090aad517cdd722e3cfafca15a7892b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Welcome to Physics 100 !!!! Dr. Gregory G. Wood Fall 2005
Welcome to Physics 100 !!!! Dr. Gregory G. Wood Fall 2005
 A bit about me…. n n Just joined CSUCI Married to Dr. Tabitha Swan-Wood ¡ Expecting a baby girl Jan. 15, 2005
A bit about me…. n n Just joined CSUCI Married to Dr. Tabitha Swan-Wood ¡ Expecting a baby girl Jan. 15, 2005
 Quiz 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) What is your name? What is your major? What is the email address you would like correspondence about this course sent to? Why are you taking physics? (Try to put something more than “because I have to…”) Tell me a bit about yourself.
Quiz 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) What is your name? What is your major? What is the email address you would like correspondence about this course sent to? Why are you taking physics? (Try to put something more than “because I have to…”) Tell me a bit about yourself.
 What is Physics? n Broadly defined: A scientific method used to explain physical phenomena in the universe using the tools of mathematics.
What is Physics? n Broadly defined: A scientific method used to explain physical phenomena in the universe using the tools of mathematics.
 Examples of Physics… n Classical Mechanics: ¡ ¡ Motion of the planets 1 -D Atomic Chain Transverse Modes-Java Applet
Examples of Physics… n Classical Mechanics: ¡ ¡ Motion of the planets 1 -D Atomic Chain Transverse Modes-Java Applet
