01f8cedda5cb720fdd25a23f17d6528e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Welcome to the Year 2 Maths Workshop 20 th October 2015
Welcome to the Year 2 Maths Workshop 20 th October 2015
 Aims: • Provide you with support to help your child with their maths skills. • To discuss the importance of having a good understanding key instant recall facts. • To show you how we teach the 4 operations at St. Martin’s.
Aims: • Provide you with support to help your child with their maths skills. • To discuss the importance of having a good understanding key instant recall facts. • To show you how we teach the 4 operations at St. Martin’s.
 Key instant recall facts (KIRFs)? Instant recall is one of the most important parts of learning mathematics. It gives children a bank of knowledge from which they can draw to help them when working with maths in a range of situations. To help develop children’s fluency in mathematics, it’s important that they learn a Key Instant Recall Fact each half term. I would hope that the children practise their KIRFs at least 3 times a week.
Key instant recall facts (KIRFs)? Instant recall is one of the most important parts of learning mathematics. It gives children a bank of knowledge from which they can draw to help them when working with maths in a range of situations. To help develop children’s fluency in mathematics, it’s important that they learn a Key Instant Recall Fact each half term. I would hope that the children practise their KIRFs at least 3 times a week.
 KIRF outline for the year Facts Key Instant Recall Year 2 Autumn 1 I know the multiplication facts for the 2, 3, 5 and 10 times table. By the end of this half term, children should know the following facts. The aim is for them to recall these facts instantly. Autumn 2 I know the division facts for the 2 and 10 times table. Spring 1 I know the division facts for the 3 and 5 times table. Spring 2 I know number bonds to 20. Summer 1 I know 10 more and 10 less from a given number to 100. Summer 2 I know doubles and halves of numbers to 20.
