81cc06960e48ad3ad3458ae5c2f43f62.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 197




 What happened next. . .
What happened next. . .
 The lessons from this:
The lessons from this:

 Imagine a world without anaesthesia. . .
Imagine a world without anaesthesia. . .

 Without anaesthesia. . .
Without anaesthesia. . .

 But what is anaesthesia?
But what is anaesthesia?
 The other triad of anaesthesia
The other triad of anaesthesia
 Anaesthesia can be:
Anaesthesia can be:
 But wait. . . there’s more:
But wait. . . there’s more:



 Perioperative system includes:
Perioperative system includes:
 But why?
But why?
 The Pre-anaesthetic Consultation
The Pre-anaesthetic Consultation


 ASA Physical Status
ASA Physical Status
 Relevance of this?
Relevance of this?

 Perioperative management
Perioperative management
 Diabetic patient for vascular surgery
Diabetic patient for vascular surgery
 History
History






 Safety Initiatives in Anaesthesia
Safety Initiatives in Anaesthesia
 Principles of Safety
Principles of Safety

 Monitoring in anaesthesia
Monitoring in anaesthesia
 Pulse oximetry
Pulse oximetry
 Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram

 Capnography
Capnography
 Oxygen monitoring
Oxygen monitoring

 Temperature monitoring
Temperature monitoring


 Other monitors
Other monitors

 Patient with polycystic ovaries for laparoscopic cystotomies as day case procedure
Patient with polycystic ovaries for laparoscopic cystotomies as day case procedure

 History
History


 Anaesthetic issues
Anaesthetic issues






 Remember:
Remember:









 Classification of drugs used for anaesthesia
Classification of drugs used for anaesthesia







 General features of IV agents
General features of IV agents
 Propofol
Propofol
 Other IV agents
Other IV agents











 Why use paralysing drugs at all?
Why use paralysing drugs at all?
 Properties of NMBDs
Properties of NMBDs
 “Sux” versus the NDNMBDs
“Sux” versus the NDNMBDs
 Nondepolarising relaxants
Nondepolarising relaxants
 Side effects of suxamethonium
Side effects of suxamethonium
 Problems with nondepolarisers
Problems with nondepolarisers
 Paralysis obviously mandates controlled ventilation
Paralysis obviously mandates controlled ventilation
 The Physiology of Controlled Ventilation
The Physiology of Controlled Ventilation
 Pharmacology 5: Local anaesthetic agents
Pharmacology 5: Local anaesthetic agents
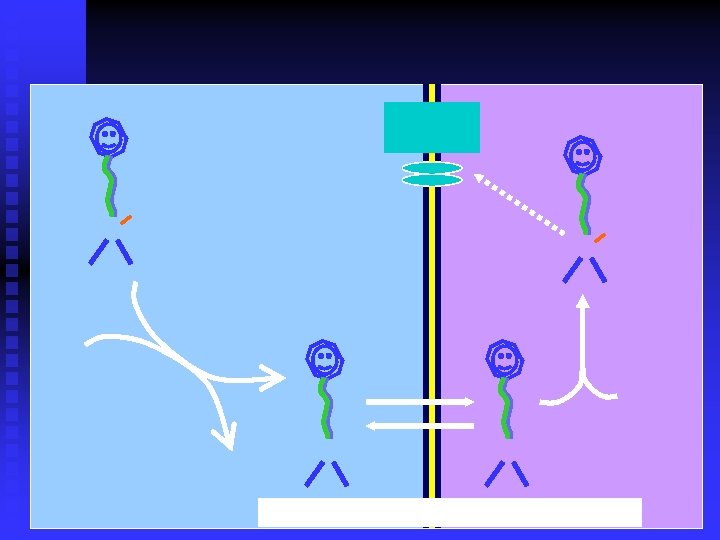



 Adjuvant agents used with LAs
Adjuvant agents used with LAs








 History
History
 Issues
Issues
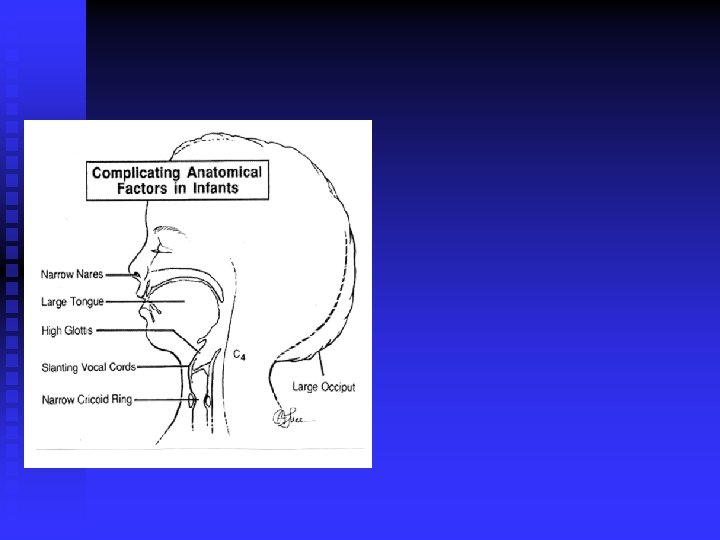
 Adult-Paediatric Differences
Adult-Paediatric Differences









