df7105456e4369fd3d0150e2179999aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 Welcome to Session 4: Making Math Language and Assessments More Accessible n Please sign in. n Fill out 3. 1: Warm-Up in Section 3 of your binder. n Coffee – in our room © 2010, EDC 1
Welcome to Session 4: Making Math Language and Assessments More Accessible n Please sign in. n Fill out 3. 1: Warm-Up in Section 3 of your binder. n Coffee – in our room © 2010, EDC 1
 Topic #1: Introduction & Assignment Discussions In this section, we will: n Follow-up on Session 3 n Go over today’s agenda n Share experiences using accessibility strategies n Discuss articles © 2010, EDC 2
Topic #1: Introduction & Assignment Discussions In this section, we will: n Follow-up on Session 3 n Go over today’s agenda n Share experiences using accessibility strategies n Discuss articles © 2010, EDC 2
 Goal Reminder: To make mathematics instruction more accessible to a Range of Learners 504 IEP IEP to Improve Student Learning © 2010, EDC 3
Goal Reminder: To make mathematics instruction more accessible to a Range of Learners 504 IEP IEP to Improve Student Learning © 2010, EDC 3
 Ground Rules Reminder n n n n Contribute your ideas Respect others’ opinions Assume positive intentions Watch your own air time No side conversations Start and end on time Turn off cell phone ringers No texting or emailing “Parking Lot” © 2010, EDC 4
Ground Rules Reminder n n n n Contribute your ideas Respect others’ opinions Assume positive intentions Watch your own air time No side conversations Start and end on time Turn off cell phone ringers No texting or emailing “Parking Lot” © 2010, EDC 4
 Looking Back: Topics n Collaborative Teaching Models n Collaborative Planning n Complexities of Collaboration n Strengthening Communication © 2010, EDC Your Feedback Positives Suggestions Your Assignments 5
Looking Back: Topics n Collaborative Teaching Models n Collaborative Planning n Complexities of Collaboration n Strengthening Communication © 2010, EDC Your Feedback Positives Suggestions Your Assignments 5
 Session 3: Agenda & Goals 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction & Assignment Discussions Language in Mathematics Word Problems Math Vocabulary Sample Lesson Accessible Classroom Assessments Adapting Tests and Quizzes Planning Accessible Assessments Goals § Learn ways to make math language and assessments more accessible § Leave with ideas to try with students © 2010, EDC 6
Session 3: Agenda & Goals 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction & Assignment Discussions Language in Mathematics Word Problems Math Vocabulary Sample Lesson Accessible Classroom Assessments Adapting Tests and Quizzes Planning Accessible Assessments Goals § Learn ways to make math language and assessments more accessible § Leave with ideas to try with students © 2010, EDC 6
 Partner Discussions: Strategies Tried Please take out: n Reflection Form, copy of strategy, & work sample from focal student Talk with a partner who you do not work with. On your turn: n Describe the strategy and your reasons for using it n How did you use the strategy? n How helpful was the strategy for your focal student? n What might you do differently if you used it again in the future? Time: 5 minutes each Strategy Reflection Form © 2010, EDC 7
Partner Discussions: Strategies Tried Please take out: n Reflection Form, copy of strategy, & work sample from focal student Talk with a partner who you do not work with. On your turn: n Describe the strategy and your reasons for using it n How did you use the strategy? n How helpful was the strategy for your focal student? n What might you do differently if you used it again in the future? Time: 5 minutes each Strategy Reflection Form © 2010, EDC 7
 Whole Group Share Out n n What’s one thing that you learned from your experience using the strategies? What’s one idea from your partner that you would like to try with your students? Why? © 2010, EDC 8
Whole Group Share Out n n What’s one thing that you learned from your experience using the strategies? What’s one idea from your partner that you would like to try with your students? Why? © 2010, EDC 8
 Discuss Article Take out the article, Building Students’ Understanding: The Equal Sign. Discuss: n What are two points that stood out for you? Why? Choose a reporter who will share a few ideas with the whole group. Time: 10 minutes © 2010, EDC 9
Discuss Article Take out the article, Building Students’ Understanding: The Equal Sign. Discuss: n What are two points that stood out for you? Why? Choose a reporter who will share a few ideas with the whole group. Time: 10 minutes © 2010, EDC 9
 Whole Group Share-Out n What’s one idea from your article discussion that you want to share with the whole group? © 2010, EDC 10
Whole Group Share-Out n What’s one idea from your article discussion that you want to share with the whole group? © 2010, EDC 10
