48bad27ef951de1007b12d73b7d39446.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 What Are the Real Gains from a Successful Doha Round? Pankaj Ghemawat WTO Workshop November 2, 2010 © 2009 Pankaj Ghemawat
What Are the Real Gains from a Successful Doha Round? Pankaj Ghemawat WTO Workshop November 2, 2010 © 2009 Pankaj Ghemawat
 The Way Forward 1. Understanding how global we really are 2. Understanding all the barriers that constrain trade 3. Thinking broadly about the gains from trade © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
The Way Forward 1. Understanding how global we really are 2. Understanding all the barriers that constrain trade 3. Thinking broadly about the gains from trade © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
 How Global Are We? A. In real estate, the mantra is 'location, location. ' For global brand managers, it might be 'localise, localise. ‘ —A consultant B. There is a balance on the spectrum between “local” and “global” that represents the “sweet spot”…[and makes for] “the race to the middle. —A manager C. The world got flat…[creating] a global, Webenabled playing field that allows for…collaboration on research and work in real time, without regard to geography, distance or, in the near future, even language. —A journalist © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
How Global Are We? A. In real estate, the mantra is 'location, location. ' For global brand managers, it might be 'localise, localise. ‘ —A consultant B. There is a balance on the spectrum between “local” and “global” that represents the “sweet spot”…[and makes for] “the race to the middle. —A manager C. The world got flat…[creating] a global, Webenabled playing field that allows for…collaboration on research and work in real time, without regard to geography, distance or, in the near future, even language. —A journalist © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
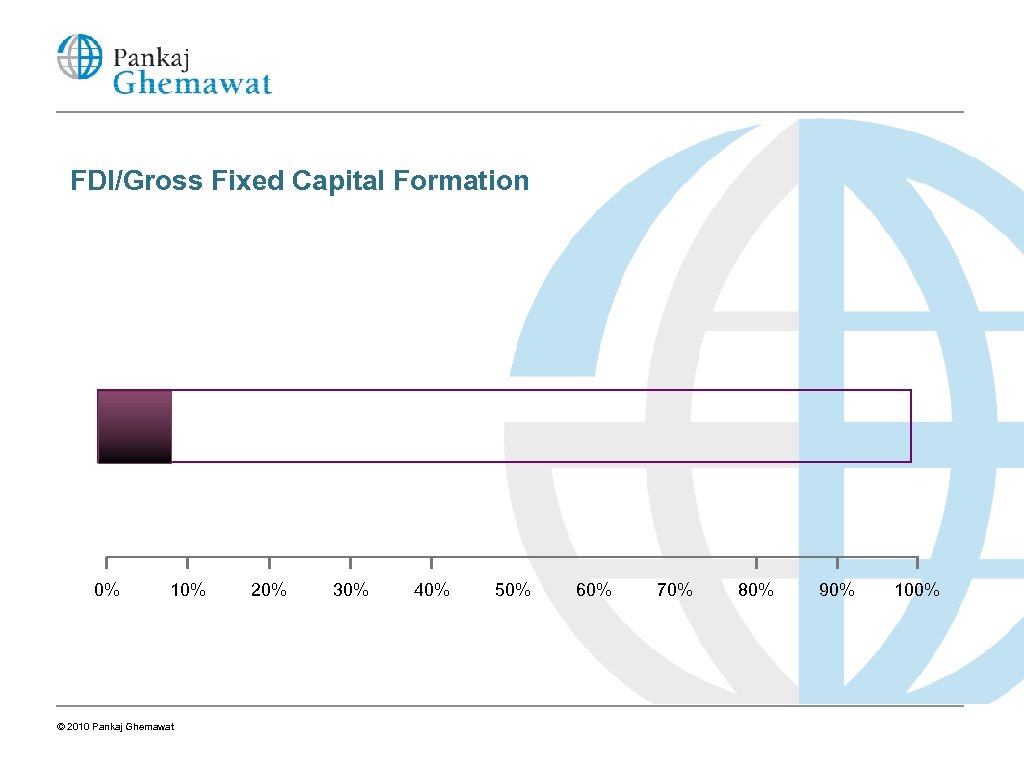 FDI/Gross Fixed Capital Formation 0% 10% © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%
