826e4631d15ffb4df151864364fa6c0d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
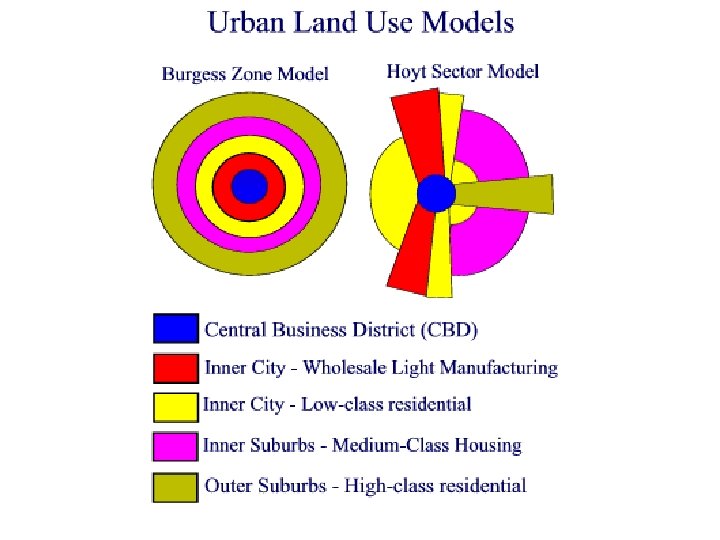
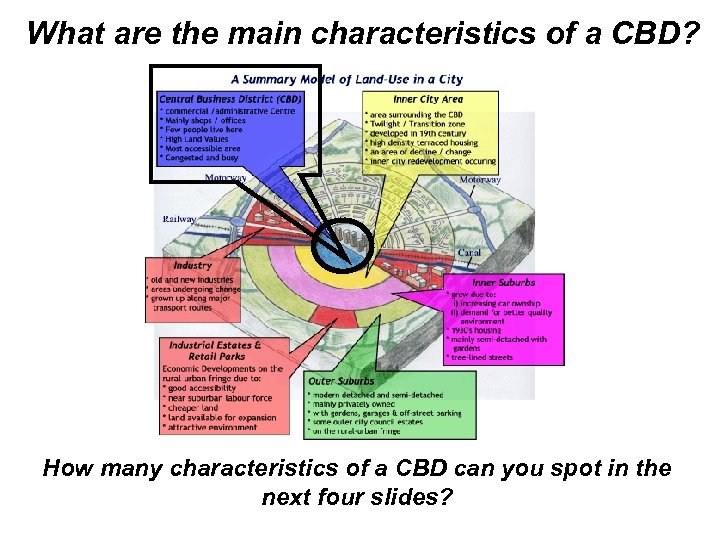
What are the main characteristics of a CBD? How many characteristics of a CBD can you spot in the next four slides?
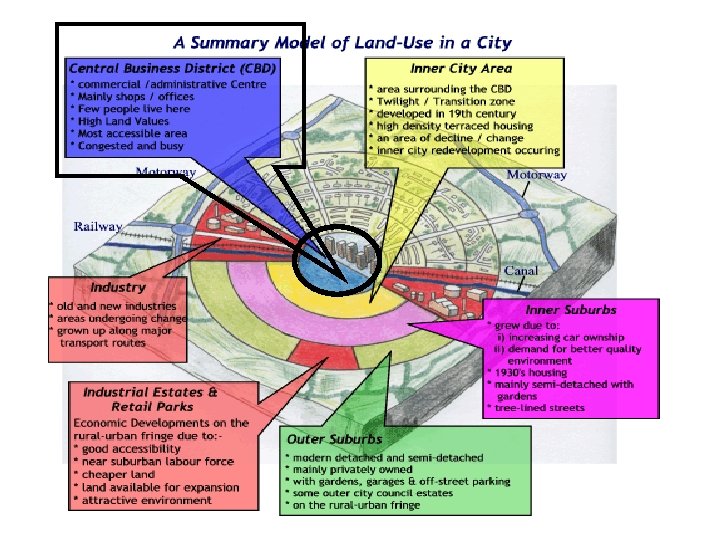

What typical characteristics of a CBD are shown here? The Tallest Buildings Why? Public Buildings eg. Corn Exchange / Town Hall Busy – lots of pedestrians Markets

Purpose built shopping centres providing undercover shopping experience Big Department Stores and National Chain Stores – why? What typical characteristics of a CBD are shown here?
