128edb2c72b634ebc87095b8b71b3733.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 What have we learnt in 15 years of about educational technology? Hermann Maurer, Graz University of Technology, Austria Keynote presentation for: ED-MEDIA 2002 Denver, Colorado June 29, 2002
What have we learnt in 15 years of about educational technology? Hermann Maurer, Graz University of Technology, Austria Keynote presentation for: ED-MEDIA 2002 Denver, Colorado June 29, 2002
 Structure of Talk 1. The strange development of using computers for education 2. On some generally accepted aspects of modern e-Learning 3. The concept of “Active Document” 4. The role of knowledge management 5. Influence of future computers on learning 6. How to use e. Learning pragmatically
Structure of Talk 1. The strange development of using computers for education 2. On some generally accepted aspects of modern e-Learning 3. The concept of “Active Document” 4. The role of knowledge management 5. Influence of future computers on learning 6. How to use e. Learning pragmatically
 1. The strange development of using computers for education First serious attempt : PLATO (early sixties) Central computer with terminals is used very cleverly for communciation, supervision, feedback, testing, score keeping, etc. HOWEVER: Simple terminals and courseware Overall, only moderately successful
1. The strange development of using computers for education First serious attempt : PLATO (early sixties) Central computer with terminals is used very cleverly for communciation, supervision, feedback, testing, score keeping, etc. HOWEVER: Simple terminals and courseware Overall, only moderately successful
 The strange development of using computers for education 1987, first of our meetings (ICCAL in Calgary): --- pedagogical matters --- how to prepare a good course --- good graphics including videodisks --- first thoughts about hypertext dominate. HOWEVER: The best part of PLATO, the network aspect, almost forgotten!
The strange development of using computers for education 1987, first of our meetings (ICCAL in Calgary): --- pedagogical matters --- how to prepare a good course --- good graphics including videodisks --- first thoughts about hypertext dominate. HOWEVER: The best part of PLATO, the network aspect, almost forgotten!
 The strange development of using computers for education At next three meetings (Dallas 89, Hagen 90, Wolfville 92) main topics: --- increasing emphasis on pedagogy/didactic matters --- intelligent tutoring systems/ simulations --- authoring tools --- CD ROMs HOWEVER, the best features of PLATO still LOST! Stand-alone systems dramatically dominating!
The strange development of using computers for education At next three meetings (Dallas 89, Hagen 90, Wolfville 92) main topics: --- increasing emphasis on pedagogy/didactic matters --- intelligent tutoring systems/ simulations --- authoring tools --- CD ROMs HOWEVER, the best features of PLATO still LOST! Stand-alone systems dramatically dominating!
 The strange development of using computers for education Next two meetings (Orlando 93, Vancouver 94): --- Discussion of learning models (behavioursism, cognitivism, constructionism) --- Advanced authoring facilities --- Hypercard like models dominate. HOWEVER, basic rules on what quality courses must look like are FORGOTTEN: Cute, easy- to- author Hypercard stacks are “in”!
The strange development of using computers for education Next two meetings (Orlando 93, Vancouver 94): --- Discussion of learning models (behavioursism, cognitivism, constructionism) --- Advanced authoring facilities --- Hypercard like models dominate. HOWEVER, basic rules on what quality courses must look like are FORGOTTEN: Cute, easy- to- author Hypercard stacks are “in”!
 The strange development of using computers for education ED-MEDIA 95 (Graz): --- break- through of WWW and networks as major topics HOWEVER, WWW seen only as information repository! But first serious discussion of “re-use” by means of “meta-data”
The strange development of using computers for education ED-MEDIA 95 (Graz): --- break- through of WWW and networks as major topics HOWEVER, WWW seen only as information repository! But first serious discussion of “re-use” by means of “meta-data”
 The strange development of using computers for education ED-MEDIA 96 (Boston): From now on: WWW remains dominating factor --- more emphasis on communicational and collaborative features HOWEVER, simple-mindedness of servers and browsers limits “working with material”: --- good ideas from simulation, ITS get lost --- old ideas (student tracking, feedback) not yet re-discovered
The strange development of using computers for education ED-MEDIA 96 (Boston): From now on: WWW remains dominating factor --- more emphasis on communicational and collaborative features HOWEVER, simple-mindedness of servers and browsers limits “working with material”: --- good ideas from simulation, ITS get lost --- old ideas (student tracking, feedback) not yet re-discovered
 The strange development of using computers for education As of 97: Title enhanced by “ED-TELECOM”: 97 (Calgary), 98 (Freiburg), 99 (Seattle): --- Educational systems without network unthinkable --- Many uses of network “re-discovered” --- The term “learning environment” starts to surface --- Re-use of modules, standardization of meta-data and courseware starts to make progress HOWEVER, personalization and truly individually working with material still rudimentary
The strange development of using computers for education As of 97: Title enhanced by “ED-TELECOM”: 97 (Calgary), 98 (Freiburg), 99 (Seattle): --- Educational systems without network unthinkable --- Many uses of network “re-discovered” --- The term “learning environment” starts to surface --- Re-use of modules, standardization of meta-data and courseware starts to make progress HOWEVER, personalization and truly individually working with material still rudimentary
 The strange development of using computers for education 2000 (Montreal), 2001 (Tampere) start to recognize: --- full value of network for collaboration --- importance of personalization --- importance of large number of functions for learners, tutors, experts, authors, administrators --- need for digital libraries as “background references” --- authoring is small part of e. Learning systems HOWEVER, e. Learning is still seen in isolation rather than as knowledge transfer in a knowledge management system!
