a3008ca38b7c9c20bb3eb238be1d3af6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

What is a Successful Digital Library? ECDL 2006, Alicante, September 18, 2006 Rao Shen, Naga Srinivas Vemuri, Weiguo Fan, and Edward A. Fox fox@vt. edu http: //fox. cs. vt. edu

Acknowledgements (Selected) • Sponsors: NSF grant ITR-0325579, ASOR, CWRU, ETANA, Vanderbilt U. , Virginia Tech • Faculty/Staff: Lillian Cassel, Debra Dudley, Manuel Perez, … • VT (Former) Students: Aaron Krowne, Ming Luo, Fernando Das Neves, Ricardo Torres, Hussein Suleman, …

Acknowledgements (Selected) • Karen Borstad, MPP • Christopher Holland, LRP • Giorgio Buccellati, UCLA • Paul Jacobs, Mississippi State U. • Douglas Clark, Walla College • Douglas Knight, Vanderbilt U. • Joanne Eustis, CWRU • Stan La. Bianca, Andrews U. • Nick Fischio, CWRU • David Mc. Creery, Willamette U. • Israel Finkelstein, Tel-Aviv University • Eric Meyers, Duke U. • Paul Gherman, Vanderbilt U. • Adam Porter, Illinois College • Andrew Graham, U. Toronto • Jack Sasson, Vanderbilt U. • Tim Harrison, U. Toronto • Tom Schaub, Indiana U. of Penn. • Larry Herr, Canadian University College • Randall Younker, Andrews U.

ETANA-DL Website
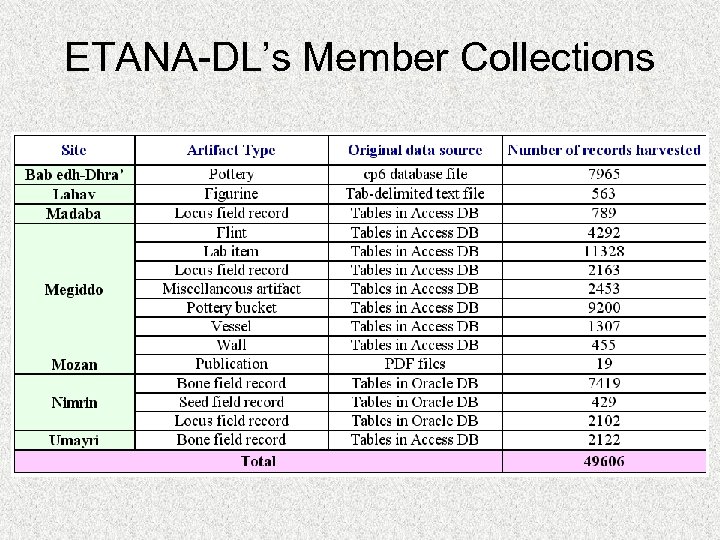
ETANA-DL’s Member Collections