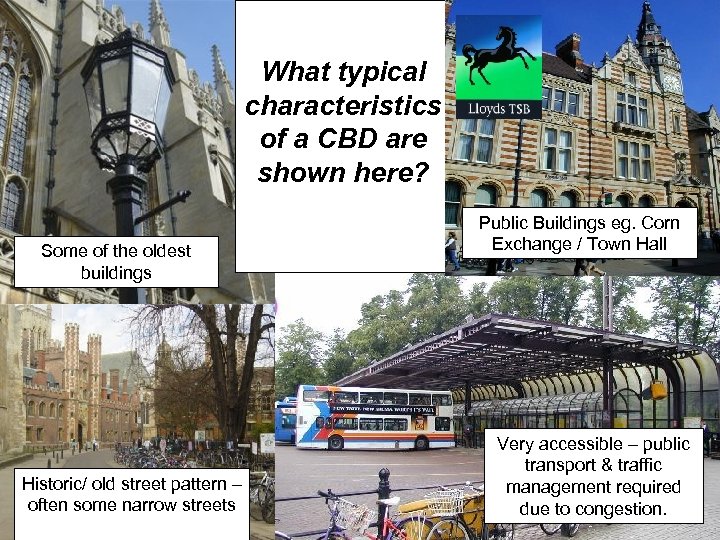
What typical characteristics of a CBD are shown here? Some of the oldest buildings Historic/ old street pattern – often some narrow streets Public Buildings eg. Corn Exchange / Town Hall Very accessible – public transport & traffic management required due to congestion.

Entertainment – e. g. restaurants Entertainment e. g. pubs What typical characteristics of a CBD are shown here? Entertainment e. g. cinemas (although increasingly these are moving further out of town)

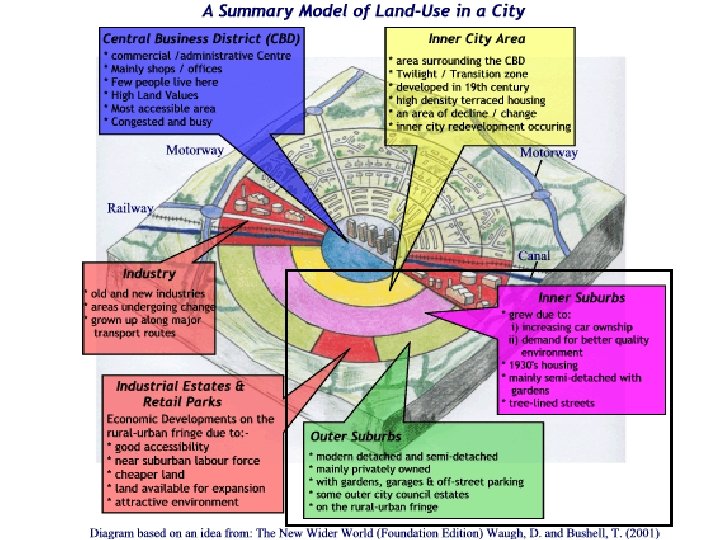
Urban land use: Zone 1 • CBD = Central Business District • The CBD is at the heart of a town or city and usually has great accessibility, large shopping and banking areas, and government buildings
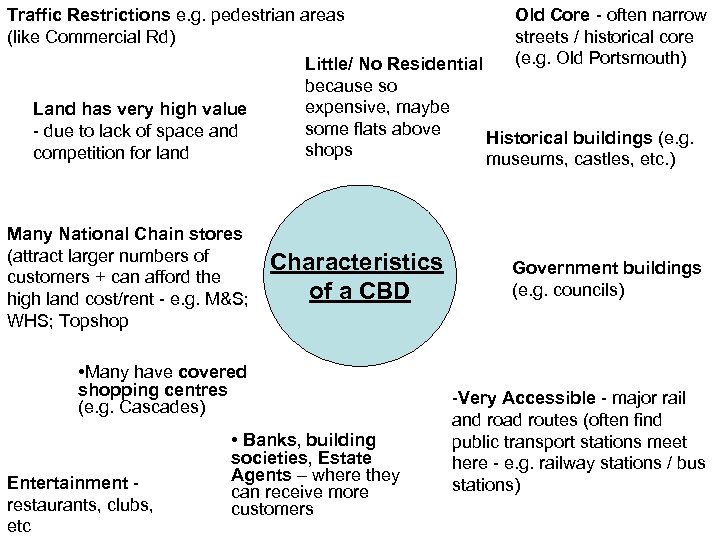
Traffic Restrictions e. g. pedestrian areas (like Commercial Rd) Land has very high value - due to lack of space and competition for land Many National Chain stores (attract larger numbers of customers + can afford the high land cost/rent - e. g. M&S; WHS; Topshop Little/ No Residential because so expensive, maybe some flats above Historical buildings (e. g. shops museums, castles, etc. ) Characteristics of a CBD • Many have covered shopping centres (e. g. Cascades) Entertainment restaurants, clubs, etc Old Core - often narrow streets / historical core (e. g. Old Portsmouth) • Banks, building societies, Estate Agents – where they can receive more customers Government buildings (e. g. councils) -Very Accessible - major rail and road routes (often find public transport stations meet here - e. g. railway stations / bus stations)