 Examples of Physics… n Light & Waves: ¡ Rainbows & Prisms ¡ Ultra-Sounds
Examples of Physics… n Light & Waves: ¡ Rainbows & Prisms ¡ Ultra-Sounds
 Examples of Physics… n Light & Waves: ¡ Atomic Scale Imaging
Examples of Physics… n Light & Waves: ¡ Atomic Scale Imaging
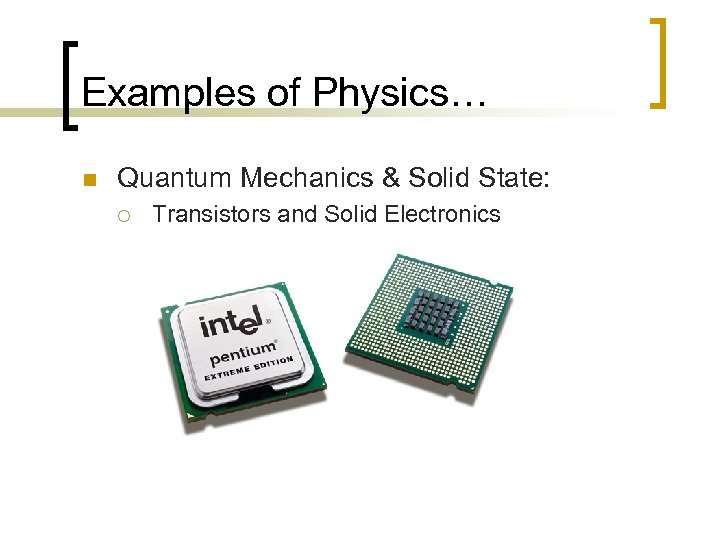 Examples of Physics… n Quantum Mechanics & Solid State: ¡ Transistors and Solid Electronics
Examples of Physics… n Quantum Mechanics & Solid State: ¡ Transistors and Solid Electronics
 Physics Permeates Your Life n n n TV Radio Computers Automobiles Plasma Screens Medical Instruments: MRI, Ultrasound, X-rays, …
Physics Permeates Your Life n n n TV Radio Computers Automobiles Plasma Screens Medical Instruments: MRI, Ultrasound, X-rays, …
 Chapter 1 n n Skim Chap. 1 and make sure you understand it. Important prefixes: Power Prefix Abbreviation 103 kilo k 10 -2 centi c 10 -3 milli m 10 -6 micro m
Chapter 1 n n Skim Chap. 1 and make sure you understand it. Important prefixes: Power Prefix Abbreviation 103 kilo k 10 -2 centi c 10 -3 milli m 10 -6 micro m
 Chapter 1 n Dimensional Analysis: ¡ Units must be equal on both sides of an equation n ¡ When adding or subtracting units must be equal n ¡ [units] = [units] + [units] Examples n n Yes: 5 m/s = 3 m/s + 2 m/s No: 5 m/s = 3 m/s 2 + 2 m/s
Chapter 1 n Dimensional Analysis: ¡ Units must be equal on both sides of an equation n ¡ When adding or subtracting units must be equal n ¡ [units] = [units] + [units] Examples n n Yes: 5 m/s = 3 m/s + 2 m/s No: 5 m/s = 3 m/s 2 + 2 m/s