Outline Ø Prior work Ø DL success model § From end user perspective Ø Case study Ø Conclusion
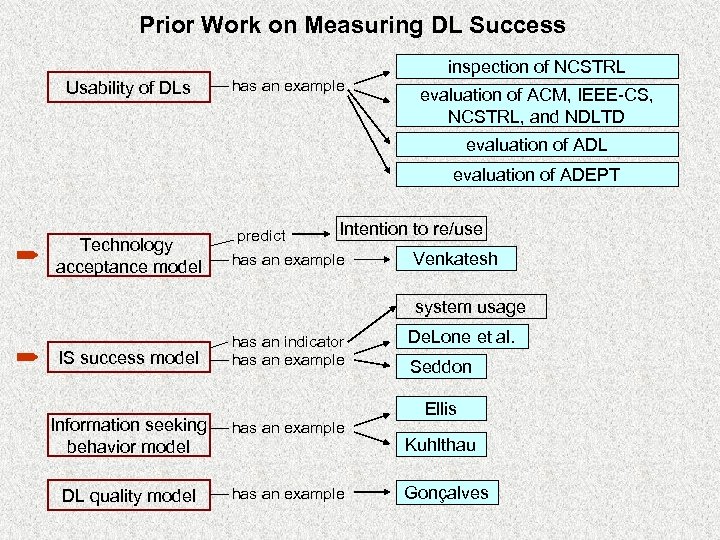
Prior Work on Measuring DL Success inspection of NCSTRL Usability of DLs has an example evaluation of ACM, IEEE-CS, NCSTRL, and NDLTD evaluation of ADL evaluation of ADEPT Technology acceptance model Intention to re/use predict Venkatesh has an example system usage IS success model has an indicator has an example De. Lone et al. Seddon Ellis Information seeking behavior model has an example DL quality model has an example Kuhlthau Gonçalves
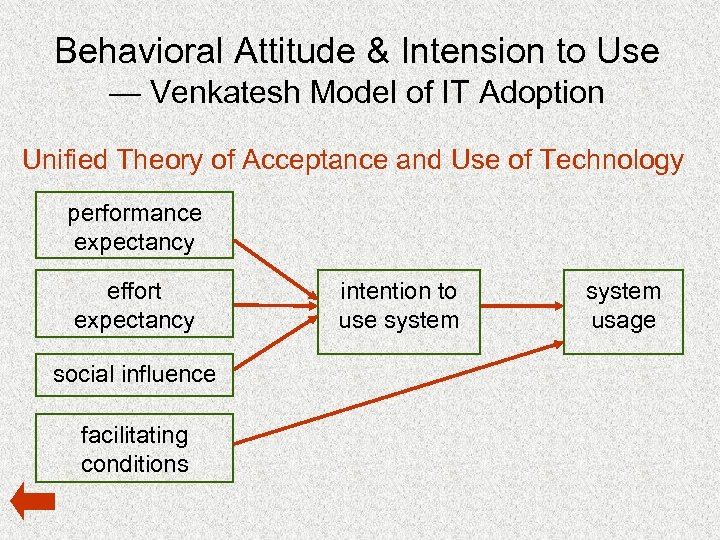
Behavioral Attitude & Intension to Use — Venkatesh Model of IT Adoption Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology performance expectancy effort expectancy social influence facilitating conditions intention to use system usage

Venkatesh Model of IT Adoption • Performance expectancy: – perceived usefulness, extrinsic motivation, job-fit, relative advantage, and outcome expectations • Effort expectancy – the degree of ease associated with the use of system • Social influence – Subjective norms, social factors, and image • Facilitating conditions – the degree to which an individual believes that an organizational and technical infrastructure exist to support the system
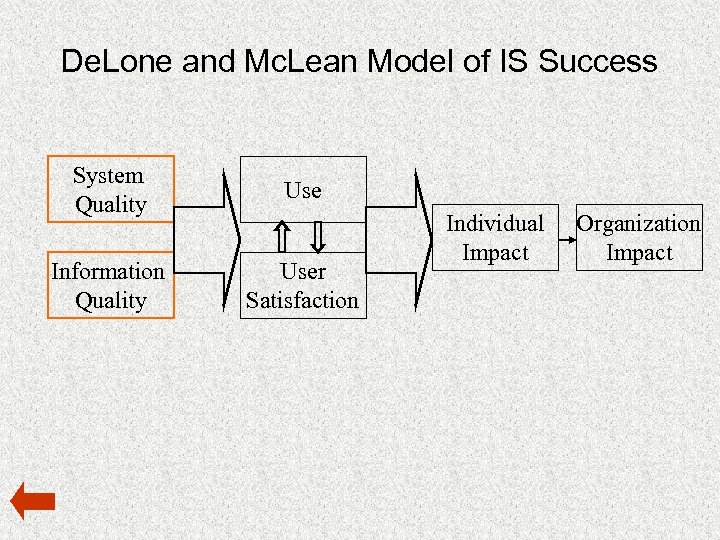
De. Lone and Mc. Lean Model of IS Success System Quality Use Information Quality User Satisfaction Individual Impact Organization Impact
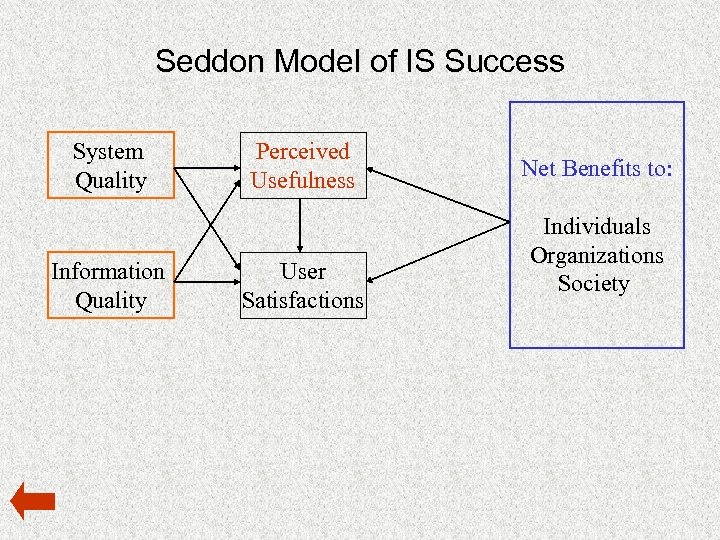
Seddon Model of IS Success System Quality Information Quality Perceived Usefulness User Satisfactions Net Benefits to: Individuals Organizations Society

