abdc4ef724b70506957b94561f13459d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

What Business People Need to Know About Data Management and Data Governance Micheline Casey Principal CDO, LLC @michelinecasey 1@gmail. com www. data. Trending. wordpress. com

Best-in-Class or Laggard? Best-in-class companies take 12 days on average to integrate new data sources into their analytical systems; industry average companies take 60 days; and, laggards 143 days Source: Aberdeen Group: Data Management for BI: Fueling the analytical engine with high-octane information • Limits ability to achieve organizational potential and to aggressively pursue new market opportunities • Limits ability to take advantage of newly emerging business opportunities • Limits success in bringing high-value products and services to customers, and in retaining and winning desired business • Limits ability to drive informationbased insights • Limits ability to be proactive
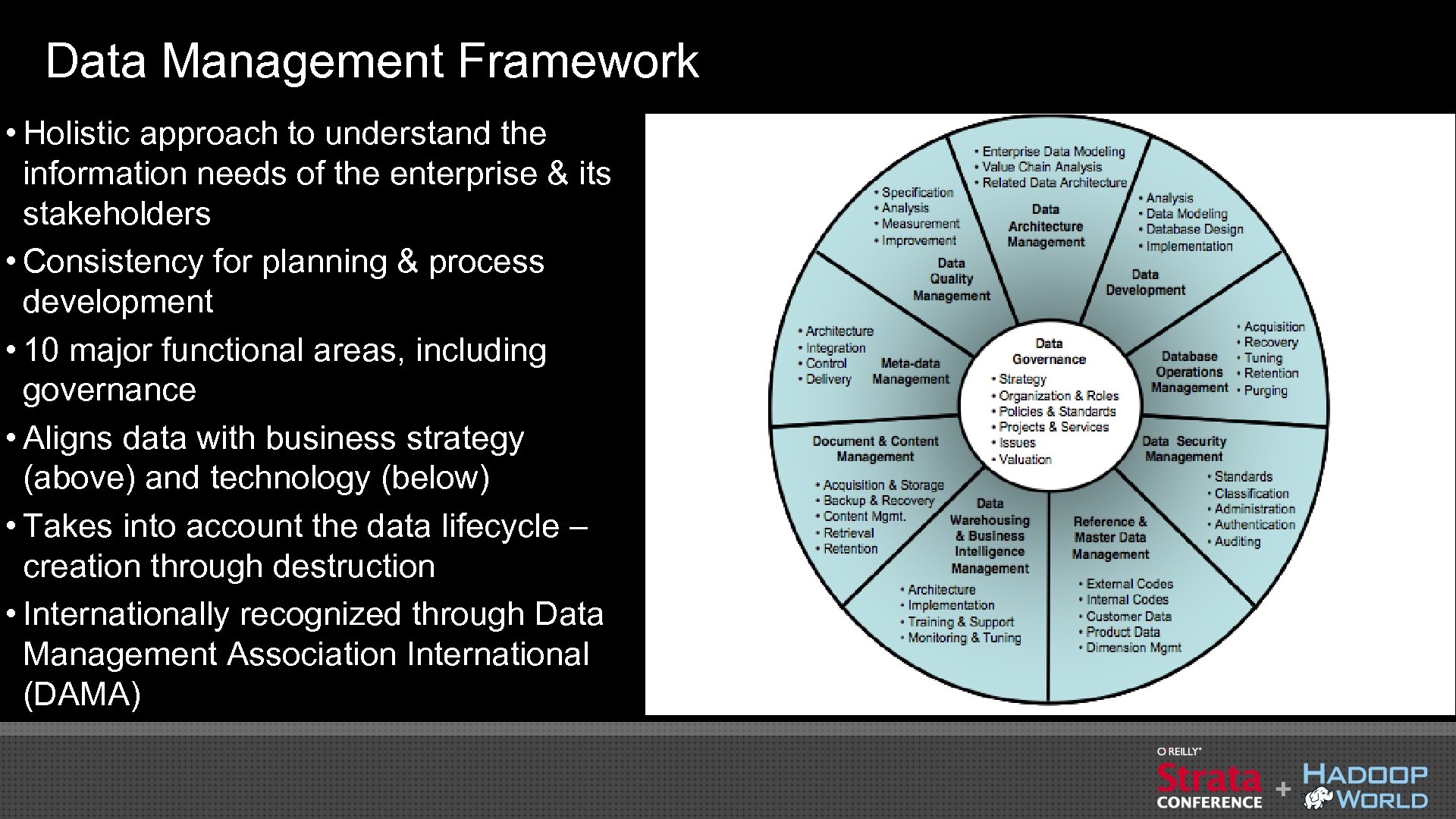
Data Management Framework • Holistic approach to understand the information needs of the enterprise & its stakeholders • Consistency for planning & process development • 10 major functional areas, including governance • Aligns data with business strategy (above) and technology (below) • Takes into account the data lifecycle – creation through destruction • Internationally recognized through Data Management Association International (DAMA)