KIRF outline for the year Facts Key Instant Recall Year 2 Autumn 1 I know the multiplication facts for the 2, 3, 5 and 10 times table. By the end of this half term, children should know the following facts. The aim is for them to recall these facts instantly. Autumn 2 I know the division facts for the 2 and 10 times table. Spring 1 I know the division facts for the 3 and 5 times table. Spring 2 I know number bonds to 20. Summer 1 I know 10 more and 10 less from a given number to 100. Summer 2 I know doubles and halves of numbers to 20.
 Top tips for KIRFs The secret to success is practising little and often. Use time wisely. Can you practise these KIRF’s while walking to school or during a car journey. You don’t need to practise them all at once: perhaps you could have a fact of the day. Use what you already know e. g. use knowledge of numbers bonds to 10 to help with number bonds to 20 Play games: www. conkersmaths. com http: //www. conkermaths. org/cmweb. nsf/products/ timestablesballoons. html
Top tips for KIRFs The secret to success is practising little and often. Use time wisely. Can you practise these KIRF’s while walking to school or during a car journey. You don’t need to practise them all at once: perhaps you could have a fact of the day. Use what you already know e. g. use knowledge of numbers bonds to 10 to help with number bonds to 20 Play games: www. conkersmaths. com http: //www. conkermaths. org/cmweb. nsf/products/ timestablesballoons. html
 Songs and chants- you can buy times tables cd’s or find multiplication songs and chants online. If your child creates their own song this can be more memorable. Test the parent Apply these facts to real life situations e. g. how many toes are their in your house 10 x ? = Time- talk about the time. Make sure you have an analogue clock in your house and that your child actually wears a watch. Ask your child the time regularly. E. g. the cakes need to come out of the oven at half past 4 etc
