: Nuclear & Cytoplasmic Polyhedrosis Virus • Protozoa: Adelina triboli, Muttesia, etc. ii. Penetrating microbes • Fungi: Aspergillus, Verticillium, etc. • Nematodes: Tripius, Mermis, etc.
5. Biological Methods a. Predator: Birds, Snakes and other Reptiles b. Parasitoids: Trichogramma, Cotesia, Isotima, etc. c. Pathogens i. Ingested microbes: • Bacteria: Bacillus, Psedomonas, etc. • Viruses: Nuclear & Cytoplasmic Polyhedrosis Virus • Protozoa: Adelina triboli, Muttesia, etc. ii. Penetrating microbes • Fungi: Aspergillus, Verticillium, etc. • Nematodes: Tripius, Mermis, etc.
 6. Biotechnological Methods a. Identification of Parasites/Pathogens/Predators: e. g. Lady Bird Beetle, Mexican Beetle b. Monitoring genetic variation in natural enemy population: e. g. BT Cotton, BT Brinjal, etc. c. Production of transgenic plants: e. g. Tomato, Brinjal, etc. d. Create Pesticide resistance in Bio-control agent e. Genetic engineering of beneficial organisms
6. Biotechnological Methods a. Identification of Parasites/Pathogens/Predators: e. g. Lady Bird Beetle, Mexican Beetle b. Monitoring genetic variation in natural enemy population: e. g. BT Cotton, BT Brinjal, etc. c. Production of transgenic plants: e. g. Tomato, Brinjal, etc. d. Create Pesticide resistance in Bio-control agent e. Genetic engineering of beneficial organisms