Key Supporting Data Management Components to Big Data • Data Governance – Exercise of authority and controls over the management of data assets. Policies, processes, standards, definitions, metrics. • Councils, stewards, trustees roles and responsibilities defined • Data Architecture - Defines data requirements, guides integration and control of data assets, aligns data investments with business strategy. • Part of an overall enterprise architecture framework • Enterprise data models, definitions, and taxonomies • Enterprise data delivery • Master Data Management – Control over master data values to enable consistent, contextual use across systems of the most accurate, timely and relevant version of truth about essential business entities. • Meta Data Management – Descriptive tags about data, concepts, and connections between data and concepts. • Business, technical, process, and stewardship • Data Security – Planning, development, and execution of security policies and procedures to provide proper authentication, authorization, access, and auditing of data and information assets.
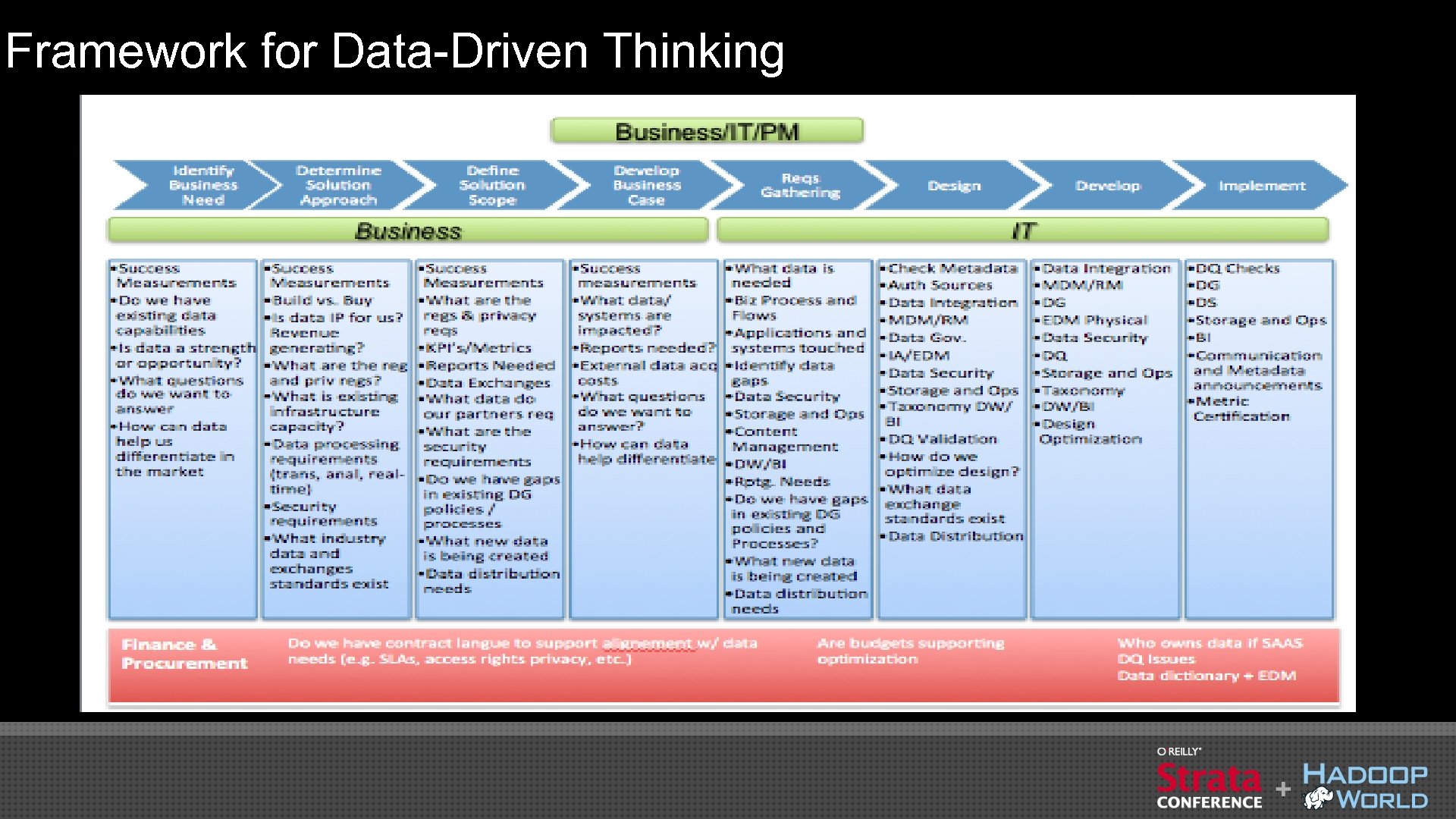
Framework for Data-Driven Thinking

Key Questions to Drive Business Value from Data • What business opportunity/problem are we trying to solve? • How do we integrate the right data together? • What questions do we need to answer to solve the problem? • How do we manage the quality of the data? • What data do we need to answer