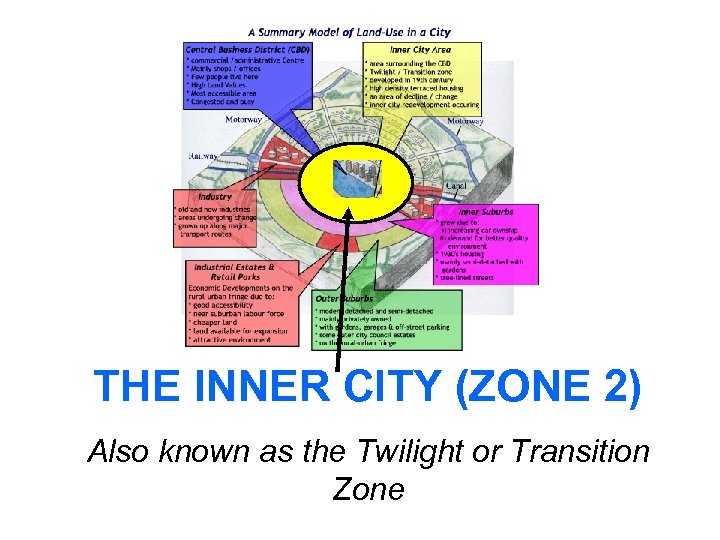
THE INNER CITY (ZONE 2) Also known as the Twilight or Transition Zone
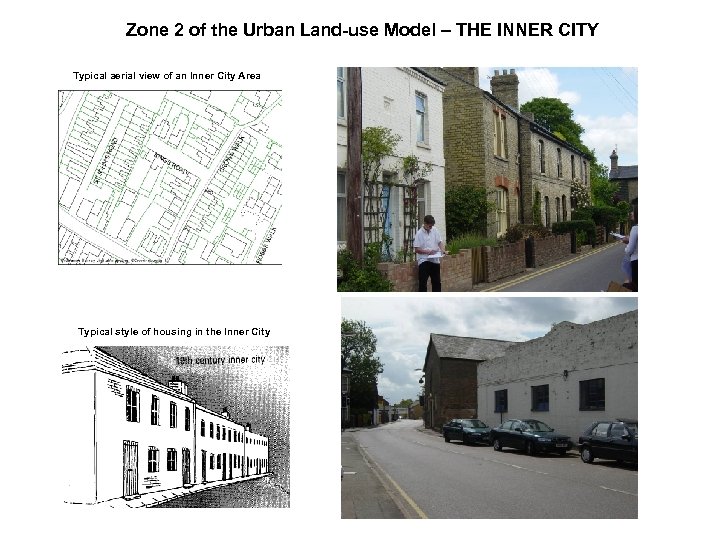
Zone 2 of the Urban Land-use Model – THE INNER CITY Typical aerial view of an Inner City Area Typical style of housing in the Inner City


When and Why did Inner City Areas Grow up? • Developed during the 19 th century – due to rapid expansion of industry (led to the demand for workers) • As more moved to the cities – there was a demand for low cost houses for the workers • This resulted in high-density cheap housing (fitting as many houses as possible in a small area • People had to live close to work due to lack of transport

What types of land-use are found in Inner City areas? 19 th Century Terraced Housing Canals and Railways Industry – large factories built during the industrial revolution (now some knocked down / converted) Main Roads (often now ring roads taking traffic out of CBDs)

Typical Characteristics of Inner City Areas • High Density Housing • Mainly terraced (some back to back) • Built in Long Straight Rows • Front doors opening onto the street • Few Amenities (little or no sanitation (often built with toilet in Back Yard • Mainly Ethnic Minorities, students, older people and unemployed (lower income groups) • Mainly private / rented

Problems in Inner City Areas (since 1950 s / 1950 s) 1. Industrial Decline (see other notes) 6. Overcrowding 2. High unemployment 7. Lack of Open Space 3. Abandoned Warehouses – eyesore and led to vandalism 8. Lack of Parking Spaces 4. High Crime Rates 5. Poor Quality Housing 9. Atmospheric Pollution (factories / traffic) 10. Lots of heavy traffic (for industry)