 Topic #2: Language in Mathematics In this section, we will: n n Learn about language demands and challenges for students Discuss focal students’ strengths and difficulties with math language © 2010, EDC 11
Topic #2: Language in Mathematics In this section, we will: n n Learn about language demands and challenges for students Discuss focal students’ strengths and difficulties with math language © 2010, EDC 11
 Math Communication Goals for Students n n Organize and consolidate their math thinking through communication Communicate their math thinking coherently and clearly Use the language of math to express math ideas precisely Analyze and evaluate the math thinking and strategies of others © 2010, EDC 12
Math Communication Goals for Students n n Organize and consolidate their math thinking through communication Communicate their math thinking coherently and clearly Use the language of math to express math ideas precisely Analyze and evaluate the math thinking and strategies of others © 2010, EDC 12
 Types of Language Demands Receptive n Reading n Listening Expressive n Writing n Speaking Common Areas of Difficulty n Reading: Decoding; Comprehension n Listening: Auditory Processing n Writing: Organizing ideas in writing n Speaking: Expressing ideas orally © 2010, EDC 13
Types of Language Demands Receptive n Reading n Listening Expressive n Writing n Speaking Common Areas of Difficulty n Reading: Decoding; Comprehension n Listening: Auditory Processing n Writing: Organizing ideas in writing n Speaking: Expressing ideas orally © 2010, EDC 13
 Focal Students & Math Language Take out Warm-Up 3. 1 Discuss with a Partner n What strengths and difficulties does your focal student have with math language? n Reading n Listening n Writing n Speaking 3. 1 Time: 5 min © 2010, EDC 14
Focal Students & Math Language Take out Warm-Up 3. 1 Discuss with a Partner n What strengths and difficulties does your focal student have with math language? n Reading n Listening n Writing n Speaking 3. 1 Time: 5 min © 2010, EDC 14
 Reading Math Texts vs. Fiction FICTION Dorothy lived in the midst of the great Kansas prairies, with Uncle Henry, who was a farmer, and Aunt Em, who was the farmer's wife. Their house was small, for the lumber to build it had to be carried by wagon many miles. Baum, L. F. p. 1 MATH TEXT Based on the pattern, how could you figure out the number of small squares in any figure number? Write an equation to find the number of squares in Figure n. What differences do you notice? © 2010, EDC 15
Reading Math Texts vs. Fiction FICTION Dorothy lived in the midst of the great Kansas prairies, with Uncle Henry, who was a farmer, and Aunt Em, who was the farmer's wife. Their house was small, for the lumber to build it had to be carried by wagon many miles. Baum, L. F. p. 1 MATH TEXT Based on the pattern, how could you figure out the number of small squares in any figure number? Write an equation to find the number of squares in Figure n. What differences do you notice? © 2010, EDC 15
 Conceptual Density of Mathematics Text “One reason students struggle with reading mathematics is the sheer number of concepts packed into the text. According to Schell, math text presents more concepts per word, sentence, and paragraph than any other content-area text. ” Source: Barton, M. and Heidema, C. (2002) p. 14 © 2010, EDC 16
Conceptual Density of Mathematics Text “One reason students struggle with reading mathematics is the sheer number of concepts packed into the text. According to Schell, math text presents more concepts per word, sentence, and paragraph than any other content-area text. ” Source: Barton, M. and Heidema, C. (2002) p. 14 © 2010, EDC 16
 What’s different about reading math texts? n n Not just left to right -- need to read in different directions Not just words – also tables, graphs diagrams, and symbols The process of decoding symbols is different from decoding words. Symbols are like “sight words. ” One challenge is that different symbols are used to describe the same process. n Multiplication *, x, (), ● © 2010, EDC 17
What’s different about reading math texts? n n Not just left to right -- need to read in different directions Not just words – also tables, graphs diagrams, and symbols The process of decoding symbols is different from decoding words. Symbols are like “sight words. ” One challenge is that different symbols are used to describe the same process. n Multiplication *, x, (), ● © 2010, EDC 17
 Topic #3: Word Problems In this section, we will: n Solve and analyze a math problem n Examine and discuss student work n Learn about research on difficulties and strategies © 2010, EDC 18
Topic #3: Word Problems In this section, we will: n Solve and analyze a math problem n Examine and discuss student work n Learn about research on difficulties and strategies © 2010, EDC 18