 Chapter 1 n Scientific Notation ¡ n 3, 240 = 3. 24 x 103 Converting Units ¡ To convert 23 seconds to units of hours: n 23 sec x 1 min x 1 hour = 0. 00639 hr = 6. 39 x 10 -3 hr 60 sec 60 min
Chapter 1 n Scientific Notation ¡ n 3, 240 = 3. 24 x 103 Converting Units ¡ To convert 23 seconds to units of hours: n 23 sec x 1 min x 1 hour = 0. 00639 hr = 6. 39 x 10 -3 hr 60 sec 60 min
 Chapter 1 n How to Approach Physics Problems: ¡ ¡ Carefully read the problem Visualize the problem n ¡ If complicated, try to separate the events n ¡ ¡ ¡ Sketch a diagram of what’s happening Set-up the appropriate physics equations Solve the equations Check your answer: units and magnitude Think about your answer
Chapter 1 n How to Approach Physics Problems: ¡ ¡ Carefully read the problem Visualize the problem n ¡ If complicated, try to separate the events n ¡ ¡ ¡ Sketch a diagram of what’s happening Set-up the appropriate physics equations Solve the equations Check your answer: units and magnitude Think about your answer
 Chapter 1 n A note on grading and partial credit ¡ ¡ Give a solid attempt at every problem Sketches will be worth something
Chapter 1 n A note on grading and partial credit ¡ ¡ Give a solid attempt at every problem Sketches will be worth something
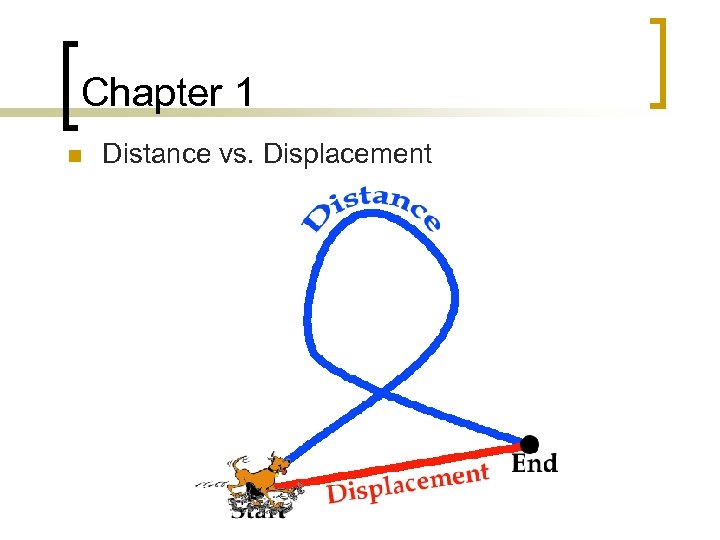 Chapter 1 n Distance vs. Displacement
Chapter 1 n Distance vs. Displacement