FDI/Gross Fixed Capital Formation 0% 10% © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%
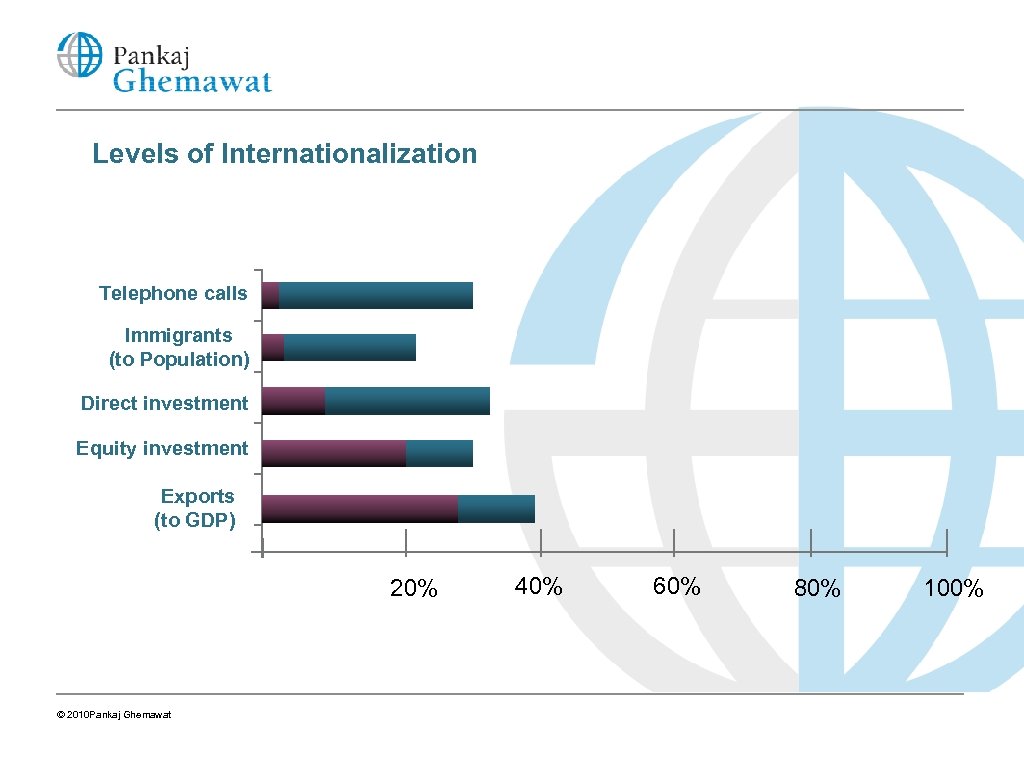 Levels of Internationalization Telephone calls Immigrants (to Population) Direct investment Equity investment Exports (to GDP) 20% © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat 40% 60% 80% 100%
Levels of Internationalization Telephone calls Immigrants (to Population) Direct investment Equity investment Exports (to GDP) 20% © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat 40% 60% 80% 100%
 The Way Forward 1. Understanding how global we really are 2. Understanding all the barriers that constrain trade 3. Thinking broadly about the gains from trade © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
The Way Forward 1. Understanding how global we really are 2. Understanding all the barriers that constrain trade 3. Thinking broadly about the gains from trade © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
 What Are the Barriers to Trade? The Mystery of the Missing Trade In 1988, Canadian provinces traded 20 times as much merchandise with each other as with U. S. states By the mid-1990 s, this multiple had come down to 12 After a decade of NAFTA, this multiple still exceeds 5—and this is just for merchandise! Note free trade agreement, common border, mostly common language/ colonizer, generally friendly relations etc. making U. S. -Canadian trade largest bilateral trade relationship in the world © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
What Are the Barriers to Trade? The Mystery of the Missing Trade In 1988, Canadian provinces traded 20 times as much merchandise with each other as with U. S. states By the mid-1990 s, this multiple had come down to 12 After a decade of NAFTA, this multiple still exceeds 5—and this is just for merchandise! Note free trade agreement, common border, mostly common language/ colonizer, generally friendly relations etc. making U. S. -Canadian trade largest bilateral trade relationship in the world © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