The strange development of using computers for education 2000 (Montreal), 2001 (Tampere) start to recognize: --- full value of network for collaboration --- importance of personalization --- importance of large number of functions for learners, tutors, experts, authors, administrators --- need for digital libraries as “background references” --- authoring is small part of e. Learning systems HOWEVER, e. Learning is still seen in isolation rather than as knowledge transfer in a knowledge management system!
 2. On some generally accepted aspects of modern e-Learning WWW as educational tool: often misused! It is NOT enough to have: – Sequence of Multimedia WWW pages – Some Question/Answer dialogues (typical: Multiple Choice) – Email for communication
2. On some generally accepted aspects of modern e-Learning WWW as educational tool: often misused! It is NOT enough to have: – Sequence of Multimedia WWW pages – Some Question/Answer dialogues (typical: Multiple Choice) – Email for communication
 Note: - Web must not use distance education in the sense of allowing to teach still larger groups simultaneously - Web must not be used as electronic book, but such books and the Web as powerful background library - Good and pleasing content is important but no need to compete with Hollywood - Creation of impressive multi-media content is not the answer: the answer is a suitable learning environment
Note: - Web must not use distance education in the sense of allowing to teach still larger groups simultaneously - Web must not be used as electronic book, but such books and the Web as powerful background library - Good and pleasing content is important but no need to compete with Hollywood - Creation of impressive multi-media content is not the answer: the answer is a suitable learning environment
 Requirements for modern e. Learning environment (user view only!): – pretests to assess level of knowledge and cognitive style – support different learning paradigms ( like: behavioristic, cognitivistic and constructionistic, implicit learning, etc …) – allow users to work with material – use WWW to break isolation: chats, collaboration spaces, discussion forums, allow student questions – background libraries with automatically generated knowledge landscapes
Requirements for modern e. Learning environment (user view only!): – pretests to assess level of knowledge and cognitive style – support different learning paradigms ( like: behavioristic, cognitivistic and constructionistic, implicit learning, etc …) – allow users to work with material – use WWW to break isolation: chats, collaboration spaces, discussion forums, allow student questions – background libraries with automatically generated knowledge landscapes
 Working with Material … insert notes for specified users … insert links for specified users … insert attachments for specified users … change material by adding material (self composed or from library!), by condensing material, by changing structure for specified users … note that this gives multiple views of courseware and background library
Working with Material … insert notes for specified users … insert links for specified users … insert attachments for specified users … change material by adding material (self composed or from library!), by condensing material, by changing structure for specified users … note that this gives multiple views of courseware and background library
 Discussion Forums … Every course must have structured discussion forum … Discussion forums for many participants are not trivial … Arbitrary document types, notes and links … New and unread contributions must be marked per user … Different levels of anonymity are desirable … Notification mechanism … Different display and sorting criteria must be provided … Search facilities … Different roles (student, evaluator, moderator, …)
Discussion Forums … Every course must have structured discussion forum … Discussion forums for many participants are not trivial … Arbitrary document types, notes and links … New and unread contributions must be marked per user … Different levels of anonymity are desirable … Notification mechanism … Different display and sorting criteria must be provided … Search facilities … Different roles (student, evaluator, moderator, …)
 Check out the URL coronet. iicm. edu A comprehensive set of collaborative tools, result of the EU Project CORONET.
Check out the URL coronet. iicm. edu A comprehensive set of collaborative tools, result of the EU Project CORONET.