 Chapter 2 n Position & Displacement… ¡ Create an axis 0 m n position 6 m At t=0 sec Marm is at 0 m and at t=3 sec Marm is at 6 m ¡ ¡ Total Displacement (6 m-0 m) = 6 m Total Time (3 sec-0 sec) = 3 sec
Chapter 2 n Position & Displacement… ¡ Create an axis 0 m n position 6 m At t=0 sec Marm is at 0 m and at t=3 sec Marm is at 6 m ¡ ¡ Total Displacement (6 m-0 m) = 6 m Total Time (3 sec-0 sec) = 3 sec
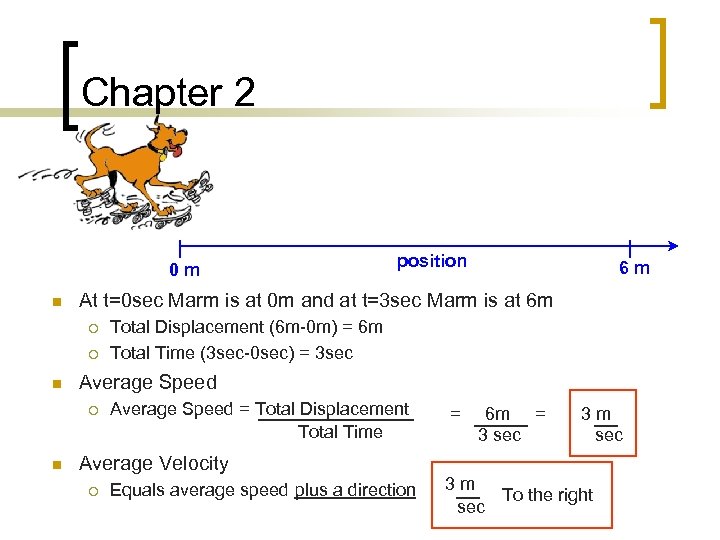 Chapter 2 0 m n ¡ Total Displacement (6 m-0 m) = 6 m Total Time (3 sec-0 sec) = 3 sec Average Speed ¡ n 6 m At t=0 sec Marm is at 0 m and at t=3 sec Marm is at 6 m ¡ n position Average Speed = Total Displacement Total Time = 6 m = 3 sec 3 m sec Average Velocity ¡ Equals average speed plus a direction 3 m To the right sec
Chapter 2 0 m n ¡ Total Displacement (6 m-0 m) = 6 m Total Time (3 sec-0 sec) = 3 sec Average Speed ¡ n 6 m At t=0 sec Marm is at 0 m and at t=3 sec Marm is at 6 m ¡ n position Average Speed = Total Displacement Total Time = 6 m = 3 sec 3 m sec Average Velocity ¡ Equals average speed plus a direction 3 m To the right sec
![Chapter 2 Slope of tangent line = instantaneous velocity n Position vs. Time [sec] Chapter 2 Slope of tangent line = instantaneous velocity n Position vs. Time [sec]](https://present5.com/presentation/090aad517cdd722e3cfafca15a7892b1/image-18.jpg) Chapter 2 Slope of tangent line = instantaneous velocity n Position vs. Time [sec] Position [m] 0. 8 1 2 2. 2 4 3 6 3. 5 Average Velocity: between t=0 sec and t=6 sec Instantaneous Velocity: at t=6 sec
