340df3daf3c2b782a8769bca6f918f17.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

What does the Acoustic Reflectance tell us about the middle ear? MEMRO 2009 Patricia Jeng, Pierre Parent, Jont Allen, Mimosa Acoustics Harry Levitt, Advanced Hearing Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009
Goals Acoustic power measurements quantify wide band complex: o Reflectance o Transmittance o Immittance These measures provide clues to our puzzle: Resonance frequencies - Stiffness vs. mass dominance • Sites of reflection • Conductive hearing loss: mild, moderate, severe – Air-bone gap & Tympanometry Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 2
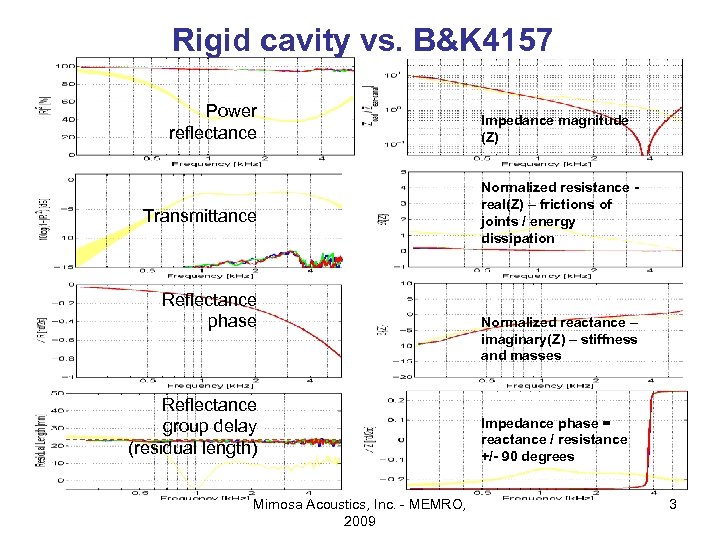
Rigid cavity vs. B&K 4157 Power reflectance Transmittance Reflectance phase Reflectance group delay (residual length) Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 Impedance magnitude (Z) Normalized resistance real(Z) – frictions of joints / energy dissipation Normalized reactance – imaginary(Z) – stiffness and masses Impedance phase = reactance / resistance +/- 90 degrees 3
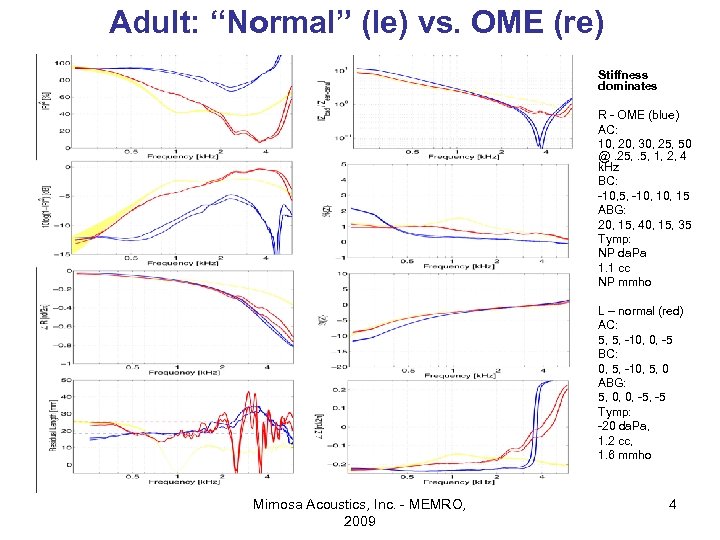
Adult: “Normal” (le) vs. OME (re) • • • R - OME (blue) AC: 10, 20, 30, 25, 50 @. 25, . 5, 1, 2, 4 k. Hz BC: -10, 5, -10, 15 ABG: 20, 15, 40, 15, 35 Tymp: NP da. Pa 1. 1 cc NP mmho • • • Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 Stiffness dominates L – normal (red) AC: 5, 5, -10, 0, -5 BC: 0, 5, -10, 5, 0 ABG: 5, 0, 0, -5 Tymp: -20 da. Pa, 1. 2 cc, 1. 6 mmho 4
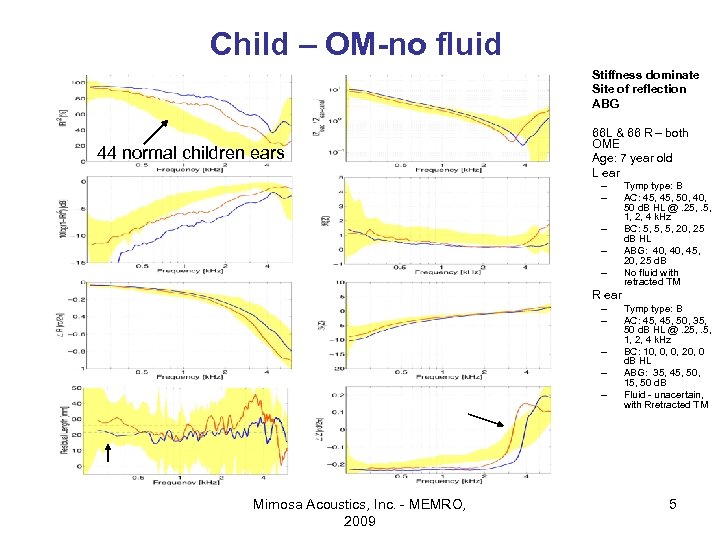