 Get to Know the Math Problem 1. 2. Work on the problem. Write down the questions that you ask yourself to get started. Discuss with a partner: § What questions did you ask yourself to get started? § How did you set up the table? § How did you come up with the algebraic expression? 3. 2 Popcorn Problem 3. 2 A Answers © 2010, EDC 19
Get to Know the Math Problem 1. 2. Work on the problem. Write down the questions that you ask yourself to get started. Discuss with a partner: § What questions did you ask yourself to get started? § How did you set up the table? § How did you come up with the algebraic expression? 3. 2 Popcorn Problem 3. 2 A Answers © 2010, EDC 19
 Share Approaches Two volunteers present different approaches to the whole group: n n n What questions did you ask yourself to get started? How did you set up the table? How did you come up with the algebraic expression? © 2010, EDC 20
Share Approaches Two volunteers present different approaches to the whole group: n n n What questions did you ask yourself to get started? How did you set up the table? How did you come up with the algebraic expression? © 2010, EDC 20
 Apply the Framework: Consider the Math Key Math Goals n Represent a situation with a table and symbolic expression n What would you add to the goals? © 2010, EDC 21
Apply the Framework: Consider the Math Key Math Goals n Represent a situation with a table and symbolic expression n What would you add to the goals? © 2010, EDC 21
 Analyze the Problem n What are the task demands on students? Language Conceptual Organization n What potential difficulties would you anticipate for your focal students? Next, we will look at actual work samples from two 7 th graders. 3. 2 Popcorn Problem Ref. A on Yellow © 2010, EDC 22
Analyze the Problem n What are the task demands on students? Language Conceptual Organization n What potential difficulties would you anticipate for your focal students? Next, we will look at actual work samples from two 7 th graders. 3. 2 Popcorn Problem Ref. A on Yellow © 2010, EDC 22
 Consider the Student: Examine Work Sample X 1. Work individually to: n n Look at the work sample for Student X Write notes on your LASW form in the first 2 columns. 2. In small groups, discuss Student X’s work: n Strengths and Difficulties n Diagnostic Questions 3. 3 LASW Tool 3. 4 Time: ~7 minutes Student X © 2010, EDC 23
Consider the Student: Examine Work Sample X 1. Work individually to: n n Look at the work sample for Student X Write notes on your LASW form in the first 2 columns. 2. In small groups, discuss Student X’s work: n Strengths and Difficulties n Diagnostic Questions 3. 3 LASW Tool 3. 4 Time: ~7 minutes Student X © 2010, EDC 23
 Discuss Student X n n n Evidence of strengths & difficulties? Questions to ask to find out more about the student’s math understanding? Strategies? A. B. C. © 2010, EDC 24
Discuss Student X n n n Evidence of strengths & difficulties? Questions to ask to find out more about the student’s math understanding? Strategies? A. B. C. © 2010, EDC 24
 Examine Work Sample from Student Y 1. Work individually to: n n Look at the work sample for Student Y Write notes on your LASW form in the first 2 columns. 2. In small groups, discuss Student Y’s work: n Strengths and Difficulties n Diagnostic Questions 3. 5 Student Y © 2010, EDC 3. 3 LASW Tool 25
Examine Work Sample from Student Y 1. Work individually to: n n Look at the work sample for Student Y Write notes on your LASW form in the first 2 columns. 2. In small groups, discuss Student Y’s work: n Strengths and Difficulties n Diagnostic Questions 3. 5 Student Y © 2010, EDC 3. 3 LASW Tool 25
 Discuss Student Y & Compare n n n Evidence of strengths & difficulties? Diagnostic Questions & Strategies Similarities & Differences for X & Y? A. B. C. © 2010, EDC 26
Discuss Student Y & Compare n n n Evidence of strengths & difficulties? Diagnostic Questions & Strategies Similarities & Differences for X & Y? A. B. C. © 2010, EDC 26
 Sample Strategies for the Popcorn Problem Examine strategies individually n Take a look at the sample strategies. Talk with a partner n What’s one strategy that you would like to try with your students? Why? n What is your experience using similar strategies? What works well? 3. 6 Sample Strategies © 2010, EDC 27
Sample Strategies for the Popcorn Problem Examine strategies individually n Take a look at the sample strategies. Talk with a partner n What’s one strategy that you would like to try with your students? Why? n What is your experience using similar strategies? What works well? 3. 6 Sample Strategies © 2010, EDC 27
 Research on Word Problems Barriers for Students n Irrelevant Information n Extra Steps n Length Research Findings n Students with math learning disabilities do much worse than peers when the first two features are present. n n Similar findings for student with attention difficulties. Students who have both math and reading disabilities have the lowest performance on word problems Source: Berch & Mazzocco, 2007; Fuchs & Fuchs, 2002 © 2010, EDC 28