Outline Ø Prior work Ø DL success model § From end user perspective Ø Case study Ø Conclusion

DL Success Model Ø 5 S and minimal DL Ø Synthesize § § IS success and adoption models (see above) Information life cycle model (Borgman et al. ) 5 S-based DL quality model (Gonçalves et al. ) Information-seeking behavior models (Ellis’ and Kuhlthau’s) Ø From end user perspective

Informal 5 S & DL Definitions DLs are complex systems that • • • help satisfy info needs of users (societies) provide info services (scenarios) organize info in usable ways (structures) present info in usable ways (spaces) communicate info with users (streams)
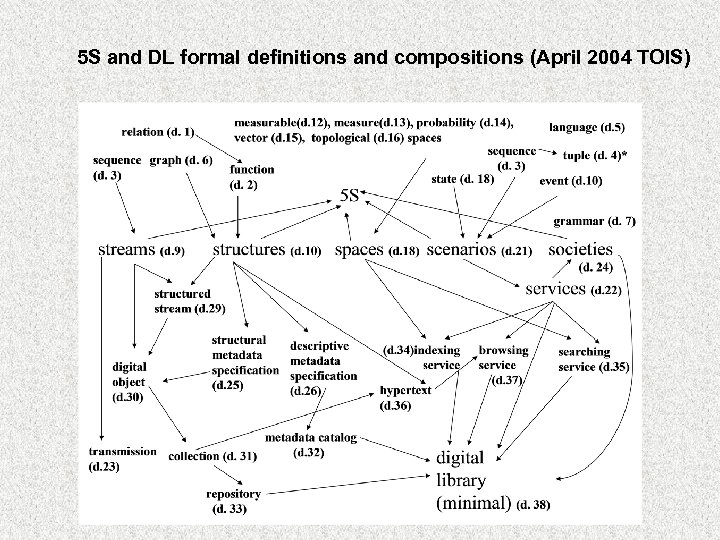
5 S and DL formal definitions and compositions (April 2004 TOIS)
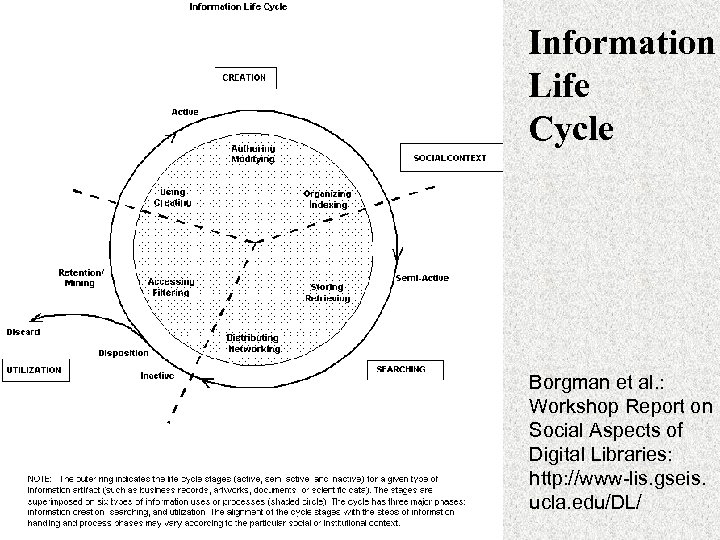
Information Life Cycle Borgman et al. : Workshop Report on Social Aspects of Digital Libraries: http: //www-lis. gseis. ucla. edu/DL/
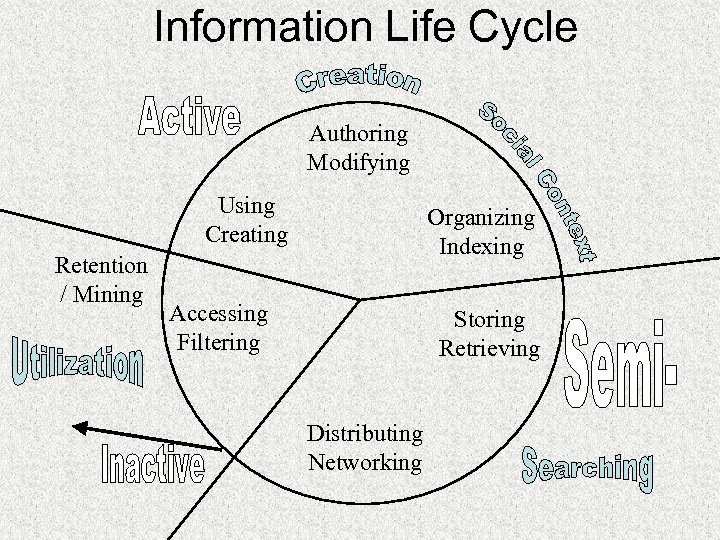