Child – OM-no fluid • • 44 normal children ears Stiffness dominate Site of reflection ABG 66 L & 66 R – both OME Age: 7 year old L ear • • – – – • R ear – – – Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 Tymp type: B AC: 45, 50, 40, 50 d. B HL @. 25, . 5, 1, 2, 4 k. Hz BC: 5, 5, 5, 20, 25 d. B HL ABG: 40, 45, 20, 25 d. B No fluid with retracted TM Tymp type: B AC: 45, 50, 35, 50 d. B HL @. 25, . 5, 1, 2, 4 k. Hz BC: 10, 0, 0, 20, 0 d. B HL ABG: 35, 45, 50, 15, 50 d. B Fluid - unacertain, with Rretracted TM 5
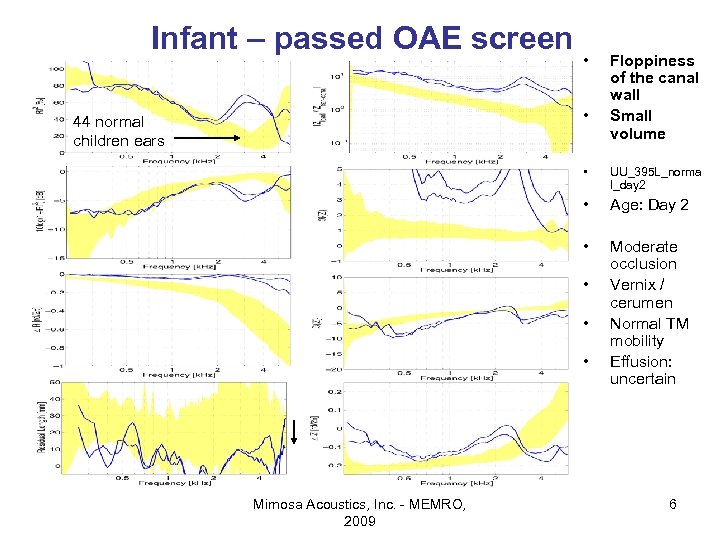
Infant – passed OAE screen • • 44 normal children ears Floppiness of the canal wall Small volume • UU_395 L_norma l_day 2 • Age: Day 2 • Moderate occlusion Vernix / cerumen Normal TM mobility Effusion: uncertain • • • Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 6
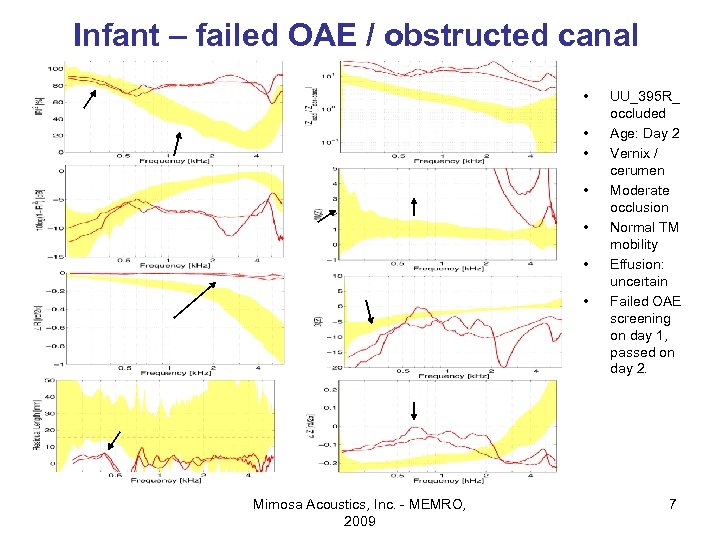
Infant – failed OAE / obstructed canal • • Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 UU_395 R_ occluded Age: Day 2 Vernix / cerumen Moderate occlusion Normal TM mobility Effusion: uncertain Failed OAE screening on day 1, passed on day 2. 7
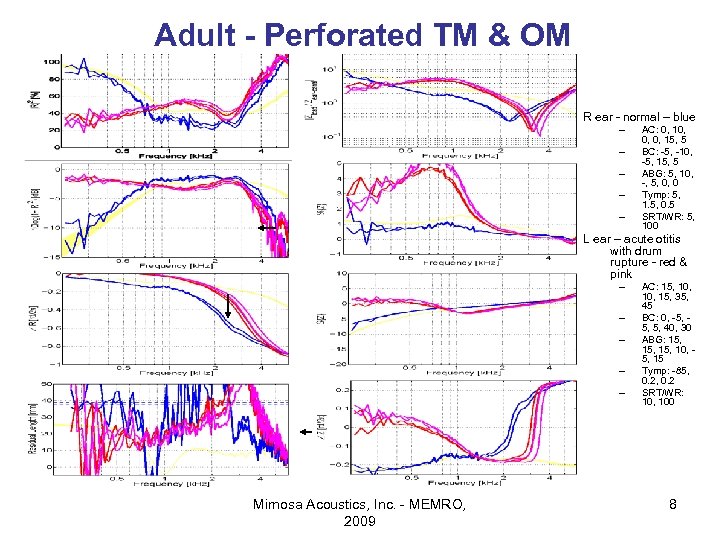
Adult - Perforated TM & OM R ear - normal – blue – – – AC: 0, 10, 0, 0, 15, 5 BC: -5, -10, -5, 15, 5 ABG: 5, 10, -, 5, 0, 0 Tymp: 5, 1. 5, 0. 5 SRT/WR: 5, 100 L ear – acute otitis with drum rupture - red & pink – – – Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 AC: 15, 10, 15, 35, 45 BC: 0, -5, 5, 5, 40, 30 ABG: 15, 15, 10, 5, 15 Tymp: -85, 0. 2 SRT/WR: 10, 100 8