Research on Word Problems Barriers for Students n Irrelevant Information n Extra Steps n Length Research Findings n Students with math learning disabilities do much worse than peers when the first two features are present. n n Similar findings for student with attention difficulties. Students who have both math and reading disabilities have the lowest performance on word problems Source: Berch & Mazzocco, 2007; Fuchs & Fuchs, 2002 © 2010, EDC 28
 Metacognitive Strategies n n n What? A “plan of action” for problem solving that uses selfquestioning and self-checking techniques. How? Use after students have understanding of the math concept or skill Teach strategies explicitly through teacher modeling, and guided & independent practice Why? Build student independence Help students solve problems Overcome memory difficulties © 2010, EDC 29
Metacognitive Strategies n n n What? A “plan of action” for problem solving that uses selfquestioning and self-checking techniques. How? Use after students have understanding of the math concept or skill Teach strategies explicitly through teacher modeling, and guided & independent practice Why? Build student independence Help students solve problems Overcome memory difficulties © 2010, EDC 29
 Sample Metacognitive Strategies A. RAFT for getting started on solving word problems Read the problem Ask yourself: What is the problem asking? Find the key information Think ahead: What will the answers look like? B. Problem Solving Checklists 3. 7: RAFT 3. 8: Problem Solving © 2010, EDC 30
Sample Metacognitive Strategies A. RAFT for getting started on solving word problems Read the problem Ask yourself: What is the problem asking? Find the key information Think ahead: What will the answers look like? B. Problem Solving Checklists 3. 7: RAFT 3. 8: Problem Solving © 2010, EDC 30
 Think Aloud Strategy What is a Think Aloud? As you solve a problem, talk about your thought processes and the questions you are asking yourself. Sample Prompts 1. What does the problem say? 2. What question(s) am I trying to answer? 3. What information do I have? Which information is important? 4. How will I solve the problem? 3. 9 © 2010, EDC 31
Think Aloud Strategy What is a Think Aloud? As you solve a problem, talk about your thought processes and the questions you are asking yourself. Sample Prompts 1. What does the problem say? 2. What question(s) am I trying to answer? 3. What information do I have? Which information is important? 4. How will I solve the problem? 3. 9 © 2010, EDC 31
 How is a Think-Aloud Different from Questions Teachers Ask Every Day? n n The think-aloud strategy places explicit focus on: n the process of self-questioning n modeling helpful questions for students to ask themselves In everyday routines students may notice the kinds of questions their teachers are asking Process for Using Think Aloud: n Teacher models “thinking aloud. ” n Students practice strategy and learn to use it independently. © 2010, EDC 32
How is a Think-Aloud Different from Questions Teachers Ask Every Day? n n The think-aloud strategy places explicit focus on: n the process of self-questioning n modeling helpful questions for students to ask themselves In everyday routines students may notice the kinds of questions their teachers are asking Process for Using Think Aloud: n Teacher models “thinking aloud. ” n Students practice strategy and learn to use it independently. © 2010, EDC 32
 Discuss Meta-cognitive Strategies 1. Look at strategies 3. 7 -3. 9. 2. Discuss: Share your experiences: n How have you used the Think Aloud strategy or other meta-cognitive strategies with students? What works well? If you want to try a strategy: n What strategy do you want to try? How might you use it with your students? © 2010, EDC 33
Discuss Meta-cognitive Strategies 1. Look at strategies 3. 7 -3. 9. 2. Discuss: Share your experiences: n How have you used the Think Aloud strategy or other meta-cognitive strategies with students? What works well? If you want to try a strategy: n What strategy do you want to try? How might you use it with your students? © 2010, EDC 33
 Topic #4: Math Vocabulary In this section, we will: n Learn about math vocabulary challenges n Try sample strategies © 2010, EDC 34
Topic #4: Math Vocabulary In this section, we will: n Learn about math vocabulary challenges n Try sample strategies © 2010, EDC 34
 Complexities of Math Vocabulary. Some terms: n are shared with everyday English but have distinct math meanings n n sound like everyday English words n n Right, volume, expression, figure, is, Sum and Some have more than one math meaning n Square, round Directions: 1. Read Handout 3. 10 2. What’s one math word that your students find confusing? 3. 10 Vocabulary © 2010, EDC 35