Zone 2: Inner City What is the Inner City? The Inner City is the land-use zone around the city centre, it is also known as the twilight zone or zone of transition. When did the Inner City grow up? Inner city areas grew up in the 19 th century as towns increased rapidly due to the Industrial Revolution. This led to the growth of factories and low-cost terraced housing around what is now the city centre.
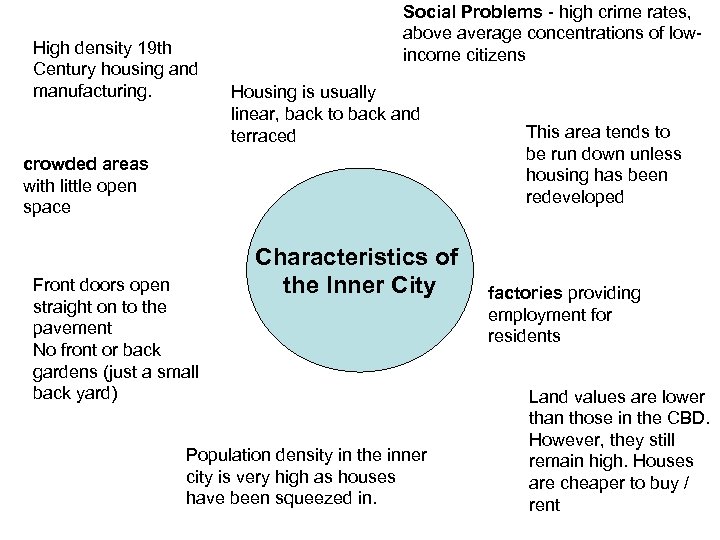
High density 19 th Century housing and manufacturing. Social Problems - high crime rates, above average concentrations of lowincome citizens Housing is usually linear, back to back and terraced crowded areas with little open space Front doors open straight on to the pavement No front or back gardens (just a small back yard) Characteristics of the Inner City Population density in the inner city is very high as houses have been squeezed in. This area tends to be run down unless housing has been redeveloped factories providing employment for residents Land values are lower than those in the CBD. However, they still remain high. Houses are cheaper to buy / rent
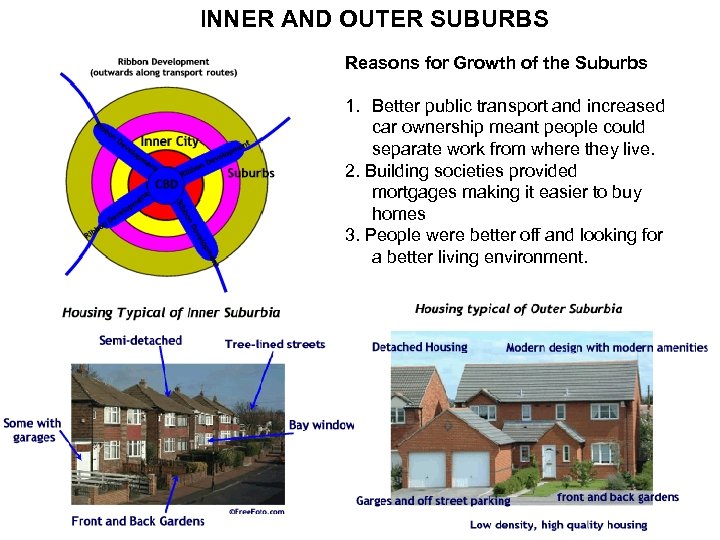
INNER AND OUTER SUBURBS Reasons for Growth of the Suburbs 1. Better public transport and increased car ownership meant people could separate work from where they live. 2. Building societies provided mortgages making it easier to buy homes 3. People were better off and looking for a better living environment.