Chapter 2 Slope of tangent line = instantaneous velocity n Position vs. Time [sec] Position [m] 0. 8 1 2 2. 2 4 3 6 3. 5 Average Velocity: between t=0 sec and t=6 sec Instantaneous Velocity: at t=6 sec
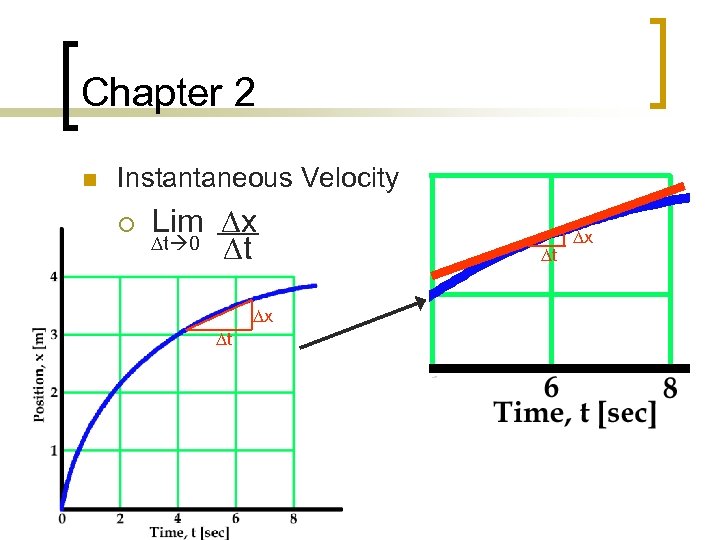 Chapter 2 n Instantaneous Velocity ¡ Lim Dx Dt 0 Dt Dx Dt Dt Dx
Chapter 2 n Instantaneous Velocity ¡ Lim Dx Dt 0 Dt Dx Dt Dt Dx
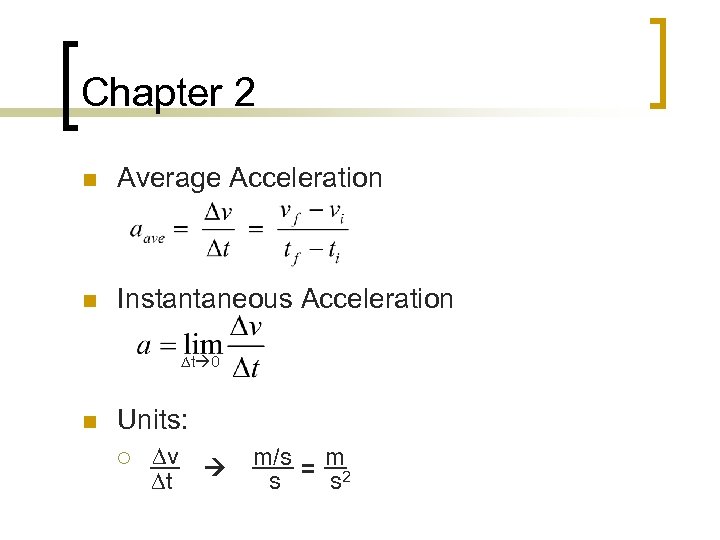 Chapter 2 n Average Acceleration n Instantaneous Acceleration Dt 0 n Units: ¡ Dv Dt m/s = m s s 2
Chapter 2 n Average Acceleration n Instantaneous Acceleration Dt 0 n Units: ¡ Dv Dt m/s = m s s 2
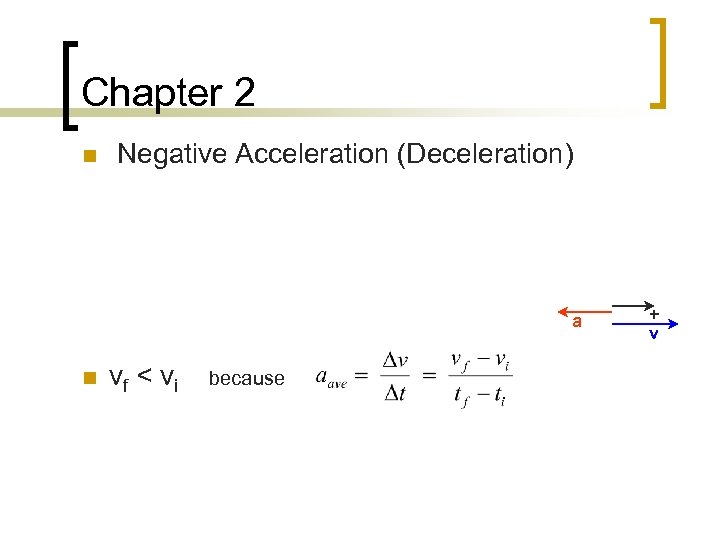 Chapter 2 n Negative Acceleration (Deceleration) a n vf < vi because + v
Chapter 2 n Negative Acceleration (Deceleration) a n vf < vi because + v
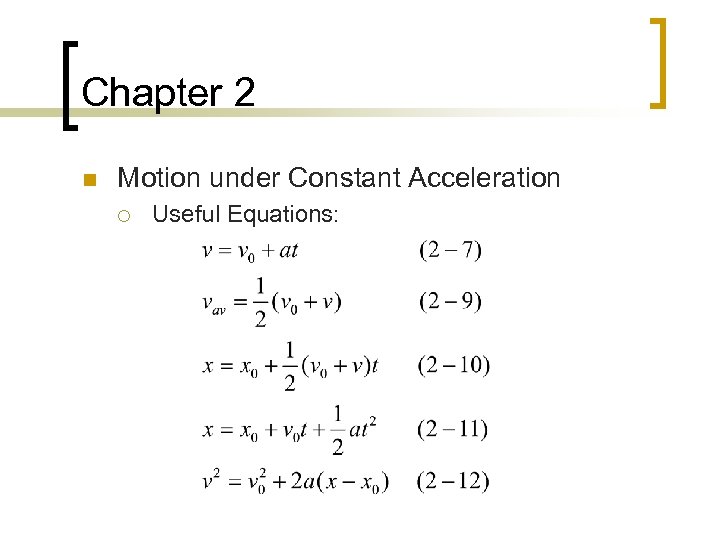 Chapter 2 n Motion under Constant Acceleration ¡ Useful Equations:
Chapter 2 n Motion under Constant Acceleration ¡ Useful Equations:
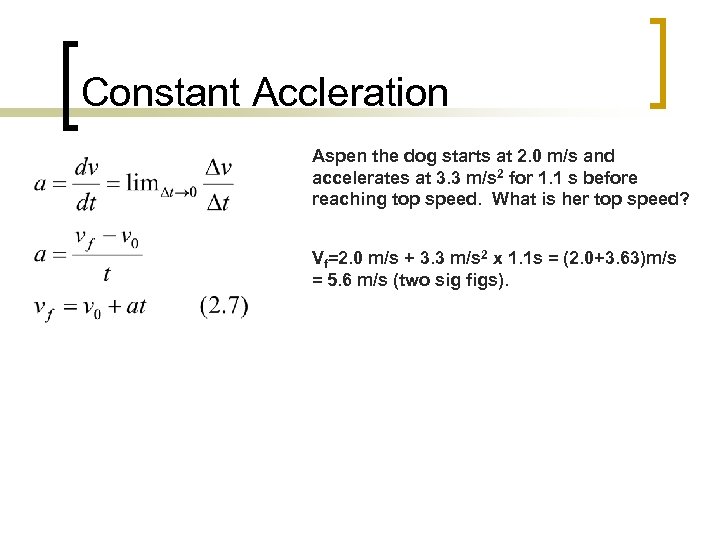 Constant Accleration Aspen the dog starts at 2. 0 m/s and accelerates at 3. 3 m/s 2 for 1. 1 s before reaching top speed. What is her top speed? Vf=2. 0 m/s + 3. 3 m/s 2 x 1. 1 s = (2. 0+3. 63)m/s = 5. 6 m/s (two sig figs).
Constant Accleration Aspen the dog starts at 2. 0 m/s and accelerates at 3. 3 m/s 2 for 1. 1 s before reaching top speed. What is her top speed? Vf=2. 0 m/s + 3. 3 m/s 2 x 1. 1 s = (2. 0+3. 63)m/s = 5. 6 m/s (two sig figs).