Songs and chants- you can buy times tables cd’s or find multiplication songs and chants online. If your child creates their own song this can be more memorable. Test the parent Apply these facts to real life situations e. g. how many toes are their in your house 10 x ? = Time- talk about the time. Make sure you have an analogue clock in your house and that your child actually wears a watch. Ask your child the time regularly. E. g. the cakes need to come out of the oven at half past 4 etc
 Operators
Operators
 Addition - Yr 1 Number lines 1. 2. First number shows where to start. Second number shows how many jumps to do. 8 + 4 =
Addition - Yr 1 Number lines 1. 2. First number shows where to start. Second number shows how many jumps to do. 8 + 4 =
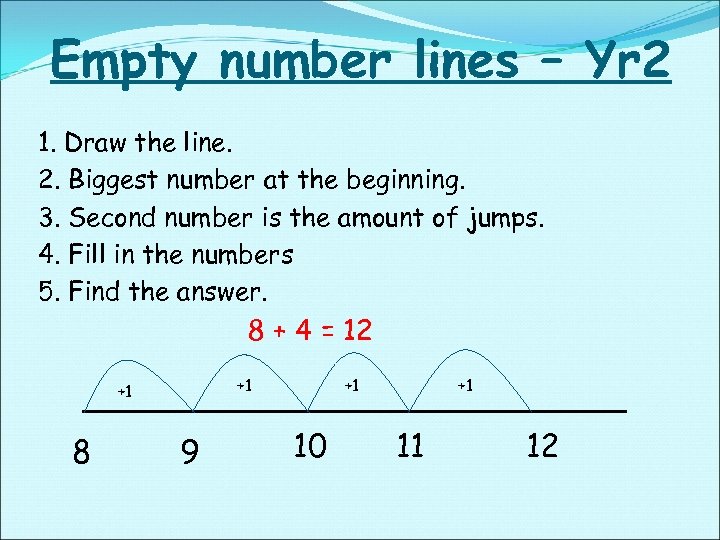 Empty number lines – Yr 2 1. Draw the line. 2. Biggest number at the beginning. 3. Second number is the amount of jumps. 4. Fill in the numbers 5. Find the answer. 8 + 4 = 12 +1 +1 8 9 +1 10 +1 11 12
Empty number lines – Yr 2 1. Draw the line. 2. Biggest number at the beginning. 3. Second number is the amount of jumps. 4. Fill in the numbers 5. Find the answer. 8 + 4 = 12 +1 +1 8 9 +1 10 +1 11 12
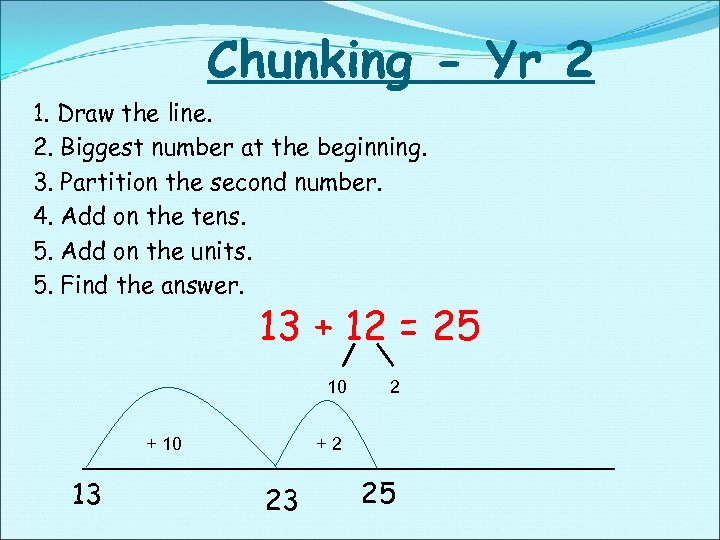 Chunking - Yr 2 1. Draw the line. 2. Biggest number at the beginning. 3. Partition the second number. 4. Add on the tens. 5. Add on the units. 5. Find the answer. 13 + 12 = 25 10 + 10 13 2 +2 23 25
Chunking - Yr 2 1. Draw the line. 2. Biggest number at the beginning. 3. Partition the second number. 4. Add on the tens. 5. Add on the units. 5. Find the answer. 13 + 12 = 25 10 + 10 13 2 +2 23 25
 Column addition (not crossing the tens) 45 + 33 TU 45 + 33 78
Column addition (not crossing the tens) 45 + 33 TU 45 + 33 78
 Column addition ( crossing the tens) 49 + 33 TU 49 +33 8 2 1
Column addition ( crossing the tens) 49 + 33 TU 49 +33 8 2 1
 Multiplication Times tables Practise, Practise!! Try: Visual posters Songs and rhymes Speed Tests
Multiplication Times tables Practise, Practise!! Try: Visual posters Songs and rhymes Speed Tests
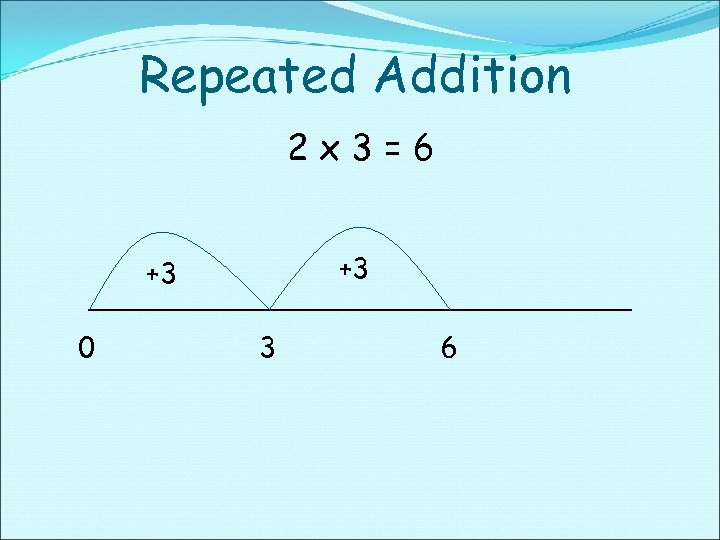 Repeated Addition 2 x 3=6 +3 +3 0 3 6
Repeated Addition 2 x 3=6 +3 +3 0 3 6