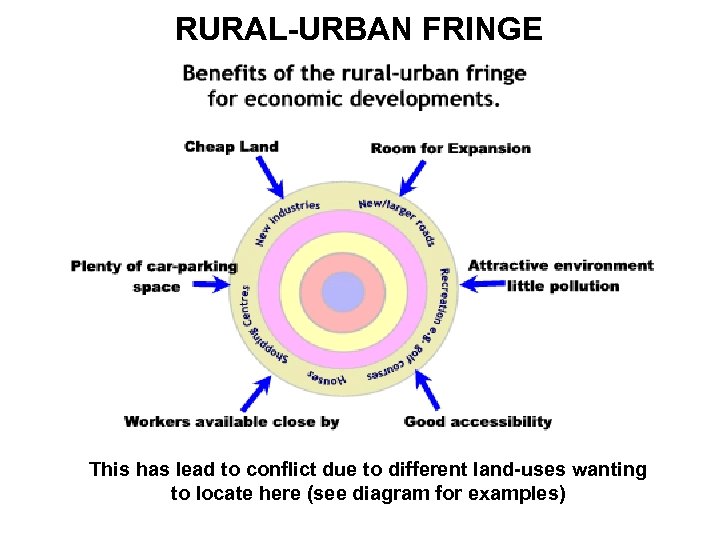
RURAL-URBAN FRINGE This has lead to conflict due to different land-uses wanting to locate here (see diagram for examples)

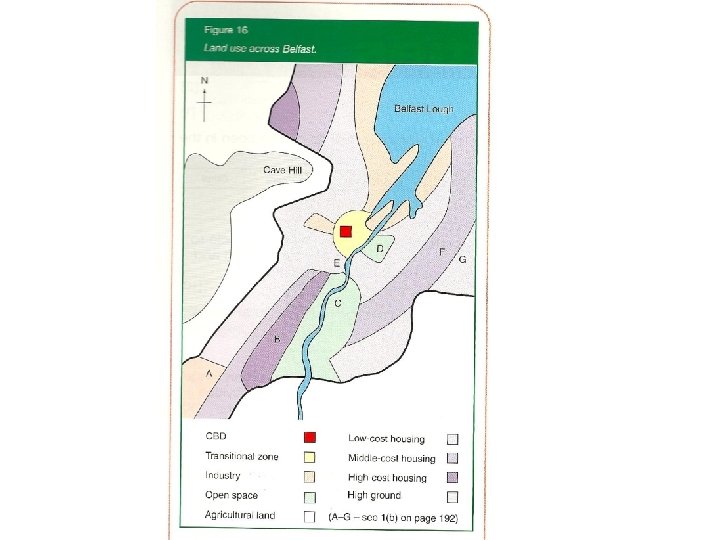
Land use in cities Land use zones.