 Student Questions Student questions must be possible at any point and fast reaction (if necessary automated) is essential. Details later under “Active Documents”
Student Questions Student questions must be possible at any point and fast reaction (if necessary automated) is essential. Details later under “Active Documents”
 Background libraries with automatically generated knowledge landscapes Example: Brockhaus: Die Enzyklopädie - Multimedial
Background libraries with automatically generated knowledge landscapes Example: Brockhaus: Die Enzyklopädie - Multimedial
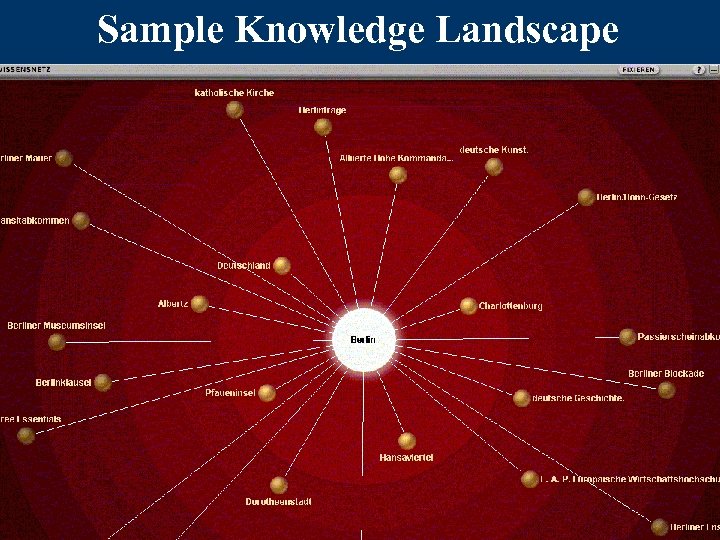 Sample Knowledge Landscape
Sample Knowledge Landscape
 3. Active documents Vision: Any document on the screen any question can be asked. Document answers the question! Is this Science Fiction? Not really!
3. Active documents Vision: Any document on the screen any question can be asked. Document answers the question! Is this Science Fiction? Not really!
 Implementation of Active Document concept: Use the fact that many users look at same page! Problem is reduced to: When are different questions x and y semantically identical?
Implementation of Active Document concept: Use the fact that many users look at same page! Problem is reduced to: When are different questions x and y semantically identical?
 Above mentioned features: implemented in e. Learning Suite, an extension of Hyperwave, a WWW based Knowledge Management System. All Hyperwave components: Free for Universities and Schools under HAUP (Hyperwave Academic User Program) for noncommercial use, see: www. HAUP. org
Above mentioned features: implemented in e. Learning Suite, an extension of Hyperwave, a WWW based Knowledge Management System. All Hyperwave components: Free for Universities and Schools under HAUP (Hyperwave Academic User Program) for noncommercial use, see: www. HAUP. org
 4. Knowledge Management: “If our employees only knew what our employees know we would be a much better organisation. ”
4. Knowledge Management: “If our employees only knew what our employees know we would be a much better organisation. ”
 Challenge: Make knowledge of all available to all; collect unobtrusively as much knowledge as possible from persons and other sources into computer system; make knowledge easily available.
Challenge: Make knowledge of all available to all; collect unobtrusively as much knowledge as possible from persons and other sources into computer system; make knowledge easily available.
 KT = Knowledge Transfer = e. Learning is part of Knowledge Management Many approaches exist!
KT = Knowledge Transfer = e. Learning is part of Knowledge Management Many approaches exist!
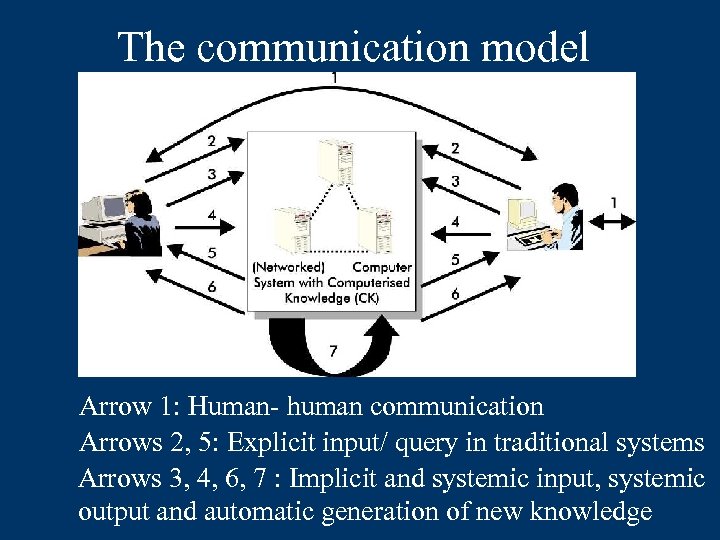 The communication model Arrow 1: Human- human communication Arrows 2, 5: Explicit input/ query in traditional systems Arrows 3, 4, 6, 7 : Implicit and systemic input, systemic output and automatic generation of new knowledge
The communication model Arrow 1: Human- human communication Arrows 2, 5: Explicit input/ query in traditional systems Arrows 3, 4, 6, 7 : Implicit and systemic input, systemic output and automatic generation of new knowledge
 Current major tools in KM … Active document concept … Similarity recognition of documents … Knowledge landscapes … Connection recognition … Growth of knowledge through additions by users
Current major tools in KM … Active document concept … Similarity recognition of documents … Knowledge landscapes … Connection recognition … Growth of knowledge through additions by users
 Connection recognition Visit of Bin Laden in Nassau, Oct. 16, 2000 Vacation of person x on Eluthera, Oct. 15 -20, 2000 Bin Laden knows person z Person x knows person z Each „connection“ adds weight to thesis that two persons or events are related. If sum of weights exceeds threshold: systems sends notification.