Information Life Cycle Authoring Modifying Using Creating Retention / Mining Organizing Indexing Accessing Filtering Storing Retrieving Distributing Networking
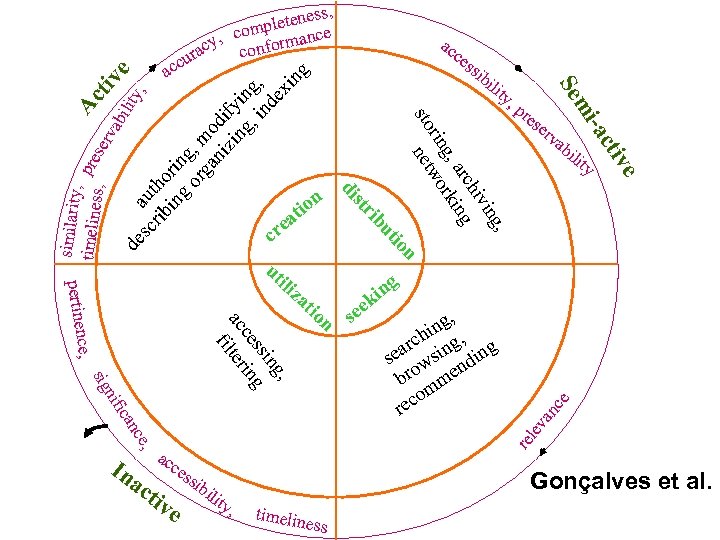
, p re se ili e ty tiv rv ab -ac mi ty , cr th ib or in in g or g, m ga o ni di zi fy ng in , i g, nd ex in g ili Se ib n g n e ica nif sig , ng i rch ing, ng sea ws ndi bro me m co re e, re nc lev se ce ce, , ing ss g ce in ac ter fil io n ki an at In ss io ut ib pertinen e cr ut ili z ce ing hiv arc ng g, rki rin wo sto net n tio a ac str di similarity , Ac timelines pres s, erv tiv ab ilit e de a y, s u ess, pleten e com y, onformanc c c ura c ac ac ac ti ce ve ssi bil Gonçalves et al. ity , timelin ess
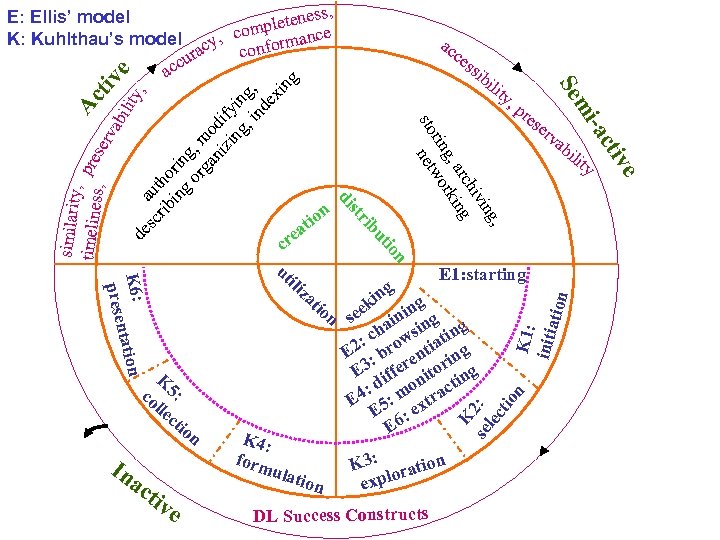
ve re n rv ab ili g nin ng i ha wsi ting c 2: bro tia g E : n 3 fere torin g E if ni in : d mo ract E 4 5: ext E 6: E e se K 1: initi ati n ki on E 1: starting K se 2: lec tio n K 4: form ulat io se K 3: ration o expl DL Success Constructs ty e ac ti , p tiv In n ty -ac mi io ili Se n co 5: lle ct