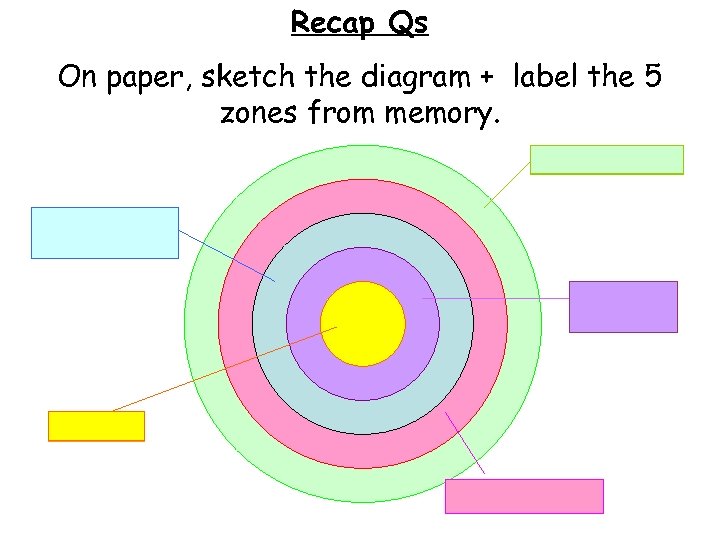
Recap Qs On paper, sketch the diagram + label the 5 zones from memory. Outer Suburbs Inner City/ Twilight Zone Industrial Zone CBD Inner Suburbs

Recap Qs 1) Which is the oldest part of the city? 2) What does ‘CBD’ stand for? 3) In which zone would you expect to find small terraced housing? 4) Why are there not many detached houses with drives near the CBD?
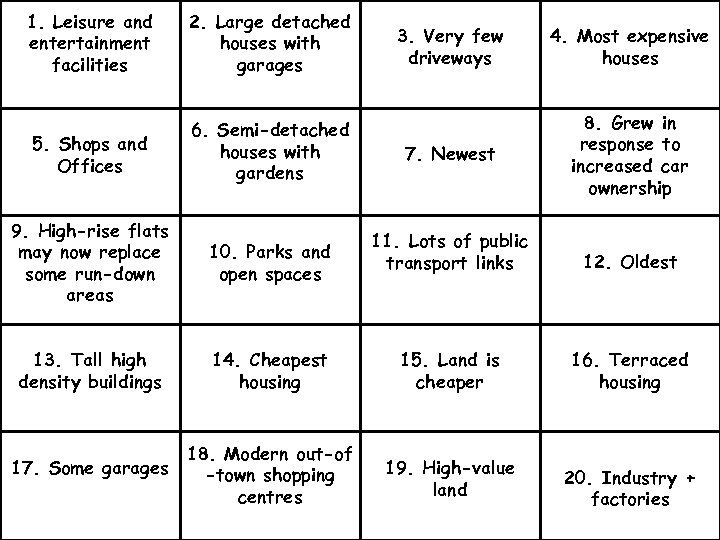
1. Leisure and entertainment facilities 2. Large detached houses with garages 5. Shops and Offices 6. Semi-detached houses with gardens 9. High-rise flats may now replace some run-down areas 10. Parks and open spaces 13. Tall high density buildings 14. Cheapest housing 18. Modern out-of 17. Some garages -town shopping centres 3. Very few driveways 4. Most expensive houses 7. Newest 8. Grew in response to increased car ownership 11. Lots of public transport links 12. Oldest 15. Land is cheaper 16. Terraced housing 19. High-value land 20. Industry + factories