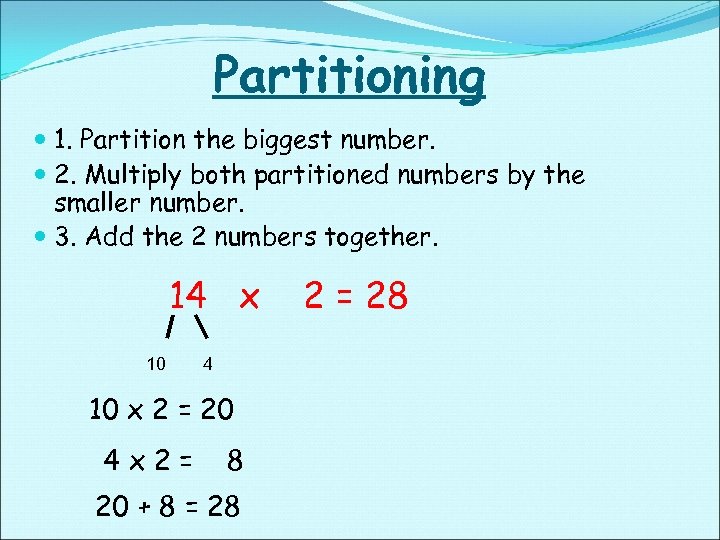 Partitioning 1. Partition the biggest number. 2. Multiply both partitioned numbers by the smaller number. 3. Add the 2 numbers together. 14 x 10 4 10 x 2 = 20 4 x 2= 8 20 + 8 = 28 2 = 28
Partitioning 1. Partition the biggest number. 2. Multiply both partitioned numbers by the smaller number. 3. Add the 2 numbers together. 14 x 10 4 10 x 2 = 20 4 x 2= 8 20 + 8 = 28 2 = 28
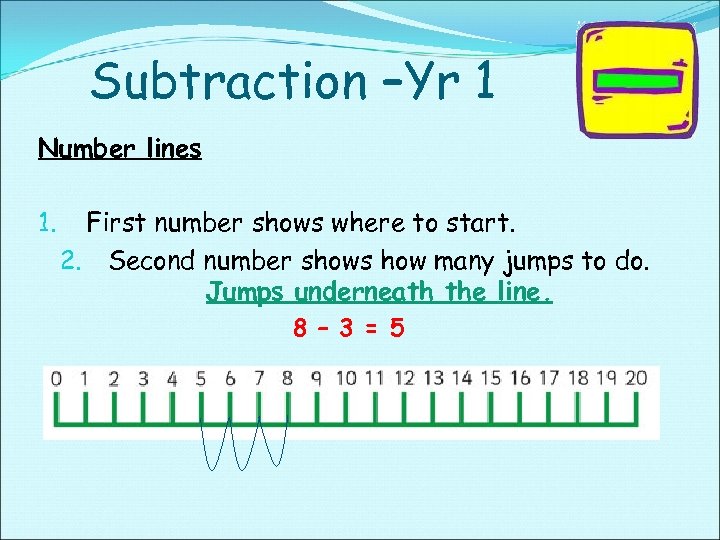 Subtraction –Yr 1 Number lines 1. First number shows where to start. 2. Second number shows how many jumps to do. Jumps underneath the line. 8 – 3 = 5
Subtraction –Yr 1 Number lines 1. First number shows where to start. 2. Second number shows how many jumps to do. Jumps underneath the line. 8 – 3 = 5
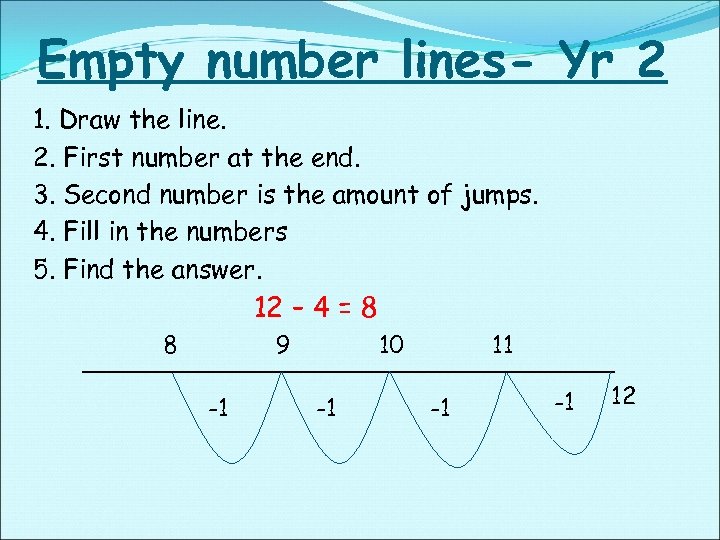 Empty number lines- Yr 2 1. Draw the line. 2. First number at the end. 3. Second number is the amount of jumps. 4. Fill in the numbers 5. Find the answer. 12 – 4 = 8 8 9 -1 10 -1 11 -1 -1 12
Empty number lines- Yr 2 1. Draw the line. 2. First number at the end. 3. Second number is the amount of jumps. 4. Fill in the numbers 5. Find the answer. 12 – 4 = 8 8 9 -1 10 -1 11 -1 -1 12
 Column subtraction (not crossing the tens) 85 – 33= 52 TU 85 -33 52
Column subtraction (not crossing the tens) 85 – 33= 52 TU 85 -33 52
 Column subtraction (crossing the tens) 43 - 29 TU 3 4 13 29 14
Column subtraction (crossing the tens) 43 - 29 TU 3 4 13 29 14
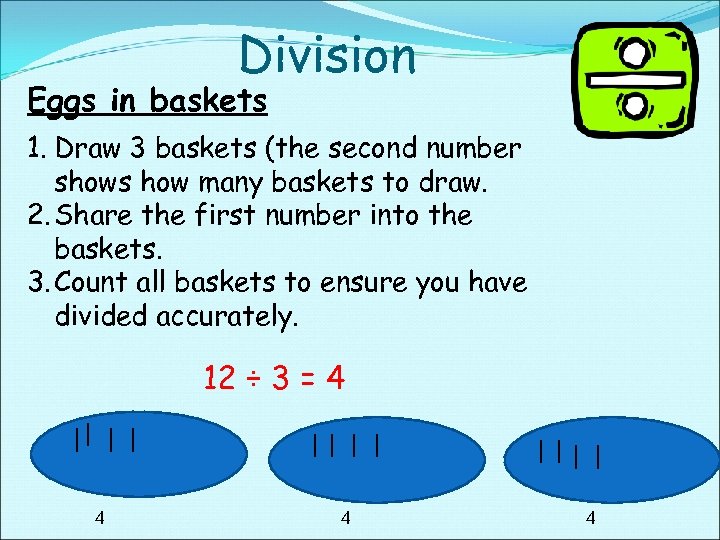 Division Eggs in baskets 1. Draw 3 baskets (the second number shows how many baskets to draw. 2. Share the first number into the baskets. 3. Count all baskets to ensure you have divided accurately. 12 ÷ 3 = 4 4
Division Eggs in baskets 1. Draw 3 baskets (the second number shows how many baskets to draw. 2. Share the first number into the baskets. 3. Count all baskets to ensure you have divided accurately. 12 ÷ 3 = 4 4
 Division-numberline-Yr 2 1. Draw the line. 2. First number at the end. 3. Keep subtracting the second number until you reach zero 4. Count the jumps 5. Find the answer. 12 ÷ 3 = -3 0 -3 3 -3 -3 6 9 12
