ff52198d0ebe13705c23d714aff9897f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 What is a Universal Waste? 1
What is a Universal Waste? 1
 Universal Waste is universally generated. 2
Universal Waste is universally generated. 2
 Universal Waste is a hazardous waste but low risk relative to other hazardous wastes. 3
Universal Waste is a hazardous waste but low risk relative to other hazardous wastes. 3
 Goals of Universal Waste Rule • Promote the environmentally sound collection and recycling of universal waste • Provide for collection opportunities for communities and businesses 4
Goals of Universal Waste Rule • Promote the environmentally sound collection and recycling of universal waste • Provide for collection opportunities for communities and businesses 4
 Types of NH Universal Waste • • • Auto antifreeze Batteries Cathode ray tubes Lamps Mercury containing devices Pesticides 5
Types of NH Universal Waste • • • Auto antifreeze Batteries Cathode ray tubes Lamps Mercury containing devices Pesticides 5
 Waste fluorescent light bulbs typically contain enough mercury to meet 6 the criteria of hazardous waste.
Waste fluorescent light bulbs typically contain enough mercury to meet 6 the criteria of hazardous waste.
 OTHER TYPES OF UNIVERSAL WASTE LAMPS (High intensity discharge (HID) lamps may also exceed the toxicity characteristic for mercury) • Mercury vapor • High pressure sodium • Metal halide lamps 7
OTHER TYPES OF UNIVERSAL WASTE LAMPS (High intensity discharge (HID) lamps may also exceed the toxicity characteristic for mercury) • Mercury vapor • High pressure sodium • Metal halide lamps 7
 Universal Waste Lamps (fluorescent light bulbs) Store in sound container(s) that are closed except when adding or removing lamps. 8
Universal Waste Lamps (fluorescent light bulbs) Store in sound container(s) that are closed except when adding or removing lamps. 8
 Universal Waste Lamps (fluorescent light bulbs) Hazardous waste permit required for universal waste lamp crushers. 9
Universal Waste Lamps (fluorescent light bulbs) Hazardous waste permit required for universal waste lamp crushers. 9
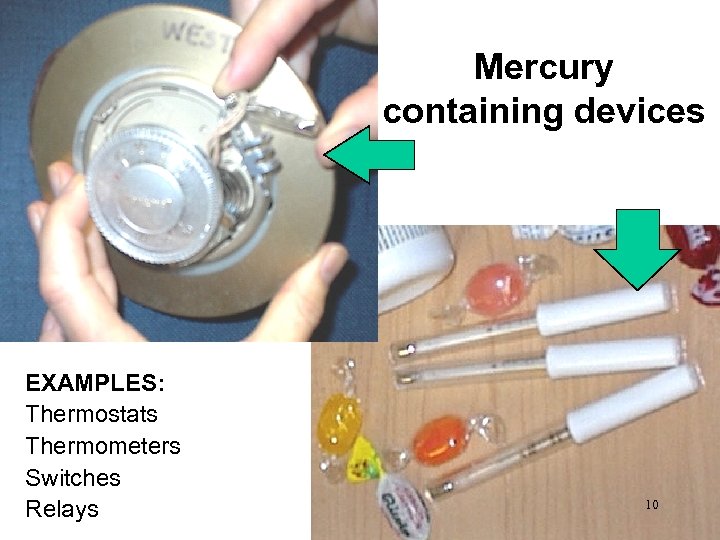 Mercury containing devices EXAMPLES: Thermostats Thermometers Switches Relays 10
Mercury containing devices EXAMPLES: Thermostats Thermometers Switches Relays 10
 BATTERIES Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd) Lithium Button cell Lead-acid 11
BATTERIES Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd) Lithium Button cell Lead-acid 11
 LEAD ACID BATTERIES May be managed under Env-Wm 809 or the Universal Waste Rule (Env-Wm 1100) 12
LEAD ACID BATTERIES May be managed under Env-Wm 809 or the Universal Waste Rule (Env-Wm 1100) 12
 Alkaline and Carbon Zinc Non-hazardous In 1996, federal law is adopted (Mercury Containing and Rechargeable Battery Act) that prohibits addition of 13 mercury to batteries (except for button cells).
Alkaline and Carbon Zinc Non-hazardous In 1996, federal law is adopted (Mercury Containing and Rechargeable Battery Act) that prohibits addition of 13 mercury to batteries (except for button cells).