ib , ing hiv arc ng g, rki rin wo sto net n io g tio K ss ut n K 6: ntatio prese e cr ut ili za ce ib str n tio a ac di similarity , Ac timelines pres s, erv tiv ab ilit e y, de a sc ut rib ho in rin g or g, m ga o ni di zi fy ng in , i g, nd ex in g ess, E: Ellis’ model pleten e m K: Kuhlthau’s model cy, co formanc con ura acc
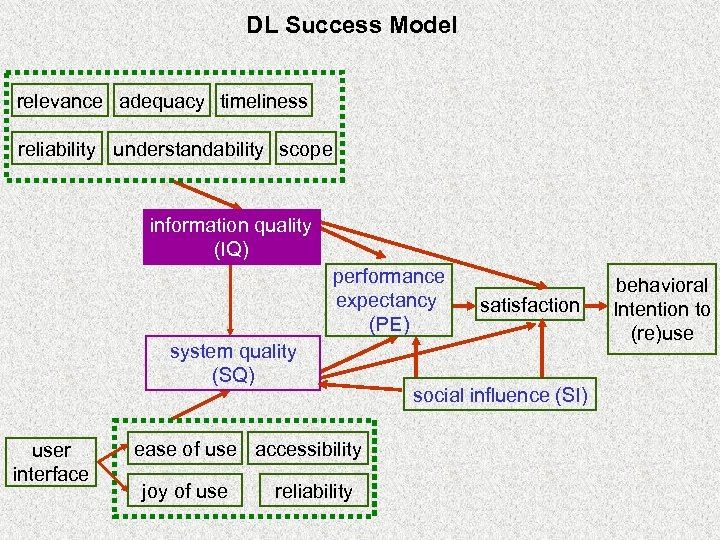
DL Success Model relevance adequacy timeliness reliability understandability scope information quality (IQ) performance expectancy (PE) system quality (SQ) user interface ease of use accessibility joy of use reliability satisfaction social influence (SI) behavioral Intention to (re)use
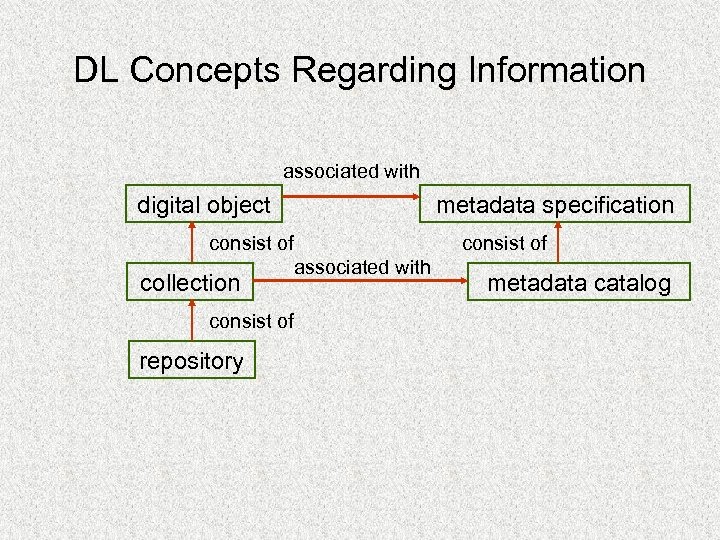
DL Concepts Regarding Information associated with digital object metadata specification consist of collection consist of repository consist of associated with metadata catalog
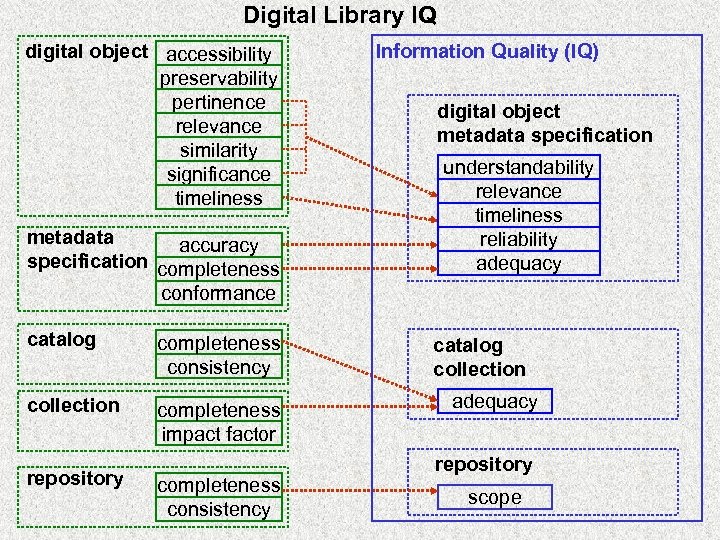
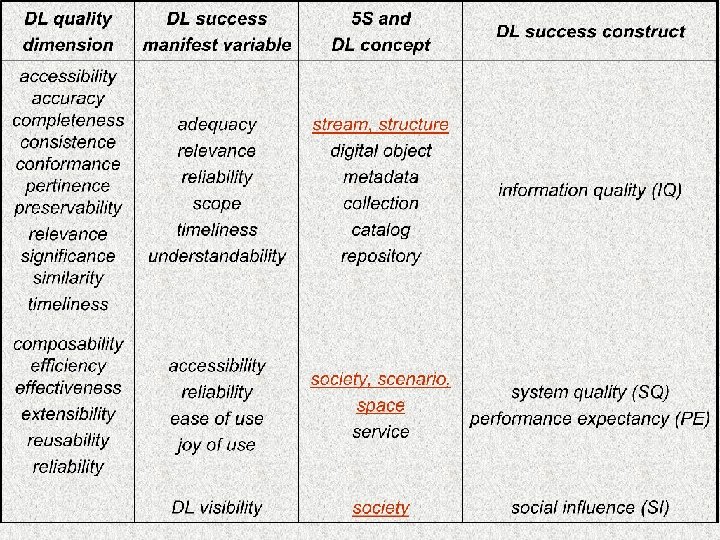