the questions? • Do we have all the data about this (person, event, thing, etc. )? • What data do we have? • What are the permissible purposes of the data? (compliance, regulatory environment) • How can data help differentiate us in the market? • What data is IP for us? Revenue generating for us? • What data does this relate to (master data)? • Who is allowed to access the data? Use this data?
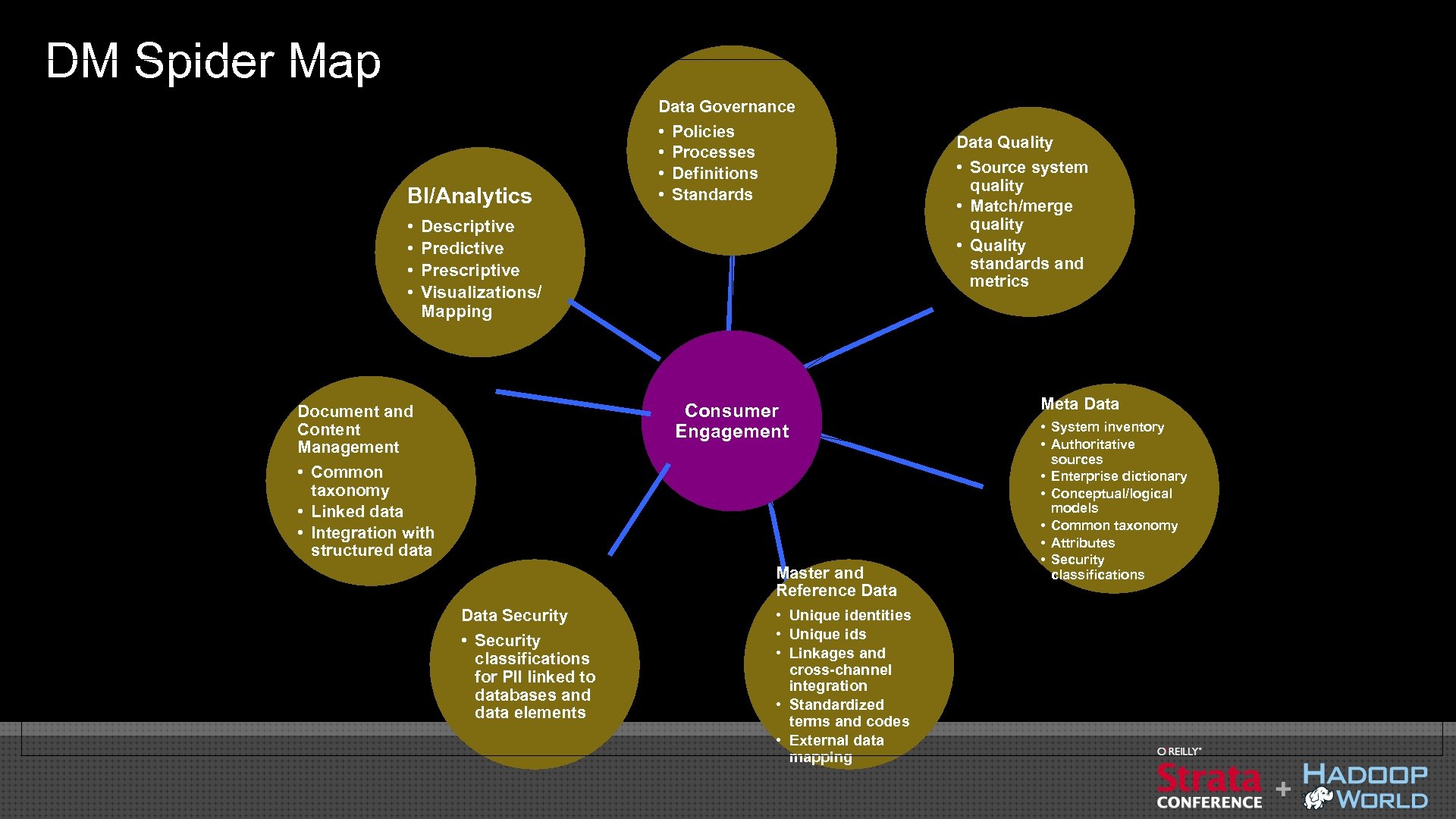
DM Spider Map BI/Analytics • • Data Governance • Policies • Processes • Definitions • Standards Descriptive Predictive Prescriptive Visualizations/ Mapping Consumer Engagement Document and Content Management • Common taxonomy • Linked data • Integration with structured data Master and