Complexities of Math Vocabulary. Some terms: n are shared with everyday English but have distinct math meanings n n sound like everyday English words n n Right, volume, expression, figure, is, Sum and Some have more than one math meaning n Square, round Directions: 1. Read Handout 3. 10 2. What’s one math word that your students find confusing? 3. 10 Vocabulary © 2010, EDC 35
 Small Words are also Important! Examples: n n n A Any Of Off And Or All Each It Is Strategies: n When reading aloud, clearly enunciate small words n Build students’ awareness of the importance of paying attention to small words © 2010, EDC 36
Small Words are also Important! Examples: n n n A Any Of Off And Or All Each It Is Strategies: n When reading aloud, clearly enunciate small words n Build students’ awareness of the importance of paying attention to small words © 2010, EDC 36
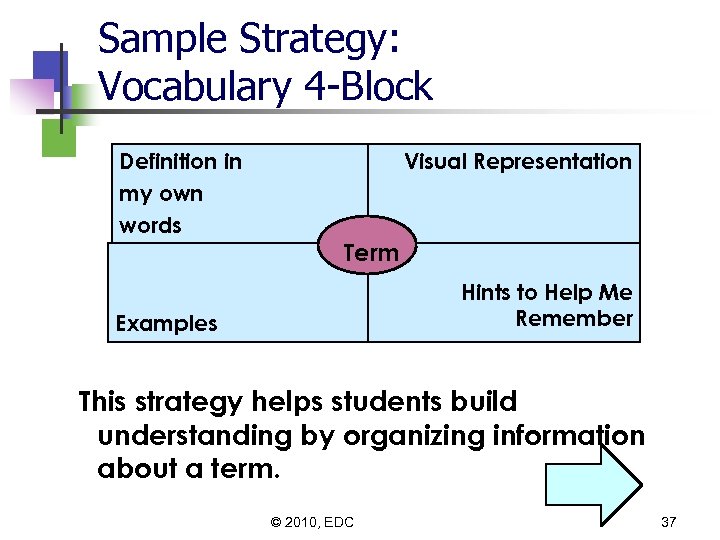 Sample Strategy: Vocabulary 4 -Block Definition in my own words Visual Representation Term Hints to Help Me Remember Examples This strategy helps students build understanding by organizing information about a term. © 2010, EDC 37
Sample Strategy: Vocabulary 4 -Block Definition in my own words Visual Representation Term Hints to Help Me Remember Examples This strategy helps students build understanding by organizing information about a term. © 2010, EDC 37
 Sample 4 -block for Median The middle value in a set of ranked data Median Don’t forget to put the numbers from smallest to largest! 1, 1, 4, 6, 7, 10, 21 Median sounds like medium --the middle 3. 11 © 2010, EDC 38
Sample 4 -block for Median The middle value in a set of ranked data Median Don’t forget to put the numbers from smallest to largest! 1, 1, 4, 6, 7, 10, 21 Median sounds like medium --the middle 3. 11 © 2010, EDC 38
 Vocabulary Activity: “I have, Who has? ” Goals: n Experience an activity that you can use with students to review math vocabulary and build fluency n Consider ways to make the activity more accessible to students with disabilities © 2010, EDC 39
Vocabulary Activity: “I have, Who has? ” Goals: n Experience an activity that you can use with students to review math vocabulary and build fluency n Consider ways to make the activity more accessible to students with disabilities © 2010, EDC 39
 Lunch © 2010, EDC 40
Lunch © 2010, EDC 40
 “I Have, Who Has” Activity: Demo 1. Everyone gets a card. 2. First player reads question on card: Who has a five-sided polygon? 3. Player with matching word responds and then asks next question. I have a pentagon. Who has a 90◦ angle? © 2010, EDC 41
“I Have, Who Has” Activity: Demo 1. Everyone gets a card. 2. First player reads question on card: Who has a five-sided polygon? 3. Player with matching word responds and then asks next question. I have a pentagon. Who has a 90◦ angle? © 2010, EDC 41
 “I have, Who has”Directions Before Playing 1. Divide into groups. Stand in a circle. 2. Each person gets one or two cards. 3. Talk with a partner about the meanings of the vocabulary words on your cards. Play the Game 4. One person begins by reading his/her question only. 5. The person who has the statement that matches, reads the statement. 6. That same person then reads the question on his/her card. 7. Play continues until all the cards have been completed. © 2010, EDC 42
“I have, Who has”Directions Before Playing 1. Divide into groups. Stand in a circle. 2. Each person gets one or two cards. 3. Talk with a partner about the meanings of the vocabulary words on your cards. Play the Game 4. One person begins by reading his/her question only. 5. The person who has the statement that matches, reads the statement. 6. That same person then reads the question on his/her card. 7. Play continues until all the cards have been completed. © 2010, EDC 42
 Discuss n n How do you or would you use the “I have, who has” vocabulary activity with your students? How do you or would you make it more accessible to your students with learning disabilities? © 2010, EDC 43
Discuss n n How do you or would you use the “I have, who has” vocabulary activity with your students? How do you or would you make it more accessible to your students with learning disabilities? © 2010, EDC 43
 Closing Thoughts on Math Vocabulary Suggestions n Identify critical terms n Introduce vocabulary in the context of doing mathematics, not in isolation n Provide multiple opportunities for students to hear, read & use terms Common Pitfall n Vocab. strategies are created but then not actively used n Word Wall turns into wall-paper n Students don’t use the dictionaries that they worked hard to make What are your suggestions for avoiding this © 2010, EDC 44
Closing Thoughts on Math Vocabulary Suggestions n Identify critical terms n Introduce vocabulary in the context of doing mathematics, not in isolation n Provide multiple opportunities for students to hear, read & use terms Common Pitfall n Vocab. strategies are created but then not actively used n Word Wall turns into wall-paper n Students don’t use the dictionaries that they worked hard to make What are your suggestions for avoiding this © 2010, EDC 44