Division-numberline-Yr 2 1. Draw the line. 2. First number at the end. 3. Keep subtracting the second number until you reach zero 4. Count the jumps 5. Find the answer. 12 ÷ 3 = -3 0 -3 3 -3 -3 6 9 12
 Application
Application
 Problem solving T= Target I= Information N= Number sentence A=Answer
Problem solving T= Target I= Information N= Number sentence A=Answer
 Mina and Ben play a game. Mina scores 70 points. Ben scores 42 points. How many points did they score in total? T= How many points did they score in total? I = 70 42 total N= 70 + 42 = A=
Mina and Ben play a game. Mina scores 70 points. Ben scores 42 points. How many points did they score in total? T= How many points did they score in total? I = 70 42 total N= 70 + 42 = A=
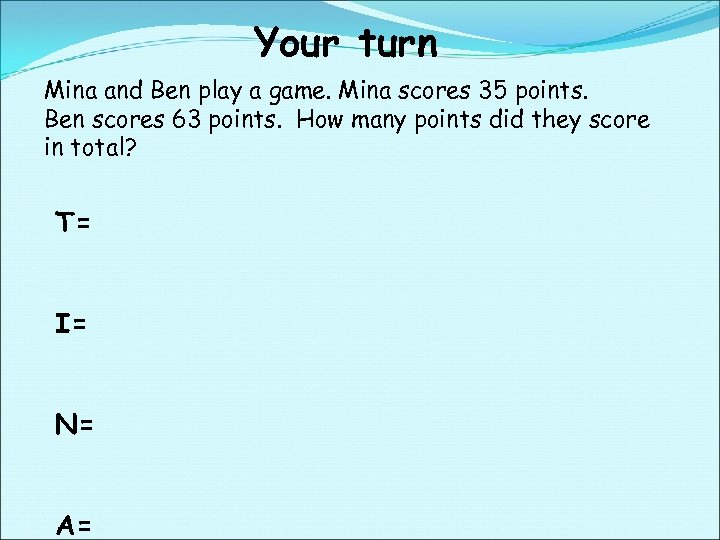 Your turn Mina and Ben play a game. Mina scores 35 points. Ben scores 63 points. How many points did they score in total? T= I= N= A=
Your turn Mina and Ben play a game. Mina scores 35 points. Ben scores 63 points. How many points did they score in total? T= I= N= A=
 Problem Solving Sita had 87 p. She spent 35 p. How much money did she have left? T= How much money did she have left? I = 87 p 35 p left N= 87 p – 35 p= A=
Problem Solving Sita had 87 p. She spent 35 p. How much money did she have left? T= How much money did she have left? I = 87 p 35 p left N= 87 p – 35 p= A=
 There are 104 children at Delton School. 48 children are girls. How many are boys? T= How many are boys? I= 104 48 - N=104 - 48 A=
There are 104 children at Delton School. 48 children are girls. How many are boys? T= How many are boys? I= 104 48 - N=104 - 48 A=
 Finally. . . • Practise is the key to retaining these KIRF’s methods. • Children should also practise these in real situations (application). • Keep going with the methods for the 4 operators alongside the application. • Keep it short, snappy and fun!! Thank you for coming!
Finally. . . • Practise is the key to retaining these KIRF’s methods. • Children should also practise these in real situations (application). • Keep going with the methods for the 4 operators alongside the application. • Keep it short, snappy and fun!! Thank you for coming!