Digital Library IQ digital object accessibility preservability pertinence relevance similarity significance timeliness metadata accuracy specification completeness conformance catalog completeness consistency collection completeness impact factor repository completeness consistency Information Quality (IQ) digital object metadata specification understandability relevance timeliness reliability adequacy catalog collection adequacy repository scope
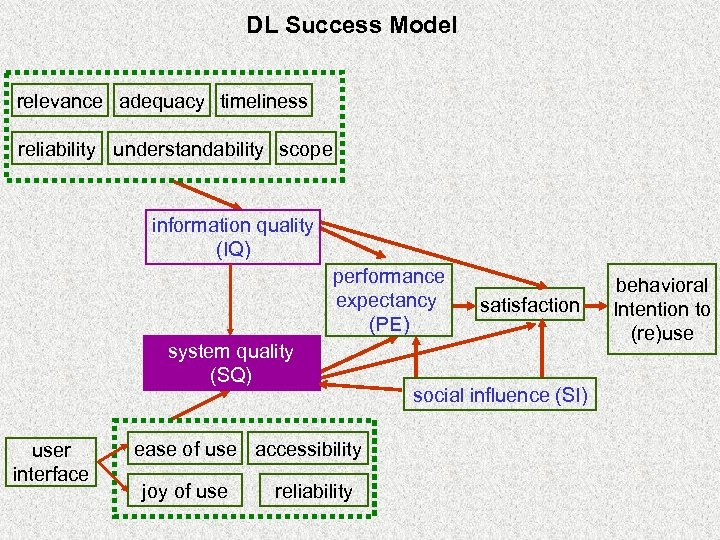
DL Success Model relevance adequacy timeliness reliability understandability scope information quality (IQ) performance expectancy (PE) system quality (SQ) user interface ease of use accessibility joy of use reliability satisfaction social influence (SI) behavioral Intention to (re)use
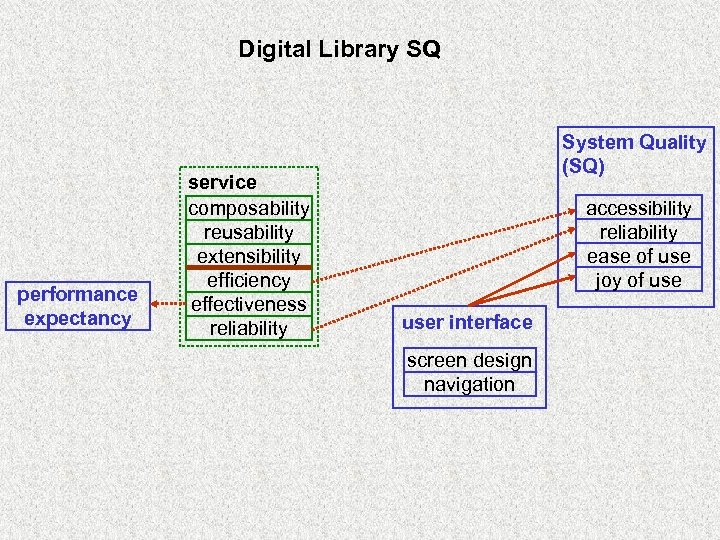
Digital Library SQ performance expectancy service composability reusability extensibility efficiency effectiveness reliability System Quality (SQ) accessibility reliability ease of use joy of user interface screen design navigation