 Topic #5: Sample Lesson In this section, we will: n Watch and discuss a video of a lesson that involves reading, discussing, and writing about abstract equations n Discuss the ways the teacher informally assesses the students’ understanding © 2010, EDC 45
Topic #5: Sample Lesson In this section, we will: n Watch and discuss a video of a lesson that involves reading, discussing, and writing about abstract equations n Discuss the ways the teacher informally assesses the students’ understanding © 2010, EDC 45
 Math Lesson in Video n n n Reviews vocabulary from their math curriculum n Factored Form: (x+1)(x+2) 2 + 3 x + 2 n Expanded Form: x Uses an area model for equations Uses Algebra Tiles (manipulatives) 1 Algebra Tiles x 2 x 3. 12 Video Background, Top © 2010, EDC 46
Math Lesson in Video n n n Reviews vocabulary from their math curriculum n Factored Form: (x+1)(x+2) 2 + 3 x + 2 n Expanded Form: x Uses an area model for equations Uses Algebra Tiles (manipulatives) 1 Algebra Tiles x 2 x 3. 12 Video Background, Top © 2010, EDC 46
 Algebra Tiles Demo Use Algebra Tiles to multiply (x+1)(x+2) © 2010, EDC 47
Algebra Tiles Demo Use Algebra Tiles to multiply (x+1)(x+2) © 2010, EDC 47
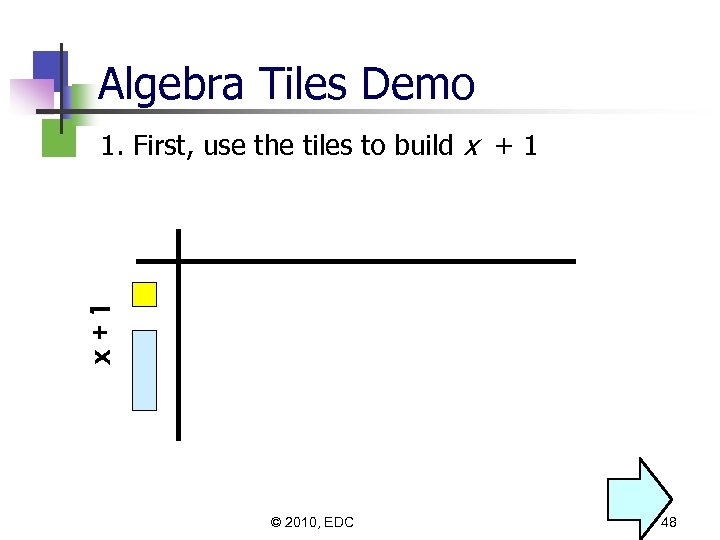 Algebra Tiles Demo x+1 1. First, use the tiles to build x + 1 © 2010, EDC 48
Algebra Tiles Demo x+1 1. First, use the tiles to build x + 1 © 2010, EDC 48
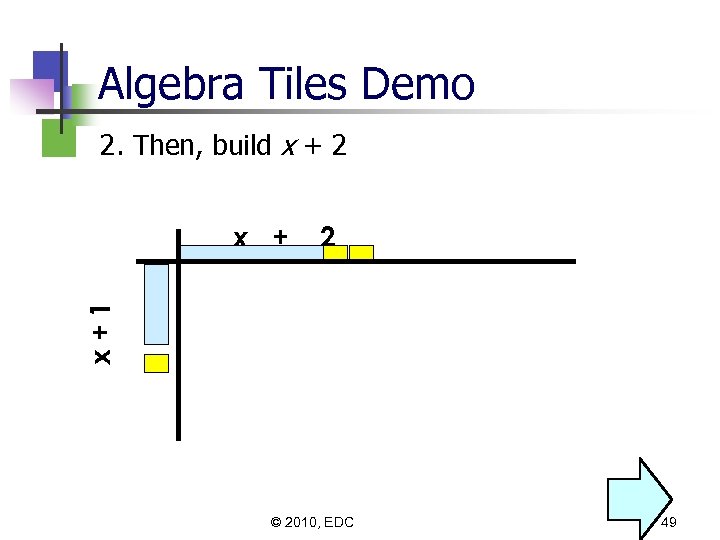 Algebra Tiles Demo 2. Then, build x + 2 2 x+1 x + © 2010, EDC 49
Algebra Tiles Demo 2. Then, build x + 2 2 x+1 x + © 2010, EDC 49
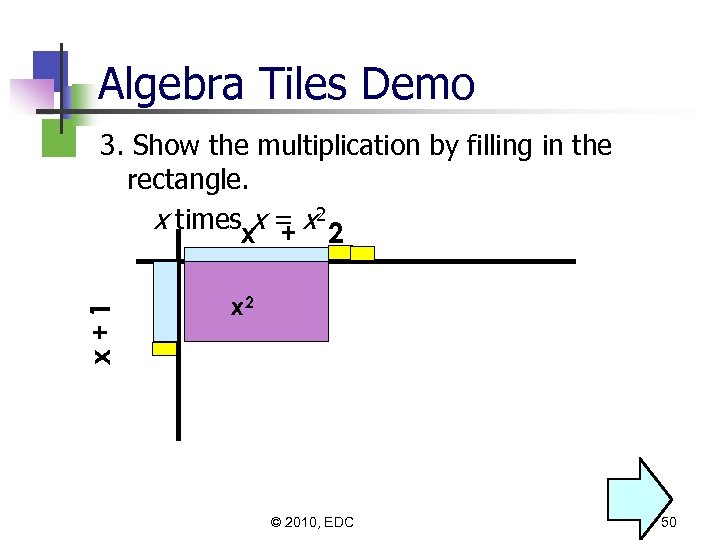 Algebra Tiles Demo x+1 3. Show the multiplication by filling in the rectangle. x timesxx = x 2 2 + x 2 © 2010, EDC 50
Algebra Tiles Demo x+1 3. Show the multiplication by filling in the rectangle. x timesxx = x 2 2 + x 2 © 2010, EDC 50
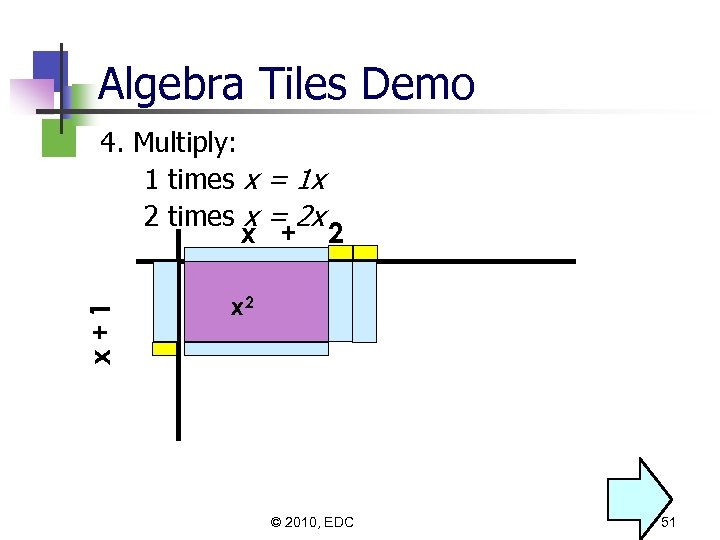 Algebra Tiles Demo x+1 4. Multiply: 1 times x = 1 x 2 times x = 2 x x + 2 x 2 © 2010, EDC 51
Algebra Tiles Demo x+1 4. Multiply: 1 times x = 1 x 2 times x = 2 x x + 2 x 2 © 2010, EDC 51
 Algebra Tiles Demo 5. Multiply the yellow tiles: 1 times 2 = 2 x+1 x + 2 x 2 The rectangle is completed. © 2010, EDC 52
Algebra Tiles Demo 5. Multiply the yellow tiles: 1 times 2 = 2 x+1 x + 2 x 2 The rectangle is completed. © 2010, EDC 52
 Algebra Tiles Demo n Dimensions: (x + 1) and (x + 2) n Area: x 2 + 3 x + 2 x+1 x 2 (x + 1)(x + 2) = x 2 + 3 x + 2 © 2010, EDC 53
Algebra Tiles Demo n Dimensions: (x + 1) and (x + 2) n Area: x 2 + 3 x + 2 x+1 x 2 (x + 1)(x + 2) = x 2 + 3 x + 2 © 2010, EDC 53
 Get to Know the Math Problem in the Video n n Read the problem on the bottom of 3. 12. Write what the problem is asking in your own words. Talk with a partner: n What did you write? n What is your approach to solving the problem? 3. 12 Bottom of Page © 2010, EDC 54
Get to Know the Math Problem in the Video n n Read the problem on the bottom of 3. 12. Write what the problem is asking in your own words. Talk with a partner: n What did you write? n What is your approach to solving the problem? 3. 12 Bottom of Page © 2010, EDC 54
 Video: Background n n n Title I Math Coach who co-teaches 8 th grade math class and provides math support Uses alternative teaching model with six 8 th grade students, including students with disabilities and ELLs, who were having difficulties in the regular math class As a group, these students tend to be very quiet, and teachers could not tell what the students understood What do these students understand? © 2010, EDC 55
Video: Background n n n Title I Math Coach who co-teaches 8 th grade math class and provides math support Uses alternative teaching model with six 8 th grade students, including students with disabilities and ELLs, who were having difficulties in the regular math class As a group, these students tend to be very quiet, and teachers could not tell what the students understood What do these students understand? © 2010, EDC 55
 As You Watch, Keep in Mind… Video Reminder n An example to spark discussion, not meant to be ideal n Observe the teacher’s practices without judging Focus Questions n What strategies does the teacher use to make the language of the mathematics accessible? n How does the teacher find out about the students’ math understanding? 3. 13 Video Notes © 2010, EDC 56
As You Watch, Keep in Mind… Video Reminder n An example to spark discussion, not meant to be ideal n Observe the teacher’s practices without judging Focus Questions n What strategies does the teacher use to make the language of the mathematics accessible? n How does the teacher find out about the students’ math understanding? 3. 13 Video Notes © 2010, EDC 56