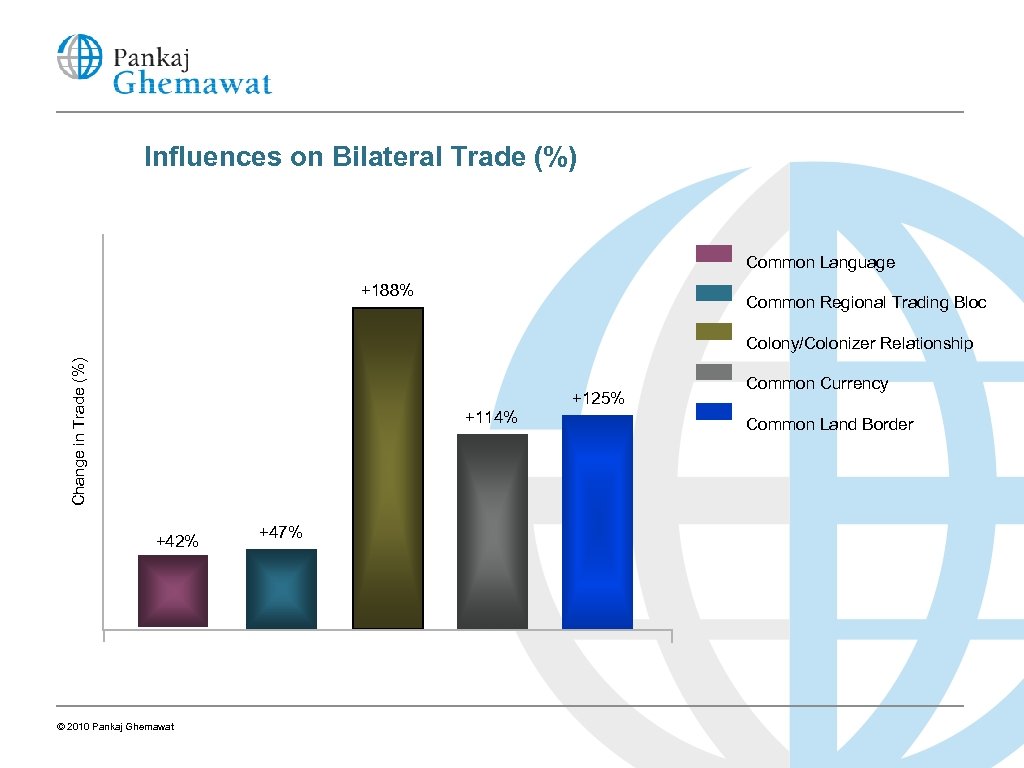 Influences on Bilateral Trade (%) Common Language +188% Common Regional Trading Bloc Change in Trade (%) Colony/Colonizer Relationship +125% +114% +42% © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat +47% Common Currency Common Land Border
Influences on Bilateral Trade (%) Common Language +188% Common Regional Trading Bloc Change in Trade (%) Colony/Colonizer Relationship +125% +114% +42% © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat +47% Common Currency Common Land Border
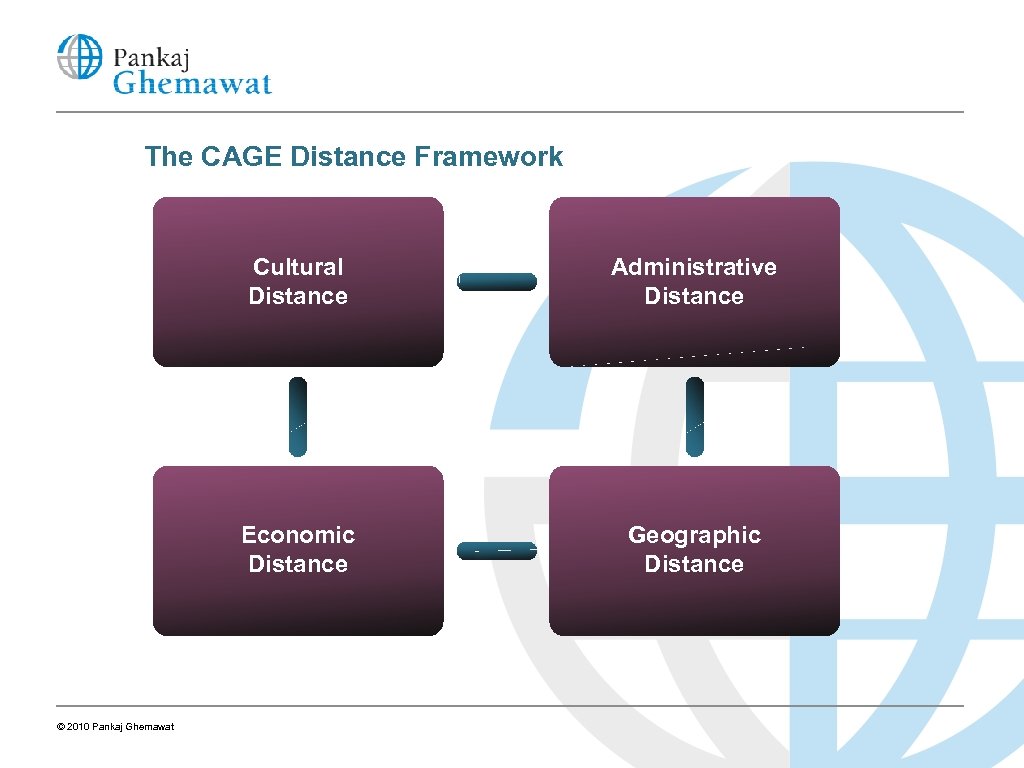 The CAGE Distance Framework Cultural Distance Economic Distance © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat Administrative Distance Geographic Distance
The CAGE Distance Framework Cultural Distance Economic Distance © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat Administrative Distance Geographic Distance
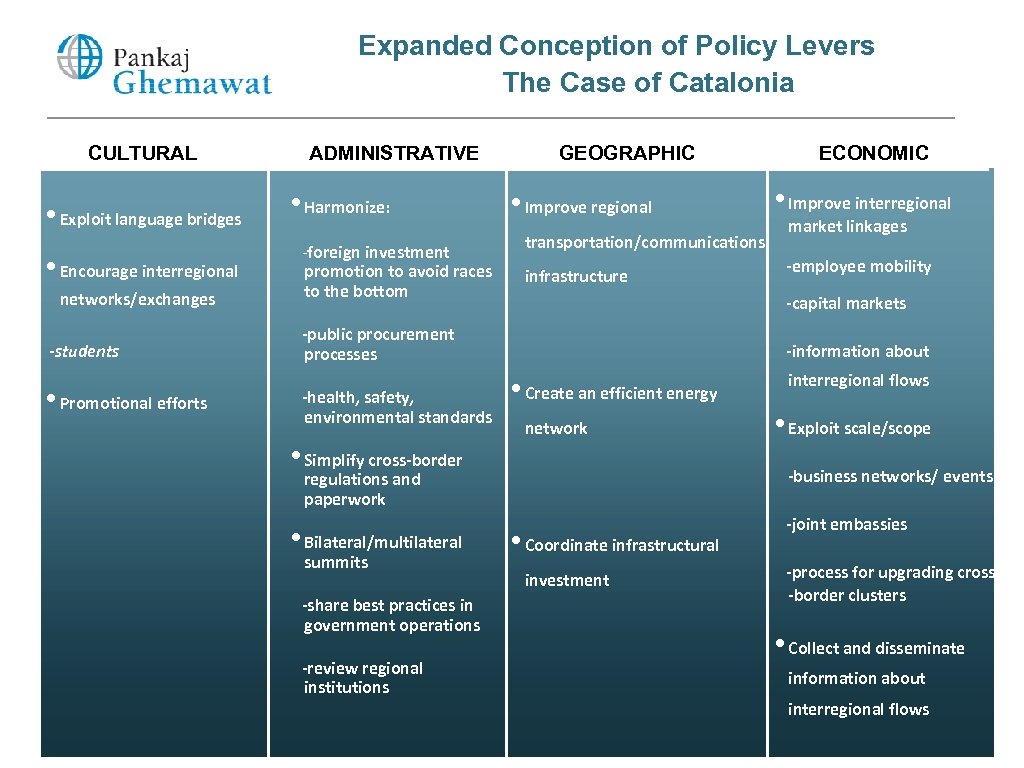 Expanded Conception of Policy Levers The Case of Catalonia CULTURAL • Exploit language bridges • Encourage interregional networks/exchanges -students • Promotional efforts ADMINISTRATIVE • Harmonize: -foreign investment promotion to avoid races to the bottom GEOGRAPHIC • Improve regional transportation/communications infrastructure • Simplify cross-border summits -share best practices in government operations -review regional institutions market linkages -employee mobility -information about • Create an efficient energy network interregional flows • Exploit scale/scope -business networks/ events regulations and paperwork • Bilateral/multilateral • Improve interregional -capital markets -public procurement processes -health, safety, environmental standards ECONOMIC • Coordinate infrastructural investment -joint embassies -process for upgrading cross -border clusters • Collect and disseminate information about interregional flows