 Storage • • Plastic bags Tape terminals Discharge Stack batteries so that electrodes are not touching 14
Storage • • Plastic bags Tape terminals Discharge Stack batteries so that electrodes are not touching 14
 Used automotive antifreeze is considered hazardous waste unless testing shows otherwise. 15
Used automotive antifreeze is considered hazardous waste unless testing shows otherwise. 15
 Through use antifreeze becomes contaminated. 16
Through use antifreeze becomes contaminated. 16
 Universal Waste Antifreeze • Do not mix with other wastes or materials. • Use dedicated funnels and containers. 17
Universal Waste Antifreeze • Do not mix with other wastes or materials. • Use dedicated funnels and containers. 17
 UNIVERSAL WASTE ANTIFREEZE RECYCLING 18
UNIVERSAL WASTE ANTIFREEZE RECYCLING 18
 The cathode ray tubes (CRTs) in color TVs and computer monitors contain lead. 19
The cathode ray tubes (CRTs) in color TVs and computer monitors contain lead. 19
 Some pesticides are considered universal waste (e. g. suspended and/or recalled pesticides under FIFRA) 20
Some pesticides are considered universal waste (e. g. suspended and/or recalled pesticides under FIFRA) 20
 UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Manage universal waste in a way that prevents releases to the environment. 21
UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Manage universal waste in a way that prevents releases to the environment. 21
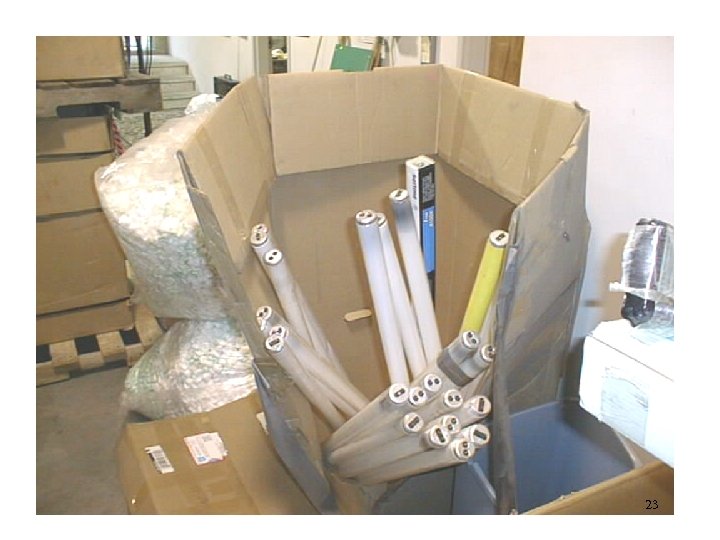
 UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Universal waste containers must be free of defects, design characteristics, or damage that could result in leakage, spillage or other environmental releases. Universal Waste Antifreeze 22
UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Universal waste containers must be free of defects, design characteristics, or damage that could result in leakage, spillage or other environmental releases. Universal Waste Antifreeze 22
 23
23
 UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Label or mark containers. Used Waste Antifreeze Universal Waste Batteries Lamps 24
UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Label or mark containers. Used Waste Antifreeze Universal Waste Batteries Lamps 24
 25
25
 UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Cover universal waste containers stored outdoors. 26
UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Cover universal waste containers stored outdoors. 26
 27
27
 UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Train employees on proper handling (in-house training okay). 28
UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Train employees on proper handling (in-house training okay). 28
 UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Immediately contain and, within 24 hours, clean up any releases of universal waste. 29
UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Immediately contain and, within 24 hours, clean up any releases of universal waste. 29
 UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Do not store for more than one year. 30
UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS Do not store for more than one year. 30
 UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS • If 5, 000 kgs (11, 000 lbs) or more (total of all types of universal waste) stored on-site – must notify NH DES and keep shipping records. 31
UNIVERSAL WASTE MANAGEMENT STANDARDS • If 5, 000 kgs (11, 000 lbs) or more (total of all types of universal waste) stored on-site – must notify NH DES and keep shipping records. 31
 UNIVERSAL WASTE TRANSPORTATION • Follow US DOT requirements when shipping. • NH hazardous waste transporter registration and manifest not required. 32
UNIVERSAL WASTE TRANSPORTATION • Follow US DOT requirements when shipping. • NH hazardous waste transporter registration and manifest not required. 32
 UNIVERSAL WASTE DESTINATION FACILITIES The destination facility must be a hazardous waste treatment, storage, disposal or recycling facility. 33
UNIVERSAL WASTE DESTINATION FACILITIES The destination facility must be a hazardous waste treatment, storage, disposal or recycling facility. 33
 IN SUMMARY - TYPES OF NH UNIVERSAL WASTE • • • Auto antifreeze Batteries Cathode ray tubes Lamps Mercury-containing devices Pesticides 34
IN SUMMARY - TYPES OF NH UNIVERSAL WASTE • • • Auto antifreeze Batteries Cathode ray tubes Lamps Mercury-containing devices Pesticides 34
 Sample Question #1 Question: Which the following is not an example of a universal waste battery? a. Ni-Cd battery b. Lithium battery (not fully discharged) c. Mercury-containing button cell d. Alkaline battery purchased in 2002 35
Sample Question #1 Question: Which the following is not an example of a universal waste battery? a. Ni-Cd battery b. Lithium battery (not fully discharged) c. Mercury-containing button cell d. Alkaline battery purchased in 2002 35
 Sample Question #2 Question: Which of the following is not a universal waste? a. Lamps b. Automotive antifreeze c. PCB lamp ballasts d. Mercury-containing devices 36
Sample Question #2 Question: Which of the following is not a universal waste? a. Lamps b. Automotive antifreeze c. PCB lamp ballasts d. Mercury-containing devices 36
 Sample Question #3 Question: Which of the following are requirements for universal waste ? a. Manage in a way to prevent releases to the environment b. Containers must be free of defects, design characteristics or damage c. Immediately contain, and within 24 hours, clean up releases d. All of the above 37
Sample Question #3 Question: Which of the following are requirements for universal waste ? a. Manage in a way to prevent releases to the environment b. Containers must be free of defects, design characteristics or damage c. Immediately contain, and within 24 hours, clean up releases d. All of the above 37
 Fact Sheet and Vendor Web Sites • www/des. nh. gov/uw. htm • www. des. nh. gov/hwcs/vendor_lists. htm 38
Fact Sheet and Vendor Web Sites • www/des. nh. gov/uw. htm • www. des. nh. gov/hwcs/vendor_lists. htm 38