Connection recognition Visit of Bin Laden in Nassau, Oct. 16, 2000 Vacation of person x on Eluthera, Oct. 15 -20, 2000 Bin Laden knows person z Person x knows person z Each „connection“ adds weight to thesis that two persons or events are related. If sum of weights exceeds threshold: systems sends notification.
 Wanted: Object Oriented (OO) Compression Techniques (CT) for Movies (M) … CT include MPG 1, MPG 2 and MPG 7. . . yields: (CT, MPG 1), (CT, MPG 2), (CT, MPG 7) … CT good for long movies (CT, lm) … long movies work well with MPG 7 (lm, MPG 7) yields (M, MPG 7) and (CT, MPG 7) Together with e. g (OO, MPG 7), (OO, MPG 7) from somewhere else yields “Incident count for MPG 7” is 6.
Wanted: Object Oriented (OO) Compression Techniques (CT) for Movies (M) … CT include MPG 1, MPG 2 and MPG 7. . . yields: (CT, MPG 1), (CT, MPG 2), (CT, MPG 7) … CT good for long movies (CT, lm) … long movies work well with MPG 7 (lm, MPG 7) yields (M, MPG 7) and (CT, MPG 7) Together with e. g (OO, MPG 7), (OO, MPG 7) from somewhere else yields “Incident count for MPG 7” is 6.
 KM relevant to e. Learning because: - e. Learning needs substantial background libraries with automatic similarity recognition and creation of knowledge maps - growth of knowledge through feedback and contributions essential - systemic actions are essential, e. g. in discussion forums
KM relevant to e. Learning because: - e. Learning needs substantial background libraries with automatic similarity recognition and creation of knowledge maps - growth of knowledge through feedback and contributions essential - systemic actions are essential, e. g. in discussion forums
 Knowledge- increase in e. Learning environment through e. g. : (1) notes, chats, discussions, collaboration (2) question/answer dialogues (3) systemic actions like automatically generated links, relationships and landscapes This needs good knowledge management system Conference on KM: Graz Austria, July 11 -12 www. know-center. at/i-know 02
Knowledge- increase in e. Learning environment through e. g. : (1) notes, chats, discussions, collaboration (2) question/answer dialogues (3) systemic actions like automatically generated links, relationships and landscapes This needs good knowledge management system Conference on KM: Graz Austria, July 11 -12 www. know-center. at/i-know 02
 5. Future computers and their influence on learning The mobile computer of the future - tiny - no screen - no keyboard as we now have it - no batteries - when turned on, automatic mobile net-connection - built in GPS - buitl in video camera and microphone
5. Future computers and their influence on learning The mobile computer of the future - tiny - no screen - no keyboard as we now have it - no batteries - when turned on, automatic mobile net-connection - built in GPS - buitl in video camera and microphone
 Visible part of a future computer:
Visible part of a future computer:
 Two-part ring as one of the many new data input devices
Two-part ring as one of the many new data input devices
 Many things we learn today we will have no need to learn in the future - arithmetic? - handwriting? - spelling? - factual knowledge? - logical thinking? - languages? -. . .
Many things we learn today we will have no need to learn in the future - arithmetic? - handwriting? - spelling? - factual knowledge? - logical thinking? - languages? -. . .
 UT 103 : http: //www. ectaco. com
UT 103 : http: //www. ectaco. com
 6. How to use e. Learning pragmatically e. Learning DIFFERENT in industry/government and schools/universities Industry: e. Learning helps to save money (in time, on the spot learning) Universities: e. Learning SUPPORTS teaching, can improve it but DOES NOT usually make it cheaper!
6. How to use e. Learning pragmatically e. Learning DIFFERENT in industry/government and schools/universities Industry: e. Learning helps to save money (in time, on the spot learning) Universities: e. Learning SUPPORTS teaching, can improve it but DOES NOT usually make it cheaper!
 Thank you for your listening! URLs: www. hyperwave. de www. haup. org www. iicm. edu/maurer www. know-center. at/i-know 02 email: hmaurer@iicm. edu Advertisement: For my newest novel about Telekinesis (SF) see www. iicm. edu/Xperten
Thank you for your listening! URLs: www. hyperwave. de www. haup. org www. iicm. edu/maurer www. know-center. at/i-know 02 email: hmaurer@iicm. edu Advertisement: For my newest novel about Telekinesis (SF) see www. iicm. edu/Xperten