Expanded Conception of Policy Levers The Case of Catalonia CULTURAL • Exploit language bridges • Encourage interregional networks/exchanges -students • Promotional efforts ADMINISTRATIVE • Harmonize: -foreign investment promotion to avoid races to the bottom GEOGRAPHIC • Improve regional transportation/communications infrastructure • Simplify cross-border summits -share best practices in government operations -review regional institutions market linkages -employee mobility -information about • Create an efficient energy network interregional flows • Exploit scale/scope -business networks/ events regulations and paperwork • Bilateral/multilateral • Improve interregional -capital markets -public procurement processes -health, safety, environmental standards ECONOMIC • Coordinate infrastructural investment -joint embassies -process for upgrading cross -border clusters • Collect and disseminate information about interregional flows
 The Way Forward 1. Understanding how global we really are 2. Understanding all the barriers that constrain trade 3. Thinking broadly about the gains from trade © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
The Way Forward 1. Understanding how global we really are 2. Understanding all the barriers that constrain trade 3. Thinking broadly about the gains from trade © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
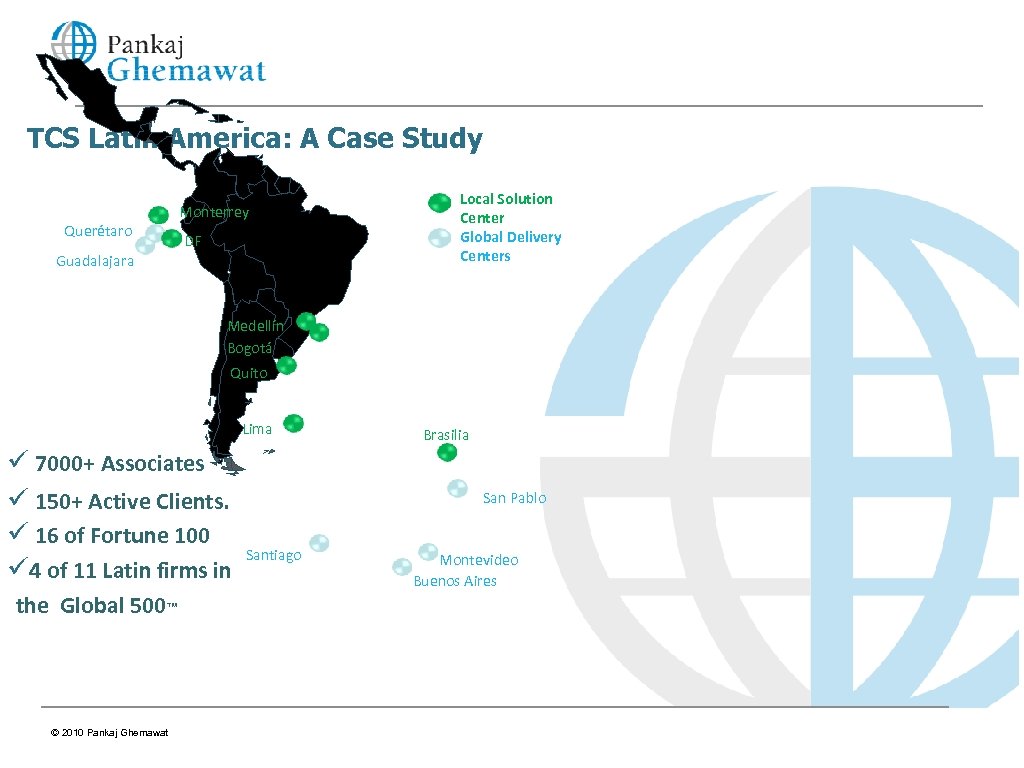 TCS Latin America: A Case Study Querétaro Monterrey DF Guadalajara Local Solution Center Global Delivery Centers Medellín Bogotá Quito Lima ü 7000+ Associates ü 150+ Active Clients. ü 16 of Fortune 100 ü 4 of 11 Latin firms in the Global 500™ © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat Brasilia San Pablo Santiago Montevideo Buenos Aires
TCS Latin America: A Case Study Querétaro Monterrey DF Guadalajara Local Solution Center Global Delivery Centers Medellín Bogotá Quito Lima ü 7000+ Associates ü 150+ Active Clients. ü 16 of Fortune 100 ü 4 of 11 Latin firms in the Global 500™ © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat Brasilia San Pablo Santiago Montevideo Buenos Aires