 Sequence for Viewing “Math Support Class” n n Vocabulary Warm-Up Introduction to Main Problem n n Student Explanations n n Discussion Teacher’s Interview 3. 13 Video Notes © 2010, EDC 57
Sequence for Viewing “Math Support Class” n n Vocabulary Warm-Up Introduction to Main Problem n n Student Explanations n n Discussion Teacher’s Interview 3. 13 Video Notes © 2010, EDC 57
 After the Video: Discuss n n What strategies do you use to encourage quiet students, including ones with disabilities and English Learners, to talk about their math ideas? What questioning strategies do you use with your students? © 2010, EDC 58
After the Video: Discuss n n What strategies do you use to encourage quiet students, including ones with disabilities and English Learners, to talk about their math ideas? What questioning strategies do you use with your students? © 2010, EDC 58
 Ideas to Take Away n Write down 1 -2 ideas from the morning that you would like to try with your students. n Write down your ideas on Reference Sheet E. n Share with a partner from another table. Time: 5 -7 minutes Ref. E on green © 2010, EDC 59
Ideas to Take Away n Write down 1 -2 ideas from the morning that you would like to try with your students. n Write down your ideas on Reference Sheet E. n Share with a partner from another table. Time: 5 -7 minutes Ref. E on green © 2010, EDC 59
 Topic #6: Accessible Classroom Assessments In this section, we will: n n Discuss the need for making accommodations to math assessments Identify strategies to help students before, during, and after assessments Note: The focus is on classroom assessments and not on state tests. © 2010, EDC 60
Topic #6: Accessible Classroom Assessments In this section, we will: n n Discuss the need for making accommodations to math assessments Identify strategies to help students before, during, and after assessments Note: The focus is on classroom assessments and not on state tests. © 2010, EDC 60
 Accessible Assessment Activity Goal n Discuss different reasons for assessing students and for making accommodations to tests and quizzes Directions 1. Read the handout. 2. 3. Highlight 2 quotes that stand out for you. Discuss in small groups. n Which quotes did you pick? Why? 3. 14: Assessment Quotes © 2010, EDC 61
Accessible Assessment Activity Goal n Discuss different reasons for assessing students and for making accommodations to tests and quizzes Directions 1. Read the handout. 2. 3. Highlight 2 quotes that stand out for you. Discuss in small groups. n Which quotes did you pick? Why? 3. 14: Assessment Quotes © 2010, EDC 61
 Before & During Assessments Activity Goal n Discuss ways to support students before and during assessments Directions 1. Divide into groups of 3 or 4. 2. Choose one sample student for the group. 3. Discuss the questions and fill out Handout. 4. Be prepared to share two ideas with the whole group. 3. 15: Sample Students 3. 16: Chart © 2010, EDC 62
Before & During Assessments Activity Goal n Discuss ways to support students before and during assessments Directions 1. Divide into groups of 3 or 4. 2. Choose one sample student for the group. 3. Discuss the questions and fill out Handout. 4. Be prepared to share two ideas with the whole group. 3. 15: Sample Students 3. 16: Chart © 2010, EDC 62
 Whole Group Share-Out A reporter from each group shares: n n What are two ideas for providing support to your sample student before and during assessments? Why do you think that these suggestions would be helpful to this student? © 2010, EDC 63
Whole Group Share-Out A reporter from each group shares: n n What are two ideas for providing support to your sample student before and during assessments? Why do you think that these suggestions would be helpful to this student? © 2010, EDC 63
 Ways to support students after assessments Suggestions n Have students analyze errors n Conceptual, careless, computational n n n What would you add to this list? 3. 17 Suggestions © 2010, EDC 64
Ways to support students after assessments Suggestions n Have students analyze errors n Conceptual, careless, computational n n n What would you add to this list? 3. 17 Suggestions © 2010, EDC 64
 Topic #7: Adapting Tests and Quizzes In this section, we will: n Consider a variety of ways to make tests more accessible n Examine sample adaptations to assessments © 2010, EDC 65
Topic #7: Adapting Tests and Quizzes In this section, we will: n Consider a variety of ways to make tests more accessible n Examine sample adaptations to assessments © 2010, EDC 65
 Examine Sample Adaptations Directions n Work in pairs. n Compare the original quiz to the adapted version. n n Tear out the original quiz to make it easier to compare. Discuss: What kinds of adaptations were made? Note: Adaptations were made for a few problems not the whole quiz 3. 18 Original Quiz - 3. 19 Adapted Quiz 3. 20 Sample Adaptations © 2010, EDC 66