Reference Data Security • Security classifications for PII linked to databases and data elements • Unique identities • Unique ids • Linkages and cross-channel integration • Standardized terms and codes • External data mapping Data Quality • Source system quality • Match/merge quality • Quality standards and metrics Meta Data • System inventory • Authoritative sources • Enterprise dictionary • Conceptual/logical models • Common taxonomy • Attributes • Security classifications
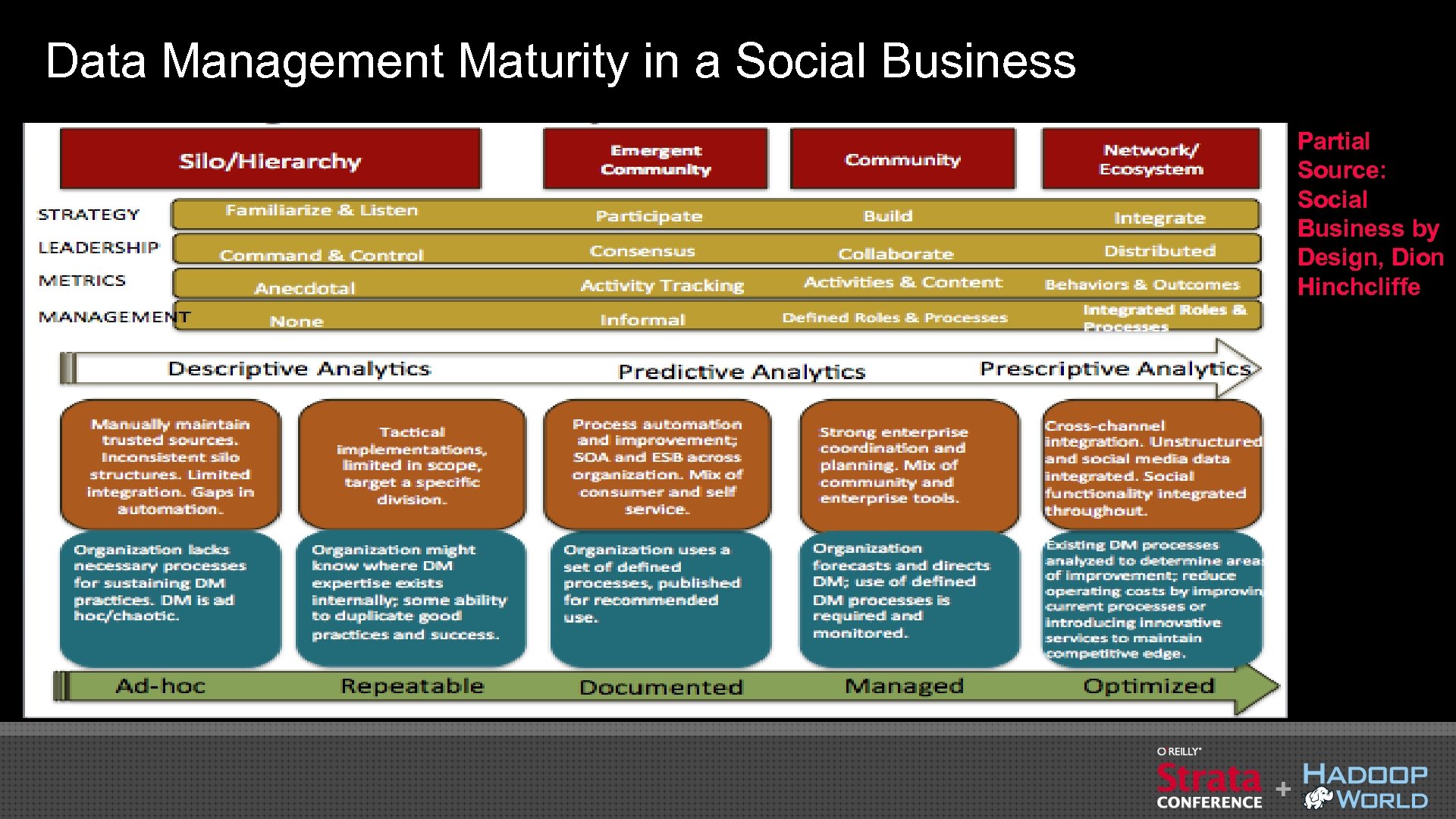
Data Management Maturity in a Social Business Partial Source: Social Business by Design, Dion Hinchcliffe
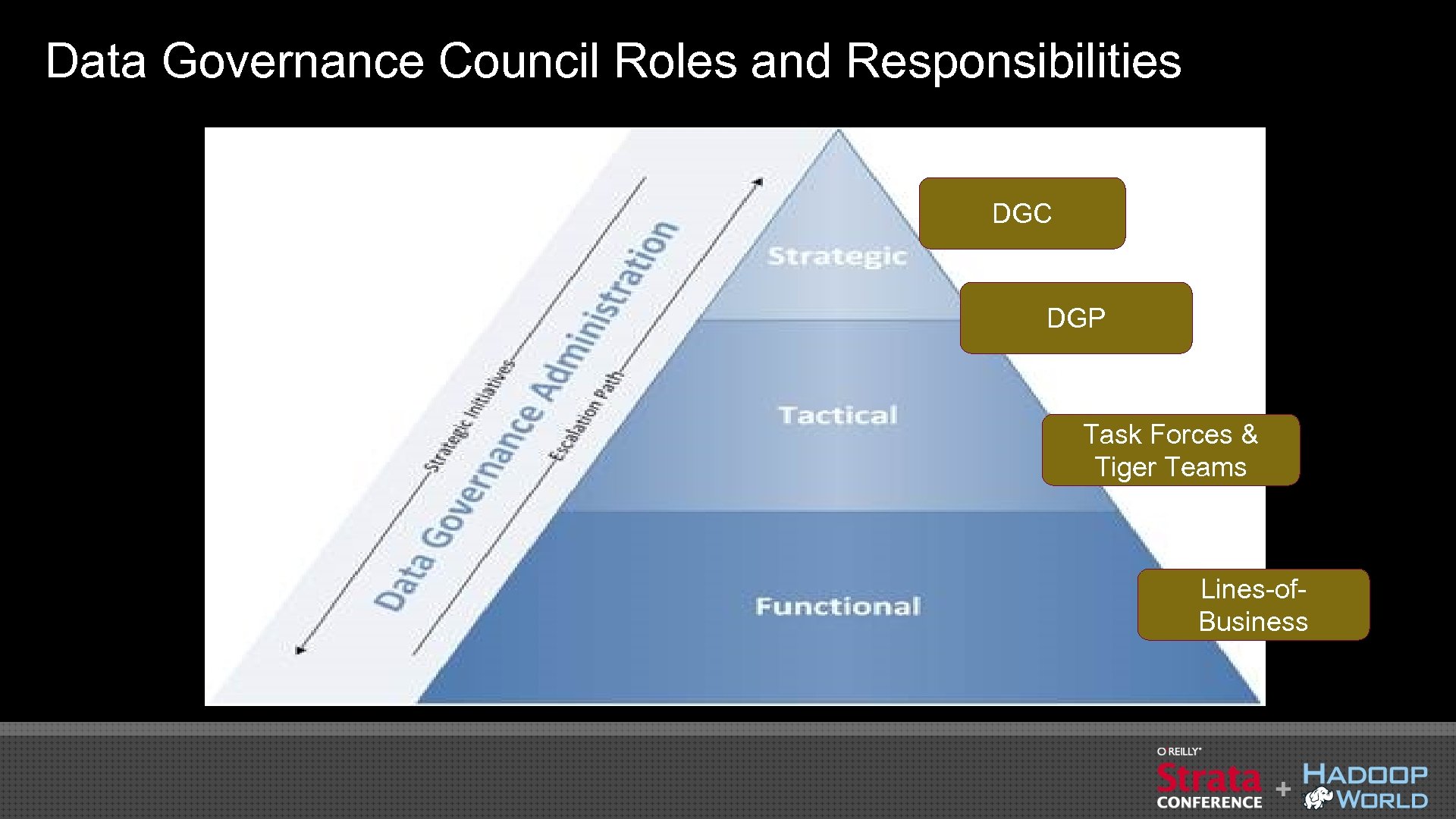
Data Governance Council Roles and Responsibilities DGC DGP Task Forces & Tiger Teams Lines-of. Business