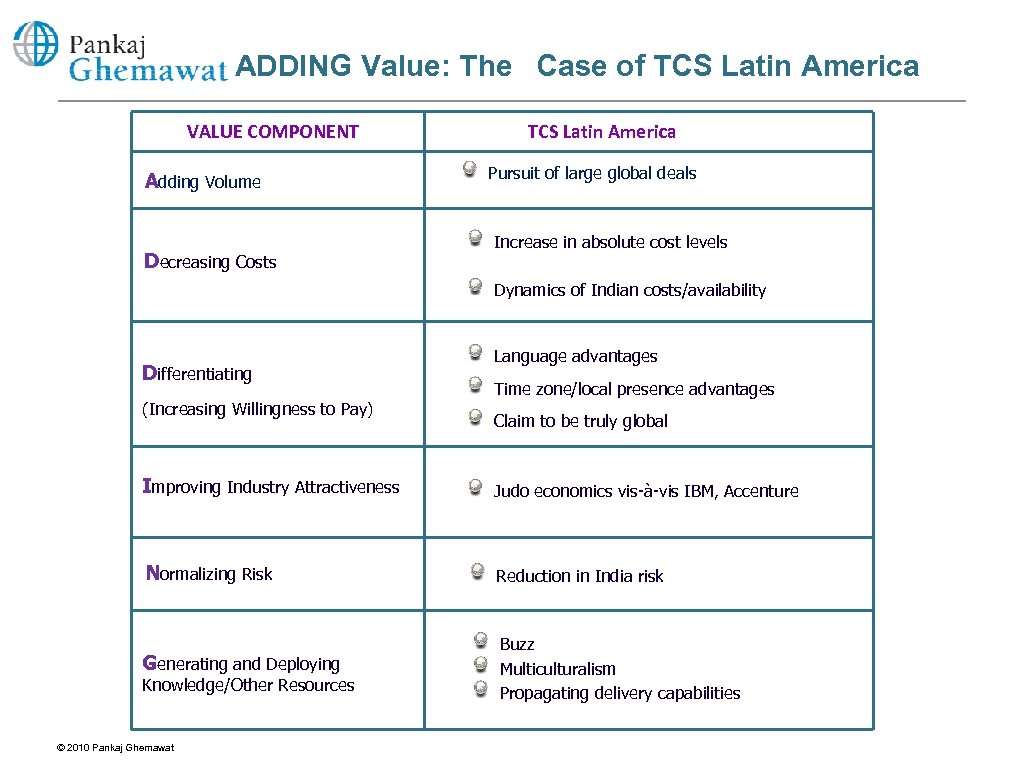 ADDING Value: The Case of TCS Latin America VALUE COMPONENT Adding Volume Decreasing Costs TCS Latin America Pursuit of large global deals Increase in absolute cost levels Dynamics of Indian costs/availability Differentiating (Increasing Willingness to Pay) Language advantages Time zone/local presence advantages Claim to be truly global Improving Industry Attractiveness Judo economics vis-à-vis IBM, Accenture Normalizing Risk Reduction in India risk Generating and Deploying Buzz Multiculturalism Propagating delivery capabilities Knowledge/Other Resources © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
ADDING Value: The Case of TCS Latin America VALUE COMPONENT Adding Volume Decreasing Costs TCS Latin America Pursuit of large global deals Increase in absolute cost levels Dynamics of Indian costs/availability Differentiating (Increasing Willingness to Pay) Language advantages Time zone/local presence advantages Claim to be truly global Improving Industry Attractiveness Judo economics vis-à-vis IBM, Accenture Normalizing Risk Reduction in India risk Generating and Deploying Buzz Multiculturalism Propagating delivery capabilities Knowledge/Other Resources © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
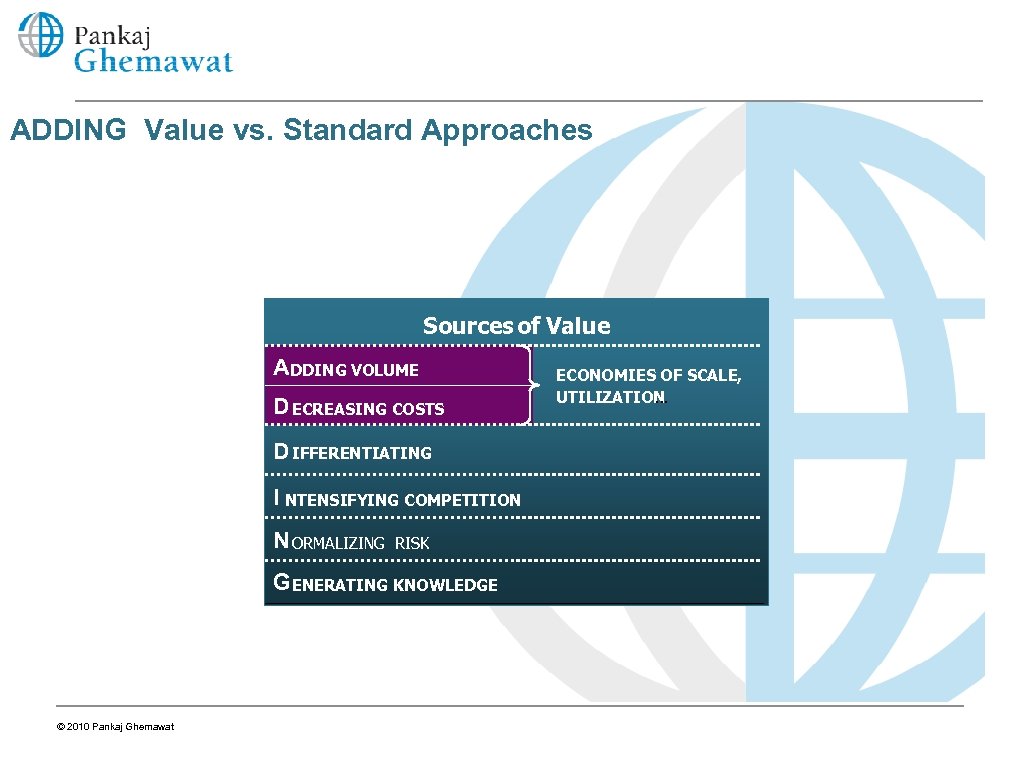 ADDING Value vs. Standard Approaches Sources of Value ADDING VOLUME D ECREASING COSTS D IFFERENTIATING I NTENSIFYING COMPETITION N ORMALIZING RISK G ENERATING KNOWLEDGE © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat ECONOMIES OF SCALE, UTILIZATION …
ADDING Value vs. Standard Approaches Sources of Value ADDING VOLUME D ECREASING COSTS D IFFERENTIATING I NTENSIFYING COMPETITION N ORMALIZING RISK G ENERATING KNOWLEDGE © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat ECONOMIES OF SCALE, UTILIZATION …
