 ? WHAT IS A PRODUCT Kolpashchikov Kirill & Klyagin Alexandr
? WHAT IS A PRODUCT Kolpashchikov Kirill & Klyagin Alexandr
 Definition of a product A product is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption and that might satisfy a want or need; it includes physical objects, services, persons, places, organizations, and ideas.
Definition of a product A product is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption and that might satisfy a want or need; it includes physical objects, services, persons, places, organizations, and ideas.
 Three levels of a product
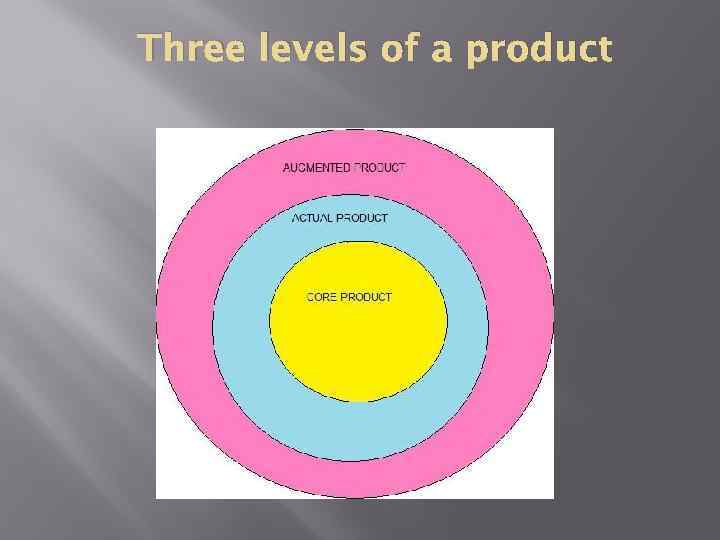
Three levels of a product
 Core product stands at the center of the total product and consists of the problem-solving services or core benefits that consumers seek when they buy a product.
Core product stands at the center of the total product and consists of the problem-solving services or core benefits that consumers seek when they buy a product.
 Actual product Actual products may have as many as five characteristics: Ø quality level Ø features Ø design Ø a brand name Ø packaging
Actual product Actual products may have as many as five characteristics: Ø quality level Ø features Ø design Ø a brand name Ø packaging
 Augmented product is built around the core and actual products by offering additional consumer services and benefits. This includes: v Warranty v After-sale service v Installation v Delivery and credit
Augmented product is built around the core and actual products by offering additional consumer services and benefits. This includes: v Warranty v After-sale service v Installation v Delivery and credit
 Product classification Products can be classified into three groups according to their durability or tangibility: ü Durable Goods. Examples : beer, soap, and salt. ü Nondurable Goods. Examples: refrigerators, automobiles, and furniture. ü Services. Examples: haircuts and home repairs.
Product classification Products can be classified into three groups according to their durability or tangibility: ü Durable Goods. Examples : beer, soap, and salt. ü Nondurable Goods. Examples: refrigerators, automobiles, and furniture. ü Services. Examples: haircuts and home repairs.
 Consumer goods Convenience goods - customer buys frequently, immediately, and with a minimum of comparison and buying effort. Examples: tobacco products, soap, and newspapers. Moreover, convenience goods are divided into staples, impulse goods, and emergency goods. Shopping goods – consumer compares on such bases as suitability, quality, price, and style. Examples : furniture, clothing, used cars, and major appliances. Shopping goods can be divided into uniform and no uniform goods. Specialty goods - goods with unique characteristics or brand identification. Unsought goods - consumer either does not know about or knows about but does not normally think of buying.
Consumer goods Convenience goods - customer buys frequently, immediately, and with a minimum of comparison and buying effort. Examples: tobacco products, soap, and newspapers. Moreover, convenience goods are divided into staples, impulse goods, and emergency goods. Shopping goods – consumer compares on such bases as suitability, quality, price, and style. Examples : furniture, clothing, used cars, and major appliances. Shopping goods can be divided into uniform and no uniform goods. Specialty goods - goods with unique characteristics or brand identification. Unsought goods - consumer either does not know about or knows about but does not normally think of buying.
 Industrial Goods Industrial goods are those bought by individuals and organizations for further processing or for use in conducting a business. Materials and parts Supplies and services Capital items
Industrial Goods Industrial goods are those bought by individuals and organizations for further processing or for use in conducting a business. Materials and parts Supplies and services Capital items
 Materials and parts are industrial goods that enter the manufacturer's product completely, either through further processing or as components. Can be divided into two groups: Raw materials Manufactured materials and parts
Materials and parts are industrial goods that enter the manufacturer's product completely, either through further processing or as components. Can be divided into two groups: Raw materials Manufactured materials and parts
 Capital items are industrial goods that partly enter the finished product. They include two groups: Installations consist of buildings (factories, offices) and fixed equipment (generators, drill presses, large computers, elevators). Accessory equipment includes portable factory equipment and tools, (hand tools, lift trucks) and office equipment (fax machines, desks).
Capital items are industrial goods that partly enter the finished product. They include two groups: Installations consist of buildings (factories, offices) and fixed equipment (generators, drill presses, large computers, elevators). Accessory equipment includes portable factory equipment and tools, (hand tools, lift trucks) and office equipment (fax machines, desks).
 Supplies and services are industrial goods that do not enter the finished product at all. operating supplies (lubricants, coal, computer paper). business services include maintenance and repair services (window cleaning) and business advisory services (legal, management consulting, and advertising).
Supplies and services are industrial goods that do not enter the finished product at all. operating supplies (lubricants, coal, computer paper). business services include maintenance and repair services (window cleaning) and business advisory services (legal, management consulting, and advertising).
 Thank you for attention
Thank you for attention