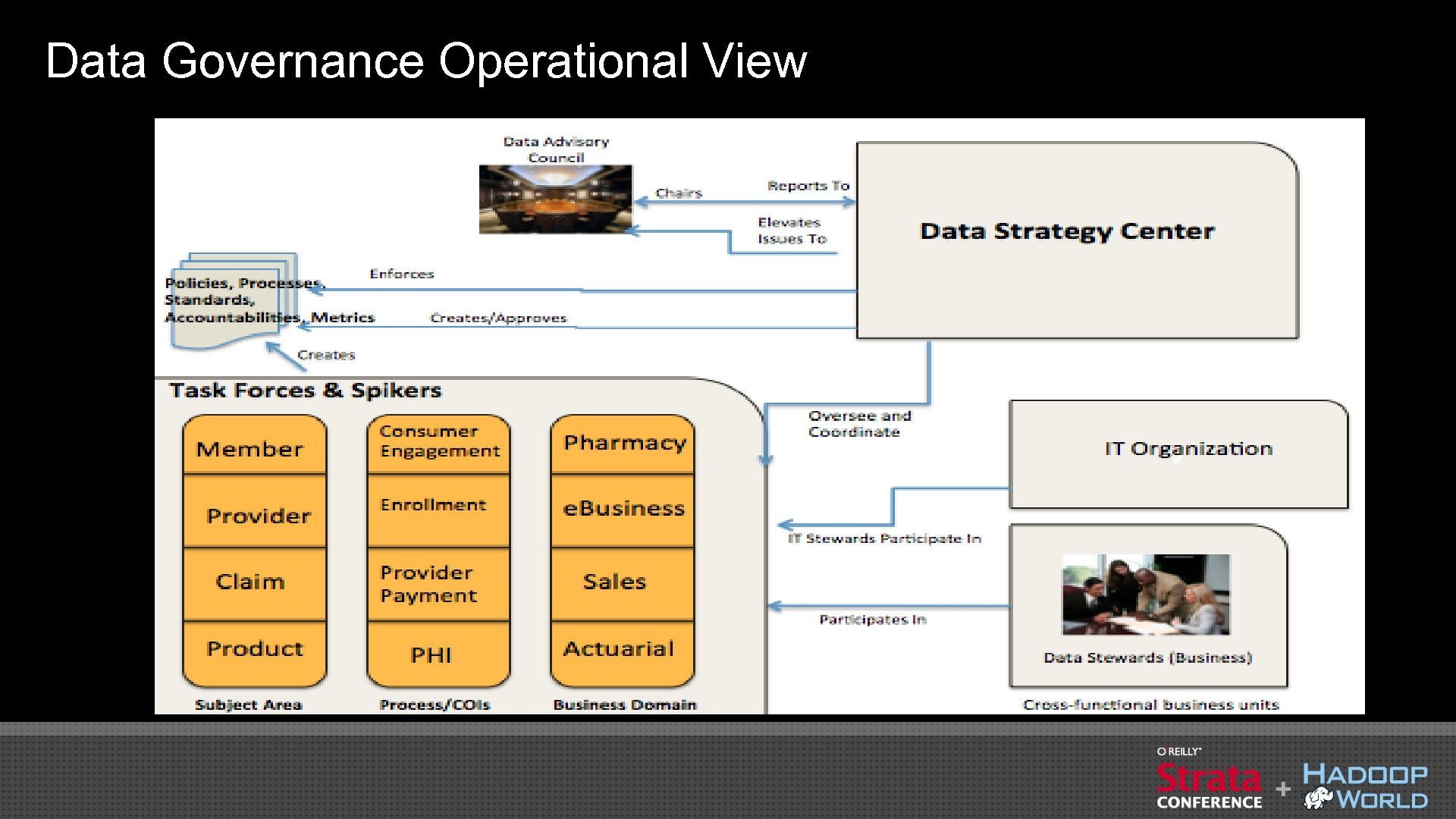
Data Governance Operational View

Success Measures • Information is trusted • Speed to market for new products or services is improved • Time spent looking for data is reduced • Time-to-answer ratio is inversed • Questions are answerable (e. g. What is the value of a customer? ) • Stratification and insight of customer is achieved • Customer intimacy achieved • Integration and development time slashed Company is data-driven

What Business People Need to Know About Data Management and Data Governance Micheline Casey Principal CDO, LLC @michelinecasey 1@gmail. com www. data. Trending. wordpress. com
abdc4ef724b70506957b94561f13459d.ppt