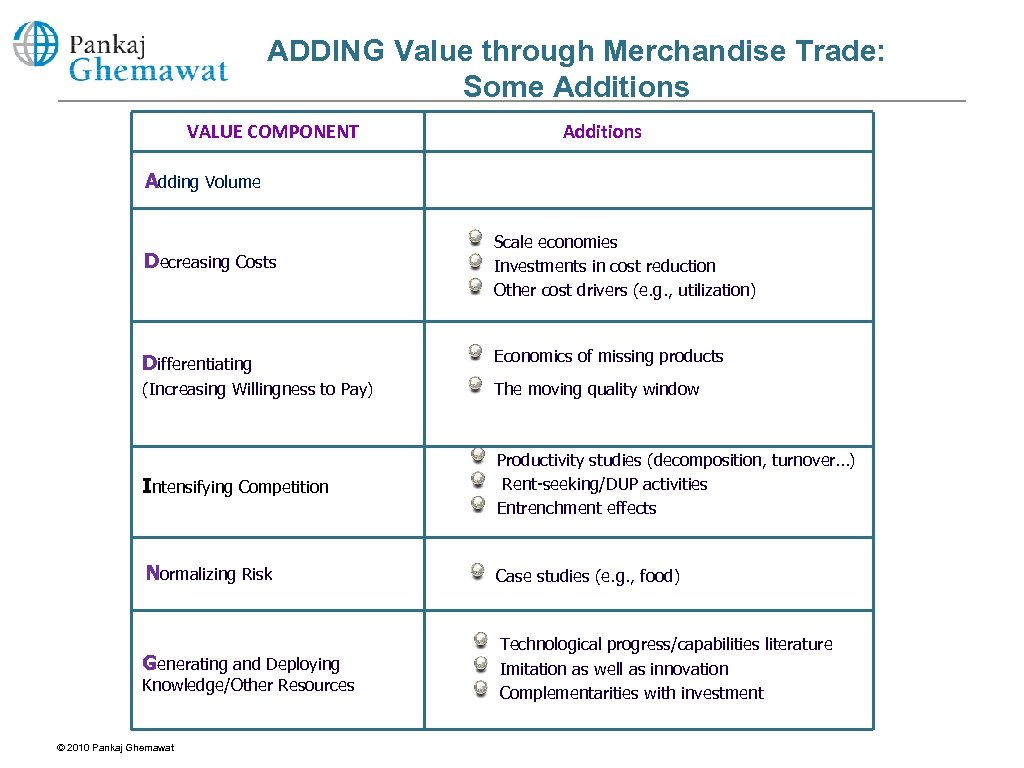 ADDING Value through Merchandise Trade: Some Additions VALUE COMPONENT Additions Adding Volume Decreasing Costs Scale economies Investments in cost reduction Other cost drivers (e. g. , utilization) Differentiating Economics of missing products (Increasing Willingness to Pay) The moving quality window Intensifying Competition Productivity studies (decomposition, turnover…) Rent-seeking/DUP activities Entrenchment effects Normalizing Risk Case studies (e. g. , food) Generating and Deploying Technological progress/capabilities literature Imitation as well as innovation Complementarities with investment Knowledge/Other Resources © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
ADDING Value through Merchandise Trade: Some Additions VALUE COMPONENT Additions Adding Volume Decreasing Costs Scale economies Investments in cost reduction Other cost drivers (e. g. , utilization) Differentiating Economics of missing products (Increasing Willingness to Pay) The moving quality window Intensifying Competition Productivity studies (decomposition, turnover…) Rent-seeking/DUP activities Entrenchment effects Normalizing Risk Case studies (e. g. , food) Generating and Deploying Technological progress/capabilities literature Imitation as well as innovation Complementarities with investment Knowledge/Other Resources © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
 Unimpressive Projected Gains? Ø Agree and abandon Ø Avert gaze and carry on Ø Adjust baseline Ø Add to the categories of effects considered © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
Unimpressive Projected Gains? Ø Agree and abandon Ø Avert gaze and carry on Ø Adjust baseline Ø Add to the categories of effects considered © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat


 © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
© 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