Match it up! • Colour code the statements to fit the 5 categories: CBD – Inner City/Twilight Zone – Industrial Zone – Inner Suburbs – Outer Suburbs • Remember to use a key
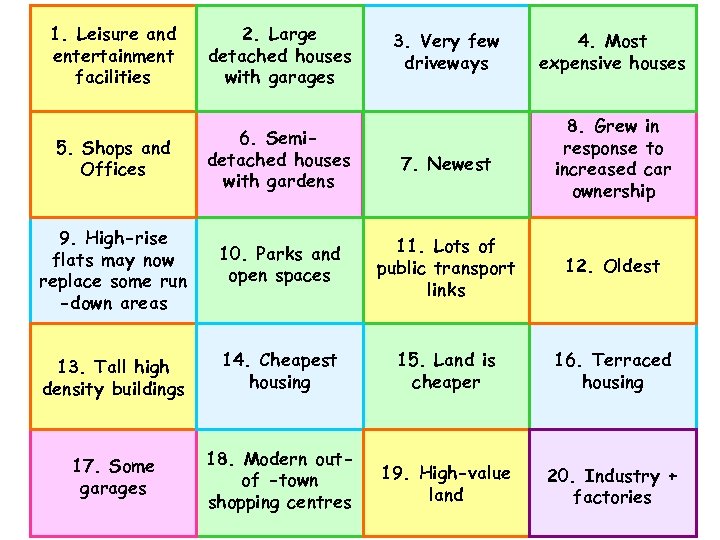
1. Leisure and entertainment facilities 2. Large detached houses with garages 5. Shops and Offices 6. Semidetached houses with gardens 9. High-rise flats may now replace some run -down areas 10. Parks and open spaces 13. Tall high density buildings 14. Cheapest housing 15. Land is cheaper 16. Terraced housing 17. Some garages 18. Modern outof -town shopping centres 19. High-value land 20. Industry + 20. Industry factories 3. Very few driveways 4. Most expensive houses 7. Newest 8. Grew in response to increased car ownership 11. public Lots of transport links 12. Oldest
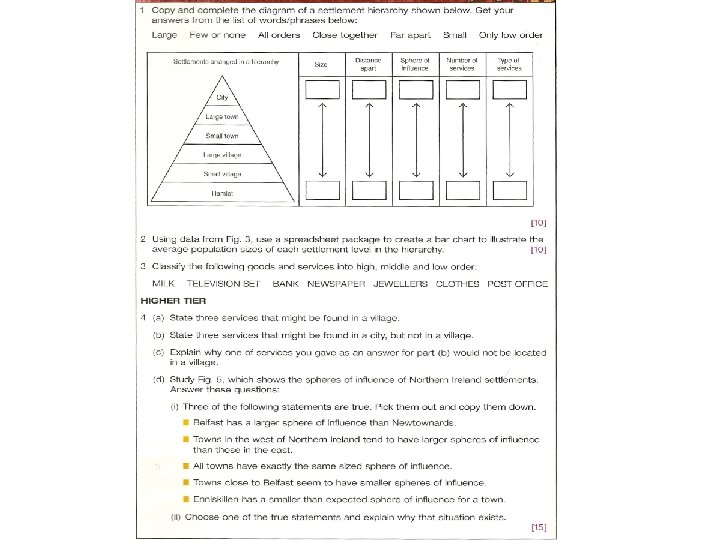
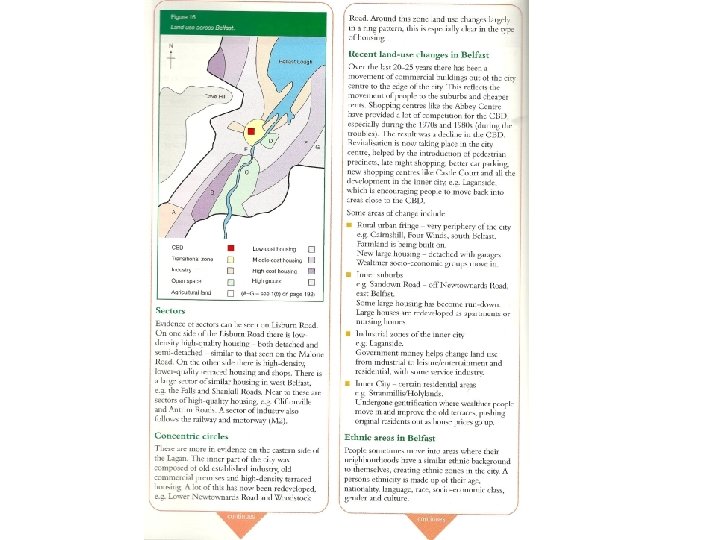
826e4631d15ffb4df151864364fa6c0d.ppt