Outline Ø Prior work Ø DL success model § From end user perspective Ø Case study Ø Conclusion

Case Study Ø Part of requirements analysis for ETANA-DL § Email interviews with 5 prestigious archaeologists § Face to face workplace interviews with 11 archaeologists Ø Associate the 4 constructs of DL success model with the activities occurring in the seeking and utilization phases
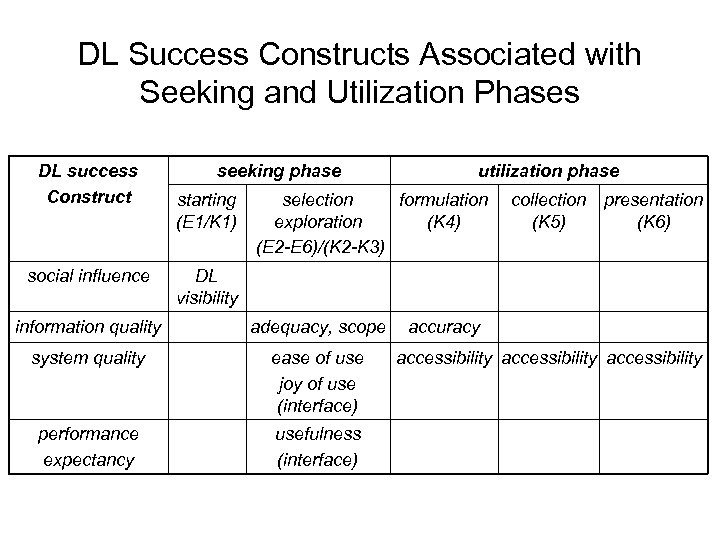
DL Success Constructs Associated with Seeking and Utilization Phases DL success Construct social influence seeking phase starting (E 1/K 1) utilization phase selection formulation exploration (K 4) (E 2 -E 6)/(K 2 -K 3) collection presentation (K 5) (K 6) DL visibility information quality adequacy, scope system quality ease of use joy of use (interface) performance expectancy usefulness (interface) accuracy accessibility