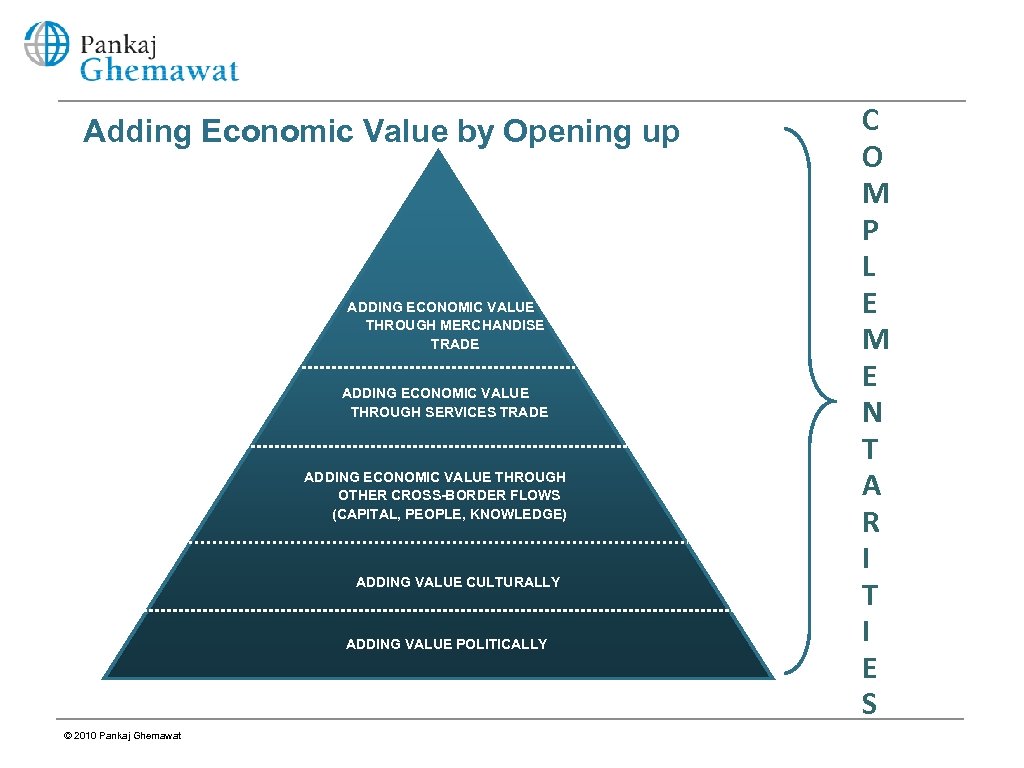 Adding Economic Value by Opening up ADDING ECONOMIC VALUE THROUGH MERCHANDISE TRADE ADDING ECONOMIC VALUE THROUGH SERVICES TRADE ADDING ECONOMIC VALUE THROUGH OTHER CROSS-BORDER FLOWS (CAPITAL, PEOPLE, KNOWLEDGE) ADDING VALUE CULTURALLY ADDING VALUE POLITICALLY © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat C O M P L E M E N T A R I T I E S
Adding Economic Value by Opening up ADDING ECONOMIC VALUE THROUGH MERCHANDISE TRADE ADDING ECONOMIC VALUE THROUGH SERVICES TRADE ADDING ECONOMIC VALUE THROUGH OTHER CROSS-BORDER FLOWS (CAPITAL, PEOPLE, KNOWLEDGE) ADDING VALUE CULTURALLY ADDING VALUE POLITICALLY © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat C O M P L E M E N T A R I T I E S
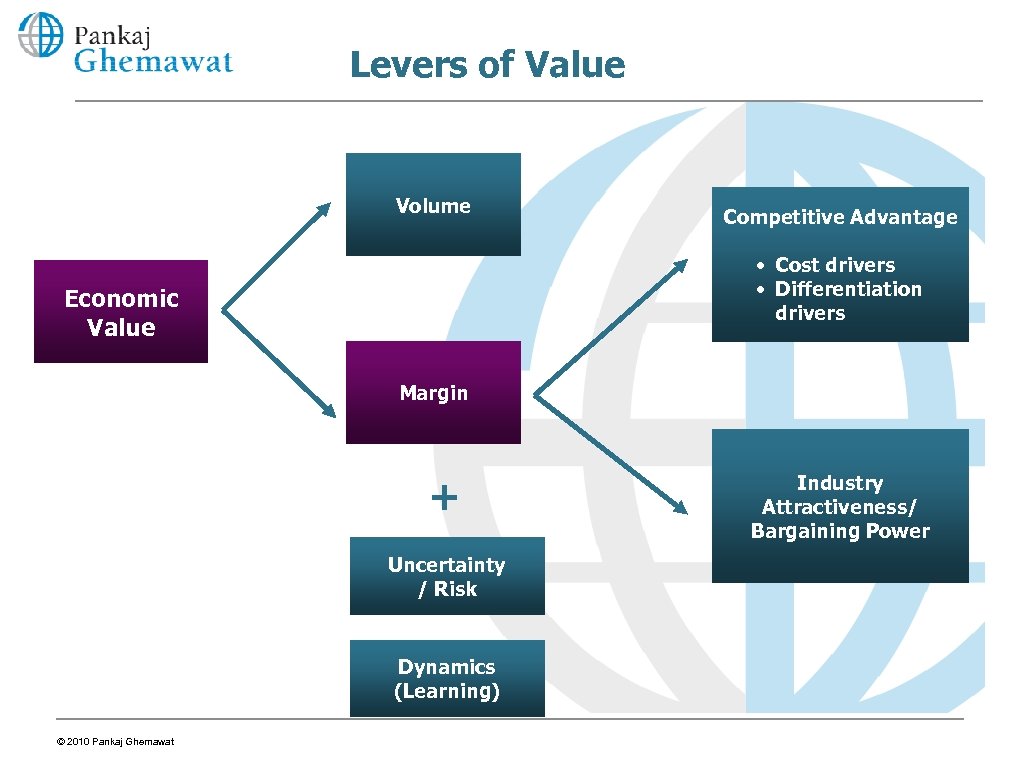 Levers of Value Volume Competitive Advantage • Cost drivers • Differentiation drivers Economic Value Margin + Uncertainty / Risk Dynamics (Learning) © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat Industry Attractiveness/ Bargaining Power
Levers of Value Volume Competitive Advantage • Cost drivers • Differentiation drivers Economic Value Margin + Uncertainty / Risk Dynamics (Learning) © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat Industry Attractiveness/ Bargaining Power
 A Key Question How far to cast our nets in identifying the gains from a successful Doha round (or, more broadly opening up)? q “If I’m not able to pin down the numbers precisely, I report just the qualitative effects” © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
A Key Question How far to cast our nets in identifying the gains from a successful Doha round (or, more broadly opening up)? q “If I’m not able to pin down the numbers precisely, I report just the qualitative effects” © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
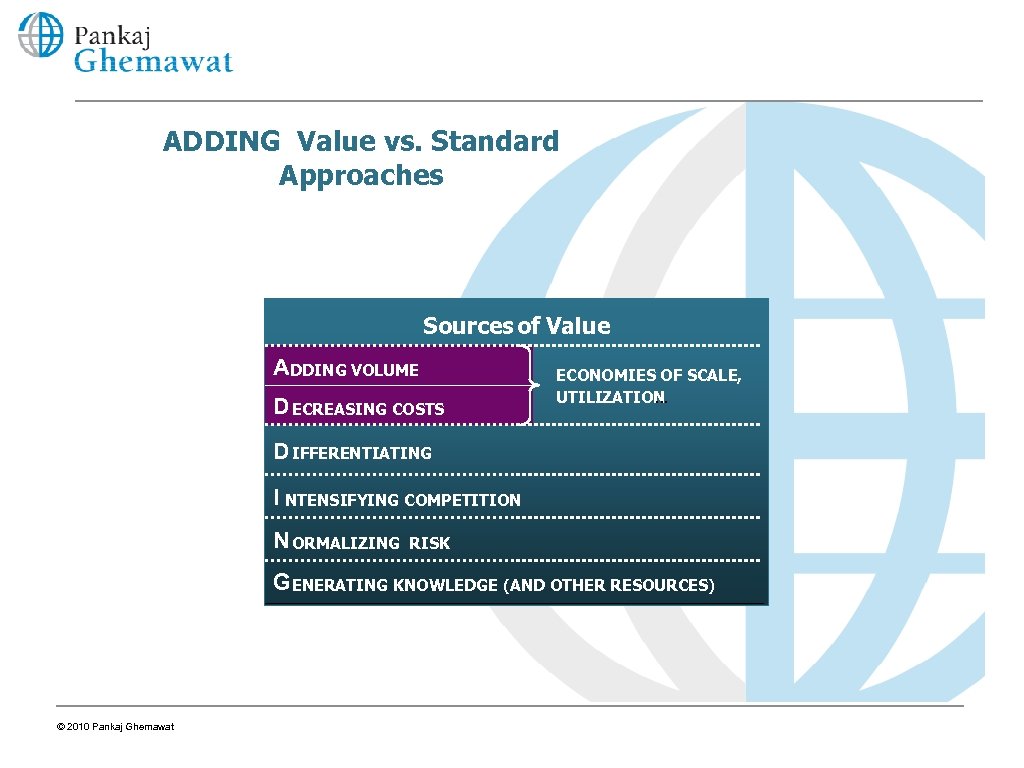 ADDING Value vs. Standard Approaches Sources of Value ADDING VOLUME D ECREASING COSTS ECONOMIES OF SCALE, UTILIZATION … D IFFERENTIATING I NTENSIFYING COMPETITION N ORMALIZING RISK G ENERATING KNOWLEDGE (AND OTHER RESOURCES) © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