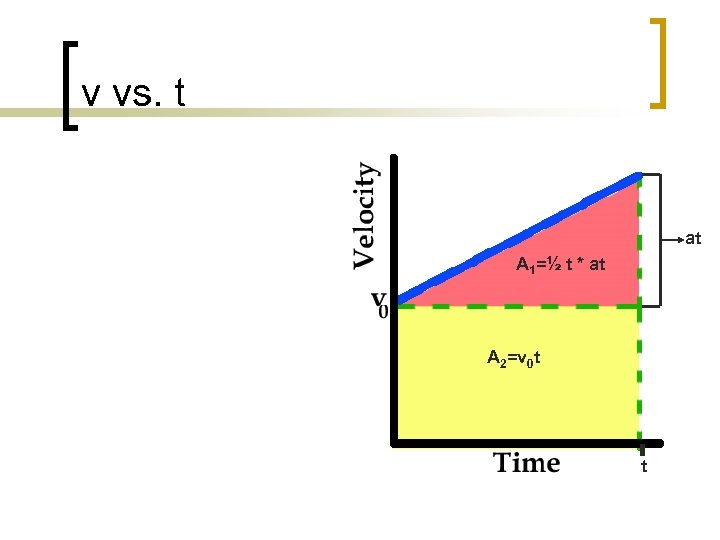 v vs. t at A 1=½ t * at A 2=v 0 t t
v vs. t at A 1=½ t * at A 2=v 0 t t
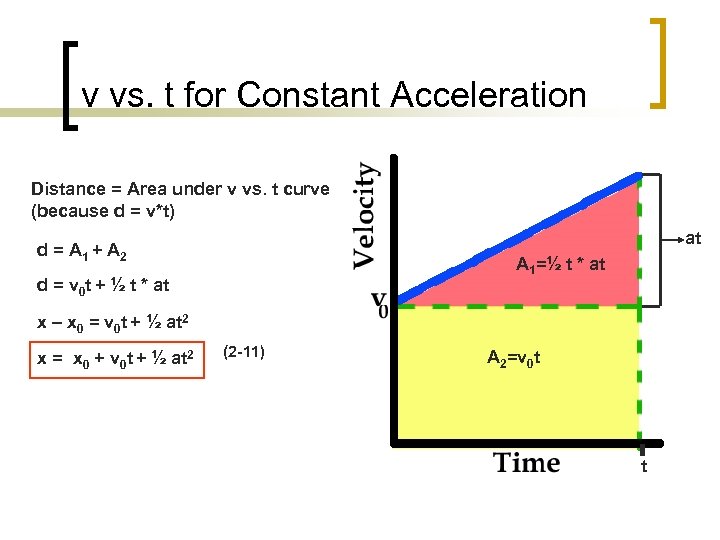 v vs. t for Constant Acceleration Distance = Area under v vs. t curve (because d = v*t) at d = A 1 + A 2 A 1=½ t * at d = v 0 t + ½ t * at x – x 0 = v 0 t + ½ at 2 x = x 0 + v 0 t + ½ at 2 (2 -11) A 2=v 0 t t
v vs. t for Constant Acceleration Distance = Area under v vs. t curve (because d = v*t) at d = A 1 + A 2 A 1=½ t * at d = v 0 t + ½ t * at x – x 0 = v 0 t + ½ at 2 x = x 0 + v 0 t + ½ at 2 (2 -11) A 2=v 0 t t
 How far? Distance is the area under the Velocity vs. time graph thus: Aspen the dog starts at 2. 0 m/s and accelerates at 3. 3 m/s 2 for 1. 1 s before reaching top speed. How far does she travel? D = area rectangle + area triangle Area triangle = ½ base x height
How far? Distance is the area under the Velocity vs. time graph thus: Aspen the dog starts at 2. 0 m/s and accelerates at 3. 3 m/s 2 for 1. 1 s before reaching top speed. How far does she travel? D = area rectangle + area triangle Area triangle = ½ base x height
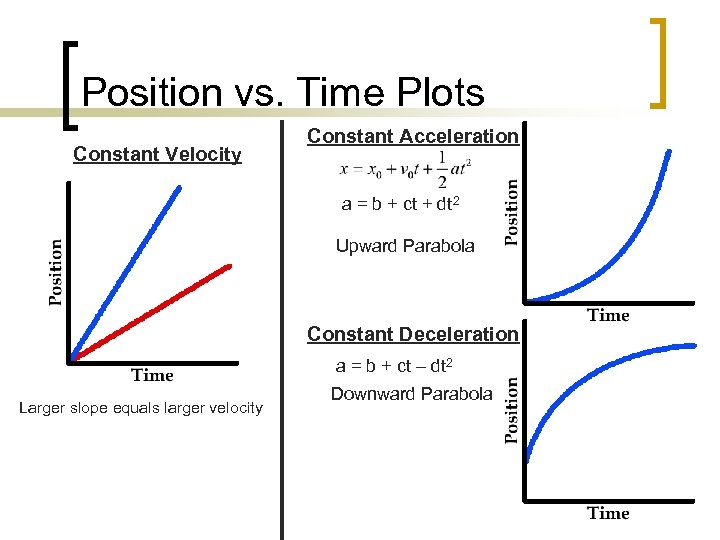 Position vs. Time Plots Constant Velocity Constant Acceleration a = b + ct + dt 2 Upward Parabola Constant Deceleration a = b + ct – dt 2 Larger slope equals larger velocity Downward Parabola
Position vs. Time Plots Constant Velocity Constant Acceleration a = b + ct + dt 2 Upward Parabola Constant Deceleration a = b + ct – dt 2 Larger slope equals larger velocity Downward Parabola
 Without time information… Solve (2. 7) for time and substitute into (2. 11) and you will find: Aspen goes from 2. 0 m/s to 5. 6 m/s over a distance of 4. 2 m, find acceleration.
Without time information… Solve (2. 7) for time and substitute into (2. 11) and you will find: Aspen goes from 2. 0 m/s to 5. 6 m/s over a distance of 4. 2 m, find acceleration.
 Chapter 2 n Example 1 (prob. #12) ¡ It was a dark and stormy night, when suddenly you saw a flash of lightening. Three-and-a-half seconds later you heard the thunder. Given that the speed of sound in air is about 340 m/s, how far away was the lightening bolt?