Examine Sample Adaptations Directions n Work in pairs. n Compare the original quiz to the adapted version. n n Tear out the original quiz to make it easier to compare. Discuss: What kinds of adaptations were made? Note: Adaptations were made for a few problems not the whole quiz 3. 18 Original Quiz - 3. 19 Adapted Quiz 3. 20 Sample Adaptations © 2010, EDC 66
 Discuss n n What adaptations were made to the quiz? How might these changes help students with learning disabilities? What kinds of adaptations do you make to classroom math tests? Note: Handout 3. 20 has a list of suggestions. 3. 19 & 3. 20 © 2010, EDC 67
Discuss n n What adaptations were made to the quiz? How might these changes help students with learning disabilities? What kinds of adaptations do you make to classroom math tests? Note: Handout 3. 20 has a list of suggestions. 3. 19 & 3. 20 © 2010, EDC 67
 Topic #8: Planning Accessible Assessments In this section, we will: n collaborate with colleagues to plan accommodations for a test or quiz from our curriculum © 2010, EDC 68
Topic #8: Planning Accessible Assessments In this section, we will: n collaborate with colleagues to plan accommodations for a test or quiz from our curriculum © 2010, EDC 68
 Goals and Cautions for Adapting Assessments Goals n Enable students to show their abilities and not be impeded by their disabilities n Align accommodations with students’ strengths and difficulties and with the math assessment goals Cautions n Lose integrity of math – Refer to the Standards (Handout) n Set expectations too low © 2010, EDC 69
Goals and Cautions for Adapting Assessments Goals n Enable students to show their abilities and not be impeded by their disabilities n Align accommodations with students’ strengths and difficulties and with the math assessment goals Cautions n Lose integrity of math – Refer to the Standards (Handout) n Set expectations too low © 2010, EDC 69
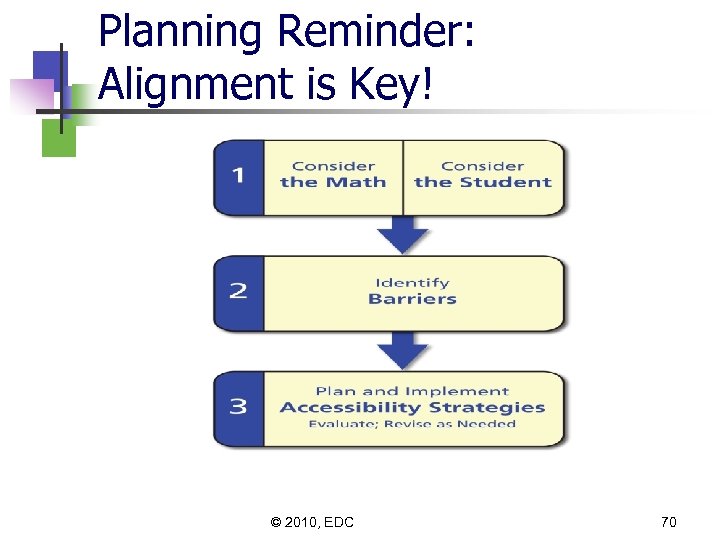 Planning Reminder: Alignment is Key! © 2010, EDC 70
Planning Reminder: Alignment is Key! © 2010, EDC 70
 Planning Time: Checklist 1. Get Organized n n Work with your teaching partner or in grade-level groups. Take out math test that you brought 2. Discuss and fill out the Planner. 3. Make adaptations to at least 2 test questions to make them more accessible to your focal students. 4. Action Plan Form: determine who, when, where, how you will gather examples of student work, lesson or assessment accommodations for your focal student. share ideas with colleagues from other groups. 3. 21 Accessible Assessment Planner © 2010, EDC 71
Planning Time: Checklist 1. Get Organized n n Work with your teaching partner or in grade-level groups. Take out math test that you brought 2. Discuss and fill out the Planner. 3. Make adaptations to at least 2 test questions to make them more accessible to your focal students. 4. Action Plan Form: determine who, when, where, how you will gather examples of student work, lesson or assessment accommodations for your focal student. share ideas with colleagues from other groups. 3. 21 Accessible Assessment Planner © 2010, EDC 71
 Share Ideas n Get organized into groups of 3 to talk with people from other planning groups. Discuss n What are 2 strategies that you used to make the test/quiz more accessible to your students? n Why did you choose these strategies? Time: 7 minutes © 2010, EDC 72
Share Ideas n Get organized into groups of 3 to talk with people from other planning groups. Discuss n What are 2 strategies that you used to make the test/quiz more accessible to your students? n Why did you choose these strategies? Time: 7 minutes © 2010, EDC 72
 Topic #9: Day 4 Wrap-Up In this section, we will: n Do a wrap-up activity n Assignment for next time (Wednesday, March 11 th, 2015) © 2010, EDC 73
Topic #9: Day 4 Wrap-Up In this section, we will: n Do a wrap-up activity n Assignment for next time (Wednesday, March 11 th, 2015) © 2010, EDC 73
 Day 4 Wrap-Up: Math Standards Expressions & Equations n Apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to algebraic expressions. n Solve real-life and mathematical problems using numerical and algebraic expressions and equations. n Analyze and solve linear equations Practice Standards 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Source: Common Core State Standards 74
Day 4 Wrap-Up: Math Standards Expressions & Equations n Apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to algebraic expressions. n Solve real-life and mathematical problems using numerical and algebraic expressions and equations. n Analyze and solve linear equations Practice Standards 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Source: Common Core State Standards 74
 Last Step n Complete Feedback Form Thanks very much for participating in the course!! © 2010, EDC 75
Last Step n Complete Feedback Form Thanks very much for participating in the course!! © 2010, EDC 75