ADDING Value vs. Standard Approaches Sources of Value ADDING VOLUME D ECREASING COSTS ECONOMIES OF SCALE, UTILIZATION … D IFFERENTIATING I NTENSIFYING COMPETITION N ORMALIZING RISK G ENERATING KNOWLEDGE (AND OTHER RESOURCES) © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
 The Way Forward 1. Understanding how global we really are 2. Understanding all the barriers that constrain trade 3. Thinking broadly about the gains from trade © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
The Way Forward 1. Understanding how global we really are 2. Understanding all the barriers that constrain trade 3. Thinking broadly about the gains from trade © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
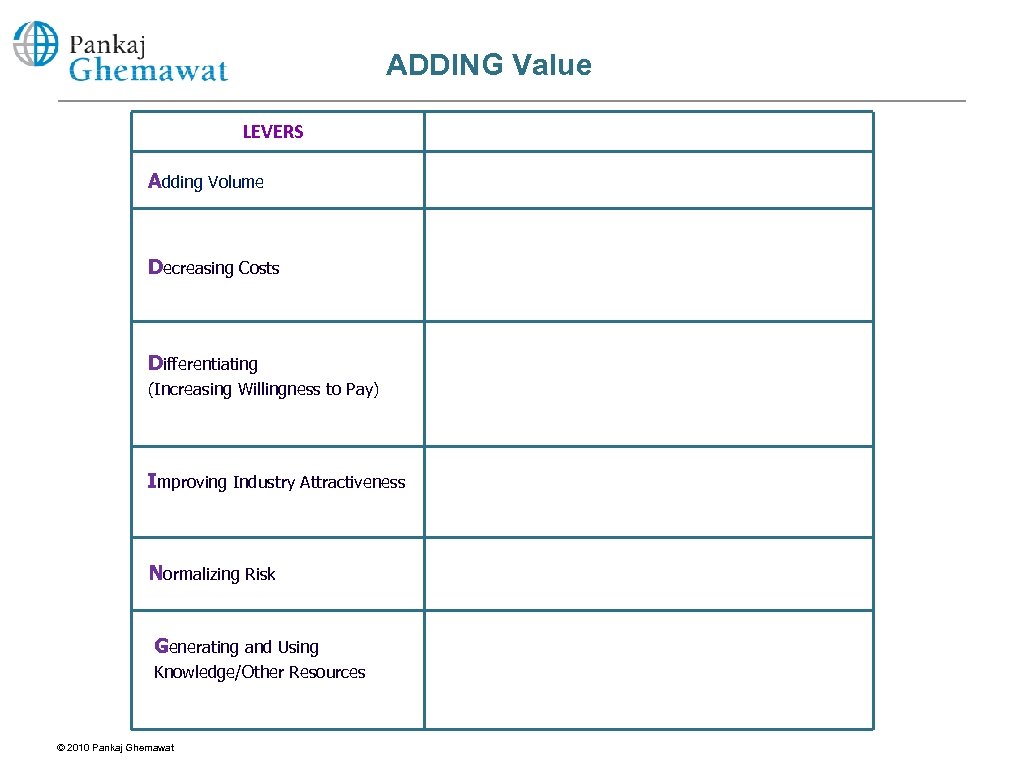 ADDING Value LEVERS Adding Volume Decreasing Costs Differentiating (Increasing Willingness to Pay) Improving Industry Attractiveness Normalizing Risk Generating and Using Knowledge/Other Resources © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
ADDING Value LEVERS Adding Volume Decreasing Costs Differentiating (Increasing Willingness to Pay) Improving Industry Attractiveness Normalizing Risk Generating and Using Knowledge/Other Resources © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
 Strategic Headroom © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
Strategic Headroom © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat
 © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat Source: www. cartoonstock. com
© 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat Source: www. cartoonstock. com
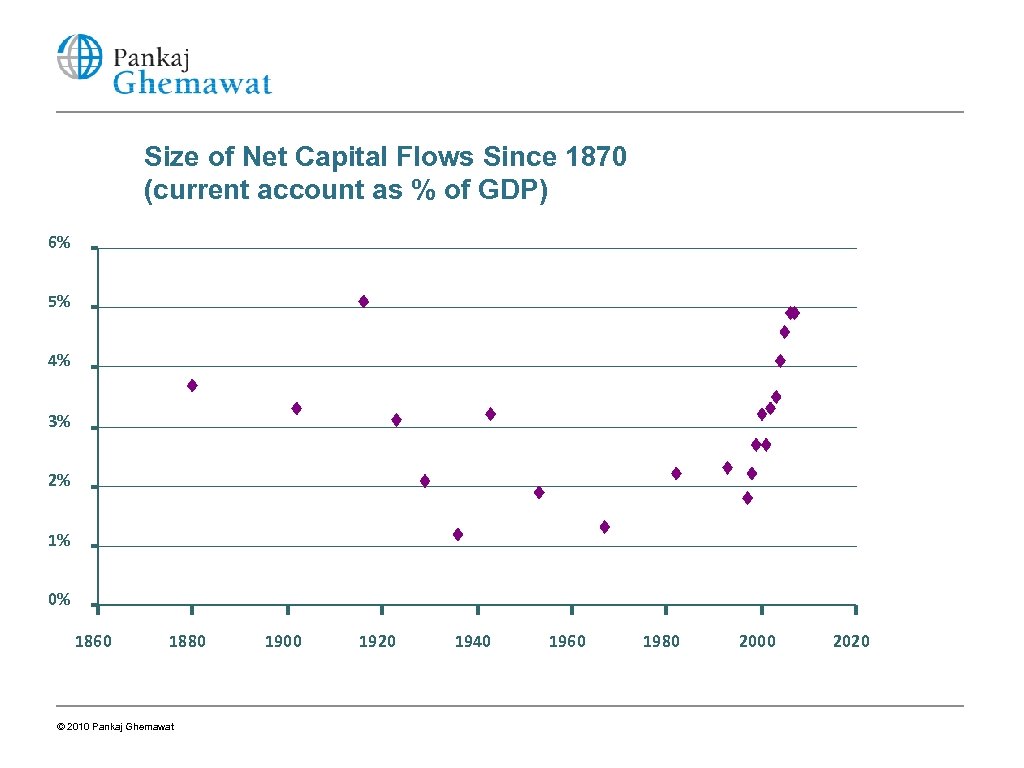 Size of Net Capital Flows Since 1870 (current account as % of GDP) 6% 5% 4% 3% 2% 1% 0% 1860 1880 © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat 1900 1920 1940 1960 1980 2000 2020
Size of Net Capital Flows Since 1870 (current account as % of GDP) 6% 5% 4% 3% 2% 1% 0% 1860 1880 © 2010 Pankaj Ghemawat 1900 1920 1940 1960 1980 2000 2020