 History
History
 Issues
Issues
 Principles
Principles
 Differences in Pregnancy
Differences in Pregnancy
 Drugs & the Placenta
Drugs & the Placenta
 Scenarios
Scenarios
 Analgesic options
Analgesic options






 Lung separation techniques:
Lung separation techniques:





 Special considerations in neurosurgical anaesthesia:
Special considerations in neurosurgical anaesthesia:
 Anaesthetic Emergencies
Anaesthetic Emergencies
 A: Emergency Anaesthesia
A: Emergency Anaesthesia
 Considerations in Emergency Anaesthesia
Considerations in Emergency Anaesthesia
 Anaesthetic management
Anaesthetic management
 Emergency Anaesthesia: Maintenance
Emergency Anaesthesia: Maintenance


 Airway Management I
Airway Management I

 Airway Management II
Airway Management II

 Airway Management III
Airway Management III
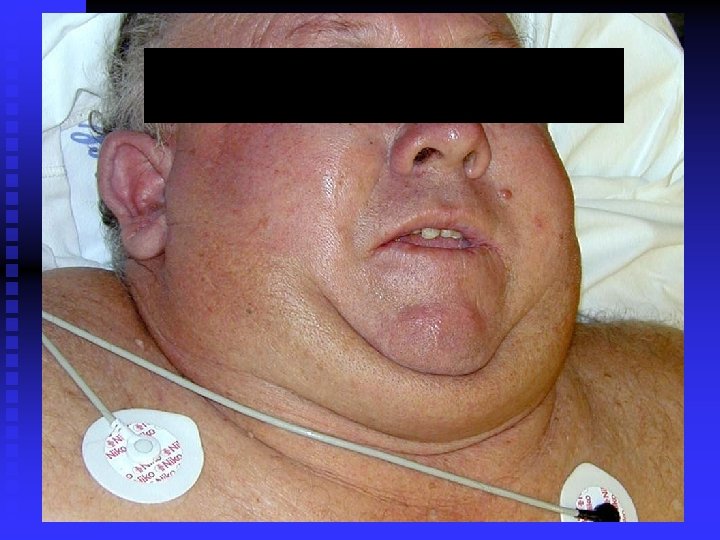

 Airway Management IV
Airway Management IV

 Respiratory Management I
Respiratory Management I

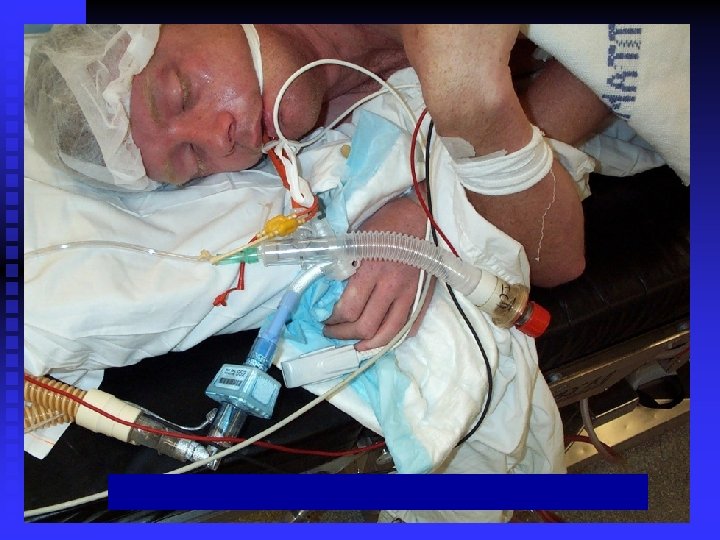
 Respiratory Management II
Respiratory Management II

 Circulatory management
Circulatory management



 Hypothermia in Trauma
Hypothermia in Trauma


 Recreational drugs
Recreational drugs
 The geriatric trauma patient
The geriatric trauma patient

 The Pregnant Patient
The Pregnant Patient
 B: Anaesthetic Emergencies & Complications
B: Anaesthetic Emergencies & Complications


 Anaesthetic Risk In Perspective
Anaesthetic Risk In Perspective