DL Success Constructs Associated with Seeking Phase Ø E 1: Starting’ activity in Ellis’ model (K 1: ‘initiation’ stage in Kuhlthau’s model) § Social Influence (SI) — DL visibility v. Publicize existence of a DL v. Provide a DL alert service

DL Success Constructs Associated with Seeking Phase Ø E 2 -E 6: ‘chaining’, ‘browsing’, ‘differentiating’, ‘monitoring’, and ‘extracting’ in Ellis’ model (K 2 -K 3: ‘selection’ and ‘exploration’ stages in Kuhlthau’s model) § Information Quality (IQ) § System Quality (SQ) § Performance Expectancy (PE)

DL Success Constructs Associated with Seeking Phase Ø E 2 -E 6: ‘chaining’, ‘browsing’, ‘differentiating’, ‘monitoring’, and ‘extracting’ in Ellis’ model (K 2 -K 3: ‘selection’ and ‘exploration’ stages in Kuhlthau’s model) § Information Quality (IQ) v Adequacy (degree of sufficiency and completeness) of DL collections and metadata catalogs v Scope of DL repository

DL Success Constructs Associated with Seeking Phases Ø E 2 -E 6: ‘chaining’, ‘browsing’, ‘differentiating’, ‘monitoring’, and ‘extracting’ in Ellis’ model (K 2 -K 3: ‘selection’ and ‘exploration’ stages in Kuhlthau’s model) § System Quality (SQ) v Ease of use v Joy of use

DL Success Constructs Associated with Seeking Phases Ø E 2 -E 6: ‘chaining’, ‘browsing’, ‘differentiating’, ‘monitoring’, and ‘extracting’ in Ellis’ model (K 2 -K 3: ‘selection’ and ‘exploration’ stages in Kuhlthau’s model) § Performance Expectancy (PE) v Usefulness

DL Success Constructs Associated with Seeking Phases Ø E 2 -E 6: ‘chaining’, ‘browsing’, ‘differentiating’, ‘monitoring’, and ‘extracting’ in Ellis’ model (K 2 -K 3: ‘selection’ and ‘exploration’ stages in Kuhlthau’s model) § System Quality & Performance Expectancy v DL interface: screen design & navigation

DL Success Constructs Associated with Utilization Phase Ø K 4 -K 6: ‘formulation’, ‘collection’, and ‘presentation’ stage in Kuhlthau’s model § Information Quality v information accuracy v information accessibility

Outline Ø Prior work Ø DL success model § From end user perspective Ø Case study Ø Conclusion

Conclusion Ø Lay the foundation for defining success of DLs from the view of DL end users Ø Assume a multi-theoretical perspective Ø Synthesize many related research areas in terms of theory and empirical work Ø Explicate and illustrate our approach by a case study with ETANA and usability Ø Connect with other work on DL quality: led by Emory funded by IMLS, DELOS …

Questions? Comments? See http: //fox. cs. vt. edu/talks/2006/ 20060918 ECDLsuccess. ppt
a3008ca38b7c9c20bb3eb238be1d3af6.ppt