Summary • 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) The intention of this presentation is to show that all the measures obtained by the power measurements provide informative clues to the middle ear transmission status by identifying the interrelations of the three impedance components (resistance, stiffness and mass); the sites of reflections; how much energy is transmitted to the middle ear structure; how much acoustic energy is dissipated by the middle ear structure; how much energy is transmitted to the cochlear; and the relationship of audiometric air-bone gap and the transmittance expressed in log scale. Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 9

Summary • • • The residual distance as computed from the reflectance group delay might be used to indicate the sites of reflections at low frequency. From the examples shown, the sites of reflections in the OME ear is at or close to the ear drum depending on the severity of the infection. In the normal ears, the sites of reflection are beyond TM. In the OME ear, the middle ear structure is much simpler in its mechanical property giving much less complex reflectance group delay than in the normal. Transmittance might provide as an objective and qualitative prediction of the audiometric air-bone gaps in screening and better identifying young children with OME who need follow up assistance. Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 10

Data come from several projects • SBIR 6554 at Mimosa Acoustics – Patrick Feeney, University of Washington – Lisa Hunter, University of Utah • Gravelino Study – – Andrea Bohnert, Mainz, DE • Mimosa Acoustics – Kyle Rust – Elizabeth Allen Mimosa Acoustics, Inc. - MEMRO, 2009 11
340df3daf3c2b782a8769bca6f918f17.ppt