Chapter 2 n Example 1 (prob. #12) ¡ It was a dark and stormy night, when suddenly you saw a flash of lightening. Three-and-a-half seconds later you heard the thunder. Given that the speed of sound in air is about 340 m/s, how far away was the lightening bolt?
 Chapter 2 n Example 2 (prob. #40) ¡ When you see a traffic light turn red you apply the brakes until you come to a sop. If your initial speed was 12 m/s, and you were heading due west, what was your average velocity during braking? Assume constant velocity.
Chapter 2 n Example 2 (prob. #40) ¡ When you see a traffic light turn red you apply the brakes until you come to a sop. If your initial speed was 12 m/s, and you were heading due west, what was your average velocity during braking? Assume constant velocity.
 Chapter 2 n Example 3 (prob. #100) ¡ You drop a ski glove from a height h onto fresh snow, and it sinks to a depth d before coming to rest. (a) In terms of g and h, what is the speed of the glove when it reaches the snow? (b) What are the magnitude and direction of the glove’s acceleration as it moves through the snow, assuming it to be constant? Give your answer in terms of g, h, and d.
Chapter 2 n Example 3 (prob. #100) ¡ You drop a ski glove from a height h onto fresh snow, and it sinks to a depth d before coming to rest. (a) In terms of g and h, what is the speed of the glove when it reaches the snow? (b) What are the magnitude and direction of the glove’s acceleration as it moves through the snow, assuming it to be constant? Give your answer in terms of g, h, and d.
 Lab One Activity: Measure a n n n 4 -setups: measure time and distance Assume constant acceleration Each group uses different angle of incline Use a variety of distances – average all a values Rest login to MP website/homework
Lab One Activity: Measure a n n n 4 -setups: measure time and distance Assume constant acceleration Each group uses different angle of incline Use a variety of distances – average all a values Rest login to MP website/homework


